Abstract
Electrochemical regeneration suffers from low regeneration efficiency due to side reactions like oxygen evolution, as well as oxidation of the adsorbent. In this study, electrically conducting nanocomposites, including graphene/SnO2 (G/SnO2) and graphene/Sb-SnO2 (G/Sb-SnO2) were successfully synthesized and characterized using nitrogen adsorption, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. Thereafter, the adsorption and electrochemical regeneration performance of the nanocomposites were tested using methylene blue as a model contaminant. Compared to bare graphene, the adsorption capacity of the new composites was ≥40% higher, with similar isotherm behavior. The adsorption capacity of G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 were effectively regenerated in both NaCl and Na2SO4 electrolytes, requiring as little charge as 21 C mg−1 of adsorbate for complete regeneration, compared to >35 C mg−1 for bare graphene. Consecutive loading and anodic electrochemical regeneration cycles of the nanocomposites were carried out in both NaCl and Na2SO4 electrolytes without loss of the nanocomposite, attaining high regeneration efficiencies (ca. 100%).
1. Introduction
Adsorption is a promising method for the removal of soluble and insoluble organics from wastewater effluents due to ease of operation, a wide range of applications, and a high level of purity of the treated water [1]. However, handling of the loaded adsorbent is a challenge because of factors that constrain disposal, including the toxicity of the adsorbate and the high cost of replacement adsorbent [2,3]. Electrochemical regeneration has shown potential for effectively recovering the adsorptive capacity of the loaded adsorbents [4,5,6,7].
Early studies of electrochemical regeneration with an activated carbon adsorbent showed that although it has a high adsorptive capacity, it requires long regeneration times, resulting in high energy consumption. This is mainly due to the porous surface and low conductivity of the activated carbon [8,9,10]. Brown et al. [11,12,13] studied an alternative material, graphite intercalation compound (GIC), which is nonporous and has high electrical conductivity. This material demonstrated high regeneration efficiency but low adsorptive capacity. In the previous study [14], reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/magnetite was chosen as an adsorbent since it has a nonporous surface, high surface area, and high electrical conductivity. The findings revealed that rGO/magnetite has satisfactory adsorptive capacity which can be completely regenerated. However, the electrochemical regeneration process caused oxidation and corrosion of the adsorbent. Similar adsorbent oxidation was also seen by Nkrumah-Amoako et al. [15] for a GIC adsorbent. Graphitic materials display behaviors of both active and inactive electrodes, but the dominant mechanism for organic oxidation is believed to be direct electron transfer [16]. This is likely the main reason for oxidation of the graphene as well.
It is essential to tackle the problem of adsorbent oxidation, and this can be done by changing the dominant mechanism from direct electron transfer to mediated degradation using electro-generated hydroxyl radicals. One approach would be to coat the surface of the carbon adsorbent, i.e., graphene, with materials that behave as inactive anodes, such as boron-doped diamond (BDD), SnO2, Sb-SnO2, or PbO2. Due to the high overpotential of the inactive materials for oxygen evolution, they are considered good candidates for organic oxidation by means of reactive oxygen species such as hydroxyl radicals. Extensive research has been conducted on inactive materials to increase the rate of reactive oxygen species production. Ozone production on Sb-SnO2/Ti, hydroxyl radical generation on fluoride-doped lead oxide, hydrogen peroxide generation on niobium lead oxide, and hydroxyl radical generation on BDD and TiO2/Ti are several good examples [17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. These materials increase the oxygen evolution overpotential, minimizing this side reaction, thus increasing the current efficiency for organic oxidation [21,24,25]. Owing to its large band gap of 5.45 eV, BDD is the best inactive, corrosion-resistant material [26]; however, due to its high cost, BDD cannot be effectively used for adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. PbO2 also has a high overpotential for oxygen evolution [27] as well as a much lower cost than BDD, but leaching of lead from the PbO2 into the solution can contaminate the treated water [28].
In the current study, graphene/SnO2 (G/SnO2) and graphene/Sb-SnO2 (G/Sb-SnO2) nanocomposites were prepared, characterized, and utilized in an adsorption and electrochemical regeneration process. Our previous study on electrochemical regeneration of graphene TiO2 adsorbents materials revealed that the addition of the TiO2 nanoparticles to the surface of the graphene increases catalytic activity, reducing the required time for complete regeneration, and also protects the graphene surface from corrosion [29]. However, the prepared adsorbents did not demonstrate good adsorptive capacity due to loss of amorphous carbon during the calcination, required for synthesis of the TiO2 nanocomposite.
The goal of the present study was to prepare new materials with higher adsorptive capacity and comparable catalytic activity to the graphene/TiO2 nanocomposite which can be applied in successive adsorption electrochemical regeneration process. In addition to the methylene blue (MB) adsorption and electrochemical regeneration behavior of these adsorbents, their electrochemical properties were also investigated. The effect of the nanomaterial loading on the nanocomposites and the electrolyte types on the electrochemical regeneration and the durability of the new materials was also assessed.
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Raman Spectra
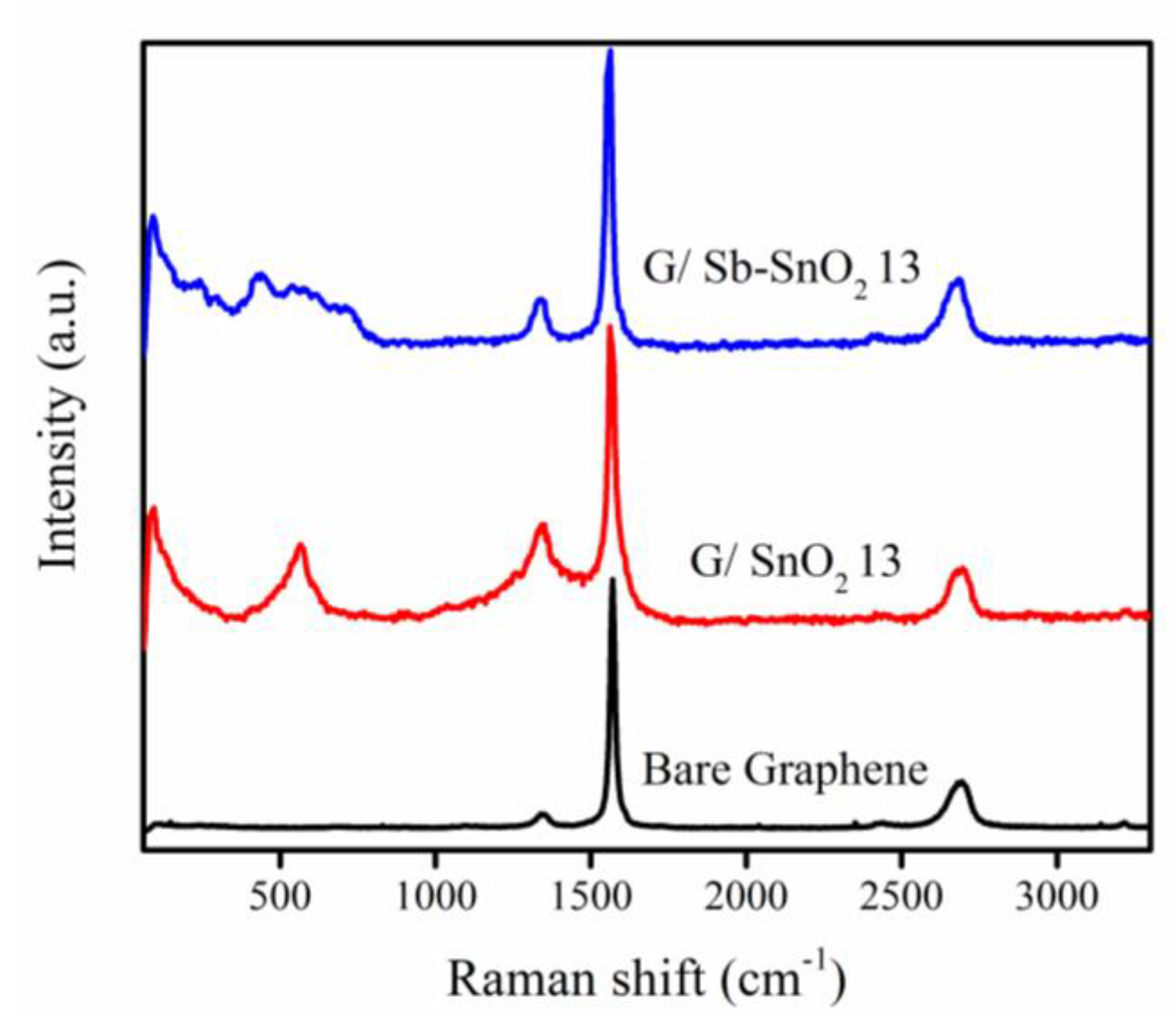
The surface chemical composition of the graphene and composite samples was characterized by Raman spectroscopy, as shown in Figure 1. The peaks observed at 1358 and 1580 cm−1 can be attributed to the D band and G band of the graphene, respectively [30]. The peak at a Raman shift of 572 cm−1 can be assigned to the cassiterite SnO2 nanoparticles; this peak is only present for nanometer-scale SnO2 particles [31,32]. The four broad Raman peaks at 458, 566, 720, and 632 cm−1 can be attributed to SnO2 nanoparticles doped with antimony. The first three peaks are the surface vibration modes [33], and the last one is the vibration in the plane perpendicular to the c-axis [34]. Thus, the Raman spectra confirm the presence of SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 on the nanocomposite materials.
