Markers for Detection of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Scope of the Review
3. Sources for Biomarker Analyses
3.1. Post-Prostatic Massage Urine
3.2. Ejaculate
4. Identifying Discriminating Markers
5. Assay Approaches & Most Promising Markers
5.1. Markers of Detection versus Prognosis
6. Comments on Selected Genetic Markers
| Variable | Coefficient | P |
|---|---|---|
| Univariate logistic regression analysis | ||
| GOLPH2 | 0.4444 | 0.0002 |
| SPINK1 | 0.25 | 0.0002 |
| PCA3 | 0.187 | 0.001 |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 0.609 | 0.034 |
| ERG | 0.043 | 0.166 |
| TFF3 | 0.11 | 0.189 |
| PSA (serum) | 0.0151 | 0.376 |
| AMACR | 0.049 | 0.45 |
| Multivariate logistic regression analysis | ||
| SPINK1 | 0.308 | 7.41E-05 |
| PCA3 | 0.191 | 0.003 |
| GOLPH2 | 0.372 | 0.004 |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 0.924 | 0.006 |
| Symbol | Description | Type of marker | Ref. | Body Fluid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA | RNA | Protein | Metabolite | ||||
| 8-OhdG | 8- HydroxydeoxyguanosineU | + | + | [58] | U | ||
| ANXA3 | Annexin A3 | + | [59,60,61,62] | PD | |||
| BHUAE | Basic human urinary arginine amidase | + | [63] | U | |||
| F3 | Coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) | + | [64] | U | |||
| GSTP1 | Glutathione S-transferase P 1 | + | [65,66,67,68,69] | PM | |||
| LOH | Loss of heterozygosity e.g., loss of PTEN | + | [70,71] | PM | |||
| MCM5 | Minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 | + | [72] | U | |||
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinases 9 | + | [73,74,75] | U | |||
| PIP | Prostatic inhibin-like peptide | + | [76] | U | |||
| PSA | Urinary prostate specific antigen | + | [77] | U | |||
| S100A9 | S100 calcium binding protein A9 (alias calgranulin B) | + | [78] | PM | |||
| SAR | Sarcosine | + | [79] | PD | |||
| SRD5A2 | Steroid 5-alpha-reductase type 2 | + | [80] | U | |||
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | + | [81,82,83] | PM | |||
| TMSB15A | Thymosin beta 15a | + | [84] | U | |||
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor | + | [85,86] | U | |||
6.1. PCA3
6.2. PCA3 Redefined
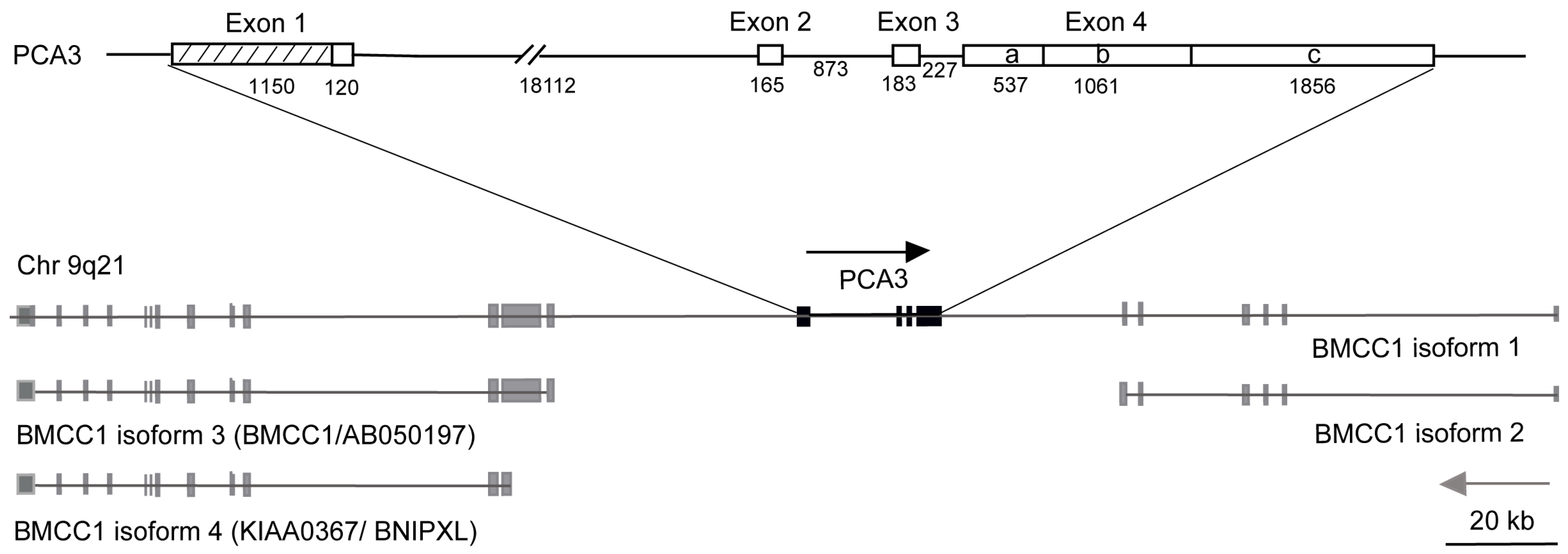
- Exon 1 over 10 times longer than previously reported
- 4 new transcription start sites
- 4 polyadenylation sites
- 2 new differentially spliced exons
- PCA3 embedded in intron 6 of the BMCC1-1 gene
6.3. ETS Gene Fusions
7. Other Markers of Detection
7.1. Early Prostate Cancer Antigen
7.2. GOLPH2
7.3. SPINK1
7.4. α-Methylacyl Coenzyme A Racemase (AMACR)
8. Specific Prognostic Markers
8.1. AZGP1 & hCAP-D3
8.2. Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAcP)
9. Multiple Markers
9.1. Annexin A3 (ANXA3)
10. MicroRNA Profiling
11. Metabonomics/Metabolomics
12. Conclusions
References
- Wilson, J.M.; Jungner, Y.G. Principles and practice of mass screening for disease. Bol. Oficina Sanit. Panam. 1968, 65, 281–393. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, F.H.; Hugosson, J.; Roobol, M.J.; Tammela, T.L.; Ciatto, S.; Nelen, V.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Lujan, M.; Lilja, H.; Zappa, M.; Denis, L.J.; Recker, F.; Berenguer, A.; Määttänen, L.; Bangma, C.H.; Aus, G.; Villers, A.; Rebillard, X.; van der Kwast, T.; Blijenberg, B.G.; Moss, S.M.; de Koning, H.J.; Auvinen, A.; ERSPC Investigators. Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriole, G.L.; Crawford, E.D.; Grubb, R.L., 3rd; Buys, S.S.; Chia, D.; Church, T.R.; Fouad, M.N.; Gelmann, E.P.; Kvale, P.A.; Reding, D.J.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Yokochi, L.A.; O'Brien, B.; Clapp, J.D.; Rathmell, J.M.; Riley, T.L.; Hayes, R.B.; Kramer, B.S.; Izmirlian, G.; Miller, A.B.; Pinsky, P.F.; Prorok, P.C.; Gohagan, J.K.; Berg, C.D.; PLCO Project Team. Mortality results from a randomized prostate-cancer screening trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1310–1319, Erratum in: N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Banks, E.; Clements, M.S.; Gardiner, R.A.; Armstrong, B.K. Evidence-based uncertainty: recent trial results on prostate-specific antigen testing and prostate cancer mortality. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 191, 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, B.S.; Crosswell, J.M. Cancer screening: the clash of science and intuition. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, H.G.; Fisher, E.S.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Barry, M.J. Detection of prostate cancer via biopsy in the Medicare-SEER population during the PSA era. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, R.K.; Saskin, R.; Lee, Y.; Liu, Y.; Law, C.; Klotz, L.H.; Loblaw, D.A.; Trachtenberg, J.; Stanimirovic, A.; Simor, A.E.; Seth, A.; Urbach, D.R.; Narod, S.A. Increasing hospital admission rates for urological complications after transrectal ultrasound guided prostatic biopsy. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobol, M.J.; Schröder, F.H.; Crawford, E.D.; Freedland, S.J.; Sartor, A.O.; Fleshner, N.; Andriole, G.L. A framework for the identi.fication of men at increased risk for prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.M.; Pauler, D.K.; Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Lippman, S.M.; Crawford, E.D.; Crowley, J.J.; Coltman, C.A., Jr. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level < or = 4.0 ng per milliliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Allsbrook, W.C., Jr.; Amin, M.B.; Egevad, L.L.; ISUP Grading Committee. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engers, R. Reproducibility and reliability of tumor grading in urological neoplasms. World J. Urol. 2007, 25, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.I.; Henshall, S.M.; Sutherland, R.L. Molecular markers of prostate cancer outcome. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 858–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopergolo, A.; Zaffaroni, N. Biomolecular markers of outcome prediction in prostate cancer. Cancer 2009, 115 (suppl. 13), 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, G.; Larré, S.; Gallina, A.; Lazar, A.; Faucon, H.; Chemama, S.; Allory, Y.; Patard, J.J.; Vordos, D.; Hoznek, A.; Yiou, R.; Salomon, L.; Abbou, C.C.; de la Taille, A. Extended 21-sample needle biopsy protocol for diagnosis of prostate cancer in 1000 consecutive patients. