The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist L-732,138 Induces Apoptosis and Counteracts Substance P-Related Mitogenesis in Human Melanoma Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Drug Treatments
2.3. Proliferation Assays
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. DAPI Staining
3. Results
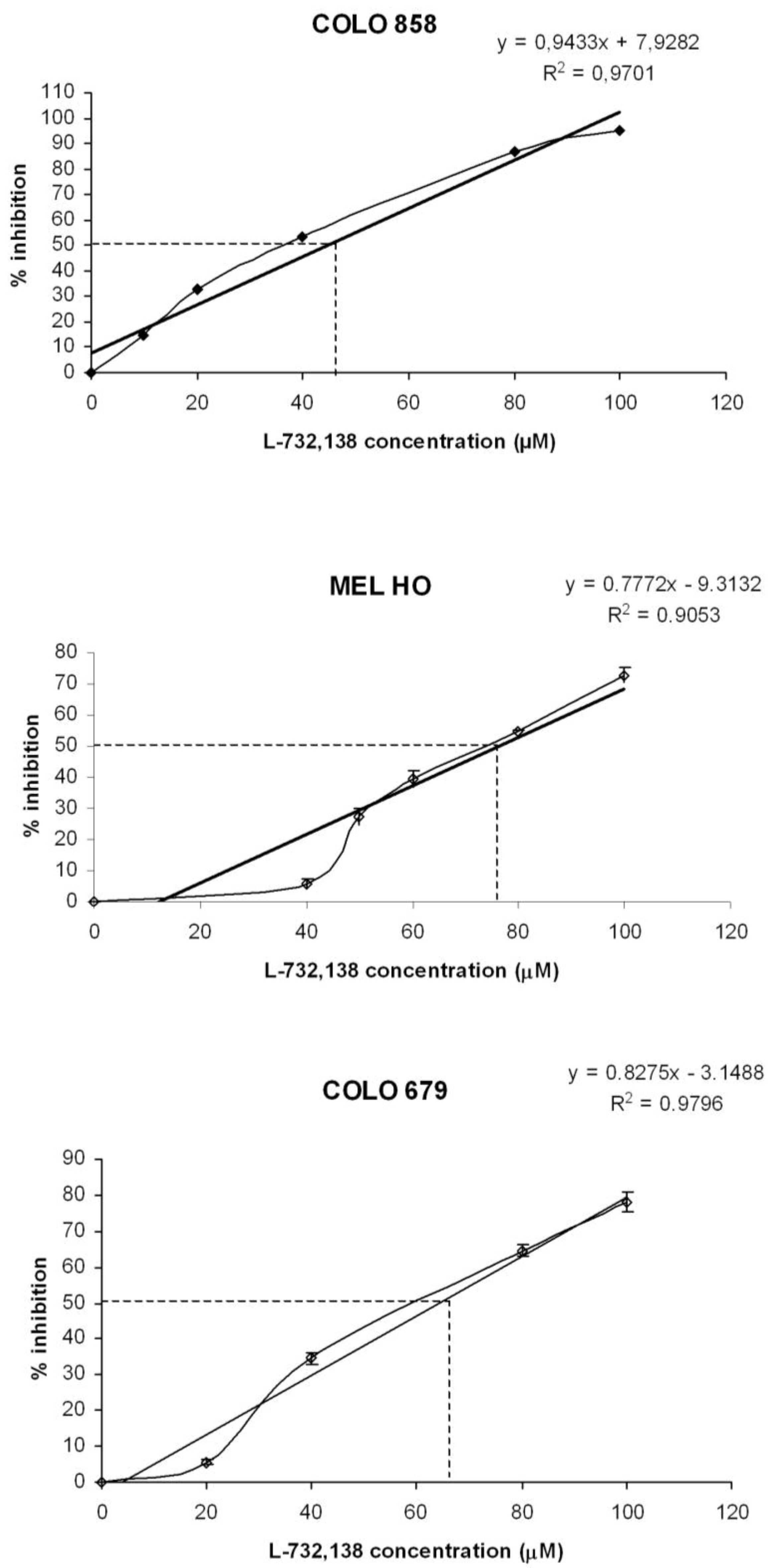
3.1. Antitumor Action of L-732,138
| Melanoma cell line | L-732,138 | |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 μM | IC100 μM | |
| COLO 858 | 44.6 | 97.6 |
| MEL-H0 | 76.3 | 140.6 |
| COLO 679 | 64.2 | 124.7 |
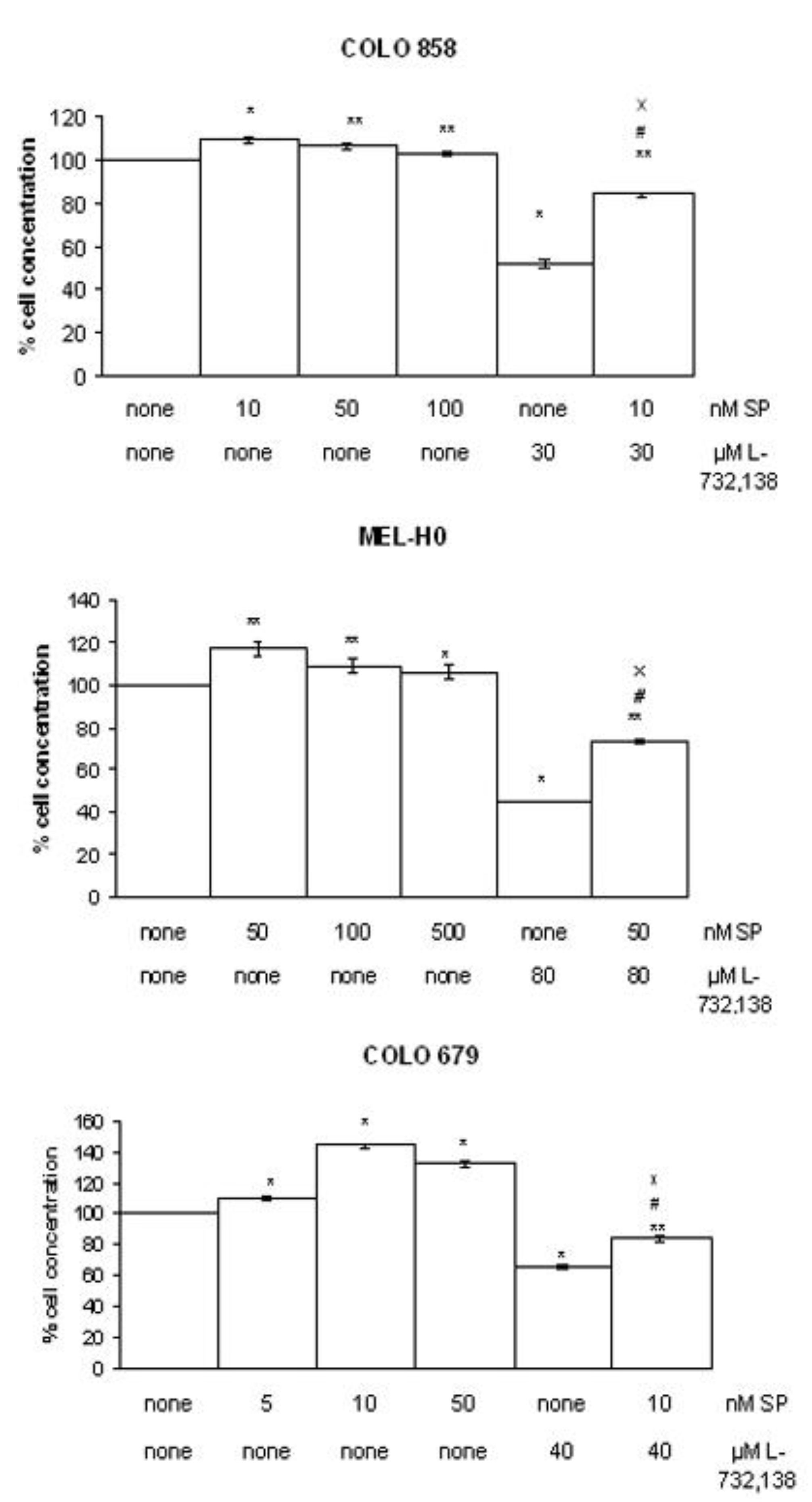
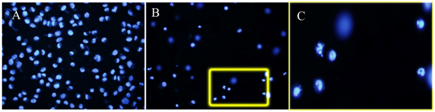
3.2. Apoptosis

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Desantis, C.; Siogel, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer Facts and Figures 2007-2008; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt, T.; Pernow, B.; Wahren, J. Substance P: a pioneer amongst neuropeptides. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 249, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Seckl, M.J.; Higgins, T.; Wildmer, F.; Rozengurt, E. [D-Arg1, D-Trp5,7,9, Leu11] Substance P: a novel potent inhibitor of signal transduction and growth in vitro and in vivo in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, S.; Geppetti, P. Substance P. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 33, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. A new frontier in the treatment of cancer: NK-1 receptor antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Robles-Frías, M.J.; Coveñas, R.; Salinas-Martín, M.V. Immunolocalization of the neurokinin-1 receptor: a new target in the treatment of the human primary retinoblastoma. In Eye Cancer Research Progress; Bospene, E.B., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 157–178. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, V.K.; Albino, A.P.; Reed, J.A. The neuropeptide/mast cell secretagogue substance P is expressed in cutaneus melanocytic lesions. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1998, 25, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Robles-Frías, M.J.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Rosso, R.; González, A.; Coveñas, R. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human melanoma and is involved in the antitumor action of the NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant on melanoma cell lines. Lab. Invest. 2010, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Pérez, A.; Rosso, M.; Zamarriego, C.; Rosso, R. Antitumoural action of NK-1 receptor antagonist L-733,060 on human melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res. 2004, 14, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Pérez, A.; Coveñas, R.; Rosso, M.; Castro, E. Antitumoural action of L-733,060 on neuroblastoma and glioma cell lines. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2004, 142, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, F.; Muñoz, M.; González-Moles, M.A.; Rosso, M. A role for substance P in cancer promotion and progression: a mechanism to counteract intracellular death signals following oncogene activation or DNA damage. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2006, 25, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Sharif, T.R.; Sharif, M. Substance P-induced mitogenesis in human astrocytoma cells correlates with activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 1995, 56, 4983–4991. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, C.; Nardelli, F.; Manzini, S.; Maggi, C.A. Substance P activates responses correlated with tumor growth in human glioma cells line bearing tachykinin NK-1 receptors. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Pérez, A.; Coveñas, R.; Zamarriego, C.; Piruat, J.I. The NK-1 receptor is involved in the antitumoural action of L-733,060 and in the mitogenic action of substance P on neuroblastoma and glioma cell lines. Neuropeptides 2005, 39, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Pérez, A.; Coveñas, R.; Rosso, R.; Zamarriego, C:; Soult, J.A.; Montero, I. Antitumoural action of the neurokinin-1- receptor antagonist L-733,060 and mitogenic action of substance P on human retinoblastoma cell lines. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2567–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. The NK-1 receptor is involved in the antitumoural action of L-733,060 and in the mitogenic action of substance P on human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2006, 3, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R.; Soult, J.A. Antitumoural action of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists on human brain cancer cell lines. In Brain Cancer: Therapy and Surgical Intervention; Yang, A.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 45–75. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. NK-1 receptor antagonists as new anti-tumoural agents: action on human neuroblastoma cell lines. In Focus on Neuroblastoma Research; Fernandes, J.A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Aguilar, F.J.; González-Moles, M.A.; Redondo, M.; Esteban, F. NK-1 receptor antagonists induce apoptosis and counteract substance P-related mitogenesis in human laryngeal cancer cell line HEp-2. Investig. New Drugs 2008, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Robles-Frías, M.J.; Coveñas, R.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Muñoz, M. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human primary gastric and colon adenocarcinomas and is involved in the antitumor action of L-733,060 and the mitogenic action of substance P on human gastrointestinal cancer cell lines. Tumor Biol. 2008, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Pacini, M.; Geppetti, P.; Alessandri, G.; Maggi, C.A. Substance P stimulates neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of cultured endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 1990, 40, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.; Drell, T.L.; Lindecke, A.; Niggemann, B.; Kaltschmidt, C; Zaenker, K.S.; Entschladen, F. Induction of a metastatogenic tumor cell type by neurotransmitters and its pharmacological inhibition by established drugs. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.; Willians, B.J.; Swain, C.J.; Ball, R.G. Piperidine-ether based hNK1 antagonists 1: determination of the relative and absolute stereochemical requirements. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M. The NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant as a broad spectrum antitumor drug. Invest. New Drugs 2010, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.M.; Merchant, K.J.; Brookfield, F.; Kelleher, F.; Stevenson, G.; Owens, A.P.; Swain, C.J.; Cascieri, M.A.; Sadowski, S.; Ber, E.; Strader, C.D.; Fong, T.M. Identification of L-tryptophan derivatives with potent and selective antagonist activity at the NK1 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, C.M.; Coderre, T.J. Attenuation of hyperalgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain after intrathecal pre- or post-treatment with a neurokinin-1 antagonist. Pain 2002, 95, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.A.; Fujii, Y.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kayasuga, R.; Kamei, C. Histamine H3 receptors regulate vascular permeability changes in the skin of mast cell-deficient mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M., Rosso; Montero, I.; González-Moles, M.A.; Robles, M.J. Neurokinin-1 receptors located in human retinoblastoma cell lines: antitumor action of its antagonist, L-732,138. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Reeve, J.G.; Bleehen, N.M. [D-Arg1-D-Phe5, D-Trp7,9, Leu11] Substance P induces apoptosis in lung cancer cell lines in vitro. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Com. 1994, 199, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, C.; Bigioni, M.; Irrissuto, C.; Nardelli, F.; Maggi, C.A.; Manzini, S. Anti-tumor activity of tachykinin Nk1 receptor antagonists on human glioma U373 MG xenograft. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigioni, M.; Benzo, A.; Irrissuto, C.; Maggi, C.A.; Goso, C. Role of NK-1 and NK-2 tachykinin receptor antagonism on the growth of human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231. Anticancer Drugs 2005, 16, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, I.M.; Laissue, J.A.; Horisberger, U.; Reubi, J.C. Substance-P receptors in human primary neoplasms: tumoral and vascular localization. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liard, V.; Shi, X.; Shrikhande, S.V.; Wang, L.; Lieb, K.; Korc, M.; Palma, C.; Zimmermann, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Buchler, M.W. Neurokinin-1 receptor expression and its potential effects on tumor growth in human pancreatic cancer. Lab. Invest. 2003, 83, 731–742. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Joshi, D.D.; Hameed, M.; Qian, J.; Gascon, P.; Maloof, P.B.; Mosenthal, A.; Rameshwar, P. Increased expression of preprotachykinin-I and neurokinin receptors in human breast cancer cells: Implications for bone marrow metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, F.; González-Moles, M.A.; Castro, D.; Martín-Jaén, M.M.; Redondo, M.; Ruiz-Avila, I.; Muñoz, M. Expression of substance P and neurokinin-1-receptor in laryngeal cancer: linking chronic inflammation to cancer promotion and progression. Histopathology 2009, 54, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Stumm, R.; Röcken, C.; Mawrin, C.; Schulz, S. Immunolocalization of full-length NK1 tachykinin receptors in human tumors. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, V.K.; Albino, A.P.; Reed, J.A. The neuropeptide/mast cell secretagogue substance P is expressed in cutaneous melanocytic lesions. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1998, 25, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.P.; Hu, D.E.; Guard, S.; Gresham, G.A.; Watling, K.J. Stimulation of angiogenesis by substance P an interleukin-1 in the rat and its inhibition by NK-1 or interleukin-1 receptor antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.A.; Hu, D.E.; Mapp, P.I.; Polak, J.M.; Blake, D.R.; Fan, T.P. Innervation and neurokinin receptors during angiogenesis in the rat sponge granuloma. Histochem. J. 1996, 28, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, H.C.; Hood, V.C.; Kidd, B.L.; Cruwys, S.C.; Walsh, D.A. Enhancement of angiogenesis by endogenous substance P release and neurokinin-1 receptors during neurogenic inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Eibl, G.; Kisfalvi, K.; Fan, R.S.; Burdick, M.; Reber, H.; Hines, O.J.; Strieter, R.; Rozengurt, E. Broad-spectrum G protein–coupled receptor antagonist, [D-Arg1, DTrp5,7,9, Leu11]SP: a dual inhibitor of growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2738–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S; Cutler, N.; Feighner, J.; Shrivastava, R.; Carman, J.; Sramek, J.J.; Reines, S.A.; Liu, G.; Snavely, D.; Wyatt-Knowles, E.; Hale, J.J.; Mills, S.G.; MacCoss, M; Swain, C.J.; Harrison, T.; Hill, R.G.; Hefti, F.; Scolnick, E.M.; Cascieri, M.A.; Chicchi, G.G.; Sadowski, S.; Williams, A.R.; Hewson, L.; Smith, D.; Carlsson, E.J.; Hargreaves, R.J.; Rupniak, N.M. Distinct mechanism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central substance P receptors. Science 1998, 81, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, R.; Sass, G.; Kiemer, A.K.; Vollmar, A.M.; Neuhuber, W.L.; Tiegs, G. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists CP-96,345 and L-733,060 protect mice from cytokine-mediated liver injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupniak, N.M.; Carlson, E.; Boyce, S.; Webb, J.K.; Hill, R.G. Enantioselective inhibition of the formalin paw late phase by the NK1 receptor antagonist L-733,060 in gerbils. Pain 1996, 67, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varty, G.B.; Cohen-Williams, M.E.; Morgan, C.A.; Pylak, U.; Duffy, R.A.; Lachowicz, J.E.; Carey, G.J.; Coffin, V.L. The gerbil elevated plus-maze II: anxiolytic-like effects of selective neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 27, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, F.D.; Rycroft, W.; Cumberbatch, M.; Mason, G.; Tye, S.; Williamson, D.J.; Hale, J.J.; Mills, S.G.; Finke, P.E.; MacCoss, M.; Sadowski, S.; Ber, E.; Cascieri, M.; Hill, R.G.; MacIntyre, D.E.; Hargreaves, R.J. The novel NK-1 receptor antagonist MK-0869 (L-754,030) and its water soluble phosphoryl prodrug, L-758,298, inhibit acute and delayed cisplatin-induced emesis in ferrets. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cadet, J.L.; Angulo, J.A. Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor antagonists abrogate methamphetamine-induced striatal dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the murine brain. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; González-Ortega, A.; Coveñas, R. The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist L-732,138 Induces Apoptosis and Counteracts Substance P-Related Mitogenesis in Human Melanoma Cell Lines. Cancers 2010, 2, 611-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020611
Muñoz M, Rosso M, González-Ortega A, Coveñas R. The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist L-732,138 Induces Apoptosis and Counteracts Substance P-Related Mitogenesis in Human Melanoma Cell Lines. Cancers. 2010; 2(2):611-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020611
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz, Miguel, Marisa Rosso, Ana González-Ortega, and Rafael Coveñas. 2010. "The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist L-732,138 Induces Apoptosis and Counteracts Substance P-Related Mitogenesis in Human Melanoma Cell Lines" Cancers 2, no. 2: 611-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020611
APA StyleMuñoz, M., Rosso, M., González-Ortega, A., & Coveñas, R. (2010). The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist L-732,138 Induces Apoptosis and Counteracts Substance P-Related Mitogenesis in Human Melanoma Cell Lines. Cancers, 2(2), 611-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020611