UV and Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) Activated Continuous Flow Persulfate Oxidation of Municipal Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
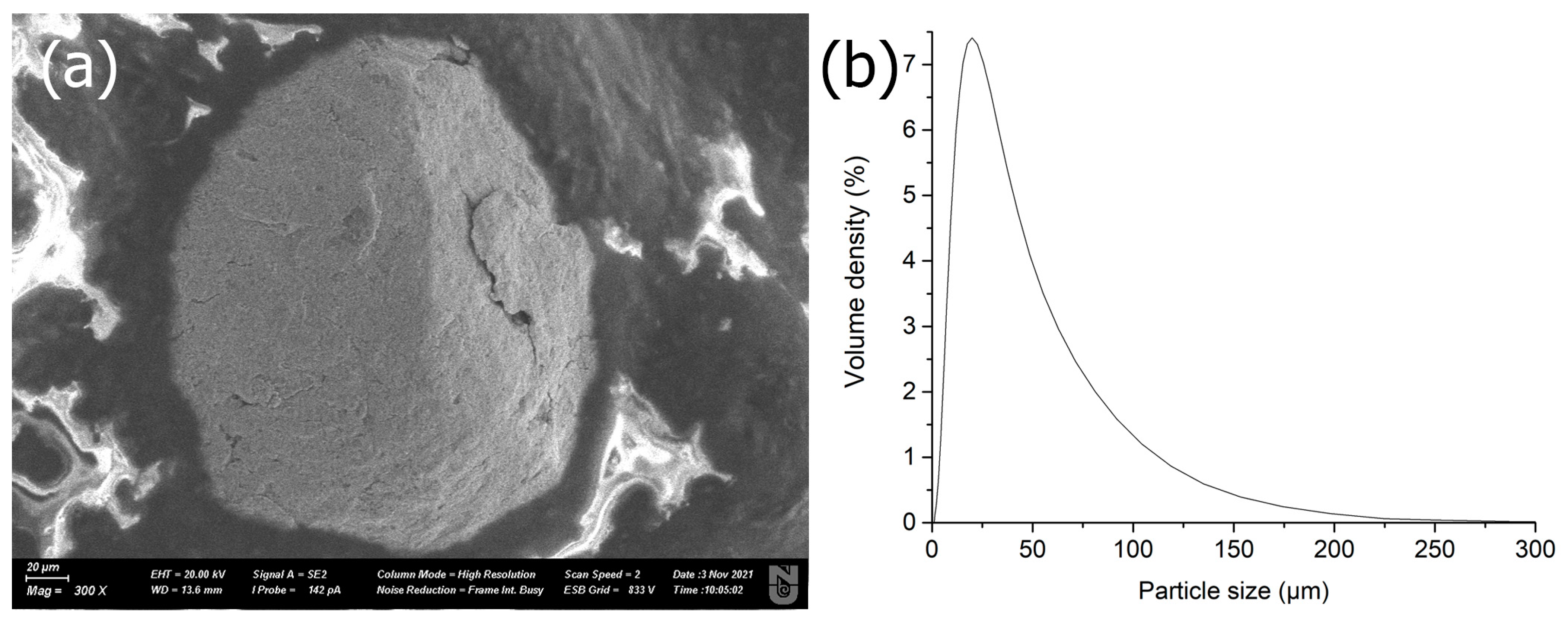
2.1. Characterization of Zero-Valent Iron
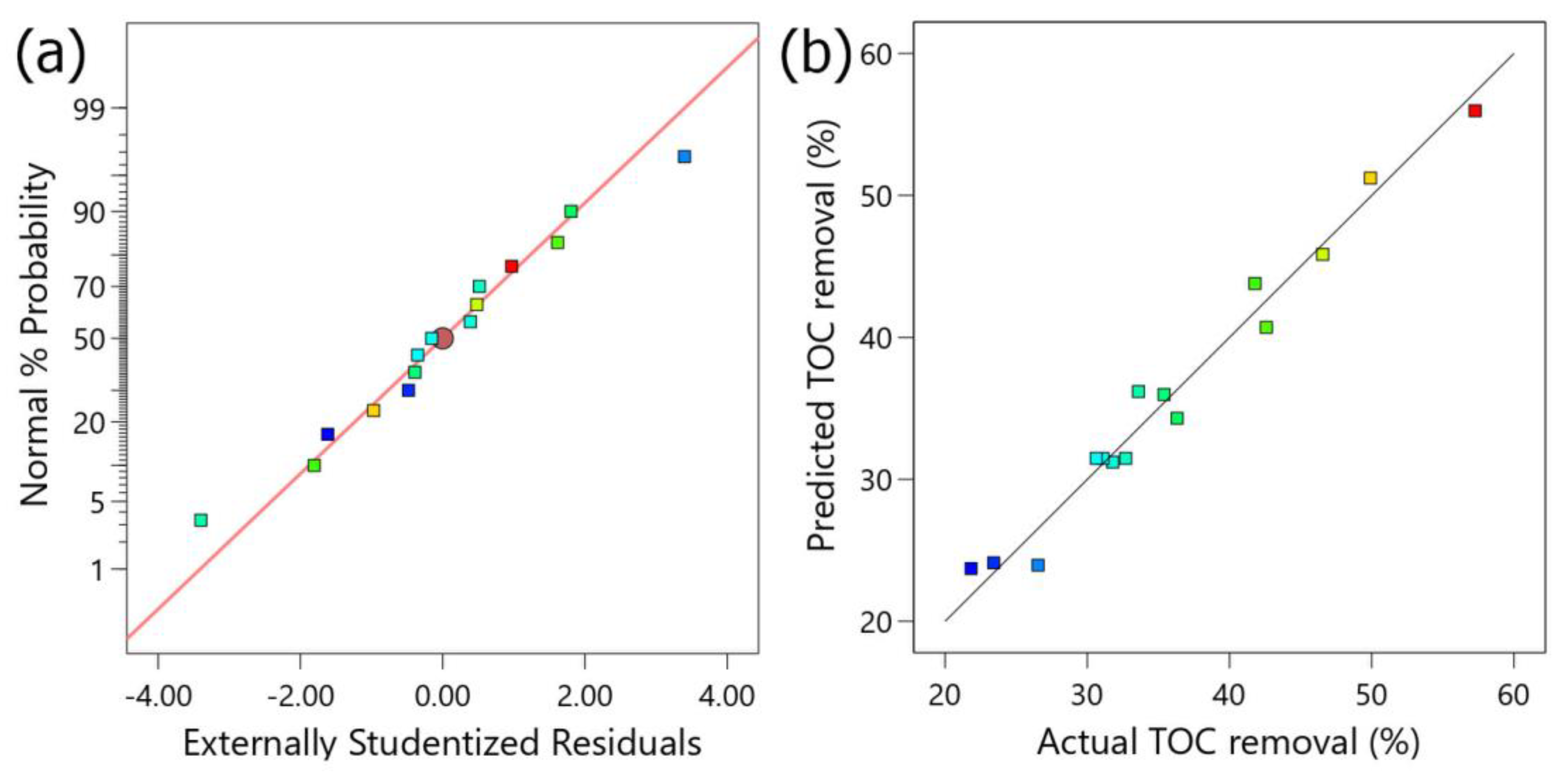
2.2. Regression Model
2.3. ANOVA
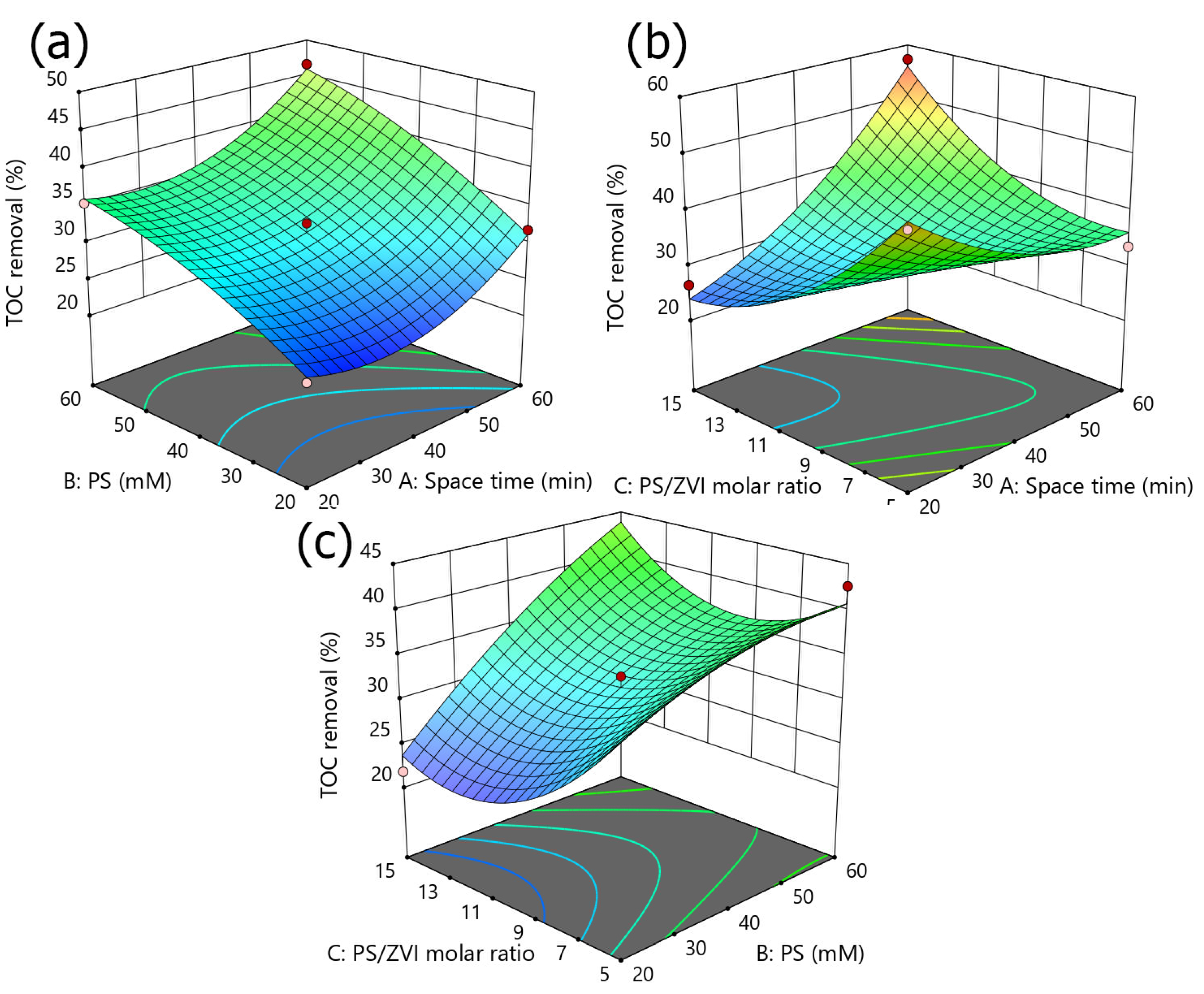
2.4. Three-Dimensional Plots for the RSM Model
2.5. Optimization of the Continuous Flow UV/PS/ZVI Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Wastewater Characteristics
3.3. Experimental Procedure
3.4. Analytical Procedure
3.5. Statistical Design and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nurdillayeva, R.N.; Zhylysbayeva, A.N.; Askarov, A.K.; Bayeshov, A. Electrochemical Method of Lead (II) Ions Removal from Wastewater Using Granular Graphite Electrodes. Bull. Karaganda Univ. Chem. Ser. 2022, 106, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P. Ecotoxicological monitoring of wastewater. Bioassays Adv. Methods Appl. 2018, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water. Summary Progress Update 2021: SDG 6-Water and Sanitation for All; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Andraka, D.; Ospanov, K.; Myrzakhmetov, M. Current state of communal sewage treatment in the republic of Kazakhstan. J. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 16, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziroyan, E. Dangerous Neighborhood [In Russian]. Kazakhstanskaya Pravda. 2019. Available online: https://kazpravda.kz/n/opasnoe-sosedstvo-3e/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Meyer, B.C.; Lundy, L. (Eds.) Integrated Water Cycle Management in Kazakhstan; Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Publishing House: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2014; 320p. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Cao, H.; Qi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, D.; Zhou, S.; Yang, B.; et al. L-cysteine boosted Fe(III)-activated peracetic acid system for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of L-cysteine and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogna, D.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. Kinetic and chemical assessment of the UV/H2O2 treatment of antiepileptic drug carbamazepine. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, M.; Mallek, M.; Dalmau, M.; Mamo, J.; Santos-Clotas, E.; Salah, A.B.; Walha, K.; Salvadó, V.; Monclús, H. Triclosan, carbamazepine and caffeine removal by activated sludge system focusing on membrane bioreactor. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 118, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Lee, C.-H. Membrane Biological Reactors: Theory, Modeling, Design, Management and Applications to Wastewater Reuse; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781780400655. [Google Scholar]
