Towards the Biological Understanding of CTC: Capture Technologies, Definitions and Potential to Create Metastasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CTC Definitions and Capture
2.1. Automated Identification of CTC
| Technology | CTC Definition | Assay Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EpCAM | CKs | CD45 | Nucleus | Morphology | Size | Num Aperture | Blind | Threshold | Healthy Donors | Ref | |
| Capture by physical properties | |||||||||||
| Label-free DC Impedance Based Microcytometer | − | − | − | − | − | + | NA | − | − | + | [13] |
| Microtube Device | + | − | − | - | − | − | NM | − | − | + | [31] |
| ISET | − | NC | − | NC | NC | − | NM | − | − | + | [32] |
| Filter Based Microdevice | − | + | − | NC | NC | − | NM | − | − | + | [33] |
| Capture by immunological properties | |||||||||||
| CellSearch | + | + | + | + | + | + | M | + | + | + | [9] |
| CTC-chip | + | + | + | NC | NC | NC | NM | + | − | + | [34] |
| HB-Chip | + | NC | + | NC | NC | NC | NM | + | + | + | [35] |
| MagSweeper | + | − | − | − | − | − | NM | − | − | + | [36] |
| Capture by physical and immunological properties | |||||||||||
| GEDI-CTC | − | − | + | + | + | − | M | + | − | + | [37] |
| posCTC-iChip | + | + | + | + | − | − | NM | − | + | + | [12] |
2.2. EpCAM+/EpCAM− CTC
2.3. Filtration-Based Technologies

3. Biological Properties of CTC
3.1. Viability
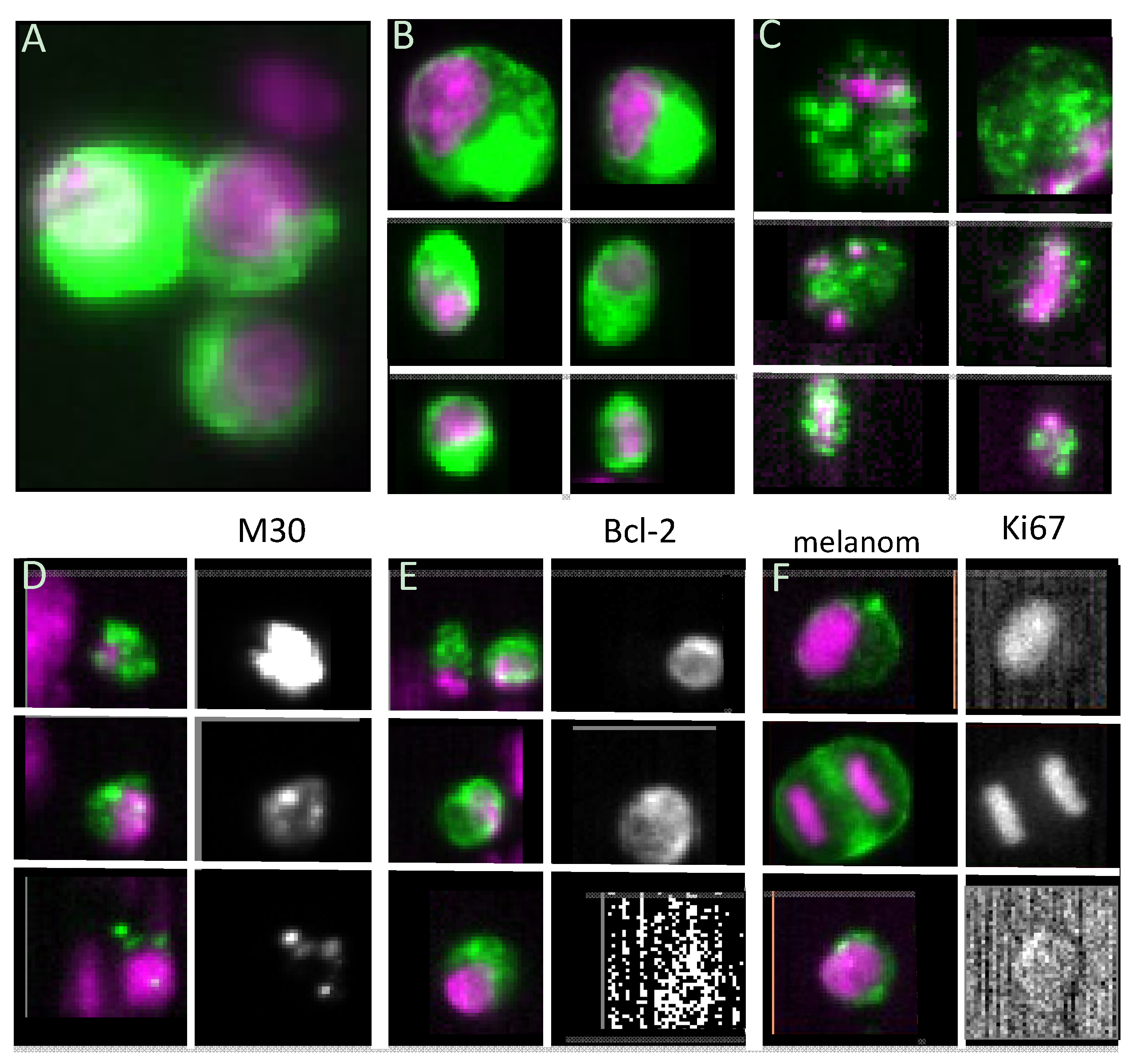
3.2. Proliferative Capacity
3.3. Stem Cell-like Properties
4. CTC in Vitro Culturing and in Vivo Models
4.1. CTC in Vitro culturing
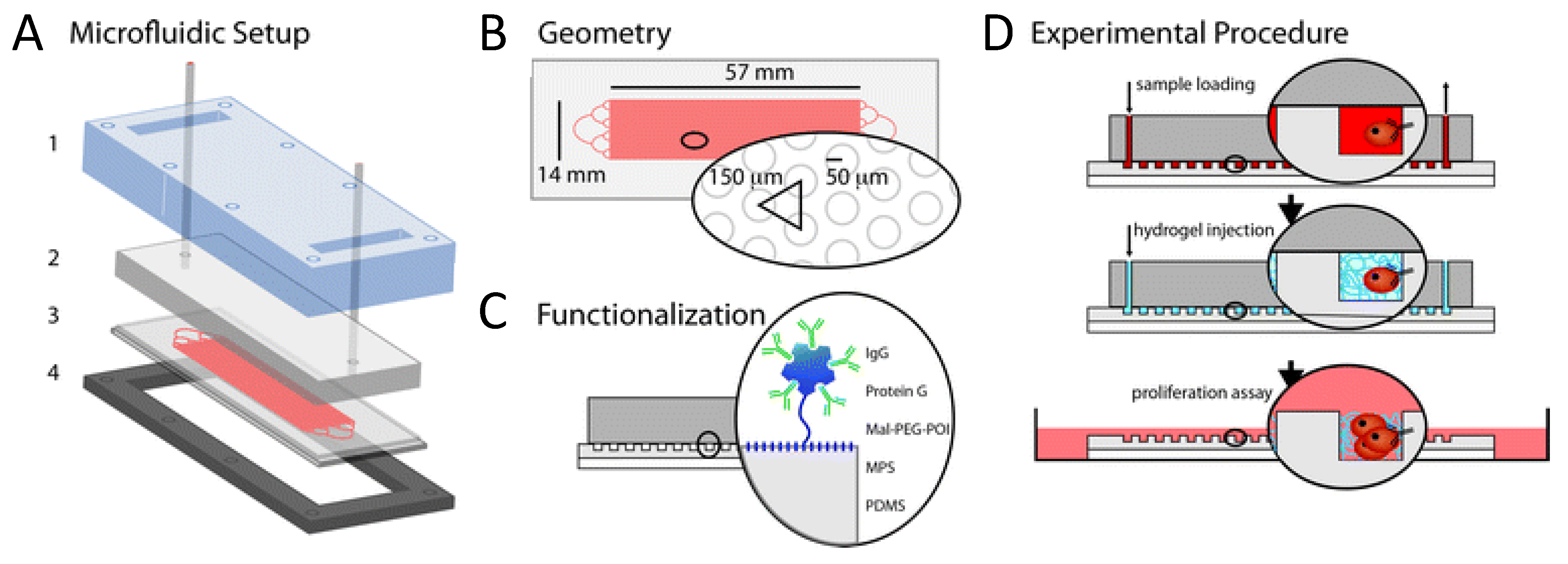
4.2. CTC in Vivo Assays Using Mouse Models
5. Conclusions
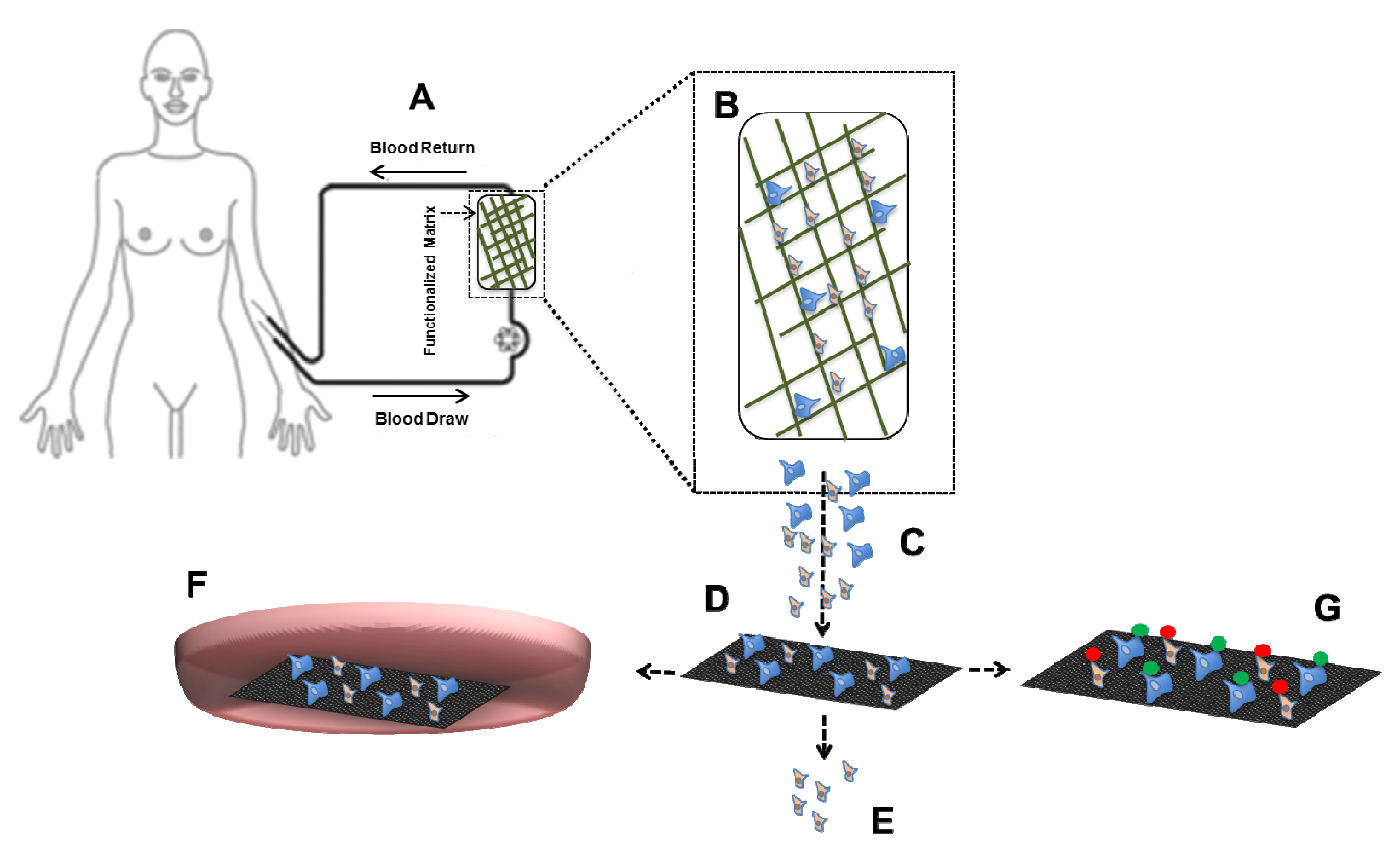
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massagué, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Pore, M.M.; van den Berg, A.; Timens, W.; Boezen, H.M.; Liesker, J.J.W.; Schouwink, J.H.; Wijnands, W.J.A; Kerner, G.S.M.A; Kruyt, F.A.E.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in small-cell lung cancer: A predictive and prognostic factor. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-M.; Krebs, M.G.; Lancashire, L.; Sloane, R.; Backen, A.; Swain, R.K.; Priest, L.J.C.; Greystoke, A.; Zhou, C.; Morris, K.; et al. Clinical significance and molecular characteristics of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor microemboli in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Lancashire, L.; Hou, J.-M.; Greystoke, A.; Ward, T.H.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G.; et al. Evaluation and prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, G.T.; Cristofanilli, M.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Borden, E.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Repollet, M.; Doyle, G.V; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Circulating tumor cells versus imaging—Predicting overall survival in metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2006, 12, 6403–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Ligthart, S.T.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Challenges in the enumeration and phenotyping of CTC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.W.; Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Li, Z.R.; Soo, R.A; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.-T.; Han, J.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Lim, C.T. Isolation and retrieval of circulating tumor cells using centrifugal forces. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial focusing for tumor antigen-dependent and -independent sorting of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, K.K.B.; Jeon, C.S.C.; Hwang, I.