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, W. Defining the problem: From subclinical disease to clinically insignificant prostate prostate cancer. In Current Clinical Urology: Prostate Biopsy: Indications, Techniques and Complications; Jones, J.S., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, G.P.; Delongchamps, N.B.; Jones, R.F.; Chandan, V.; Serio, A.M.; Vickers, A.J.; Jumbelic, M.; Threatte, G.; Korets, R.; Lilja, H.; de la Roza, G. Needle biopsies on autopsy prostates: sensitivity of cancer detection based on true prevalence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djavan, B.; Zlotta, A.; Remzi, M.; Ghawidel, K.; Basharkhah, A.; Schulman, C.C.; Marberger, M. Optimal predictors of prostate cancer on repeat prostate biopsy: a prospective study of 1,051 men. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, V.; Vockler, C.; Friedlander, M.; Walsh, B.; Willcox, M.D. Lacryglobin in human tears, a potential marker for cancer. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 2001, 29, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.T.; Schatz, C.B.; Myers, L.J.; Kosty, M.; Gonczy, C.; Kroener, J.; Tran, M.; Kurtzhals, P.; Heath, S.; Koziol, J.A.; Arthur, N.; Gabriel, M.; Hemping, J.; Hemping, G.; Nesbitt, S.; Tucker-Clark, L.; Zaayer, J. The use of canines in the detection of human cancers. J. Altern. Complement Med. 2008, 14, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, D.; Klein Gunnewiek, J.M.; van Oort, I.; Karthaus, H.F.; van Leenders, G.J.; van Balken, B.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Witjes, J.A.; Schalken, J.A. DD3(PCA3)-based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradet, Y.; Saad, F.; Aprikian, A.; Dessureault, J.; Elhilali, M.; Trudel, C.; Masse, B.; Piche, L.; Chypre, C. uPM3, a new molecular urine test for the detection of prostate cancer. Urology 2004, 64, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinzl, M.; Marberger, M.; Horvath, S.; Chypre, C. DD3PCA3 RNA analysis in urine--a new perspective for detecting prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, M.P.; Hessels, D.; van Hooij, O.; Jannink, S.A.; Peelen, W.P.; Hanssen, S.L.; Witjes, J.A.; Cornel, E.B.; Karthaus, H.F.; Smits, G.A.; Dijkman, G.A.; Mulders, P.F.; Schalken, J.A. The time-resolved fluorescence-based PCA3 test on urinary sediments after digital rectal examination; a Dutch multicenter validation of the diagnostic performance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, M.P.; Cornel, E.B.; Hessels, D.; Peelen, W.P.; Witjes, J.A.; Mulders, P.F.; Rittenhouse, H.G.; Schalken, J.A. Molecular PCA3 diagnostics on prostatic fluid. Prostate 2007, 67, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, D.; Smit, F.P.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Witjes, J.A.; Cornel, E.B.; Schalken, J.A. Detection of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts and prostate cancer antigen 3 in urinary sediments may improve diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxman, B.; Morris, D.S.; Yu, J.; Siddiqui, J.; Cao, J.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Tsodikov, A.; Wei, J.T.; Tomlins, SA.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. A first-generation multiplex biomarker analysis of urine for the early detection of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.P.; Munson, K.W.; Gu, J.W.; Lamparska-Kupsik, K.; Chan, K.G.; Yoshida, J.S.; Kawachi, M.H.; Crocitto, L.E.; Wilson, T.G.; Feng, Z.; Smith, S.S. Performance of a single assay for both type III and type VI TMPRSS2:ERG fusions in noninvasive prediction of prostate biopsy outcome. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shappell, S.B.; Fulmer, J.; Arguello, D.; Wright, B.S.; Oppenheimer, J.R.; Putzi, M.J. PCA3 urine mRNA testing for prostate carcinoma: patterns of use by community urologists and assay performance in reference laboratory setting. Urology 2009, 73, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Bracken, B.; Burke, B.; Chung, E.; Liang, J.; Ho, S.M. A duplex quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay based on quantification of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase transcripts and prostate cancer antigen 3 in urine sediments improved diagnostic accuracy for prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 2508–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.S.; Fradet, Y.; Deras, I.L.; Blasé, A.; Mathis, J.; Aubin, S.M.; Cancio, A.T.; Desaulniers, M.; Ellis, W.J.; Rittenhouse, H.; Groskopf, J. PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology 2007, 69, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschwège, P.; Moutereau, S.; Droupy, S.; Douard, R.; Gala, J.L.; Benoit, G.; Conti, M.; Manivet, P.; Loric, S. Prognostic value of prostate circulating cells detection in prostate cancer patients: a prospective study. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgason, A.R.; Adolfsson, J.; Dickman, P.; Arver, S.; Fredrikson, M.; Gothberg, M.; Steineck, G. Sexual desire, erection, orgasm and ejaculatory functions and their importance to elderly Swedish men: a population-based study. Age Ageing 1996, 25, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanker, M.H.; Bosch, J.L.; Groeneveld, F.P.; Bohnen, A.M.; Prins, A.; Thomas, S.; Hop, W.C. Erectile and ejaculatory dysfunction in a community-based sample of men 50–78 years old: prevalence, concern and relation to sexual activity. Urology 2001, 57, 763–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, B.W.; Bohnen, A.M.; Bosch, J.L.; Bernsen, R.M.; Deckers, J.W.; Dohle, G.R.; Thomas, S. Erectile dysfunction prospectively associated with cardiovascular disease in the Dutch general population: results from the Krimpen Study. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2008, 20, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, G.D.; Carter, B.; Beaty, T.; Childs, B.; Walsh, P. Family history and the risk of prostate cancer. Prostate 1990, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agalliu, I.; Karlins, E.; Kwon, E.M.; Iwasaki, L.M.; Diamond, A.; Ostrander, E.A.; Stanford, J.L. Rare germline mutations in the BRCA2 gene are associated with early-onset prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, A.J.; Dawson, S.J.; Samaratunga, H.; De Luca, A.; Antill, Y.C.; Hopper, J.L.; Thorne , H.J. kConFab Investigators. Loss of heterozygosity at the BRCA2 locus detected by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification is common in prostate cancers from men with a germline BRCA2 mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.M.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Meitz, J.; Hamoudi, R.; Hope, Q.; Osin, P.; Jackson, R.; Southgate, C.; Singh, R.; Falconer, A.; Dearnaley, D.P.; Ardern-Jones, A.; Murkin, A.; Dowe, A.; Kelly, J.; Williams, S.; Oram, R.; Stevens, M.; Teare, D.M.; Ponder, B.A.; Gayther, S.A.; Easton, D.F.; Eeles, R.A.; Cancer Research UK/Bristish Prostate Group UK Familial Prostate Cancer Study Collaborators; British Association of Urological Surgeons Section of Oncology. Two percent of men with early-onset prostate cancer harbor germline mutations in the BRCA2 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuten, J.; Gelfond, J.A.