Abstract
Conventional wearable sensors are mainly used to detect the physiological and activity information of individuals who wear them, but fail to perceive the information of the surrounding environment. This paper presents a wearable thermal sensing system to detect and perceive the information of surrounding human subjects. The proposed system is developed based on a pyroelectric infrared sensor. Such a sensor system aims to provide surrounding information to blind people and people with weak visual capability to help them adapt to the environment and avoid collision. In order to achieve this goal, a low-cost, low-data-throughput binary sampling and analyzing scheme is proposed. We also developed a conditioning sensing circuit with a low-noise signal amplifier and programmable system on chip (PSoC) to adjust the amplification gain. Three statistical features in information space are extracted to recognize static humans and human scenarios in indoor environments. The results demonstrate that the proposed wearable thermal sensing system and binary statistical analysis method are efficient in static human detection and human scenario perception.
1. Introduction
Human scenario recognition has been highly investigated due to its applications in security, surveillance, health-care, smart house, energy efficient control, etc. “Human scenarios” refers to the number of humans, human status, and human interactions. Conventional approaches to human scenario recognition employ video cameras, since video cameras can capture rich visible information of humans and environments [1,2,3]. However, video cameras usually have the challenges of processing a large volume of data and associate data for multiple targets. In addition, video cameras are highly affected by illumination conditions.
In comparison, wireless sensors-based human scenario recognition systems have become more popular due to their low computational complexity and robustness to various environmental conditions. Thermal, pressure, and laser sensors are the typical ones for wireless sensor-based human scenario recognition systems [4,5,6]. Among them, pyroelectric infrared (PIR) sensors are the most commercialized and widely applied in human detection, human tracking and identification, human scenario recognition, etc. PIR sensors are widely used in human sensing due to the advantages of (1) fitting the wave range of human thermal radiations; (2) measuring targets at a distance; (3) tolerating severe environmental conditions and cosmetic conditions.
Many researchers are conducting human sensing research with PIR sensors. People counting is an important element in human scenario recognition; using distributed PIR sensors, it is feasible to achieve this goal [7]. Lu has developed an efficient space-coding-based method for indoor human localization and tracking with wireless PIR sensors [8]. PIR sensor arrays are developed for human movement direction detection [9,10]. In our previous work [11], we presented a distributed PIR sensor network for moving human subject detection and human scenario recognition.
Although PIR sensors have good performance in human scenario recognition, their weakness is that PIR sensors can only detect mobile humans, but not static humans. In the applications of human tracking, human gait identification, and human scenario recognition, they all require mobile targets, since PIR sensors are only able to detect the movement of thermal radiations. Obviously, this mode of PIR sensor is not appropriate to recognize scenarios containing static humans. Therefore, in this work, we design a wearable PIR sensing system to actively detect humans. Since the PIR sensors are wearable, when the user swings arms, the movement of the PIR sensors can generate detection signals. Thus, to generate relative movement to be able to detect static targets. This wearable PIR sensing system has the following advantages:
- (1)
- It is able to detect static targets.
- (2)
- It is portable with users.
- (3)
- It is highly useful to blind people and disabled people with visual problems for the perception of surrounding human scenarios.
2. System Setup
2.1. PIR Sensor Circuit Design
In order to deliver a small-size wearable device but maintain sufficient information acquisition capabilities, we assemble two PIR sensors on our designed sensor circuit board, as shown in Figure 1a. In our sensor circuit design, we employ an amplifier to amplify the PIR signal within a certain bandwidth. A programmable system on chip (PSoC) works on the analog signal to perform as a sine filter and binary signal generator. The other major components on the circuit board include a mote interface, AD5241, and programming interface, as shown in Figure 1b.
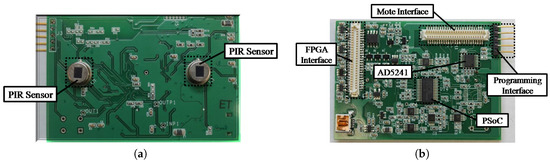
Figure 1.
Wearable pyroelectric infrared (PIR) sensing circuit board. (a) front; (b) back. PSoC: programmable system on chip.