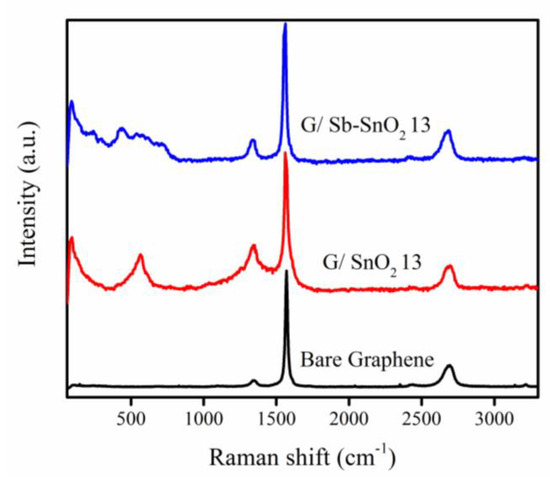
Figure 1.
Raman spectra of Bare graphene, SnO2, Sb-SnO2, G/SnO2, and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites.
2.2. SEM and TEM
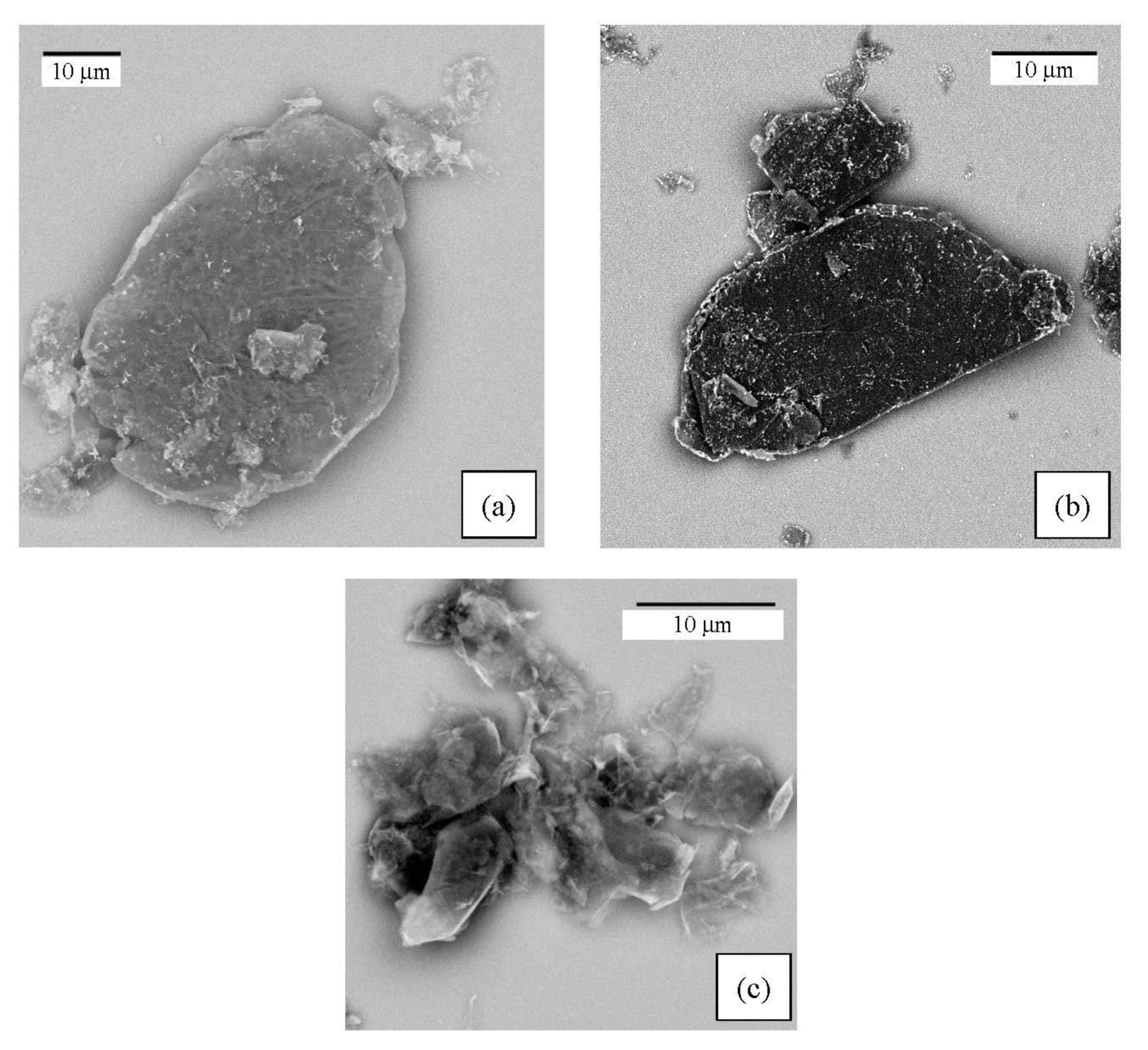
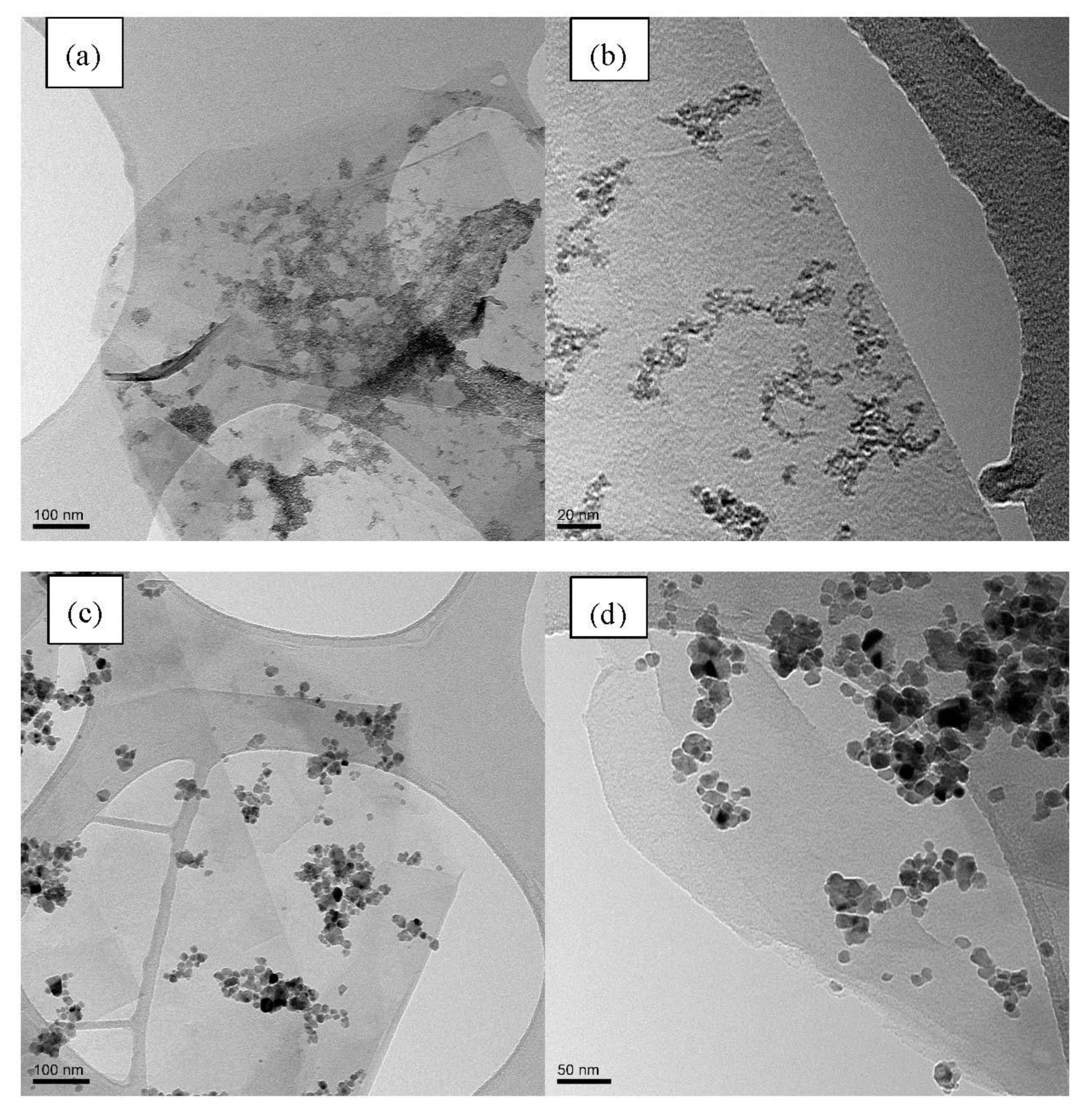
The morphology of the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites were observed using TEM and SEM (Figure 2 and Figure 3). A comparison between the SEM image of bare graphene, G/SnO2, and G/Sb-SnO2 reveals that SnO2 nanoparticles have adhered to the surface of the graphene; however, due to the SEM limitations, it is not possible to make more quantitative comments on the nanoparticle distribution. The TEM images, Figure 3b,d show that the average sizes of SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 nanoparticles are around 5 and 30 nm, respectively. It can also be inferred that the nanoparticles have not been distributed uniformly on the surface; they tend to aggregate due to their high surface energy [35].
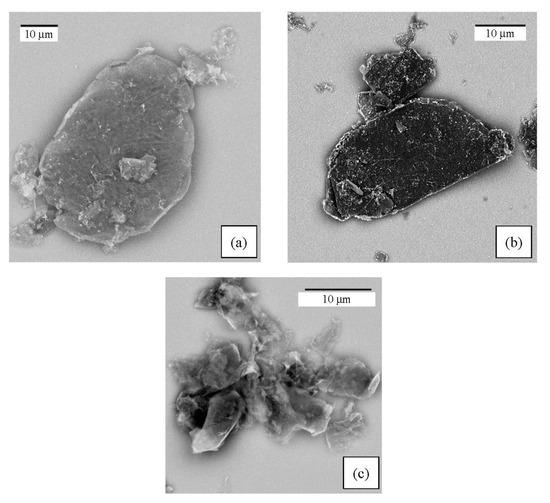
Figure 2.
SEM images of the (a) G/SnO2 nanocomposite, (b) G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposite, and (c) bare graphene.
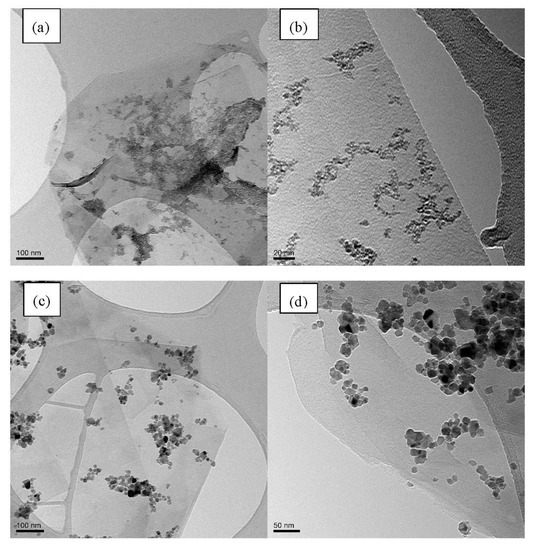
Figure 3.