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; Weldon, K.S.; Crandall, A.C.; Rojas-Martinez, A.; Thompson, I.M.; Leach, R.J. Association of chromosome 8q variants with prostate cancer risk in Caucasian and Hispanic men. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, C.; Torres, J.B.; Hooker, S.; Bonilla, C.; Hernandez, W.; Candreva, A.; Ahaghotu, C.; Kittles, R.; Carpten, J. Confirmation study of prostate cancer risk variants at 8q24 in African Americans identifies a novel risk locus. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C.H.; Schwartz, A.G.; Ruterbusch, J.J.; Levin, A.M.; Neslund-Dudas, C.; Land, S.J.; Wenzlaff, A.S.; Reich, D.; McKeigue, P.; Chen, W.; Heath, E.I.; Powell, I.J.; Kittles, R.A.; Rybicki, B.A. Results from a prostate cancer admixture mapping study in African-American men. Hum. Genet. 2009, 126, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, G.; Neville, P.J.; Liu, X.; Plummer, S.J.; Cicek, M.S.; Krumroy, L.M.; Curran, A.P.; McGreevy, M.R.; Catalona, W.J.; Klein, E.A.; Witte, J.S. Podocalyxin variants and risk of prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeles, R.A.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Al Olama, A.A.; Giles, G.G.; Guy, M.; Severi, G.; Muir, K.; Hopper, J.L.; Henderson, B.E.; Haiman, C.A.; et al.; UK Genetic Prostate Cancer Study Collaborators/British Association of Urological Surgeons' Section of Oncology; UK ProtecT Study Collaborators; PRACTICAL Consortium, Easton DF Identification of seven new prostate cancer susceptibility loci through a genome-wide association study. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramaki, O.; Visakorpi, T. Chromosomal aberrations in prostate cancer. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Joshua, A.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Coudry, R.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Ludkovski, O.; Zielenska, M.; Soares, F.A.; Squire, J.A. Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, M.M.; Beckwith, C.A.; Regan, M.M.; Wyman, S.K.; Petrovics, G.; Chen, Y.; Hawksworth, D.J.; Schumacher, F.R.; Mucci, L.; Penney, K.L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Chan, J.A.; Ardlie, K.G.; Fritz, B.R.; Parkin, R.K.; Lin, D.W.; Dyke, M.; Herman, P.; Lee, S.; Oh, W.K.; Kantoff, P.W.; Tewari, M.; McLeod, D.G.; Srivastava, S.; Freedman, M.L. Evaluation of the 8q24 prostate cancer risk locus and MYC expression. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5568–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, M.; Hanley, J.A.; Boivin, J.F.; McLean, R.G. Screening for prostate cancer: estimating the magnitude of overdetection. CMAJ 1998, 159, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Etzioni, R.; Penson, D.F.; Legler, J.M.; di Tommaso, D.; Boer, R.; Gann, P.H.; Feuer, E.J. Overdiagnosis due to prostate-specific antigen screening: lessons from U.S. prostate cancer incidence trends. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Muston, D.; Melia, J.; Moss, S.; Dearnaley, D. A model of the natural history of screen-detected prostate cancer, and the effect of radical treatment on overall survival. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1122–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, M.; Kim, S.S.; Soloway, M.S. A prospective study measuring penile length in men treated with radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2002, 169, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schover, L.R.; Fouladi, R.T.; Warneke, C.L.; Neese, L.; Klein, E.A.; Zippe, C.; Kupelian, P.A. Defining sexual outcomes after treatment for localized prostate cancer. Cancer 2002, 95, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnas, J.L.; Pierpaoli, S.; Ladd, P.; Valenzuela, R.; Aviv, N.; Parker, M.; Waters, W.B.; Flanigan, R.C.; Mulhall, J.P. The prevalence and nature of orgasmic dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2004, 94, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, F.J.; Burney, S.; Millar, J.L.; Frydenberg, M.; Ng, K.T. Disease-specific quality of life among patients with localized prostate cancer: an Australian perspective. BJU Int. 2006, 97, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedland, S.J.; Presti, J.C., Jr.; Amling, C.L.; Kane, C.J.; Aronson, W.J.; Dorey, F.; Terris, M.K.; SEARCH Database Study Group. Time trends in biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy: results of the SEARCH database. Urology 2003, 61, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L. Low-risk prostate cancer: the trials and tribulations of active surveillance. World J. Urol. 2008, 26, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, R.A.; Hamdy, F.C. Editorial: Management of low-risk prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2008, 26, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaspishvili, T.; Kral, M.; Khomeriki, I.; Student, V.; Kolar, Z.; Bouchal, J. Urine markers in monitoring for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010, 13, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Chan, E.C.; Wu, T.L.; Tsao, K.C.; Wu, J.T. Urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and its analogs as DNA marker of oxidative stress: development of an ELISA and measurement in both bladder and prostate cancers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, V.; Creutz, C.E.; Moss, S.E. Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schostak, M.; Schwall, G.P.; Poznanovic, S.; Groebe, K.; Müller, M.; Messinger, D.; Miller, K.; Krause, H.; Pelzer, A.; Horninger, W.; Klocker, H.; Hennenlotter, J.; Feyerabend, S.; Stenzl, A.; Schrattenholz, A. Annexin A3 in urine: a highly specific noninvasive marker for prostate cancer early detection. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kollermann, J.; Schlomm, T.; Bang, H.; Schwall, G.P.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Simon, R.; Schostak, M.; Huland, H.; Berg, W.; Sauter, G.; Klocker, H.; Schrattenholz, A. Expression and prognostic relevance of annexin a3 in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Miyashita, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Umeda, T.; Akihama, S. Clinical application of basic arginine amidase in human male urine. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 19, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwaleed, B.A.; Francis, J.L.; Chisholm, M. Urinary tissue factor levels in patients with bladder and prostate cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 26, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessl, C.; Muller, M.; Heicappell, R.; Krause, H.; Miller, K. DNA-based detection of prostate cancer in blood, urine, and ejaculates. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 945, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Goessl, C.; Muller, M.; Heicappell, R.; Krause, H.; Straub, B.; Schrader, M.; Miller, K. DNA-based detection of prostate cancer in urine after prostatic massage. Urology 2001, 58, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, C.; Usadel, H.; Henrique, R.; Silva, C.; Oliveira, J.; Lopes, C.; Sidransky, D. Quantitative GSTP1 hypermethylation in bodily fluids of patients with prostate cancer. Urology 2002, 60, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalgo, M.L.; Pavlovich, C.P.; Lee, S.M.; Nelson, W.G. Prostate cancer detection by GSTP1 methylation analysis of postbiopsy urine specimens. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar]