2.2. Wearable Sensor Node Design
In our wearable sensor node design, two PIR sensors are assembled and distributed along a vertical orientation to be able to capture the spatial geometrical information of targets to be captured. Naked sensors are only able to form a single detection, while single detection cannot capture rich information. Instead, a Fresnel lens was adopted in our sensing module design to enable multiplex sensing. Coded masks (Figure 2a) were also developed to form different detection patterns. Fresnel lenses have been widely used in PIR sensing systems [12], and coded masks have been developed for a couple of our previous projects on human sensing with PIR sensors [13,14]. Integrating all these elements together, the designed sensing module is able to do multiplex sensing with various detection patterns. The sensor node is shown in Figure 3.
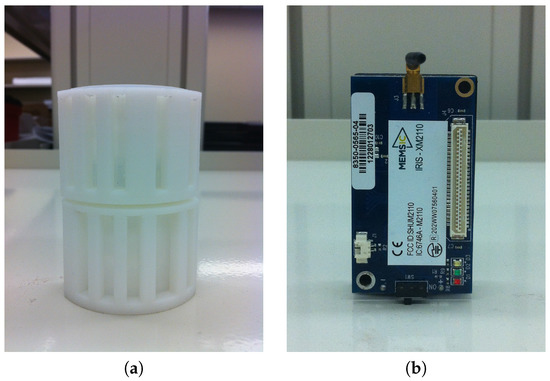
Figure 2.
(a) Coded mask for wearable PIR sensor; (b) Iris wireless sensor mote.
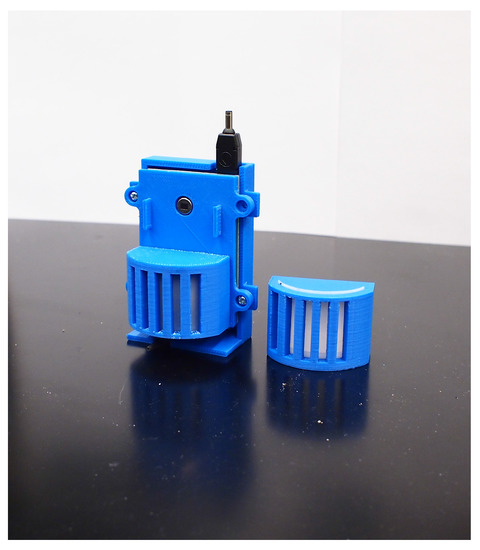

Figure 3.
Wearable pyroelectric infrared sensor node.
In order to ensure a certain signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), a programmable system on chip (PSoC) was integrated in the sensing board. The PSoC reads the ADC data and enables the sensor node to change the amplification gains when the target’s distance is changing. Furthermore, a binary generator is created in the PSoC of our wearable sensor node. Then, the output of our sensor node is a binary signal. Compared to binarizing the analog signals at the computation end, our scheme can reduce errors resulting from data lost during transmission. The system diagram of the wearable sensor node is shown in Figure 4. We also designed two thin slots on the case of the sensor node so that a band can be placed across through the sensor node.
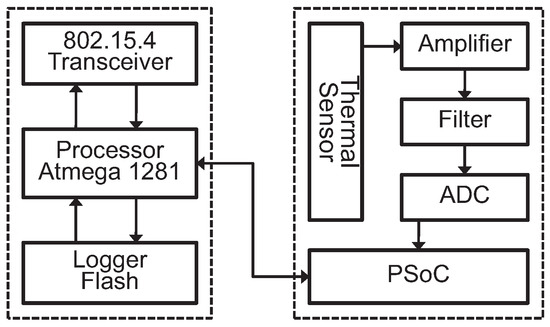
Figure 4.
System diagram of the wearable PIR sensor node.
2.3. Wireless Platform
The wireless communication platform is based on MEMSIC Iris sensor mote and TinyOS. Iris is a 2.4 GHz mote model specially signed for low-power embedded sensor systems (see Figure 2b). It integrates a transceiver with IEEE 802.15.4 wireless communication protocol. Iris was connected with our sensor circuit through the 51 pins interface. Through TinyOS, we can receive the data from the sensor circuit and send the data to the computing unit.
2.4. Active Sensing Protocol
The PIR sensor is a kind of thermal sensor which is able to detect the movement of a heat source. As the most general heat source in indoor environments, humans with motion can be detected by PIR sensors. However, this sensor cannot detect static human subjects. We call this sensing mode “passive sensing”, since the sensor itself is passively triggered by moving subjects.
