The Formation of Mn-Ce-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO and Propane Oxidation: The Role of Element Content Ratio
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
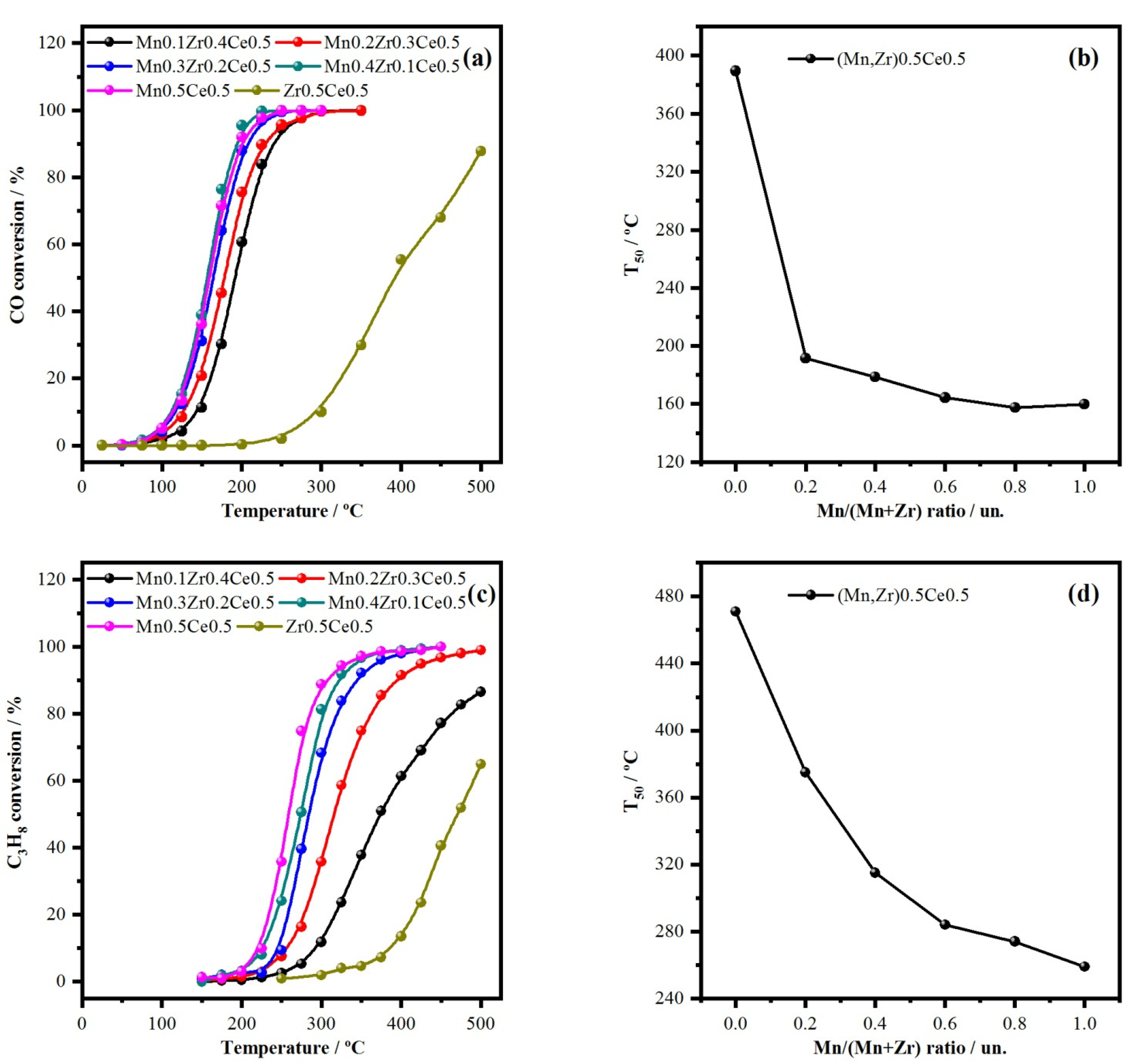
2.1. Variation of Mn/(Mn + Zr) Molar Ratio
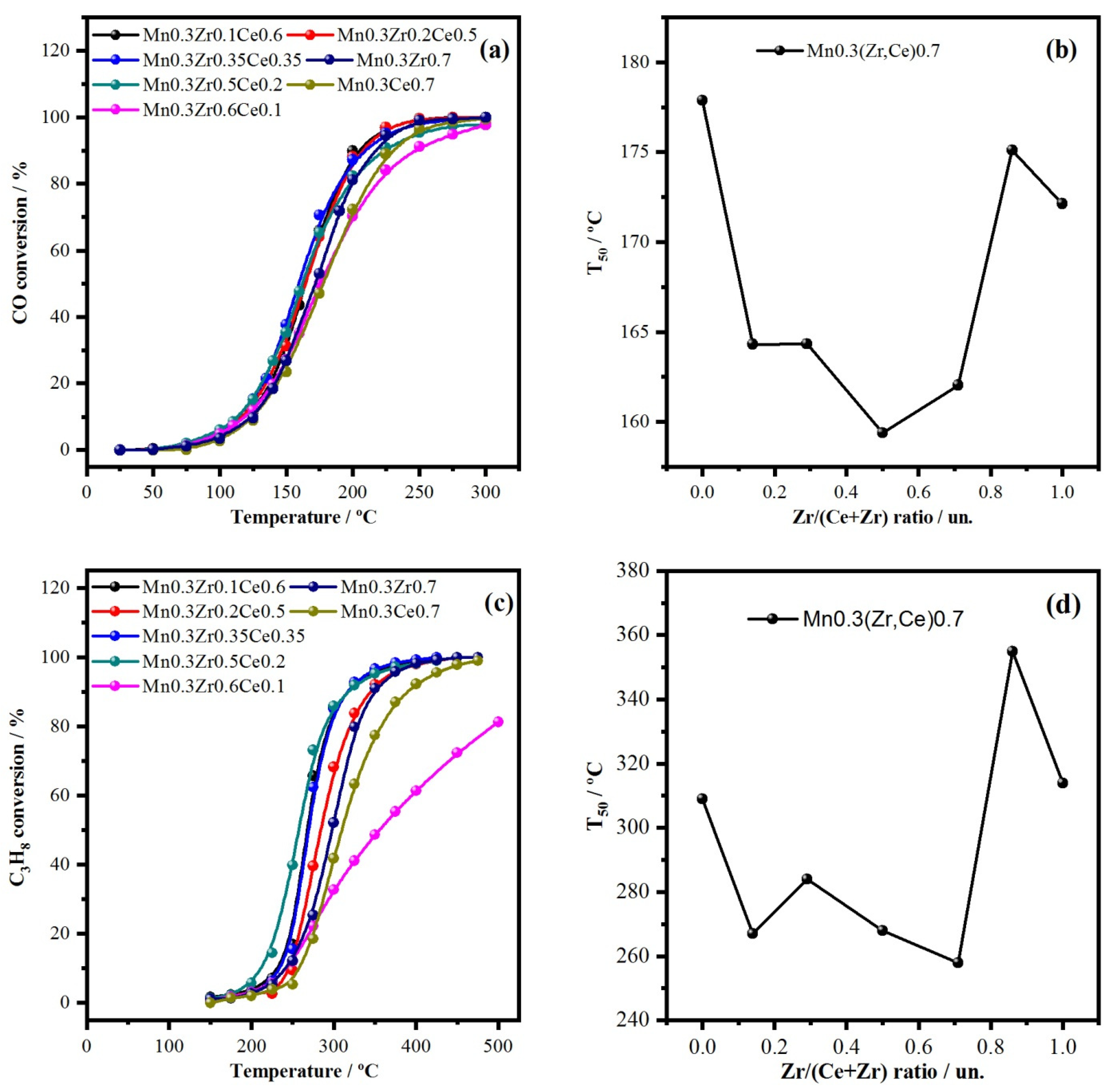
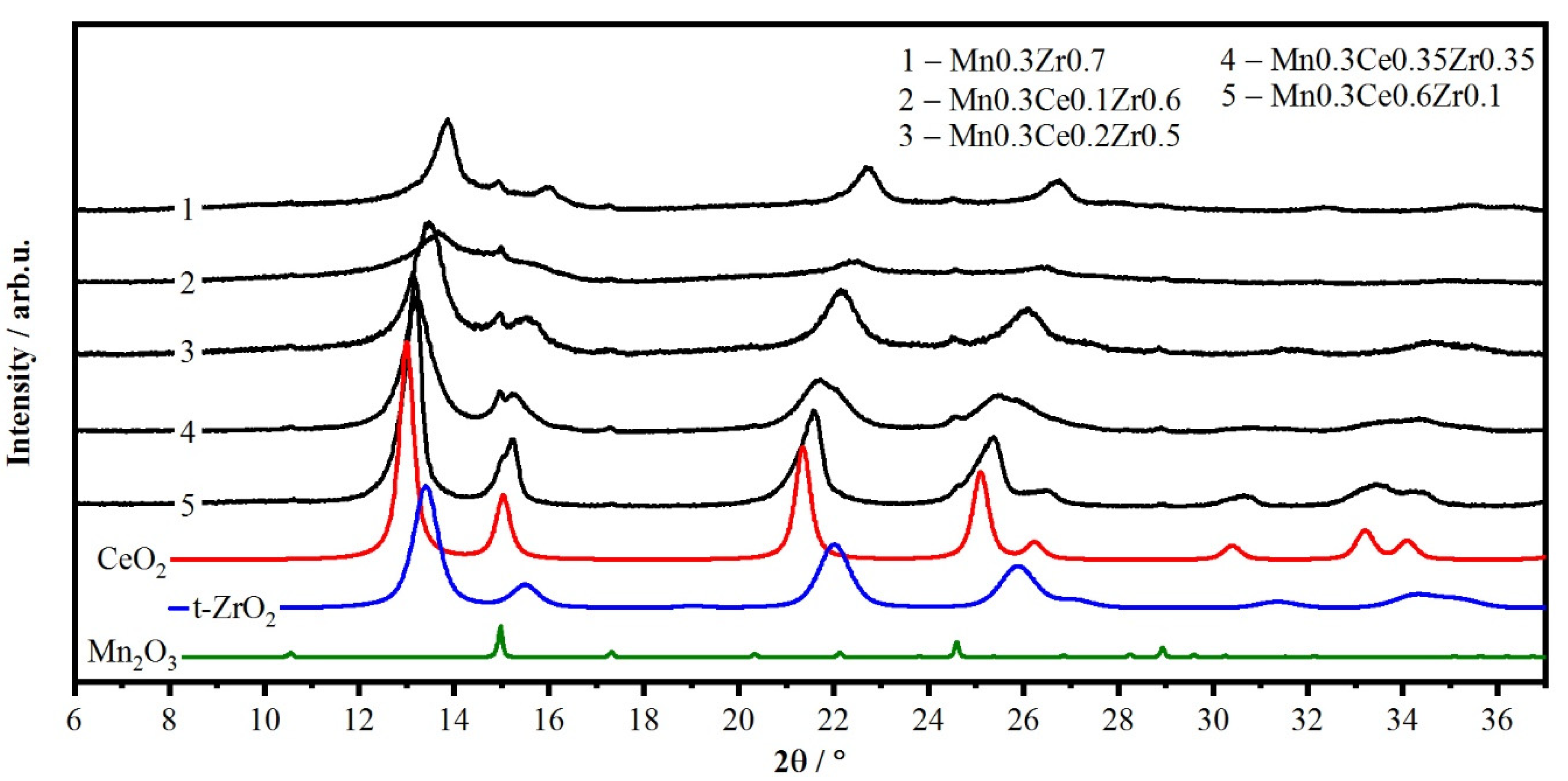
2.2. Variation of Zr/(Ce + Zr) Molar Ratio
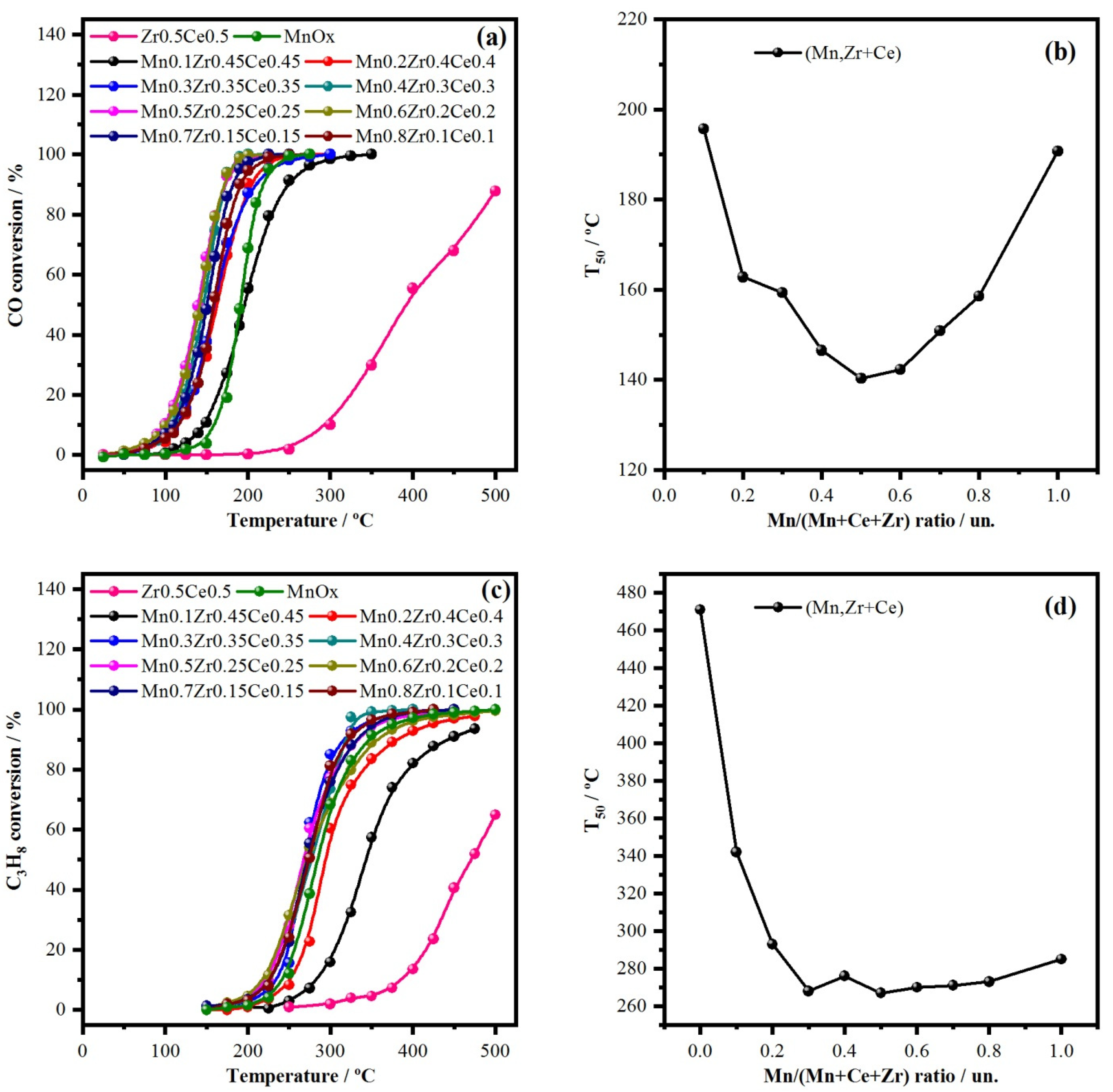
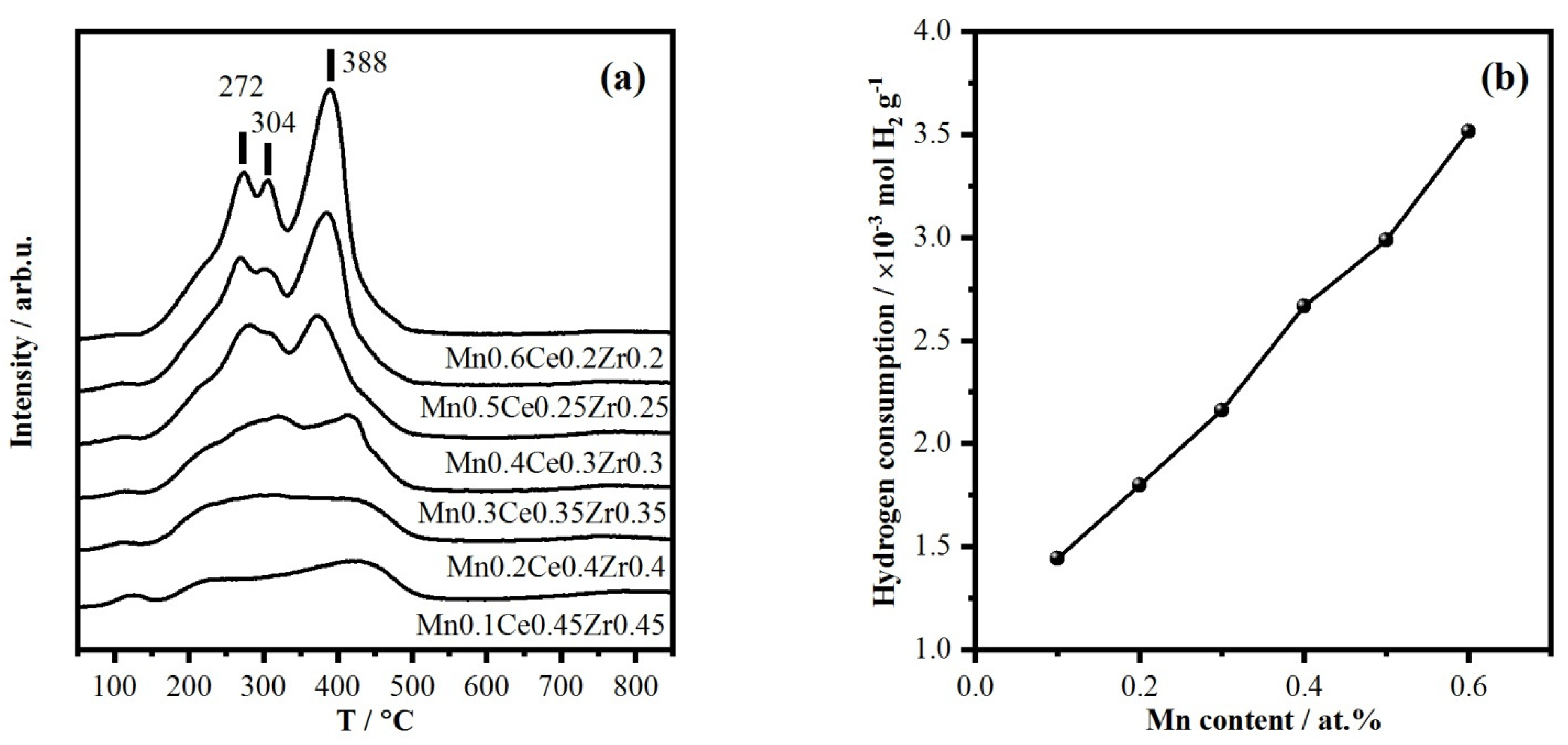
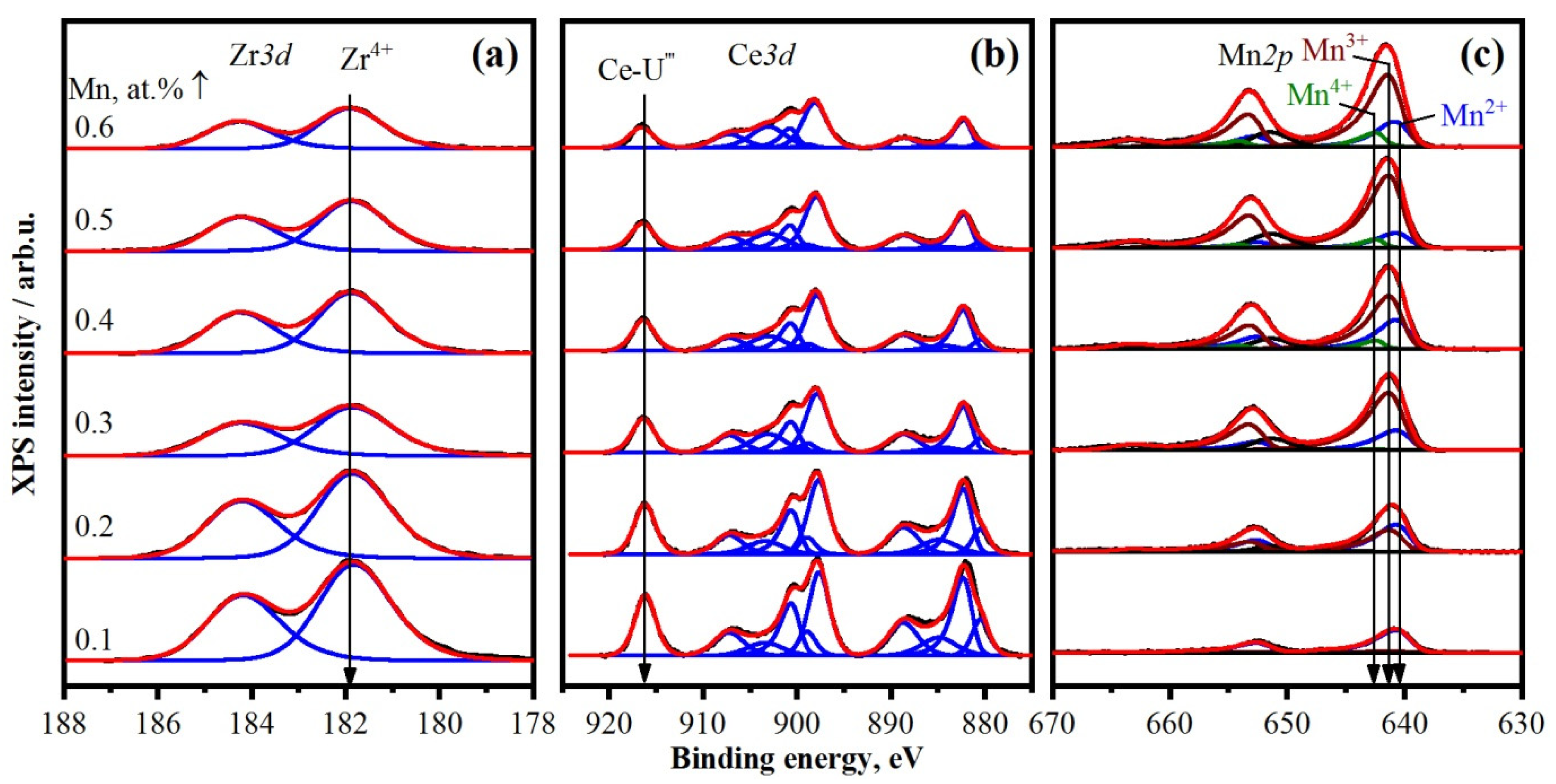
2.3. Variation of Mn/(Mn + Ce + Zr) Ratio
3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Catalyst Preparation
4.2. Catalyst Characterization
4.3. Catalyst Tests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z.; Liu, W.; Mei, J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, S. Gaseous Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions over Mn-Based Oxides for Environmental Applications: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8879–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.K. Factors affecting CO oxidation reaction over nanosized materials: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, M.G.; Shin, D.; Han, J.W. Design of Ceria Catalysts for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.; Iablokov, V.; Sáfrán, G.; Osán, J.; Sajó, I.; Szukiewicz, R.; Chenakin, S.; Kruse, N. Nanostructured MnOx as highly active catalyst for CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. MnOx–CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts for complete oxidation of formaldehyde: Effect of preparation method and calcination temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terribile, D.; Trovarelli, A.; de Leitenburg, C.; Primavera, A.; Dolcetti, G. Catalytic combustion of hydrocarbons with Mn and Cu-doped ceria–zirconia solid solutions. Catal. Today 1999, 47, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Murata, Y.; Kishikawa, K.; Zhang, D.; Ikeue, K. On the Reasons for High Activity of CeO2 Catalyst for Soot Oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4489–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.E.; Schulz, K.H. Surface chemistry and microstructural analysis of CexZr1-xO2-y model catalyst surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 210, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azalim, S.; Franco, M.; Brahmi, R.; Giraudon, J.M.; Lamonier, J.F. Removal