Abstract
New carbonized biomass–metakaolin (PSD/MK_Fe) granular composite catalyst materials were manufactured for the catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO) of bisphenol A (BPA). These catalysts were characterized using different analytical and spectroscopic techniques, and results showed that the catalysts’ final properties were influenced by the addition of metakaolin (MK), polyvinyl alcohol, boric acid, and iron. Under the optimal CWAO experimental conditions (p: 20 bar, T: 160 °C, initial pH: 5–6, c[catalyst]: 1.0 g/L), nearly complete BPA conversion (>98%) and total organic carbon (TOC) conversion of 70% were reached. A key factor behind the enhanced catalytic activity was high specific surface area, although catalytic activity was also affected by surface acidity. These results confirmed the high efficiency of the current BPA conversion process involving the use of the easily separable and reusable PSD/MK_Fe catalyst. Therefore, biomass composite catalysts can be regarded as efficient catalysts for the oxidation of BPA during the CWAO process.
1. Introduction
Catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO) is one of the most economical and environmentally friendly wastewater treatment technologies used to break down organic matters into a more easily biodegradable form. CWAO has been used for the treatment of refractory organic pollutants, such as carboxylic acids and phenolic compounds (e.g., bisphenol A, BPA) [1,2,3]. The CWAO process can be efficiently conducted under mild operating conditions (low temperature and pressure) owing to the performance of heterogeneous catalysts [4,5,6]. In finding new catalytic materials with high activity and stability, various heterogeneous catalysts (e.g., noble metals, metal oxides, and carbon materials) have been prepared and tested for the CWAO of model compounds and real wastewater [5,7]. However, during the CWAO of organic compounds, heterogeneous catalysts are deactivated by metal leaching and by carbonaceous deposits on their surface [3,8]. Therefore, further optimization of the catalyst design is needed.
Utilization of industrial side streams are driven by international and national strategies and legislation. Various industrial processes generate carbonaceous side streams; additionally, waste biomass (e.g., sawdust) is formed in huge amounts annually (e.g., 2–3 million m3 per year in Finland) [9]. Modification of these waste biomasses into activated carbon (AC) or other utilization applications is desired to improve the circular economy and the bioeconomy. An AC’s unique and versatile properties, such as its stability under both acidic and basic reaction conditions, high surface area, and highly porous structure, have been recognized in many catalytic research works related to the prevention of environmental pollution [2,10,11]. Moreover, surface oxygen complexes, such as carboxyl, carbonyl, phenol, quinone, and lactone groups, are especially considered important because they can act as anchoring sites that interact with metallic precursors and metals that improve dispersion [12,13,14]. Different oxidizing agents, such as nitric acid, potassium permanganate, and hydrogen peroxide, have been used to increase the surface functionality of carbon [2,15,16,17]. In addition, it has been shown that the stability and catalytic activity of carbon in CWAO improves when metals, such as iron, platinum, and ruthenium, are incorporated onto the carbon surface [2,18,19].
When an AC catalyst is to be used at the industrial level, it is typically shaped into various forms, such as granules, extrudates, and pellets [20]. Granules are the most preferred form for industrial products because they demonstrate high packing density, and they are easy to reuse and regenerate [21,22,23]. Typically, for raw materials with low level of hardness (e.g., wood), suitable binders, such as starch, calcium carbonate, organic resins, or siliceous, and aluminous materials (e.g., metakaolin (MK)), are added in order to achieve the desired shapes of materials [24,25,26,27]. MK is a highly reactive material as its surface silicon–oxygen and aluminum–oxygen structures can enhance mineralization through surface reactions [28]. Furthermore, MK, especially when treated with acid (e.g., phosphoric acid), increases the number of acidic sites and improves the strength and resistance of a material to high temperatures and to chemicals [29,30,31]. On the other hand, the mechanical strength and water stability of the material can be tailored using a crosslinking agent (e.g., boric acid) together with organic polar polymer, such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) [32]. Hence, the combination of a modified AC and MK/PVA is expected to enhance the properties of the resulting composite catalyst for an application in CWAO. To our knowledge, the modification of a biomass-based acid-activated carbon with acid-activated MK/PVA blends has not yet been reported in the literature. In addition, the manufacturing process for biomass-based catalyst demonstrates a good scalability owing to the ample supply of lignocellulosic biomass, which exists both as a virgin material and a waste material worldwide.
In this study, carbonized biomass and commercial AC as reference material were used as support materials for granulated carbon catalysts. The surface composition of these materials were modified by oxidation treatment with 6 M nitric acid. The oxidized carbons were mixed with MK, calcium carbonate, and PVA together with a solvent (phosphoric acid) and then shaped into granules. The granules were placed in boric acid aqueous bath to achieve a stable structure. Finally, iron was impregnated as an active metal into the prepared catalyst. This research mainly aimed to produce novel tailored granular biomass-based composite catalysts from sawdust and to determine their efficiency in the CWAO of BPA. The efficiency of the prepared catalysts was studied by analyzing the BPA and TOC conversions; the possible oxidation by-products were also analyzed. Moreover, the influence of the surface chemistry of the studied materials on the efficiency of the CWAO process was investigated.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Support Materials and the Catalysts
The evolution of surface porosity, pH, and point of zero charge pH (pHzpc) of the solution during the material processing is shown in Table 1. Expectedly, the material processing gradually reduced the specific surface area (SSA) due to the liquid-phase oxidation with nitric acid (AC1 and PSD1), due to ball milling, and due to the possible inorganic matter deposition during the treatments. However, the SSA remained relatively high, and no major differences in SSA were observed between the composite granules (AC/MK and AC/MK_Fe vs. PSD/MK and PSD/MK_Fe). The commercial AC-based granular composite materials (i.e., AC/MK and AC/MK_Fe) were found to be more microporous than mesoporous compared with the biomass-based materials, and throughout the modifications, these porosity types did not change. By contrast, the porosity types of the carbonized biomass granular composite materials (i.e., PSD/MK_NM and PSD/MK_Fe) was closer to the 1:1 ratio, which slightly decreased during the modification. For the PSD/MK_Fe material, the total pore volume did not change, whereas its pore size decreased compared to that of the precursor (PSD1). This decrease was assumed to be a result of material densification given that the microporosity of the materials also decreased compared with that of PSD1. For the AC-based materials, both the pore volume and size remained stable compared with those of the precursor (AC1). Moreover, the evolution of the pHzpc values throughout the material modification process can be clearly seen; the nature of both the main raw materials (AC0 and PSD0) changed gradually from highly basic to highly acidic, indicating that possible acidic functionalities were incorporated onto the surface of the catalyst materials.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the studied materials.
The main components of the materials were analyzed by an elemental analyzer and by ICP-OES, and the results are presented in Table 2. No major differences in elemental composition were observed between the studied catalysts. The high silicon/aluminum ratio indicates high amounts of quartz [33]. The iron content of the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe were 0.5 and 0.8 wt%, respectively, indicating that the iron impregnation was inefficient for these samples given that the target value for iron was 3 wt%. This result was probably due to the too acidic reaction conditions for iron impregnation. In dilute solutions with pH < 9, boric acid exists in a non-ionized form (pKa 9.2). However, at higher boron concentrations (>0.025 M), boric acid acts as a much stronger acid, and the formation of triborate ([]) and tetraborate [] occurs [34]. In our study, the boron concentration was 0.04 M. Moreover, the pH of the boric acid–iron salt bath varied between 2 and 2.5, indicating that the surface of the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe was positively charged (pH for the precursors AC1 and PSD1 < pHzpc for AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe; Table 1). Thus, the electrostatic interactions favored the bonding with boron species over the bonding with iron cations. Between the catalysts with and without iron doping, the latter had an iron content that was lower by only 0.2–0.3%-points. This iron originates from the MK and carbon materials. As shown by the elemental analysis results, oxygen content increased by around 3–5% due to the modification of the catalyst materials. This high oxygen content was consistent with the pH and pHzpc results (Table 1) given that the oxygen surface groups of the carbons are mainly acidic [35,36]. This finding was further supported by the silicon/aluminum ratio, wherein the higher silicon/aluminum ratio resulted in lower pH and pHzpc values and vice versa.

Table 2.
Elemental analysis of the samples.
