Application of Partial Discrete Logarithms for Discrete Logarithm Computation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Algebraic Relations
3. Results
3.1. General Formula for Computing Discrete Logarithms in the Field
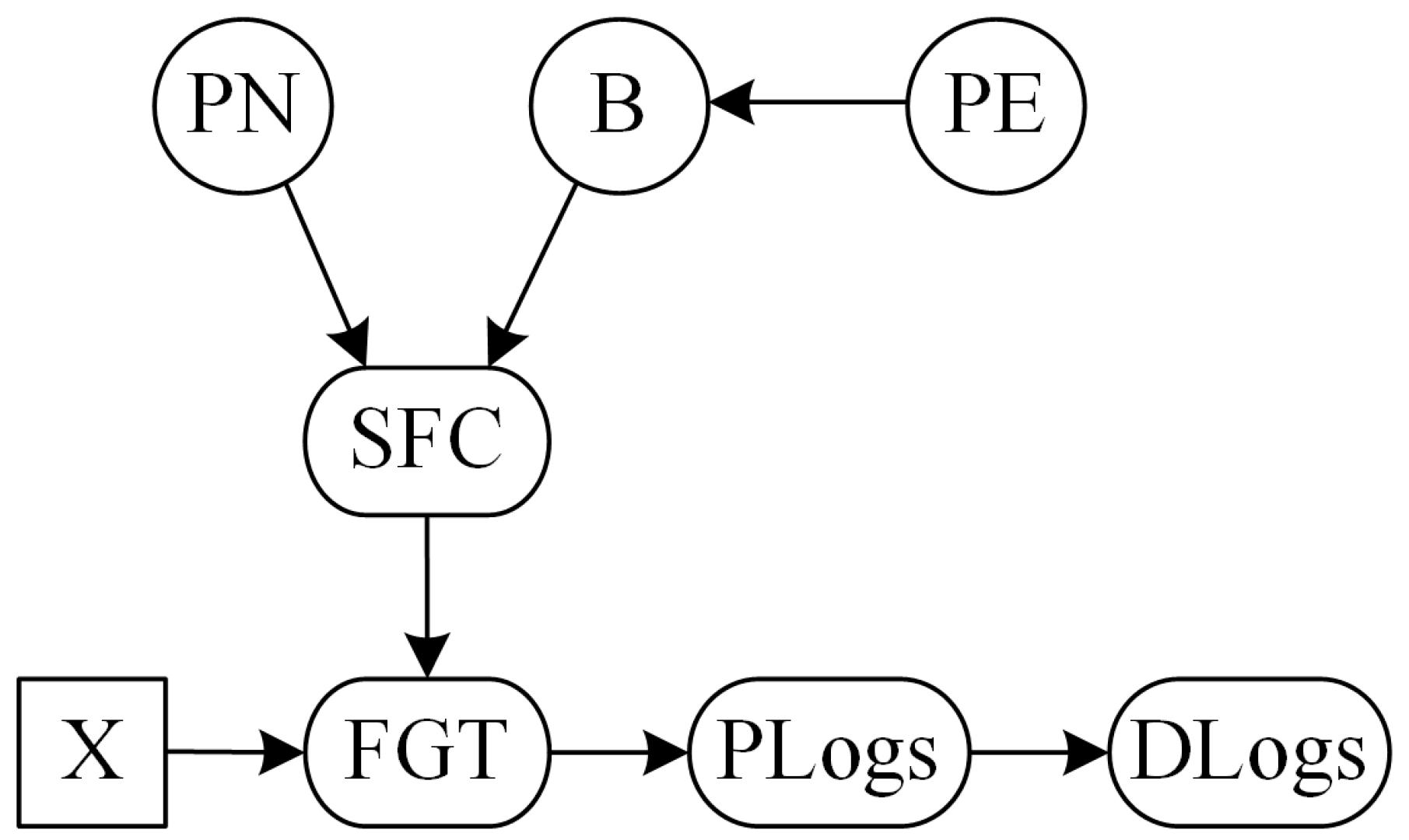
3.2. Concept of Partial Discrete Logarithms
3.3. Computation of Discrete Logarithms via Partial Discrete Logarithms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- General formulation: We derived an explicit analytic expression for the discrete logarithm valid for any Galois field, including those obtained via algebraic extensions.