of oxygenated volatile organic compounds by catalytic oxidation over Zr-Ce-Mn catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, M.V.; Garbarino, G.; Colman Lerner, J.E.; Finocchio, E.; Busca, G.; Sambeth, J.E.; Peluso, M.A. An Ir And Flow Reactor Study Of Chloroform Oxidation Over Manganese Oxides. Lat. Am. Appl. Res. 2021, 51, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, L.; Yu, P.; Wei, P.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X. High catalytic performance of Mn-doped Ce-Zr catalysts for chlorobenzene elimination. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Golubina, E.V.; Shishova, V.V.; Maslakov, K.I.; Fionov, A.V.; Isaikina, O.Y.; Lunin, V.V. Efficiency of manganese modified CTAB-templated ceria-zirconia catalysts in total CO oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Feng, J.; Lin, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y. The performance of manganese-based catalysts with Ce0.65 Zr0.35O2 as support for catalytic oxidation of toluene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhadchamazketi, A.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y.; Nemati, A. Catalytic evaluation of promoted CeO2-ZrO2 by transition, alkali, and alkaline-earth metal oxides for diesel soot oxidation. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Escribano, V.; Fernández López, E.; Gallardo-Amores, J.M.; del Hoyo Martínez, C.; Pistarino, C.; Panizza, M.; Resini, C.; Busca, G. A study of a ceria-zirconia-supported manganese oxide catalyst for combustion of Diesel soot particles. Combust. Flame 2008, 153, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Xiang, J.; Su, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.; Hu, S.; Lei, S. The activity and characterization of MnOx-CeO2-ZrO2/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, X.; Mu, J.; Fan, S.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Qin, M.; Tadé, M.; Liu, S. Improvement of catalytic activity over Mn-modified CeZrOx catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, T. The effect of Ce-Zr on NH3-SCR activity over MnOx(0.6)/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Sun, R.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, G.; Zhao, W. One-pot synthesis of monolithic Mn-Ce-Zr ternary mixed oxides catalyst for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Lu, S.; Liew, K.M. CO Oxidation over Nanostructured Ceria Supported Bimetallic Cu–Mn Oxides Catalysts: Effect of Cu/Mn Ratio and Calcination Temperature. Catal. Lett. 2017, 148, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Jin, X.