On the contrary, with wearable sensing techniques, the PIR sensor is able to move with human limbs, thus generating relative movement to detect static subjects. In this mode, the sensor is able to actively generate detection signals, so it is called “active sensing”. Such an active sensing mode is very useful in many applications, especially for blind people or people who have weak visibility to detect other people and perceive the surrounding environment.
3. Wearable PIR Sensing and Statistical Feature Extraction
3.1. Wearable PIR Sensing for Static Targets
With wearable PIR sensors, the user is able to detect both dynamic and static targets. For the detection of static targets, the user can wave their arms to generate relative movement, thus generating detection signals. In order to further recognize the category of static targets, we propose the measurement of the information of static targets in both horizontal and vertical directions. This is achieved by waving arms left, right, up, and down, as shown in Figure 5. In this way, the size, shape, and orientation information of the target can be covered and captured.
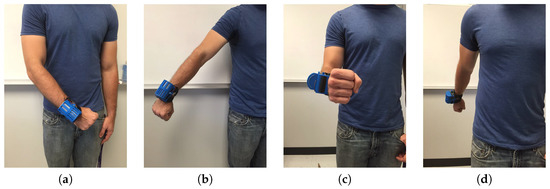
Figure 5.
(a) Swing left; (b) Swing right; (c) Swing up; (d) Swing down.
3.2. Wearable PIR Sensing for Scenario Perception
In an indoor environment, the situations of human subjects are very important information for surveillance, security, and perception. For blind people and people with weak visual capabilities, this information is more useful for use in perceiving surrounding human scenarios. Human scenarios contain a number of humans and their interactions. In this paper, we mainly focus on the number of humans information, but not interactions. Static human subjects are more difficult to detect than moving ones. This is not only because of the detection principle of PIR sensors, but also because of the natural feature of static state. More specifically, when two human subjects are standing or sitting close to talk or work, there must be one line that can cross both of them. Then, if the sensor node is also on the same line, from the perspective of the sensor, there is only one subject. In other words, one subject is occluded by the other. This phenomenon will result in a false alarm. To overcome this problem, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) detection method. In addition to swinging the wearable sensor left, right, up, and down, we add another dimension: back and forth. This is achieved by turning around a certain degree, then the left and right wave in the new coordinate can generate a partial back and forth wave in the original measured coordinates. Another method is to use a data fusion scheme to combine the sensing signals from two locations to implement recognition. The advantage is that sensing from two locations is equal to detecting from two angles. Even if there is an occlusion in one detection angle, in the other one, both targets can be seen.
3.3. Buffon’s Needle-Based Target Detection
The sensing principle of PIR sensors is that when human subjects walk through the field of view (FOV) of a sensor, the intersection of human subjects and radiation beams will trigger the detection. Such a detection process could be described by a Buffon’s Needle model. Accordingly, the moving human subjects could be regarded as needles, and the detection beams are the lines. Furthermore, as we know, Buffon’s Needle theory deals with intersection and nonintersection issues and their possibilities; apparently, it is a binary problem. Hence, it perfectly matches with the proposed binary sampling structure. Based on Buffon’s Needle theory, when a human subject’s moving direction is orthogonal to the direction of detection beams, the detection probability can be represented as [15]
where l is the length of waving arms of human subjects, d is the distance between two detection beams, and θ is the angle of the waving arms.
