Abstract
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have been described as a “next development of networked learning”, and they have the potential to mediate sensory learning. To understand this phenomenon, the present systematic review examines the research techniques, subjects, and trends of MOOC research on sensory learning, in order to provide a thorough understanding of the MOOC relevant to sensory (olfactory) learning phenomena by evaluating 65 (four studies are about multisensorial learning and 61 are about multisensorial empirical MOOCs researches) empirical MOOC studies published between 2008 and 2021 by searching through databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. The results indicated that most studies were based on quantitative research methods followed by mixed research methods and the qualitative research approaches; most of the studies were surveys, followed by platform databases and interviews; almost half of the studies were conducted using at least two methods for data collection: survey and interviews; most were replicated. The most highlighted subjects included student retention, learning experience, social learning, and engagement. Implications and studies into the future have been considered in order to obtain a more evolved understanding of the acquisition of knowledge through the senses.
1. Introduction
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have been described as a “next development of networked learning” and as a platform for expanding accessibility to higher education and supporting new education methods. Coined in 2008 [1], MOOCs refer to online courses offered by colleges that draw thousands of participants, partially because they are “open”, generally referring to the fact that they do not offer credit and hence are free to someone with an internet connection (Figure 1). Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) are courses that extend the learning process to thousands of students. These courses respond to the challenges that educational and training institutions face in critical times such as these. MOOCs, in fact, represent quality training at a low cost [2]. While there is limited official study into the nascent discipline, many fans of the format have enthusiastically embraced its implementation. The development and application of MOOCs in many fields of higher education and, more lately, health education and live science have increased dramatically [1,3].
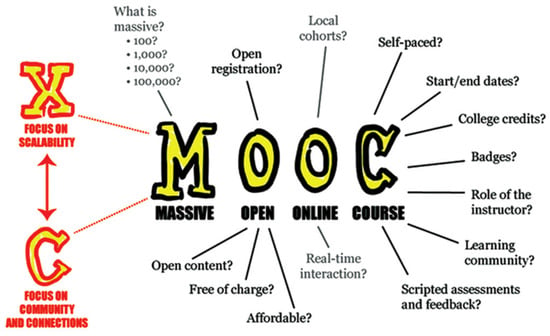
Figure 1.
Evolution of the MOOC.
A long-studied strategy in the realm of training is to evaluate success and effectiveness and to advise on courses improvements. However, the distinctions between teaching in MOOCs and regular face-to-face classes mean that the same standard evaluation methodologies cannot be adapted. For instance, MOOCs often do not include entry, withdrawal, or submission of assignments or assessments restrictions [4]. The approaches employed in web-based education and e-learning do not always apply to MOOCs because web-based or e-learning courses are sometimes delivered under curricula, which differ from MOOCs according to expectations of students. The low terminal completion rates of MOOCs indicate that there is a lack of self-regulation and self-motivation with respect to what is expected of students [5].
It is not appropriate to compare MOOCs directly with higher education courses using typical assessment standards and criteria. Our review focused on the queries highlighted in Figure 2, from which it can be seen that the research questions refer to empirical MOOCs, research referred to a multisensory approach (in the last twelve years), the research methodologies used in empirical MOOC, the analysis regarding the nations that have investigated MOOCs the most, and the diffusion of research, at a regional level, of empirical MOOCs referred to a multisensory approach.

Figure 2.
Research questions.
Despite the limitations in MOOC evaluation methodologies, multiple reviews of MOOC-related research methods have been undertaken without focusing especially on MOOC evaluations [6]. Two recent systemic reviews have been published summarizing methodologies and topics for MOOC research. Zhu et al. [7,8] and Bozkurt et al. (2021) [9,10] advocated additional research on MOOC evaluation methodological techniques. This study focused little on the quality of the procedures and methodologies used. Furthermore, a considerable number of MOOC studies evaluate general pedagogic factors without assessing the course. While the broad review of MOOC education and pedagogy is valuable, it is also essential to evaluate courses [7]. The assessment of the quality of learning through MOOCs has become an “educational” variant of the Big Data problem, as it is mediated by learning analytics [11]. The application of learning analytics allows the identification of problems and potential. The dropout rate is an indicator not significantly associated with the effectiveness of MOOCs. Stracke [12] underlined that some students consider their educational objectives to be achieved even by simply downloading the materials available to pursue self-regulated learning and using them outside the time provided by the MOOC. MOOCs allow a large number of users to be reached, guaranteeing easy and immediate access to knowledge and content and mediating online communication with the teacher or among peers [12]. The online tutor is essential to favor monitoring processes in MOOCs with respect to both to the levels of completion of the course and to the management of information of a more qualitative nature, thus enhancing the relational dimension within the learning process [13]. MOOCs allow the communication of automatic and personalized feedback by placing the individual in direct comparison with his or her colleagues. Students learn by comparing themselves with more or less experienced colleagues [14]. MOOCs are offered in any different subject areas, such as STEM, art, medicine, and business, with differences in each subject area [15,16]. Studies on learning, and in particular on perceptual learning, have focused on learning stimuli consisting of a single sensory modality. However, our experience in the world involves constant multisensory stimulation. For example, visual and auditory information is integrated into the performance of many tasks that involve locating and tracking moving objects. Therefore, the human brain is likely to have evolved to develop, learn, and operate optimally in multisensory environments. Multisensory learning is determined by a multisensory stimulation that induces a unified perception. Multisensory information has been shown to facilitate learning [17]. Typically, MOOCs covers two sensory channels: sight and hearing. In this review, the authors analyze all the studies where MOOCs include a multisensory approach. One of them is the sense of smell. Smell is the greatest ally of memories: it allows us to travel through time and therefore ensures that the sense of smell is chosen as a privileged sense by memory. A smell or a perfume already smelled has the unparalleled power to rematerialize even our intimate memories, to make us present in distant events. No other sensory data is as memorable as a smell, equally resistant to the wear and tear of time, equally evocative of the past, and equally capable of stimulating all the other senses. The sense of smell demonstrates a close relationship with episodic memory. Of all the sensory stimuli, smells seem to trigger the most vivid and emotional memories: in fact, the olfactory input has direct connections via the olfactory bulb and the primary olfactory cortex (piriformis) on two key structures involved in emotion and memory (the amygdala and hippocampus), without passing through the thalamus. The strong anatomical connection between olfactory and memory structures therefore makes the sense of smell a privileged sense for accessing memories [18]. Olfaction, the sense of smell, is closely linked to learning, and certain research indicates that olfactory sensory abilities play a role in the performance of visual memory (VM). For example, the removal of the olfactory bulb inhibits visuospatial education in rats [19], and training in odor identification leads to improved visuospatial learning in rats [20]. Zelcer et al. [19] focuses on whether olfactory memory training in adult humans would have positive impacts on both VM and olfactory task performance. The olfactory system has a remarkable biological and functional flexibility [9]. The taste buds and olfactory system are a challenge to include in your eLearning course design, but it is achievable. These two senses can be mixed with vivid images and descriptive phrases. For example, when the flavor of a food or the smell in the air is described, the mind performs tricks to visualize the environment [21].