The FESEM back-scattering image of the AC/MK_Fe catalyst is presented in Figure S1. The heterogeneous surface of the AC/MK_Fe catalyst was occupied by different metal particles as shown in Figure S1. Based on an EDS analysis, this catalyst contained iron and aluminum, which are indicated by colored squares with symbols in Figure S1. The other catalysts had similar surface morphology as AC/MK_Fe (results not shown).
As seen in the XRD spectra (Figure 1), the raw MK exhibited two main phases that were associated with quartz (2θ = 26.6°) (ICDD: 01-070-7344) and potassium aluminum silicate (2θ = 17.5°, 19.6°, and 20.8°) (ICDD: 00-046-0741) [29]. The AC/MK, AC/MK_Fe, PSD/MK, and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts exhibited similar XRD patterns compared to MK, and the main crystalline phase belonged to quartz, supporting the results of the elemental studies (Table 2). This finding indicates that the MK did not change during the preparation process, thereby acting as a filler in the matrix and providing a denser structure to the materials, supporting the results of the surface area and porosity studies (Table 1). The other possible phases in the studied samples were iron phosphate hydroxide (2θ = 27.8°, 26.6°, 44.2°) (ICDD: 04-012-1302), boron phosphate (2θ = 20.7°, 26.3°, 36.3°) (ICDD: 00-011-0237), and aluminum phosphate (2θ = 20.3°, 26.2°, 26.6°) (ICDD: 04-019-3429); however, a definite identification was not possible due to peak overlapping. A “hump” between 20° and 30° 2θ and 40° and 50° 2θ can be clearly seen in all PSD-based materials, a very typical feature for amorphous or semi-amorphous materials [30,37,38]. A typical phase construction for graphite (ICDD: 00-056-0159) was exhibited by PSD1, whereas the AC1 XRD spectrum resembled quartz, a typical component found in coal-based AC [39].
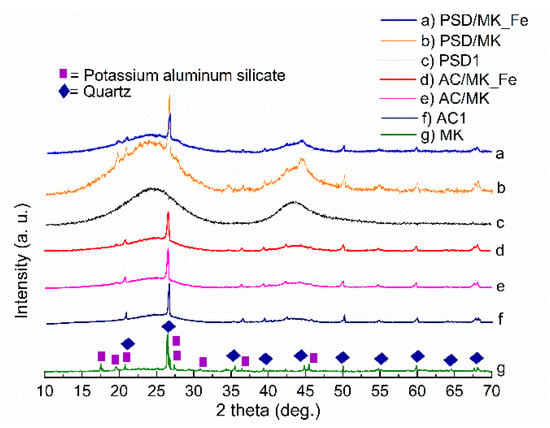
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractograms of the studied materials. The crystalline phases marked to the MK diffractogram are identified as SiO2 (ICDD: 01-070-7344) and KAl3Si3O11 (ICDD: 00-046-0741).
2.2. Spectroscopic Studies
An XPS measurement was conducted to study the chemical bonding and nature of the functionalities of carbon, oxygen, silicon, and boron of the samples. The following surface carbon species were considered: C–C, single C–O bonds, double C=O/O–C=O bonds, and π–π* in aromatic rings. The surface oxygen species bonded to carbon were identified as carbonyl or quinone oxygen (C=O/O–C=O), lactonic oxygen or anhydride oxygen (C–O/C–O–C), and carboxyl oxygen (COOH). The binding energies and the relative atomic abundancies obtained from the C1s and O1s fittings [40,41,42] are shown in Tables S1 and S2. The results analysed by Avantage V5 program were well in line with the bulk characterization results obtained for carbon and oxygen (Table 2), and the variations within the results are due to the different analytical techniques used.
Among the acidic groups detected (Table S2), the lactonic groups were the most abundant in almost every catalyst material; the abundance of the carbonyl or quinone and carboxylic groups was found to be similar. Surprisingly, the amount of these functionalities were lowest in the AC/MK_Fe catalyst, which displayed the most acidic pH and the lowest pHzpc value (Table 1). This finding indicates that inorganic acidic functionalities also contribute to the acidity of the materials. However, as shown in these results, acidic functionalities were successfully introduced onto the carbon surface through carbon oxidation with nitric acid. This result was consistent with previous findings [2,43].
The silica XPS 2p and the boron XPS 1s spectra of the PSD/MK catalyst are presented in Figure S2. The atomic abundance within the materials was similar, consistent with the results for the elemental and ICP-OES analyses (Table 2). The atomic abundance for boron was 8.9–13.0% and that for silicon was 1.8–2.5%. The B1s spectrum peaked at 192.5 eV, a typical binding energy attributed to boron oxide (B2O3) [44,45]. The peak detected at 103.5 eV corresponds to the Si 2p binding energy, which is assigned to silicon dioxide [46], supporting the XRD results (Figure 1). The same peaks were found in the other studied materials (results not shown).
The surface chemistry, especially the acidic properties, of carbon plays an important role in oxidative reaction efficiency. Surface acidity has been demonstrated to increase catalytic activity, for example in the studies conducted by Quantanilla et al., 2007 [2], Wang et al., 2014 [16], and Yang et al., 2007 [47]. Therefore, the acidity of the manufactured catalysts was studied using in-situ DRIFT spectroscopy that involved a 20-minute ammonia adsorption followed by a 5-minute argon flushing, and the results for the AC and carbonized biomass (PSD) materials are presented in Figure 2A,B, respectively.
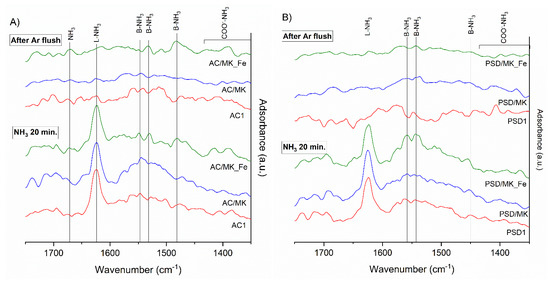
Figure 2.
DRIFT spectra after 20 min ammonia adsorption and after 5 min Ar flush over (A) activated carbon (AC) and (B) carbonized biomass materials. Abbreviation “B” indicates Brønsted acid site and “L” Lewis acid site.
The strong peak observed for both the AC- (Figure 2A) and PSD-based (Figure 2B) catalysts at 1624 cm−1 after ammonia adsorption is assigned to the weakly adsorbed ammonium on the Brønsted and Lewis acid sites [48]. The bands at 1525–1550 cm−1 after the adsorption of ammonia onto the AC-based materials and the strong peaks determined at 1545 and 1568 cm−1 in the PSD support material were identified as C–NH vibrations [49,50,51], indicating ammonium adsorption on the Brønsted acid sites. In the PSD-based catalysts, the doublet identified at around 1640–1650 cm−1 and the peak identified at around 1480–1490 cm−1 were assigned as the N–H vibrations on the Lewis sites of the surface mainly due to the formed amides [51,52,53]. Peaks at around 1680 cm−1 and 3330–3360 cm−1 (not shown) were attributed to gaseous ammonia (e.g., Bahrami et al., [54]). In the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst, the peaks at 1598 and 1474 cm−1 were assigned as NH2 and ammonium, respectively, on the Lewis acid sites [48,49,51,55]. It is worth noting that ammonium salts are produced in the reaction of gaseous ammonia with carboxylic acid sites on the carbon support (Tables S3 and S4); the formed ammonium salts on the surface carboxylic acids (COO−) were identified at 1518 cm−1 and in the 1250–1390 cm−1 region [53,56]. The differences in the ammonia adsorption in the AC and PSD samples could be assumed to have been caused by the difference in the chemical composition of the samples’ carbonaceous species (fossil carbon vs. biomass carbon, respectively) and by the inorganic compounds (e.g., phosphorus, silicon, and boron) present in the samples (Table 2). In addition, the chemical compositions of the parent AC/MK and PSD/MK versus the Fe-doped samples only slightly differed (Table 2), and their acidity and basicity (Brønsted and Lewis) could only be roughly estimated based on their spectra. Based on these results, it is impossible to determine whether iron exerts an effect on acidic site formation or on the strength of the studied materials.
2.3. Non-Catalytic Experiments
Preliminary wet air oxidation (WAO) experiments and experiments not involving an oxidant were performed to evaluate the stability of BPA under the operating conditions used in CWAO. The results are presented in Figure 3. The pH of the BPA solution (5–6) was not adjusted during the experiments and thus the electrostatic interactions are not expected to occur as BPA should be in the non-ionic form (pKa 9.6–10.2) [57].
