Abstract
Mastermind is a two players zero sum game of imperfect information. Starting with Erdős and Rényi (1963), its combinatorics have been studied to date by several authors, e.g., Knuth (1977), Chvátal (1983), Goodrich (2009). The first player, called “codemaker”, chooses a secret code and the second player, called “codebreaker”, tries to break the secret code by making as few guesses as possible, exploiting information that is given by the codemaker after each guess. For variants that allow color repetition, Doerr et al. (2016) showed optimal results. In this paper, we consider the so called Black-Peg variant of Mastermind, where the only information concerning a guess is the number of positions in which the guess coincides with the secret code. More precisely, we deal with a special version of the Black-Peg game with n holes and colors where no repetition of colors is allowed. We present upper and lower bounds on the number of guesses necessary to break the secret code. For the case , the secret code can be algorithmically identified within less than queries. This result improves the result of Ker-I Ko and Shia-Chung Teng (1985) by almost a factor of 2. For the case , we prove an upper bound of . Furthermore, we prove a new lower bound of n for the case , which improves the recent bound of Berger et al. (2016). We then generalize this lower bound to k queries for the case .
MSC:
91A46
1. Introduction
In this paper, we deal with Mastermind, which is a popular board game that in the past three decades has become interesting from an algorithmic point of view. Mastermind is a two-player board game invented in 1970 by the postmaster and telecommunication expert Mordecai Meirowitz. The original version of Mastermind consists of a board with twelve (or ten, or eight) rows containing four holes and pegs of six different colors. The idea of the game is that the codemaker chooses a secret color combination of n pegs from k possible colors and the codebreaker has to identify the code by a sequence of queries and corresponding information that is provided by the codemaker. All queries are also color combinations of n pegs. Information is given about the number of correctly positioned colors and further correct colors, respectively. Mathematically, the codemaker selects a vector and the codebreaker gives in each iteration a query in form of a vector . The codemaker replies with a pair of two numbers, called and , respectively. The first one is the number of positions in which both vectors x and y coincide and the second one is the number of additional pegs with a right color but a wrong position:
The Black-Peg game is a special version of Mastermind, where answers are provided by information only. A further version is the so-called AB game, a.k.a. Bulls and Cows, in which all colors within a code must be distinct. Actually, this version is supposed to be much older than the commercial variant of Mastermind. It is an interesting open question whether both variants are of the same complexity for the codebreaker or if one version is significantly harder because, in the AB game, the space of possible solutions as well as the space of possible queries are both restricted. In this paper, we deal with a special combination of the Black-Peg game and the AB game, where both the secret vector and the guesses must be composed of pairwise distinct colors () and the answers are given by the information only. In a breakthrough paper, Doerr et al. [1] state that is the most popular case in research, where the information is redundant for the AB game.
Related Works: The study of Mastermind in its different variants has a long lasting history in combinatorial game theory. In 1963, several years before the invention of Mastermind as a commercial board game, Erdős and Rényi [2] analyzed the same problem with two colors. One of the earliest analyses of this game after its commercialization dealing with the case of four pegs and six colors was done by Knuth [3]. He presented a strategy that identifies the secret code in at most five guesses. For the AB game with four pegs, it is known that at least seven guesses are required in the worst case [4]. Ever since the work of Knuth, the general case of arbitrary many pegs and colors has been intensively investigated in combinatorics and computer science literature. In the field of complexity, Stuckman and Zhang [5] showed that it is -complete (most likely impossible in polynomial time) to determine if a sequence of queries and answers is satisfiable. Concerning the approximation aspect, there are many works regarding different methods [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The Black-Peg game was first introduced by Chvátal for the case . He gave a deterministic adaptive strategy that uses guesses. Later, Goodrich [17] improved the result of Chvátal for arbitrary n and k to guesses. Moreover, he proved in the same paper that this kind of game is -complete. A further improvement to for and for was done by Jäger and Peczarski [18]. Doerr et al. [1] provided a randomized codebreaker strategy that only needs queries in expectation. They also showed that this asymptotic order even holds for up to colors, if both black and white information is allowed. For the AB game, Jäger and Peczarski [19] proved exact worst-case numbers of guesses for fixed and arbitrary k. Concerning the combination of both variants, Black-Peg game and AB game, for almost three decades, the work due to Ker-I Ko and Shia-Chung Teng [20] was the only contribution that provides an upper bound for the case . They presented a strategy that identifies the secret permutation in at most guesses and proved that the corresponding counting problem is -complete.
