Reassessing the Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 in Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Lesions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
3. Results
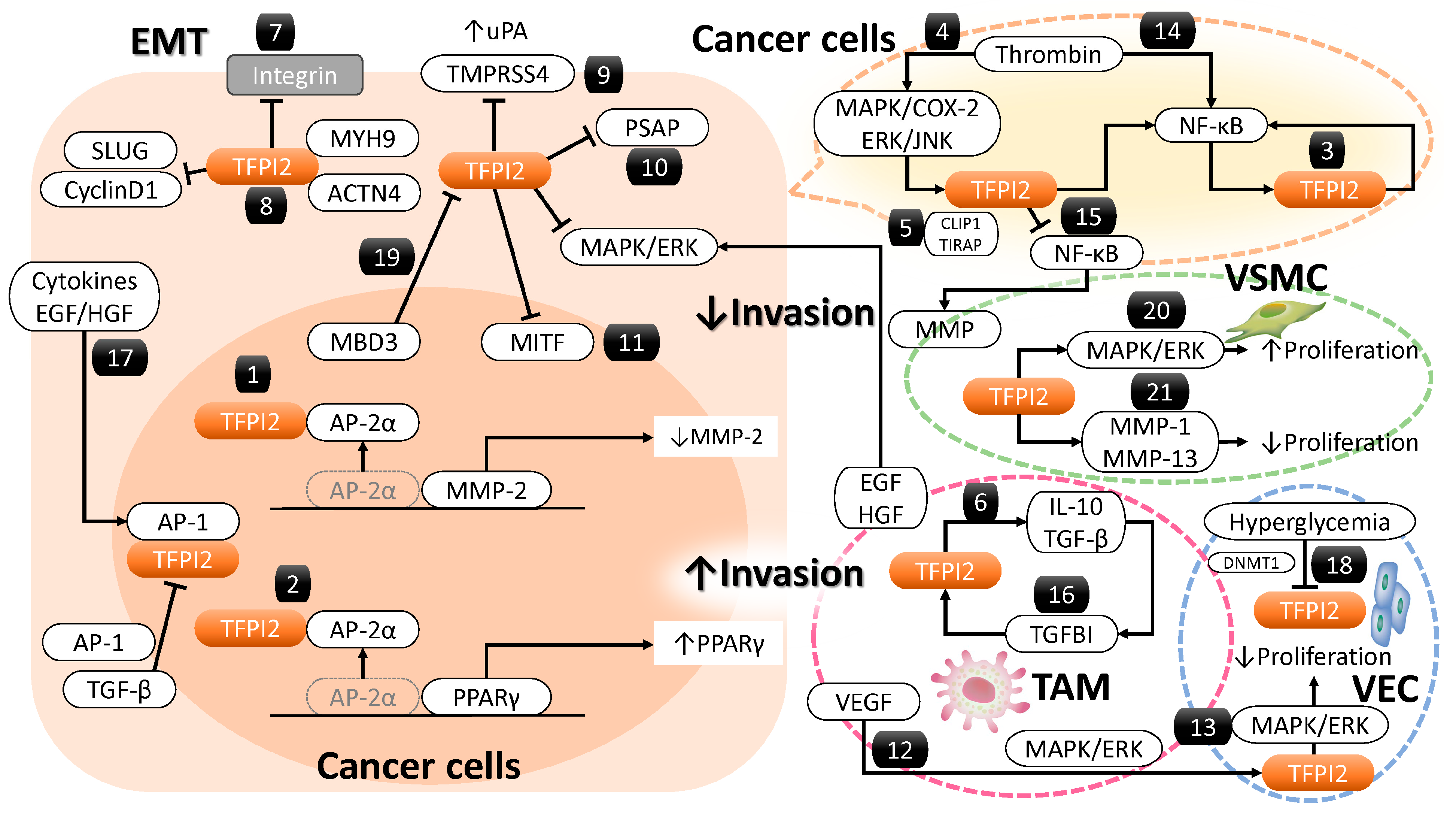
3.1. Localization and Function of the TFPI2 Molecule
3.2. Molecules and Signaling Pathways Regulated by TFPI2
3.2.1. MMP-2 Regulation by TFPI2
3.2.2. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARγ) and Its Regulation by TFPI2