- Kanafin, Y.N.; Makhatova, A.; Meiramkulova, K.; Poulopoulos, S.G. Treatment of a poultry slaughterhouse wastewater using advanced oxidation processes. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafin, Y.N.; Makhatova, A.; Zarikas, V.; Arkhangelsky, E.; Poulopoulos, S.G. Photo-Fenton-like treatment of municipal wastewater. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseghe, E.O.; Idris, A.O.; Feleni, U.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. A review on water treatment technologies for the management of oxoanions: Prospects and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 61979–61997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galban-Malag, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolong, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, M.R.; Matsuura, T. A review of the effects of emerging contaminants in wastewater and options for their removal. Desalination 2009, 239, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsburger, N.; Zaouri, N.; Cheng, H.; Hong, P.Y. The use of UV/H2O2 to facilitate removal of emerging contaminants in anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluents. Environ. Res. 2020, 198, 110479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanafin, Y.N.; Satayeva, A.; Arkhangelsky, E.; Poulopoulos, S.G. Treatment of a Biological Effluent Containing Metronidazole. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valhondo, C.; Carrera, J. Water as a finite resource: From historical accomplishments to emerging challenges and artificial recharge. Sustain. Water Wastewater Process. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, S.; He, H. Enhanced degradation of organic contaminants by Fe(III)/peroxymonosulfate process with L-cysteine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on the Use of Treated Municipal Wastewater Effluents and Sludge in the Production of Crops for Human Consumption, National Research Council. Use of Reclaimed Water and Sludge in Food Crop Production—Committee on the Use of Treated Municipal Wastewater Effluents and Sludge in the Production of Crops for Human Consumption, Commission on Geosciences, Environment and Resources, Division on Earth; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Von Sonntag, C. Advanced oxidation processes: Mechanistic aspects. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. What is the role of light in persulfate-based advanced oxidation for water treatment? Water Res. 2021, 189, 116627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathoulopoulos, A.; Mantzavinos, D.; Frontistis, Z. Coupling persulfate-based AOPs: A novel approach for piroxicam degradation in aqueous matrices. Water 2020, 12, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Qi, C.; Cao, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, S.; He, H. Enhanced degradation of sulfamethoxazole by microwave-activated peracetic acid under alkaline condition: Influencing factors and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Moholkar, V.S. Sulfadiazine degradation using hybrid AOP of heterogeneous Fenton/persulfate system coupled with hydrodynamic cavitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 121294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Von Gunten, U.; Kim, J.H. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Rodríguez, E.; Singh, D.N.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Assessment of sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Water 2018, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusevova Crincoli, K.; Huling, S.G. Contrasting hydrogen peroxide- and persulfate-driven oxidation systems: Impact of radical scavenging on treatment efficiency and cost. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhong, H.; Li, X.; Du, W.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Zeng, G. A novel pretreatment process of mature landfill leachate with ultrasonic activated persulfate: Optimization using integrated Taguchi method and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldemer, R.H.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L.; Nurmi, J.T. Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate: Kinetics and products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Dong, C. Zero-valent iron (ZVI) Activation of Persulfate (PS) for Degradation of Para-Chloronitrobenzene in Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioglou, E.; Frontistis, Z.; Vakros, J.; Manariotis, I.D.; Mantzavinos, D. Activation of persulfate by biochars from valorized olive stones for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole. Catalysts 2019, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Gong, Z.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; Shi, J.; et al. Enhanced removal of methylparaben mediated by cobalt/carbon nanotubes (Co/CNTs) activated peroxymonosulfate in chloride-containing water: Reaction kinetics, mechanisms and pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Kuntus, L.; Tikker, P.; Kattel, E.; Trapido, M.; Dulova, N. Photo-induced oxidation of ceftriaxone by persulfate in the presence of iron oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; San Martín, I.; Amunategui, F.J.; Patterson, D.A. Mineralization of aniline using hydroxyl/sulfate radical-based technology in a waterfall reactor. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, K.; Li, Z.; Ma, P.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. A review of activation persulfate by iron-based catalysts for degrading wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamsi, M.A.; Thomson, N.R. Treatment of organic compounds by activated persulfate using nanoscale zerovalent iron. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13564–13571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubh, A.M.; Baghdadi, M.; Abdoli, M.A.; Aminzadeh, B. Zero-valent iron nanofibers (ZVINFs) immobilized on the surface of reduced ultra-large graphene oxide (rULGO) as a persulfate activator for treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6568–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandi, M.R.; Dargahi, A.; Zolghadr Nasab, H.; Ghahramani, E.; Salehi, S. Degradation of azo dye Acid Red 14 (AR14) from aqueous solution using H2O2/nZVI and S2O82−/nZVI processes in the presence of UV irradiation. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Ruan, J. Experimental Study on the Treatment of Landfill Leachate by Electro-Assisted ZVI/UV Synergistic Activated Persulfate System. Catalysts 2022, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seong, J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, H.H.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C. Chloride-enhanced oxidation of organic contaminants by Cu(II)-catalyzed Fenton-like reaction at neutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tang, P.; Lyu, S.; Brusseau, M.L.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Sui, Q. Enhanced redox degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons by the Fe(II)-catalyzed calcium peroxide system in the presence of formic acid and citric acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Meric, S.; Guida, M.; Kassinos, D.; Belgiorno, V. Heterogenous photocatalytic degradation kinetics and detoxification of an urban wastewater treatment plant effluent contaminated with pharmaceuticals. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4070–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonaro, S.; Sugihara, M.N.; Strathmann, T.J. Continuous-flow photocatalytic treatment of pharmaceutical micropollutants: Activity, inhibition, and deactivation of TiO2 photocatalysts in wastewater effluent. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretto, P.R.P.; Palácio, S.M.; De Campos, É.A.; Pazini, C.R.; Veit, M.T. Sulfamethoxazole photocatalytic degradation in a continuous flow reactor using artificial radiation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.R.; Khor, S.W.; Mohamad, S.; Tay, K.S. Development of UV/Persulfate based laboratory-scale continuous-flow leachate treatment system. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N.; Iwano, S.; Narazaki, Y. Mechanistic consideration of zinc ion removal by zero-valent iron. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2011, 221, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M. Influence of particle size of zero-valent iron and dissolved silica on the reactivity of activated persulfate for degradation of acid orange 7. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, T.Q.Q.; Khoi, V.H.; Thi Huong Giang, N.; Thi Van Anh, H.; Dat, N.M.