Canine Mammary Cancer Stem Cells are Radio- and Chemo- Resistant and Exhibit an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Tumorsphere Formation
2.2. Tumorsphere Forming Efficiency
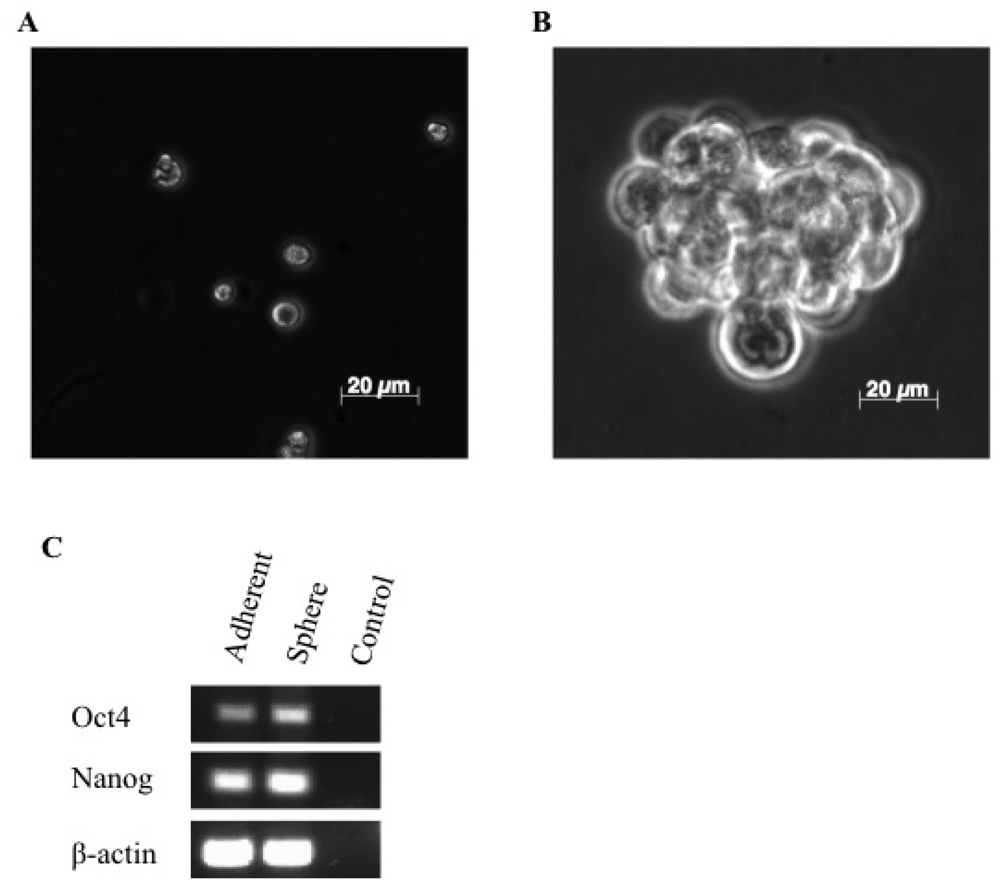
2.3. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription PCR Analysis
- Oct4 sense 5′-CTCTGCAGCCAATCAACCACAA-3′
- antisense 5′-GGAGAGGGGGATGAGAAGTACAAT-3′
- Nanog sense 5′-CTATAGAGGAGAGCACAGTGAAG-3′
- antisense 5′-GTTCGGATCTACTTTAGAGTGAGG-3′
- β-Actin sense 5′-CATGTTTGAGACCTTCAACACCC-3′
- antisense 5′-GCCATCTCTTGCTCGAAGTCCAG-3′
2.4. Irradiation and Drug Treatments of Cells
2.5. Protein Detection
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Invasion Assay
2.9. Wound-induced Migration Assay
2.10. Statistical analysis
3. Results
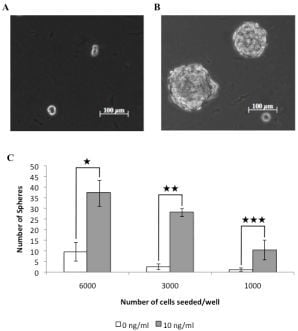
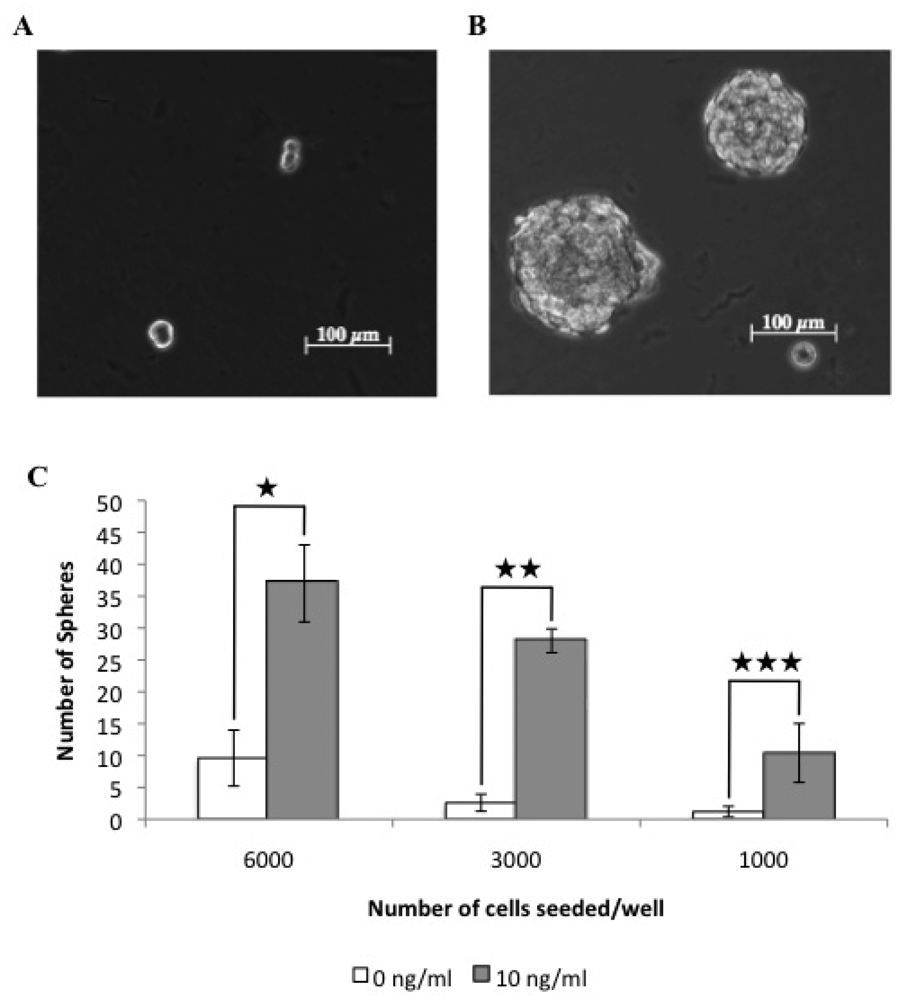
3.1. A Subpopulation of Canine Mammary Carcinoma Cells Have Tumorsphere-forming Capacity
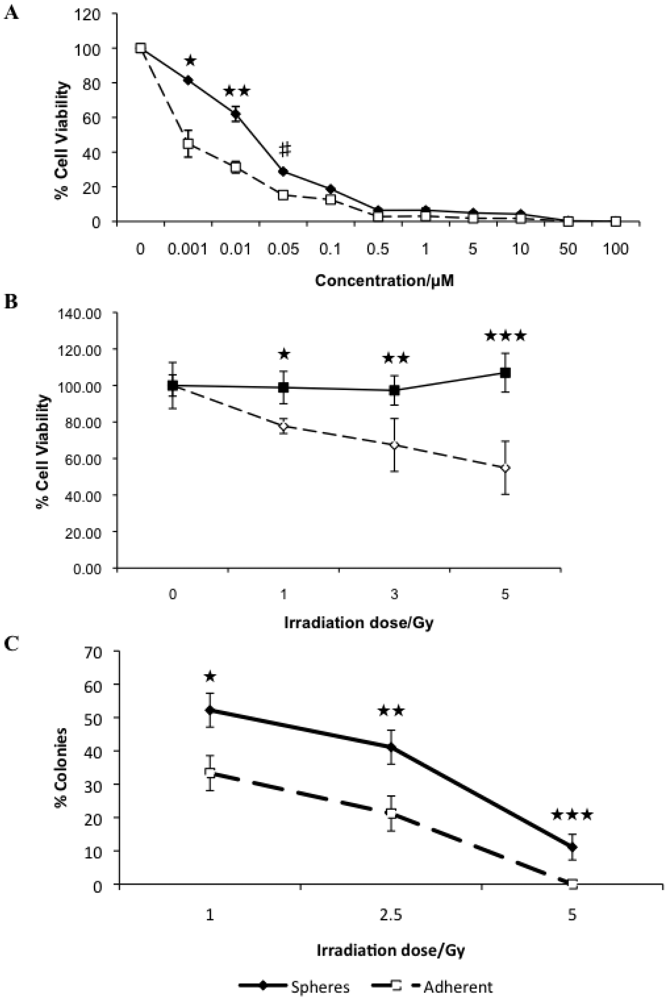
3.2. Canine Mammary Carcinoma Stem Cells Exhibit Greater Resistance to Chemo- and Radiation Therapy
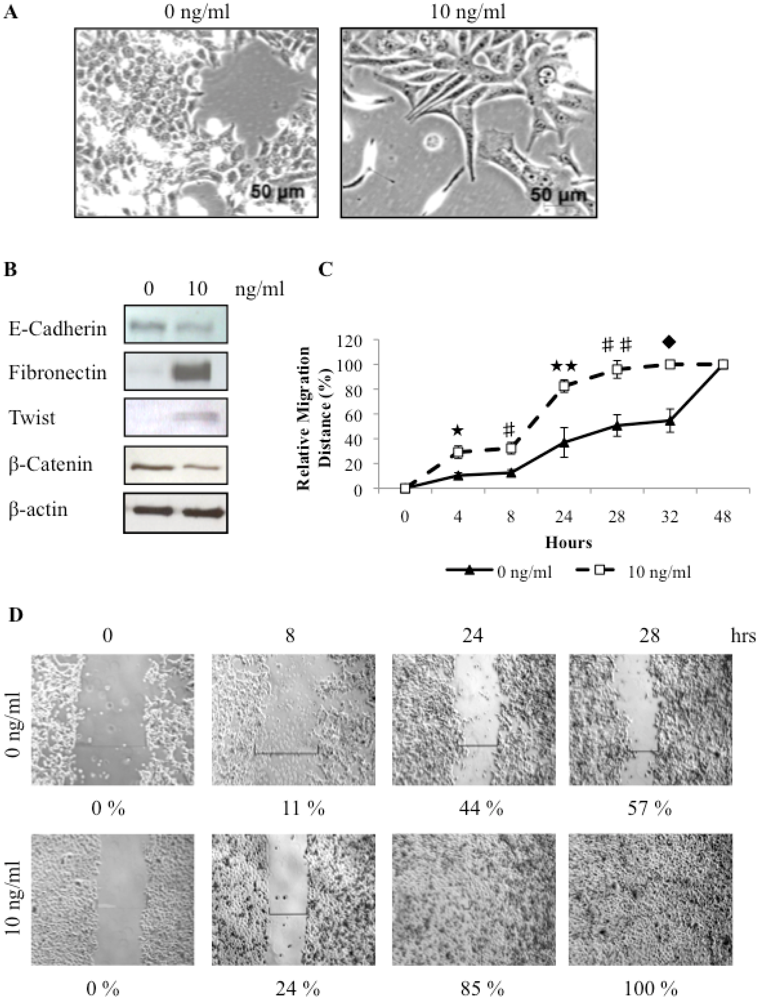
3.3. Tumorspheres Display Mesenchymal Features and are More Invasive
3.4. TGFβ Treatment of REM134 Cells Induces an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Enhances Tumorsphere Forming Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions

Acknowledgments
References
- Benjamin, S.A.; Lee, A.C.; Saunders, W.J. Classification and behavior of canine mammary epithelial neoplasms based on life-span observations in beagles. Vet. Pathol. 1999, 36, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fidler, I.J.; Brodey, R.S. The biological behavior of canine mammary neoplasms. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1967, 151, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Priester, W.A.; Mantel, N. Occurrence of tumors in domestic animals. Data from 12 united states and canadian colleges of veterinary medicine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1971, 47, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.; Reif, J.S.; Brodey, R.S.; Keiser, H. Epidemiological analysis of the most prevalent