3.2.3. Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) and Its Regulation by TFPI2
3.2.4. Regulation of TFPI2-Dependent NF-κB Activation by CAP-Gly Domain-Containing Linker Protein 1 (CLIP1)
3.2.5. Regulation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK)/ERK Pathway by TFPI2
3.2.6. Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β) Signaling by TFPI2
3.2.7. TFPI2 and Integrin-Mediated Focal Adhesion Dynamics
3.2.8. Cytoskeletal Regulation by TFPI2
3.2.9. TFPI2-Mediated Regulatory Role of Transmembrane Protease Serine 4 (TMPRSS4)
3.2.10. TFPI2-Mediated Regulatory Role of Prosaposin (PSAP)
3.2.11. TFPI2-Mediated Suppression of Melanocyte-Induced Transcription Factor (MITF)
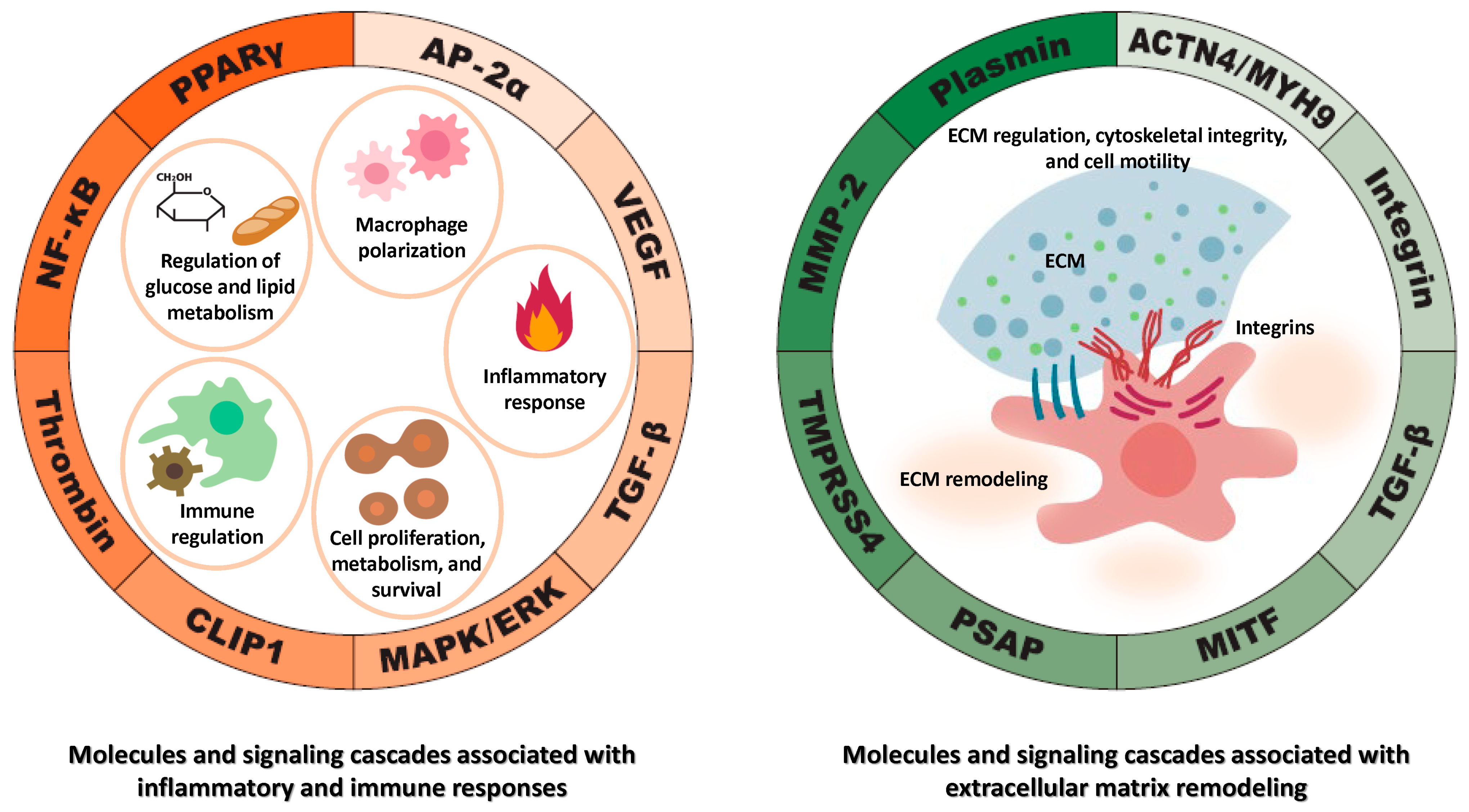
3.3. Regulation of TFPI2 Expression: Molecular Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways
