Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
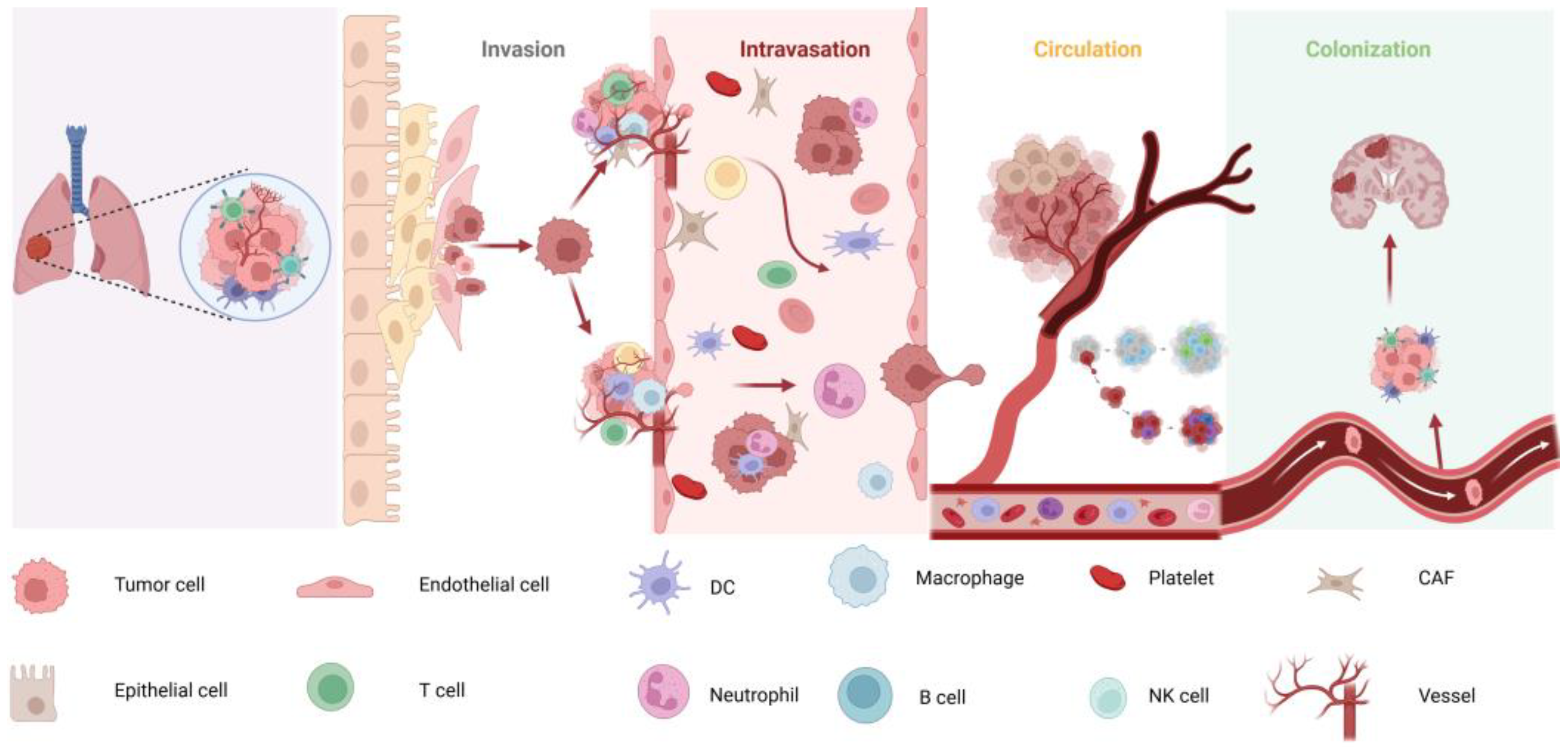
2. Biology of Lung Cancer Brain Metastases
2.1. Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Brain Metastases
2.2. Impact of the TME on BM
2.3. The Role of the BBB in Metastasis
3. Classification of Model Sources
3.1. Immunologically Sound Mice
3.2. Immunodeficient Mice
3.3. Source of Transplanted Cells
4. Methods of Constructing BMs Models for Lung Cancer
4.1. Stereotactic Intracranial Injection
4.2. Tail Vein Injection
4.3. In Situ Injection
| Modeling Method | Metastatic Cascade Replication | Clinical Relevance | Technical Difficulty | Immune Compatibility | Metastasis Rate (%) | Key Applications | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stereotactic Intracranial Injection | Partial (skips BBB transmigration) | Low | Low | Immunodeficient | 90–100 | Pharmacological drug testing | [40,41] |
| Tail Vein Injection | Partial (lung retention bias) | Moderate | Low | Immunocompetent/Deficient | 5–15 | Metastatic seeding studies | [42,43,44] |
| Carotid Artery Injection | High (hematogenous spread) | High | High | Immunocompetent | 70–85 | BBB transmigration studies | [31,45] |
| Left Ventricular Injection | High (systemic circulation) | High | Moderate | Immunodeficient | 60–75 | Systemic metastasis dynamics | [46,47] |
| Orthotopic Implantation | Full (primary tumor progression) | Very High | High | Immunocompetent | 20–40 | Tumor-microenvironment interactions | [48,49,50] |
4.4. Left Ventricular Injection
4.5. Carotid Injection
5. Brain Metastasis Modeling Assays
5.1. Imaging Tests
5.2. Pathological Testing
5.2.1. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining
5.2.2. Immunohistochemistry and Immunoblotting
5.2.3. Biomarker Analysis
| Biomarker | Source | Detection Method | Clinical Utility | Sensitivity/ Specificity | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100B | Serum/CSF | ELISA | Predicts BBB disruption | 78%/85% | [80,81] |
| CD44v6 | Tumor tissue | IHC | EMT and metastasis prediction | 82%/76% | [82] |
| E-cadherin | Tumor tissue | IHC/Western blot | Loss correlates with BM risk | 68%/89% | [83,84] |
| CSF-ctDNA | Cerebrospinal fluid | NGS/ddPCR | Guides targeted therapy selection | 90%/95% | [85,86] |
| Exosomal miRNA-21 | Plasma exosomes | qRT-PCR | Early detection of BM | 75%/80% | [87,88] |
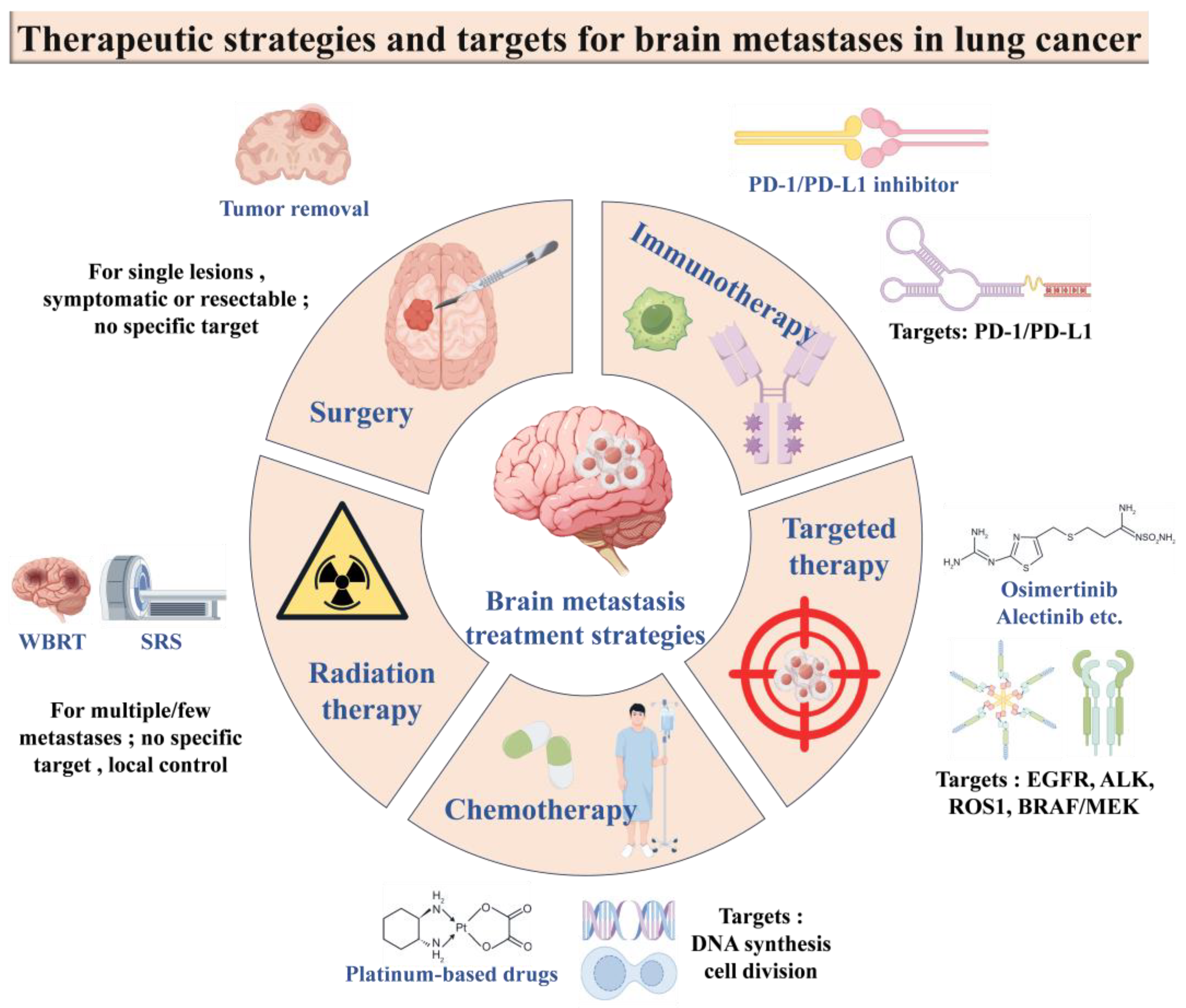
6. Current Status of Treatment of LCBM
6.1. Clinical Diagnosis of LCBM
6.1.1. Imaging Joint AI and DL Technologies
6.1.2. Nanotechnology
6.1.3. Liquid Biopsy Techniques
6.2. Conventional Treatment Strategies
6.2.1. Surgical Treatment
6.2.2. Radiotherapy
6.2.3. Chemotherapy
6.2.4. Targeted Therapies
6.2.5. Immunotherapy
6.3. Natural Product-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Targeting
6.3.1. Microparticle-Targeted Delivery Systems
6.3.2. Targeted Delivery Systems for Surface Modification of Carrier Materials
| Therapy | Mechanism | Advantages | Limitations | Median Survival Benefit | Key Clinical Trials/Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBRT | Targets all CNS lesions via ionizing radiation | Rapid symptom relief | Neurocognitive decline | 3–6 months | QUARTZ Trial [128] |
| SRS | Precise high-dose radiation to focal lesions | Sparing of healthy tissue | Limited to ≤4 lesions | 10–12 months | N107C/CEC.3 Trial [129] |
| EGFR-TKIs | Inhibits EGFR-driven tumor growth | BBB penetration, systemic control | Resistance mutations (e.g., T790M/C797S) | 15–20 months | AURA3 Trial [130] |
| ICI | Blocks PD-1/PD-L1 interaction | Durable responses | Low CNS penetration | 8–12 months | KEYNOTE-189 [131] |
| Nanoparticle Drug Delivery | Enhances BBB permeability via ligand targeting | Improved drug accumulation in brain | Toxicity of carrier materials | Under investigation | Preclinical studies (e.g., SPIONs for MRI-guided delivery) [132] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulahannan, D.; Khalifa, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Lee, S.M. Emerging treatment paradigms for brain metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer: An overview of the current landscape and challenges ahead. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Yao, B.; Dong, T.; Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tumor-resident intracellular microbiota promotes metastatic colonization in breast cancer. Cell 2022, 185, 1356–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiente, M.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Boire, A.; Brastianos, P.K.; Goldberg, S.B.; Lee, E.Q.; Le Rhun, E.; Preusser, M.; Winkler, F.; Soffietti, R. The Evolving Landscape of Brain Metastasis. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz, A.; Ramlau, R.; Stencel, K. Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Duan, W.; Xu, M.; Li, M.; Tang, M.; Wei, S.; Lin, M.; Li, E.