Patterns of Comorbidities in Lung Cancer Patients and Survival
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Socio-Economic and Healthcare Setting
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Comorbidities
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
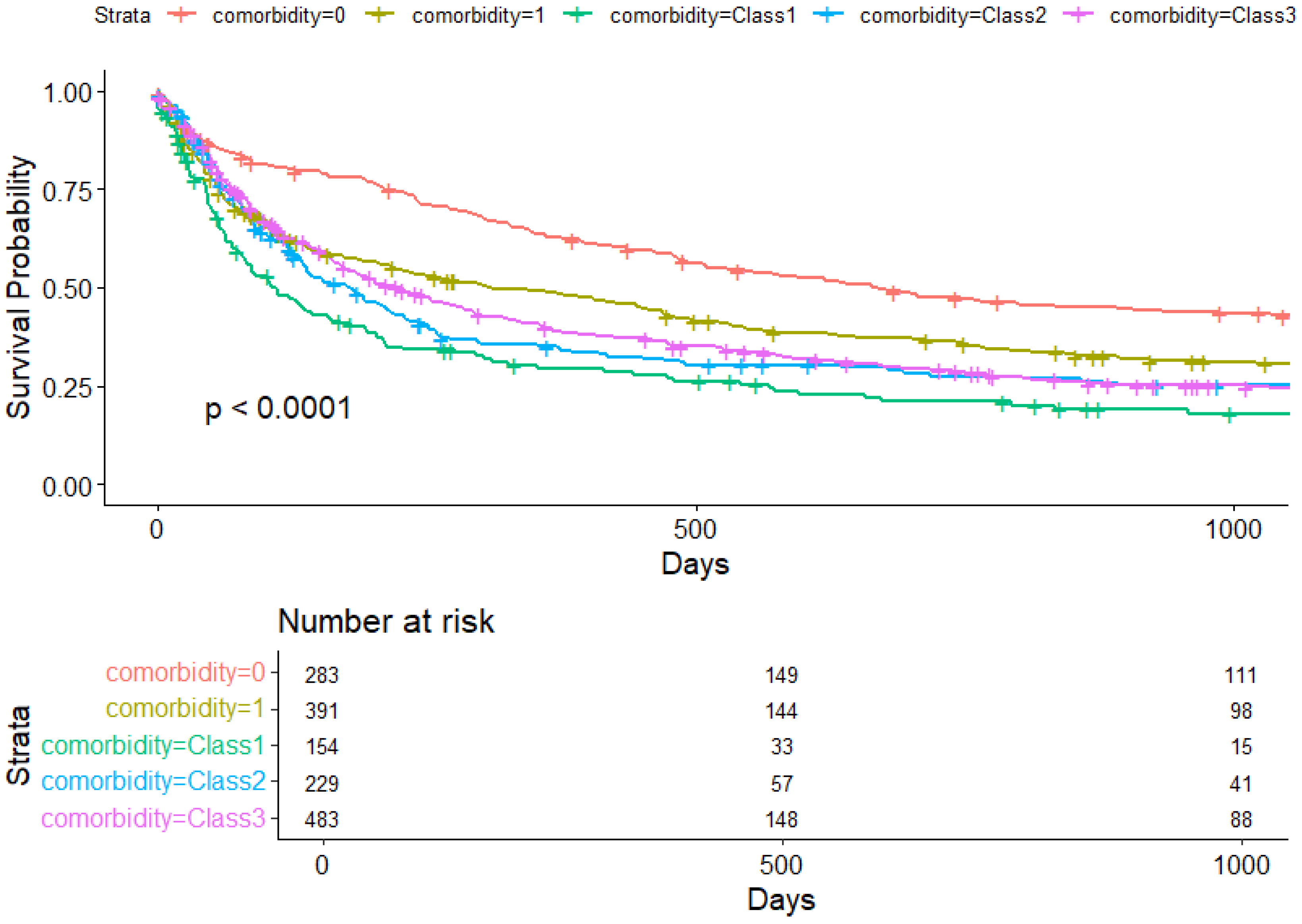
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klastersky, J.A. The conquest of lung cancer in Central Europe. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.; Ambs, S. How Comorbidities Shape Cancer Biology and Survival. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Metwally, E.M.; Rivera, M.P.; Durham, D.D.; Lane, L.; Perera, P.; Lamb, D.; Henderson, L.M. Lung Cancer Screening in Individuals With and Without Lung-Related Comorbidities. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2230146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, R.; Cheung, M.C.; Pedroso, F.E.; Byrne, M.M.; Koniaris, L.G.; Zimmers, T.A. Obesity and weight loss at presentation of lung cancer are associated with opposite effects on survival. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 170, e75–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammemagi, C.M.; Neslund-Dudas, C.; Simoff, M.; Kvale, P. In lung cancer patients, age, race-ethnicity, gender and smoking predict adverse comorbidity, which in turn predicts treatment and survival. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuran, T.; Thomsen, R.W.; Nørgaard, M.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Rasmussen, T.R.; Søgaard, M. Comorbidity and survival of Danish lung cancer patients from 2000–2011: A population-based cohort study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 1), 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.M.M.; Jiang, X.; Anggondowati, T.; Lin, G.; Ganti, A.K. Comorbidity and Survival in Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkowska, A.; Antczak, A. Comorbidities in Lung Cancer. Adv. Respir. Med. 2016, 84, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irisa, K.; Masago, K.; Togashi, Y.; Fujita, S.; Hatachi, Y.; Fukuhara, A.; Sakamori, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Mio, T.; Mishima, M. Significance of pretreatment comorbidities in elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy or epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grose, D.; Morrison, D.S.; Devereux, G.; Jones, R.; Sharma, D.; Selby, C.; Docherty, K.; McIntosh, D.; Louden, G.; Nicolson, M.; et al. Comorbidities in lung cancer: Prevalence, severity and links with socioeconomic status and treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawski, M.; Walter, J.; Schwarzkopf, L. Assessing the lung cancer comorbidome: An analysis of German claims data. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.; Cheng, C.Y.; Hernandez-Villafuerte, K.; Schlander, M. Survival and comorbidities in lung cancer patients: Evidence from administrative claims data in Germany. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2023, 30, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iachina, M.; Jakobsen, E.; Møller, H.; Lüchtenborg, M.; Mellemgaard, A.; Krasnik, M.; Green, A. The effect of different comorbidities on survival of non-small cells lung cancer patients. Lung 2015, 193, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM). ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective 1 October 2011. Available online: https://archive.cdc.gov/www_cdc_gov/nchs/icd/icd9cm_addenda_guidelines.htm (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Stoica, P.; Selen, Y. Model-order selection: A review of information criterion rules. IEEE Signal Process. 