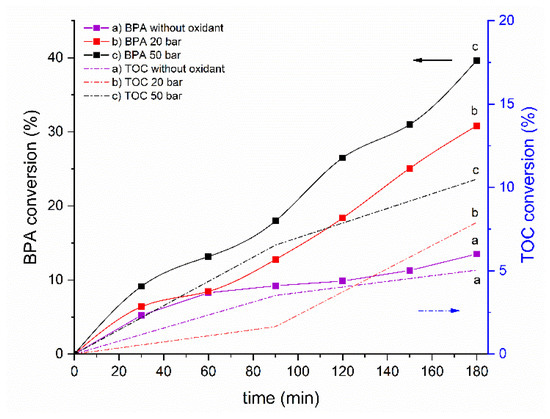
Figure 3.
BPA and TOC conversion as a function of reaction time in non-catalytic experiments. Operating conditions: p (air): 20/50 bar, c (BPA): 60 mg/L, T: 160 °C, 800 rpm, pH initial 5–6. RSD ± 2%. Note the different scales on both y-axes.
Moderate conversion of BPA (around 40%) and low TOC conversion (around 10%) (Figure 3) were revealed by the analyses of the BPA solutions in the WAO experiments. The pH of the BPA solution (5–6) changed during the oxidizing reaction to around pH 4.5, and it was associated with a color change from bright to light yellow. Although the identification of aromatic intermediate compounds was not feasible, the color change indicates the formation of a by-product, which was identified as hydroquinone by other researchers [58]. Expectedly, the experiments without an oxidant resulted in even lower BPA and TOC conversion rates, that is, less than 20% and around 5%, respectively. No color change was observed in this case, and the pH of the final solution was around 6.4. The influence of the reaction pressure (20 or 50 bar) was also evaluated; when a higher pressure was used, the BPA conversion was higher by only around 10%-points, and the TOC conversion was around 2.5%-points.
2.4. CWAO Experiments
At first, the catalytic experiments were performed at a pressure of 20 and 50 bar and at a catalyst load of 2.0 g/L. The effect of the higher reaction pressure on BPA removal was found to be negligible. For both the studied catalysts (AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe), the BPA conversion was nearly 100%, whereas the TOC conversion was around 10–15% higher when the higher reaction pressure was used. Therefore, 20 bar was selected for further experiments given the reduced energy consumption of the process under this condition, leading to a higher cost-efficiency.
The AC/MK, AC/MK_Fe, PSD/MK, and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts were compared in the CWAO experiments involving model BPA solutions (60 mg/L). The experiments were conducted at 160 °C and 20 bar to investigate the influence of catalyst loading (0.5–2.0 g/L) on BPA adsorption and on BPA and TOC conversions. In addition, experiments involving the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts were performed at a lower reaction temperature (130 °C) using 1.0 g/L catalyst loading. BPA adsorption was evaluated during the heating period (under nitrogen gas flow), and the BPA and TOC conversions within the reaction time of 180 min were determined. The results are presented in Figure 4.
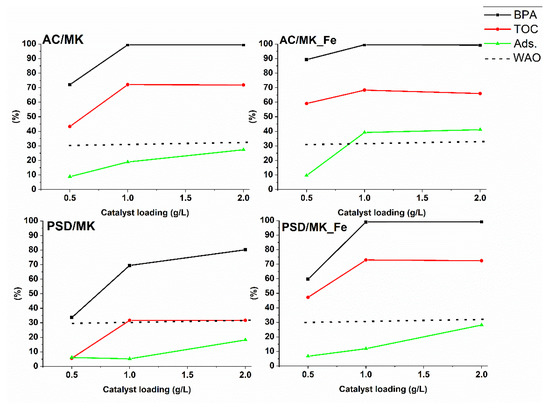
Figure 4.
BPA and TOC conversions and BPA adsorption (Ads.) of AC/MK, AC/MK_Fe, PSD/MK, and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts with different catalyst loading. BPA and TOC conversions are presented at the reaction time 180 min and BPA adsorption after the heating period. The result of homogenous WAO is presented with a dashed line. Operating conditions: p (air): 20 bar, c (BPA): 60 mg/L, T: 160 °C, 800 rpm, pH initial 5–6. RSD ± 4%.
As shown in Figure 4, the highest amount of BPA was adsorbed on the microporous AC/MK_Fe catalyst at 160 °C, regardless of the amount of the catalyst. The AC-based materials were found to be more microporous than the PSD-based materials (Table 1), and this characteristic of the former may have enhanced the adsorption process [59,60]. When a lower reaction temperature (130 °C) and a catalyst dosage of 1.0 g/L were used, around 35% and 12% of BPA were adsorbed by the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts, respectively. The amount of adsorbed BPA at this temperature was similar to that observed in the experiments performed at 160 °C. Besides the porosity and surface area, pH is also known to affect the adsorption process [61]. During the CWAO reaction for all the studied catalysts, the pH decreased to pH 3–4, indicating that the surface of the catalysts was negatively charged (pH > pHpzc, Table 1) and therefore should not favor BPA adsorption as it exists in neutral form at a pH below 8 [57]. Hence, the adsorption of BPA onto a catalysts is believed to be controlled by interactions other than electrostatic interactions. It has been shown that when non-electrostatic interactions (e.g., π–π dispersion or hydrophobic interactions) are responsible for the adsorption of organic molecules, adsorption depends mainly on the porosity of the sorbent [59].
The AC-based catalyst materials performed similarly and slightly better in terms of BPA and TOC conversions than the PSD-based catalysts during the catalyzed oxidizing reaction. However, a significant difference was observed among the PSD-based materials: In the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst, when the catalyst loading is up to 1.0 g/L, the BPA and TOC conversions ranged from around 60% to 99% and from around 45% to 70%, respectively. These conversions are approximately 30–40% higher than those of the PSD/MK catalyst. In all of the studied catalysts, when 2.0 g/L catalyst loading was used, the BPA and TOC conversions remained the same or slightly lower than the conversions obtained when the catalyst concentration was 1.0 g/L. This result is expected to have been caused by the radical scavenging effect wherein higher catalyst loadings reduce the catalyst performance by decreasing the overall oxidation reaction [62]. A widely proposed mechanism that could explain the CWAO reaction process is the free radical chain reaction mechanism [63,64], which is assumed to be stationary [65,66] and wherein a catalyst is seen to play a two-fold role, that is, it acts both as an initiator and a terminator of free radicals. In such a chain reaction cycle, the rate of free radical formation compete with the rate of destruction, and the reaction rate is related to the increase in catalyst loading. However, the amount of active sites on the catalyst (i.e., catalyst loading) determines the rate of free radical formation. Thus, at a lower catalyst loading (up to 1.0 g/L), free radical formation dominates, whereas at a higher loading (2.0 g/L), free radical destruction dominates. Therefore, 1.0 g/L was an optimal catalyst loading for the conversion of BPA and TOC at 160 °C and at 20 bar. Similar results for phenol removal using a ceria-based copper oxide catalyst [67] and alumina-supported ceria catalysts [68] have been reported.
When the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst was used in an oxidizing reaction at a lower temperature (130 °C) and at a catalyst loading of 1.0 g/L, the BPA conversion decreased (around 87%), but the TOC conversion (around 70%) did not change compared with those obtained in experiments performed at 160 °C. Similarly, a TOC conversion of around 70% was observed when the AC/MK_Fe catalyst was used at a reaction temperature of 130 °C. These results were expected given that higher conversion rates are typically obtained at higher reaction temperatures [69]. During the catalyzed oxidizing reaction, the pH of the BPA solution (5–6) decreased to around pH 3–4 in all of the studied catalyst materials and in the studied reaction temperatures (160 °C and 130 °C), indicating the formation of acidic intermediates during the reaction. No color change was observed in these experiments.