(a) Low magnification TEM image of the G/SnO2 nanocomposite (b) High-magnification TEM image of the G/SnO2 nanocomposite. (c) Low-magnification TEM image of the G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposite. (d) High-magnification TEM image of the G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposite.
2.3. Adsorption Study
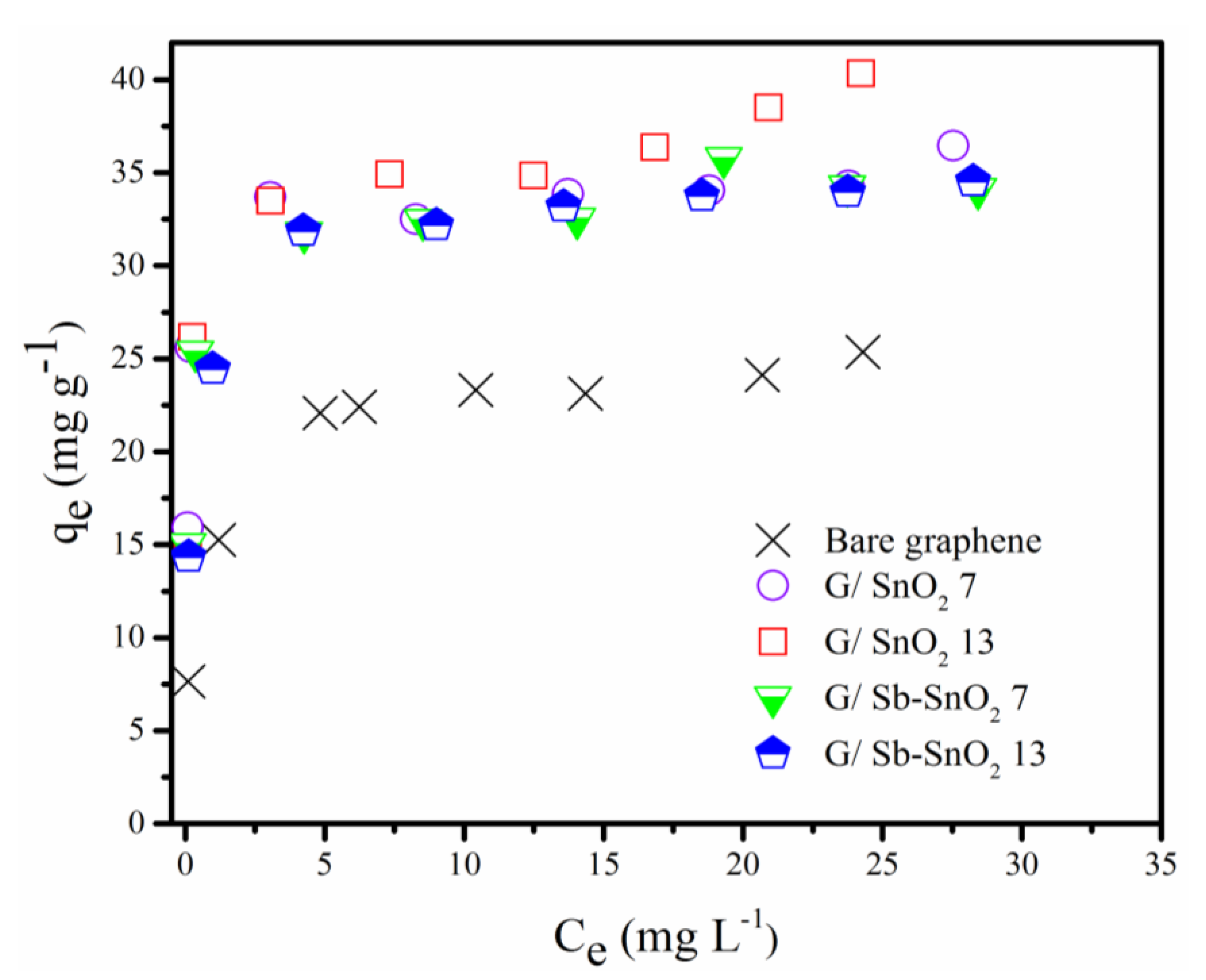
Adsorption isotherm studies were carried out to find the adsorptive capacity of the prepared samples and to determine the adsorption range to be used for adsorbent regeneration studies. The results obtained are depicted in Figure 4. Table 1 shows the calculated surface area for each sample using the BET method. It can be seen that G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 have higher adsorptive capacities than the bare graphene. As the surface area of the graphene and composite materials are all similar, we can conclude that the surface area is not responsible for higher uptake capacity of the composite adsorbents. The difference in the adsorptive capacity can be either due to contribution of the metal oxide in adsorption or the better dispersion of the nanocomposite in the water (i.e., agglomeration of the bare graphene particles may lead to a loss of adsorptive capacity).