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.K.H.C.; Chung, T.D. A label-free DC impedance-based microcytometer for circulating rare cancer cell counting. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; van Dalum, G.; Beck, M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Filter characteristics influencing circulating tumor cell enrichment from whole blood. PLoS One 2013, 8, e61770. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-G.; Jeong, H.; Oh, J.-M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, D.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, J.H.; et al. Highly efficient assay of circulating tumor cells by selective sedimentation with a density gradient medium and microfiltration from whole blood. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7400–7407. [Google Scholar]
- Issadore, D.; Chung, J.; Shao, H.; Liong, M.; Ghazani, A.A; Castro, C.M.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Ultrasensitive clinical enumeration of rare cells ex vivo using a micro-hall detector. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Sim, T.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, H.; Park, J.-M.; Moon, H.-S.; Kim, S.I.; Gurel, O.; Lee, S.S.; et al. SSA-MOA: A novel CTC isolation platform using selective size amplification (SSA) and a multi-obstacle architecture (MOA) filter. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2874–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Brandt, B. Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorges, T.M.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells as therapy-related biomarkers in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balic, M.; Lin, H.; Williams, A. Progress in circulating tumor cell capture and analysis: Implications for cancer management. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells: Liquid biopsy of cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 1, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.; Ligthart, S.T.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Interpretation of changes in Circulating Tumor Cell counts. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, D.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Jeffreyallard, W.; Doyle, G.V; Terstappen, L.W.W.M. Circulating Tumor cells at each follow-up time point during therapy of metastatic breast cancer patients predict progression-free and overall survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, B.; Degroot, M.R.; Mastboom, W.J.; Vermes, I.; Vanderpalen, J.; Tibbe, A.G.; Terstappen, L.W. Circulating tumor cells, disease recurrence and survival in newly diagnosed breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Mathiot, C.; Delaloge, S.; Brain, E.; Giachetti, S.; de Cremoux, P.; Marty, M.; Pierga, J.-Y. Single circulating tumor cell detection and overall survival in nonmetastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jueckstock, J.K.; Rack, B.K.; Zwingers, T.; Hepp, P.G.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Beckmann, M.W.; Lichtenegger, W.; Sommer, H.L.; Pantel, K.T.H.; Forstbauer, H.; et al. Prognostic relevance of circulating tumor cells (CTC) before adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer: Results of the German SUCCESS trial. J Clin Oncol 2011, 29, Abstr. 1033. [Google Scholar]