In summary, BPA conversion was clearly enhanced when the catalysts were present, and most of the BPA conversion can be attributed to catalytic oxidation. It is recognized that the catalytic activity of carbon materials are significantly influenced by the textural and chemical properties, such as surface area, porosity profile, surface acidity, and surface functional groups, of catalysts [70]. Regarding the BET surface area measurements (Table 1), each of the studied catalyst material demonstrated a high SSA. The differences in the materials’ SSAs support the results obtained from the CWAO reactions: the lowest SSA (212 m2/g) belonged to the PSD/MK catalyst, which had the lowest catalytic activity, whereas the highest catalytic activity as well as the highest SSA belonged to the AC/MK catalyst (around 400 m2/g). The AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts demonstrated a comparable SSA and catalytic activity (i.e., SSA was approximately 300 m2/g). Moreover, the catalytic activity was evidently enhanced by the acidity of the catalyst, because the SSA cannot completely explain the high catalytic activity observed in both the iron-doped catalysts. The enhanced activity most likely originates not only from the oxidized carbon (Table 1 and Table S2, Figure 2) but also from the amorphous aluminum silicates of MK (Table 2) and boron trioxide (Figure S2). For example, the AC/MK_Fe catalyst had the lowest amount of acidic carbon functional groups as revealed by the XPS study (Table S2). However, this catalyst had the lowest pH and pHzpc values (Table 1), indicating that part of the catalytic activity is due to aluminum silicates and/or boron trioxide. Boron intrinsically accepts electrons, and this may lead to high affinity towards oxygen, thus improving the adsorption of oxygen and the formation of oxygen reactive species, which again may enhance the oxidation of organic compounds [71]. Similar results for phenol removal using phosphorus-, boron-, and nitrogen-doped carbon blacks in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation have been presented elsewhere [44]. In this study, the kinetic rate constants of hydrogen peroxide degradation were up to eight times larger when doped carbons were used than when non-modified carbons were utilized. In addition, the acidity of aluminosilicates is a well-known fact and it has been shown to be dependent on the silicon/aluminum ratio; when this ratio increases, the acidity also increases. This finding supports our results, as the PSD/MK showed the lowest catalytic activity. According to the characterization results, the PSD/MK had the lowest silicon/aluminum ratio (Table 2) and the highest pH and pHzpc values (Table 1) compared with the other catalysts. Furthermore, the presence of iron (Table 2), which is acidic itself, may partly explain the increased acidity of the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts (Table 1). Similar results for phenol removal using AC oxidized with nitric acid and impregnated with iron have been presented elsewhere [2]. The iron-doped carbons were found to enhance the activity by around 30% compared with the ACs containing the same amount of oxygen surface groups. Based on the above discussion and given the amount of the adsorbed BPA (around 40% for AC/MK_Fe vs. 10% for PSD/MK_Fe at a catalyst loading of 1.0 g/L), the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst was found to be the catalytically most active material for BPA conversion under the studied reaction conditions.
2.5. Kinetic Modeling
The pseudo-first order rate law was used for the kinetic modeling of BPA conversion for the most catalytically active catalysts, namely PSD/MK_Fe and AC/MK_Fe. The measured data was fitted by using a standard non-linear least squares algorithm, as shown in Equation (1):
where total conversion (Rtot) and rate constant (k) were used as fitting parameters; t refers to oxidation time. The sum of the square error (SSE) function was used to evaluate the model functionality between the experimental () and the predicted concentration () of BPA, and it was minimized as an objective function, as shown in Equation (2):
Residual errors were calculated as average relative percentage. Figure 5 shows the experimental (symbols) and the fitted (lines) BPA conversion rates as a function of time for the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts and of the WAO reaction at 160 °C. The reaction rates and the average relative error are presented in Table 3. A good agreement between the experimental and the predicted results was seen in the results, with an average relative error of less than 5% for both the studied catalysts. The CWAO process was found to be 2.0–6.5 times faster than the WAO reactions (Table 3). Comparison of the catalyst materials showed that the AC/MK_Fe performed 2.9 times faster than the PSD/MK_Fe. This result is in line with the previously presented adsorption results (Figure 5), which showed that the AC/MK_Fe adsorbed the highest amount of BPA, a feature that typically also promotes the reaction rate [5,16].
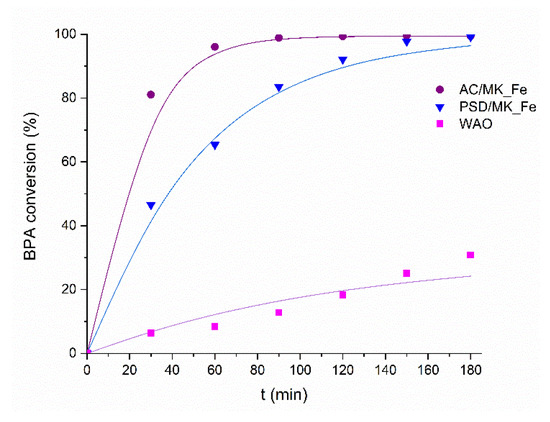
Figure 5.
Bisphenol A conversion as a function of time for AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts. Operating conditions: p (air): 20 bar, c (BPA): 60 mg/L, c (cat): 1 g/L, 800 rpm, T: 160 °C.

Table 3.
The rate constant and average relative error for the CWAO and WAO.
2.6. Stability and Reusability of Catalysts
The stability of catalysts is vital in many respects because leaching of metals and other elements can cause unwanted secondary pollution and because the reusability of catalysts is dependent on the stability of catalysts. Therefore, AAS (iron and calcium) and ICP-OES (aluminum, silicon, phosphorus, and boron) analyses were performed on the terminal water samples for all the studied catalysts after the oxidation reaction; in addition, the leaching of the particles from the granular composite catalysts and the reusability of the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst were studied twice.
No leaching of iron or aluminum was detected in any of the samples. Moreover, the possibility of nickel and chromium contamination due to ball milling and the possibility of contamination coming from the pressure reactor were studied; no chromium was detected, and the amount of nickel varied between 0.2 and 0.7 mg/L (≡0.0034–0.0119 mmol/L). This amount was two or even three orders of magnitude lower than that obtained in a homogenous WAO experiment of phenol over a nickel catalyst (nickel concentration: 2 mmol/L [72]); therefore, nickel is not expected to contribute to the conversion of BPA in this study. The amount of leached calcium was also low (1.3–2.0 mg/L), whereas the amounts of leached phosphorus (8.4–14.8 mg/L), silica (13.0–14.0 mg/L), and boron (23.3–42 mg/L) were significant. This result indicates that during the material processing and washing, the washing step was insufficiently effective in removing the excess chemicals.
The masses of the granules after the CWAO experiments (performed at 160 °C and at 20 bar) were determined; an example of the results obtained at a catalyst loading of 1.0 g/L is presented in Figure 6. The mass loss between the materials varied from 20% to 80%, and it was associated mainly with the loss of silicon and boron that were released from the materials. It was assumed that the crosslinking between PVA and boric acid is the key factor that could explain the observed granular stability. However, as the leaching results showed, this crosslinking was likely not the only explanation because even though a significant amount of boron was leached, the granules were not broken down completely. The morphology of both catalyst materials without iron doping (AC/MK and PSD/MK) were maintained better compared with that of the iron-doped catalysts, indicating a higher degree of crosslinking between boric acid and PVA. Between the iron-doped catalysts, the AC/MK_Fe showed a mass loss that was almost twice as high as that in the PSD/MK_Fe. The difference in the stability of these materials could be partly explained by their different porosity profiles, as discussed earlier (Table 1). In addition, the lower silicon/aluminum ratio (Table 2) seems to favor stability, and the stability was found to decrease in the following order: PSD/MK > PSD/MK_Fe > AC/MK > AC/MK_Fe. The leaching resistance and mechanical stability will be optimized in a future work.
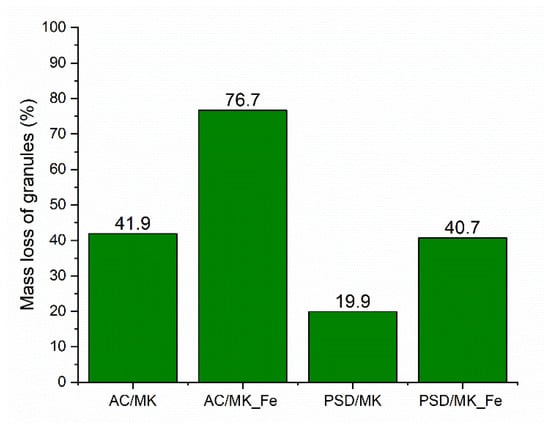
Figure 6.
