CDDO-Me: A Novel Synthetic Triterpenoid for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CDDO-Me Inhibits the Growth of Pancreatic Carcinoma Cells
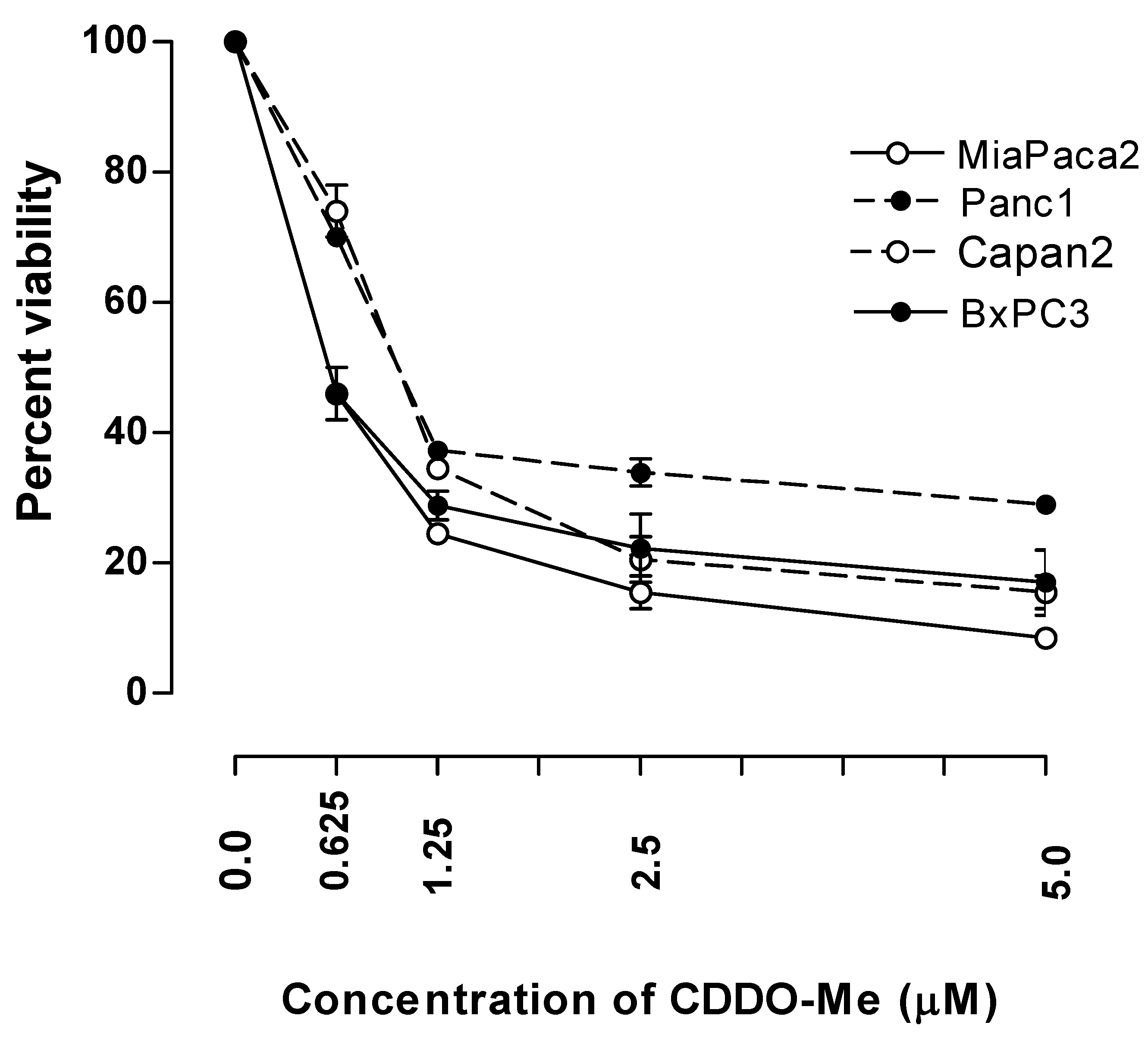
2.2. CDDO-Me Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
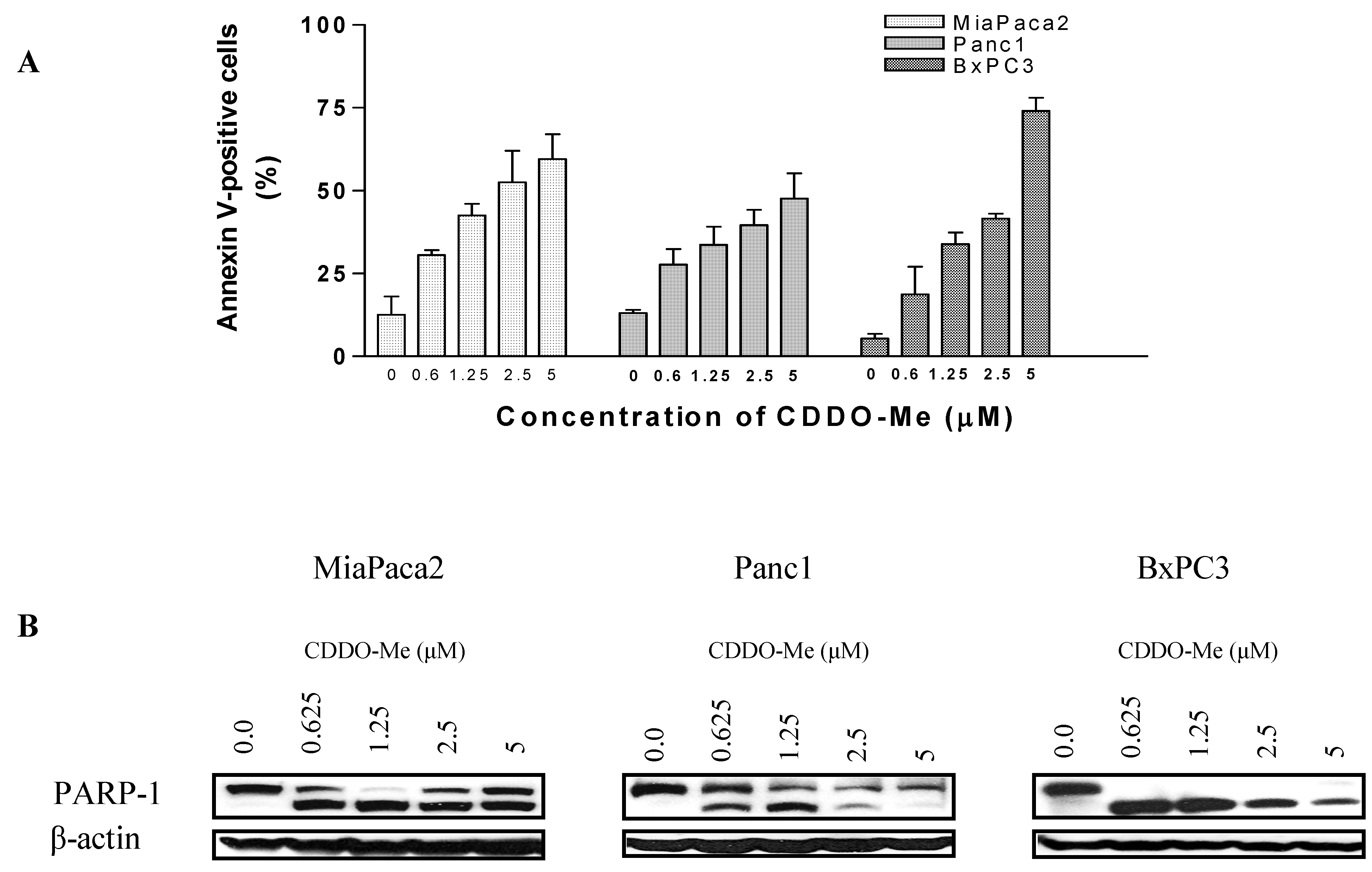
2.3. CDDO-Me Induces Cleavage of Procaspases, Mitochondrial Depolarization and Release of Cytochrome C
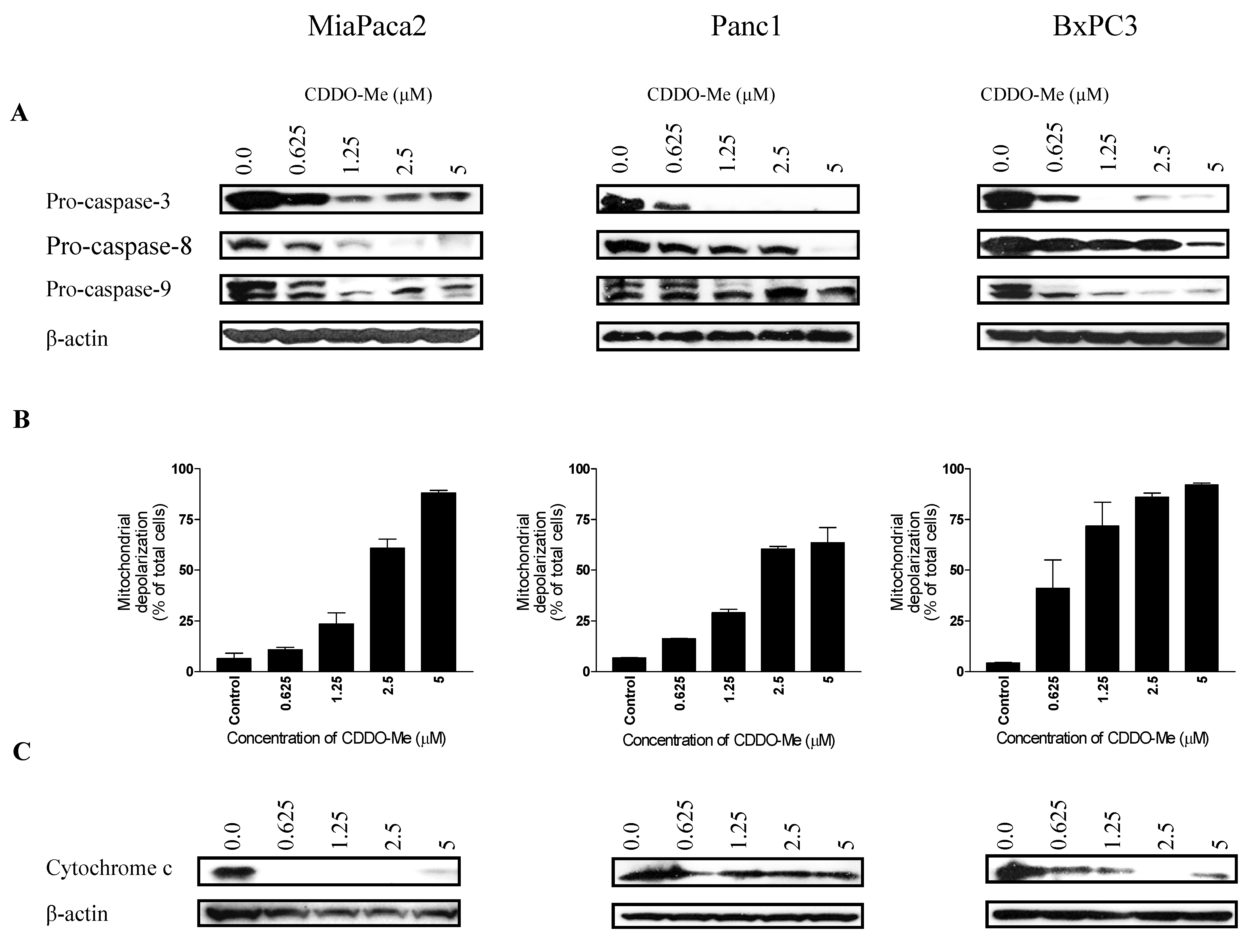
2.4. CDDO-Me Inhibits Akt, NF-κB and mTOR and Downstream Signaling Proteins
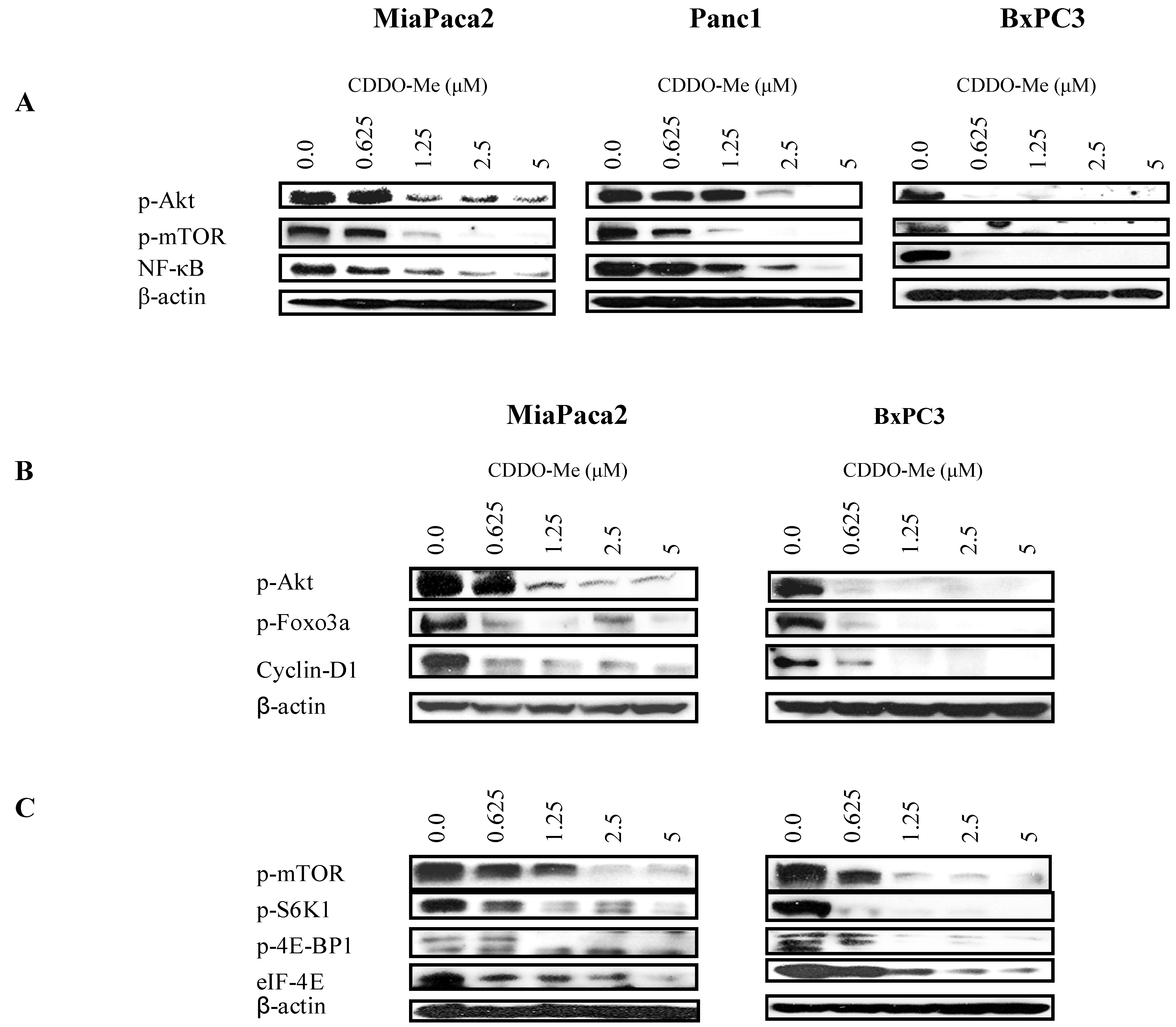
2.5. Akt and mTOR Are Relevant Targets of CDDO-Me
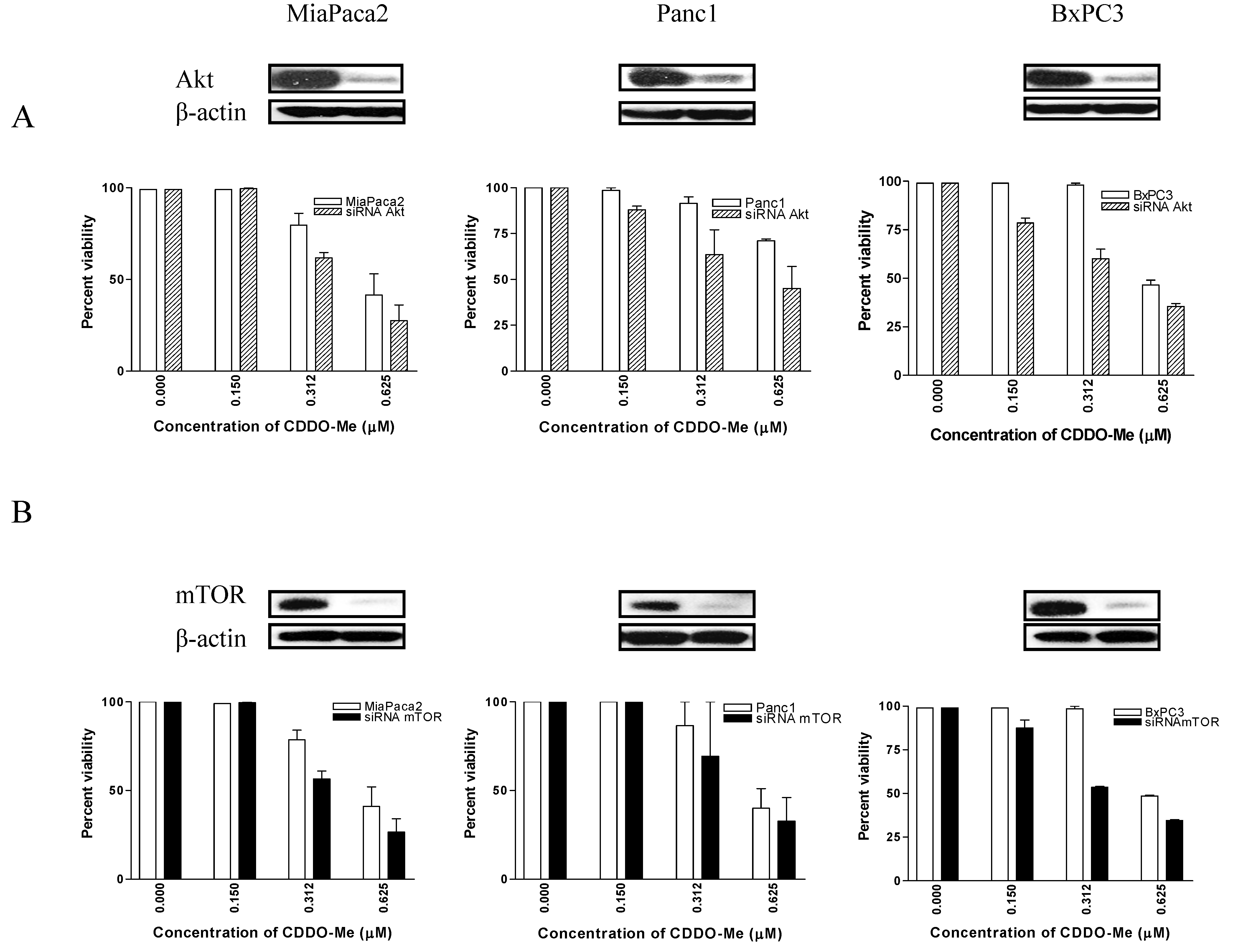
2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Cell Lines
3.3. MTS Assay
3.4. Apoptosis Assay
3.5. Mitochondrial Depolarization Assay
3.6. Western Blotting
3.7. DNA Transfection
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Murray, T.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statitics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008, 58, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute; U.S. National Institutes of Health; Cancer.gov. Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: http:www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/pancreatic (accessed on 4 June 2010).