Multisensory learning through MOOCs is an important educational element for students with dyslexia. Orton Gillingham is now linked with multisensory learning. In particular, multisensory instruction involves several senses that support of the student’s learning (Figure 3). This would ideally include the senses of sight, hearing, and touch or movement and enable individuals to link their learning strengths, visually, auditively, and kinesthetically, to areas of learning that are harder for them [6]. In order to address the gaps in MOOC literature evaluation methods, the objective of this systemic review was to identify and examine current MOOC assessment methodologies and their multisensory approach. This review aimed at informing the future MOOC assessment process [9].

Figure 3.
Multisensory learning.
Understanding the potential of sensory learning through MOOCs would allow the improvement of learning processes in response to students’ needs (Figure 4). This review therefore aims to analyze the studies already conducted on the above topic to bring out the possibilities of improving practice through a more evolved understanding of knowledge acquisition through the senses.

Figure 4.
The language triangle.
The analysis of the state of art aims to understand how it is possible to acquire knowledge through the senses and which teaching methods can improve and make learning more efficient through MOOCs. The implications of what emerged have the potential to produce an evolution of MOOCs and inaugurate new avenues of research for training conveyed through multisensory stimulation.
2. Results
The total number of reviewed articles are 65 distributed in their publication years on MOOCs delivery, as shown in the below graph in Appendix A.
Figure 5 shows that the highest percentage of articles published is for the year 2020 followed by 2019. In addition, not taking into account the additional miscellaneous sourcing classified as “other”, most of the studies are from the United States, followed by the United Kingdom (Figure 6). The nationality of the search is associated based on the context of the search. The results, emerging from the comparison of the selected studies, indicated that most studies [22,23] were based on quantitative research methods, followed by mixed research methods and qualitative research approaches [24,25]; most of the studies were surveyed, followed by platform databases and interviews [26,27]; almost half of the studies were conducted using at least two methods for data collection: survey and interview [28,29]; and most were replicated [30,31]. The most highlighted subjects included student retention, learning experience, social learning, and engagement. In particular, it emerges that the video lessons of MOOCs are a tool to increase skills, improve performance in summative assessments [32], and catalyze powerful behavioral changes [33]. Furthermore, MOOCs have the advantage of facilitating the learning process by offering materials and enabling information-sharing [34].
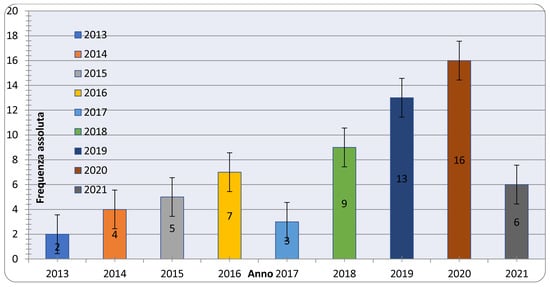
Figure 5.
Distribution of MOOC publications.
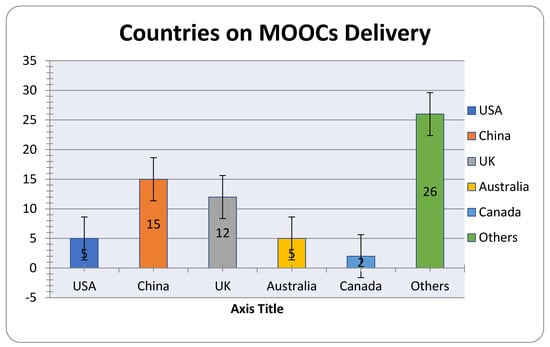
Figure 6.
Distribution of countries on MOOCs Delivery.
The distribution of contribution on MOOCs learning worldwide is shown in the graph below.
What has been discussed is confirmed by all the selected studies, although there is a clear need to promote research in the field by presenting the evidence. In support of this, medical and healthcare students report that they are more motivated to learn through MOOCs, which allow for a beneficial sharing of digital material and a practical approach thanks to informal and transmedia learning environments [34,35]. MOOCs unlock new opportunities for training and lifelong learning by improving the safety and quality of health services in supporting patients to achieve a better quality of life [36].
Consistent with connectivist learning theory, during a MOOC course, learners contributed their own sources of nutritional information to discussions using their own knowledge networks to teach and share information, and their information was derived primarily from websites. It emerged that nutrition professionals need to understand the principles of connectivist learning behaviors to engage course recipients [37]. A small number of articles have been published on the topic of multisensory stimulation through MOOCs, one of which illustrates the MERGO Project [38], which offers an MOOC in oenology and wine tasting combined with an olfactory experience, allowing the user to improve and train their olfactory knowledge on oenology, viticulture, and wine experimentation.
In the following, we explore what was found through these results.
3. Discussion
The motivation behind this precise audit of the examination standards and themes identified with MOOCs just as MOOC research distribution outlets and creators’ topographical disseminations was to acquire a deeper comprehension of the MOOC marvel. The 65 examinations inspected in this deliberate survey uncovered a few fascinating patterns with respect to the exact exploration on MOOCs distributed between January 2008 and February 2021 [39].