- Lucci, A.; Hall, C.S.; Lodhi, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Anderson, A.E.; Xiao, L.; Bedrosian, I.; Kuerer, H.M.; Krishnamurthy, S. Circulating tumour cells in non-metastatic breast cancer: A prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.; Siesling, S.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Detection of cancer before distant metastasis. BMC Cancer 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.C.; Niederacher, D.; Topp, S.A.; Honisch, E.; Schumacher, S.; Schmitz, N.; Zacarias, F.L.; Vay, C.; Hoffmann, I.; Kasprowicz, N.S.; et al. Diagnostic leukapheresis enables reliable detection of circulating tumor cells of nonmetastatic cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.D.; Mattison, J.; Western, L.T.; Powderly, J.D.; Greene, B.T.; King, M.R. Microtube device for selectin-mediated capture of viable circulating tumor cells from blood. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.K.; Zheng, S.; Williams, A.J.; Balic, M.; Groshen, S.; Scher, H.I.; Fleisher, M.; Stadler, W.; Datar, R.H.; Tai, Y.-C.; et al. Portable filter-based microdevice for detection and characterization of circulating tumor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5011–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, G.; Sabile, A.; Louha, M.; Sitruk, V.; Romana, S.; Franco, D.; Pazzagli, M.; Vekemans, M.; Lacour, B.; Paterlini-bre, P. Isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, S.L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Tsukrov, D.I.; Yu, M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Waltman, B.A.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Shah, A.M.; Smas, M.E.; Korir, G.K.; et al. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18392–18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Powell, A.A.; Huber, D.E.; Berbee, J.G.; Roh, K.-H.; Yu, W.; Xiao, W.; Davis, M.M.; Pease, R.F.; Mindrinos, M.N.; et al. Isolating highly enriched populations of circulating epithelial cells and other rare cells from blood using a magnetic sweeper device. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, B.J.; Jodari, M.; Loftus, M.S.; Gakhar, G.; Pratt, E.D.; Chanel-Vos, C.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Santana, S.M.; Liu, H.; Smith, J.P.; et al. Functional characterization of circulating tumor cells with a prostate-cancer-specific microfluidic device. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart, S.T.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Attard, G.; Cassidy, A.M.; de Bono, J.S.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Unbiased and automated identification of a circulating tumour cell definition that associates with overall survival. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27419. [Google Scholar]
- Ligthart, S.T.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Bidard, F.-C.; Simkens, L.H.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; de Groot, M.R.; Attard, G.; de Bono, J.S.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Circulating tumor cells count and morphological features in breast, colorectal and prostate cancer. PLoS One 2013, 8, e67148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Went, P.T.H.; Lugli, A.; Meier, S.; Bundi, M.; Mirlacher, M.; Sauter, G.; Dirnhofer, S. Frequent EpCam protein expression in human carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzpis, M.; McLaughlin, P.M.J.; de Leij, L.M.F.H.; Harmsen, M.C. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: More than a carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.G.; Chianese, D.; Doyle, G.V. Expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule in carcinoma cells present in blood and primary and metastatic tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffey, M.J.; Mills, S.E.; Swanson, P.E.; Zarbo, R.J.; Shah, A.R.; Wick, M.R. Immunoreactivity for BER-EP4 in adenocarcinomas, adenomatoid tumors, and malignant mesotheliomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastl, G.; Spizzo, G.; Obrist, P.; Dünser, M.; Mikuz, G. Ep-CAM overexpression in breast cancer as a predictor of survival. Lancet 2000, 356, 1981–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Spizzo, G.; Fong, D.; Wurm, M.; Ensinger, C.; Obrist, P.; Hofer, C.; Mazzoleni, G.; Gastl, G.; Went, P. EpCAM expression in primary tumour tissues and metastases: An immunohistochemical analysis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 64, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, J.H.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; Komurov, K.; Zhou, A.Y.; Gupta, S.; Yang, J.; Hartwell, K.; Onder, T.T.; Gupta, P.B.; Evans, K.W.; et al. Core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interactome gene-expression signature is associated with claudin-low and metaplastic breast cancer subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15449–15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, R.A. Twisted epithelial-mesenchymal transition blocks senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Gorges, T.M.; Tinhofer, I.; Drosch, M.; Röse, L.; Zollner, T.M.; Krahn, T.; von Ahsen, O. Circulating tumour cells escape from EpCAM-based detection due to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Marengo, M.S.; Oltean, S.; Kemeny, G.; Bitting, R.L.; Turnbull, J.D.; Herold, C.I.; Marcom, P.K.; George, D.J.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Circulating tumor cells from patients with advanced prostate and breast cancer display both epithelial and mesenchymal markers. Mol. CancerRes. 2011, 9, 997–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Kallergi, G.; Papadaki, M.A.; Politaki, E.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V.; Agelaki, S. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers expressed in circulating tumour cells of early and metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, C.; Gradilone, A.; Naso, G.; Vincenzi, B.; Petracca, A.; Nicolazzo, C.; Palazzo, A.; Saltarelli, R.; Spremberg, F.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness features in circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mego, M.; de Giorgi, U.; Dawood, S.; Wang, X.; Valero, V.; Andreopoulou, E.; Handy, B.; Ueno, N.T.; Reuben, J.M.; Cristofanilli, M. Characterization of metastatic breast cancer patients with nondetectable circulating tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Sieuwerts, A.M.; Kraan, J.; Bolt, J.; van der Spoel, P.; Elstrodt, F.; Schutte, M.; Martens, J.W.M.; Gratama, J.-W.; Sleijfer, S.; Foekens, J.A. Anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies and the detection of circulating normal-like breast tumor cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, B.; Kraan, J.; Bolt-de Vries, J.; van der Spoel, P.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Schutte, M.; Timmermans, A.M.; Foekens, R.; Martens, J.W.M.; Gratama, J.-W.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer may improve through enrichment with anti-CD146. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, B.; Kraan, J.