- Maitra, A.; Hruban, R.H. Pancreatic cancer. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, K.; Wolff, R.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004, 363, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, M.F.; Wahl, A.O.; Small, W., Jr. The current status of combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced or resected pancreas cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Netw. 2005, 3, 637–642. [Google Scholar]
- Pino, S.M.; Xiong, H.Q.; McConkey, D.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Novel therapies for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 6, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzubak, P.; Hajduch, M.; Vydra, D.; Hustova, A.; Kvasnica, M.; Biedermann, D.; Markova, L.; Urban, M.; Sarek, J. Pharmacological activities of natural triterpenoids and therapeutic implications. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 394–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.T.; Ho, C.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ferraro, T.; Lou, Y.R.; Stauber, K.; Ma, W.; Georgiadis, C.; Laskin, J.D.; Conney, A.H. Inhibition of skin tumorigenesis by rosemary and its constituents carnosol and ursolic acid. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, H.; Nishino, A.; Takayasu, J.; Hasegawa, T.; Iwashima, A.; Hirabayashi, K.; Iwata, S.; Shibata, S. Inhibition of the tumor-promoting action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-accetate by some oleanane-type triterpenoid compounds. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 5210–5215. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, T.; Rounds, B.V.; Gribble, G.W.; Suh, N.; Wang, Y.; Sporn, M.B. Design and synthesis of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid, a novel and highly active inhibitor of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages. Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 2711–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.; Honda, T.; Finlay, H.J.; Barchowsky, A.; Williams, C.; Benoit, N.E.; Xie, Q.W.; Nathan, C.; Gribble, G.W.; Sporn, M.B. Triterpenoids suppress inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and inducible cyclooxigenase (COX-2) in mouse macrophages. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Deeb, D.