- Crocitto, L.E.; Korns, D.; Kretzner, L.; Shevchuk, T.; Blair, S.L.; Wilson, T.G.; Ramin, S.A.; Kawachi, M.H.; Smith, S.S. Prostate cancer molecular markers GSTP1 and hTERT in expressed prostatic secretions as predictors of biopsy results. Urology 2004, 64, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussenot, O.; Teillac, P.; Berthon, P.; Latil, A. Noninvasive detection of genetic instability in cells from prostatic secretion as a marker of prostate cancer. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 12, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuret, R.; Chantrel-Groussard, K.; Azzouzi, A.R.; Villette, J.M.; Guimard, S.; Teillac, P.; Berthon, P.; Houlgatte, A.; Latil, A.; Cussenot, O. Clinical relevance of genetic instability in prostatic cells obtained by prostatic massage in early prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Stoeber, K.; Swinn, R.; Prevost, A.T.; de Clive-Lowe, P.; Halsall, I.; Dilworth, S.M.; Marr, J.; Turner, W.H.; Bullock, N.; Doble, A.; Hales, C.N.; Williams, G.H. Diagnosis of genito-urinary tract cancer by detection of minichromosome maintenance 5 protein in urine sediments. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M.A.; Wiederschain, D.; Loughlin, K.R.; Zurakowski, D.; Lamb, C.C.; Freeman, M.R. Increased incidence of matrix metalloproteinases in urine of cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Louis, G.; Loughlin, K.R.; Wiederschain, D.; Kilroy, S.M.; Lamb, C.C.; Surakowski, D.; Moses, M.A. Tumor-specific urinary matrix metalloproteinase fingerprinting: identification of high molecular weight urinary matrix metalloproteinase species. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6610–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.W.; Moses, M.A.; Goley, E.; Sproull, M.; Muanza, T.; Coleman, C.N.; Figg, W.D.; Albert, P.S.; Ménard, C.; Camphausen, K. Urinary VEGF and MMP levels as predictive markers of 1-year progression-free survival in cancer patients treated with radiation therapy: a longitudinal study of protein kinetics throughout tumor progression and therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Teni, T.R.; Bandivdekar, A.H.; Sheth, A.R.; Sheth, N.A. Prostatic inhibin-like peptide quantified in urine of prostatic cancer patients by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Chem. 1989, 35, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, J.; Salomon, L.; Soulie, M.; Zlotta, A.; de la Taille, A.; Dore, B.; Millet, C. Urinary/serum prostate-specific antigen ratio: comparison with free/total serum prostate-specific antigen ratio in improving prostate cancer detection. Urology 2005, 65, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, I.; Azzouzi, A.R.; Catto, J.W.; Allen, S.; Cross, S.S.; Feeley, K.; Meuth, M.; Hamdy, F.C. Proteomic analysis of voided urine after prostatic massage from patients with prostate cancer: a pilot study. Urology 2004, 64, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.E.; Hudson, P.B. Preliminary evaluation of 5 alpha-reductase type 2 in urine as a potential marker for prostate disease. Steroids 1997, 62, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meid, F.H.; Gygi, C.M.; Leisinger, H.J.; Bosman, F.T.; Benhattar, J. The use of telomerase activity for the detection of prostatic cancer cells after prostatic massage. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 1802–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, C.; Gravina, G.L.; Angelucci, A.; Pascale, E.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Muzi, P.; Di Leonardo, G.; Fileni, A.; Tubaro, A.; Festuccia, C.; Bologna, M. Detection of telomerase activity in prostate massage samples improves differentiating prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 130, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchkina, G.I.; Kim, R.H.; Botchkina, I.L.; Kirshenbaum, A.; Frischer, Z.; Adler, H.L. Noninvasive detection of prostate cancer by quantitative analysis of telomerase activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3243–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, L.M.; Chang, E.L.; Becker, C.M.; Shih, M.C.; Brice, M.; DeWolf, W.C.; Gaston, S.M.; Zetter, B.R. Use of thymosin beta15 as a urinary biomarker in human prostate cancer. Prostate 2005, 64, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Muramaki, M.; Kurahashi, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Hara, I. Urinary levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with prostate cancer as a predictor of disease progression. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Bok, R.A.; Halabi, S.; Fei, D.T.; Rodriquez, C.R.; Hayes, D.F.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Kantoff, P.; Shuman, M.A.; Small, E.J. Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor urine levels as predictors of outcome in hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients: a cancer and leukemia group B study. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Bussemakers, M.J.; van Bokhoven, A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Smit, F.P.; Karthaus, H.F.; Schalken, J.A.; Debruyne, F.M.; Ru, N.; Isaacs, W.B. DD3: a new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5975–5979. [Google Scholar]
