Synthesis of a SiO2/Co(OH)2 Nanocomposite Catalyst for SOX/NOX Oxidation in Flue Gas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
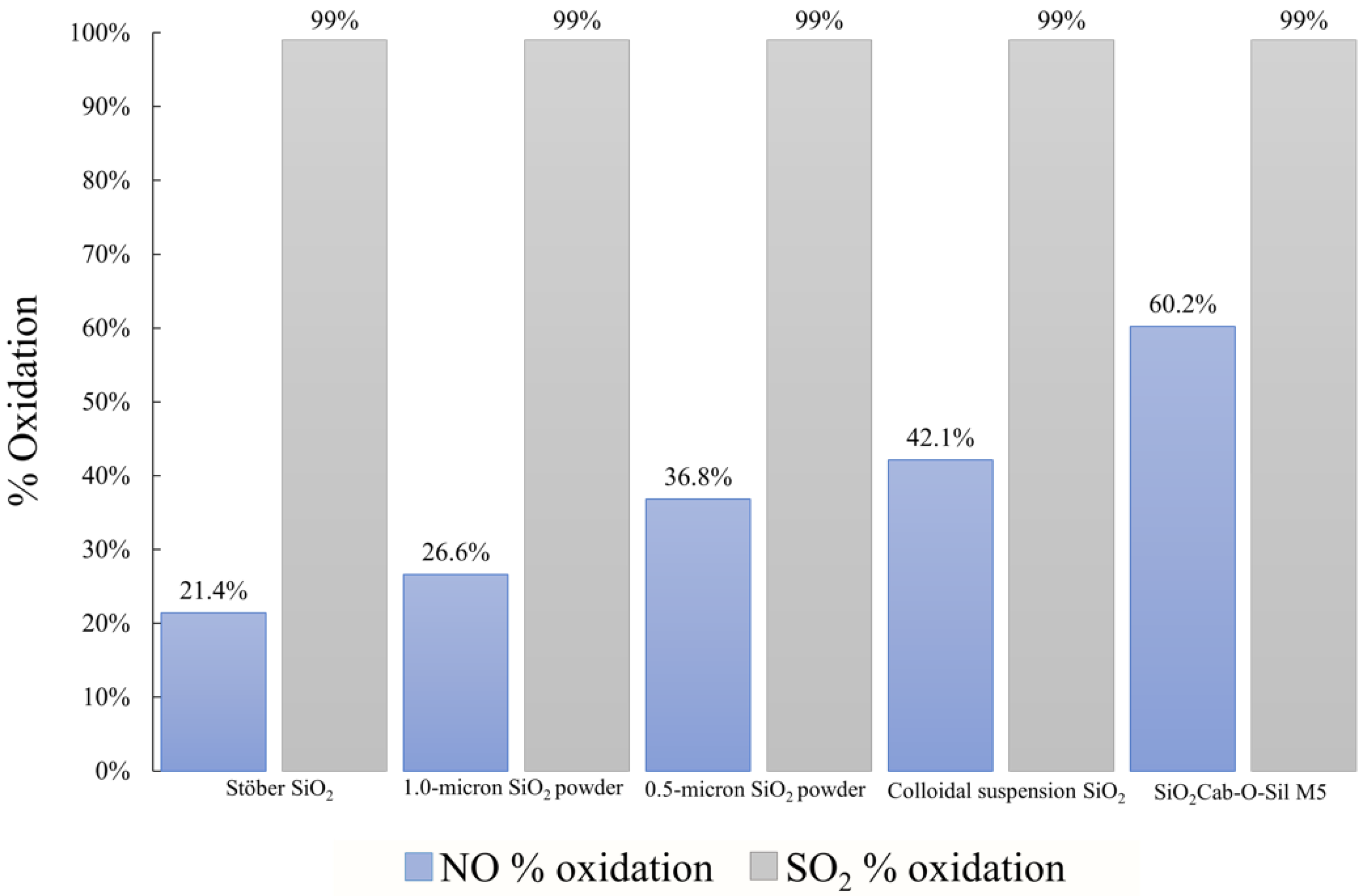
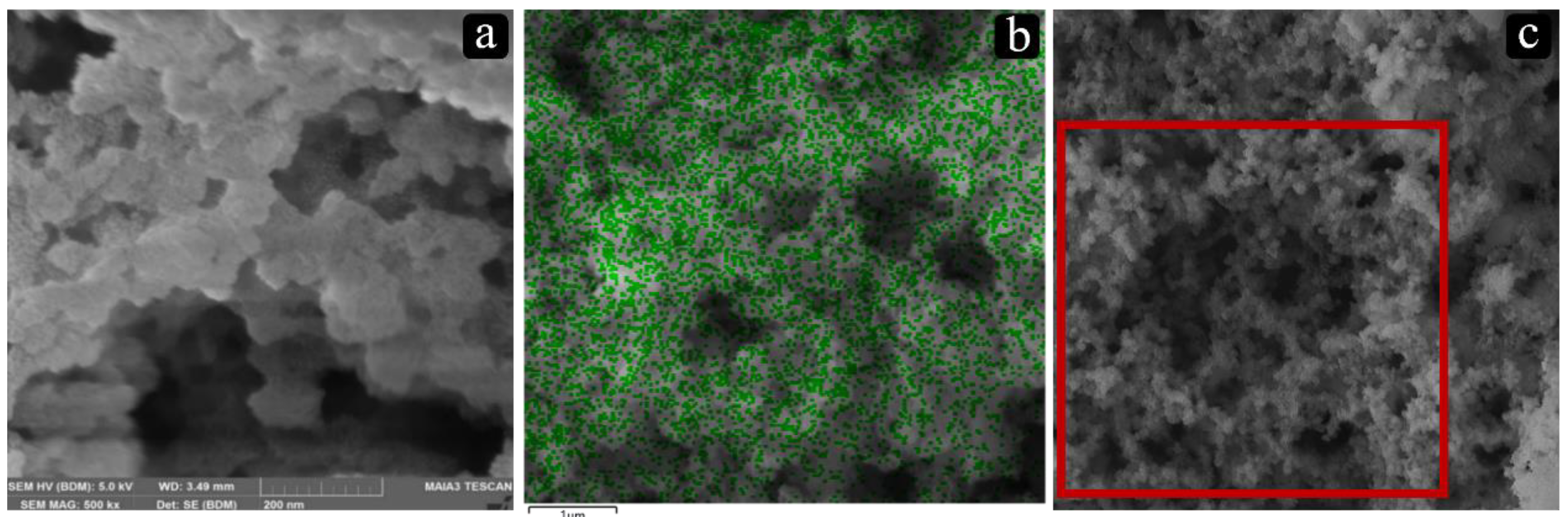
2.1. Comparison of SiO2 Carriers
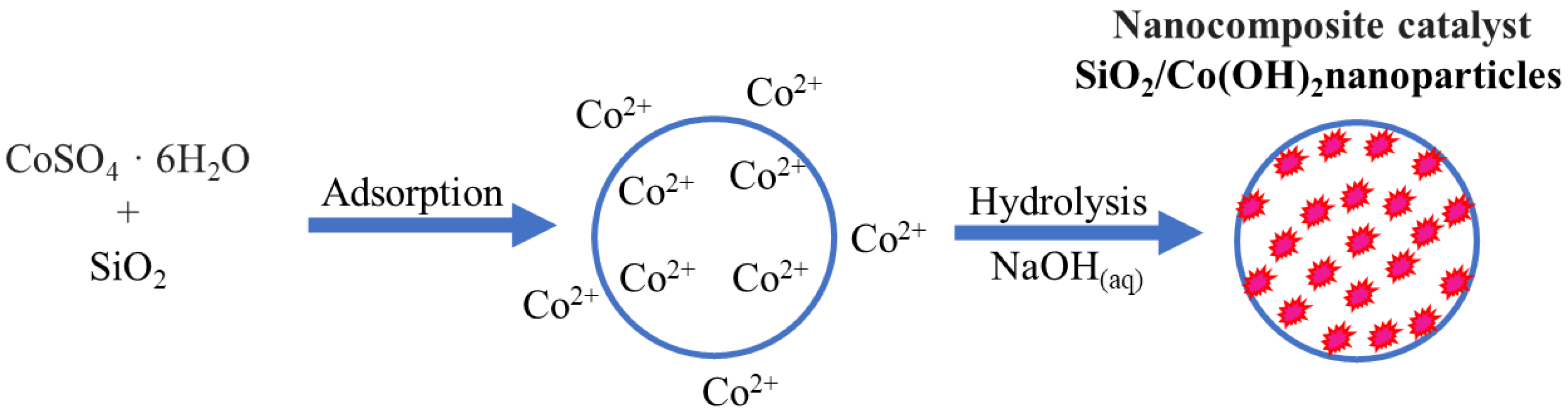
2.1.1. Catalyst Synthesis Using Cab-O-Sil M5