3.1. Distribution Diaries for MOOC Research
The current examination investigated the distribution diaries for MOOC research just as exploration techniques directed, information assortment strategies, information examination techniques, research foci, creator’s geographic data, creators’ cooperation types, geographic data with respect to the conveyance of MOOCs, and the dispersion of the MOOC research by year of distribution [35,40]. Figure 5 shows that the highest percentage of published articles refer to the year 2020, followed by 2019. Furthermore, most of the studies come from the United States, followed by the United Kingdom (Figure 6).
3.2. Multimodality in the Classroom
The introduction of multimodality in the classroom requires an effort to accommodate teaching practice. Multimodal practice consists of the integration of specific modal resources: writing a recipe and then transforming it into a didactic discourse with the support of the Interactive Writing Boards (IWB); writing drafts and project texts starting from literary excerpts; debating in a reasoned way by developing a written text but then focusing on speech, its understanding, and critical analysis, as well as on the action; narrating starting from a video stimulus, transcribing spoken passages, and rewriting on the basis of a literary model [41].
3.3. Area of Cognitive Styles
Multimodality is usually considered a perceptual multimodality; it leverages the idea that learners use different sensory modalities (visual, auditory, and body mobility). The discussed area of cognitive styles, understood as a multiplicity of approaches to learning contents, is added. In other words, beyond the perceptual level, information is organized and processed according to individual modalities that are affected by one’s personal history of learning [42,43].
According to the current studies, in olfactory learning and not visual learning, transfer effects are detected, while task difficulties and learning rates were equivalent in both training tasks.
Based on our findings, we anticipate that olfactory system MOOCs learning could lead to more cross-sensory transmission than is the case of the visual system (which is the dominant model for cognitive interventions). Our results also underscore that the transfer of learning is often unrelated to the extent of the gains made in the MOOCs [37,44].
3.4. Future Perspectives
Further research is needed before the value of olfactory cognitive MOOCs learning can be determined. It is not obvious if the multimodal character of the learning tasks or the unknown variations in cognitive demands were the result of this shift, rather than the commitment of olfaction per se [45,46]. This may lead to additional studies: each MOOCs learning exercise uses one type of sensory stimuli. Therefore, we consider that the sensory complexity has a great value for a new generation of MOOCs. In this direction, further study is needed where multimodal complexity of training tasks is changed [47,48]. In conclusion, the comparison of the selected articles revealed the effectiveness of MOOCs in relation to the learning achieved by students and the increase of their motivation. Furthermore, these online courses facilitate the sharing and democratization of knowledge and the acquisition of practical skills in university and training environments. The new frontier is represented by the multisensory stimulation mediated by MOOCs to facilitate learning.
We believe that the outcomes of our study will motivate more research on cognitive MOOCS learning based on odors [49]. Such operations could be advantageous for elderly people because olfactory deficits are the early indicators of cognitive impairment and dementia related to age [50,51,52].
4. Materials and Methods
The Search Strategy
The search was performed according to the guidelines recommended by the PRISMA statement for systematic reviews and meta-analyses [13]. This paper intends to carry out a systematic review analyzing the state of the art on the topic of MOOCs in association with sensory learning. Literature was searched for the appropriate studies from the online databases of the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar published from 2008 until February 2021 (Figure 7). The combinations of key words used for the search were as follows: “MOOC”, “Massive open online course”, “olfactory”, “sensory”, “gustatory”, and “learning”. The articles were selected based on three guiding principles: “MOOC facilitates sensory learning”, “olfactory learning is a rapidly developing sector”, and “gustatory learning has had more space in experimentation until 2019”, because, until the pandemic, it was easier to combine online learning with face-to-face experimentation with experts. During the COVID-19 phase, the course became fully online. Regarding the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the articles were selected from peer-reviewed English journals that aimed to describe or evaluate the dimensions and variables expressed with respect to the research topics mentioned above (screening). The publications unrelated to the topic, and the concerned age group were excluded, as well as those for which the complete text (relevance) was not available. Book chapters, books, news articles, and legal reports were also excluded. A qualitative synthesis of the most relevant information was also conducted with comparisons between the various publications.
Figure 7.
Databases research.
The process for including studies in the systematic review is described in Figure 8.
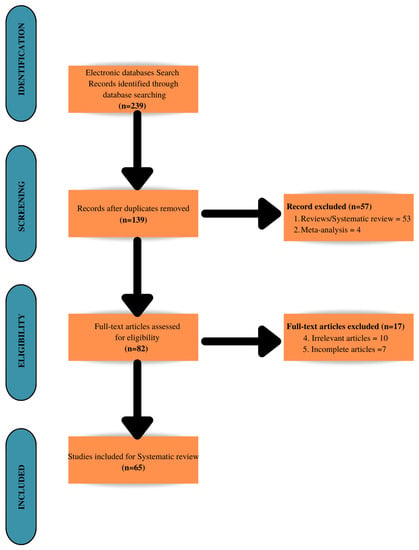
Figure 8.
Prisma flow diagram.
No filters were adopted, which is why all products such as papers, books, reviews, documents, etc., were included. Furthermore, all results were accepted without any constraints regarding the type of data analysis, measurement, sample, and tools used.
A total of 239 results emerged after searching through the various databases, of which 100 were duplicates. Of the 139 results, 57 were excluded because they consisted of reviews and meta-analyses. Of the 82 articles selected through the previous steps, 17 were excluded because they were incomplete or irrelevant (irrelevant articles n = 10; other reasons = 7). In conclusion, 65 studies were included (Figure 8). The AMSTAR 2 guidelines were followed for the critical appraisal of the methods adopted in the review (Beverley et al., 2017). The 16 items of the instrument were adhered to by engaging two practitioners, who were responsible for item collection and selection and operated independently.
All study participants synthesized and compared the selected studies. The method used to synthesize the results consisted of defining for each study the following characteristics: title, author, country, keywords, and results (Figure 5).
The information in this examination was gathered from Scopus and companion explored diaries and needed to meet the accompanying rules for the determination (see additionally Zhu et al. [53] Ebben 2014 [40]). To begin with, given that MOOCs previously arose in 2007 and 2008 [54,55,56], the investigations of this audit were distributed somewhere in the range of 2008 and 2021. Second, the investigations must be experimental examinations. Third, the investigations inspected MOOCs from instructive viewpoints and were not just about specialized issues or plans of action [57]. Fourth, we utilized catchphrases “MOOC” and “Huge Online Open Course(s)” to screen titles, abstracts, and the writing chosen. Fifth, the investigations were distributed in scholastic diaries instead of as book parts, websites, magazines, and so forth, and were distributed in English. We just included friend surveyed diaries on the grounds that such papers commonly address better expectations of exploration thoroughness and believability (Utah State University Library 2020) [54].