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q. Mesothelin promotes brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by activating MET. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, C.D.; Ferraro, G.B.; Jain, R.K. The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Xiao, D.; Huang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhai, K.; Fang, X.; Kim, J.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; et al. CD44(+) lung cancer stem cell-derived pericyte-like cells cause brain metastases through GPR124-enhanced trans-endothelial migration. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Park, J.; Kim, E.J.; Ko, Y.H.; Hong, S.A.; Yang, S.H.; Ahn, Y.H. Noggin contributes to brain metastatic colonization of lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Wa, Y.; Ding, S.; Yang, Y.; Liao, J.; Tong, L.; Xiao, G. Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Immunotherapy in Brain Metastasis From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhanani, O.; Ben-Uri, R.; Keren, L. Spatial profiling technologies illuminate the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elewaut, A.; Estivill, G.; Bayerl, F.; Castillon, L.; Novatchkova, M.; Pottendorfer, E.; Hoffmann-Haas, L.; Schonlein, M.; Nguyen, T.V.; Lauss, M.; et al. Cancer cells impair monocyte-mediated T cell stimulation to evade immunity. Nature 2025, 637, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, D.; Ko, S.; Kim, A.; Mo, K.; Yoon, H. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Smith, Q.R.; Liu, X. Brain penetrating peptides and peptide-drug conjugates to overcome the blood-brain barrier and target CNS diseases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempe, R.G.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood—Brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow. Metab. 2016, 36, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, V.; Dakal, T.C.; Maurya, P.K.; Johnson, M.S.; Sharma, N.K.; Kumar, A. Role of RGD-binding Integrins in ovarian cancer progression, metastasis and response to therapy. Integr. Biol. 2025, 17, zyaf003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, A.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Metastasis: Potential as Therapeutic Targets and Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qin, C.; Dewanjee, S.; Bhattacharya, H.; Chakraborty, P.; Jha, N.K.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Jha, S.K.; Liu, Q. Tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles in cancer invasion and metastasis: Molecular mechanisms, and clinical significance. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; Merlino, G.; Van Dyke, T. Preclinical mouse cancer models: A maze of opportunities and challenges. Cell 2015, 163, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, S.; Xiao, Z.; Pan, Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, K.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Guo, F.; Liu, H.F.; et al. The development and improvement of immunodeficient mice and humanized immune system mouse models. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1007579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschnagel, A.M.; Kaushik, S.; Durmaz, A.; Goldstein, S.; Ong, I.M.; Abel, L.; Clark, P.A.; Gurel, Z.; Leal, T.; Buehler, D.; et al. Development and characterization of patient-derived xenografts from non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, T.; Gotoh, N. Patient-Derived Xenograft Models of Breast Cancer and their Application. Cells 2019, 8, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oser, M.G.; Macpherson, D.; Oliver, T.G.; Sage, J.; Park, K.S. Genetically-engineered mouse models of small cell lung cancer: The next generation. Oncogene 2024, 43, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Reese, T.A. Making Mouse Models that Reflect Human Immune Responses. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.; de Pennington, N.; Zakaria, R.; Larkin, J.R.; Serres, S.; Sarkar, M.; Kirkman, M.A.; Bristow, C.; Croal, P.; Plaha, P.; et al. VCAM-1-targeted MRI Improves Detection of the Tumor-brain Interface. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, J.A.; Spehar, J.M.; Steck, S.A.; Bratasz, A.; Shakya, R.; Powell, K.; Sizemore, G.M. Modeling Brain Metastases through Intracranial Injection and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 160, 10.3791/61272. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, T.; James, C.D. Establishing intracranial brain tumor xenografts with subsequent analysis of tumor growth and response to therapy using bioluminescence imaging. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 41, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.H.; Li, C.H.; Jeong, Y.I.; Jang, W.Y.; Choi, J.M.; Jung, S. Enhancing Radiotherapeutic Effect with Nanoparticle-Mediated Radiosensitizer Delivery Guided by Focused Gamma Rays in Lewis Lung Carcinoma-Bearing Mouse Brain Tumor Models. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8861–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, N.; Lateef, Z.; Martey, O.; Bland, A.R.; Nimick, M.; Rosengren, R.; Ashton, J.C. Does the mouse tail vein injection method provide a good model of lung cancer? F1000Research 2019, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hatori, T.; Nonaka, H. An experimental model of brain metastasis of lung carcinoma. Neuropathology 2008, 28, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lowery, F.J.; Yu, D. Intracarotid Cancer Cell Injection to Produce Mouse Models of Brain Metastasis. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 120, 55085. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, P.D.; Zhang, X.H.; Nadal, C.; Shu, W.; Gomis, R.R.; Nguyen, D.X.; Minn, A.J.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Gerald, W.L.; Foekens, J.A.; et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 2009, 459, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.L.; Li, R.Z.; Mai, C.T.; Guan, X.X.; Li, J.X.; Wang, X.R.; Ma, L.R.; Zhang, F.Y.; Wang, J.; He, F.; et al. A method establishment and comparison of in vivo lung cancer model development platforms for evaluation of tumour metabolism and pharmaceutical efficacy. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tanzhu, G.; Chen, L.; Ning, J.; Wang, H.; Xiao, G.; Peng, H.; Jing, D.; Liang, H.; Nie, J.; et al. Radiotherapy in Preclinical Models of Brain Metastases: A Review and Recommendations for Future Studies. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jakobsson, V.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Khong, P.L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Glioblastoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 40391–40410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, N.H.; Mitchell, R.; Savant, S.D.; Bachmeier, C.J.; Hatch, G.M.; Miller, D.W. Examination of blood–brain barrier (BBB) integrity in a mouse brain tumor model. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 111, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokabi, F.; Khosravi, A.; Jazi, M.S.; Asadi, J. A reliable mouse model of liver and lung metastasis by injecting esophageal cancer stem cells (CSCs) through tail-vein injection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 3401–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Inoue, H.; Ohba, S.; Kohda, Y.; Usami, I.; Masuda, T.; Kawada, M.; Nomoto, A. New metastatic model of human small-cell lung cancer by orthotopic transplantation in mice. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Feng, L.; Yuan, H.; Benhabbour, S.R.; Mumper, R.J. Development of a novel orthotopic non-small cell lung cancer model and therapeutic benefit of 2′-(2-bromohexadecanoyl)-docetaxel conjugate nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kabraji, S.; Xie, S.; Pan, P.; Liu, Z.; Ni, J.; Zhao, J.J. Improving orthotopic mouse models of patient-derived breast cancer brain metastases by a modified intracarotid injection method. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.Y.; Kao, C.W.; Liu, K.S.; Tang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.W.; Liu, S.J. Treating Intracranial Abscesses in Rats with Stereotactic Injection of Biodegradable Vancomycin-Embedded Microparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Wang, Z.; Johnson, G.N.; Ho, Y.J.; Ganesh, K.; Umeda, S.; Gan, S.; Mujal, A.M.; Delconte, R.B.; et al. STING inhibits the reactivation of dormant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2023, 616, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sheng, Z.; Cheng, C.; Zheng, H.; Lanuti, M.; Liu, R.; Wang, P.; Shen, Y.; Xie, Z. Anesthetic Propofol Promotes Tumor Metastasis in Lungs via GABA(a) R-Dependent TRIM21 Modulation of Src Expression. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuya, W.L.; Kong, L.R.; Syn, N.L.; Ding, L.W.; Cheow, E.; Wong, R.; Wang, T.; Goh, R.; Song, H.; Jayasinghe, M.K.; et al. FAM3C in circulating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles promotes non-small cell lung cancer growth in secondary sites. Theranostics 2023, 13, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, Z.; Li, X.; Qiu, F.; Feng, Y.; You, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Overcoming tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in lung cancer brain metastasis with CTLA4 blockade. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 1882–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, K.; Zenmyo, M.; Watari, K.; Iguchi, H.; Fotovati, A.; Kimura, Y.N.; Hosoi, F.; Shoda, T.; Nagata, K.; Osada, H.; et al. Inhibition of bone and muscle metastases of lung cancer cells by a decrease in the number of monocytes/macrophages. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Qin, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yu, X.; Su, C. GABA regulates metabolic reprogramming to mediate the development of brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Fang, W.; Guo, Y.; Hu, P.; Shi, J. Nebulized Therapy of Early Orthotopic Lung Cancer by Iron-Based Nanoparticles: Macrophage-Regulated Ferroptosis of Cancer Stem Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24153–24165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, I.D.; Ella, E.; Dominsky, O.; Smith, Y.; Abraham, M.; Wald, H.; Shlomai, Z.; Zamir, G.; Feigelson, S.W.; Shezen, E.; et al. In the hunt for therapeutic targets: Mimicking the growth, metastasis, and stromal associations of early-stage lung cancer using a novel orthotopic animal model. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.N.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Kurie, J.M.; Kim, J. A Method for Orthotopic Transplantation of Lung Cancer in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2374, 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.J.; Seol, H.J.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, K.H.; Gorospe, M.; Nam, D.H.; Kim, H.H. MicroRNA-146a suppresses metastatic activity in brain metastasis. Mol. Cells 2012, 34, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Liu, Z.; Tallman, R.M.; Mohammad, A.; Sprowls, S.A.; Saralkar, P.A.; Vickers, S.D.; Pinti, M.V.; Gao, W.; Lockman, P.R. Drug resistance occurred in a newly characterized preclinical model of lung cancer brain metastasis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balathasan, L.; Beech, J.S.; Muschel, R.J. Ultrasonography-guided intracardiac injection: An improvement for quantitative brain colonization assays. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocking, K.L.; Jones, J.C.; Everds, N.E.; Buetow, B.S.; Roudier, M.P.; Miller, R.E. Use of low-molecular-weight heparin to decrease mortality in mice after intracardiac injection of tumor cells. Comp. Med. 2009, 59, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Su, B.; Yin, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wei, W.; Mei, Q.; et al. Targeting polarized phenotype of microglia via IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling to reduce NSCLC brain metastasis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunalli, G.; Dieterly, A.M.; Kemet, C.M.; Weng, H.Y.; Soepriatna, A.H.; Goergen, C.J.; Shinde, A.B.; Wendt, M.K.; Lyle, L.T. Dynamic transition of the blood-brain barrier in the development of non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6334–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho-Pereira, J.; Vaz, D.; Figueira, I.; Aniceto-Romao, J.; Krizbai, I.; Malho, R.; Rocha, J.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Simoes, S.; Gaspar, M.M.; et al. Breast Cancer Brain Metastases: Implementation and Characterization of a Mouse Model Relying on Malignant Cells Inoculation in the Carotid Artery. Cells 2023, 12, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhong, W.; Zhao, J. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of Gefitinib in a mouse model of non-small-cell lung carcinoma with brain metastasis. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Liu, H.; Zeng, J.; Ye, Z.; Ning, W.; Liang, Y.; et al. A novel optimized orthotopic mouse model for brain metastasis with sustained cerebral blood circulation and capability of multiple delivery. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2025, 42, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Dong, C.; Yin, S.; Liang, L.; Zhou, A. Protocol for generating brain metastatic tumor cells through repeated intracardiac injections in mice. STAR Protoc. 2025, 6, 103531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ren, J.; Wei, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Integrated analyses of multi-omic data derived from paired primary lung cancer and brain metastasis reveal the metabolic vulnerability as a novel therapeutic target. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, S.H.A.E.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Smits, M. Brain metastases: The role of clinical imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz De Mendivil, A.; Martín-Medina, P.; García-Cañamaque, L.; Jiménez-Munarriz, B.; Ciérvide, R.; Diamantopoulos, J. Challenges in radiological evaluation of brain metastases, beyond progression. Radiología 2024, 66, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikici, E.; Nguyen, X.V.; Bigelow, M.; Prevedello, L.M. Augmented networks for faster brain metastases detection in T1-weighted contrast-enhanced 3D MRI. Comput. Med. Imaging. Graph. 2022, 98, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, X.; Kimm, M.A.; Stechele, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wildgruber, M.; Ma, X. In vivo optical molecular imaging of inflammation and immunity. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsawaftah, N.; Farooq, A.; Dhou, S.; Majdalawieh, A.F. Bioluminescence Imaging Applications in Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.E.; Byrd, B.K.; Patil, R.A.; Strawbridge, R.R.; Davis, S.C.; Bellini, C.; Niedre, M. Heterogeneity of circulating tumor cell dissemination and lung metastases in a subcutaneous Lewis lung carcinoma model. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Bulte, J. Enzyme-mediated intratumoral self-assembly of nanotheranostics for enhanced imaging and tumor therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, L.; Emery, E.; Levallet, G.; Lechapt-Zalcman, E. Histopathologic diagnosis of brain metastases: Current trends in management and future considerations. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2017, 34, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Varinot, J.; Uzan, C.; Duval, A.; Brocheriou, I.; Canlorbe, G. The Role of Immunohistochemistry Markers in Endometrial Cancer with Mismatch Repair Deficiency: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, A.; Weitbrecht, T.; Gorbokon, N.; Buscheck, F.; Luebke, A.M.; Kluth, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Hinsch, A.; Hoflmayer, D.; Weidemann, S.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic impact of cytokeratin 18 expression in human tumors: A tissue microarray study on 11,952 tumors. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.; Waseem, N.H.; Nguyen, T.; Mohsin, S.; Jamal, A.; Teh, M.T.; Waseem, A. Vimentin is at the Heart of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Mediated Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Jing, W.; Zhu, H.; Li, M.; Zou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Kong, L.; Yue, J.; Yu, J. Clinical value of carcinoembryonic antigen for predicting the incidence of brain metastases and survival in small cell lung cancer patients treated with prophylactic cranial irradiation. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagna, J.P.; Feia, K. Isolated brain metastasis of prostate carcinoma in the setting of normal prostate specific antigen. Urol. Case Rep. 2018, 21, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.; Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; Mu, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y. Over-expression of S100B protein as a serum marker of brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer and its prognostic value. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Masaryk, T.; Mazzone, P.; Mekhail, T.; Fazio, V.; Mccartney, S.; Marchi, N.; Kanner, A.; Janigro, D. S100beta as a predictor of brain metastases: Brain versus cerebrovascular damage. Cancer 2005, 104, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Wei, Y. Association between brain metastasis from lung cancer and the serum level of myelin basic protein. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wu, G.S.; Wu, K. Enrichment of CD44 in basal-type breast cancer correlates with EMT, cancer stem cell gene profile, and prognosis. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Brlek, P.; Bukovac, A.; Kafka, A.; Pecina-Slaus, N. TWIST1 upregulation affects E-cadherin expression in brain metastases. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, M.; Nygaard, A.D.; Madsen, J.S.; Bechmann, T. S100B as a biomarker for brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 12, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Ma, H.; Shi, J.; Zhen, D. The expression of S100B protein in serum of patients with brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer and its clinical significance. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7107–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeda, N.; Iinuma, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsukahara, D.; Midorikawa, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Kumata, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Fukagawa, T.; et al. Plasma exosome-encapsulated microRNA-21 and microRNA-92a are promising biomarkers for the prediction of peritoneal recurrence in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4467–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.P.; Huang, G.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, K.T.; Chen, Y.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, M.C.; Wang, C.C. E-cadherin expression in the tumor microenvironment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinoma and the association with prognosis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhosary, E.; Shibel, P.; Eltoukhy, M.; Talaat, R.; Kamel, M.; Soliman, N.A. Downregulation of lncRNA-MALAT1, Altered Immunohistochemical Expression of Cyclin D1 Protein and E-Cadherin Protein in Correlation to Meningioma Grades. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2024, 25, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, N.; Li, D.