Investigation of the Hβ Molecular Sieve Inactivation Caused by Reactants and Products and Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
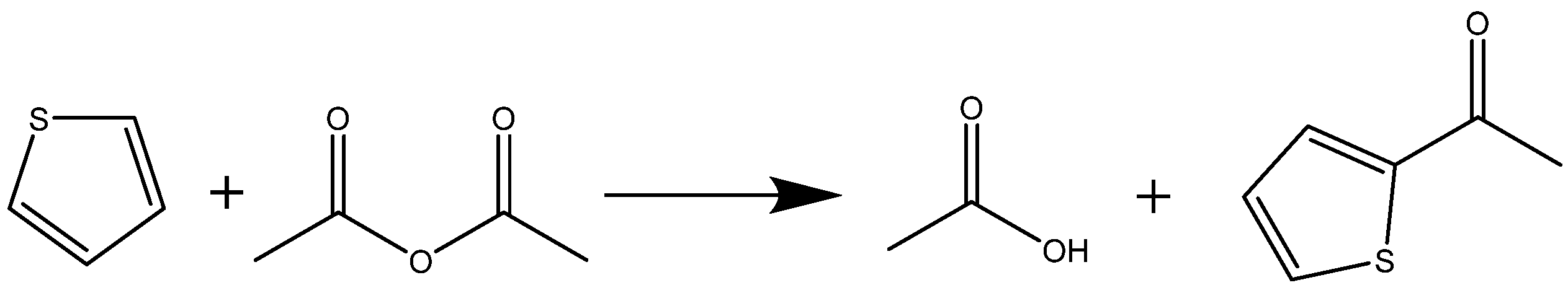
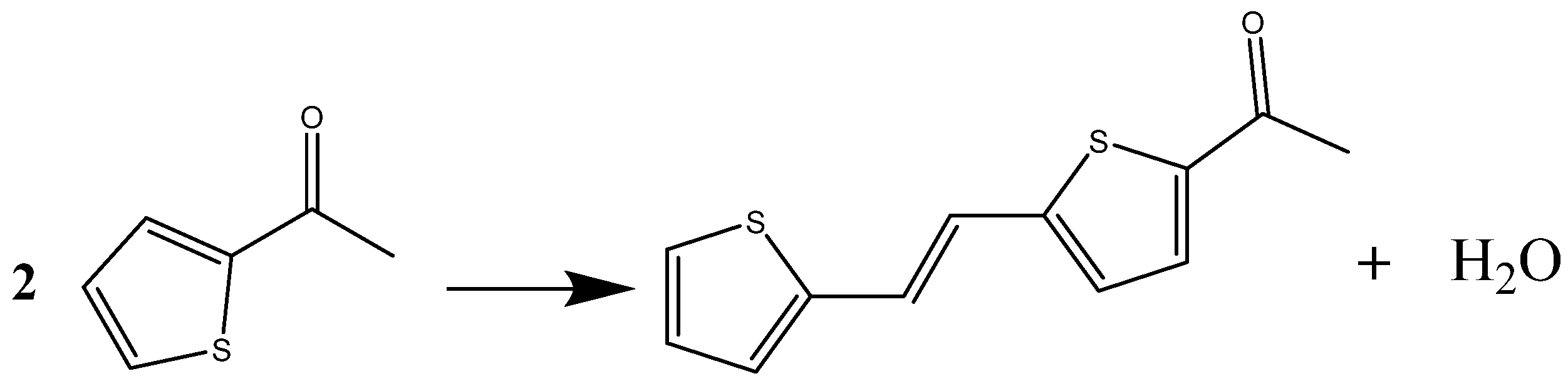
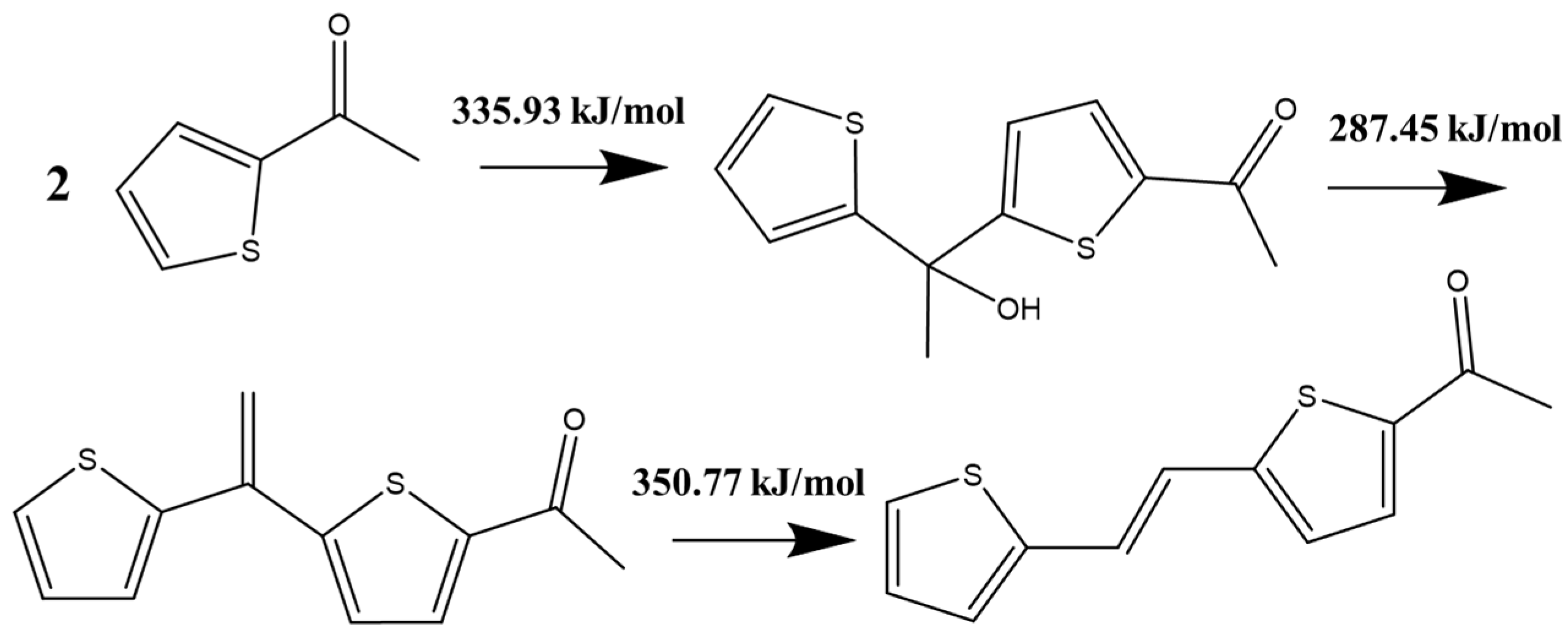
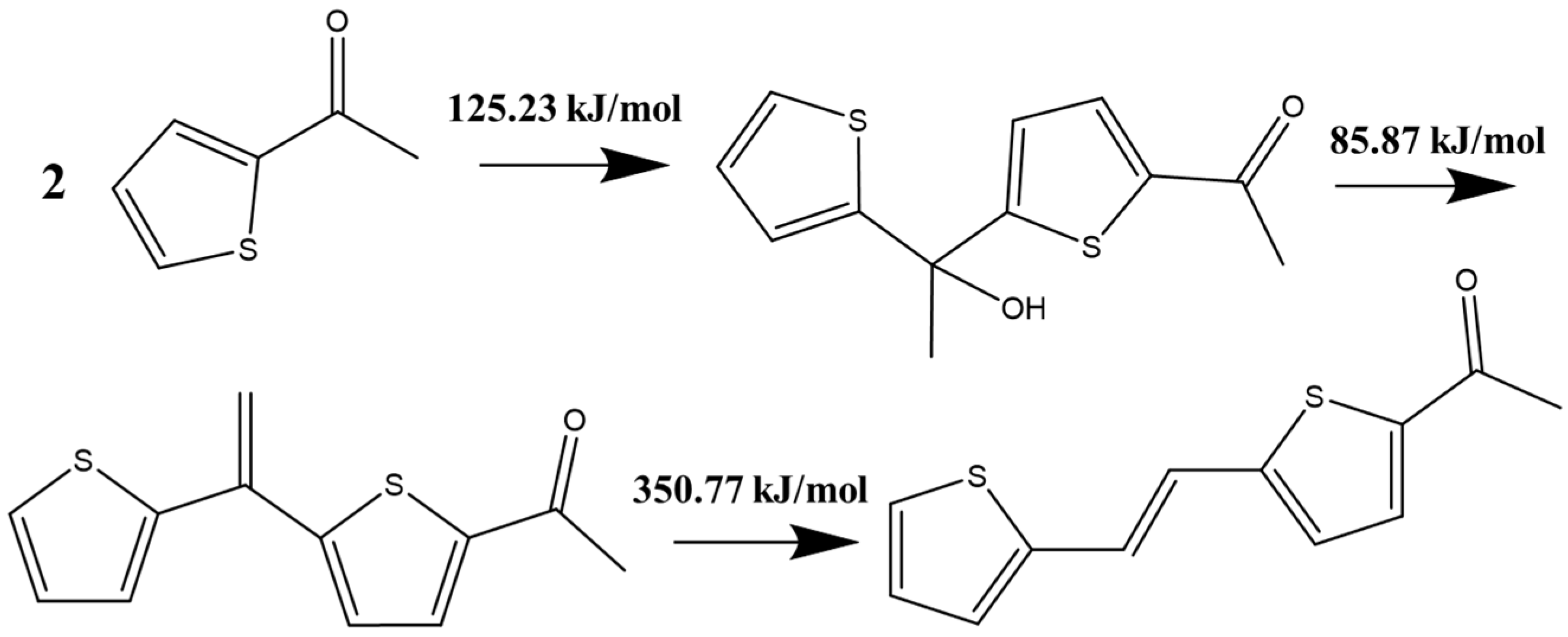
2. The Mechanism of Catalyst Inactivation
2.1. Molecular Simulation
2.2. Soaking Molecular Sieve Inactivation Experiment
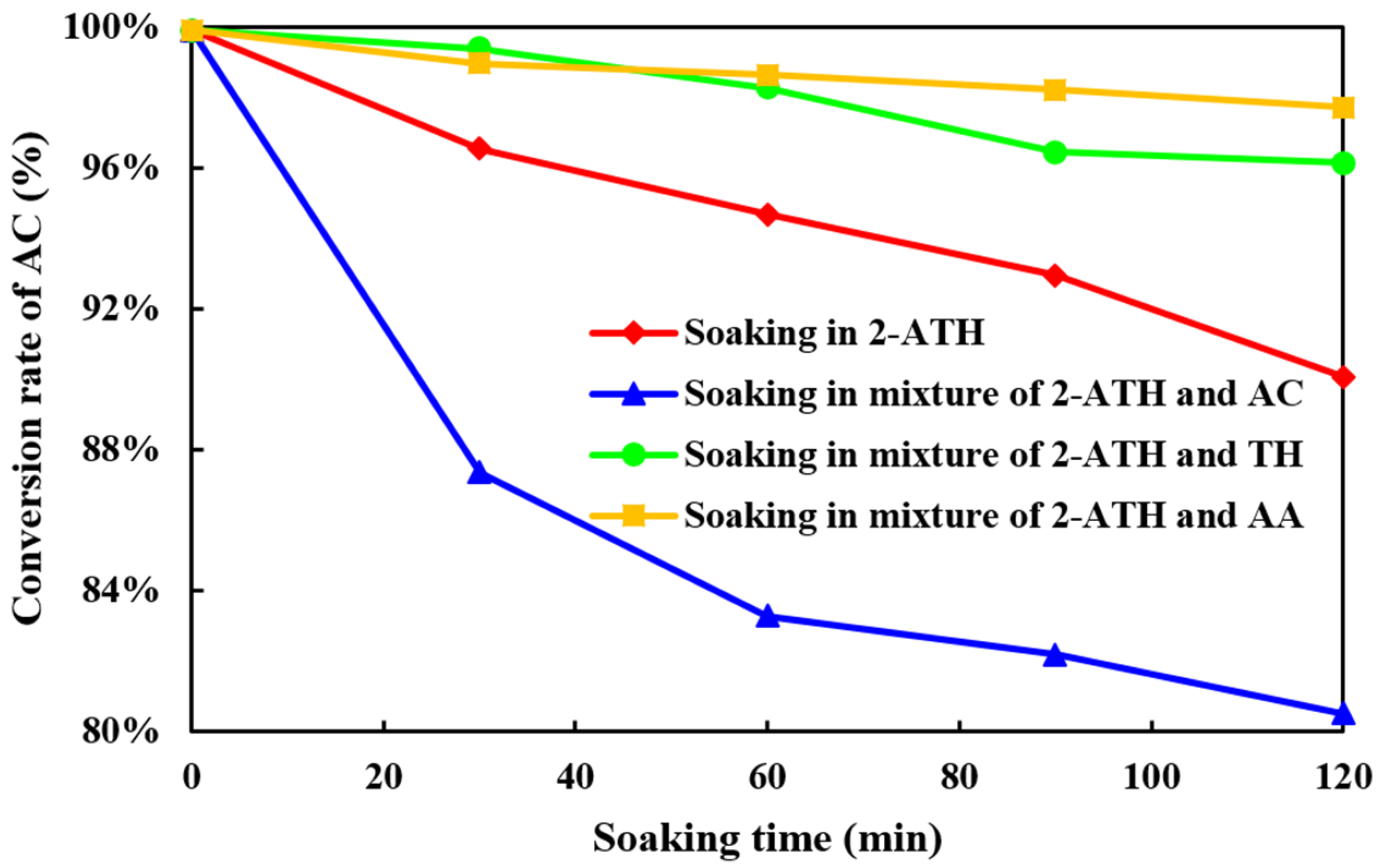
2.2.1. The Influence of Components on the Inactivation of Hβ Molecular Sieve
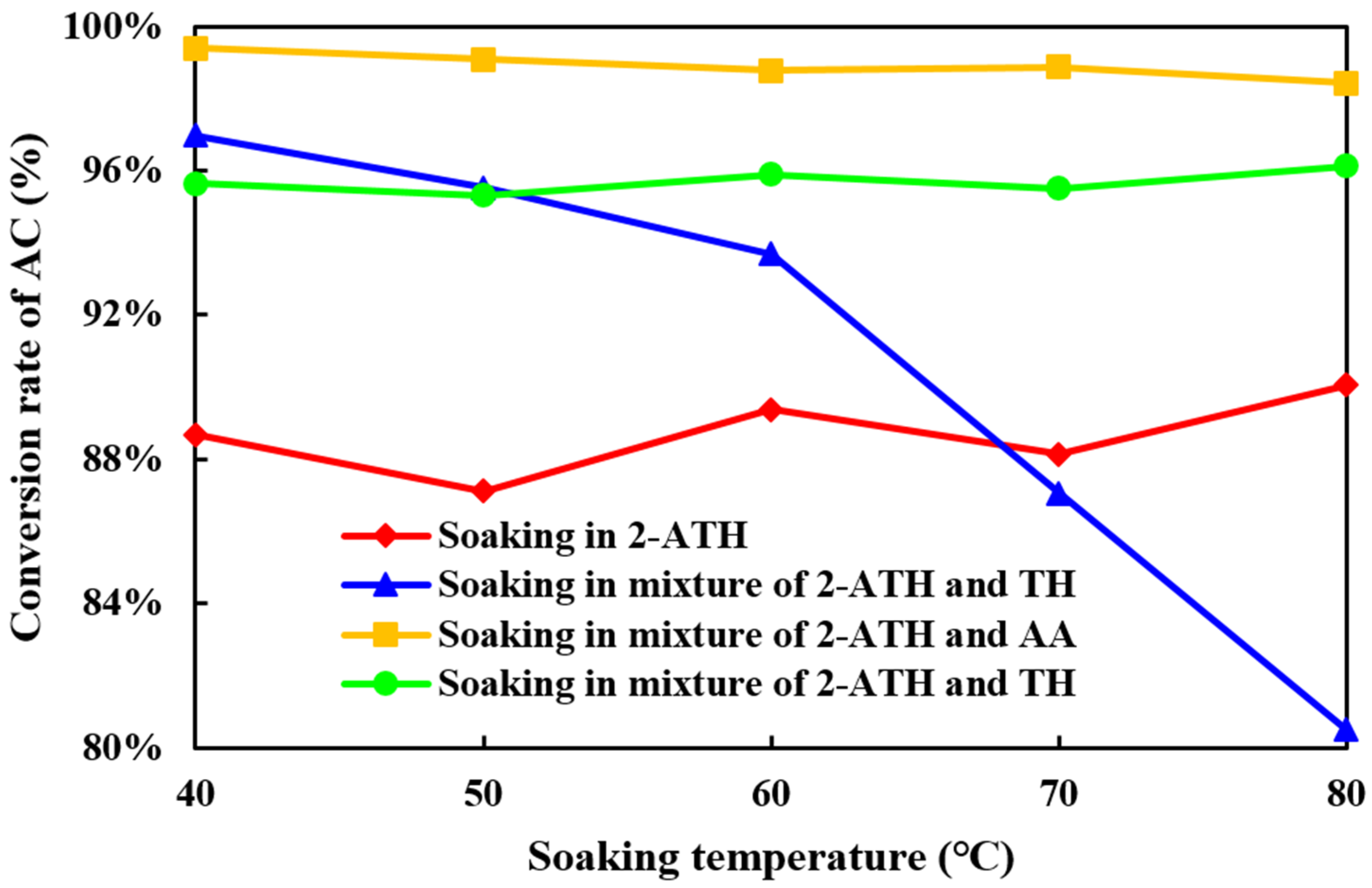
2.2.2. The Influence of Temperature on the Inactivation of Hβ Molecular Sieve
2.2.3. Discussion
3. Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation
3.1. Feasibility Verification
3.2. Continuous Experiment
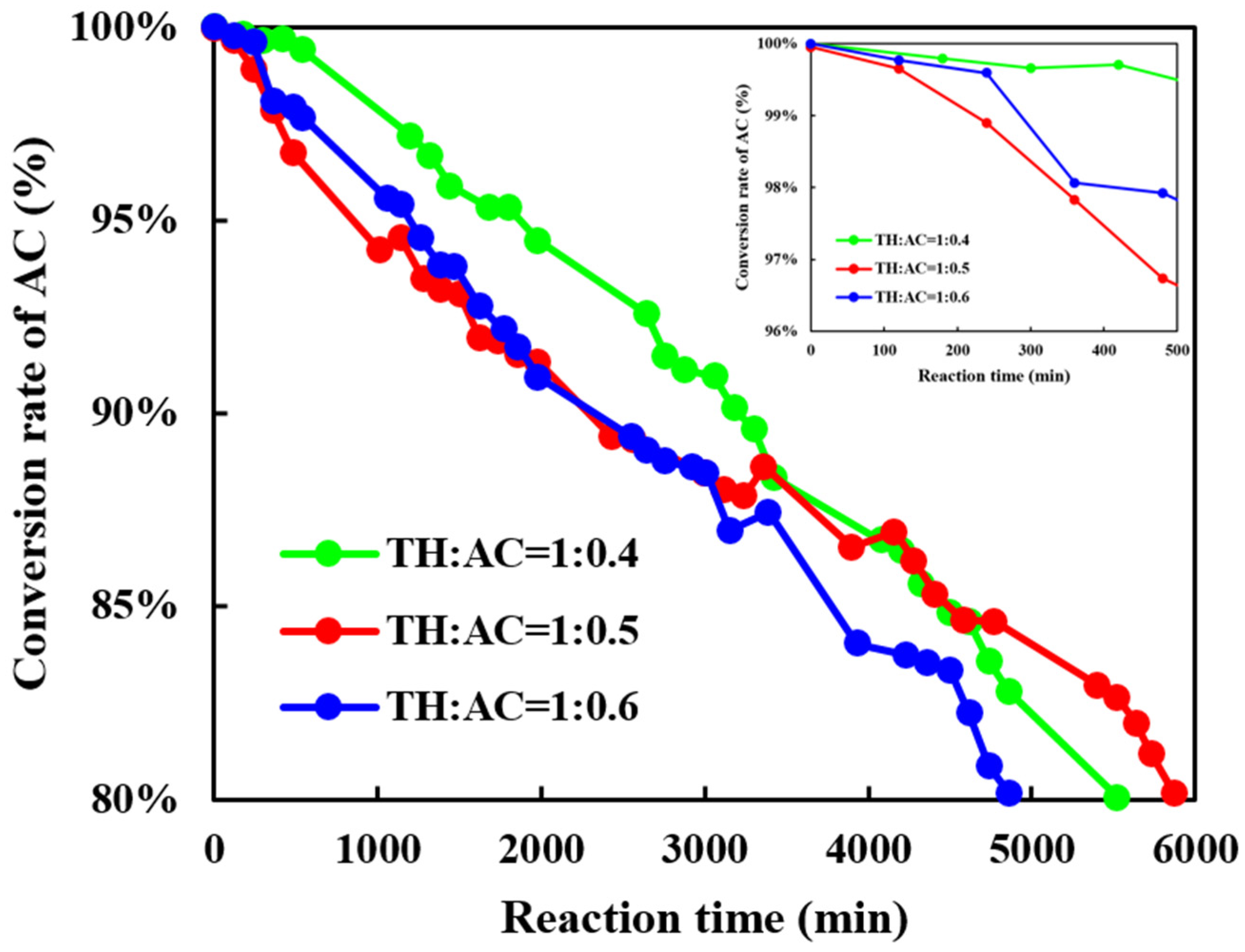
3.2.1. The Influence of the Molar Ratio of AC to TH on the Continuous Acylation of Thiophene
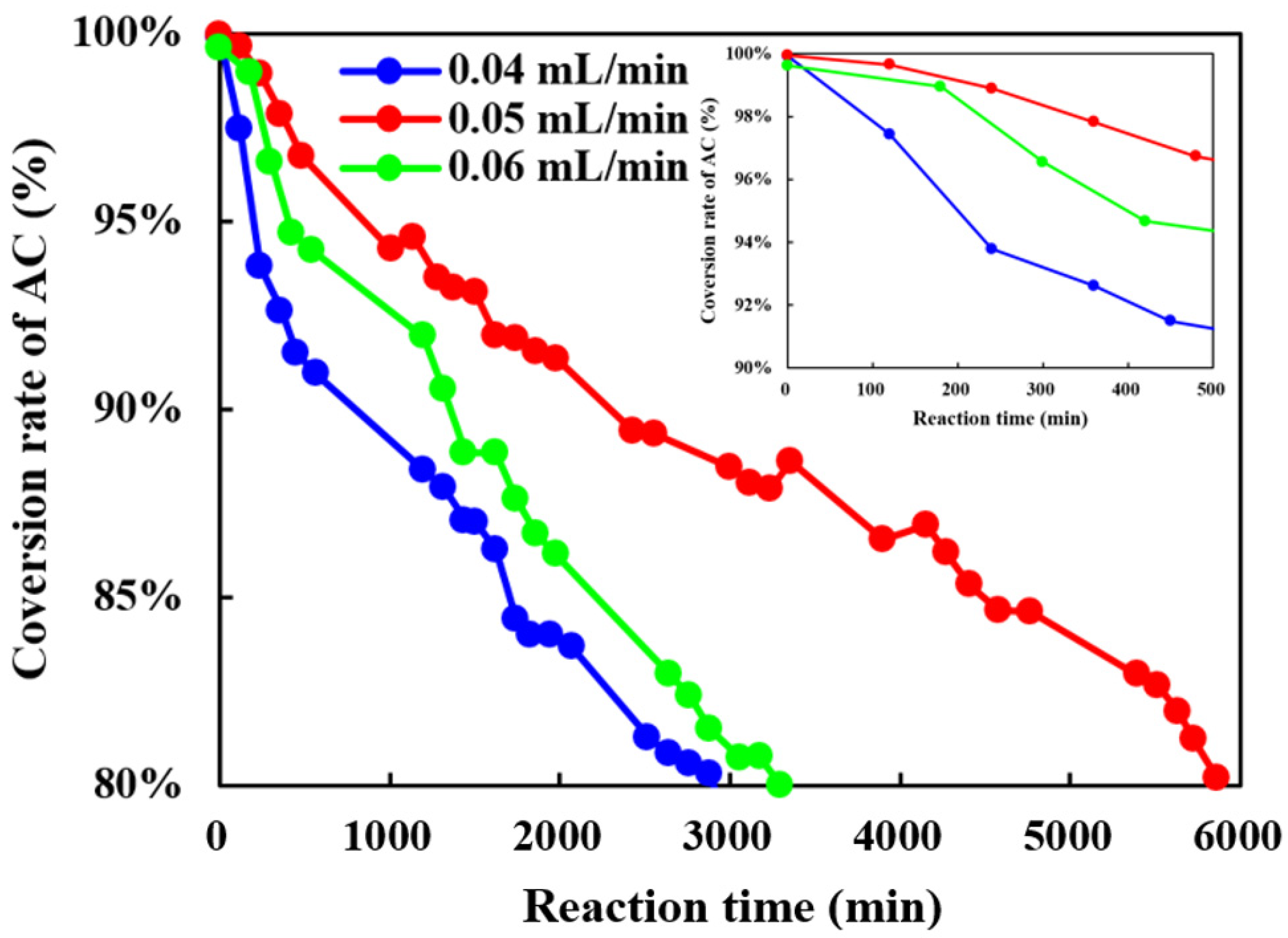
3.2.2. The Influence of VF of Raw Material on the Continuous Acylation of Thiophene
3.2.3. The Influence of Solvents on the Continuous Acylation of Thiophene
4. Experimental Preparation
4.1. Materials
4.2. Catalyst Pretreatment
4.3. Soaking Experiment