2.1.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.1.3. X-ray Diffraction
2.1.4. Cobalt Leaching—The Effect of pH
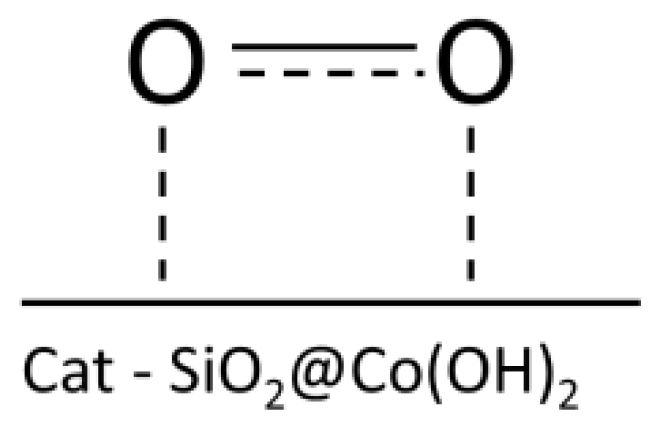
2.2. Activation of Atmospheric Oxygen by the Nanocomposite Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Catalyst Synthesis
3.3.1. Catalyst Synthesis Using Nanopowders
- (i)
- Dissolution of CoSO4·6H2O in water at different concentrations.