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Liang, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. Dynamic monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor DNA to identify unique genetic profiles of brain metastatic tumors and better predict intracranial tumor responses in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A prospective cohort study (GASTO 1028). BMC Med. 2022, 20, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Hou, X.; Zheng, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, W.; Shao, Y.; Mou, Y.; et al. Utilizing phenotypic characteristics of metastatic brain tumors to improve the probability of detecting circulating tumor DNA from cerebrospinal fluid in non-small-cell lung cancer patients: Development and validation of a prediction model in a prospective cohort study. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100305. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Wan, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K.; et al. Anti-EGFR ScFv functionalized exosomes delivering LPCAT1 specific siRNAs for inhibition of lung cancer brain metastases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Khan, P.; Maurya, S.K.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Santamaria-Barria, J.A.; Batra, S.K.; Nasser, M.W. Liquid biopsies to occult brain metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, R. Metabolic Imaging of Brain Tumor Recurrence. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, O.; Lallement, A.; Jarnet, D.; Noblet, V.; Clavier, J.B.; Meyer, P. Automatic detection and segmentation of brain metastases on multimodal MR images with a deep convolutional neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 95, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkova, J.; Chen, R.J.; Chen, B.; Lu, M.Y.; Barbieri, M.; Shao, D.; Vaidya, A.J.; Chen, C.; Zhuang, L.; Williamson, D.; et al. Artificial intelligence for multimodal data integration in oncology. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liao, R.; Mahmood, A.A.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Q. PH-responsive pHLIP (pH low insertion peptide) nanoclusters of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a tumor-selective MRI contrast agent. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, A.; Rao, J.; Chaudhary, N.; Sharma, M.; Chang, S.D. Gold Nanoparticles for Brain Tumor Imaging: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Qian, H.; Yu, Y. Nanoparticles Mediated the Diagnosis and Therapy of Glioblastoma: Bypass or Cross the Blood–Brain Barrier. Small 2023, 19, e2302613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic—Implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype of circulating tumor cells is associated with distant metastasis in patients with NSCLC. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Jiang, B.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhong, W.Z.; Tu, H.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Unique genetic profiles from cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: A new medium of liquid biopsy. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catelan, S.; Olioso, D.; Santangelo, A.; Scapoli, C.; Tamanini, A.; Pinna, G.; Sala, F.; Lippi, G.; Nicolato, A.; Cabrini, G.; et al. MiRNAs in Serum Exosomes for Differential Diagnosis of Brain Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Yee, G.T. Surgical resection versus stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases in the motor cortex; A meta-analysis and systematic review. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2024, 41, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E.L. Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockemeyer, K.G.; Rusthoven, C.G.; Pike, L. Advances in the Management of Lung Cancer Brain Metastases. Cancers 2024, 16, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicella, G.; Paolini, M.; Deantonio, L.; Masini, L.; Krengli, M. Radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma: Review of recent literature results. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2016, 21, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puataweepong, P.; Dhanacha, M.; Ruangkanchanasetr, R.; Boonyawan, K.; Hansasuta, A.; Saetia, K.; Yongvithisatid, P. Long-term clinical outcomes of stereotactic radiotherapy for bilateral vestibular schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2 patients. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 164, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Bauman, G.; Bradfield, L.; Burri, S.H.; Cabrera, A.R.; Cunningham, D.A.; Eaton, B.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kim, M.M.; Kotecha, R.