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Statistical screening and optimization of photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by ZnO–TiO2/rGO nanocomposite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarnejad, R.; Nasiri, S. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment using an advanced oxidation process: Optimization study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Tureli, G.; Olmez-Hanci, T. Optimization of the photo-Fenton-like process for real and synthetic azo dye production wastewater treatment using response surface methodology. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2009, 8, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, T.Q.Q.; Nhu, T.H.; Thinh, D.B.; Trinh, D.N.; Giang, N.T.H.; Dat, N.M.; Hai, N.D.; Nam, H.M.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Optimization of TiO2 immobilized—Reduce graphene oxide photocatalyst toward organic compounds in aqueous medium. Synth. Met. 2021, 280, 116867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarijoo, N.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Bagheri, M.; Ehteshami, M. Assessment of effective parameters in landfill leachate treatment and optimization of the process using neural network, genetic algorithm and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 106, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergenbayeva, S.; Poulopoulos, S.G. Comparative study on UV-AOPs for efficient continuous flow removal of 4-tert-butylphenol. Processes 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petala, A.; Spyrou, D.; Frontistis, Z.; Mantzavinos, D.; Kondarides, D.I. Immobilized Ag3PO4 photocatalyst for micro-pollutants removal in a continuous flow annular photoreactor. Catal. Today 2019, 328, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kong, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Liu, G.; Li, F.; Lv, W. A sulfate radical based ferrous-peroxydisulfate oxidative system for indomethacin degradation in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22802–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, Z.; Samadi, M.T.; Seid-Mohammadi, A.; Asgari, G. Removal of p-chlorophenol from aqueous solution using ultraviolet/zerovalent-iron (UV/ZVI)/persulfate process. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2016, 4, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Sang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, C. Activation of persulfate by manganese oxide-modified sludge-derived biochar to degrade Orange G in aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Pei, Y. Persulfate-enhanced continuous flow three-dimensional electrode dynamic reactor for treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO11733 ISO 11733:2004; Water Quality—Determination of the Elimination and Biodegradability of Organic Compounds in an Aqueous Medium—Activated Sludge Simulation Test. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/34416.html (accessed on 14 November 2022).