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; van der Spoel, P.; Bolt-de Vries, J.; Prager-van der Smissen, W.J.C.; Smid, M.; Timmermans, A.M.; Martens, J.W.M.; Gratama, J.W.; et al. CD49f-based selection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) improves detection across breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Lett. 2012, 319, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, S.H. A sieve for the isolation of cancer cells and other large cells from the blood. Cancer 1964, 17, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desitter, I.; Guerrouahen, B.S.; Benali-Furet, N.; Wechsler, J.; Janne, P.A.; Kuang, Y.; Yanagita, M.; Wang, L.; Berkowitz, J.A.; Distel, R.J.; et al. A New device for rapid isolation by size and characterization of rare circulating tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.; Makarova, O.; Zhu, P.; Li, S.A.P. Isolation of circulating tumor cells by size exclusion using lithography fabricated precision microfilters. In Proceedings of the 102th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–6 April 2011; AACR: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. Abstract Number 2369. [Google Scholar]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; van Dalum, G.; Beck, M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Filtration parameters influencing circulating tumor cell enrichment from whole blood. PLoS One 2013, 8, e61774. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, V.; Ilie, M.I.; Long, E.; Selva, E.; Bonnetaud, C.; Molina, T.; Vénissac, N.; Mouroux, J.; Vielh, P.; Hofman, P. Detection of circulating tumor cells as a prognostic factor in patients undergoing radical surgery for non-small-cell lung carcinoma: Comparison of the efficacy of the CellSearch AssayTM and the isolation by size of epithelial tumor cell method. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Hou, J.-M.; Sloane, R.; Lancashire, L.; Priest, L.; Nonaka, D.; Ward, T.H.; Backen, A.; Clack, G.; Hughes, A.; et al. Analysis of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using epithelial marker-dependent and -independent approaches. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dalum, G.; Lenferink, A.; LWMM, T. Detection of EpCAM negative Circulating Tumor Cells. In Proceedings of the 104th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Washington, DC, USA, 6–10 April 2013; AACR: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. Abstract Number 1459. [Google Scholar]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Doggen, C.J.M.; Attard, G.; de Bono, J.S.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. All circulating EpCAM+CK+CD45− objects predict overall survival in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1851–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.J.; Moreno, J.G.; Pienta, K.J.; Gross, S.; Repollet, M.; O’hara, S.M.; Russell, T.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Apoptosis of circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer patients. Cytom. Part A 2004, 62, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Leers, M.P.; Kölgen, W.; Björklund, V.; Bergman, T.; Tribbick, G.; Persson, B.; Björklund, P.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Björklund, B.; Nap, M.; et al. Immunocytochemical detection and mapping of a cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope exposed during early apoptosis. J. Pathol. 1999, 187, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callagy, G.M.; Webber, M.J.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Caldas, C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, T.J.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature 1991, 349, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerage, J.B.; Budd, G.T.; Doyle, G.V; Brown, M.; Paoletti, C.; Muniz, M.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.I.; Chianese, D.A.; Connelly, M.C.; et al. Monitoring apoptosis and Bcl-2 on circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.-R.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, S.-J.; Shi, R.-Y.