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Shireman, J.M.; Shiue, K.; Kamer, A.; Boyd, L.; Zang, Y.; Mukherjee, N.; Miller, J.; Kulwin, C.; Cohen-Gadol, A.; et al. Preoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with 1-4 brain metastases: A single-arm phase 2 trial outcome analysis (NCT03398694). Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2024, 11, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chou, L.S.; Wu, Y.H.; Kuo, J.S.; Mehta, M.P.; Shiau, A.C.; Liang, J.A.; Hsu, S.M.; Wang, T.H. Developing an AI-assisted planning pipeline for hippocampal avoidance whole brain radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 181, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, I.; Rau, A.; Kellner, E.; Reisert, M.; Fennell, J.T.; Rothe, T.; Nieder, C.; Urbach, H.; Egger, K.; Grosu, A.L.; et al. Hippocampus-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy is Efficient in the Long-Term Preservation of Hippocampal Volume. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 714709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Planchard, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, C.K.; Valdiviezo, N.; Laktionov, K.; Yang, T.Y.; Yu, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, L.; Qian, J.Q.; Qiu, T.Z.; Shu, Y.Q.; Liu, P. Temozolomide for treatment of brain metastases: A review of 21 clinical trials. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcuoglu, B.; Karakurt, G.; Kaya, O.O.; Diniz, G.; Kirbiyik, O.; Evkan, A.; Yalniz, E. Investigation of EGFR and ALK mutation frequency and treatment results in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2023, 19, S183–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sznol, M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Cohen, J.; Vortmeyer, A.; Jilaveanu, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: Early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvartsman, G.; Ferrarotto, R.; Massarelli, E. Checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer: Latest developments and clinical potential. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Xue, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, H.; Hou, X.; Kang, D.D.; Liu, Z.; Tian, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Intravenous administration of blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugates facilitate biomacromolecule transport into central nervous system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Petrisor, G.; Motelica, L.; Craciun, L.N.; Oprea, O.C.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A. Melissa officinalis: Composition, Pharmacological Effects and Derived Release Systems-a Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Sofias, A.M.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Nanoparticle Delivery to Tumours: From EPR and ATR Mechanisms to Clinical Impact. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Du, C.; Guo, N.; Teng, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Galons, H. Composition design and medical application of liposomes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.L.; Devarajan, P.V. Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated, targeted and sustained brain delivery of curcumin microemulsion. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, M.; Lin, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, S. Delivery of quercetin for breast cancer and targeting potentiation via hyaluronic nano-micelles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, T.; Zheng, T.; Wang, Y.; You, C. Biodegradable micelles enhance the antiglioma activity of curcumin in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2721–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Gao, S.; Asghar, S.; Liu, G.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; Ping, Q.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y. Hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for delivery of curcuminoid and its in vitro evaluation in glioma cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Valenteen, F.; Mikhael, S.; Wang, H.; Sims, J.; Taguiam, M.; Teh, J.; Sances, S.; Wong, M.; Miao, T.; Srinivas, D.; et al. Systemic HER3 ligand-mimicking nanobioparticles enter the brain and reduce intracranial tumour growth. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2025, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylawsky, D.E.; Kiguchi, H.; Vaynshteyn, J.; Gerwin, J.; Shah, J.; Islam, T.; Boyer, J.A.; Boue, D.R.; Snuderl, M.; Greenblatt, M.B.; et al. P-selectin-targeted nanocarriers induce active crossing of the blood-brain barrier via caveolin-1-dependent transcytosis. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Pan, M.; Hu, D.; Chu, B.; Qu, Y.; Qian, Z. Genetically programmable cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles for targeted combination therapy of colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.U.; Ni, J.; Ju, X.; Miao, T.; Chen, H.; Han, L. Escape from abluminal LRP1-mediated clearance for boosted nanoparticle brain delivery and brain metastasis treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, M.; Liljenback, H.; Virta, J.; Karna, S.; Viitanen, R.; Elo, P.; Gardberg, M.; Teuho, J.; Saipa, P.; Rajander, J.; et al. High folate receptor expression in gliomas can be detected in vivo using folate-based positron emission tomography with high tumor-to-brain uptake ratio divulging potential future targeting possibilities. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, A.; Tornesello, A.L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. Cell Penetrating Peptides as Molecular Carriers for Anti-Cancer Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvenna, P.; Nankivell, M.; Barton, R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Wilson, P.; Mccoll, E.; Moore, B.; Brisbane, I.; Ardron, D.; Holt, T.; et al. Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): Results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.D.; Klamer, B.G.; Ballman, K.V.; Brown, P.D.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; et al. Association of Long-term Outcomes with Stereotactic Radiosurgery vs Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Resected Brain Metastasis: A Secondary Analysis of the N107C/CEC.3 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology/Canadian Cancer Trials Group) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Han, J.Y.; Katakami, N.; Kim, H.R.; Hodge, R.; Kaur, P.; Brown, A.P.; Ghiorghiu, D.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib in Patients with T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Data From a Randomized Phase III Trial (AURA3). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garassino, M.C.; Gadgeel, S.; Speranza, G.; Felip, E.; Esteban, E.; Domine, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; Bischoff, H.G.; Peled, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab Plus Pemetrexed and Platinum in Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes From the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-189 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Koonjoo, N.; Boele, T.; Lu, J.; Waddington, D.; Zhang, M.; Rosen, M.S. Enhancing organ and vascular contrast in preclinical ultra-low field MRI using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.; Fletcher, N.; Mccart, R.A.; Flint, M.; Thurecht, K.; Saunus, J.; Lakhani, S.R. Modeling Brain Metastasis by Internal Carotid Artery Injection of Cancer Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 186, e64216. [Google Scholar]
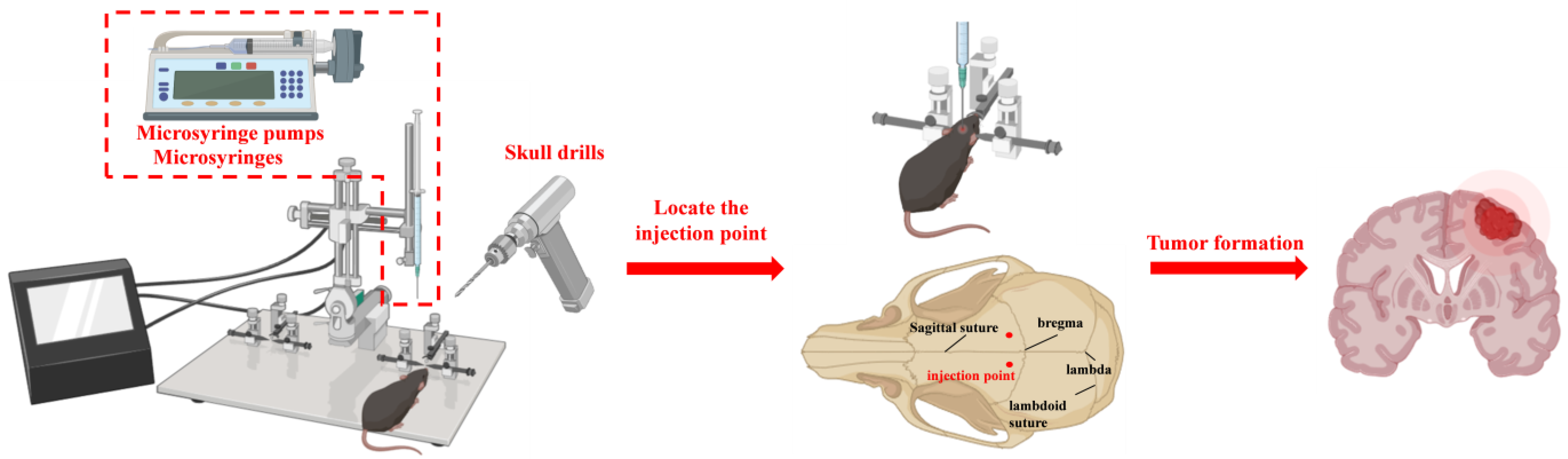

| Modeling Method | Applicable Research Scope | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stereotactic Intracranial Injection | Suitable for pharmacological evaluation of anti-brain tumor drugs | The high success rate in the model establishment | Cannot simulate the process of tumor cells forming in situ and then colonizing in the brain through the BBB |
| Tail Vein Injection | It better simulates the various processes of tumor development, progression, and metastasis, and is suitable for research on the occurrence mechanism, diagnosis, and treatment of brain metastasis of lung cancer | Simple operation, high likelihood of invasion and metastasis | Low brain specificity, prone to metastasis in other sites causing premature death in mice |
| In situ Injection | High consistency with clinical lung cancer, high tumor formation rate, and ability to metastasize | High technical difficulty in operation, prone to causing pneumothorax and death in mice, low brain metastasis rate, and short survival time | |
| Left Ventricular Injection | Consistent with the biological characteristics of brain metastasis, high success rate in model establishment | High surgical difficulty, prone to causing death in mice during model establishment | |
| Carotid Injection | Well simulates the hematogenous metastasis process of lung cancer, high brain specificity, and higher success rate in model establishment | High surgical skill requirement, need to be familiar with the anatomical relationship of the carotid artery |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Liu, L.; Li, R. Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091588
Chen Y, Zhang A, Wang J, Pan H, Liu L, Li R. Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091588
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ying, Ao Zhang, Jingrong Wang, Hudan Pan, Liang Liu, and Runze Li. 2025. "Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091588
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhang, A., Wang, J., Pan, H., Liu, L., & Li, R. (2025). Refining Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis Models for Spatiotemporal Dynamic Research and Personalized Therapy. Cancers, 17(9), 1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091588