Mass loss of the studied catalyst materials at CWAO reaction conditions: p (air): 20 bar, c (BPA): 60 mg/L, c (catalyst): 1 g/L T: 160 °C, 800 rpm.
During a catalyzed oxidation reaction, the access of reactants to the active sites of a catalyst is blocked by the possible deposition of carbonaceous materials onto a catalyst surface, decreasing the catalyst activity [4,69,73]. To test the reusability of the most active and stable catalyst material found in our study, we run two consecutive CWAO experiments at 160 °C with PSD/MK_Fe as catalyst, and the results are summarized in Figure 7. As can be seen, when the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst was reused, its catalytic activity remained stable throughout the experiments; even without the regeneration step, no decrease in conversion was observed. These results imply that the prepared carbonized biomass catalyst was not deactivated during the CWAO experiments. In addition, these results confirmed the high efficiency of the current BPA conversion process involving the easily separable and reusable PSD/MK_Fe catalyst. The leaching of phosphorus, silicon, and boron was also analyzed during the catalyst recyclability test, and it was noticed that the leaching was highest after the first experiment. During the first reuse, the amount of leached boron was below the detection limit; as for phosphorus and silica, the concentration was 0.8 mg/L. Therefore, these leached elements are not expected to affect the catalytic activity, as shown in Figure 7.
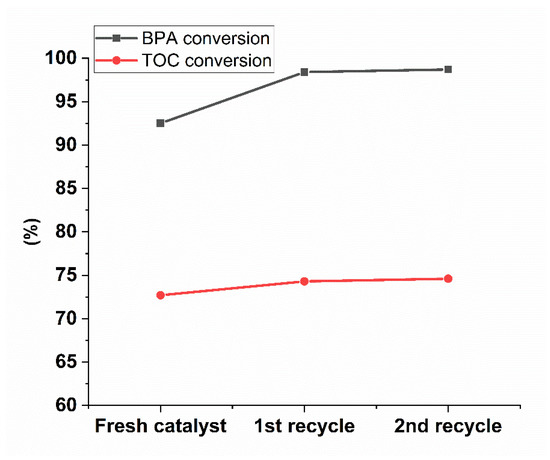
Figure 7.
Recycling results for PSD/MK_Fe at reaction time 180 min. Operating conditions: p (air): 20 bar, c (BPA): 60 mg/L, c (catalyst): 1 g/L, T: 160 °C, 800 rpm. RSD ± 3%. Note the y-axis scale.
2.7. Analysis of By-Products
As noticed (e.g., in Figure 5), complete mineralization of organic compounds was not achieved after 180 min of reaction in the CWAO of BPA, indicating that refractory by-products formed during the reaction. Moreover, the acidity of the reaction solution was found to increase during the CWAO process; therefore, acidic by-products were assumed to have formed. HPLC was used in the qualitative analysis, and the peaks were identified by directly comparing the retention times with the corresponding standards. The selected standards studied in this research were formic acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, malonic acid, and maleic acid, all of which have been detected as by-products in the CWAO of phenolic compounds [2,4,74,75]. In all of the peaks, four principal by-products were identified, namely maleic acid, oxalic acid, formic acid, and acetic acid (results not shown). Among them, acetic and formic acids are refractory to oxidation into water and carbon dioxide under the experimental conditions used in this study [4,76,77,78]. However, these compounds are readily biodegradable due to their low eco-toxicity [62,75]. By contrast, maleic and oxalic acids are called inert carboxylic acids, that is, they are not readily biodegradable [79]. However, although these compounds were inert, no toxicity effect was observed by Suares-Ojeda et al. [79].
2.8. Characterization of the Spent Catalysts
The textural properties of the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts after the oxidation reactions were characterized by liquid nitrogen adsorption, elemental analysis, and DRIFT spectroscopy. Compared with the fresh catalysts, both composites showed an increased SSA (Table S3): 30%-point for AC/MK_Fe and 20%-point for PSD/MK_Fe. This result was due to the leaching of inorganic materials, as indicated earlier. For the AC/MK_Fe catalyst, the porosity profile also changed, and up to 20%-point decrease in microporosity was detected compared with that in the fresh catalyst. This finding could be due to the adsorption of BPA onto the surface of the material. Quantanilla et al. [80] reported similar changes in the microporosity of carbon catalysts after the CWAO of phenol. In the case of the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst, the porosity profile remained almost unchanged. Based on the ICP-OES and elemental analysis results for the spent iron catalysts (Table S4), the amount of metals (aluminum, iron, and calcium) and nitrogen remained similar to that found in the fresh catalysts. However, the content of phosphorus, hydrogen, oxygen, and silicon decreased; their corresponding amounts decreased by 1.4-, 6.0-, 2.0-, and 0.4%-points in the AC/MK_Fe catalyst and by 0.8-, 2.0-, 2.0-, and 1.6%-points in the PSD/MK_Fe catalyst. Boron was almost completely removed (0.02–0.04 wt% remaining) from both catalysts due to leaching. The carbon content of the spent catalysts increased, and the increase was slightly higher in the AC/MK_Fe (12.5%-point) than in the PSD/MK_Fe (9.2%-point). This result may indicate a coke deposition on the surface of the catalysts during the CWAO reaction. Moreover, the coke deposition could explain the porosity results discussed previously, as the coke could block the small pores. It has been reported by others [17] that coke deposition was more significant for the microporous carbon materials, such as AC/MK_Fe, than for the mesoporous ones, such as PSD/MK_Fe.
The results of the DRIFT spectroscopy conducted to analyze the acidity of the spent AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts indicated that the acidic sites almost totally disappeared after the BPA catalytic oxidation experiments (spectra not shown). However, these DRIFT measurements were done ex-situ, and given that the measured IR spectra are not quantitative, the exact changes in the surface acidity sites cannot be estimated.
In summary, based on the characterization results for the spent catalysts, the catalyst activity can be affected by the following factors: decrease in porosity due to adsorption and/or coke deposition, changes in the acidic surface sites and in SSA due to leaching of inorganic substances. Between the AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe catalysts, in the latter, the porosity profile remained unchanged (Table S3) and the low amount of carbon deposits (Table S4) on its surface did not affect its catalytic activity as seen in the recycling experiments (Figure 7). Moreover, the PSD/MK_Fe was more stable in terms of particle leaching from granules (Figure 6), that is, this catalyst material kept its granular form better compared with the AC/MK_Fe and thus was more easily separated and reused after the CWAO experiments. Furthermore, the manufactured PSD/MK_Fe retained its performance and catalytic activity after two consecutive runs (Figure 7). These results confirmed the high efficiency of the current BPA conversion process involving the use of the easily separable and reusable PSD/MK_Fe catalyst. Therefore, the carbonized biomass granular composites developed in this study can be regarded as efficient, long-term catalysts for the oxidation of refractory organic compounds, such as BPA, during the CWAO process.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
The studied pine sawdust was obtained from a Finnish sawmill Kuhmo Oy. Dried sawdust was carbonized under nitrogen gas (flow rate 200 mL/min) at 800 °C, followed by the activation at 800 °C for two hours in steam (120 g/h). This sample was named PSD0. Based on the preliminary studies, the carbonized biomass contained water-soluble nutrients, such as sodium (860 mg/kg) and calcium (104 mg/kg). Moreover, heavy metals such as nickel or chromium were not detected. Commercial activated carbon (virgin coal-based) was used as a reference material and it was purchased from Calgon Carbon Corporation (Chemiviron pulsorb, Pittsburg, PA, USA). This sample was named AC0. Used binders were CaCO3 (≥99%, Riedel-de Haen, Seelze, Germany), and metakaolin (Aquaminerals Finland Ltd., Paltamo, Finland, including Al2O3 40.3%, SiO2 53.1%, K2O 2.72%, and Fe2O3 1.89%). Bisphenol A (BPA, ≥99%, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany), H3PO4 (85%, Merck Darmstadt, Germany), HNO3 (65%, AnalaR Normapur VWR Chemicals, Helsinki, Finland), ortho-boric acid (B(OH)3, 100%, AnalaR Normapur VWR chemicals, Helsinki, Finland), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, 72,000 g/mol, hydrolysis 85–89%, Biochemica PanReac Applichem, Chicago, IL, USA), glycerol (100%, VWR chemicals, Helsinki, Finland) and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (≥99%, Acros Organics, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) were of reagent grade. The carbons and binder materials were in powder form (particle size < 150 µm).