Our Contribution: In this paper, we consider the Black-Peg game without color repetition. We first present a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm that identifies the secret permutation in less than queries in the case and in less than queries in the case . In a conference version (extended abstract) “Improved Approximation Algorithm for the Number of Queries Necessary to Identify a Permutation”, upper bounds of this paper have been presented with some sketches of the proofs [21]. Our result for the case improves the result of Ker-I Ko and Shia-Chung Teng [20] by almost a factor of 2. Furthermore, we analyze the worst-case performance of query strategies for both variants of the Game and give a new lower bound of n queries for the case , which improves the recently presented lower bound of by Berger et al. [22]. We note, however, that the corresponding asymptotic bound of is long-established. For we generalize this lower bound to k. Both lower bounds even hold if the codebreaker is allowed to use repeated colors in his guesses.
2. Upper Bounds on the Number of Queries
We first consider Black-Peg Mastermind with and the demand for pairwise distinct colors in both the secret code and all queries, i.e., we deal with permutations in .
2.1. Black-Peg AB-Mastermind, Case
For convenience, we will use the term permutation for both, a mapping in and its one-line representation as a vector. Our algorithm for finding the secret permutation includes two main phases that are based on two ideas. In the first phase, the codebreaker guesses an initial sequence of n permutations that has a predefined structure. In the second phase, the structure of the initial sequence and the corresponding information by the codemaker enable us to identify correct components of the secret code one after another, each by using a binary search. Recall that, for two codes and , we denote by the number of components in which w and x are equal. We denote the mapping x restricted to the set with , .
Phase 1. Consider the n permutations, , which are defined as follows: corresponds to the identity map and, for , we obtain from by a circular shift to the right. For example, if , we have , , and . Within those n permutations, every color appears exactly once at every position and, thus, we have
The codebreaker guesses and obtains the additional information from Equation (1).
Phase 2. The strategy of the second phase identifies the values of y one after another. This is done by using two binary search routines, called findFirst and findNext, respectively. The idea behind both binary search routines is to exploit the information that, for we have , , and , while, except for an infrequent special case, findFirst is used to identify the first correct component of the secret code, and findNext identifies the remaining components in the main loop of the algorithm. Actually, findFirst would also be able to find the remaining components but requires more guesses than findNext (twice as many in the worst case). On the other hand, findNext only works if at least one value of y is already known such that we have to identify the value of one secret code component in advance.
Identifying the First Component: Equation (1) implies that either holds for all or that we can find a with .
In the first case, which is infrequent, we can find one correct value of y by guessing at most modified versions of some initial guess, say . Namely, if we define a guess by swapping a pair of components of , we will obtain , if and only if one of the swapped components has the correct value in .
In the frequent second case, we find the first component by findFirst in at most guesses. The routine findFirst is outlined as Algorithm 1 and works as follows. In the given case, we can either find a with but and set , or we have but and set and . We call such an index j an active index. Now, for every we define the code
and call the peg at position ℓ in the pivot peg. Note that notations of the form substitute and vanish in the case . From the information for , we conclude that is actually a new permutation as required. The fact that implies that the number of correct pegs up to position in is either (if ) or (if ). For our algorithm, we will only need to know if there exists one correct peg in up to position . The question is cleared up, if . On the other hand, if , we can define a new guess by swapping the pivot peg with a wrong peg in . We define
| Algorithm 1: Routine findFirst |
 |
For the case , we may assume that we applied our query procedure for an already, proving that the first pegs in are wrong, particularly . Now, we obtain , if and only if the pivot peg had a wrong color in meaning that there is one correct peg in in the first places. Thus, we can find the position m of the leftmost correct peg in by a binary search as outlined in Algorithm 1.
Identifying a Further Component: For the implementation of findNext (Algorithm 2), we deal with a partial solution vector x that satisfies for all . We call the (indices of the) non-zero components of the partial solution fixed. They indicate the components of the secret code that have already been identified. The (indices of the) zero components are called open. Whenever findNext makes a guess , it requires knowing the number of open components in which the guess coincides with the secret code, i.e., the number
Note that the term is known by the codebreaker and not greater than . After the first component of y has been found and fixed in x, there exists a such that . As long as we have open components in x, we can either find a with but and set , or we have but and set and . Again, we call such an index j an active index. Let j be an active index and r its related index. Let c be the color of some component of y that is already identified and fixed in the partial solution x. With and we denote the position of color c in and , respectively. The peg with color c serves as a pivot peg for identifying a correct position m in that is not fixed yet. There are two possible modes for the binary search that depend on the fact if . The mode is indicated by a Boolean variable and determined by lines 5 to 10 of findNext. Clearly, if . Otherwise, the codebreaker guesses
By the information we obtain that . We further know that every open color has a wrong position in . For that reason, implies that .