4.4. Continuous Experiment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bejblova, M.; Prochazkova, D.; Cejka, J. Acylation Reactions over Zeolites and Mesoporous Catalysts. Chem. Sustain. Chem. 2009, 2, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; Grieken, R.V.; Morales, G.; Nuno, V. Friedel Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds over arenesulfonic containing mesostructured SBA-15 materials. Catal. Commun. 2004, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, I.; Matsuo, J.I.; Kobayashi, S. Catalytic Friedel–Crafts Acylation of Heteroaromatics. Top. Catal. 2002, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinichen, H.K.; Holderich, W.F. Acylation of 2-Methoxynaphthalene in the Presence of Modified Zeolite HBEA. J. Catal. 1999, 185, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Finiels, A.; Meric, P.; Fajula, F. Acetylation of 2-methoxynaphthalene in the presence of beta zeolites: Influence of reaction conditions and textural properties of the catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2003, 85, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromentin, E.; Coustard, J.M.; Guisnet, M.; Mol, J. Acetylation of 2-methoxynaphthalene with acetic anhydride over a HBEA zeolite. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 159, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, G.; Maggi, R. Update 1 of: Use of Solid Catalysts in Friedel-Crafts Acylation, Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 181–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Lewis acids: From conventional homogeneous to green homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4307–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Lewis acids as catalysts in oxidation reactions: From homogeneous to heterogeneous systems. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3837–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, L.; Zhao, G.; Xu, Z.; Usman, M.; Zhang, S. 12-Tungstophosphoric acid niched in Zr-based metal-organic framework: A stable and efficient catalyst for Friedel-Crafts acylation. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.; Jiang, S.; Ji, S. Heteropoly acid encapsulated into zeolite imidazolate framework (ZIF-67) cage as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for Friedel-Crafts acylation. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 233, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endud, S.; Basir, N.M.; Lintang, H.O. Friedel-Crafts acylationof anisole over heteropoly acid supported on porous montmorillonite. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 846, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, Z.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, S.S. Liquid phase acylation of 2-methylnaphthalene catalyzed by H-beta zeolite. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 280, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J. Acylation of toluene with acetic anhydride over H beta zeolite. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2003, 31, 624–627. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, V.D.; Saroja, G.; Ratnamala, A. Vapor phase acylation of phenol over H beta, CeH beta and SO42−/ZrO2. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2003, 79, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Qin, Z.; Dong, M. Friedel-Crafts acylation of anisole and toluene with acetic anhydride over nano-sized beta zeolites. Catal. Lett. 2007, 117, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Qin, Z.; Dong, M. Acylation of anisole with acetic anhydride over Hbeta/MCM-41 composite molecular sieves. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2008, 36, 621–624. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Dou, H.; Fan, X. Synthesis of p-Methoxyacetophenone Catalyzed by Phosphoric Acid Modified Hbeta Zeolite. Fine Chem. 2009, 26, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, H. Acylation between anisole and acetic anhydride catalyzed by hierarchical porous Hbeta molecular sieve. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2019, 39, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Zeng, A. Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reaction of Liquid Thiophene Catalyzed by C25. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2012, 26, 989–993. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Xie, T.; Wu, J. Study on the synthesis of antidepression drug duloxetine hydrochloride and its impurity of intermediates. Chin. J. Synth. Chem. 2018, 26, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Mi, C.; He, X. Synthesis of a novel sedative-hypnotic indiplon. Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 16, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zeng, A. Continuous synthesis of 2-acetyl thiophene with C25 zeolite molecular sieve. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2014, 33, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, Y.; Tong, T.; Zeng, A. Effects of acid-modified HBEA zeolites on thiophene