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J. Circulating stem cell-like epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive tumor cells indicate poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méhes, G.; Witt, A.; Kubista, E.; Ambros, P. Circulating Breast cancer cells are frequently apoptotic. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Fassan, M.; Aieta, M.; Zilio, F.; Celadin, R.; Borin, M.; Grassi, A.; Troiani, L.; Basso, U.; Barile, C.; et al. Dynamic changes of live/apoptotic circulating tumour cells as predictive marker of response to sunitinib in metastatic renal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Basso, U.; Celadin, R.; Zilio, F.; Pucciarelli, S.; Aieta, M.; Barile, C.; Sava, T.; Bonciarelli, G.; Tumolo, S.; et al. M30 neoepitope expression in epithelial cancer: Quantification of apoptosis in circulating tumor cells by CellSearch analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G.; Konstantinidis, G.; Markomanolaki, H.; Papadaki, M.A.; Mavroudis, D.; Stournaras, C.; Georgoulias, V.; Agelaki, S. Apoptotic Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in early and metastatic breast cancer patients. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehm, T.; Becker, S.; Becker-Pergola, G.; Sotlar, K.; Gebauer, G.; Dürr-Störzer, S.; Neubauer, H.; Wallwiener, D.; Solomayer, E.-F. Presence of apoptotic and nonapoptotic disseminated tumor cells reflects the response to neoadjuvant systemic therapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulukaya, E.; Yilmaztepe, A.; Akgoz, S.; Linder, S.; Karadag, M. The levels of caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 are elevated in serum from patients with lung cancer and helpful to predict the survival. Lung Cancer 2007, 56, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swennenhuis, J.F.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Levink, R.; Sipkema, R.C.J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Characterization of circulating tumor cells by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytometry 2009, 75, 520–527. [Google Scholar]
- Campoli, M.R.; Chang, C.C.; Kageshita, T.; Wang, X.; McCarthy, J.B.; Ferrone, S. Human high molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen (HMW-MAA): A melanoma cell surface chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MSCP) with biological and clinical significance. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 24, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, M.T.; Dowsett, M. Current and emerging biomarkers in breast cancer: Prognosis and prediction. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, R245–R262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Stahmann, N.; Riethdorf, S.; Goetz, A.; Ja, F.; Pantel, K. Circulating Tumor Cells in breast cancer: Correlation to bone marrow micrometastases, heterogeneous response to systemic therapy and low proliferative activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3678–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicha, M.S.; Liu, S.; Dontu, G. Cancer stem cells: An old idea—A paradigm shift. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Hernandez, A.B.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, D.; Costa, A.; Zaffaroni, N.; Pratesi, G. Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5506–5511. [Google Scholar]