To accomplish proficiency and improve the dependability of this examination, the authors performed the underlying inquiry in an equivalent division of diary sources Ebben 2014 [40]. One specialist looked through articles from five key diaries in Scopus, which would in general distribute articles identified with MOOCs (for example, PCs and Education, British Journal of Educational Technology, The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, Distance Education, and Educational Media International). She additionally led a hunt in a few different diaries not filed by Scopus yet have been known to distribute MOOC research. as we can see in Table 1 (e.g., Online Learning, the International Journal on E-Learning, Journal of Interactive Media in Education, Journal of Online Learning Research, and the Journal of Open Flexible and Distance Learning). The subsequent analyst looked through the remainder of the articles found in the Scopus search [55].

Table 1.
Sensory learning results.
The relevant literature correlated with the sensory learning is depicted below.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) represent a large-scale learning modality that is changing the higher education landscape. Yu and collaborators (2017) [58] highlight the role that artificial intelligence (AI) assumes in the design and delivery of MOOCs. In particular, the authors highlight how virtual learning accompanied by human characteristics, such as curiosity and emotion, can improve the learning experience. It is also highlighted that, through artificial intelligence techniques, the learning sequence can be customized according to the needs of each student. Furthermore, qualitative and quantitative analyses carried out in a study on the delivery of a MOOC on behavioral medicine showed that the participating students were enthusiastic about interacting with virtual patients and, therefore, about experimenting; they were excited to apply the new knowledge they had acquired. The study also suggested incorporating several interactive cases with many varied levels of complexity [59].
In this particular historical moment, the COVID-19 pandemic has caused enormous difficulties in the world of education. Virtual resources have, therefore, assumed a key role, and previously developed MOOCs have received a positive reception by learners and a net increase in use, guaranteeing learning in a way that is completely innovative for many [60]. Currently, some developing countries, such as Malaysia, are adopting mass open online courses (MOOCs) in higher education. Related to this implementation is the need to make the monitoring of MOOCs easier. Asli [39] highlighted that a key component of these courses is the design of the interactive visualization: the detailed characterization and abstraction of the domain problem help the designer to derive the design requirements to generate an appropriate visualization solution.
A statistical sensitivity analysis was carried out for the many studies (in Figure 5, [1,6,12,18,20,33,36,45,54]) containing missing data with respect to the research hypothesis, which is common in each research study. The data were analyzed excluding the missing values; thus, only the complete data were analyzed; then, the missing values were imputed through single or multiple imputations and, eventually, the analyses were traced back to the imputed data. The research hypothesis in the latter case has been confirmed.
The literature review provides access to a deeper understanding of the sensory learning process mediated by MOOCs. Selected studies are identified above.
5. Conclusions
Most MOOC exploration, particularly on sensory learning, to date has zeroed in on student issues, for example, the student experience, social learning, commitment, self-controlled learning, inspiration, execution, and MOOC finish.
Instead, research on MOOC teachers has a minor impact [34,61]. To address this hole, MOOC specialists later on might target educators or plan more extensive investigations of different MOOC partners such as students, teachers, educational originators, or program heads. More examinations of MOOC teachers’ plan cycle and discernments would enhance the comprehension of MOOC wonder. Such exploration could advance a more profound comprehension of the nature of MOOCs, social affectability in MOOCs, MOOC instructional methods including course intuitiveness and commitment, and evaluation rehearsals from MOOC educators’ points of view [61,62].
We suggest that training protocols employing a single sensory stimulus regime do not involve multisensory learning mechanisms and, therefore, may not be optimal for learning [9].
The senses mediate knowledge, but they do not mediate it univocally, and, in any case, knowledge itself, once it is acquired through the senses, frees itself from them and is defined according to amodal values, substantially devoid of references to sensitivity. The vicarious process is proposed as the main guarantee of the didactic values of learning mediated by the different sensory systems; therefore, the use of a multisensory approach in the construction of knowledge is legitimized [52,63]. There are numerous design hypotheses for a consistent and as structured as possible use of MOOCs at the national university level, an important analysis also aimed at identifying further innovative ways of quality training in our country.
It emerges that the participants in the MOOCs of the study by An et al. [8] wanted to gamify their MOOCs to increase social interactions and student retention. The need to ensure that the themes of social learning democracy apply to content areas outside the social sciences emerges from the Paek study [64]. The perspective concludes with suggestions for the future of research on the applicability and adequacy of MOOCocracy in K–12 contexts and the knowledge and skills that learners may need to participate in and benefit from a democracy of social learning. The increasing aging of the population and the increasing prevalence of non-communicable diseases require innovation and professional skills mastered in the health sector [65,66]. MOOCs in the nursing sector open up new opportunities for training and lifelong learning, improving the safety and quality of health services in supporting patients to achieve a better quality of life.
Limitation
This review was subject to some limitations. Firstly, the review cannot draw definitive conclusions due to the heterogeneity of the interventions and the small number of available articles that focus on sensory stimulation. The second limitation is applicable to all systematic reviews; the search results are limited by the search terms and refinements used (for example, included journals and publication period). While the systematic review may not accurately reflect all of the existing literature relevant to this study, it does provide insight into current research findings and the impact of sensory stimulation in MOOCs.
The last limitation is that, despite the PRISMA quality criteria and the authors’ adherence to the AMSTAR 2 guidelines to ensure a certain methodological rigor, the authors cannot fully control publication biases and therefore cannot guarantee full access to data within this systematic review.
Since our results are positive, we hope that the literature will soon be enriched with new studies investigating the efficacy of multisensory stimulation in more specific and larger populations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.L. and S.P.; methodology, G.A.T.; validation, R.D.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B.; writing—review and editing, G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MERGO Erasmus Plus Progect grant number 2020-1-IT02-KA203-080040 and The APC was funded by Department of Humanistic studies of University of Foggia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Data Review.