As for static targets, it is more challenging. Instead of keeping the wrist with the sensor node static, the user has to wave her/his wrist to generate relative movement. Such a movement can be regarded as the relative movement of static human subjects to the sensor node. For such cases, the detection probability will be
To be noted that although the mathematical representation of static target cases is the same as that of dynamic target cases, both l and θ have different physical meanings. Here, l is the length of waving arms of users other than human subjects, and θ is the waving angle of users which can be regarded as the relative waving angle of human subjects. α is the angle between the planes of the sensor node and the human subject. As the practical detection beams are not lines but rather thin strips, the width of these strips should also be taken into account. If a thin strip is regarded as the combination of multiple lines, then the case converts to have a longer waving arms , but with a single line. Accordingly, the distance between detection beams becomes longer—it should be . Then, the detection probability could be represented by
3.4. Target Feature Extraction
3.4.1. Probability of Intersection Process
With the Buffon Needle-based detection model, we can estimate any variable in the detection probability equation with the other variables known. In the actual experiments, usually intersections occur not for just a moment, but last for seconds. Therefore, we prefer to call it an intersection process. Basically, there are three phases in an intersection process: start, duration, and finish. The data patterns describe these three phases are (01), (11), and (10), respectively. In order to extract features of the whole intersection process, we analyze the second-order statistical information of each binary stream. In general, a weight should be assigned to each data stream. Denoting as the weight of the data stream and as the probability of the intersection process, we can get
when all sensors are under normal condition, they should have the same weight. As for our case, when both sensors work normally, we have . The probability of an intersection process is a significant feature to classify scenarios, since it describes the times and durations of thermal sources detection.
3.4.2. Temporal Statistical Feature
Temporal features represent the transition of thermal sources in the temporal domain. In particular, the temporal transition of thermal sources relates to the gesture/posture, action, and movement velocity of thermal sources in a horizontal orientation (temporal domain). Such transitions can be reflected from the pattern changes of adjacent bits along the data streams. By regarding the two-bit streams as a one-bit stream, the adjacent two bits will be one sample of a bivariate Bernoulli distribution. Denoting the bivariate Bernoulli random variables as —which takes values from (0,0), (0,1), (1,0), and (1,1) in Cartesian space—its probability density function can be represented by
where , , , and . is the joint probability and . Then, the covariance of the bivariate Bernoulli distribution can be represented by joint probabilities as
Hence, the correlation of bivariate Bernoulli variables is
where and are the marginal probabilities.
3.4.3. Spacial Statistical Feature
“Spacial feature” represents the geometric information of thermal sources in the spacial domain, such as shape, length, size, etc. Conventional single sensor architecture without geometry cannot capture the spacial information of thermal sources. In comparison, in our sensor node architecture, two sensors are coupled with a certain geometry and distributed along the vertical orientation (spacial domain). Combined with different coded mask patterns, such an architecture is able to capture the spacial information of thermal sources. As the sensory data is a two-bit stream, the spacial feature can be represented by the similarity of these two binary random variables. The coefficient is the appropriate option here to measure the similarity of two binary random variables, and it can be interpreted as the proportion of 1s shared by the variables in the same position.
where [] are the joint probabilities of two binary random variables in spatial domain.
4. Experiment and Evaluation
4.1. Experiment Setup
For an indoor environment, scenes may consist of both mobile and static human subjects. The goal of this paper is to develop and present an active sensing system via PIR sensor that is able to detect static human subjects and recognize human subjects with different status and scenarios. The experiment setup is shown in Figure 6. The experiments are implemented in a 2.5 m × 2.5 m area. This area is an open area specially reserved for human sensing experiments. In the experiments, a user wearing the proposed PIR sensor node detects human subjects at the border of the experimental area. The static human subjects are arranged in the experimental area with standing and sitting status. The sensing frequency of the proposed PIR sensor node is 8 Hz. The first goal is to detect and recognize the static human subjects with different status. We then further investigate different scenarios of static human subjects. In this paper, we simplify the scenarios to be scenes with different numbers of human subjects. Since the experimental setup is simple and there are no complicated components involved, the number of subjects basically distinguishes the different scenarios. In order to better describe the performance of the proposed system, we applied two classifiers here to demonstrate recognition accuracy. These two classifiers are k-centroid and k-nearest neighbors. They are selected here because they are practical and efficient for multi-dimension multi-class classification applications.

Figure 6.
Experiment setup.
4.2. Static Human Subject Recognition
Static human subjects can be detected by using the proposed wearable PIR sensing system. Figure 7 shows the binary signals of one static subject and two static subjects cases, respectively. The results of static human recognition are shown in Figure 8. Standing and sitting static subjects are successfully distinguished because of their different sizes and shapes. When people are sitting, their sizes become smaller than that of standing cases. Then, sitting human subjects have a smaller intersection probability than standing human subjects. In addition, since their shapes become simpler, they have higher temporal correlation ρ. Table 1 shows the static human subject status recognition performance of the proposed wearable thermal sensing system. As shown in this table, the knn classifier achieved a better recognition result. Its accuracy on status recognition was higher than 90%. With respect to the static subjects in the same status, they could also be distinguished, as long as they were various in size, shape, or weight.