- (ii)
- Addition of the SiO2 NPs powder to the Co solution with constant stirring to form a homogeneous suspension.
- (iii)
- Addition of 1.0 M NaOH, along with rapid stirring, until reaching pH 10.
3.3.2. Catalyst Synthesis Using the Colloidal Suspension
3.4. Cobalt Leaching Tests
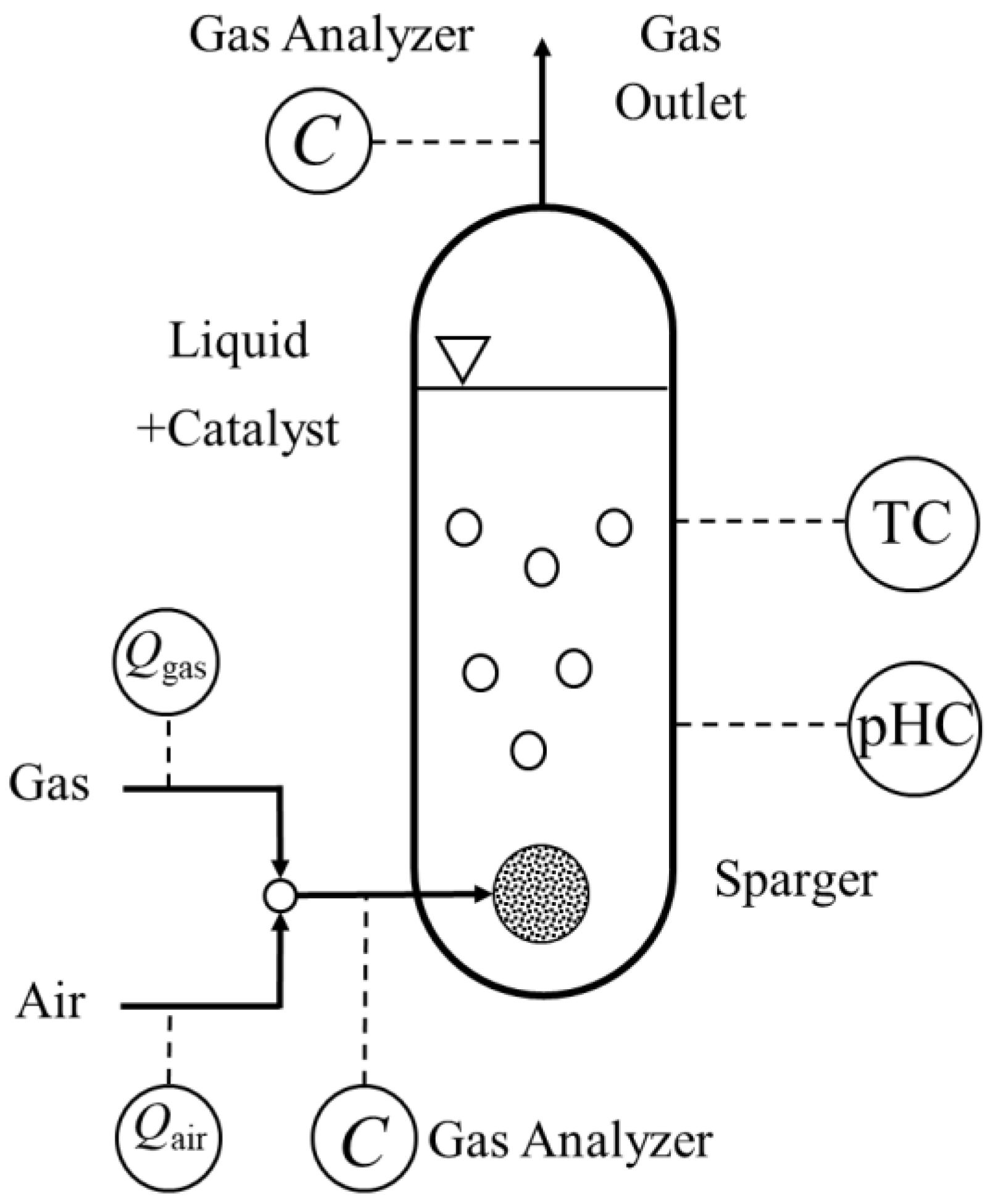
3.5. Bubble Column Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe Health Aspects of Air Pollution: Results from the WHO Project in Systematic Review of Health Aspects of Air Pollution in Europe; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Amoatey, P.; Omidvarborna, H.; Baawain, M.S.; Al-Mamun, A. Emissions and exposure assessments of SOX, NOX, PM10/2.5 and trace metals from oil industries: A review study (2000–2018). Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 123, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, H.A. An overview of the clean air act amendments of 1990. Environ. Law 1991, 21, 1721–1816. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345329 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Khoder, M.I. Atmospheric conversion of sulfur dioxide to particulate sulfate and nitrogen dioxide to particulate nitrate and gaseous nitric acid in an urban area. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba, P. Status of Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) systems from coal-fired power plants: Overview of the physic-chemical control processes of wet limestone FGDs. Fuel 2015, 144, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Jozewicz, W. Flue Gas Desulfurization: The State of the Art. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 1676–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Ward, C.R. Chapter 4—Coal Combustion. In Applied Coal Petrology the Role of Petrology in Coal Utiliztion; Suárez-Ruiz, I., Crelling, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Burlington, VT, USA, 2008; pp. 85–117. ISBN 978-0-08-045051-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hrastel, I.; Gerbec, M.; Stergaršek, A. Technology Optimization of Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization Process. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2007, 30, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Sun, L.; Deng, Y. Modeling and optimization research of CFB-FGD based on improved genetic algorithms and BP neural network. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 610–613, 1601–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zheng, C.; Jin, K.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Cen, K. Cost-effectiveness optimization for SO2 emissions control from coal-fired power plants on a national scale: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lee, J.-M. Conventional and New Materials for Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NOx. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kasipandi, S.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Ryu, J.-H.; Bae, J.-W. Current Catalyst Technology of Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) for NOx Removal in South Korea. Catalysts 2020, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, R. Compilation of Henry’s law constants (version 4.0) for water as solvent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4399–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.W.; Vosper, A.J. Solubility of nitric oxide in aqueous and nonaqueous solvents. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1977, 73, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, Z.; Sun, L. A review: Comparison of multi-air-pollutant removal by advanced oxidation processes—Industrial implementation for catalytic oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulphur Oxides (SOx) and Particulate Matter (PM)—Regulation 14. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Sulphur-oxides-(SOx)-–-Regulation-14.aspx (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)—Regulation 13. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Nitrogen-oxides-(NOx)-–-Regulation-13.aspx (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Zidki, T.; Zhang, L.; Shafirovich, V.; Lymar, S.V. Water oxidation catalyzed by cobalt(II) adsorbed on silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14275–14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted Application of Silica Nanoparticles. A Review. Silicon 2020, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolly, G.S.; Sermiagin, A.; Meyerstein, D.; Zidki, T. Silica Support Affects the Catalytic Hydrogen Evolution by Silver. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidki, T.; Bar-Ziv, R.; Green, U.; Cohen, H.; Meisel, D.; Meyerstein, D. The effect of the nano-silica support on the catalytic reduction of water by gold, silver and platinum nanoparticles—Nanocomposite reactivity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15422–15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolly, G.S.; Meyerstein, D.; Yardeni, G.; Bar-Ziv, R.; Zidki, T. New insights into HER catalysis: The effect of nano-silica support on catalysis by silver nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 6401–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidki, T.; Hänel, A.; Bar-Ziv, R. Reactions of methyl radicals with silica supported silver nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Rad. Chem. Phys. 2016, 124, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidki, T.; Cohen, H.; Meyerstein, D.; Meisel, D. Effect of Silica-Supported Silver Nanoparticles on the Dihydrogen Yields from Irradiated Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10461–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Wingen, L.M.; Sumner, A.L.; Syomin, D.; Ramazan, K.A. The heterogeneous hydrolysis of NO2 in laboratory systems and in outdoor and indoor atmospheres: An integrated mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent & Lundy. IPM Model—Updates to Cost and Performance for APC Technologies SDA FGD Cost Development Methodology, Project 13527-001; Chicago, IL, 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-05/documents/attachment_5-2_sda_fgd_cost_development_methodology.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Randall, D.D.; Schaffner, K.S.; Richardson Fry, C. SCR Cost Manual Chapter 2: Selective Catalytic Reduction; Sorrels, J.L., Ed.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Elkordy, A.A.; Essa, E.A.; Dhuppad, S.; Jammigumpula, P. Liquisolid technique to enhance and to sustain griseofulvin dissolution: Effect of choice of non-volatile liquid vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 434, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, R.D. Stability of silica dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 35, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.J.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sherwood, P.M.A. XPS studies of solvated metal atom dispersed (SMAD) catalysts. Evidence for layered cobalt-manganese particles on alumina and silica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, C.V.; Dillard, J.G.; Murray, J.W. Surface analysis and the adsorption of Co(II) on goethite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 95, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumkin, A.V.; Kraut-Vass, A.; Gaarenstroom, S.W.; Powell, C.J. NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database. Available online: https://doi.org/10.18434/T4T88K (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- El-Didamony, H.; El-Fadaly, E.; Amer, A.A.; Abazeed, I.H. Synthesis and characterization of low cost nanosilica from sodium silicate solution and their applications in ceramic engobes. Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Vidr. 2020, 59, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.S.; Rajagopalan, R.; Amruthalakshmi, A.; Joseph, J.; Ajay, A.; Shakir, I.; Nair, S.V.; Balakrishnan, A. Mesoscopic architectures of Co(OH)2 spheres with an extended array of microporous threads as pseudocapacitor electrode materials. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2015, 470, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, H.; Wu, Z.; Ji, X. An Asymmetric Ultracapacitors Utilizing α-Co(OH)2/Co3O4 Flakes Assisted by Electrochemically Alternating Voltage. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 141, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, R.; Osada, M.; Takada, K.; Sasaki, T. Selective and Controlled Synthesis of α- and β-Cobalt Hydroxides in Highly Developed Hexagonal Platelets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13869–13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, N.K. Water Quality Guidelines for Total Gas Pressure: First Update: Overview Report; Ministry of Water, Land and Air Protection: Victoria BC, Canada, 2004; Volume 7197.
- Kosmulski, M. A literature survey of the differences between the reported isoelectric points and their discussion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2003, 222, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, H.; Rösch, L.; Weis, J. Fumed Silica—Production, Properties, and Applications. In Organosilicon Chemistry Set; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 761–778. ISBN 9783527620777. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.C.; Maciel, G.E. The Fumed Silica Surface: A Study by NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 5103–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabra, A.; Pinhasi, G.A.; Zidki, T. NOX and SOX Flue Gas Treatment System Based on Sulfur-Enriched Organic Oil in Water Emulsion. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2570–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| 2p3/2 | 2p1/2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | MP | SS | DS | MP | SS | DS |
| 25 | 781.53 | 786.38 | 4.85 | 797.42 | 803.26 | 5.84 |
| 70 | 780.60 | 785.60 | 5.00 | 796.22 | 802.01 | 5.79 |
| 95 | 781.23 | 785.88 | 4.65 | 797.22 | 803.76 | 6.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khabra, A.; Cohen, H.; Pinhasi, G.A.; Querol, X.; Córdoba Sola, P.; Zidki, T. Synthesis of a SiO2/Co(OH)2 Nanocomposite Catalyst for SOX/NOX Oxidation in Flue Gas. Catalysts 2023, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010029
Khabra A, Cohen H, Pinhasi GA, Querol X, Córdoba Sola P, Zidki T. Synthesis of a SiO2/Co(OH)2 Nanocomposite Catalyst for SOX/NOX Oxidation in Flue Gas. Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhabra, Alon, Haim Cohen, Gad A. Pinhasi, Xavier Querol, Patricia Córdoba Sola, and Tomer Zidki. 2023. "Synthesis of a SiO2/Co(OH)2 Nanocomposite Catalyst for SOX/NOX Oxidation in Flue Gas" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010029
APA StyleKhabra, A., Cohen, H., Pinhasi, G. A., Querol, X., Córdoba Sola, P., & Zidki, T. (2023). Synthesis of a SiO2/Co(OH)2 Nanocomposite Catalyst for SOX/NOX Oxidation in Flue Gas. Catalysts, 13(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010029