3.2. Pretreatment of Carbon Materials
Commercial activated carbon (AC0) and carbonized biomass (PSD0) were first oxidized for three hours at 85 °C using 6 M HNO3. After the oxidation, the samples were washed with deionized water until the pH was neutral and dried overnight at 105 °C. Samples were named as AC1 and PSD1.
The scheme of the catalysts’ shaping process is presented in Figure 8. During the preliminary studies, several different carbon to binder ratios were studied but only the results for optimum carbon to binder ratio, namely 80/20, are being reported. At first, carbon and binders (MK and CaCO3) were wet ground and mixed for three hours at 300 rpm in a planetary ball mill (Retch PM200, Haan, Germany) to ensure the thorough mixing of materials and to avoid large particle size distribution. After milling, the suspension was filtered and dried overnight at 105 °C. Dry materials were combined with total of 8 mL of deionized water and phosphoric acid (ratio 1:1). After that, glycerol (0.5 mL) was added to prevent agglomeration and embrittlement after shaping. Additionally, the polymeric organic resin PVA (10 wt% in aq, 1 mL/g of carbon) was added. Further, the mixture was placed to the ultrasound (US) bath for 4 h at 40 °C to make sure that all the materials were wetted and mixed completely. Finally, the formable mass was shaped into small granules (diameter 3–4 mm) and immersed in a bath containing the crosslinking agent B(OH)3 (6 wt%) and iron salt (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, 3 wt% of Fe) for 24 h at 70 °C under mild stirring. The pH of the solution varied between 2–2.5. Prepared granular composite catalysts were named as AC/MK_Fe and PSD/MK_Fe. Samples prepared without iron were named as AC/MK and PSD/MK. After this, the materials were filtered and washed with deionized water and left to cure in an oven overnight at 60 °C. This was followed by calcination at 280 °C for 3 h under N2-gas (0.3 L/min).
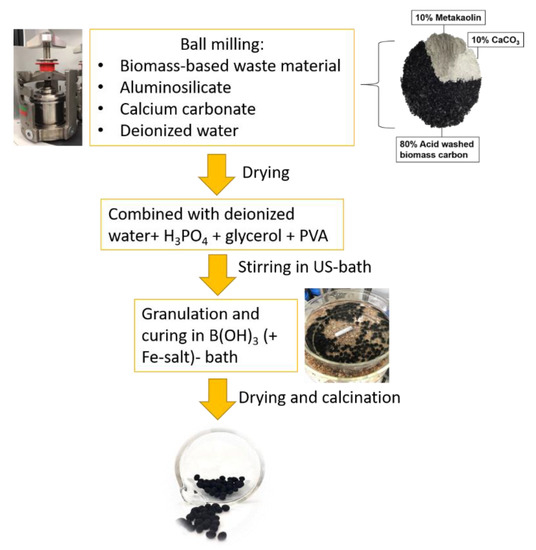
Figure 8.
Illustration of the catalysts’ preparation process.
3.3. Characterization of Catalysts
The metal content of the AC and composite granules were measured with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, Thermo Electron iCAP 6500 Duo), and the elemental analysis of the samples was carried out in a Flash 2000 organic elemental analyzer OEA (Thermo Scientific with Eager Xperience software, 1.4, Waltham, MA, USA, 2016) to determine the C, H, N, and O content. Both ICP-OES and Flash 2000 OEA are manufactured by Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA. The surface morphology and chemical compositions of the samples were investigated using a Zeiss ULTRA plus field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GMbH, Jena, Germany) combined with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analyzer at the Centre for Material Analysis, University of Oulu (Finland). The porosity of the samples was determined from nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms at the temperature of liquid nitrogen (–196 °C), using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 equipment (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA). The specific surface areas and the pore volumes were calculated using Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) and Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) equations [81], and the pore size distribution was calculated using density functional theory (DFT) [36,82].
The pH of the materials (0.15 g) was determined in water suspension (12.5 mL) after heating at 90 °C and then cooling to room temperature. The mass titration (MT) method, outlined by Noh and Schwartz [83], was used to study the pH of zero-point charge (pHzpc) of the bulk material. The experiments were conducted at room temperature with 0.005 M NaCl as a background electrolyte. The experiments were carried out with multiple samples with increasing mass of the studied materials, which were added to a known volume of the electrolyte solution in a centrifuge tube and allowed to equilibrate for 72 h. The pH of each solution was measured and the value of pHzpc was determined on the curve of pH vs. percentage mass to volume ratio of suspensions.
The crystalline phase identification of the materials was studied using PANalytical X’Pert Pro X-ray diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands). The XRD patterns were recorded by the monochromatic Cu Kα1 (λ = 1.5406 Å) at 45 kV and 40 mA with a scan speed of 0.036°/s and 2θ ranging from 10° to 70°. The crystalline phases and structures were analyzed by HighScore Plus software using the Powder Diffraction File standards from the International Centre for Diffraction DATA ICDD (PDF-4+ 2020 RDB). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was performed using an ESCALAB 250 Xi XPS System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at the Centre for Material Analysis, University of Oulu. The X-ray excitation was provided by a monochromatic Al Kα (1486.7 eV) source. The surface contents of C, O, Si, and B were measured for all the composite catalysts. The measurement data were analyzed with the Thermo Avantage V5 program. Charge compensation of the binding energies (BEs) was performed by applying the C1s line at 284.8 eV as a reference.
Ammonia was used as a probe molecule to study the surface acidity by the Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transfer Spectroscopy (DRIFTS) using Bruker Vertex 80 V (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with Harrick Praying MantisTM Diffuse Reflection Accessory and High Temperature Reaction chamber. Prior to the in-situ measurement, diluted samples (sample:KBr 1:100) were dried in the oven overnight at 105 °C. The acidity measurements were done by NH3 adsorption. The sample was first purged with Ar flow (50 mL/min) for 10 min at 150 °C, followed by cooling to 100 °C under Ar flow. Then, 1% NH3/Ar gas (50 mL/min) was inserted into the chamber for 20 min at 100 °C for NH3 adsorption, followed by purging with Ar flow for 5 min to remove gaseous and physisorbed ammonia. The spectra were recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm−1 with 200 scans.
3.4. Catalytic Oxidation Experiments
All the oxidation experiments were conducted in a 300 mL high-pressure Hastelloy C22 stainless-steel reactor (Parr, Moline, IL, USA). The reactor was loaded with 160 mL of an aqueous BPA (60 mg/L, pH 5–6) solution with or without a catalyst (CWAO and WAO process, respectively). The stirring rate was 800 rpm. The reactor was purged with nitrogen and heated up to the reaction temperature. A static catalyst basket (Parr) was used in the reactor to contain the granular catalysts. The oxidation reaction was started by introducing air from the cylinder into the reactor and samples were collected as a function of oxidation time from the reactor and filtered through 0.45 µm filter paper. The pH was monitored during the experiment. Different reaction conditions were studied: temperature (130 °C and 160 °C), total pressure (20 bar and 50 bar), and catalyst loading (0.5–2.0 g/L). The experiments were performed at least in duplicate with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of ±2–5%.
The stability of the catalytically most active granular composite catalyst (PSD/MK_Fe) was further studied with the CWAO experiments conducted in two consecutive runs at 160 °C, 20 bar and catalyst loading of 1.0 g/L. The catalyst was recovered by filtration from the solution after the catalytic experiment, washed with distilled water, and dried at 105 °C overnight. The second run was performed in the same reaction conditions. Moreover, the leaching of the particles from the granular composite catalysts was followed.
Analysis of Water Samples
The concentration of BPA was detected with high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with Waters 996 photodiode array (PDA) detector (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA), using a 226 nm wavelength. A mixture of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in water and 0.1% TFA in methanol was used as the eluent (flow rate 0.4 mL/min), and the compounds were separated with the SunFireTM C18 5 m 2.1 × 100 mm column (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA), operated at a temperature of 30 °C. Possible by-products were also analyzed with HPLC, using a 210 nm wavelength, 5 mM H2SO4 as the eluent (flow rate 1.0 mL/min), and Shodex sugar SH1821 8.0 × 300 mm column (New York, NY, USA), operated at 40 °C, was used for the separation. TOC was measured in the BPA samples by using the Skalar FormacsHT Total Organic Carbon/Total Nitrogen analyzer (Breda, Netherlands). The amount of possible leached metals after the oxidation reactions was detected with ICP-OES (Thermo Electron iCAP 6500 Duo, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) (aluminum, silicon, phosphorus and boron) and with flame-AAS (Varian 240FS, including Varian SPS 3 autosampler, Mulgrave, Victoria, Australia) (iron and calcium). Moreover, nickel and chromium were analyzed with flame-AAS to detect the possible contamination from the reactor and/or ball milling.