2004, 21, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, R.; Wuensch, M.; Edlinger, R.; Hammerl-Ferrari, B.; Kramer, L.; Geissler, K. Komorbiditätsorientierte Onkologie—Ein Uberblick [Comorbidity oriented oncology—An overview]. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2010, 122, 203–218. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, C.; Antoni, D.; Charloux, A.; Falcoz, P.E.; Quoix, E. Comorbidities in the management of patients with lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, I.; Cooper, M.; Memon, A.; Forbes, L.; van Marwijk, H.; Ford, E. The effect of comorbidities on diagnostic interval for lung cancer in England: A cohort study using electronic health record data. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gould, M.K.; Munoz-Plaza, C.E.; Hahn, E.E.; Lee, J.S.; Parry, C.; Shen, E. Comorbidity Profiles and Their Effect on Treatment Selection and Survival among Patients with Lung Cancer. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birim, O.; Kappetein, A.P.; Bogers, A.J. Charlson comorbidity index as a predictor of long-term outcome after surgery for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2005, 28, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, A.; Yaşar, A.; Karcı, E.; Köksoy, E.B.; Ürün, M.; Şenler, F.Ç.; Ürün, Y.; Tuncay, G.; Ergün, H.; Akbulut, H. Severe drug interactions and potentially inappropriate medication usage in elderly cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2017, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluchart, H.; Chanoine, S.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Chouaid, C.; Frey, G.; Villa, J.; Degano, B.; Levra, M.G.; Bedouch, P.; Toffart, A.C. Lung cancer, comorbidities, and medication: The infernal trio. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1016976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Frank, M.S.; Bodtger, U. An Individualized Approach to Comorbidities in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, F.; Russo, A.; Andreano, A.; Braga, M.; Renzi, C. Diagnostic pathways and outcomes by comorbidity in cancer patients: A study in Northern Italy. Eur. J. Public Health 2024, 34 (Suppl. 3), ckae144.1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimptsch, U. Disease-Specific Trends of Comorbidity Coding and Implications for Risk Adjustment in Hospital Administrative Data. Health Serv. Res. 2016, 51, 981–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Number (%) | Mean (%) Comorbidities | |
|---|---|---|
| GENDER | ||
| Females | 611 (36.50) | 1.93 (51.81) |
| Males | 1063 (63.50) | 2,18 (58.72) |
| AGE CLASS AT DIAGNOSIS | ||
| <65 | 316 (18.88) | 1.89 (49.83) |
| 65–69 | 207 (12.37) | 1.99 (54.74) |
| 70–74 | 328 (19.59) | 1.90 (52.61) |
| 75–79 | 3509 (18.46) | 2.11 (56.94) |
| 80–84 | 245 (14.64) | 2.28 (62.66) |
| >85 | 269 (16.07) | 2.44 (62.55) |
| NUMBER OF COMORBIDITIES | ||
| 0 | 283 (16.91) | |
| 1 | 391 (23.36) | |
| 2 | 309 (18.46) | |
| 3 | 245 (14.64) | |
| 4 | 172 (10.27) | |
| 5 | 82 (4.9) | |
| 6 | 37 (2.21) | |
| 7 | 16 (0.96) | |
| ≥8 | 5 (0.30) | |
| Missing data | 134 (8.0) | |
| ICD9-CM DISEASE CATEGORY CLASSIFICATION | ||
| Respiratory System | 608 (36.32) | |
| Circulatory System | 596 (35.6) | |
| Factors Influencing Health Status (V_codes) | 404 (24.13) | |