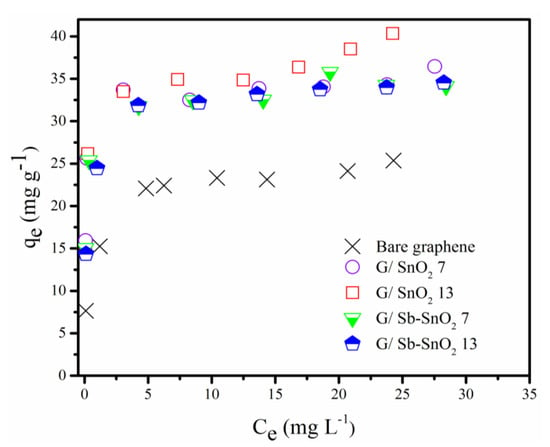
Figure 4.
Equilibrium adsorption of methylene blue (MB) on bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13.

Table 1.
Specific surface area of the graphene loaded with metal oxide.
The Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherm models were fitted to the experimental data for MB adsorption on bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13. The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms were used to evaluate the equilibrium conditions, and they can be expressed by the mathematical Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
where qe is the loading of adsorbate on the adsorbent in equilibrium with a solution concentration of Ce, KL and b are the Langmuir isotherm constants, and KF and n are the Freundlich isotherm constants.
Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 show the isotherm constants and the determination coefficient (R2) obtained by nonlinear regression for each adsorbent. By comparing the value of R2 for each adsorbent, it can be observed that Langmuir isotherm provides a better fit to the experimental data than the Freundlich isotherm model. Separation factor (RL) [36] (Equation (3)) and the magnitude of n [37] are important parameters in the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm as they can indicate whether the adsorption is favorable or not. Area value of RL or n of less than one indicates favorable adsorption.

Table 2.
Langmuir constants for adsorption of MB on Bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13.

Table 3.
Dimensionless Langmuir constants (RL) for adsorption of MB on bare graphene at low and high concentrations for different adsorbents.

Table 4.
Freundlich constants for adsorption of MB on bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13.
It can be seen from the RL values in Table 3 that the adsorption process of MB on graphene nanocomposites is favorable at all concentrations, particularly at low concentrations. The values of n obtained for the Freundlich isotherm are consistent with the with RL values.
The surface area of the nanocomposite can be estimated using MB. As the adsorption of MB on the nanocomposites follows the Langmuir isotherm, it can be concluded that a monolayer of MB has been adsorbed on the surface. It has been reported that one molecule of MB can occupy 130 Å2 on the surface of the adsorbent [38,39]. Table 1 shows the surface area for each adsorbent. It can be seen surface area calculated using BET and MB are more or less the same.
2.4. Electrochemical Regeneration
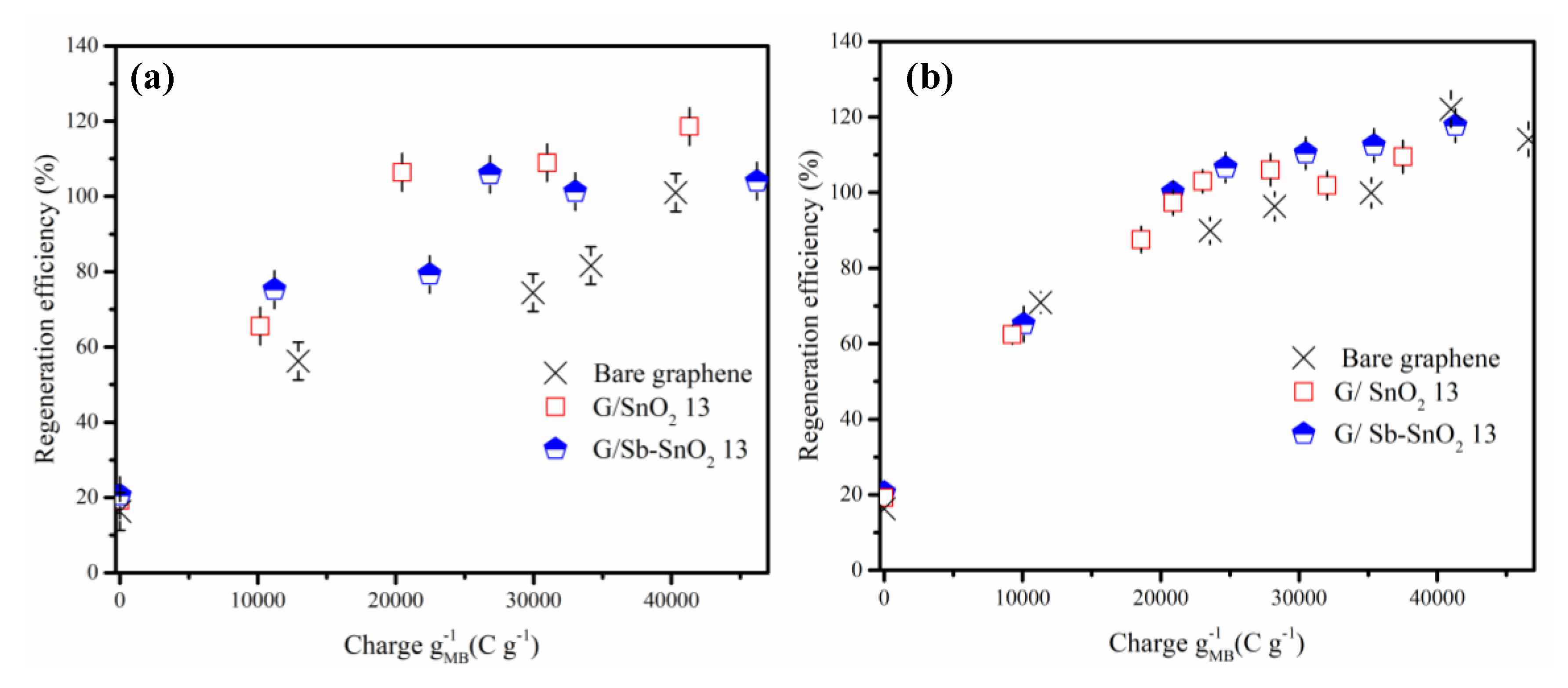
Figure 5a,b and Figure S1a,b demonstrate the evolution of the regeneration efficiency with the charge passed through the electrolytic cell using NaCl and Na2SO4 electrolytes. For all of the adsorbents in both electrolytes, the regeneration efficiency shows a steep increase as the charge was increased from 0 to 1000 C g−1, and then it slowly increases until it reaches complete regeneration. The findings reveal that the adsorptive capacity of all of the adsorbents can be completely restored.