4. Conclusions
In this research, carbonized biomass was granulated together with binders (MK and CaCO3) to produce novel, porous, and stable composite materials for catalytic water treatment applications. The influence of the surface chemistry of the studied materials on the efficiency of the CWAO process was studied. The CWAO experiments were conducted in a batch reactor at 160 °C and at 20 bar (air). Of the studied catalysts, the biomass-based PSD/MK_Fe demonstrated the most efficient BPA conversion. A nearly complete BPA conversion was achieved, and the TOC conversion was 70%, indicating the presence of by-products, which were confirmed to be short-chain carboxylic acids by HPLC analysis. The key factor behind this enhanced catalytic activity was high SSA, although the catalytic activity is also significantly influenced by surface acidity. This acidity was caused by the oxidized carbon, MK, and boron trioxide. Characterization and stability tests of the fresh and spent PSD/MK_Fe confirmed that this granular composite catalysts could be regenerated and reused without displaying loss of catalytic activity. Therefore, this novel granulated carbonized biomass material demonstrates the potential to be used in wastewater treatment systems as it could be easily recovered after use. This property increases its ease of use in wastewater treatment systems given that the recovery of powdered catalysts is challenging. Moreover, 80% of the catalyst materials used were carbonized biomass waste material, promoting circular economy and waste minimization. Additionally, the production of biomass-based catalysts is scalable because lignocellulosic biomass is available as a virgin material and as a waste material worldwide.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/11/2/251/s1. Figure S1: SEM micrograph of AC/MK_Fe; Figure S2: B1s and Si2p XPS spectra for the PSD/MK sample; Table S1: Data obtained from XPS C1s spectrum. Binding energies and relative atomic contents; Table S2: Data obtained from XPS O1s spectrum. Binding energies and relative atomic contents; Table S3: Specific surface area and porosity profile of spent catalysts; Table S4: Elementary analysis of spent catalysts.
Author Contributions
R.J.; methodology, R.J.; software, R.J., M.H., T.H.; investigation, R.J., D.B.; data curation, R.J.; writing—original draft preparation, R.J.; writing—review and editing, all authors, visualization, R.J.; supervision, A.H., S.T., U.L.; funding acquisition, R.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fortum Foundation, grant number 20190004.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article (tables and figures). The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from Fortum Foundation is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank the staff at the Center of Microscopy and Nanotechnology, University of Oulu, for their assistance with the elementary and XPS analysis. Sari Tuikkanen, Riina Hemmilä, Jarno Karvonen, Elisa Wirkkala, Teija Kangas, Hanna Prokkola, Henrik Romar, and Satu Ojala are acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Guerra-Que, Z.; Pérez-Vidal, H.; Torres-Torres, G.; Arévalo-Pérez, J.C.; Silahua Pavón, A.A.; Cervantes-Uribe, A.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.; Lunagómez-Rocha, M.A. Treatment of phenol by catalytic wet air oxidation: A comparative study of copper and nickel supported on γ-alumina, ceria and γ-alumina–ceria. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8463–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with modified activated carbons and Fe/activated carbon catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 76, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heponiemi, A.; Azalim, S.; Hu, T.; Vielma, T.; Lassi, U. Efficient removal of bisphenol A from wastewaters: Catalytic wet air oxidation with Pt catalysts supported on Ce and Ce–Ti mixed oxides. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2019, 6, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjavec, B.; Kaplan, R.; Djinović, P.; Pintar, A. Catalytic wet air oxidation of bisphenol A model solution in a trickle-bed reactor over titanate nanotube-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 132–133, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüber, F.; Font, J.; Fortuny, A.; Bengoa, C.; Eftaxias, A.; Fabregat, A. Carbon materials and catalytic wet air oxidation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Top. Catal. 2005, 33, 3–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žerjav, G.; Kaplan, R.; Pintar, A. Catalytic wet air oxidation of bisphenol A aqueous solution in trickle-bed reactor over single TiO2 polymorphs and their mixtures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschetto, E.G.; Sicardi, M.I.; Elías, V.R.; Ferrero, G.O.; Carraro, P.M.; Casuscelli, S.G.; Eimer, G.A. Metal modified silica for catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO) of glyphosate under atmospheric conditions. Adsorption 2019, 25, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistan, M.; Tišler, T.; Pintar, A. Catalytic and Photocatalytic Oxidation of Aqueous Bisphenol A Solutions: Removal, Toxicity, and Estrogenicity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8826–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljonen, T.; Ruska, M.; Flyktman, M.; Forström, J.; Kiviluoma, A.J.; Kirkinen, J.; Lehtilä, A.; Ahkala, K.P. Energiaresurssit ja—Markkinat. Teknologian Tutkimuskeskus VTT Tiedotteita 2489. 2009. Available online: https://www.vttresearch.com/sites/default/files/pdf/tiedotteet/2009/T2489.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J. Reaction pathway of the catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with a Fe/activated carbon catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 67, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Lu, Q.; Qu, Q. Graphene-based materials: Fabrication and application for adsorption in analytical chemistry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H.P.; Voll, M. Basische Oberflächenoxide auf Kohlenstoff—I. Adsorption von säuren. Carbon 1970, 8, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.B. The chemical reactivity of carbons. Carbon 1968, 6, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, W.; He, X.; Yang, S.; Zhu, W. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with functionalized carbon materials as catalysts: Reaction mechanism and pathway. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayral, C.; Lebigue, C.J.; Stüber, F.; Wilhelm, A.; Delmas, H. Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation of Phenolic Compounds and Mixtures over Activated Carbon: Conversion, Mineralization, and Catalyst Stability. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 49, 10707–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Pérez, E.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Ismael Águeda, V.; Delgado, J.A.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Insights into the removal of Bisphenol A by catalytic wet air oxidation upon carbon nanospheres-based catalysts: Key operating parameters, degradation intermediates and reaction pathway. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.C.; Jablonski, E.L.; Baronetti, G.T.; Castro, A.A.; de Miguel, S.R.; Scelza, O.A.; Blanco, M.D.; Penã Jiménez, M.A.; Fierro, J.L.G. Effect of the carbon pre-treatment on the properties and performance for nitrobenzene hydrogenation of Pt/C catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 161, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccrae, P.D.; Zhang, T.; Walker, D.R. Method of Making Shaped Activated Carbon. Patent No. CA2442243A1, 2002. Available online: worldwide.espacenet.com (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Auer, E.; Freund, A.; Pietsch, J.; Tacke, T. Carbons as supports for industrial precious metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1998, 173, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iveson, S.M.; Litster, J.D.; Hapgood, K.; Ennis, B.J. Nucleation, growth and breakage phenomena in agitated wet granulation processes: A review. Powder Technol. 2001, 117, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, K.L. Granulation Technology for Bioproducts. Drying Technol 1993, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyal, B.; Johns, M.M.; Marshall, W.E.; Ahmedna, M.; Rao, R.M. The effect of binders and agricultural by-products on physical and chemical properties of granular activated carbons. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 68, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedna, M.; Marshall, W.E.; Rao, R.M. Production of granular activated carbons from select agricultural by-products and evaluation of their physical, chemical and adsorption properties1Louisiana Agricultural Experiment Station manuscript 99-21-0066.1. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, E.M. The properties and forming of catalysts and absorbents by granulation. Powder Technol. 2004, 140, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhola, R.; Heponiemi, A.; Tuomikoski, S.; Hu, T.; Prokkola, H.; Romar, H.; Lassi, U. Biomass-based composite catalysts for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of bisphenol A: Preparation and characterization studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Yoza, B.A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.X.; Guo, S.; Chen, C. Kaolinite based catalysts for efficient ozonation of recalcitrant organic chemicals in water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 175, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, B. Effect of phosphoric acid content on the microstructure and compressive strength of phosphoric acid-based metakaolin geopolymers. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Ping, L.; Xue-Min, C.; Shu-Heng, Q.; Jun-Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Preparation of phosphoric acid-based porous geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, M.; Barre, M.; Toumi, M. Synthesis, thermal properties and electrical conductivity of phosphoric acid-based geopolymer with metakaolin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 180, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Duan, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, W. Environmental reduction of carbon nanomaterials affects their capabilities to accumulate aromatic compounds. NanoImpact 2016, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Gitari, M.W.; Tutu, H.; DeBeer, M. Efficiency of ball milled South African bentonite clay for remediation of acid mine drainage. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 8, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydo, P.; Turek, M. Boron transport and removal using ion-exchange membranes: A critical review. Desalination 2013, 310, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramon, M.V.; Stoeckli, F.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Carrasco-Marin, F. On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques. Carbon 1999, 37, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valix, M.; Cheung, W.H.; Zhang, K. Role of heteroatoms in activated carbon for removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.P.; van Riessen, A. Determination of the reactive component of fly ashes for geopolymer production using XRF and XRD. Fuel 2010, 89, 3683–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Effect of the Alkali Metal Activator on the Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 3932–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, B. A comprehensive analysis of various structural parameters of Indian coals with the aid of advanced analytical tools. Int. J. Coal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; López-Ramón, M.V.; Carrasco-Marın, F. Changes in surface chemistry of activated carbons by wet oxidation. Carbon 2000, 38, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Bergna, D.; Villa, A.; Spontoni, P.; Bianchi, C.L.; Hu, T.; Romar, H.; Lassi, U. Carbons from second generation biomass as sustainable supports for catalytic systems. Catal. Today 2018, 301, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczyk, M.; Świątkowski, A.; Pakuła, M.; Biniak, S. Electrochemical studies of the interaction between a modified activated carbon surface and heavy metal ions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegawa, K.; Nishikubo, K.; Kodama, M.; Adachi, Y.; Yoshida, H. Oxidative degradation of carbon blacks with nitric acid: II. Formation of water-soluble polynuclear aromatic compounds. Carbon 2002, 40, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, O.S.; Rocha, R.P.; Órfão, J.J.; Pereira, M.F.; Figueiredo, J.L. Mechanothermal Approach for N-, S-, P-, and B-Doping of Carbon Nanotubes: Methodology and Catalytic Performance in Wet Air Oxidation. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolel-Veetil, M.; Gamache, R.M.; Bernstein, N.; Goswami, R.; Qadri, S.B.; Fears, K.P.; Miller, J.B.; Glaser, E.R.; Keller, T.M. Substitution of silicon within the rhombohedral boron carbide (B4C) crystal lattice through high-energy ball-milling. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11705–11716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, B.; Barr, T.L.; Barrie, P.J.; Klinowski, J. Spectroscopic Studies of 5-Coordinate Silicon Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 4570–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) as an efficient catalyst for catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onida, B.; Gabelica, Z.; Lourenço, J.; Garrone, E. Spectroscopic Characterization of Hydroxyl Groups in SAPO-40. 1. Study of the Template-Free Samples and Their Interaction with Ammonia. Am. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 11072–11079. [Google Scholar]
- Bandosz, T.J.; Petit, C. On the reactive adsorption of ammonia on activated carbons modified by impregnation with inorganic compounds. J. Colloid 2009, 338, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peng, P.; Lin, L.; Yang, T.C.K.; Huang, C. Facile Preparation of Nitrogen-Doped Activated Carbon for Carbon Dioxide Adsorption. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, J.; Rappeport, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Langer, J.; Economy, J. Activated carbon fiber composites for gas phase ammonia adsorption. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 234, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przepiórski, J.; Skrodzewicz, M.; Morawski, A.W. High temperature ammonia treatment of activated carbon for enhancement of CO2 adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 225, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Sánchez-García, L.; Oliveira Jardim, E.d.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Ammonia Removal Using Activated Carbons: Effect of the Surface Chemistry in Dry and Moist Conditions. Environ. Sci. 2011, 45, 10605–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, B.; Komvokis, V.G.; Singh, U.G.; Ziebarth, M.S.; Alexeev, O.S.; Amiridis, M.D. In situ FTIR characterization of NH3 adsorption and reaction with O2 and CO on Pd-based FCC emission control additives. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiong, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, T. An efficient and sulfur resistant K-modified activated carbon for SCR denitrification compared with acid- and Cu-modified activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.J.J.; van Bekkum, H. Amination and ammoxidation of activated carbons. Carbon 1994, 32, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Snyder, S.A.; Esparza, M. HPLC-fluorescence detection and adsorption of bisphenol A, 17β-estradiol, and 17α-ethynyl estradiol on powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Los Monteros, A.E.; Lafaye, G.; Cervantes, A.; Del Angel, G.; Barbier, J., Jr.; Torres, G. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over metal catalyst (Ru,Pt) supported on TiO2–CeO2 oxides. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C. Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon 2004, 42, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, C.M. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, L.R.; Mureno-Castilla, C.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Carbon materials as adsorbents in aqueous solutions. In Chemistry and Physics of Carbon; Marcel-Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 227–405. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M.; Saroha, A.K. Performance of various catalysts on treatment of refractory pollutants in industrial wastewater by catalytic wet air oxidation: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, F.J.; Kolaczkowski, S.T.; Beltrán, F.J.; McLurgh, D.B. Development of a model for the wet air oxidation of phenol based on a free radical mechanism. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1998, 53, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; Chang, D.J.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.C. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol by CeO2 catalyst—Effect of reaction conditions. Water Res. 2003, 37, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.J.; Lin, S.S.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, S.P.; Ho, W.L. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol using CeO2 as the catalyst. Kinetic study and mechanism development. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Substain. Environ. Eng. 2002, 37, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Weng, H. Liquid-phase oxidation of cyclohexane using CoAPO-5 as the catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1993, 105, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anurag, G.; Alok, M. Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Wet Air Oxidation Using Nonnoble Metal-Based Catalysts. J. Hazard. Tox. Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Chen, I.; Lin, S. An assessment of the suitable operating conditions for the CeO2/γ-Al2O3 catalyzed wet air oxidation of phenol. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levec, J.; Pintar, A. Catalytic wet-air oxidation processes: A review. Catal. Today Adv. Catal. Oxid. Process. 2007, 124, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R. The role of surface chemistry in catalysis with carbons. Catal. Today 2010, 150, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serp, P.; Machado, B. Doped Nanostructured Carbon Materials as Catalysts. Nanostructured Carbon Materials for Catalysis; The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2015, pp. 268–311. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/chapter/bk9781849739092-00268/978-1-84973-909-2 (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Fu, D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Liang, X. Simultaneous removal of nitrobenzene and phenol by homogenous catalytic wet air oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Ihm, S. Wet oxidation of phenol over transition metal oxide catalysts supported on Ce0.65Zr0.35O2 prepared by continuous hydrothermal synthesis in supercritical water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Yustos, P.; Quintanilla, A.; García-Ochoa, F.; Casas, J.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Evolution of Toxicity upon Wet Catalytic Oxidation of Phenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Yustos, P.; Rodriguez, S.; Garcia-Ochoa, F. Wet oxidation of phenol, cresols and nitrophenols catalyzed by activated carbon in acid and basic media. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 65, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. The surface properties and the activities in catalytic wet air oxidation over CeO2–TiO2 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8499–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debellefontaine, H.; Chakchouk, M.; Foussard, J.N.; Tissot, D.; Striolo, P. Treatment of organic aqueous wastes: Wet air oxidation and wet peroxide oxidation®. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 92, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debellefontaine, H.; Foussard, J.N. Wet air oxidation for the treatment of industrial wastes. Chemical aspects, reactor design and industrial applications in Europe. J. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Ojeda, M.E.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A.; Fabregat, A.; Stüber, F.; Fortuny, A.; Font, J.; Carrera, J. Integrated catalytic wet air oxidation and aerobic biological treatment in a municipal WWTP of a high-strength o-cresol wastewater. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, A.; Menéndez, N.; Tornero, J.; Casas, J.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Surface modification of carbon-supported iron catalyst during the wet air oxidation of phenol: Influence on activity, selectivity and stability. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, N.A.; Walton, J.P. A new analysis method for the determination of the pore size distribution of porous carbons from nitrogen adsorption measurements. Carbon 1989, 27, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.S.; Schwarz, J.A. Estimation of the point of zero charge of simple oxides by mass titration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 130, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).