| Symptoms, Signs, and Undefined Conditions | 291 (17.38) | |
| Endocrine, Nutrition, Metabolism, and Immune Disorders | 231 (13.8) | |
| Genitourinary System | 178 (10.63) | |
| Blood and Hematopoietic Organs | 164 (9.8) | |
| Digestive System | 163 (9.74) | |
| Injuries and Poisoning | 151 (9.02) | |
| Nervous System and Sense Organs | 123 (7.35) | |
| Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue | 117 (6.99) | |
| Infectious and Parasitic Diseases | 89 (5.32) | |
| Mental Disorders | 69 (4.12) | |
| ICD9-CM Disease Category Classification | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious and Parasitic Diseases | 0.01% | 26.62% | 2.35% |
| Endocrine, Nutrition, Metabolism, and Immune Disorders | 32.54% | 26.91% | 20.79% |
| Blood and Hematopoietic Organs | 8.78% | 25.22% | 15.76% |
| Mental Disorders | 7.16% | 6.11% | 8.26% |
| Nervous System and Sense Organs | 6.86% | 6.61% | 16.71% |
| Circulatory System | 99.91% | 52.57% | 51.44% |
| Respiratory System | 83.16% | 45.34% | 56.93% |
| Digestive System | 3.44% | 36.11% | 9.58% |
| Genitourinary System | 19.12% | 35.31% | 10.13% |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | 4.53% | 15.08% | 12.51% |
| Symptoms, Signs, and Undefined Conditions | 10.48% | 25.74% | 36.93% |
| Injuries and Poisoning | 1.08% | 19.99% | 17.32% |
| Factors Influencing Health Status (V codes) | 1.90% | 29.58% | 59.27% |
| All-Cause Deaths | Lung Cancer Deaths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (Lower-Upper) | p-Value | HR (Lower-Upper) | p-Value | |
| Presence of comorbidity | 1.33 (1.11–1.59) | 0.002 | 1.17 (1.0–1.43) | 0.114 |
| Comorbidity Class 1 | 1.74 (1.39–2.17) | <0.001 | 1.49 (1.2–1.91) | 0.001 |
| Comorbidity Class 2 | 1.44 (1.18–1.77) | <0.001 | 1.25 (1.0–1.57) | 0.048 |
| Comorbidity Class 3 | 1.62 (1.36–1.93) | <0.001 | 1.23 (1.0–1.48) | 0.035 |
| Male gender | 1.26 (1.12–1.42) | <0.001 | 1.11 (1.0–1.26) | 0.130 |
| Age | 1.03 (1.03–1.04) | <0.001 | 1.02 (1.0–1.03) | 0.000 |
| Stage II | 2.54 (1.64–3.94) | <0.001 | 1.61 (0.8–3.21) | 0.177 |
| Stage III | 5.27 (3.70–7.51) | <0.001 | 3.12 (1.7–5.67) | <0.001 |
| Stage IV | 11.95 (8.59–16.63) | <0.001 | 5.32 (3.0–9.45) | <0.001 |
| Missing stage | 11.01 (6.97–17.39) | <0.001 | 9.17 (4.7–17.94) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buja, A.; Di Pumpo, M.; Rugge, M.; Zorzi, M.; Rea, F.; Pantaleo, I.; Scroccaro, G.; Conte, P.; Rigon, L.; Arcara, G.; et al. Patterns of Comorbidities in Lung Cancer Patients and Survival. Cancers 2025, 17, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091577
Buja A, Di Pumpo M, Rugge M, Zorzi M, Rea F, Pantaleo I, Scroccaro G, Conte P, Rigon L, Arcara G, et al. Patterns of Comorbidities in Lung Cancer Patients and Survival. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091577
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuja, Alessandra, Marcello Di Pumpo, Massimo Rugge, Manuel Zorzi, Federico Rea, Ilaria Pantaleo, Giovanna Scroccaro, Pierfranco Conte, Leonardo Rigon, Giorgio Arcara, and et al. 2025. "Patterns of Comorbidities in Lung Cancer Patients and Survival" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091577
APA StyleBuja, A., Di Pumpo, M., Rugge, M., Zorzi, M., Rea, F., Pantaleo, I., Scroccaro, G., Conte, P., Rigon, L., Arcara, G., Pasello, G., & Guarneri, V., on behalf of Rete Oncologica Veneta and Periplo Foundation. (2025). Patterns of Comorbidities in Lung Cancer Patients and Survival. Cancers, 17(9), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091577