- Groskopf, J.; Aubin, S.M.; Deras, I.L.; blasé, A.; Bodrug, S.; Clark, C.; Brentano, S.; Mathis, J.; Pham, J.; Meyer, T.; Cass, M.; Hodge, P.; Macairan, M.L.; Marks, L.S.; Rittenhouse, H. APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: development of a method to aid in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deras, I.L.; Aubin, S.M.; blasé, A.; Day, J.R.; Koo, S.; Partin, A.W.; Ellis, W.J.; Marks, L.S.; Fradet, Y.; Rittenhouse, H.; Groskopf, J. PCA3: a molecular urine assay for predicting prostate biopsy outcome. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haese, A.; de la Taille, A.; van Poppel, H.; Marberger, M.; Stenzl, A.; Mulders, P.F.; Huland, H.; Abbou, C.C.; Remzi, M.; Tinzl, M.; Feyerabend, S.; Stillebroer, A.B.; van Gils, M.P.; Schalken, J.A. Clinical utility of the PCA3 urine assay in European men scheduled for repeat biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H.; Groskopf, J.; Fritsche, H.A.; Bhadkamkar, V.; blasé, A.; Kumar, S.V.; Davis, J.W.; Troncoso, P.; Rittenhouse, H.; Babaian, R.J. PCA3 molecular urine assay correlates with prostate cancer tumor volume: implication in selecting candidates for active surveillance. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1804–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoll, L.J.; Ellis, W.; Lange, P.; Noteboom, J.; Elliott, D.J.; Deras, I.L.; blasé, A.; Koo, S.; Sarno, M.; Rittenhouse, H.; Groskopf, J.; Vessella, R.L. A multicenter evaluation of the PCA3 molecular urine test: pre-analytical effects, analytical performance, and diagnostic accuracy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 389, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosoian, J.J.; Loeb, S.; Kettermann, A.; Landis, P.; Elliot, D.J.; Epstein, J.I.; Partin, A.W.; Carter, H.B.; Sokoll, L.J. Accuracy of PCA3 measurement in predicting short-term biopsy progression in an active surveillance program. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.A.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, A.Y.; Roper, K.; Fang, Z.M.; Samaratunga, H.; Lavin, M.F.; Gardiner, R.A. New Genomic Structure for Prostate Cancer Specific Gene PCA3 within BMCC1: Implications for prostate cancer detection and progression. PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, M.F.; Clarke, R.; Gardiner, R.A. Differential expression of PCA3 and BMCC1 in prostate cancer. Prostate 2009, 69, 1713–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kok, J.B.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Roelofs, RW.; Hessels, D.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Aalders, T.W.; Swinkels, D.W.; Schalken, J.A. DD3(PCA3), a very sensitive and specific marker to detect prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2695–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Landers, K.A.; Samaratunga, H.; Teng, L.; Burger, M.J.; Scells, B.; Lavin, M.F.; Gardiner, R.A. Identification of Metastatic Markers for Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, D.; van Gils, M.P.; van Hooij, O.; Jannink, S.A.; Witjes, J.A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Schalken, J.A. Predictive value of PCA3 in urinary sediments in determining clinico-pathological characteristics of prostate cancer. Prostate 2010, 70, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Perner, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Mehra, R.; Sun, X.W.; Varambally, S.; Cao, X.H.; Tchinda, J.; Kuefer, R.; et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 2005, 310, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Beroukhim, R.; Schmidt, F.H.; Mosquera, J.M.; Setlur, S.; Tchinda, J.; Tomlins, S.A.; Hofer, M.D.; Pienta, K.G.; Kuefer, R.; Vessella, R.; Sun, X.W.; Meyerson, M.; Lee, C.; Sellers, W.R.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rubin, M.A. TMPRSS2: ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8337–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Tomlins, S.A.; Shen, R.; Nadeem, O.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.T.; Pienta, K.J.; Ghosh, D.; Rubin, M.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Shah, R.B. Comprehensive assessment of TMPRSS2 and ETS family gene aberrations in clinically localized prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.J.; Rohan, S.; Kao, J.; Kitabayashi, N.; Mathew, S.; Chen, Y.T. Gene fusions between TMPRSS2 and ETS family genes in prostate cancer: frequency and transcript variant analysis by RT-PCR and FISH on paraffin-embedded tissues. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Sinha, C.; Tomlins, S.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Merson, S.; Jhavar, S.; Flohr, P.; Edwards, S.; Foster, C.S.; Eeles, R.; Martin, F.L.; Phillips, D.H.; Crundwell, M.; Christmas, T.; Thompson, A.; Fisher, C.; Kovacs, G.; Cooper, C.S. Diversity of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts in the human prostate. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, R.K.; Sugar, L.; Yang, W.; Srivastava, S.; Klotz, L.H.; Yang, L.Y.; Stanimirovic, A.; Encioiu, E.; Neill, M.; Loblaw, D.A.; Trachtenberg, J.; Narod, S.A.; Seth, A. Expression of the TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene predicts cancer recurrence after surgery for localised prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhavar, S.; Reid, A.; Clark, J.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Christmas, T.; Thompson, A.; Woodhouse, C.; Ogden, C.; Fisher, C.; Corbishley, C.; De-Bono, J.; Eeles, R.; Brewer, D.; Cooper, C. Detection of TMPRSS2-ERG translocations in human prostate cancer by expression profiling using GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST arrays. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.D.; Kuefer, R.; Maier, C.; Herkommer, K.; Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Paiss, T.; Vogel, W.; Rubin, M.A.; Hoegel, J. Genome-wide linkage analysis of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion in familial prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.M.; Mehra, R.; Regan, M.M.; Perner, S.; Genega, E.M.; Bueti, G.; Shah, R.B.; Gaston, S.; Tomlins, S.A.; Wei, J.T.; Kearney, M.C.; Johnson, L.A.; Tang, J.M.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Sanda, M.G. Prevalence of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion prostate cancer among men undergoing prostate biopsy in the United States. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4706–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Ren, C.; Ittmann, M. Expression of variant TMPRSS2/ERG fusion messenger RNAs is associated with aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8347–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxman, B.; Tomlins, S.A.; Mehra, R.; Morris, D.S.; Wang, L.; Helgeson, B.E.; Shah, R.B.; Rubin, M.A.; Wei, J.T.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Noninvasive detection of TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcripts in the urine of men with prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Bjartell, A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Jenster, G.; Nam, R.K.; Rubin, M.A.; Schalken, J.A. ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer: from discovery to daily clinical practice. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, S.; Mosquera, J.M.; Demichelis, F.; Hofer, M.D.; Paris, P.L.; Simko, J.; Collins, C.; Bismar, T.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; De Marzo, A.M.; Rubin, M.A. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion prostate cancer: an early molecular event associated with invasion. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusato, B.; Gao, C.L.; Ravindranath, L.; Chen, Y.; Cullen, J.; McLeod, D.G.; Dobi, A.; Srivastava, S.; Petrovics, G.; Sesterhenn, I.A. Mapping of TMPRSS2-ERG fusions in the context of multi-focal prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, B.G.; Abramovitz, M.; Kodani, M.; Moreno, C.S.; Nam, R.; Tang, W.; Bouzyk, M.; Seth, A.; Leyland-Jones, B. Prostate cancer genes associated with TMPRSS2–ERG gene fusion and prognostic of biochemical recurrence in multiple cohorts. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.H.; Attard, G.; Ambroisine, L.; Fisher, G.; Kovacs, G.; Brewer, D.; Clark, J.; Flohr, P.; Edwards, S.; Berney, D.M.; Foster, C.S.; Fletcher, A.; Gerald, W.L.; Møller, H.; Reuter, V.E.; Scardino, P.T.; Cuzick, J.; de Bono, J.S.; Cooper, C.S; Transatlantic Prostate Group. Molecular characterisation of ERG, ETV1 and PTEN gene loci identifies patients at low and high risk of death from prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Tomlins, S.A.; Yu, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, L.; Menon, A.; Rubin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J.; Shah, R.B.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Characterization of TMPRSS2-ETS gene aberrations in androgen-independent metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.; Clark, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Fisher, G.; Kovacs, G.; Flohr, P.; Berney, D.; Foster, C.S.; Fletcher, A.; Gerald, W.L.; Moller, H.; Reuter, V.; De Bono, J.S.; Scardino, P.; Cuzick, J.; Cooper, C.S.; Transatlantic Prostate Group. Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.P.; Munson, K.W.; Gu, J.W.; Lamparska-Kupsik, K.; Chan, K.G.; Yoshida, J.S.; Kawachi, M.H.; Crocitto, L.E.; Wilson, T.G.; Feng, Z.; Smith, S.S. Performance of a single assay for both type III and type VI TMPRSS2:ERG fusions in noninvasive prediction of prostate biopsy outcome. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, L.M.; Agalliu, I.; Johnson, K.; Miller, M.A.; Kwon, E.M.; Hurtado-Coll, A.; Fazli, L.; Rajput, A.B.; Gleave, M.E.; Cox, M.E.; Ostrander, E.A.; Stanford, J.L.; Huntsman, D.G. Association of TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion with clinical characteristics and outcomes: results from a population-based study of prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlur, S.R.; Mertz, K.D.; Hoshida, Y.; Demichelis, F.; Lupien, M.; Perner, S.; Sboner, A.; Pawitan, Y.; Andrén, O.; Johnson, L.A.; Tang, J.; Adami, H.O.; Calza, S.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rhodes, D.; Tomlins, S.; Fall, K.; Mucci, L.A.; Kantoff, P.W.; Stampfer, M.J.; Andersson, S.O.; Varenhorst, E.; Johansson, J.E.; Brown, M.; Golub, T.R.; Rubin, M.A. Estrogen-dependent signaling in a molecularly distinct subclass of aggressive prostate cancer. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, A.; Leversha, M.A.; Satagopan, J.M.; Zhou, Q.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Fine, S.W.; Eastham, J.A.; Scardino, P.T.; Scher, H.I.; Tickoo, S.K.; Reuter, V.E.; Gerald, W.L. TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion is not associated with outcome in patients treated by prostatectomy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, E.S.; Cannon, G.W.; Trock, B.J.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Mangold, L.; Partin, A.W.; Getzenberg, R.H. EPCA-2: a highly specific serum marker for prostate cancer. Urology 2007, 69, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, E.S.; Magheli, A.; Cannon, G.W.; Mangold, L.; Partin, A.W.; Getzenberg, R.H. Analysis of a serum test for prostate cancer that detects a second epitope of EPCA-2. Prostate 2009, 69, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamamdis, E.P. POINT: EPCA-2: a promising new serum biomarker for prostatic carcinoma? Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 1437–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, G. Immunohistochemical algorithms in prostate diagnostics: what's new? Pathologe 2009, 30 (Suppl 2), 146–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Yu, J.; Varambally, S.; Mehra, R.; Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Helgeson, B.E.; Laxman, B.; Morris, D.S.; Cao, Q.; Cao, X.; Andrén, O.; Fall, K.; Johnson, L.; Wei, JT.; Shah, R.B.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Eastham, J.A.; Eggener, S.E.; Fine, S.W.; Hotakainen, K.; Stenman, U.H.; Tsodikov, A.; Gerald, W.L.; Lilja, H.; Reuter, V.E.; Kantoff, P.W.; Scardino, P.T.; Rubin, M.A.; Bjartell, A.S.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The role of SPINK1 in ETS rearrangement-negative prostate cancers. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, H.; Luck, W.; Hennies, H.C.; Classen, M.; Kage, A.; Lass, U.; Landt, O.; Becker, M. Mutations in the gene encoding the serine protease inhibitor, Kazal type 1, are associated with chronic pancreatitis. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, E.; Choudhuri, G.; Sikora, S.S.; Landt, O.; Kage, A.; Becker, M.; Witt, H. Tropical calcific pancreatitis: strong association with SPINK1 trypsin inhibitor mutations. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paju, A.; Stenman, U.H. Biochemistry and clinical role of trypsinogens and pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 43, 103–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paju, A.; Hotakainen, K.; Cao, Y.; Laurila, T.; Gadaleanu, V.; Hemminki, A.; Stenman, U.H.; Bjartell, A. Increased expression of tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor, TATI, in prostate cancer and in androgen-independent 22Rv1 cells. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Mehra, R.; Suleman, K.; Tomlins, S.A.; Wang, L.; Singhal, N.; Linetzky, K.A.; Palanisamy, N.; Zhou, M.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Shah, R.B. Characterization of ETS gene aberrations in select histologic variants of prostate carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.A.; Zhou, M.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Varambally, S.; Barrette, T.R.; Sanda, M.G.; Pienta, K.J.; Ghosh, D.