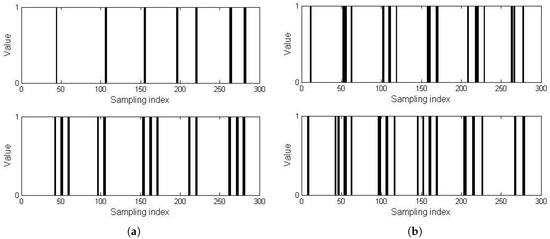
Figure 7.
Binary signals of static human subjects with wearable PIR sensor. (a) One subject; (b) Two subjects.
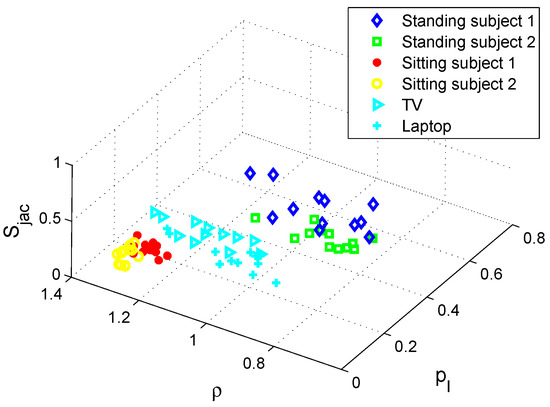
Figure 8.
Static human subjects and non-human thermal sources detection with wearable PIR sensor.

Table 1.
Static human subjects and non-human thermal sources recognition performance.
Regarding the non-human thermal sources, we tested some electronic devices (e.g., TV, laptop) and common objects in the indoor environment (e.g., chair, desk). We have shown the testing results of the electronic devices in Figure 8. It can be seen that such thermal sources can be detected and successfully classified due to their high temperatures and infrared radiations. Compared with human subjects, such thermal sources have smaller and regular sizes; thus, they have smaller detection probability, but higher temporal correlation ρ and spatial correlation . As for the other common objects, since they have much lower temperature, their radiation is very weak and the proposed PIR sensing system is not sensitive to their radiation wavelengths. Therefore, their signals are so weak that we can neglect or regard them as noise. Table 1 also shows the recognition accuracy for electronic devices. It can be seen that the accuracy was very high, and could achieve 100%. The reason is that their shapes are regular and their radiation wavelengths are different from that of human subjects.
4.3. Human Scenario Recognition
Aside from the status information of human subjects, the number of humans is another element describing human scenarios. Figure 9 shows the classification results for one human subject, two human subjects with occlusion, two human subjects without occlusion, three human subjects, and four human subjects scenarios. The scenarios with different numbers of humans can be recognized with high accuracy, since the clusters of them are well separated. However, for the two subjects with occlusion scenario, its cluster is mixed with the one subject scenario, and thus the recognition accuracy will be lower. Table 2 shows the results of human scenario recognition. As we can see, the recognition accuracy for two subjects without occlusion is the highest, since without occlusion, both subjects can be completely detected. Furthermore, compared with cases with more subjects, the two subjects case is simpler, and so the recognition accuracy is higher. That is why for three and four subjects cases, the recognition accuracy is lower than for two subjects cases. represents the detection probability, so it is higher for the three and four human subjects scenarios. It is easy to understand that with more subjects, the thermal radiation is more, and there are more intersections between human subjects and detection beams. In comparison, the temporal correlation ρ becomes lower when the number of subjects is larger. This is because with different human subjects, the correlation is lower due to their various shapes and sizes.
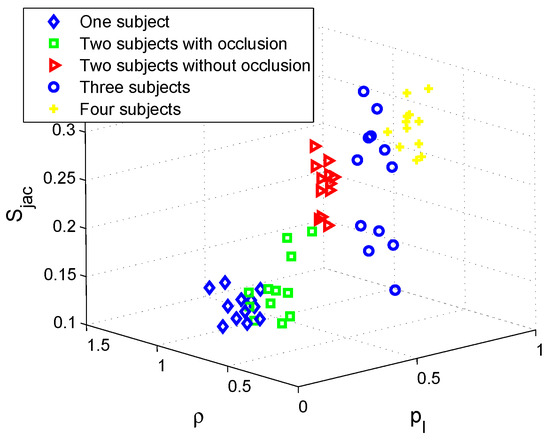
Figure 9.