Table A1.
Data Review.
| Title | Author | Year | Country | Keywords | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Measuring growth in students’ proficiency in MOOCs: Two component dynamic extensions for the Rasch model | Abbakumov et al. | 2018 | Belgium | psychometrics; item response theory; cross-classification multilevel logistic model; learning effects |
| 2 | Psychometrics of MOOCs: Measuring Learners’ Proficiency | Abbakumov et al. | 2020 | Belgium | psychometrics; item response theory; massive open online courses; learning analytics |
| 3 | Massive open online nutrition and cooking course for improved eating behaviors and meal composition | Adam et al. | 2015 | USA | nutrition; cooking; online education; eating behaviors; meal composition |
| 4 | Using the Internet: Nutrition Information-Seeking Behaviours of Lay People Enrolled in a Massive Online Nutrition Course | Adamski et al. | 2020 | Australia | nutrition education; information-seeking behavior; nutrition misinformation; online learning; social media |
| 5 | Applying MOOCocracy learning culture themes to improve digital course design and online learner engagement | Akinkuolie and Shortt | 2021 | USA | massively open online courses; MOOC; MOOCocracy; Online learning culture; online course design |
| 6 | Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs): Data on higher education | Al-Rahmi et al. | 2018 | Malaysia | Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs); higher education; systematic literature review |
| 7 | Data Collection Approaches to Enable Evaluation of a Massive Open Online Course About Data Science for Continuing Education in Health Care: Case Study | Alturkistani et al. | 2019 | United Kingdom | education, distance; education; teaching; online learning; online education; MOOC; massive open online course |
| 8 | Principles of synthetic biology: a MOOC for an emerging field | Anderson et al. | 2019 | USA | synthetic biology; massive open online course (MOOC); edX; education; curriculum building |
| 9 | Lessons learned on teaching a global audience with massive open online courses (MOOCs) on health impacts of climate change: a commentary | Barteit et al. | 2019 | Germany | health; climate change; global health; global education; global audience; capacity building; massive open online course; MOOC |
| 10 | Genomic Education at Scale: The Benefits of Massive Open Online Courses for the Healthcare Workforce | Bishop et al. | 2019 | United Kingdom | workforce development; genomic medicine; Massive Open Online Course; evaluation; genomic education; multi-disciplinary education; online learning |
| 11 | Stepping back and stepping in: Facilitating learner-centered experiences in MOOCs | Blum-Smith et al. | 2021 | USA | distance education and online learning; pedagogical issues; teaching/learning strategies; cooperative/collaborative learning; adult learning |
| 12 | One Health education in Kakuma refugee camp (Kenya): From a MOOC to projects on real world challenges | Bolon et al. | 2020 | Switzerland | One Health; global health; MOOC; blended learning; project-based learning; refugee camp |
| 13 | Self-regulated spacing in a massive open online course is related to better learning | Carvalho et al. | 2020 | USA | MOOC; learning |
| 14 | Researching for better instructional methods using AB experiments in MOOCs: results and challenges | Chen et al. | 2016 | USA | technology; learning; MOOC |
| 15 | Teachers’ networked professional learning with MOOCs | Chen et al. | 2020 | USA | technology; learning; MOOC |
| 16 | Twelve tips for integrating massive open online course content into classroom teaching | de Jong et al. | 2019 | Netherlands | learning; MOOC; teaching |
| 17 | Application of PBL Mode in a Resident-Focused Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography Training Program: A Perspective of MOOC Environment | Dong et al. | 2020 | China | residents training; TEE; MOOC; PBL; LBL |
| 18 | Deep Learning for Discussion-Based Cross-Domain Performance Prediction of MOOC Learners Grouped by Language on Future Learn | Duru et al. | 2021 | Turkey | MOOCs; deep learning; English as a second language; FutureLearn; predictive models; natural language processing |
| 19 | Transformation of the mathematics classroom with the internet | Engelbrecht et al. | 2020 | South Africa | humans-with-media; learning environments; blended learning; mathematics teaching; mathematics teacher education; MOOC; hyper-personalization; collaboration; learning management system |
| 20 | Do Individual Differences in Cognition and Personality Predict Retrieval Practice Activities on MOOCs? | Fellman et al. | 2020 | Sweden | retrieval practice; test-enhanced learning; e-learning; MOOC; personality; cognition |
| 21 | Making MOOCs meaningful and locally relevant? Investigating IDCourserians—an independent, collaborative, community hub in Indonesia | Firmansyah and Timmis | 2016 | United Kingdom | MOOCs; learning community; communities of practice; collaborative learning; globalisation; self-regulated learning |
| 22 | Could a massive open online course be part of the solution to sport-related concussion? Participation and impact among 8368 registrants | Fremont et al. | 2020 | Canada | MOOC |
| 23 | Promoting Evidence Based Nutrition Education Across the World in a Competitive Space: Delivering a Massive Open Online Course | Gibson et al. | 2020 | Australia | distance education; global education; health promotion; internet; nutrition misinformation; online learning; social media |
| 24 | Structural limitations of learning in a crowd: communication vulnerability and information diffusion in MOOCs | Gillani et al. | 2014 | United Kingdom | MOOC; distance learning; learning |
| 25 | Relationship between participants’ level of education and engagement in their completion of the Understanding Dementia Massive Open Online Course | Goldberg et al. | 2015 | Australia | dementia; online learning; MOOC; level of education; engagement |
| 26 | Symposium report on “Examining the Changing Landscape of Course Delivery and Student Learning”: Experimental Biology 2017 | Halpin et al. | 2018 | United Kingdom | Massive Open Online Course; online teaching; webcasting |
| 27 | A Massive Open Online Course for teaching physiotherapy students and physiotherapists about spinal cord injuries | Harvey et al. | 2014 | Australia | MOOC; learning; physiotherapy |
| 28 | Teaching modes and social-epistemological dimensions in medical Massive Open Online Courses: Lessons for integration in campus education | Hendriks et al. | 2019 | Netherlands | MOOC; medical MOOC; learning |
| 29 | Instructional design quality in medical Massive Open Online Courses for integration into campus education | Hendriks et al. | 2019 | Netherlands | MOOC; medical MOOC; learning; education |
| 30 | Uncovering motivation and self- regulated learning skills in integrated medical MOOC learning: a mixed methods research protocol | Hendriks et al. | 2020 | Netherlands | medical MOOC; learning; MOOC; research |
| 31 | Design for now, but with the future in mind: a “cognitive flexibility theory” perspective on online learning through the lens of MOOCs | Hu and Spiro | 2021 | USA | cognitive flexibility theory (CFT); MOOC; adaptive worldview; online learning |
| 32 | The utilization of data analysis techniques in predicting student performance in massive open online courses (MOOCs) | Hughes and Dobbins | 2015 | United Kingdom | open learning; prediction; data analysis |