- Partial discrete logarithms: We introduced and formalized the notion of partial discrete logarithms, which enable a substantial reduction in the number of operations required compared with classical algorithms such as Joux’s, Pohlig–Hellman, etc.
- Practical relevance: We showed that the proposed method can be directly applied in digital signal processing and multivalued logic, with potential extensions to applications such as UAV-based monitoring, radio holography, and information security systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.W.; Liu, J.C.; Chang, C.C.; Horng, J.H. Reversible Data Hiding in Crypto-Space Images with Polynomial Secret Sharing over Galois Field. Electronics 2024, 13, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, L.G.; Nepomuceno, E.G.; Bastos, G.T.; Santos, T.A.; Butusov, D.N.; Arias-Garcia, J. A reliable chaos-based cryptography using Galois field. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 31, 91101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzazi, M.M.; Attuluri, S.; Bassfar, Z.; Joshi, K. A novel cipher-based data encryption with Galois field theory. Sensors 2023, 23, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.S.; Savory, S.J. Digital signal processing for coherent transceivers employing multilevel formats. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, L.E.; Batanov, V.V. Analysis of Noise Immunity of Optimal Symbol-by-Symbol Reception of Phase-Keyed Signals with Correcting Codes in Non-Binary Galois Fields. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2022, 67, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Garcia-Herrero, F.; Ruano, O.; Maestro, J.A. RISC-V Galois field ISA extension for non-binary error-correction codes and classical and post-quantum cryptography. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2022, 72, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D. Discrete logarithm problem. In Encyclopedia of Cryptography, Security and Privacy; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 678–679. [Google Scholar]
- Grémy, L.; Guillevic, A.; Morain, F.; Thomé, E. Computing discrete logarithms in F(p6). In Selected Areas in Cryptography–SAC 2017, Proceedings of the 24th International Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- Adj, G.; Canales-Martínez, I.; Cruz-Cortés, N.; Menezes, A.; Oliveira, T.; Rivera-Zamarripa, L.; Rodríguez-Henríquez, F. Computing discrete logarithms in cryptographically-interesting characteristic-three finite fields. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2016. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekerå, M. Quantum algorithms for computing general discrete logarithms and orders with tradeoffs. J. Math. Cryptol. 2021, 15, 359–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F. A secure cloud storage system based on discrete logarithm problem. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM 25th International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Vilanova i la Geltrú, Spain, 14–16 June 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan-Gibbs, H.; Kogan, D. The discrete-logarithm problem with preprocessing. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Tel Aviv, Israel, 29 April–3 May 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 415–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wronski, M.; Dzierzkowski, L. Base of exponent representation matters-more efficient reduction of discrete logarithm problem and elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem to the QUBO problem. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2024, 24, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetteler, M.; Naehrig, M.; Svore, K.M.; Lauter, K. Quantum resource estimates for computing elliptic curve discrete logarithms. In International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 241–270. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: Developing Encryption Against Quantum Attacks. J. Innov. Technol. 2018, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jerbi, S.; Gyurik, C.; Marshall, S.; Briegel, H.; Dunjko, V. Parametrized quantum policies for reinforcement learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 28362–28375. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, R.; Kleinjung, T.; Zumbrägel, J. On the discrete logarithm problem in finite fields of fixed characteristic. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 2018, 370, 3129–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbulescu, R.; Gaudry, P.; Joux, A.; Thomé, E. A heuristic quasi-polynomial algorithm for discrete logarithm in finite fields of small characteristic. In Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Adj, G.; Menezes, A.; Oliveira, T.; Rodriguez-Henriquez, F. Computing discrete logarithms using Joux’s algorithm. ACM Commun. Comput. Algebra 2015, 49, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, S.D.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F. Computing elliptic curve discrete logarithms with improved baby-step giant-step algorithm. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2015. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rubinstein-Salzedo, S. The diffie–hellman key exchange and the discrete logarithm problem. In Cryptography; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlig, S.C.; Hellman, M.E. An improved algorithm for computing logarithms over GF(p) and its cryptographic significance. In Democratizing Cryptography: The Work of Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 415–430. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.A. An alternative approach for computing discrete logarithms in compressed SIDH. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, H.T.; Kim, H. Quantum cryptanalysis landscape of Shor’s algorithm for elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem. In Information Security Applications, Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference, WISA 2021, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 11–13 August 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ekerå, M. Revisiting Shor’s quantum algorithm for computing general discrete logarithms. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09084. [Google Scholar]
- Odlyzko, A. Discrete Logarithms: The Past and the Future. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 2000, 19, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Guha Roy, D.; Datta, P. An Overview of the Discrete Logarithm Problem in Cryptography. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications, ICACA 2024, Kolkata, India, 23–24 February 2024; Giri, D., Das, S., Corchado Rodríguez, J.M., De, D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenov, I.E.; Vitulyova, Y.S.; Kabdushev, S.B.; Bakirov, A.S. Improving the efficiency of using multivalued logic tools. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernov, V.M. Calculation of Fourier-Galois transforms in reduced binary number systems. Comput. Opt. 2018, 42, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Tang, L.; He, S.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Z. Low-complexity encoding of quasi-cyclic codes based on Galois Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnigk-Emden, T.; Wehn, N. Complexity evaluation of non-binary Galois field LDPC code decoders. In Proceedings of the 2010 6th International Symposium on Turbo Codes & Iterative Information Processing, Brest, France, 6–10 September 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Suleimenov, I.E.; Vitulyova, Y.S.; Kabdushev, S.B.; Bakirov, A.S. Improving the efficiency of using multivalued logic tools: Application of algebraic rings. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-G.; Lee, Y.; Go, G.-T.; Pei, M.; Jung, S.; Jeong, Y.H.; Lee, W.; Park, H.-L.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, H.; et al. Versatile Neuromorphic Electronics by Modulating Synaptic Decay of Single Organic Synaptic Transistor: From Artificial Neural Networks to Neuro-Prosthetics. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumyusenge, A.; Melianas, A.; Keene, S.T.; Salleo, A. Materials Strategies for Organic Neuromorphic Devices. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2021, 51, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauhausen, I.; Koutsouras, D.A.; Melianas, A.; Keene, S.T.; Lieberth, K.; Ledanseur, H.; Sheelamanthula, R.; Giovannitti, A.; Torricelli, F.; Mcculloch, I.; et al. Organic Neuromorphic Electronics for Sensorimotor Integration and Learning in Robotics. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabl5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Tian, B.; Zhu, Q.; Dkhil, B.; Duan, C. Ferroelectric Polymers for Neuromorphic Computing. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 021309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sabbagh, B.; Chen, Y.; Yossifon, G. Geometrically Scalable Iontronic Memristors: Employing Bipolar Polyelectrolyte Gels for Neuromorphic Systems. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 15025–15034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Fan, F.; Gu, J.; Chen, X.; Yan, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, S.; Yan, Q.; et al. 90% Yield Production of Polymer Nano-Memristor for in-Memory Computing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenov, I.; Gabrielyan, O.; Kopishev, E.; Kadyrzhan, A.; Bakirov, A.; Vitulyova, Y. Advanced Applications of Polymer Hydrogels in Electronics and Signal Processing. Gels 2024, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, J. On a Problem of da Costa. In Essays on the Foundations of Mathematics and Logic 2; Sica, G., Ed.; Polimetrica: Lima, Peru, 2005; pp. 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.T. Representations of logic functions. Kybernetes 1995, 24, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Avestimehr, A.S. Coded computing for secure Boolean computations. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Inf. Theory 2021, 2, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selezneva, S.N. Finding periods of Zhegalkin polynomials. Discret. Math. Appl. 2022, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenov, I.E.; Matrassulova, D.K. Using the Relationship between the Theory of Algebraic Fields and Number Theory for Developing Promising Methods of Digital Signal Processing. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd Asia Conference on Computers and Communications (ACCC), Shanghai, China, 16–18 December 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- van der Waerden, B.L. Algebra; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 1, 265p. [Google Scholar]