Human scenarios recognition with wearable PIR sensor.

Table 2.
Human scenarios recognition performance.
It is interesting to see that the simplest scenarios with one subject and two subjects (occlusion) achieve the lowest recognition accuracy. It is only around 80%—much lower than the average accuracy of 87.22%. Although knn method can improve the accuracy, it is still lower than other scenarios. This is because the occlusion constrains the detection of both subjects in a certain scope. With occlusion, two subjects could be regarded as only one subject in the sensor’s vision at a certain moment. So, the sensor will be confused about one subject and two subjects with occlusion scenarios. Therefore, the one subject scenario is affected by mis-classifying two subjects (occlusion) scenarios.
5. Conclusions
In this work, a wearable PIR thermal sensing system was proposed and developed. Compared with conventional wearable sensing systems that focus on physiological information acquisition for users by themselves, such a proposed PIR thermal sensing system is able to acquire surrounding human scenario information. The experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed system and method are effective in static human detection and human scenario recognition. The wearable PIR sensing system is a good tool to assist blind people and disabled people with weak visual abilities in their daily and social lives to perceive surrounding human scenarios and human activities. In future work, the efficient detection method for occlusion cases will be further improved. The wearable PIR sensor can also be combined with other wearable sensors to perform more applications.
Author Contributions
Qingquan Sun designed the mathematical model, proposed the method, and wrote major part of the paper; Ju Shen and Haiyan Qiao developed the algorithms and wrote part of the paper; Xinlin Huang and Fei Hu contributed tools and performed experiments; Chen Chen analyzed the data. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Song, B.; Vaswani, N.; Roy-Chowdhury, A.K. Closed-Loop Tracking and Change Detection in Multi-Activity Sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8.
- Oliver, N.M.; Rosario, B.; Pentland, A.P. A Bayesian computer vision system for modeling human interactions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.C.; Lin, Y.; Weng, M.; Liao, H.Y.M. Cross-Camera Knowledge Transfer for Multiview People Counting. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 2015, 24, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Hu, F.; Xiao, Y. Multiple human tracking and identification with wireless distributed hydroelectric sensor systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2009, 3, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, F.; Hao, Q. Human Movement Modeling and Activity Perception Based on Fiber-Optic Sensing System. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2014, 44, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, E.; Intille, S.; Larson, K. Activity recognition in the home using simple and ubiquitous sensors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pervasive Computing, Vienna, Austria, 21–23 April 2004; pp. 158–175.
- Wahl, F.; Milenkovic, M.; Amft, O. A Distributed PIR-based Approach for Estimating People Count in Office Environments. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 15th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–7 December 2012; pp. 640–647.
- Lu, J.; Gong, J.; Hao, Q.; Hu, F. Space encoding based compressive multiple human tracking with distributed binary pyroelectric infrared sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 13–15 September 2012; pp. 180–185.
- Zappi, P.; Farella, E.; Benini, L. Tracking Motion Direction and Distance With Pyroelectric IR Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Song, M. Detecting Direction of Movement Using Pyroelectric Infrared Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, F.; Hao, Q. Mobile Target Scenario Recognition Via Low-Cost Pyroelectric Sensing System: Toward a Context-Enhanced Accurate Identification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2014, 44, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.R.; Lovell, N.H.; Celler, B.G. Evaluation of PIR detector characteristics for monitoring occupancy patterns of elderly people living alone at home. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 23–26 August 2007; pp. 2802–2805.
- Lu, J.; Zhang, T.; Hu, F.; Hao, Q. Preprocessing Design in Pyroelectric Infrared Sensor-Based Human-Tracking System: On Sensor Selection and Calibration. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 47, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, F.; Hao, Q. Context Awareness Emergence for Distributed Binary Pyroelectric Sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 5–7 September 2010; pp. 162–167.
- Yue, T.; Hao, Q.; Brady, D.J. Distributed binary geometric sensor arrays for low-data-throughput human gait biometrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hoboken, NJ, USA, 17–20 June 2012; pp. 457–460.
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).