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. alpha-Methylacyl coenzyme A racemase as a tissue biomarker for prostate cancer. JAMA 2000, 287, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, C.G.; Yan, G.; Zha, S.; Gonzalgo, M.L.; Isaacs, W.B.; Luo, J.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, W.G.; Pavlovic, H.C.P. Prostate cancer detection on urinalysis for alpha methylacyl coenzyme a racemase protein. J. Urol. 2004, 172, (4 Pt 1). 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielie, P.J.; Mobley, J.A.; Ebb, R.G.; Jiang, Z.; Blute, R.D.; Ho, S.M. A novel diagnostic test for prostate cancer emerges from the determination of alpha-methylacyl-coenzyme a racemase in prostatic secretions. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.I.; Kumar, V.; Singh, T.P.; Yadav, S. Purification and characterization of zinc alpha2-glycoprotein-prolactin inducible protein complex from human seminal plasma. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 2318–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, L.P.; Price, D.T.; Sanchez, L.M.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Madden, J.F. Zinc alpha-2-glycoprotein is expressed by malignant prostatic epithelium and may serve as a potential serum marker for prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 846–853. [Google Scholar]
- Bondar, O.P.; Barnidge, D.R.; Klee, E.W.; Davis, B.J.; Klee, G.G. LC-MS/MS quantification of Zn-alpha2 glycoprotein: a potential serum biomarker for prostate cancer. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, S.M.; Horvath, L.G.; Quinn, D.I.; Eggleton, S.A.; Grygiel, J.J.; Stricker, P.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Kench, J.G.; Sutherland, R.L. Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein expression as a predictor of metastatic prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, J.; Malhotra, S.; Higgins, J.P.; Bair, E.; Thompson, M.; Salari, K.; Giacomini, C.P.; Ferrari, M.; Montgomery, K.; Tibshirani, R.; van de Rijn, M.; Brooks, J.D.; Pollack, J.R. hCAP-D3 expression marks a prostate cancer subtype with favorable clinical behavior and androgen signaling signature. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moul, J.W.; Connelly, R.R.; Perahia, B.; McLeod, D.G. The contemporary value of pretreatment prostatic acid phosphatase to predict pathological stage and recurrence in radical prostatectomy cases. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Piantadosi, S.; Zahurak, M.L.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Epstein, J.I.; Walsh, P.C.; Partin, A.W. Serum acid phosphatase level and biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy for men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Urology 2001, 57, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.C.; Dattoli, M.; Taira, A.; True, L.; Sorace, R.; Wallner, K. Prostatic acid phosphatase adversely affects cause-specific survival in patients with intermediate to high-risk prostate cancer treated with brachytherapy. Urology 2008, 71, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svatek, R.S.; Jeldres, C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Suardi, N.; Walz, J.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Montorsi, F.; Slawin, K.M.; Shariat, S.F. Pre-treatment biomarker levels improve the accuracy of post-prostatectomy nomogram for prediction of biochemical recurrence. Prostate 2009, 69, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köllermann, J.; Schlomm, T.; Bang, H.; Schwall, G.P.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Simon, R.; Schostak, M.; Huland, H.; Berg, W.; Sauter, G.; Klocker, H.; Schrattenholz, A. Expression and prognostic relevance of annexin A3 in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, V.; Creutz, C.E.; Moss, S.E. Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schostak, M.; Schwall, G.P.; Poznanović, S.; Groebe, K.; Müller, M.; Messinger, D.; Miller, K.; Krause, H.; Pelzer, A.; Horninger, W.; Klocker, H.; Hennenlotter, J.; Feyerabend, S.; Stenzl, A.; Schrattenholz, A. Annexin A3 in urine: a highly specific noninvasive marker for prostate cancer early detection. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, C.C. Return to the RNAi world: rethinking gene expression and evolution (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 6985–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Arif, M.A.; Seumel, G.I.; Ossowski, S.; Weigel, D.; Reski, R.; Frank, W. Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs. Cell 2010, 140, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porkka, K.P.; Pfeiffer, M.J.; Waltering, K.K.; Vessella, R.L.; Tammela, T.L.; Visakorpi, T. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6130–6135. [Google Scholar]
- Ambs, S.; Prueitt, R.L.; Yi, M.; Hudson, R.S.; Howe, T.M.; Petrocca, F.; Wallace, T.A.; Liu, C.G.; Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Yfantis, H.G.; Stephens, RM.; Croce, C.M. Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6162–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Shapiro, A.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8164–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catto, J.W.; Miah, S.; Owen, H.C.; Bryant, H.; Myers, K.; Dudziec, E.; Larré, S.; Milo, M.; Rehman, I.; Rosario, D.J.; Di Martino, E.; Knowles, M.A.; Meuth, M.; Harris, A.L.; Hamdy, F.C. Distinct microRNA alterations characterize high- and low-grade bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8472–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, A.C.; Nelson, L.J.; Fleischer, C.L.; Majlessi, M.; Becker, M.M.; Vessella, R.L.; Reynolds, M.A. Molecular assays for the detection of microRNAs in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Hagman, Z.; Larne, O.; Edsjö, A.; Bjartell, A.; Ehrnström, R.A.; Ulmert, D.; Lilja, H.; Ceder, Y. miR-34c is down regulated in prostate cancer and exerts tumor suppressive functions. Int. J. Cancer 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.F.; Imfield, H. The role of citric acid in the physiology of the prostate: a preliminary report. J. Urol. 1959, 81, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Marberger, H.; Marberger, E.; Mann, T.; Lutwak-Mann, C. Citric acid in human prostatic secretion and metastasizing cancer of the prostate gland. Br. Med. J. 1962, 1, 835–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.E.; Farid, I. The role of citric acid in the physiology of the prostate. Lactic/citrate ratios in benign and malignant prostatic homogenates as an index of prostatic malignancy. J. Urol. 1964, 92, 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.U.; Fair, W.R. Physical and chemical determinations of prostatic secretion in benign hyperplasia, prostatitis and adenocarcinoma. Invest. Urol. 1976, 14, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh, J.P. Sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, citrate and chloride content of human prostatic and seminal fluid. J. Reprod. Fert. 1985, 75, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B.; Narayan, P. Review article: citrate in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Prostate 1999, 38, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.E.; Vath, J.E. Tandem mass spectrometry of glycolipids. Meth. Enzymol. 