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, D. Recent Progress of Thermocatalytic and Photo/Thermocatalytic Oxidation for VOCs Purification over Manganese-based Oxide Catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4268–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonasenko, T.N.; Glyzdova, D.V.; Konovalova, V.P.; Saraev, A.A.; Aydakov, E.E.; Bulavchenko, O.A. Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Properties of Mn–Zr–Ce Catalysts in the Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide. Kinet. Catal. 2022, 63, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonasenko, T.N.; Glyzdova, D.V.; Yurpalov, V.L.; Konovalova, V.P.; Rogov, V.A.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Bulavchenko, O.A. The Study of Thermal Stability of Mn-Zr-Ce, Mn-Ce and Mn-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Materials 2022, 15, 7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavchenko, O.A.; Konovalova, V.P.; Saraev, A.A.; Kremneva, A.M.; Rogov, V.A.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Afonasenko, T.N. The Catalytic Performance of CO Oxidation over MnOx-ZrO2 Catalysts: The Role of Synthetic Routes. Catalysts 2023, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, G.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Catalytic removal of benzene over CeO2–MnOx composite oxides prepared by hydrothermal method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 138-139, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobbe, E.R.; De Boer, B.A.; Geus, J.W. The reduction and oxidation behaviour of manganese oxides. Catal. Today 1999, 47, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavchenko, O.A.; Venediktova, O.S.; Afonasenko, T.N.; Tsyrul’Nikov, P.G.; Saraev, A.A.; Kaichev, V.V.; Tsybulya, S.V. Nonstoichiometric oxygen in Mn-Ga-O spinels: Reduction features of the oxides and their catalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11598–11607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittet, M.J.; Crocombette, J.P.; Gautier-Soyer, M. Bonding and XPS chemical shifts in ZrSiO4 versus SiO2 and ZrO2: Charge transfer and electrostatic effects. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2001, 63, 1251171–1251177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Jiménez-López, A.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Olivera-Pastor, P.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Rozière, J. Surface characterisation of zirconium-doped mesoporous silica. Chem. Commun. 1997, 5, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, S.; Asami, K.; Ito, S.; Yashima, M.; Sugimoto, T. XPS study of the phase transition in pure zirconium oxide nanocrystallites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, H.; Borchert, Y.; Kaichev, V.V.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Alikina, G.M.; Lukashevich, A.I.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Moroz, E.M.; Paukshtis, E.A.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I.; et al. Nanostructured, Gd-doped ceria promoted by Pt or Pd: Investigation of the electronic and surface structures and relations to chemical properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20077–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, S.Y.; Álvarez-Galván, M.C.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Efstathiou, A.M. Suppression of the oxygen storage and release kinetics in Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 induced by P, Ca and Zn chemical poisoning. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 106, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yamaguchi, D.; Burke, N.; Trimm, D.; Chiang, K. Methane decomposition over ceria modified iron catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampaiah, D.; Venkataswamy, P.; Tur, K.M.; Ippolito, S.J.; Bhargava, S.K.; Reddy, B.M. Effect of MnOx loading on structural, surface, and catalytic properties of CeO2-MnOx mixed oxides prepared by sol-gel method. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2015, 641, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavchenko, O.A.; Vinokurov, Z.S.; Afonasenko, T.N.; Tsyrul’Nikov, P.G.; Tsybulya, S.V.; Saraev, A.A.; Kaichev, V.V. Reduction of mixed Mn-Zr oxides: In situ XPS and XRD studies. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15499–15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I.; de Rivas, B.; López-Fonseca, R.; Martín, S.; González-Velasco, J.R. Structure of Mn-Zr mixed oxides catalysts and their catalytic performance in the gas-phase oxidation of chlorocarbons. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Fang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, G. Influence of preparation methods on the physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of Mn-Ce catalysts for lean methane combustion. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 579, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzer, E.; Döbber, D.; Kießling, D.; Wendt, G. MnOx/CeO2-ZrO2 and MnOx/WO3-TiO2 catalysts for the total oxidation of methane and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 143, 489–497. [Google Scholar]
- Mobini, S.; Meshkani, F.; Rezaei, M. Supported Mn catalysts and the role of different supports in the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 197, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavchenko, O.A.; Afonasenko, T.N.; Osipov, A.R.; Pochtar’, A.A.; Saraev, A.A.; Vinokurov, Z.S.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Tsybulya, S.V. The formation of mn-ce oxide catalysts for co oxidation by oxalate route: The role of manganese content. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Qu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hao, Z. Efficient defect engineering in Co-Mn binary oxides for low-temperature propane oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 282, 119512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, D.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G. Effect of Ceria Crystal Plane on the Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Pd/Ceria for CO and Propane Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Qu, Z.; Dong, C.; Song, L.; Qin, Y.; Huang, N. Low-temperature abatement of toluene over Mn-Ce oxides catalysts synthesized by a modified hydrothermal approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, E.Y.; Kleusov, B.S.; Naumkin, A.V.; Zagaynov, I.V.; Konkova, T.V.; Simakina, E.A.; Izotova, A.O. Thermal Stability and Catalytic Activity of the MnOx–CeO2 and the MnOx–ZrO2–CeO2 Highly Dispersed Materials in the Carbon Monoxide Oxidation Reaction. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2021, 12, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, N. CasaXPS. Available online: www.casaxps.com (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Shirley, D.A. High-Resolution X-Ray Photoemission Spectrum of the Valence Bands of Gold. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 4709–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, J.H. Hartree-Slater subshell photoionization cross-sections at 1254 and 1487 eV. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1976, 8, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalyst | Phase Content, % Wt. | Lattice Parameter *, Å | CSR, Å | SBET, m2/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn0.1Ce0.5Zr0.4 | 60% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.371 | 100 | 87 |
| 40% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.213 | 70 | ||
| Mn0.2Ce0.5Zr0.3 | 46% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.391 | 70 | 103 |
| 52% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.297 | 40 | ||
| 2% Mn2O3 | - | 230 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.5Zr0.2 | 53% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.383 | 80 | 91 |
| 43% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.307 | 30 | ||
| 4% Mn2O3 | - | 270 | ||
| Mn0.4Ce0.5Zr0.1 | 36% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.414 | 50 | 77 |
| 56% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.354 | 130 | ||
| 6% Mn2O3 | - | 110 | ||
| 2% Mn3O4 | - | 80 | ||
| Ce0.5Zr0.5 | 40% (Ce,Zr)O2 | 5.396 | 120 | 66.5 |
| 60% t-(Zr,Ce)O2 | 5.241 | 60 | ||
| Mn0.5Ce0.5 | 87% Ce(Mn)O2 | 5.397 | 80 | 55.5 |
| 8% Mn2O3 | - | 110 | ||
| 5% Mn3O4 | - | 150 | ||
| Mn0.1Ce0.5Zr0.4 | 60% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.371 | 100 | 87 |
| 40% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.213 | 70 | ||
| Mn0.2Ce0.5Zr0.3 | 46% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.391 | 70 | 103 |
| 52% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.297 | 40 | ||
| 2% Mn2O3 | - | 230 |
| Catalyst | Phase Content, % Wt. | Lattice Parameter *, Å | CSR, Å | SBET, m2/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn0.3Ce0.6Zr0.1 | 20% amorphous ZrO2 | - | - | 57.5 |
| 74% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.383 | 90 | ||
| 6% Mn2O3 | - | 110 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.5Zr0.2 | 53% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.383 | 80 | 91 |
| 43% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.307 | 30 | ||
| 4% Mn2O3 | - | 270 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.35Zr0.35 | 66% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.338 | 70 | 132 |