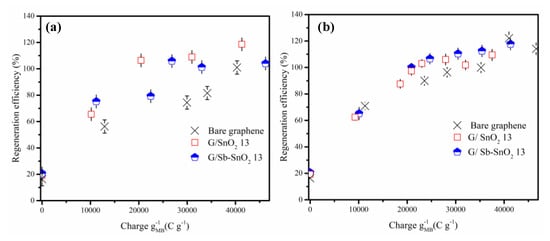
Figure 5.
Effect of charge passed on regeneration efficiency of MB adsorption on bare graphene, G/SnO2 13, and G/Sb-SnO2 13. (a) NaCl electrolyte and (b) Na2SO4 electrolyte (current density of 10 mA cm−2).
In previous studies, it has been reported that the utilization of NaCl instead of Na2SO4 as the electrolyte in the regeneration cell leads to higher regeneration efficiency [8,40]. However, the results of this study suggest that the choice of electrolyte has minimal impact on the regeneration efficiency. Moreover, with sodium sulfate as the electrolyte, if more charge is passed through the cell after complete regeneration of the spent adsorbents, the adsorptive capacity increases less compared to regeneration with a sodium chloride electrolyte. Previous studies have indicated that electrochemical regeneration efficiencies of greater than 100% are associated with oxidation of graphite adsorbent surfaces [12,15]. Thus, the previous studies suggest that with sodium sulfate, less oxidation of the adsorbent’s surface occurs, allowing it to remain almost intact. A secondary benefit of using the sodium sulfate electrolyte is that it can hinder the formation of toxic chlorinated hydrocarbons [11].
Previous work has shown that complete regeneration of graphene TiO2 nanocomposite loaded with MB dye could be achieved by passing a charge of 21 C mg−1 through the cell [29]. The two main problems associated with this nanocomposite compared to bare graphene were lower adsorptive capacity and a higher cell voltage required for electrochemical regeneration. As explained previously, G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 showed higher adsorptive capacity compared to bare graphene.
Table 5 shows the specific charge required for complete regeneration of the loaded adsorbents. The prepared nanocomposites had a required charge for complete oxidation as low as 21 C mg−1 for G/SnO2 using NaCl as an electrolyte and for G/Sb-SnO2 using Na2SO4 as an electrolyte, which is comparable to the graphene TiO2 nanocomposite results previously reported. Energy consumption for 100% regeneration of the loaded adsorbents is calculated by multiplying the required charge by the cell voltage. As shown in Table 5, the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites demonstrate lower charge requirements for complete regeneration than bare graphene using NaCl or Na2SO4 as the electrolyte, with similar cell voltages (≈2.6 V). Thus the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 adsorbents require less energy for complete regeneration. These results confirm the higher electrocatalytic activity of the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites for regeneration compared to bare graphene.

Table 5.
Specific charge required for 100% regeneration efficiency of bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13 adsorbents loaded with MB, (regeneration at 10 mA cm−2).
2.5. Adsorption/Regeneration Cycles
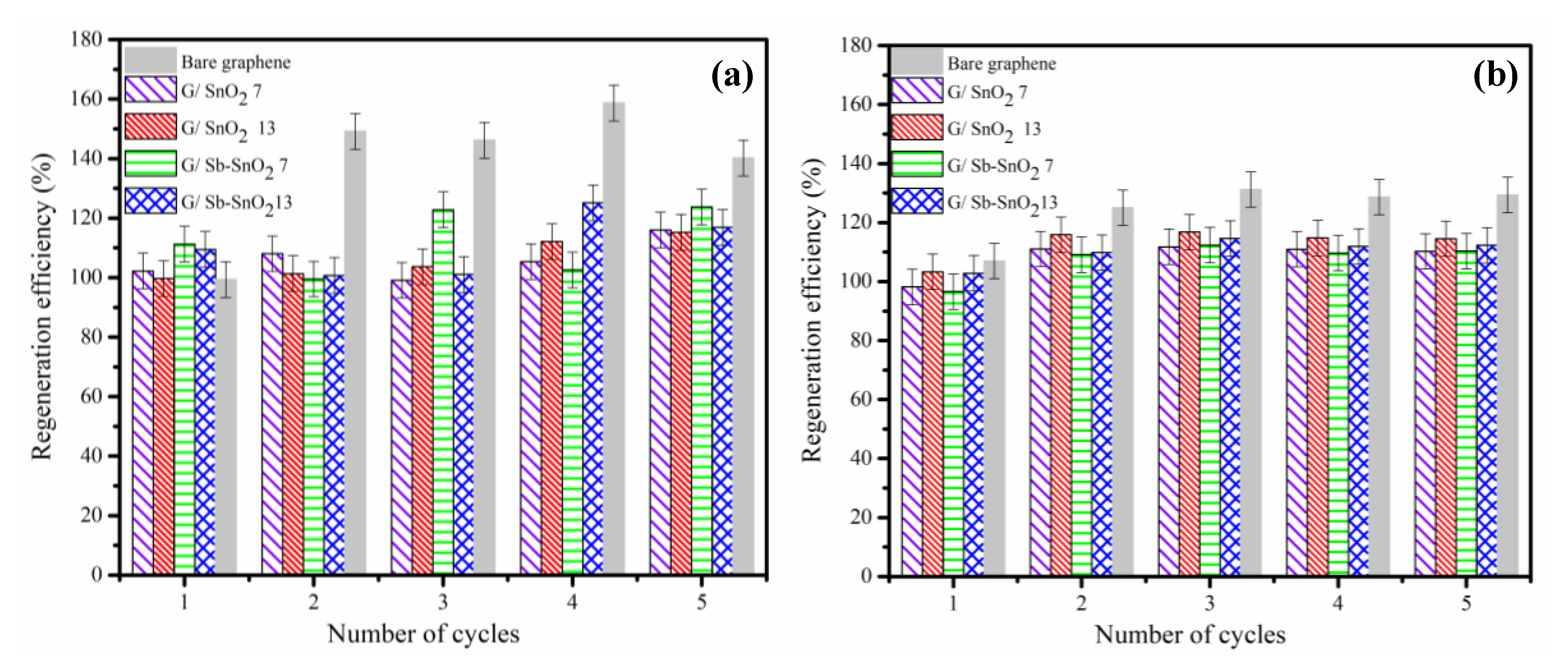
Multiple loading and electrochemical regeneration cycles were carried out to investigate the reusability of the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites. The adsorbents were utilized to adsorb MB and regenerated for five successive cycles using either 2 wt. % NaCl or Na2SO4 as electrolytes and 10 mA cm−2 current density. For each adsorbent, the required electrochemical treatment time for 100% regeneration was estimated based on the data plotted in Figure 5a,b and Figure S1a,b Table 6 shows the mass of adsorbent recovered after each cycle for the five different adsorbent materials. For the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites, only around 10% of the mass of adsorbent was lost over five cycles of adsorption and regeneration. The loss was within 1% to 2% of the loss observed from a control experiment to determine the physical losses associated with the recovery of the adsorbent after filtration. In contrast, with the bare graphene adsorbent, around 30% of the mass was lost over the five cycles of adsorption and regeneration, confirming that significant corrosive oxidation of the graphene was occurring during regeneration.