acylation and the origin of deac-tivation of zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 482, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Iwasa, N.; Fujita, S.I.; Arai, M. Dealumination of zeolite beta catalyst under controlled conditions for enhancing its activity in acylation and esterification. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.N.; Chen, W.Q.; Ma, J.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Zeng, A.W. Methods to delay deactivation of zeolites on furannacylation: Continuous liquid-phase technology and solvent effects. Rsc. Adv. 2015, 5, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.N.; Chen, W.Q.; Zeng, A.W. Optimization for catalytic performances of Hβ zeolite in the acylation of 2-methylfuran by surface modification and solvents effect. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 1557–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, A.R. Molecular Modelling Principles and Applications; World Book Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.S.; Ren, Q.; Chen, F.W.; Lu, T. Comparative study on the methods for predicting the reactive site of nucleophilic reaction. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.V.; Temprado, M.; Jime’nez, P.; Notario, R.; Chickos, J.S.; Santos, A.F.L.O.M.; da Silva, M.A.V.R. Thermochemis-try of 2-and 3-acetylthiophenes: Calorimetric and computational study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 11084–11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 2-ATH | CT | TH | AA | AC | DMF | DMSO | DI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipole moment | 3.1439 | 0.0000 | 0.5357 | 1.7199 | 4.0654 | 4.2862 | 4.4153 | 2.9972 |
| Number | Volume Flowrate (mL/min) | Catalyst Dosage (g) | Type of Solvent | Molar Ratio of Raw Material (TH:AC:X) | Initial Conversion Rate (%) | Lifetime (min) | Production Capacity of Catalyst (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 6.00 | No | 1:0.4:0 | 100.00 | 5520 | 18.07 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 6.00 | No | 1:0.5:0 | 100.00 | 5870 | 21.56 |
| 3 | 0.05 | 6.00 | No | 1:0.6:0 | 100.00 | 4860 | 19.92 |
| 4 | 0.04 | 6.00 | No | 1:0.5:0 | 100.00 | 2880 | 8.55 |
| 5 | 0.06 | 6.00 | No | 1:0.5:0 | 99.67 | 3300 | 15.06 |
| 6 | 0.05 | 6.00 | AA | 1:0.5:0.1 | 99.82 | 2910 | 10.09 |
| 7 | 0.05 | 6.00 | AA | 1:0.5:0.3 | 100.00 | 2850 | 9.38 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 6.00 | AA | 1:0.5:0.5 | 99.94 | 3300 | 10.04 |
| 9 | 0.05 | 6.00 | DI | 1:0.5:0.5 | 99.61 | 2800 | 8.01 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 6.00 | CT | 1:0.5:0.5 | 100.00 | More than 15,000 | More than 45.00 |
| Previous best results | 0.05 | 6.00 | AA | 1:2:1 | 99.98 | 4215 | 15.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Zeng, A. Investigation of the Hβ Molecular Sieve Inactivation Caused by Reactants and Products and Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030298
Yang S, Zeng A. Investigation of the Hβ Molecular Sieve Inactivation Caused by Reactants and Products and Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation. Catalysts. 2021; 11(3):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030298
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shunjin, and Aiwu Zeng. 2021. "Investigation of the Hβ Molecular Sieve Inactivation Caused by Reactants and Products and Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation" Catalysts 11, no. 3: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030298
APA StyleYang, S., & Zeng, A. (2021). Investigation of the Hβ Molecular Sieve Inactivation Caused by Reactants and Products and Improvement of Continuous Thiophene Acylation. Catalysts, 11(3), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030298