| 29% c-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.162 | 50 | ||
| 5% Mn2O3 | - | 310 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.2Zr0.5 | Amorphous | - | - | 162 |
| t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.234 | 40 | ||
| Mn2O3 | - | 130 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.1Zr0.6 | Amorphous | - - - | - - - | 223 |
| CeO2 | ||||
| Mn2O3 | ||||
| Mn0.3Zr0.7 | 54% amorphous | - | - | 176 |
| 40% t-Zr(Mn)O2 | 5.100 | 80 | ||
| 6% Mn2O3 | - | 90 |
| Catalyst | Phase Content, % Wt. | Lattice Parameter *, Å | CSR, Å | SBET, m2/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn0.1Ce0.45Zr0.45 | 47% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.351 | 70 | 106 |
| 53% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.216 | 50 | ||
| Mn0.2Ce0.4Zr0.4 | 64% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.328 | 60 | 123 |
| 36% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.210 | 50 | ||
| Mn0.3Ce0.35Zr0.35 | 47% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.352 5.220 - | 60 | 132 |
| 47% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 40 | |||
| 6% Mn2O3 | 170 | |||
| Mn0.4Ce0.3Zr0.3 | 37% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.314 | 75 | 138.5 |
| 55% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.258 | 20 | ||
| 4% Mn2O3 | - | 220 | ||
| 4% Mn3O4 | - | 170 | ||
| Mn0.5Ce0.25Zr0.25 | 34% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.330 | 60 | 141.3 |
| 48% t-Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.234 | 20 | ||
| 7% Mn2O3 | - | 225 | ||
| 11% Mn3O4 | - | 140 | ||
| Mn0.6Ce0.2Zr0.2 | 29% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.345 | 60 | 150.3 |
| 43% Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 5.189 | 20 | ||
| 12% Mn2O3 | - | 220 | ||
| 15% Mn3O4 | - | 125 | ||
| Mn0.7Ce0.15Zr0.15 | 36% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.364 | 50 | 118 |
| 14% Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 4.922 | 230 | ||
| 38% Mn2O3 | - | 160 | ||
| 12% Mn3O4 | - | 40 | ||
| Mn0.8Ce0.1Zr0.1 | 22% Ce(Mn,Zr)O2 | 5.371 | 50 | 92.7 |
| 11% Zr(Ce,Mn)O2 | 4.961 | 50 | ||
| 30% Mn2O3 | - | 245 | ||
| 22% Mn3O4 | - | 160 | ||
| 15% MnO2 | - | 55 | ||
| MnOx | Mn2O3 | - | 210 |
| Catalyst | [Mn]/[Mn + Ce + Zr] | [O]/[Me] | Ce3+, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | %, Mn2+ | %, Mn3+ | %, Mn4+ | |||
| Mn0.1Ce0.45Zr0.45 | 0.13 | 92 | 8 | 0 | 2.31 | 22 |