| Algorithm 2: Routine findNext |
 |
The binary search for the exact value of m is done in the interval , where m is initialized as n and as
(lines 11 to 16 of findNext). In order to determine if there is an open correct component on the left side of the current center ℓ of in , we can define a case dependent permutation:
In the first case, the first components of coincide with those of . The remaining components of cannot coincide with the corresponding components of the secret code if they have not been fixed yet. This is because the ℓ-th component of has the already fixed value c, components to coincide with the corresponding components of , which satisfies and the remaining components have been checked to be wrong in this case (cf. former definition of in line 5 and line 9, respectively). Thus, there is a correct open component on the left side of ℓ in , if and only if . In the second case, the same holds for similar arguments. Now, if there is a correct open component to the left of ℓ, we update the binary search interval by . Otherwise, we update by .
The Main Algorithm. The main algorithm is outlined as Algorithm 3. It starts with an empty partial solution and finds the components of the secret code y one-by-one. Herein, the vector v does keep records about the number of open components in which the permutations equal y and is, thus, initialized by , and . As mentioned above, the main loop always requires an active index. For that reason, if in the beginning, we fix one solution peg in and update x and v, correspondingly. Every call of findNext in the main loop augments x by a correct solution value. Since one call of findNext requires at most guesses, Algorithm 3 does not need more than queries for (inclusive initial guesses, guesses to find the first correct peg, calls of findNext and 2 final queries) to break the secret code.
| Algorithm 3: Algorithm for Permutations |
 |
Example 1.
We consider the case and suppose that the secret code y is
Figure 1 (upper panel) shows n possible initial queries. We illustrate the procedure findNext and further suppose that we have already identified the positions of three colors indicated in the partial solution x:
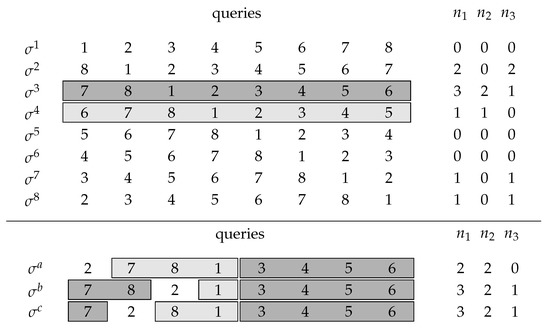
Figure 1.
Upper panel: initial queries with associated responses , coincidences with a partial solution , and the difference of both . Lower panel: binary search queries to extend the partial solution. The highlighted subsequences correspond to the subsequences of the selected initial queries.
From the values in Figure 1, we see that and , so we choose 3 as our active index applying findNext with the highlighted initial queries, and . Choosing the already identified color 2 as a pivot color, findNext does its binary search to identify the next correct peg as demonstrated in the lower panel of Figure 1. Since the information for query is 0 (cf. lines 7–9 of Algorithm 2), all correctly placed but unidentified pegs in are in the first four places. Thus, we can apply a binary search for the leftmost correct peg in the first four places of query using the pivot peg. Here, the binary search is done by queries and and identifies the peg with color 7 (in general, the peg that is left to the leftmost pivot position for which is non-zero). If the response to would have been greater than 0, we would have found analogously a new correct peg among the last four places of .
2.2. More Colors Than Positions
Now, we consider the variant of Black-Peg Mastermind where and color repetition is forbidden. Let be the code that must be found. We use the same notations as above.
Phase 1. Consider the k permutations , where corresponds to the identity map on and for , we obtain from by a circular shift to the right. We define k codes by , . For example, if and , we have , , , and . Within those k codes, every color appears exactly once at every position, and, thus, we have
similar to Equation (1). Since , this implies
Lemma 1.
There is a with .