| 33 | The Practitioner’s Guide to Global Health: an interactive, online, open-access curriculum preparing medical learners for global health experiences | Jacquet et al. | 2018 | USA | global health; international; MOOC; online; curriculum |
| 34 | Twelve tips for teaching medical students online under COVID-19 | Jiang et al. | 2020 | China | COVID-19; medical MOOC; e-learning; SPOC; assessment |
| 35 | How to make a MOOC With forethought and support, science instructors can design effective massive open online courses. | Kellogg | 2013 | USA | digital learning; MOOC; technology |
| 36 | Training Primary Health Professionals in Breast Cancer Prevention: Evidence and Experience from Mexico | Magaña-Valladares et al. | 2016 | Mexico | face-to-face learning; blended learning; MOOC; breast cancer; Mexico; training courses; virtual education and multidisciplinary training; health promoters |
| 37 | Massive Open Online Courses: Concept and Implications | Mahajan et al. | 2019 | India | e-learning; life-long learner; open courses; ubiquitous learning |
| 38 | Protocol for a mixed-methods evaluation of a massive open online course on real world evidence | Meinert et al. | 2018 | United Kingdom | digital learning; MOOC; technology; e-learning |
| 39 | Real-world evidence for postgraduate students and professionals in healthcare: protocol for the design of a blended massive open online course | Meinert et al. | 2018 | United Kingdom | digital learning; MOOC; technology; e-learning; blended learning |
| 40 | How health professionals regulate their learning in massive open online courses | Milligan and Littlejohn | 2016 | United Kingdom | massive open online courses; self-regulated learning; professional learning |
| 41 | Continuing Medical Education: MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) and Their Implications for Radiology Learning | Murphy and Munk | 2013 | Canada | continuing medical education (CME); MOOC; learning |
| 42 | MOOC Learning Assessment in Clinical Settings: Analysis from Quality Dimensions | Olivares et al. | 2021 | Mexico | educational assessment; clinical teaching; online education; massive open online course; faculty development |
| 43 | Massive Open Online Course for Health Informatics Education | Paton et al. | 2014 | United Kingdom | distance education; medical informatics; professional education; social media; computer-assisted instruction |
| 44 | Delivering a medical school elective with massive open online course (MOOC) technology | Robinson | 2016 | USA | MOOC; medical education; medical school elective; business |
| 45 | First ‘Global Flipped Classroom in One Health’: From MOOCs to research on real world challenges | de Castañeda et al. | 2018 | Switzerland | One Health; global health; MOOC; e-learning; flipped-classroom; project-based learning |
| 46 | Leveraging massive open online courses to expand quality of healthcare education to health practitioners in Rwanda | Scott et al. | 2019 | USA | MOOC; education |
| 47 | Blended learning in medical physiology improves nursing students’ study efficiency | Shang and Liu | 2018 | China | blended learning; China; MOOC; physiology education; teaching reform |
| 48 | Leveraging Digital Platforms to Scale Health Care Workforce Development: The Career 911 Massive Open Online Course | Simon et al. | 2019 | USA | workforce development; health disparities; community-based participatory research; massive open online course; research training; health professions; education technology |
| 49 | Study design and protocol for a comprehensive evaluation of a UK massive open online course (MOOC) on quality improvement in healthcare | Smith-Lickess et al. | 2019 | United Kingdom | MOOC; learning; healthcare |
| 50 | Development and impact of a massive open online course (MOOC) for antimicrobial stewardship | Sneddon et al. | 2017 | Scotland | antimicrobial; MOOC |
| 51 | Transformation of a face-to-face workshop into a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC): A design and development case | Sommer et al. | 2019 | USA | instructional design; online learning; sample size; power analysis; case study; MOOC; formative evaluation |
| 52 | Beyond xMOOCs in healthcare education: study of the feasibility in integrating virtual patient systems and MOOC platforms | Stathakarou et al. | 2014 | Sweden | virtual patients; healthcare education; e-learning; massive open online courses; integration |
| 53 | Discover Dentistry: encouraging wider participation in dentistry using a massive open online course (MOOC) | Stokes et al. | 2015 | United Kingdom | dentistry; MOOC; learning |
| 54 | The contribution of a MOOC to community discussions around death and dying | Tieman et al. | 2018 | Australia | death attitudes; palliative care; community education; online learning; MOOC |
| 55 | An Introduction to the Inverted/Flipped Classroom Model in Education and Advanced Training in Medicine and in the Healthcare Professions | Tolks et al. | 2016 | Germany | inverted classroom; flipped classroom; medical education; educational video; Open Educational Resources; MOOCs; blended learning; screencasts; podcasts; E-Learning |
| 56 | SEPSIS. Educational and Best Practice Frontiers. Beyond the Boundaries of Fatality, Enhancing Clinical Skills and Precision Medicine | Trovato | 2020 | Italy | sepsis; bioinformatics; ultrasound; e-learning; MOOC; genomics; research models |
| 57 | Who will pass? Analyzing learner behaviors in MOOCs | Tseng et al. | 2016 | Taiwan | MOOCs; learning engagement; learning behavior; learning analytics |
| 58 | Deconstructing self-regulated learning in MOOCs: In search of help-seeking mechanisms | Vilkova and Shcheglova | 2020 | Russia | MOOC; self-regulated learning; education research; validation; OSLQ |
| 59 | Development and Evaluation of Affective Domain Using Student’s Feedback in Entrepreneurial Massive Open Online Courses | Wu et al. | 2019 | Taiwan | entrepreneurship education; social entrepreneurship; affective development; MOOCs; content analysis |
| 60 | Study Partners Recommendation for xMOOCs Learners | Xu and Yang | 2015 | China | digital learning; MOOC; technology; e-learning |
| 61 | The Distance Teaching Practice of Combined Mode of Massive Open Online Course Micro-Video for Interns in Emergency Department During the COVID-19 Epidemic Period | Zhou et al. | 2020 | China | COVID-19; MOOC micro-video; intern; distance teaching; telemedicine |
References