| Mn0.2Ce0.4Zr0.4 | 0.27 | 51 | 49 | 0 | 2.35 | 20 |
| Mn0.3Ce0.35Zr0.35 | 0.49 | 22 | 77 | 1 | 1.86 | 18 |
| Mn0.4Ce0.3Zr0.3 | 0.51 | 29 | 64 | 7 | 1.98 | 18 |
| Mn0.5Ce0.25Zr0.25 | 0.58 | 14 | 80 | 6 | 1.80 | 16 |
| Mn0.6Ce0.2Zr0.2 | 0.65 | 20 | 70 | 10 | 1.76 | 20 |
| Catalyst | Preparation Method | Calcination Temperature, °C | Concentration of C3H8 (CO) | GHSV, mL/(g*h) | T50, °C | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propane Oxidation | ||||||
| Ce0.76Zr0.19Mn0.05O(2-x) | co-precipitation | 650 | 1 mol.% | 50,000 | 408 | [6] |
| Mn0.3Ce0.2Zr0.5 | co-precipitation | 600 | 1 vol.% | 37,200 | 258 | This work |
| CO Oxidation | ||||||
| Mn0.45Ce0.45Zr0.1 | co-precipitation | 550 | 4 vol.% | 1800 | 105 | [45] |
| MnOx–Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 | co-precipitation | 500 | 2 vol.% | 36,000 | 160 | [12] |
| Mn0.5Ce0.25Zr0.25 | co-precipitation | 600 | 1 vol.% | 58,440 | 140 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afonasenko, T.N.; Yurpalova, D.V.; Vinokurov, Z.S.; Saraev, A.A.; Aidakov, E.E.; Konovalova, V.P.; Rogov, V.A.; Bulavchenko, O.A. The Formation of Mn-Ce-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO and Propane Oxidation: The Role of Element Content Ratio. Catalysts 2023, 13, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010211
Afonasenko TN, Yurpalova DV, Vinokurov ZS, Saraev AA, Aidakov EE, Konovalova VP, Rogov VA, Bulavchenko OA. The Formation of Mn-Ce-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO and Propane Oxidation: The Role of Element Content Ratio. Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010211
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfonasenko, Tatyana N., Daria V. Yurpalova, Zakhar S. Vinokurov, Andrey A. Saraev, Egor E. Aidakov, Valeriya P. Konovalova, Vladimir A. Rogov, and Olga A. Bulavchenko. 2023. "The Formation of Mn-Ce-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO and Propane Oxidation: The Role of Element Content Ratio" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010211
APA StyleAfonasenko, T. N., Yurpalova, D. V., Vinokurov, Z. S., Saraev, A. A., Aidakov, E. E., Konovalova, V. P., Rogov, V. A., & Bulavchenko, O. A. (2023). The Formation of Mn-Ce-Zr Oxide Catalysts for CO and Propane Oxidation: The Role of Element Content Ratio. Catalysts, 13(1), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010211