sites and types of canine neoplasia observed in a veterinary hospital. Cancer Res. 1974, 34, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Schneider, R.; Dorn, C.R.; Taylor, D.O. Factors influencing canine mammary cancer development and postsurgical survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1969, 43, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Moulton, J.E.; Rosenblatt, L.S.; Goldman, M. Mammary tumors in a colony of beagle dogs. Vet. Pathol. 1986, 23, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Clarke, M.F. Self-renewal and solid-tumor stem cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant 2005, 11, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Pang, L.Y.; Argyle, D.J. Using naturally occurring tumours in dogs and cats to study telomerase and cancer stem cell biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009, 1792, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Diehn, M.; Cho, R.W.; Lobo, N.A.; Kalisky, T.; Dorie, M.J.; Kulp, A.N.; Qian, D.; Lam, J.S.; Ailles, L.E.; Wong, M.; Joshua, B.; Kaplan, M.J.; Wapnir, I.; Dirbas, F.M.; Somlo, G.; Garberoglio, C.; Paz, B.; Shen, J.; Lau, S.K.; Quake, S.R.; Brown, J.M.; Weissman, I.L.; Clarke, M.F. Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature 2009, 458, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Diehn, M.; Clarke, M.F. Cancer stem cells and radiotherapy: New insights into tumor radioresistance. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fang, D.; Nguyen, T.K.; Leishear, K.; Finko, R.; Kulp, A.N.; Hotz, S.; Van Belle, P.A.; Xu, X.; Elder, D.E.; Herlyn, M. A tumorigenic subpopulation with stem cell properties in melanomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9328–9337. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Schatton, T.; Murphy, G.F.; Frank, N.Y.; Yamaura, K.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gasser, M.; Zhan, Q.; Jordan, S.; Duncan, L.M.; Weishaupt, C.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C.; Kupper, T.S.; Sayegh, M.H.; Frank, M.H. Identification of cells initiating human melanomas. Nature 2008, 451, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Terasaki, M.; Bonn, V.E.; Hawkins, C.; Squire, J.