- Bali, M. MOOC Pedagogy Gleaning Good Practice from Existing MOOCs. MERLOT J. Online Learn. Teach. 2014, 10, 44–56. Available online: https://oerknowledgecloud.org/sites/oerknowledgecloud.org/files/bali_0314.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Cachay-Huamán, L.; Ramírez-Hernández, D. Open, interdisciplinary and collaborative educational innovation to train in energy sustainability through MOOC: Perception of competency development. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2019, 13, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulfin, S.; Pangrazio, L.; Selwyn, N. Making ‘MOOCs’: The construction of a new digital higher education within news media discourse. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2014, 15, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, L.; Harrison, L.M. MOOCs and Democratic Education. Lib. Educ. 2013, 99, 20. Available online: https://aacu.org/liberaleducation/2013/fall/carver-harrison (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Dang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, F.; Shi, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, W. Construction of Z-scheme Fe3O4/BiOCl/BiOI heterojunction with superior recyclability for improved photocatalytic activity towards tetracycline degradation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 893, 162251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, I.; Ho, A.D. HarvardX and MITx: Four Years of Open Online Courses—Fall 2012–Summer 2016. 2016. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2889436 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Coffrin, C.; Corrin, L.; de Barba, P.; Kennedy, G. Visualizing patterns of student engagement and performance in MOOCs. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge—LAK′14, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 24–28 March 2014; Pistilli, M., Willis, J., Koch, D., Arnold, K., Teasley, S., Pardo, A., Eds.; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhu, M.; Bonk, C.J.; Lin, L. Exploring instructors’ perspectives, practices, and perceived support needs and barriers related to the gamification of MOOCs. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2021, 33, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H. The structure of knowledge synthesis: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowl. Soc. 1988, 1, 104–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, A.; Zawacki-Richter, O. Trends and Patterns in Distance Education (2014–2019): A Synthesis of Scholarly Publications and a Visualization of the Intellectual Landscape. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2021, 22, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C. Dropout prediction model in MOOC based on clickstream data and student sample weight. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 8971–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, C.M. The Quality of MOOCs: How to improve the design of open education and online courses for learners? In International Conference on Learning and Collaboration Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, J.W.; Plano-Clark, V.L. Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alshehri, M.; Alamri, A.; Cristea, A.I.; Stewart, C.D. Towards Designing Profitable Courses: Predicting Student Purchasing Behaviour in MOOCs. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2021, 31, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doleck, T.; Lemay, D.J.; Brinton, C.G. Evaluating the efficiency of social learning networks: Perspectives for harnessing learning analytics to improve discussions. Comput. Educ. 2021, 164, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno, D.P.; Pizzolato, N. Teacher professional development in the context of the “Open Discovery of STEM laboratories” project: Is the MOOC methodology suitable for teaching physics? J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1512, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaedinger, A.; Gurden, H.; Gourévitch, B.; Martin, C. Multisensory learning between odor and sound enhances beta oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Alvaro, S.; Alkasasbeh, A.A.; García-López, E.; García-Cabot, A.; Rozinaj, G.; Ghinea, G. Exploring Impact of Olfactory Stimuli on User Performance on Mobile Platforms. In Interactive Mobile Communication, Technologies and Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1015–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijzingen, I.M.; Gispen, W.H.; Spruijt, B.M. Olfactory bulbectomy temporarily impairs morris maze performance: An ACTH (4–9) analog accellerates return of function. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 58, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelcer, I.; Cohen, H.; Richter-Levin, G.; Lebiosn, T.; Grossberger, T.; Barkai, E. A cellular correlate of learning-induced metaplasticity in the hippocampus. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creed-Dikeogu, G.; Clark, C. Are you MOOC-ing yet? A review for academic libraries. Kans. Libr. Assoc. Coll. Univ. Libr. Sect. Proc. 2013, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Sambyal, N. An understanding approach towards MOOCs. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2013, 3, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Twiner, A.; Littleton, K.; Whitelock, D.; Coffin, C. Combining sociocultural discourse analysis and multimodal analysis to explore teachers’ and pupils’ meaning making. Learn. Cult. Soc. Interact. 2021, 30, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, J.A. What are digital media? Discourse Context Media 2021, 41, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, R.A. Being suspicious of the sense of ease and undeterred by the sense of difficulty: Looking back at Schmidt and Bjork (1992). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 13, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašević, D.; Kovanović, V.; Joksimović, S.; Siemens, G. Where is research on massive open online courses headed? A data analysis of the MOOC research initiative. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2014, 15, 134–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, G.; Guo, Y. Social Network Analysis of 50 Years of International Collaboration in the Research of Educational Technology. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2016, 53, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoglund, L.; Brundin, R.; Olofsson, T.; Kalimo, H.; Ingvast, S.; Blom, E.S.; Glaser, A. Frontotemporal dementia in a large Swedish family is caused by a progranulin null mutation. Neurogenetics 2009, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanciu, I.; Larsson, M.; Nordin, S.; Adolfsson, R.; Nilsson, L.G.; Olofsson, J.K. Olfactory impairment and subjective olfactory complaints independently predict conversion to dementia: A longitudinal, population-based study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014, 20, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanand, D.P.; Lee, S.; Manly, J.; Andrews, H.; Schupf, N.; Doty, R.L.; Mayeux, R. Olfactory deficits predict cognitive decline and Alzheimer dementia in an urban community. Neurology 2015, 84, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hew, K.F.; Cheung, W.S. Students’ and instructors’ use of massive open online courses (MOOCs): Motivations and challenges. Educ. Res. Rev. 2014, 12, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbakumov, D.; Desmet, P.; Van den Noortgate, W. Measuring growth in students’ proficiency in MOOCs: Two component dynamic extensions for the Rasch model. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.; Young-Wolff, K.C.; Konar, E.; Winkleby, M. Massive open online nutrition and cooking course for improved eating behaviors and meal composition. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, R.A.; De Jong, P.G.M.; Admiraal, W.F.; Reinders, M.E.J. Uncovering motivation and self-regulated learning skills in integrated medical MOOC learning: A mixed methods research protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.W.; Dushime, T.; Rusanganwa, V.; Woskie, L.; Attebery, C.; Binagwaho, A. Leveraging massive open online courses to expand quality of healthcare education to health practitioners in Rwanda. BMJ Open Qual. 2019, 8, e000532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, J.M.; Machado, P.P.