1990, 193, 738–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreult, H.; Costello, C.E. Liquid secondary ionization, tandem and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric characterization of glycosphingolipid derivatives. Org. Mass Spectr. 1994, 29, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, A. Preparation and desorption mass spectometry of permethyl and peracetyl derivatives of oligosaccharides. Meth. Enzymol. 1990, 193, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Modern methods of bile acid analysis by mass spectrometry: A view into the metabolome. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2007, 3, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.W.; Cheng, L.L. NMR-based metabolomics approach to target biomarkers for human prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2007, 4, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkova, N.J.; Spratlin, J.L.; Eckhardt, S.G. NMR-based metabolomics: Translational application and treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Mol. Therapeut. 2007, 9, 572–585. [Google Scholar]
- Sitter, B.; Bathen, T.F.; Tessem, M.B.; Gribbestad, I.S. High-resolution magic angle spinning (HR MAS) MR spectroscopy in metabolic characterization of human cancer. Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 2009, 54, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.J.; Nicholson, J.K. Proton MRS of human prostatic fluid: correlations between citrate, spermine and myo-inositol levels and changes with disease. Prostate 1997, 30, 284–255. [Google Scholar]
- Averna, T.A.; Kline, E.E.; Smith, A.Y.; Sillerud, L.O. A decrease in 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopically determined citrate in human seminal fluid accompanies the development of prostate adenocarcinoma. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, E.E.; Treat, E.G.; Averna, T.A.; Davis, M.S.; Smith, A.Y.; Sillerud, L.O. Citrate concentrations in human seminal fluid and expressed prostatic fluid determined via 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy outperform prostate specific antigen in prostate cancer detection. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkova, N.J.; Gamito, E.J.; Jones, R.H.; O'Donnell, C.; Brown, J.L.; Green, S.; Sullivan, H.; Hedlund, T.; Crawford, E.D. The metabolites citrate, myo-inositol, and spermine are potential age-independent markers of prostate cancer in human expressed prostatic secretions. Prostate 2008, 68, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraul, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lynch, M.J.; Lindon, J.C. Application of the one-dimensional TOCSY pulse sequence in 750 MHz 1H-NMR spectroscopy for assignment of endogenous metabolite resonances in biofluids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.L.; Wu, C.L.; Smith, M.R.; Gonzalez, R.G. Non-destructive quantitation of spermine in human prostate tissue samples using HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy at 9.4 T. FEBS Lett. 2001, 494, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Asten, J.J.A.; Cuijpers, V.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Soede-Huijbregts, C.; Witjes, J.A.; Verhofstad, A.; Heerschap, A. High resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic assessment of cancer presence and Gleason score in human prostate needle biopsies. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2008, 21, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.G.; Vigneron, D.B.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Males, R.G.; Schmitt, L.; Carroll, P.R.; James, J.K.; Hurd, R.E.; Kurhanewicz, J. Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.G.; Zektzer, A.S.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Simko, J.; Jarso, S.; Keshari, K.R.; Schmitt, L.; Carroll, P.R.; Shinohara, K.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J. Quantitative analysis of prostate metabolites using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 55, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoka, S.; Trierweiler, M. Improvement of the ERETIC method by digital synthesis of the signal and addition of a broadband antenna inside the NMR probe. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2002, 30, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessem, M.B.; Swanson, M.G.; Keshari, K.R.; Albers, M.J.; Joun, D.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Simko, J.P.; Shinohara, K.; Nelson, S.J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Kurhanewicz, J. Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 60, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, Y.S.; Albers, M.J.; Butler, T.N.; Spielman, D.; Peehl, D.M.; Kurhanewicz, J. Methods for Metabolic Evaluation of Prostate Cancer Cells Using Proton and 13C HR-MAS Spectroscopy and [3-13C] Pyruvate as a Metabolic Substrate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.D.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; Nyati, M.K.; Ahsan, A.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Han, B.; Cao, X.H.; Byun, J.; Omenn, G.S.; Ghosh, D.; Pennathur, S.; Alexander, D.C.; Berger, A.; Shuster, J.R.; Wei, J.T.; Varambally, S.; Beecher, C.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Clarke, R.A.; Schirra, H.J.; Catto, J.W.; Lavin, M.F.; Gardiner, R.A. Markers for Detection of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 1125-1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021125
Clarke RA, Schirra HJ, Catto JW, Lavin MF, Gardiner RA. Markers for Detection of Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2010; 2(2):1125-1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021125
Chicago/Turabian StyleClarke, Raymond A., Horst J. Schirra, James W. Catto, Martin F. Lavin, and Robert A. Gardiner. 2010. "Markers for Detection of Prostate Cancer" Cancers 2, no. 2: 1125-1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021125
APA StyleClarke, R. A., Schirra, H. J., Catto, J. W., Lavin, M. F., & Gardiner, R. A. (2010). Markers for Detection of Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 2(2), 1125-1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021125