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bapat, S.A.; Mali, A.M.; Koppikar, C.B.; Kurrey, N.K. Stem and progenitor-like cells contribute to the aggressive behavior of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3025–3029. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Collins, A.T.; Berry, P.A.; Hyde, C.; Stower, M.J.; Maitland, N.J. Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10946–10951. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Eramo, A.; Lotti, F.; Sette, G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Di Virgilio, A.; Conticello, C.; Ruco, L.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wilson, H.; Huelsmeyer, M.; Chun, R.; Young, K.M.; Friedrichs, K.; Argyle, D.J. Isolation and characterisation of cancer stem cells from canine osteosarcoma. Vet J. 2008, 175, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. Emt, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Christiansen, J.J.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8319–8326. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Xia, W.; Cao, X.; Shih, J.Y.; Wei, Y.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of twist gene expression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bolos, V.; Peinado, H.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. The transcription factor slug represses e-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: A comparison with snail and e47 repressors. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wellner, U.; Schubert, J.; Burk, U.C.; Schmalhofer, O.; Zhu, F.; Sonntag, A.; Waldvogel, B.; Vannier, C.; Darling, D.; zur Hausen, A.; Brunton, V.G.; Morton, J.; Sansom, O.; Schuler, J.; Stemmler, M.P.; Herzberger, C.; Hopt, U.; Keck, T.; Brabletz, S.; Brabletz, T. The emt-activator zeb1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting micrornas. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; Campbell, L.L.; Polyak, K.; Brisken, C.; Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Morel, A.P.; Lievre, M.; Thomas, C.; Hinkal, G.; Ansieau, S.; Puisieux, A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2888. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Else, R.W.; Norval, M.; Neill, W.A. The characteristics of a canine mammary carcinoma cell line, rem 134. Br. J. Cancer 1982, 46, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Villa, A.; Snyder, E.Y.; Vescovi, A.; Martinez-Serrano, A. Establishment and properties of a growth factor-dependent, perpetual neural stem cell line from the human cns. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 161, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Pan, G.; Thomson, J.A. Nanog and transcriptional networks in embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Penzo, C.; Ross, M.; Muirhead, R.; Else, R.; Argyle, D.J. Effect of recombinant feline interferon-omega alone and in combination with chemotherapeutic agents on putative tumour-initiating cells and daughter cells derived from canine and feline mammary tumours. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2009, 7, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.M.; Dedhar, S.; Kalluri, R.; Thompson, E.W. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Khanna, C.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Vail, D.; London, C.; Bergman, P.; Barber, L.; Breen, M.; Kitchell, B.; McNeil, E.; Modiano, J.F.; Niemi, S.; Comstock, K.E.; Ostrander, E.; Westmoreland, S.; Withrow, S. The dog as a cancer model. Nat. Biotechnol 2006, 24, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Porrello, A.; Cardelli, P.; Spugnini, E.P. Oncology of companion animals as a model for humans. An overview of tumor histotypes. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 25, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lindblad-Toh, K.; Wade, C.M.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Karlsson, E.K.; Jaffe, D.B.; Kamal, M.; Clamp, M.; Chang, J.L.; Kulbokas, E.J., 3rd; Zody, M.C.; et al. Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog. Nature 2005, 438, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.; Smith, K.C.; Ostrander, E.A.; Galibert, F.; Breen, M. Chromosome aberrations in canine multicentric lymphomas detected with comparative genomic hybridisation and a panel of single locus probes. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Klopfleisch, R.; Lenze, D.; Hummel, M.; Gruber, A.D. Metastatic canine mammary carcinomas can be identified by a gene expression profile that partly overlaps with human breast cancer profiles. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 618. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Campeau, P.M.; Foulkes, W.D.; Tischkowitz, M.D. Hereditary breast cancer: New genetic developments, new therapeutic avenues. Hum. Genet. 2008, 124, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rivera, P.; Melin, M.; Biagi, T.; Fall, T.; Haggstrom, J.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; von Euler, H. Mammary tumor development in dogs is associated with brca1 and brca2. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8770–8774. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Pang, L.Y.; Argyle, D. Cancer stem cells and telomerase as potential biomarkers in veterinary oncology. Vet J. 2010, 185, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Locke, M.; Heywood, M.; Fawell, S.; Mackenzie, I.C. Retention of intrinsic stem cell hierarchies in carcinoma-derived cell lines. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8944–8950. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.G.; Patrawala, L.; Calhoun, T.; Bhatia, B.; Choy, G.; Schneider-Broussard, R.; Jeter, C. Prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells: Identification, characterization, and implications. Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chambers, I.; Colby, D.; Robertson, M.; Nichols, J.; Lee, S.; Tweedie, S.; Smith, A. Functional expression cloning of nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 2003, 113, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gidekel, S.; Pizov, G.; Bergman, Y.; Pikarsky, E. Oct-3/4 is a dose-dependent oncogenic fate determinant. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- NICE Early and locally advanced breast cancer: Diagnosis and treatment. Nice clinical guideline 80. Available online: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/12132/43314/43314.pdf (accessed on 04 November 2010).