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Ribeiro, R.; Vieira, F.; Costa, P. Easiness, usefulness and intention to use a MOOC in nursing. Nurse Educ. Today 2021, 97, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, M.; Truby, H.; Klassen, K.M.; Cowan, S.; Gibson, S. Using the Internet: Nutrition Information-Seeking Behaviours of Lay People Enrolled in a Massive Online Nutrition Course. Nutrients 2020, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiniello, L.; Borrelli, L.; Toto, G.A. Design of a MOOC for teaching and research: The innovative experience of the MERGO project. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Technology Enhanced Learning Environments for Blended Education (teleXbe2021), Foggia, Italy, 21–22 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Asli, M.F.; Hamzah, M.; Ibrahim, A.A.A.; Ayub, E. Problem characterization for visual analytics in MOOC learner’s support monitoring: A case of Malaysian MOOC. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebben, M.; Murphy, J.S. Unpacking MOOC scholarly discourse: A review of nascent MOOC scholarship. Learn. Media Technol. 2014, 39, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Spiro, R.J. Design for now, but with the future in mind: A “cognitive flexibility theory” perspective on online learning through the lens of MOOCs. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2021, 69, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.; Dobbins, C. The utilization of data analysis techniques in predicting student performance in massive open online courses (MOOCs). Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2015, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Taylor, S.; Tom, L.S. Leveraging Digital Platforms to Scale Health Care Workforce Development: The Career 911 Massive Open Online Course. Prog. Community Health Partnersh. Res. Educ. Action 2019, 13, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, G.A.; Umoren, R.A.; Hayward, A.S.; Myers, J.G.; Modi, P.; Dunlop, S.J.; Sarfaty, S.; Hauswald, M.; Tupesis, J.P. The Practitioner’s Guide to Global Health: An interactive, online, open-access curriculum preparing medical learners for global health experiences. Med. Educ. Online 2018, 23, 1503914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wu, H.; Cheng, H.; Wang, W.; Xie, A.; Fitzgerald, S.R. Twelve tips for teaching medical students online under COVID-19. Med. Educ. Online 2021, 26, 1854066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Lickess, S.K.; Woodhead, T.; Burhouse, A.; Vasilakis, C. Study design and protocol for a comprehensive evaluation of a UK massive open online course (MOOC) on quality improvement in healthcare. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, S. Online learning: How to make a MOOC. Nature 2013, 499, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneddon, J.; Barlow, G.; Bradley, S.; Brink, A.; Chandy, S.J.; Nathwani, D. Development and impact of a massive open online course (MOOC) for antimicrobial stewardship. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaña-Valladares, L.; González-Robledo, M.C.; Rosas-Magallanes, C.; Mejía-Arias, M.; Arreola-Ornelas, H.; Knaul, F.M. Training Primary Health Professionals in Breast Cancer Prevention: Evidence and Experience from Mexico. J. Cancer Educ. 2018, 33, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.; Gupta, P.; Singh, T. Massive Open Online Courses: Concept and Implications. Indian Pediatr. 2019, 56, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinert, E.; Alturkistani, A.; Car, J.; Carter, A.; Wells, G.; Brindley, D. Real-world evidence for postgraduate students and professionals in healthcare: Protocol for the design of a blended massive open online course. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e025196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Munk, P.L. Continuing Medical Education: MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) and Their Implications for Radiology Learning. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2013, 64, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Huang, S.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, Y. The distance teaching practice of combined mode of massive open online course micro-video for interns in emergency department during the COVID-19 epidemic period. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 26, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, S. Places to go: Connectivism & connective knowledge. Innov. J. Online Educ. 2008, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fini, A. The Technological Dimension of a Massive Open Online Course: The Case of the CCK08 Course Tools. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2009, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, R.; Scott, D. Education for Innovation and Independent Learning; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Benckendorff, P. A Contemporary Review of Research Methods Adopted to Understand Students’ and Instructors’ Use of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs). Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2017, 7, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Miao, C.; Leung, C.; White, T.J. Towards AI-powered personalization in MOOC learning. Npj Sci. Learn. 2017, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, A.H.; Biguet, G.; Stathakarou, N.; Westin-Hägglöf, B.; Jeding, K.; McGrath, C.; Kononowicz, A.A. Virtual patients in a behavioral medicine massive open online course (MOOC): A qualitative and quantitative analysis of participants’ perceptions. Acad. Psychiatry 2017, 41, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- France, K.; Hangorsky, U.; Wu, C.W.; Sollecito, T.P.; Stoopler, E.T. Participation in an existing massive open online course in dentistry during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Dent. Educ. 2021, 85, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, C.; Littlejohn, A. How health professionals regulate their learning in massive open online courses. Internet High. Educ. 2016, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C. Massive Open Online Course for Health Informatics Education. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2014, 20, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R. Delivering a medical school elective with massive open online course (MOOC) technology. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.A. Research perspective on the concept of learning culture: MOOCs and other online contexts. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2021, 69, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, S.L.O.; Hernández, R.I.E.; Corolla, M.L.T.; Alvarez, J.P.N.; Sánchez-Mendiola, M. MOOC Learning Assessment in Clinical Settings: Analysis from Quality Dimensions. Med. Sci. Educ. 2021, 31, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castañeda, R.R.; Garrison, A.; Haeberli, P.; Crump, L.; Zinsstag, J.; Ravel, A.; Flahault, A.; Bolon, I. First ‘Global Flipped Classroom in One Health’: From MOOCs to research on real world challenges. One Health 2018, 5, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).