Table 6.
Mass of the adsorbent recovered after five consecutive cycles of adsorption and regeneration.
As shown in Figure 6a,b, the electrochemical oxidation resulted in no reduction of regeneration efficiency, even after five cycles. Figure 6a,b also shows that the change in regeneration efficiency of the bare graphene was much more than the G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites. This increase in the regeneration efficiency was due to the oxidation of the bare graphene during electrochemical regeneration, which led to the creation of more adsorption sites, either by increasing the surface area or the number of functional groups [15,41]. The adsorptive capacity and consequently regeneration efficiency of the nanocomposites changed less than for bare graphene, which suggests that the addition of the SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 provides some protection of the surface of the graphene from oxidation. By comparing Figure 6a,b, it is evident that the regeneration efficiency of the adsorbents in sodium sulfate increased less than that observed with sodium chloride. This result is consistent with the charge loading results (Figure 5a,b, and Figure S1a,b and confirms that there is a greater tendency for surface oxidation of the graphene using NaCl electrolyte.
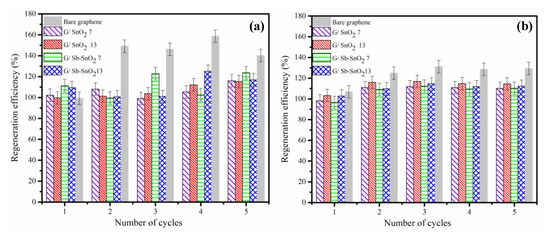
Figure 6.
Regeneration efficiency for a series of adsorption and electrochemical regeneration cycles of MB adsorption on bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13 nanocomposites in (a) NaCl electrolyte and (b) Na2SO4 electrolyte. Adsorption was carried out under conditions that give close to the maximum loading of MB on the adsorbent. Regeneration of the bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13 adsorbents were carried out for 14, 10, 10, 12, and 12 min, respectively, at a current density of 10 mA cm−2.
A common major problem associated with using NaCl in an electrochemical water treatment process is the formation of chlorinated compounds, which may be more toxic than the primary pollutants [42]. Thus, in addition to reduced oxidation of the graphene, sodium sulfate can be a lower-risk alternative to sodium chloride for regeneration of G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposite adsorbents.
2.6. Electrochemical Characterization of the Adsorbents
2.6.1. Linear Sweep Voltammetry
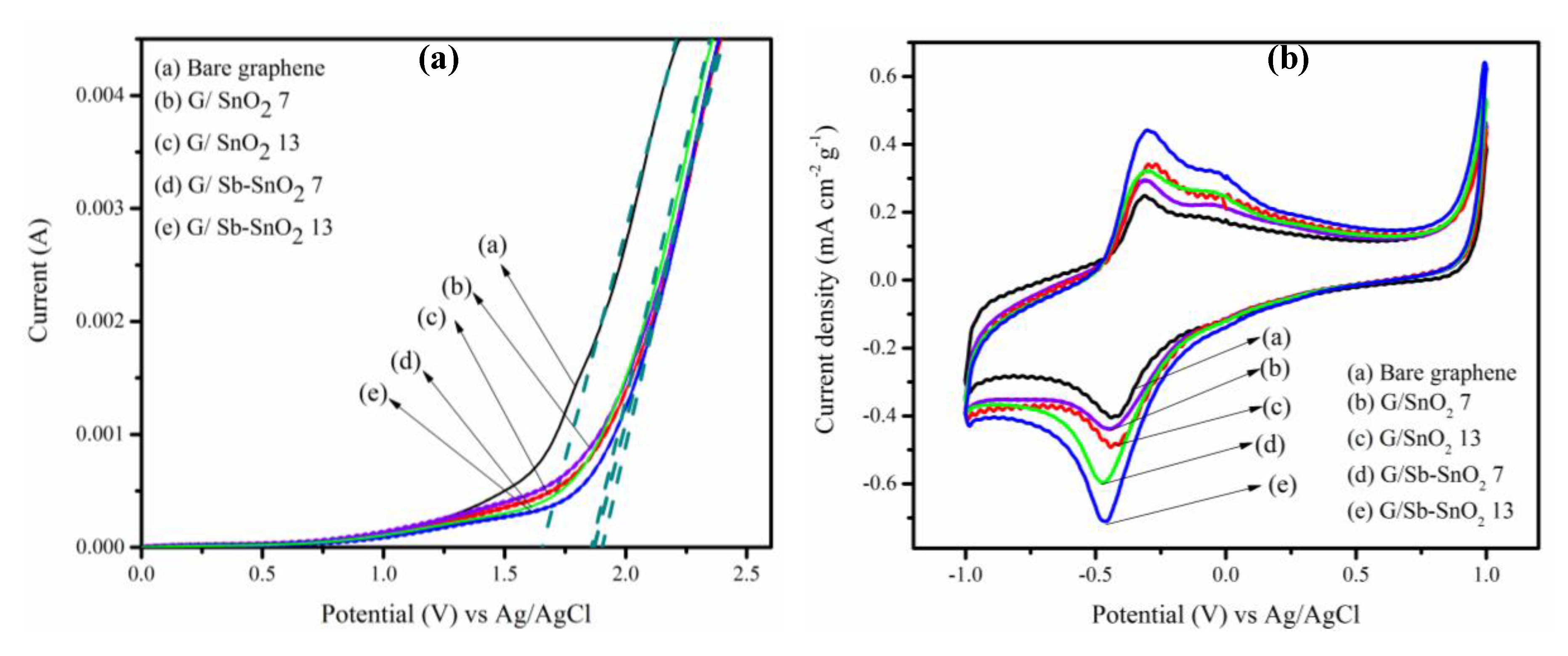
In order to assess the electrochemical characteristics of the nanocomposites, linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) was carried out. Figure 7a shows the results for bare graphene, G/SnO2, and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites, in which the current flow was measured as the applied potential was increased. The experiments were performed in 0.5 M Na2SO4 at a scan rate of 100 mVs−1, with Ag/AgCl and platinum wire used as reference and counter electrodes respectively. Onset potentials of 1.65, 1.87, 1.87, 1.9, and 1.87 V were measured for bare graphene, G/SnO2 7, G/SnO2 13, G/Sb-SnO2 7, and G/Sb-SnO2 13 adsorbents, respectively, for the oxygen evolution reaction. The delay in the onset potential indicates the suppression of this side reaction and increasing the charge efficiency for generating reactive oxygen species. Such a trend has also been observed by different researchers for SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 electrocatalyst materials [21,25,43,44].
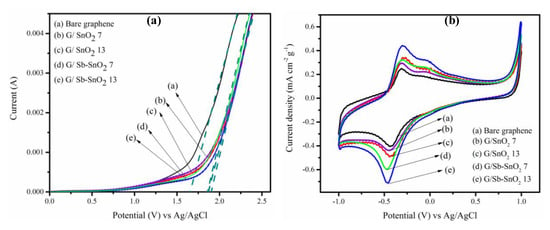
Figure 7.
(a) Linear sweep voltammograms of (a) bare graphene, (b) G/SnO2 7, (c) G/SnO2 3, (d) G/Sb-SnO2 7, and (e) G/Sb-SnO2 13. Experiments were conducted using 0.5 mol L−1 sodium sulfate at a scan rate of 100 mV S−1 (b) Cyclic voltammetry of (a) bare graphene, (b) G/SnO2 7, (c) G/SnO2 13, (d) G/Sb-SnO2 7, and (e) G/Sb-SnO2 13 at a scan rate of 10 mV S−1 using a solution containing 25 ppm MB and 0.5 mol L−1 sodium sulphate.