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Dulchavsky, S.; Gautam, S. Synthetic triterpenoids inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in human glioblastoma and neuroblastoma cells through inhibition of prosurvival Akt, NF-kB and Notch1 signaling. J. Neurooncol. 2007, 84, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopleva, M.; Tsao, T.; Ruvolo, P.; Stiouf, I.; Estrov, Z.; Leysath, C.E.; Zhao, S.; Harris, D.; Chang, S.; Jackson, C.E.; Munsell, M.; Suh, N.; Gribble, G.; Honda, T.; May, W.S.; Sporn, M.B.; Andreeff, M. Novel triterpenoid CDDO-Me is a potent inducer of apoptosis and differentiation in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishodia, S.; Sethi, G.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. A synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO-Me, inhibits IkappaBalpha kinase and enhances apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents through down-regulation of expression of nuclear factor kappaB-regulated gene products in human leukemic cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.E.; Suh, N.; Williams, C.R.; Risingsong, R.; Honda, T.; Honda, Y.; Gribble, G.W.; Leesnitzer, L.M.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Rosen, E.; Sporn, M.B. The novel synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO-imidazolide, inhibits inflammatory response and tumor growth in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar]
- Liby, K.; Royce, D.B.; Williams, C.R.; Risingsong, R.; Yore, M.M.; Honda, T.; Gribble, G.W,; Dmitrovsky, E.; Sporn, T.A,; Sporan, M.B. The synthetic triterpenoid CDDO-methyl ester and CDDO-amide prevent lung cancer induced by vinyl carbomate in A/J mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2414–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopleva, M.; Tsao, T.; Estrov, Z.; Lee, R.M.; Wang, R.Y.; Jackson, C.E.; McQueen, T.; Monaco, G.; Munsell, M.; Belmont, J.; Kantarjian, H.; Sporn, M.B.; Andreeff, M. The synthetic triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid induces caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7927–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Pandey, P.; Sporn, M.B; Datta, R.; Kharbanda, S.; Kufe, D. The novel triterpenoid CDDO induces apoptosis and differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by a caspase-8 dependent mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Konopleva, M.; Contractor, R.; Kurinna, S.M.; Chen, W.; Andreeff, M.; Ruvolo, P.P. The novel triterpenoid CDDO-Me suppresses MAPK pathways and promotes p38 activation