- Balic, M.; Lin, H.; Young, L.; Hawes, D.; Giuliano, A.; McNamara, G.; Datar, R.H.; Cote, R.J. Most early disseminated cancer cells detected in bone marrow of breast cancer patients have a putative breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5615–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulos, P.A.; Polioudaki, H.; Agelaki, S.; Kallergi, G.; Saridaki, Z.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V. Circulating tumor cells with a putative stem cell phenotype in peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestier, C.; Hur, M.; Charafe-Jauffret, E. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Ginestier, C.; Iovino, F.; Tarpin, C.; Diebel, M.; Esterni, B.; Houvenaeghel, G.; Extra, J.; Bertucci, F.; Jacquemier, J.; et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cancer stem cells mediate metastasis and poor clinical outcome in inflammatory breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, W.; Huff, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Malehorn, M.T.; Barber, J.; Tanhehco, Y.; Smith, B.D.; Civin, C.I.; Jones, R.J. Characterization of clonogenic multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2004, 103, 2332–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, D.A.; Meyerrose, T.E.; Wirthlin, L.; Craft, T.P.; Herrbrich, P.E.; Creer, M.H.; Nolta, J.A. Functional characterization of highly purified human hematopoietic repopulating cells isolated according to aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Blood 2004, 104, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.J.; Taussig, D.; Simpson, C.; Allen, K.; Rohatiner, A.Z.; Lister, T.A.; Bonnet, D. Characterization of cells with a high aldehyde dehydrogenase activity from cord blood and acute myeloid leukemia samples. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.; Squire, J. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgeer, M.; Ganju, V.; Szczepny, A.; Russell, P.A.; Prodanovic, Z.; Kumar, B.; Wainer, Z.; Brown, T.; Schneider-Kolsky, M.; Conron, M.; et al. The prognostic significance of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 (ALDH1A1) and CD133 expression in early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G.; Agelaki, S.; Kalykaki, A.; Stournaras, C.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V. Phosphorylated EGFR and PI3K/Akt signaling kinases are expressed in circulating tumor cells of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkaya, H.; Paulson, A.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Ginestier, C.; Brown, M.; Dutcher, J.; Clouthier, S.G.; Wicha, M.S. Regulation of mammary stem/progenitor cells by PTEN/Akt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wulfkuhle, J.; Zhang, H.; Gu, P.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Margolick, J.B.; Liotta, L.A.; Petricoin, E.; Zhang, Y. Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16158–16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Hoffmann, O.; Wallwiener, D.; Kimmig, R.; Fehm, T. Expression of stem cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in primary breast cancer patients with circulating tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, M.; Takeda, K. Enumeration, characterization, and collection of intact circulating tumor cells by cross contamination-free flow cytometry. Cytometry 2011, 79, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichsel, C.A.; Gobaa, S.; Kobel, S.; Secondini, C.; Thalmann, G.N.; Cecchini, M.G.; Lutolf, M.P. Diagnostic microchip to assay 3D colony-growth potential of captured circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2313–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.H.; Krause, S.; Tobin, H.; Mammoto, A.; Kanapathipillai, M.; Ingber, D.E. A combined micromagnetic-microfluidic device for rapid capture and culture of rare circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumor, C.; Williams, A.; Rawal, S.; Ao, Z.; Torres-munoz, J.; Balic, M.; Zhou, M. Clinical Translation of a Novel Microfilter Technology. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Point-of-Care Healthcare Technologies Meeting, Bangalore, India, 16–18 January 2013.