Phase 2. Having more colors than holes, we can perform our binary search for the next correct position without using a pivot peg. The corresponding simplified version of findNext is outlined as Algorithm 4. Using that version of findNext also allows to simplify our main algorithm (Algorithm 3) by adapting lines 2 and 3, and, due to Lemma 1, skipping lines 4–10, as findNext can be already applied to find the first correct peg. Thus, for the required number of queries to break the secret code, we have: the initial guesses, a call of the modified findNext for all but the last two positions (at most guesses per position) and one or two final guesses. This yields the modified Mastermind Algorithm breaking the secret code in at most queries.
| Algorithm 4: Routine findNext for |
 |
3. Lower Bounds on the Number of Queries
In the following, we consider the case that the secret code has no repetition but arbitrary questions are allowed. Note that the lower bounds for that case especially hold true for Black-Peg AB-Mastermind, since the codebreaker will not be able to detect a secret code with less attempts, if the set of allowed queries is restricted to the corresponding subset. Similar to the upper bounds, we prove the respective lower bounds on the necessary number of queries by construction.
3.1. Black-Peg AB-Mastermind, Case
In each iteration, the worst case for the code breaker is simulated by allowing the codemaker to replace his secret code with another permutation from the remaining feasible search space. For we denote the m-th query of the code breaker with and the m-th secret code adaption of the codemaker with . The remaining feasible search space consists of all permutations that agree with the first m pairs of queries and answers:
Now, a simple strategy of the codemaker is to reply every query , , with the smallest possible number
choosing his new secret code such that . We obtain our lower bound on the necessary number of queries by proving the following Lemma.
Lemma 2.
It holds that for all .
In particular, none of the first queries will be answered with n. Thus, the secret code cannot be identified with less than n queries.
Proof.
Assuming that our claim is wrong, we fix the smallest number with . Let
be the set of colors that are correctly placed in the current query with respect to the current secret code. For every let be the set of all colors that do not occur at position i in any of the former queries nor in the current secret code, i.e.,
The intersections , are not empty since but at most m of the n colors are missing in . This fact will enable us to determine a new feasible secret code such that for all but , a contradiction to the minimality of . The new secret code z is constructed from by changing the colors of some components that coincide with , choosing the new color at a given position i from . The precise procedure is outlined as Algorithm 5. Starting with any position where and have the same color, we choose another color . Since , there must be another position such that . Thus, for we can iteratively determine positions where and have the same color, , and choose a new color (while loop, lines 5–9). The iteration stops, if the chosen color corresponds with a color that appears in at some position , , that has been considered before (indicated by the set A). Note that the iteration must terminate with , since A is empty in the beginning, and . The set of chosen colors is equal to the set of colors at the corresponding positions in . Hence, the new secret code z (defined in lines 10–11) is again a permutation. Now, let be the number of some former query. Since the definition of implies . However, also holds since (), and, for each position i with we have (). Furthermore, the construction of z immediately yields since z is obtained from by changing some pegs that coincided in and . Thus, z is indeed a secret permutation in that contradicts the minimality of . ☐
| Algorithm 5: Secret code adaption, |
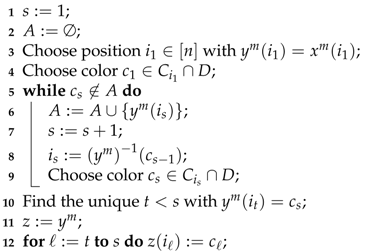 |
3.2. More Colors Than Positions
Considering the case , we adapt the codemaker strategy from the former subsection, i.e., in each turn m, the codemaker chooses the new secret code such that the answer is the smallest possible answer . We easily obtain a lower bound of k queries by the following:
Lemma 3.
It holds that for all .
Proof.
Assume for a moment that there exists an with . Like before, let
Similar to Algorithm 5, we now replace certain entries of by elements of the corresponding . The detailed procedure is described in Algorithm 6.
| Algorithm 6: Secret code adaption, |
 |
We start with position one and choose a color . As soon as we have , we construct z by starting with and then replacing the color by the color for any . The set of chosen colors is equal to the set of colors except for , which only appears in the first set and which only appears in the second. Since we know that z has no color occurring twice.
If the iteration stops because of , the procedure is identical to the one in Algorithm 5. Thus, in both cases, we find that and for any , in contradiction to the minimality of . ☐
4. Discussion
We present deterministic algorithms for the identification of a secret code in “Black-Peg AB-Mastermind” as well as a “cheating algorithm” for the codemaker. Our constructive algorithms yield new upper and lower bounds on the necessary number of queries. A challenge of the considered Mastermind variant is that no color repetition is allowed for a query while most strategies for other Mastermind variants exploit the property of color repetition. We improve the recent lower bound of Berger et al. [22] and show that the worst case number of queries for Black-Peg AB-Mastermind with is at least n, another matter than the asymptotic bound of , which is long-established. Ko and Teng [20] conjecture that this number is actually , a proof of which would close the gap to the upper bound, answering the question of whether the AB game is harder than the general game. The lower bound proof of Berger et al. is derived by solely considering the search space partition with respect to the number of coincidences with the very first query. On the other hand, our algorithmic proof does not exploit any structure property of the remaining search space. For both reasons, we expect at least some room for improvements of the lower bound. Our corresponding general lower bound for Black-Peg AB-Mastermind (case ) is k. In the future, we will keep both bounds in focus, but the real challenge is to prove or disprove the conjecture of Ko and Teng. It would also be interesting to examine the impact of further restrictions concerning the answers by the codemaker. We conjecture that our binary search approach will also work if the codemaker answers a query by only indicating if there is at least one black peg.