in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.; Roberts, A.B.; Birkey Reffey, S.; Miyazono, K.; Itoh, S.; ten Dijke, P.; Heiss, E.H.; Place, A.E.; Risingsong, R.; Williams, C.R.; Honda, T.; Gribble, G.W.; Sporn, M.B. Synthetic triterpenoids enhance transforming growth factor beta/Smad signaling. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Deeb, D.; Gao, X.; Dulchavsky, S.A.; Gautam, S.C. CDDO-Me induces apoptosis and inhibits Akt, mTOR and NF-κB in prostate cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar]
- Deeb, D.; Gao, X.; Jiang, H.; Dulchavsky, S.A.; Gautam, S.C. Oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by independently targeting pro-survival Akt and mTOR. Prostate 2009, 69, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudio, I.; Konopleva, M.; Hail, N., Jr.; Shi, Y-X.; McQueen, T.; Hsu, T.; Evans, R.; Honda, T.; Gribble, G.W.; Sporn, M.; Gilbert, H.F.; Safe, S.; Andreeff, M. 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-imidazolide (CDDO-Im) directly targets mitochondrial glutathione to induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36273–36282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X-M.; MacFarlane, M.; Zhuang, J.; Wolf, B.B.; Green, D.R.; Cohen, G.M. Distinct caspase cascades are initiated in receptor-mediated and chemical-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5053–5060. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Dixit, V.M. Death receptors: Signaling and modulation. Science 1998, 281, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, D.A.; Testa, J.R. Perturbations of the Akt signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsti, M.A.; Houghton, P.J. The TOR pathway; a target for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.R.; Dudek, H.; Tao, X.; Masters, S.; Fu, H.; Gotoh, Y.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt phosphorylation of Bad couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 1997, 91, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Bonni, A.; Zigmond, M.J.; Lin, M.Z.; Juo, P.; Hu, L.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Arden, K.C.; Blenis, J.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999, 96, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, F.; Cardelli, J.A.; Martin, K.A.; Blenis, J.; Huang, S. Rapamycin inhibits cell motility by suppression of mTOR-mediated S6K1 and 4E-BP1 pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7029–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Figures
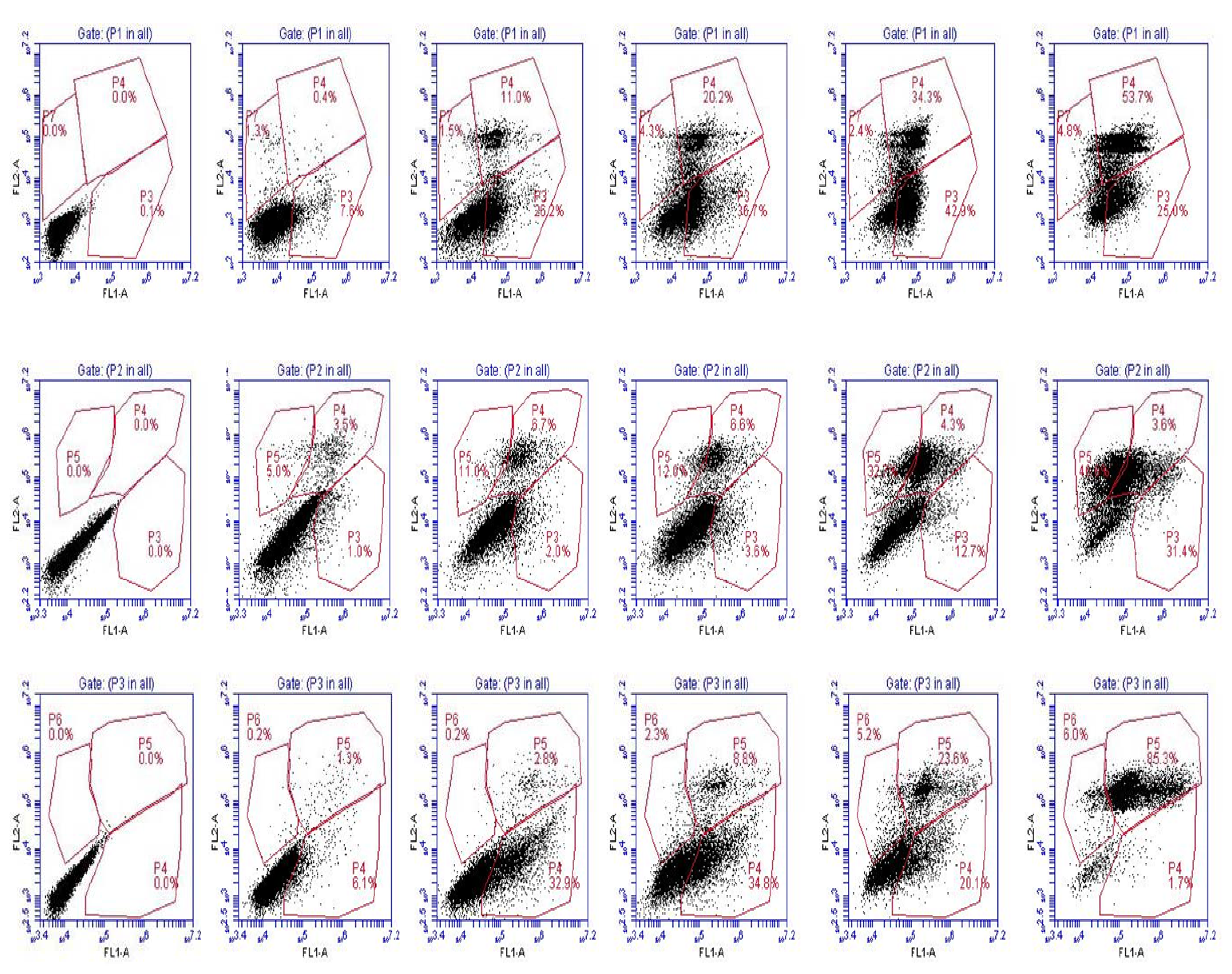
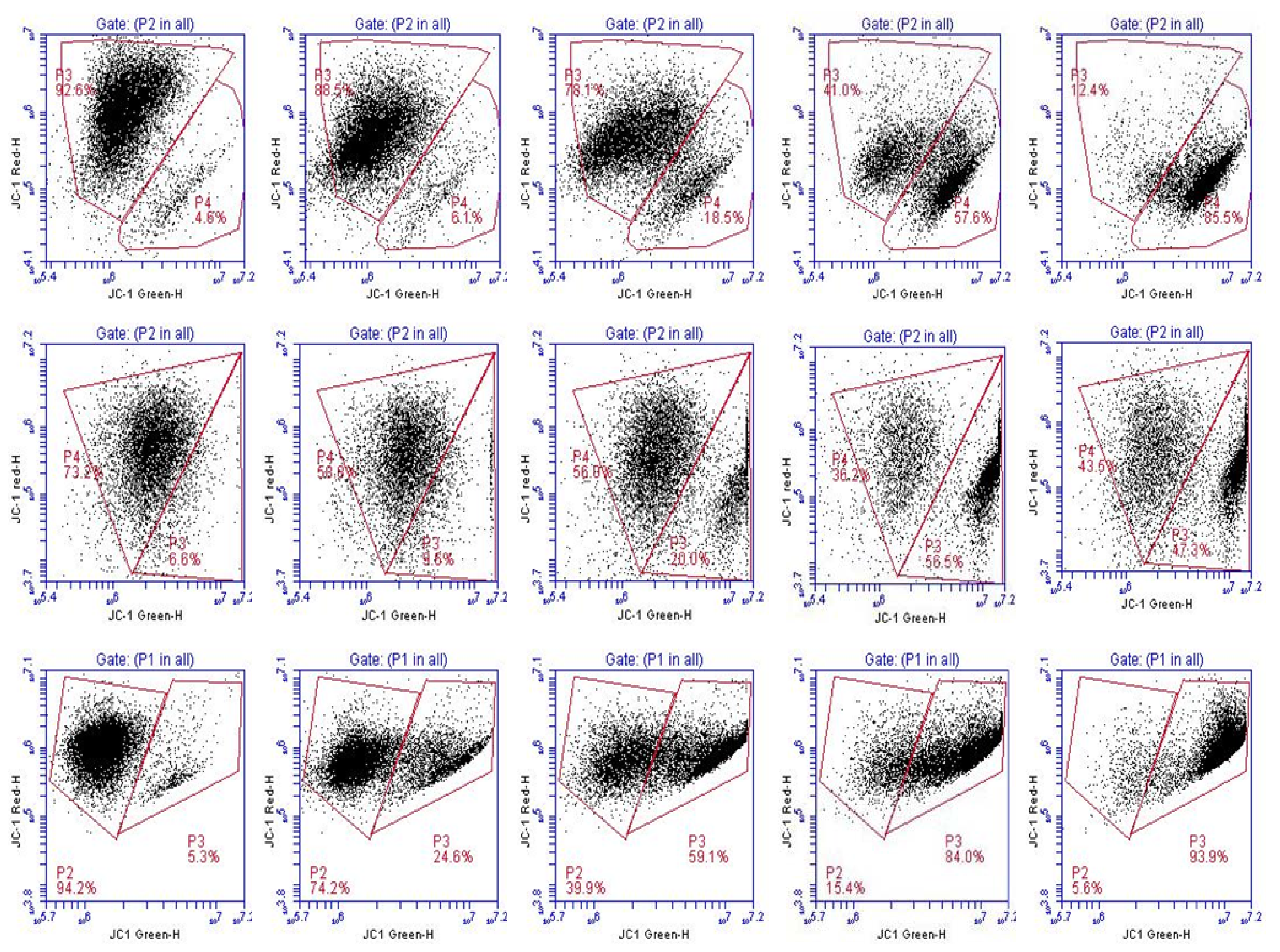
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Deeb, D.; Gao, X.; Arbab, A.S.; Barton, K.; Dulchavsky, S.A.; Gautam, S.C. CDDO-Me: A Novel Synthetic Triterpenoid for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 1779-1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2041779
Deeb D, Gao X, Arbab AS, Barton K, Dulchavsky SA, Gautam SC. CDDO-Me: A Novel Synthetic Triterpenoid for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2010; 2(4):1779-1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2041779
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeeb, Dorrah, Xiaohua Gao, Ali S. Arbab, Kenneth Barton, Scott A. Dulchavsky, and Subhash C. Gautam. 2010. "CDDO-Me: A Novel Synthetic Triterpenoid for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 2, no. 4: 1779-1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2041779
APA StyleDeeb, D., Gao, X., Arbab, A. S., Barton, K., Dulchavsky, S. A., & Gautam, S. C. (2010). CDDO-Me: A Novel Synthetic Triterpenoid for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 2(4), 1779-1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2041779