2.6.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
Figure 7b shows the cyclic voltammogram of the bare graphene, G/SnO2, and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites in 0.5 mol L−1 Na2SO4 solution containing 25 mg L−1 of MB. The current density was normalized by the graphene loading for all of the adsorbents. Unlike the bare graphene, G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 demonstrate a well-defined pair of redox peaks for MB oxidation and reduction. In addition, the peak separation, ΔEp, was smaller for G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites relative to bare graphene, demonstrating that the electron transfer was faster for these nanocomposites. It can be seen that the SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 nanoparticles-coated graphene show a higher oxidation peak than that of bare graphene. This implies that the addition of SnO2 and Sb-SnO2 nanoparticles to the graphene increases the electrocatalytic activity, apparently due to synergic effects of the presence of both an n-type semiconductor with a large band gap and graphene [45,46]. It can also be seen that by increasing the nanoparticles loading from 7 to 13 wt. %, the current density increased for both G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites. Furthermore, at the same loading of the nanoparticles, G/Sb-SnO2 shows better catalytic activity compared to G/SnO2 nanocomposites, as the Sb-SnO2 acts similar to a metal electrocatalyst and exhibits a high overpotential of oxygen evolution, which can increase its electrocatalytic activity [47,48,49].
3. Experimental
Nanocomposite preparation: a known volume of as-received sol of SnO2 (15 wt. %) or Sb-SnO2 (20 wt. %) (Nyacol Inc., Ashland, MA, USA) was added to 150 mL of a suspension of graphene (GNPs 25 M, XG sciences Inc., Lansing, MI, USA) in DI water (containing 1 g L−1 of graphene) and mixed for 24 h. The mixture was dried at 70 °C for 12 h. In this paper, the nanocomposites are named with respect to their composition: thus G/SnO2 7 corresponds to a graphene/SnO2 composite with a loading of 7 wt. % SnO2. Similarly, G/SnO2 13 has a loading of 13 wt. % SnO2, and G/Sb-SnO2 7 and G/Sb-SnO2 13 have loadings of 7 wt. % and 13 wt. % Sb-SnO2, respectively.
Characterization: The morphologies of the prepared nanocomposites were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on a Zeiss Supra55 field-emission SEM (Carl Zeiss Microscopy LLC, White Plains, NY, USA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using a Tecnai TF20 G2 FEG-TEM (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) with a 200−kV acceleration voltage. A Witec alpha 300 R Confocal Raman Microscope (Witec GmbH, Ulm, Germany) was utilized to obtain Raman spectra using a 532 nm laser. The surface area was measured with N2 physisorption (TriStar 3000, Micromeritics Instrument Corp., Norcross, GA, USA) at −196 °C. Before measurement, all samples were degassed at 150 °C for 12 h. The specific surface area was calculated using the Brunauer¬–Emmett–Teller (BET) method in the relative pressure (P/Po) range of 0.01 e 0.99. The concentration of MB in the synthetic wastewater was measured using UV-Visible absorption spectroscopy (UV-2600, Shimadzu, Columbia, MD, USA) at a wavelength of 664 nm [50].
Adsorption study: to obtain the adsorption isotherm, experiments were carried out via a ‘bottle point’ method. Briefly, 0.1 g of adsorbent was mixed for 30 minutes with 150 mL of the MB solution with different concentrations at room temperature. Synthetic wastewater was prepared using deionized water and MB only. The treated water was filtered, and the filtrate concentration was measured using UV-Visible spectrophotometer.
Electrochemical regeneration: an electrolytic cell was used to regenerate the spent adsorbents using a graphite plate as the anode and a stainless-steel plate as the cathode, as described in an earlier study [14]. Sodium chloride and sodium sulfate (VWR, Radnor, PA, USA) were used as electrolytes. A constant current density of 10 mA cm−2 was applied to the cell using a Metrohm Autolab PGSTAT potentiostat (Metrohm AG, Herisaum, Switzerland). The regeneration efficiency was calculated as the ratio of the adsorptive capacity after regeneration to the initial adsorptive capacity, each measured under the same adsorption conditions [51,52].
Electrochemical properties: electrochemical measurements, including cyclic voltammetry (CV) and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) were performed using the Autolab PGSTAT potentiostat. A volume of 100 mL of a 0.5 mol L−1 Na2SO4 containing 25 ppm MB (VWR, Radnor, PA, USA) was used as an electrolyte. Modified glassy carbon with nanocomposites, Ag/AgCl, and platinum wire were used as working, reference, and counter electrodes, respectively. The modified glassy carbon was prepared by drop-casting a suspension of the nanocomposites (1 mg of adsorbent in 1 mL of Nafion solution, from IonPower, New Castle, DE, USA, with a Nafion-to-adsorbent mass ratio of ~0.1) on a glassy carbon electrode and drying at 70 °C. CV was carried out in a potential range of −1.0 V to +1.0 V at a scanning rate of 10 mV S−1.
4. Conclusions
This study reported the application of G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites in an adsorption and electrochemical regeneration process, using both the high conductivity of the graphene and the large band gap of the tin oxide to improve regeneration efficiency. The adsorptive capacity obtained for the nanocomposites was ≥35 mg g−1, which is approximately 1.4- and 1.75-fold higher than the bare graphene and previously reported graphene titanium oxide [29], respectively.
All the prepared nanocomposites showed the ability to attain 100% regeneration efficiency in both NaCl and Na2SO4 electrolytes. With the assistance of SnO2 and Sb-SnO2, the charge efficiency of the process was significantly improved. The results indicate that the required charge passed for complete oxidation of the MB decreased by 50% and 30% for G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 in an NaCl electrolyte and 35% and 40% for G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 in an Na2SO4 electrolyte. The reason could be the higher oxygen evolution onset potential along with the higher activity of the SnO2 and Sb-SnO2. Although the cyclic voltammetry results suggested that G/Sb-SnO2 has higher catalytic activity than G/SnO2, the regeneration results show similar charge requirements for complete regeneration for both G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 nanocomposites. The higher catalytic activity of the Sb-SnO2-modified graphene observed is consistent with previous studies that have demonstrated the suitability of this for electrocatalysis for advanced oxidation combined with a high oxygen overpotential [46,47,50]. An advantage of G/SnO2 and G/Sb-SnO2 over TiO2/graphene nanocomposites is that they have less of an impact on the electrical conductivity of the graphene, minimizing the ohmic losses during regeneration, reducing the energy required.
In addition to the nanocomposites having better performance if Na2SO4 is used as the regeneration electrolyte, using a chloride-free electrolyte reduces the risk of creating toxic breakdown products. This makes sodium sulfate a good electrolyte substitute for sodium chloride.
The possibility of formation of breakdown products that may be released into the treated water was not investigated in this study, and further work is needed to explore this aspect. In addition, the effect of the multiple cycles of regeneration on the structure and surface properties of the nanocomposite adsorbent and the lifetime of the adsorbent should also be investigated.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/10/2/263/s1, Figure S1. Effect of charge passed on regeneration efficiency of MB adsorption on bare graphene, G/SnO2 7 and G/Sb-SnO2 7, and (a) NaCl electrolyte and (b) Na2SO4 electrolyte (current density of 10 mA cm2).