Acknowledgments
Christian Glazik and Volkmar Sauerland contributed to this work while supported by DFG Cluster of Excellence 80. We also would like to acknowledge financial support by Land Schleswig-Holstein within the funding programme Open Access Publikationsfonds.
Author Contributions
Mourad El Ouali invented the codebreaker strategies that yield the upper bounds. Christian Glazik invented the codemaker strategies and proved the corresponding lower bounds. Volkmar Sauerland implemented and tested the codebreaker strategies. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the version submitted to games.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Doerr, B.; Doerr, C.; Spöhel, R.; Thomas, H. Playing Mastermind with Many Colors. J. ACM 2016, 63, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, P.; Rényi, C. On Two Problems in Information Theory. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 1963, 8, 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, D.E. The computer as a master mind. J. Recreat. Math. 1977, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, J. Strategies for playing MOO, or “Bulls and Cows”. 2010. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d839/f794cccd174790b0cde695d3626f00caf7e1.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- Stuckman, J.; Zhang, G. Mastermind is NP-Complete. INFOCOMP J. Comput. Sci. 2006, 5, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, L.; Goossens, D.; Leus, R. Efficient solutions for Mastermind using genetic algorithms. Comput. Op. Res. 2009, 36, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cunha, C.; Homer, S. Finding a Hidden Code by Asking Questions. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Computing and Combinatorics (COCOON 1996), Hong Kong, China, 17–19 June 1996; pp. 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chvátal, V. Mastermind. Combinatorica 1983, 3, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, B.; Winzen, C. Playing Mastermind with Constant-Size Memory. In Proceedings of the 29th Symposium on Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science (STACS 2012), Paris, France, 29 February–3 March 2012; pp. 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Focardi, R.; Luccio, F.L. Cracking Bank PINs by Playing Mastermind. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Fun with Algorithms (FUN 2010), Ischia, Italy, 2–4 June 2010; pp. 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Guervós, J.J.M.; Cotta, C.; Gacia, A.M. Improving and Scaling Evolutionary Approaches to the Mastermind Problem. Proceedings of Applications of Evolutionary Computation (EvoApplications 2011), Torino, Italy, 27–29 April 2011; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Guervós, J.J.M.; Mora, A.M.; Cotta, C. Optimizing worst-case scenario in evolutionary solutions to the Mastermind puzzle. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2011), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–8 June 2011; pp. 2669–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich, M.T. The Mastermind Attack on Genomic Data. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP 2009), Oakland, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; pp. 204–218. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, G.; Peczarski, M. The number of pessimistic guesses in Generalized Mastermind. Inf. Process. Lett. 2009, 109, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisker, T.; Camens, D. Solving Mastermind Using Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO 2003), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 July 2003; pp. 1590–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, K.; Lai, T.W. An optimal Mastermind strategy. J. Recreat. Math. 1993, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich, M.T. On the algorithmic complexity of the Mastermind game with black-peg results. Inf. Process. Lett. 2009, 109, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, G.; Peczarski, M. The number of pessimistic guesses in Generalized Black-peg Mastermind. Inf. Process. Lett. 2011, 111, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, G.; Peczarski, M. The worst case number of questions in Generalized AB game with and without white-peg answers. Discret. Appl. Math. 2015, 184, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Teng, S. On the Number of Queries Necessary to Identify a Permutation. J. Algorithms 1986, 7, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouali, M.; Sauerland, V. Improved Approximation Algorithm for the Number of Queries Necessary to Identify a Permutation. In Proceedings of the 24th International Workshop on Combinatorial Algorithms (IWOCA 2013), Rouen, France, 10–12 July 2013; pp. 443–447. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.; Chute, C.; Stone, M. Query Complexity of Mastermind Variants. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1607.04597. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).