- Argyle, D.J.; Brearley, M.J.; Turek, M.M. Decision Making in Small Animal Oncology; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, Iowa, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Withrow, S.J.; Vail, D.M. Withrow & Macewan's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 4th ed.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Alman, B.A. Side population cells in human cancers. Cancer Lett. 2008, 268, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, B.; Zhou, F.; Xiong, J.X.; Wu, H.S.; Tao, J.; Zhao, G.; Yang, M.; Gou, S.M. Persistence of side population cells with high drug efflux capacity in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2008, 14, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Francipane, M.G.; Alea, M.P.; Lombardo, Y.; Todaro, M.; Medema, J.P.; Stassi, G. Crucial role of interleukin-4 in the survival of colon cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4022–4025. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Todaro, M.; Alea, M.P.; Di Stefano, A.B.; Cammareri, P.; Vermeulen, L.; Iovino, F.; Tripodo, C.; Russo, A.; Gulotta, G.; Medema, J.P.; Stassi, G. Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Woodward, W.A.; Chen, M.S.; Behbod, F.; Alfaro, M.P.; Buchholz, T.A.; Rosen, J.M. Wnt/beta-catenin mediates radiation resistance of mouse mammary progenitor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Lee, T.K.; Zheng, B.J.; Chan, K.W.; Guan, X.Y. Cd133+ hcc cancer stem cells confer chemoresistance by preferential expression of the akt/pkb survival pathway. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.V.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, B.; Quinlan, M.P.; Takahashi, F.; Maheswaran, S.; McDermott, U.; Azizian, N.; Zou, L.; Fischbach, M.A.; Wong, K.K.; Brandstetter, K.; Wittner, B.; Ramaswamy, S.; Classon, M.; Settleman, J. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 2010, 141, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Witta, S.E.; Gemmill, R.M.; Hirsch, F.R.; Coldren, C.D.; Hedman, K.; Ravdel, L.; Helfrich, B.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Chan, D.C.; Sugita, M.; Chan, Z.; Baron, A.; Franklin, W.; Drabkin, H.A.; Girard, L.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. Restoring e-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Kudo-Saito, C.; Shirako, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Kawakami, Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during snail-induced emt of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lombaerts, M.; van Wezel, T.; Philippo, K.; Dierssen, J.W.; Zimmerman, R.M.; Oosting, J.; van Eijk, R.; Eilers, P.H.; van de Water, B.; Cornelisse, C.J.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M. E-cadherin transcriptional downregulation by promoter methylation but not mutation is related to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Mani, S.A.; Donaher, J.L.; Ramaswamy, S.; Itzykson, R.A.; Come, C.; Savagner, P.; Gitelman, I.; Richardson, A.; Weinberg, R.A. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 2004, 117, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bankfalvi, A.; Terpe, H.J.; Breukelmann, D.; Bier, B.; Rempe, D.; Pschadka, G.; Krech, R.; Lelle, R.J.; Boecker, W. Immunophenotypic and prognostic analysis of e-cadherin and beta-catenin expression during breast carcinogenesis and tumour progression: A comparative study with cd44. Histopathology 1999, 34, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Park, D.; Karesen, R.; Axcrona, U.; Noren, T.; Sauer, T. Expression pattern of adhesion molecules (e-cadherin, alpha-, beta-, gamma-catenin and claudin-7), their influence on survival in primary breast carcinoma, and their corresponding axillary lymph node metastasis. APMIS 2007, 115, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dalerba, P.; Cho, R.W.; Clarke, M.F. Cancer stem cells: Models and concepts. Annu. Rev. Med. 2007, 58, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Winquist, R.J.; Boucher, D.M.; Wood, M.; Furey, B.F. Targeting cancer stem cells for more effective therapies: Taking out cancer's locomotive engine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, L.Y.; Cervantes-Arias, A.; Else, R.W.; Argyle, D.J. Canine Mammary Cancer Stem Cells are Radio- and Chemo- Resistant and Exhibit an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype. Cancers 2011, 3, 1744-1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3021744
Pang LY, Cervantes-Arias A, Else RW, Argyle DJ. Canine Mammary Cancer Stem Cells are Radio- and Chemo- Resistant and Exhibit an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype. Cancers. 2011; 3(2):1744-1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3021744
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Lisa Y., Alejandro Cervantes-Arias, Rod W. Else, and David J. Argyle. 2011. "Canine Mammary Cancer Stem Cells are Radio- and Chemo- Resistant and Exhibit an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype" Cancers 3, no. 2: 1744-1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3021744
APA StylePang, L. Y., Cervantes-Arias, A., Else, R. W., & Argyle, D. J. (2011). Canine Mammary Cancer Stem Cells are Radio- and Chemo- Resistant and Exhibit an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype. Cancers, 3(2), 1744-1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3021744