Author Contributions
E.P.L.R.: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, project administration, writing—review and editing; F.S.: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing original draft, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC 435634-2013 and RGPIN-2018-03725) and the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI 32613).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ali, I. Water treatment by adsorption columns: Evaluation at ground level. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Cheng, M.J. Adsorption of phenol and m-chlorophenol on organobentonites and repeated thermal regeneration. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sangeetha, D. Recycling of agricultural solid waste, coir pith: Removal of anions, heavy metals, organics and dyes from water by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, R.; Marco-Lozar, J.P.; Quijada, C.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Electrochemical regeneration and porosity recovery of phenol-saturated granular activated carbon in an alkaline medium. Carbon N. Y. 2010, 48, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Balasubramanian, N. Electrochemical regeneration of granular activated carbon saturated with organic compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, H.M.A.; Hussain, S.N.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Brown, N.W. Removal of humic acid from water using adsorption coupled with electrochemical regeneration. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, H.M.A.; Hussain, S.N.; Sattar, H.; Brown, N.W.; Roberts, E.P.L. Electrochemically synthesized GIC-based adsorbents for water treatment through adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narbaitz, R.M.; Cen, J. Electrochemical regeneration of granular activated carbon. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Otón, M.; Montilla, F.; Lillo-Rodenas, M.A.; Morallon, E.; Vázquez, J.L. Electrochemical regeneration of activated carbon saturated with toluene. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Quan, X.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, W. Integrated electrochemically enhanced adsorption with electrochemical regeneration for removal of acid orange 7 using activated carbon fibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 59, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Roberts, E.P.; Garforth, A.; Dryfe, R.A. Electrochemical regeneration of a carbon-based adsorbent loaded with crystal violet dye. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 3269–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.W.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Chasiotis, A.; Cherdron, T.; Sanghrajka, N. Atrazine removal using adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.W.; Roberts, E.P.L. Electrochemical pre-treatment of effluents containing chlorinated compounds using an adsorbent. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, F.; Gagnon, L.R.; Mulmi, S.; Roberts, E.P.L. Electrochemical regeneration of a reduced graphene oxide/magnetite composite adsorbent loaded with methylene blue. Water Res. 2017, 114, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkrumah-Amoako, K.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Brown, N.W.; Holmes, S.M. The effects of anodic treatment on the surface chemistry of a Graphite Intercalation Compound. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 135, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueffer, M.; Bejan, D.; Bunce, N.J. Graphite: An active or an inactive anode? Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntsendwana, B.; Mamba, B.B.; Sampath, S.; Arotiba, O.A. Synthesis, characterisation and application of an exfoliated graphite-diamond composite electrode in the electrochemical degradation of trichloroethylene. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24473–24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleyeju, M.G.; Umukoro, E.H.; Babalola, J.O.; Arotiba, O.A. Electrochemical Degradation of an Anthraquinonic Dye on an Expanded Graphite-Diamond Composite Electrode. Electrocatalysis 2016, 7, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hoffmann, M.R. Synthesis and Stabilization of Blue-Black TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Electrochemical Oxidant Generation and Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11888–11894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmann, J.R.; Borch, T.; Sale, T.C.; Blotevogel, J. Advanced Electrochemical Oxidation of 1, 4-Dioxane via Dark Catalysis by Novel Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Pellets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8817–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xue, F.; Qian, Y.; Wang, C. Enhanced electrochemical oxidation of synthetic dyeing wastewater using SnO2-Sb-doped TiO2-coated granular activated carbon electrodes with high hydroxyl radical yields. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 220, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, D.; Wan, J.; Yu, X. Preparation and electrochemical property of TiO2/Nano-graphite composite anode for electro-catalytic degradation of ceftriaxone sodium. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, J. The influence of TiO2 and aeration on the kinetics of electrochemical oxidation of phenol in packed bed reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zhao, G.; Lei, Y.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Liu, M. Novel vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes embedded with Sb-doped SnO2 electrode with high oxygen evolution potential and long service time. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Meng, X.; Sun, P.; Niu, J.; Jiang, W.; Bottomley, L.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Crittenden, J. Electrochemical oxidation of ofloxacin using a TiO2-based SnO2-Sb/polytetrafluoroethylene resin-PbO2 electrode: Reaction kinetics and mass transfer impact. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Kaiser, W.; Krohn, H. Boron doped diamond (BDD)-layers on titanium substrates as electrodes in applied electrochemistry. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 4691–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Fan, J.; He, Z.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, X. Electrochemical degradation of azo dye CI Reactive Red 195 by anodic oxidation on Ti/SnO2–Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Fabianska, A.; Stolte, S.; Nienstedt, A.; Ossowski, T.; Stepnowski, P.; Thöming, J. Electrocatalytic oxidation of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride: Effect of the electrode material. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 5560–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, F.; Roberts, E.P.L. Anodic electrochemical regeneration of a graphene/titanium dioxide composite adsorbent loaded with an organic dye. Chemosphere 2019, 241, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wen, T.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Liao, J.; Hu, J.; Shao, D.; Wang, X. Preconcentration of U (VI) ions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6182–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Qian, Y. Study of the Raman spectrum of nanometer SnO2. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 1835–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-López, M.A.; Galeana-Camacho, J.R.; Esparza-García, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, C.; Julien, C.M. Characterization of nanostructured SnO2 films deposited by reactive DC-magnetron sputtering. Superf. Vacío 2013, 26, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.M.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, G.H. Influence of Sb doping on the structural and optical properties of tin oxide nanocrystals. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 3296–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonu, V.; Das, A.; Sivadasan, A.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Dhara, S. Invoking forbidden modes in SnO2 nanoparticles using tip enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, V.; Srinivasarao, U.; Ramachandran, R.; Saranya, M.; Grace, A.N. Synthesis of tin oxide/graphene (SnO2/G) nanocomposite and its electrochemical properties for supercapacitor applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 84, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Rahman, A.A. Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from biomass material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Luz-Asunción, M.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; Castaño, V.M.; Velasco-Santos, C. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions by carbon nanomaterials of one and two dimensions: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Nanomater. 2015, 16, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, D.; Parise, M. Weathering as a predisposing factor to slope movements: An introduction. Geol. Soc. Lond. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2010, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.H.; Chen, S.F. Methylene blue adsorption by clays saturated with different inorganic cations. Int. Inf. Syst. Agric. Sci. Technol. 1978, 26, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Regeneration of exhausted activated carbon by electrochemical method. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, H.M.A.; Hussain, S.N.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Campen, A.K.; Brown, N.W. Pre-treatment of adsorbents for waste water treatment using adsorption coupled-with electrochemical regeneration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Sedlak, D.L. Challenges and opportunities for electrochemical processes as next-generation technologies for the treatment of contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11292–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Cui, X.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, T.; Li, H.; Lei, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, D. Electrochemical Degradation of Refractory Pollutant Using a Novel Microstructured TiO2 Nanotubes/Sb-Doped SnO2 Electrode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. TiO2-NTs/SnO2-Sb anode for efficient electrocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: Effect of TiO2-NTs architecture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 102, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurzulaikha, R.; Lim, H.N.; Harrison, I.; Lim, S.S.; Pandikumar, A.; Huang, N.M.; Lim, S.P.; Thien, G.S.H.; Yusoff, N.; Ibrahim, I. Graphene/SnO2 nanocomposite-modified electrode for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shen, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. In situ chemical synthesis of SnO2–graphene nanocomposite as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Shi, S.; Zhu, X.; Ni, J. Effect of Sb dopant amount on the structure and electrocatalytic capability of Ti/Sb-SnO2 electrodes in the oxidation of 4-chlorophenol. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Mho, S. Electrocatalytic reactions of phenolic compounds at ferric ion co-doped SnO2: Sb5+ electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 568, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldararu, M.; Thomas, M.F.; Bland, J.; Spranceana, D. Redox processes in Sb-containing mixed oxides used in oxidation catalysis: I. Tin dioxide assisted antimony oxidation in solid state. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 209, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, T.; Cao, D.; Xu, P.; Hochstetter, D.; Wang, Y. Adsorption of methylene blue onto activated carbon produced from tea (Camellia sinensis L.) seed shells: Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics studies. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2013, 14, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.N.; Asghar, H.M.A.; Sattar, H.; Brown, N.W.; Roberts, E.P.L. Removal of Tartrazine From Water by Adsorption with Electrochemical Regeneration. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 202, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.M.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Campen, A.K.; Brown, N.W. Wastewater treatment by multi-stage batch adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2012, 2, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).