| Run | Independent Variables | Removal (Y, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Actual | Predicted | Actual | |
| Space Time, Min | PS, mM | PS/ZVI Molar Ratio | TOC | TOC | CBZ | |
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 23.42 | 24.12 | 86.97 |
| 2 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 33.60 | 36.19 | 97.18 |
| 3 | 40 | 20 | 15 | 21.83 | 23.71 | 95.56 |
| 4 | 40 | 20 | 5 | 36.31 | 34.3 | 100.00 |
| 5 | 40 | 60 | 15 | 41.79 | 43.8 | 99.71 |
| 6 | 60 | 20 | 10 | 31.79 | 31.22 | 98.10 |
| 7 | 20 | 40 | 15 | 26.54 | 23.95 | 99.61 |
| 8 | 60 | 60 | 10 | 46.55 | 45.85 | 99.39 |
| 9 | 40 | 60 | 5 | 42.59 | 40.71 | 99.56 |
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 5 | 49.91 | 51.22 | 99.50 |
| 11 | 60 | 40 | 15 | 57.27 | 55.96 | 96.78 |
| 12 | 40 | 40 | 10 | 31.10 | 31.48 | 97.60 |
| 13 | 20 | 60 | 10 | 35.40 | 35.98 | 96.23 |
| 14 | 40 | 40 | 10 | 30.63 | 31.48 | 98.79 |
| 15 | 40 | 40 | 10 | 32.70 | 31.48 | 99.43 |
| Parameter | TOC Removal |
|---|---|
| Standard deviation | 2.68 |
| Mean | 36.10 |
| CV% | 7.43 |
| R2 | 0.9737 |
| Adj-R2 | 0.9265 |
| Pred-R2 | 0.6035 |
| Adequate precision | 14.7219 |
| PRESS | 543.29 |
| F-value | 20.60 |
| p-value | 0.0019 |
| Wastewater | Space Time, Min | PS, mM | PS/ZVI Molar Ratio | Removal, % | Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | TOC | CBZ | |||||
| Actual | Predicted | Actual | |||||
| Synthetic | 60 | 60 | 15 | 71.14 | 65 | 100 | 6.14 |
| Real | 50 | 50 | 15 | 60.48 | 65 | 100 | 4.52 |
| Content | Concentration, mg/L |
|---|---|
| Peptone | 192 |
| Lab lemco powder | 138 |
| Glucose monohydrate | 19 |
| Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) | 23 |
| Anhydrous potassium monohydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4) | 16 |
| Disodium hydrogenphosphate dihydrate (Na2HPO4·2H2O) | 32 |
| Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) | 294 |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 60 |
| Iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O) | 4 |
| Carbamazepine | 2 |
| Type of Wastewater | TC, mg/L | TOC, mg/L | TIC, mg/L | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic | 209.2 ± 3.3 | 176.3 ± 2.9 | 32.8 ± 1.2 | 7.65 ± 0.1 |
| Real | 223.6 ± 0.2 | 145.8 ± 0.2 | 77.8 ± 0.2 | 7.51 ± 0.1 |
| Symbol | Factor | Levels of Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| A | Space time (min) | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| B | PS concentration (mM) | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| C | PS/ZVI molar ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanafin, Y.N.; Abdirova, P.; Kanafina, D.; Arkhangelsky, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Poulopoulos, S.G. UV and Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) Activated Continuous Flow Persulfate Oxidation of Municipal Wastewater. Catalysts 2023, 13, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010025
Kanafin YN, Abdirova P, Kanafina D, Arkhangelsky E, Kyzas GZ, Poulopoulos SG. UV and Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) Activated Continuous Flow Persulfate Oxidation of Municipal Wastewater. Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanafin, Yerkanat N., Perizat Abdirova, Dinara Kanafina, Elizabeth Arkhangelsky, George Z. Kyzas, and Stavros G. Poulopoulos. 2023. "UV and Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) Activated Continuous Flow Persulfate Oxidation of Municipal Wastewater" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010025
APA StyleKanafin, Y. N., Abdirova, P., Kanafina, D., Arkhangelsky, E., Kyzas, G. Z., & Poulopoulos, S. G. (2023). UV and Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) Activated Continuous Flow Persulfate Oxidation of Municipal Wastewater. Catalysts, 13(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010025