- Zhang, L.; Ridgway, L.D.; Wetzel, M.D.; Ngo, J.; Yin, W.; Kumar, D.; Goodman, J.C.; Groves, M.D.; Marchetti, D. The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Cavnar, S.P.; Walker, A.C.; Luker, K.E.; Gupta, M.; Tung, Y.-C.; Luker, G.D.; Takayama, S. Microfluidic endothelium for studying the intravascular adhesion of metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5756. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, S.; Son, S.; Amodei, D.; Cermak, N.; Shaw, J.; Ho, J.; Hecht, V.C. Characterizing deformability and surface friction of cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7580–7585. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.S.; Zervantonakis, I.K.; Chung, S.; Kamm, R.D.; Charest, J.L. In vitro model of tumor cell extravasation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e56910. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, M.; Reinhart-King, C.A.; Erickson, D. Elucidating mechanical transition effects of invading cancer cells with a subnucleus-scaled microfluidic serial dimensional modulation device. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Fan, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Gu, Z.; Damm, D.; Mosig, A.; Wei, X. Circulation times of prostate cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma cells by in vivo flow cytometry. Cytometry 2011, 79, 848–854. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.-C.; Yan, J.; Liu, G.-D.; Tan, X.-Y.; Weng, X.-F.; Wu, W.-Z.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.-B. Real-time monitoring of rare circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells in an orthotopic model by in vivo flow cytometry assesses resection on metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juratli, M.A.; Sarimollaoglu, M.; Siegel, E.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Galanzha, E.; Suen, J.Y.; Zharov, V.P. Real-time monitoring of circulating tumor-cell release during tumor manipulation using in vivo photoacoustic and fluorescent flow cytometry. Head Neck 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bäuerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circulating Tumor Cells TheRapeutic APheresis (CTCTRAP). Available online: http://www.utwente.nl/tnw/ctctrap/ (accessed on 1 September 13).
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Barradas, A.M.C.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Towards the Biological Understanding of CTC: Capture Technologies, Definitions and Potential to Create Metastasis. Cancers 2013, 5, 1619-1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers5041619
Barradas AMC, Terstappen LWMM. Towards the Biological Understanding of CTC: Capture Technologies, Definitions and Potential to Create Metastasis. Cancers. 2013; 5(4):1619-1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers5041619
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarradas, Ana M.C., and Leon W.M.M. Terstappen. 2013. "Towards the Biological Understanding of CTC: Capture Technologies, Definitions and Potential to Create Metastasis" Cancers 5, no. 4: 1619-1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers5041619
APA StyleBarradas, A. M. C., & Terstappen, L. W. M. M. (2013). Towards the Biological Understanding of CTC: Capture Technologies, Definitions and Potential to Create Metastasis. Cancers, 5(4), 1619-1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers5041619