- Suleimenov, I.; Kadyrzhan, A.; Matrassulova, D.; Vitulyova, Y. Peculiarities of Applying Partial Convolutions to the Computation of Reduced Numerical Convolutions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudunkaya, S.M.; Kiri, A.I. Galois groups of polynomials and the construction of finite fields. Pure Appl. Math. J. 2012, 1, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, K.-S.; König, J. On Galois extensions with prescribed decomposition groups. J. Number Theory 2021, 220, 266–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitulyova, E.S.; Matrassulova, D.K.; Suleimenov, I.E. Construction of generalized Rademacher functions in terms of ternary logic: Solving the problem of visibility of using Galois fields for digital signal processing. Int. J. Electron. Telecommun. 2022, 68, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siam, A.I.; El-khobby, H.A.; Elnaby, M.M.A.; Abdelkader, H.S.; El-Samie, F.E.A. A Novel Speech Enhancement Method Using Fourier Series Decomposition and Spectral Subtraction for Robust Speaker Identification. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 108, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.V.; Savchenko, L.V. Two-stage algorithm of spectral analysis for the automatic speech recognition systems. Meas. Tech. 2024, 67, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirov, A.; Matrassulova, D.; Vitulyova, Y.; Shaltykova, D.; Suleimenov, I. The specifics of the Galois field GF (257) and its use for digital signal processing. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyrzhan, A.; Matrassulova, D.; Vitulyova, Y.; Suleimenov, I. Discrete Cartesian Coordinate Transformations: Using Algebraic Extension Methods. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenov, I.; Bakirov, A. Prospects for Using Finite Algebraic Rings for Constructing Discrete Coordinate Systems. Symmetry 2025, 17, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.Y. Hamilton’s quaternions. In Handbook of Algebra; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 429–454. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, A.; Ahuja, K.; Busnel, Y. AI algorithm for predicting and optimizing trajectory of massive UAV swarm. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2025, 186, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitseva, E.; Mukhamediev, R.; Levashenko, V.; Kovalenko, A.; Kvassay, M.; Kuchin, Y.; Symagulov, A.; Oksenenko, A.; Sultanova, Z.; Zhaxybayev, D. Comparative Reliability Analysis of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Swarm Based on Mathematical Models of Binary-State and Multi-State Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Huo, M.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Qi, N. Graph-based multi-agent reinforcement learning for large-scale UAVs swarm system control. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 109166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, P.; Mehmood, G.; Khan, A.; Fayaz, M. An Ant-Hocnet Routing Protocol Based on Optimized Fuzzy Logic for Swarm of UAVs in FANET. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 6783777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Abreo, O.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; García-Cerezo, A.; García-Martínez, J.R. Fuzzy logic controller for UAV with gains optimized via genetic algorithm. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermukhambetova, B.; Mun, G.; Kabdushev, S.; Kadyrzhan, A.; Kadyrzhan, K.; Vitulyova, Y.; Suleimenov, I.E. New approaches to the development of information security systems for unmanned vehicles. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2023, 31, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitulyova, Y.; Kadyrzhan, K.; Kadyrzhan, A.; Shaltykova, D.; Suleimenov, I. Reducing the description of arbitrary wave field converters to tensor form. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2024, 17, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Song, L. Reconfigurable holographic surface: A new paradigm to implement holographic radio. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2023, 18, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Chapursky, V.V.; Cherepenin, V.A. Super-resolution of radar and radio holography systems based on a MIMO retrodirective antenna array. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2021, 66, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazoev, A.L.; Shoydin, S.A. Transmission of 3D holographic information over a radio channel by a method close to SSB. J. Sci. Tech. Inf. Technol. Mech. Opt. 2023, 147, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamediev, R.I.; Yakunin, K.; Aubakirov, M.; Assanov, I.; Kuchin, Y.; Symagulov, A.; Levashenko, V.; Zaitseva, E.; Sokolov, D.; Amirgaliyev, Y. Coverage Path Planning Optimization of Heterogeneous UAVs Group for Precision Agriculture. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 5789–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesha, M.K.; Herold, M.; De Sy, V.; Duchelle, A.E.; Martius, C.; Branthomme, A.; Garzuglia, M.; Jonsson, O.; Pekkarinen, A. An assessment of data sources, data quality and changes in national forest monitoring capacities in the Global Forest Resources Assessment 2005–2020. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamediev, R.I.; Terekhov, A.; Amirgaliyev, Y.; Popova, Y.; Malakhov, D.; Kuchin, Y.; Sagatdinova, G.; Symagulov, A.; Muhamedijeva, E.; Gricenko, P. Using Pseudo-Color Maps and Machine Learning Methods to Estimate Long-Term Salinity of Soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, D.B.; Tiwari, M.K.; Patel, G.R. Estimation of Surface and Subsurface Soil Moisture Using Microwave Remote Sensing: A Typical Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Sidhu, H.; Bhowmik, A. Remote Sensing Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Water Stress Detection: A Review Focusing on Specialty Crops. Drones 2025, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguettaya, A.; Zarzour, H.; Kechida, A.; Taberkit, A.M. Deep learning techniques to classify agricultural crops through UAV imagery: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9511–9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashov, S.I.; Capineri, L.; Bechtel, T.D.; Razevig, V.V.; Inagaki, M.; Gueorguiev, N.L.; Kizilay, A. Design and Applications of Multi-Frequency Holographic Subsurface Radar: Review and Case Histories. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashov, S.I.; Razevig, V.V.; Vasiliev, I.A.; Zhuravlev, A.V.; Bechtel, T.D.; Capineri, L. Holographic Subsurface Radar of RASCAN Type: Development and Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Lualdi, M. Step-Frequency Ground Penetrating Radar for Agricultural Soil Morphology Characterisation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, M.; Tange, K.; Dragoni, N. Foundations and Evolution of Modern Computing Paradigms: Cloud, IoT, Edge, and Fog. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150936–150948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, B.; Akin Gultakti, C.; Koker, Z.; Anantram, M.P.; Oren, E.E. Electronic Properties of DNA Origami Nanostructures Revealed by In Silico Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 4646–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. Propelling DNA Computing with Materials’ Power: Recent Advancements in Innovative DNA Logic Computing Systems and Smart Bio-Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ Era and Beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| 2 | 9 | 12 | 4 |
| 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 | 9 | 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 1 | 12 | 12 |
| 7 | 3 | 8 | 11 |
| 8 | 9 | 1 | 9 |
| 9 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 10 | 3 | 12 | 10 |
| 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| N | n/nw | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 |
| 6 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 1 |
| 7 | 6 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 |
| 8 | 7 | 11 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 1 |
| 9 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 |
| 10 | 9 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 |
| 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 12 | 11 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| n\N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 1 |
| 3 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 1 |
| 5 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 1 |
| 6 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 12 | 1 |
| 7 | 11 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 1 |
| 8 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 |
| 9 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 8 | 1 |
| 10 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 11 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plog1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Plog2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| DLog | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 0 |
| n | FPlog1,2 | FPlog1,2 | FDLog |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 12 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 3 | 11 | 0 | 11 |
| 4 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| 8 | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaltykova, D.; Vitulyova, Y.; Kadyrzhan, K.; Suleimenov, I. Application of Partial Discrete Logarithms for Discrete Logarithm Computation. Computers 2025, 14, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090343
Shaltykova D, Vitulyova Y, Kadyrzhan K, Suleimenov I. Application of Partial Discrete Logarithms for Discrete Logarithm Computation. Computers. 2025; 14(9):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090343
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaltykova, Dina, Yelizaveta Vitulyova, Kaisarali Kadyrzhan, and Ibragim Suleimenov. 2025. "Application of Partial Discrete Logarithms for Discrete Logarithm Computation" Computers 14, no. 9: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090343
APA StyleShaltykova, D., Vitulyova, Y., Kadyrzhan, K., & Suleimenov, I. (2025). Application of Partial Discrete Logarithms for Discrete Logarithm Computation. Computers, 14(9), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090343