3.3.1. Factors Contributing to TFPI2 Upregulation (Figure 4, Left)
Signaling Pathway
Inflammatory Cytokines
Transcription Factors
miRNA/lncRNA
Others
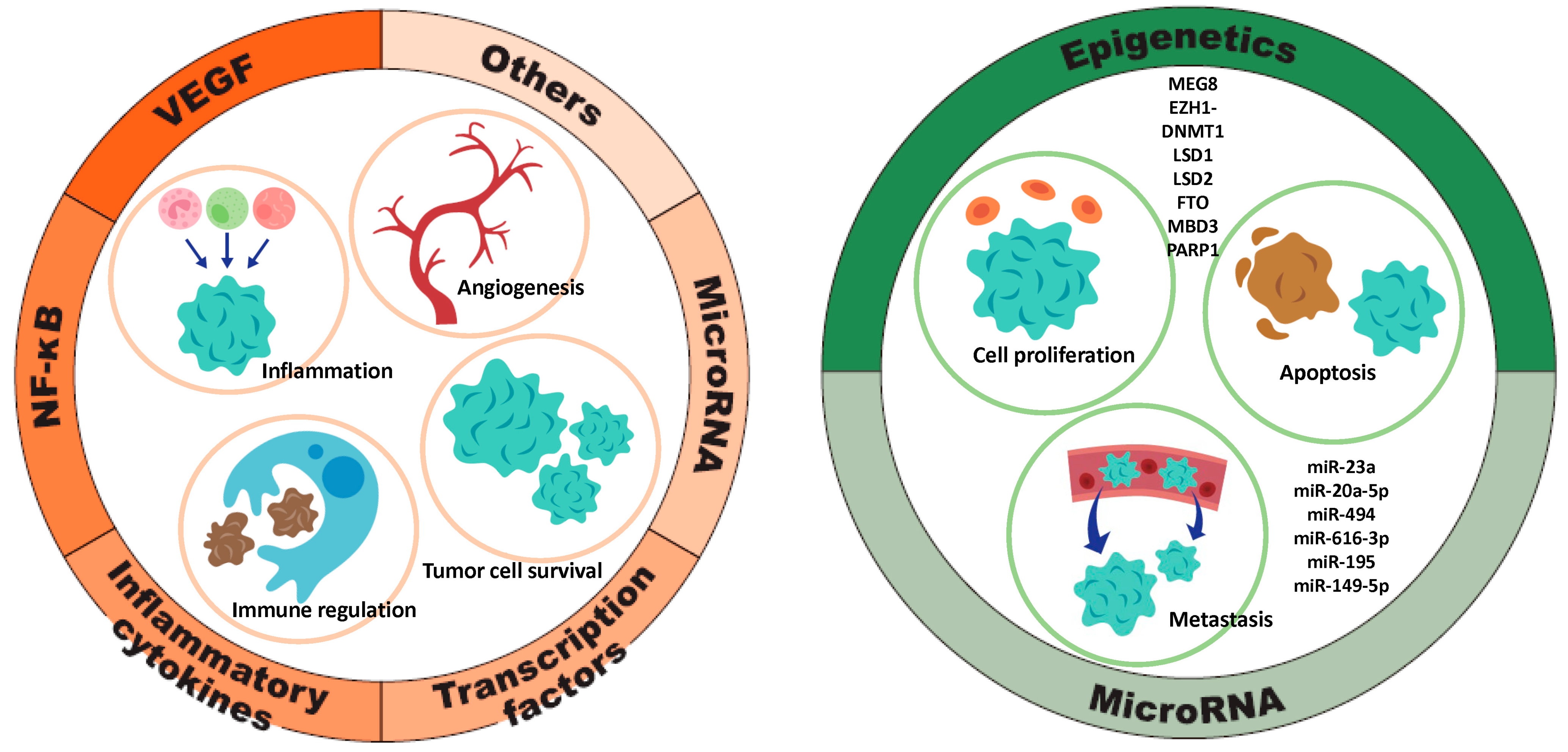
3.3.2. Factors That Downregulate TFPI2 Expression (Figure 4, Right)
miRNA
Epigenetic Regulation of TFPI2 Expression
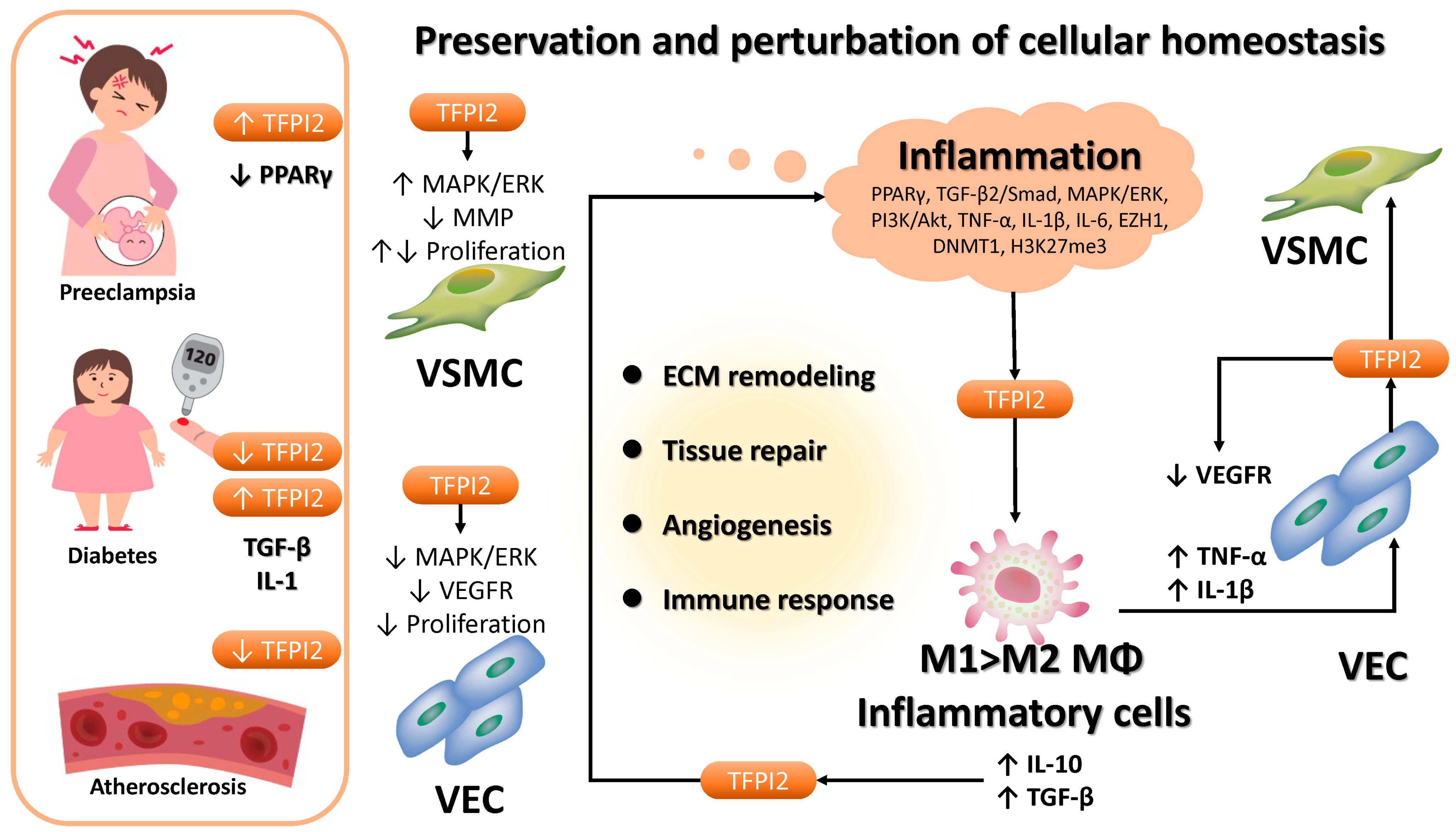
3.4. Role of TFPI2 in Non-Neoplastic Diseases
3.5. Effects of TFPI2 on Cancer Malignancy
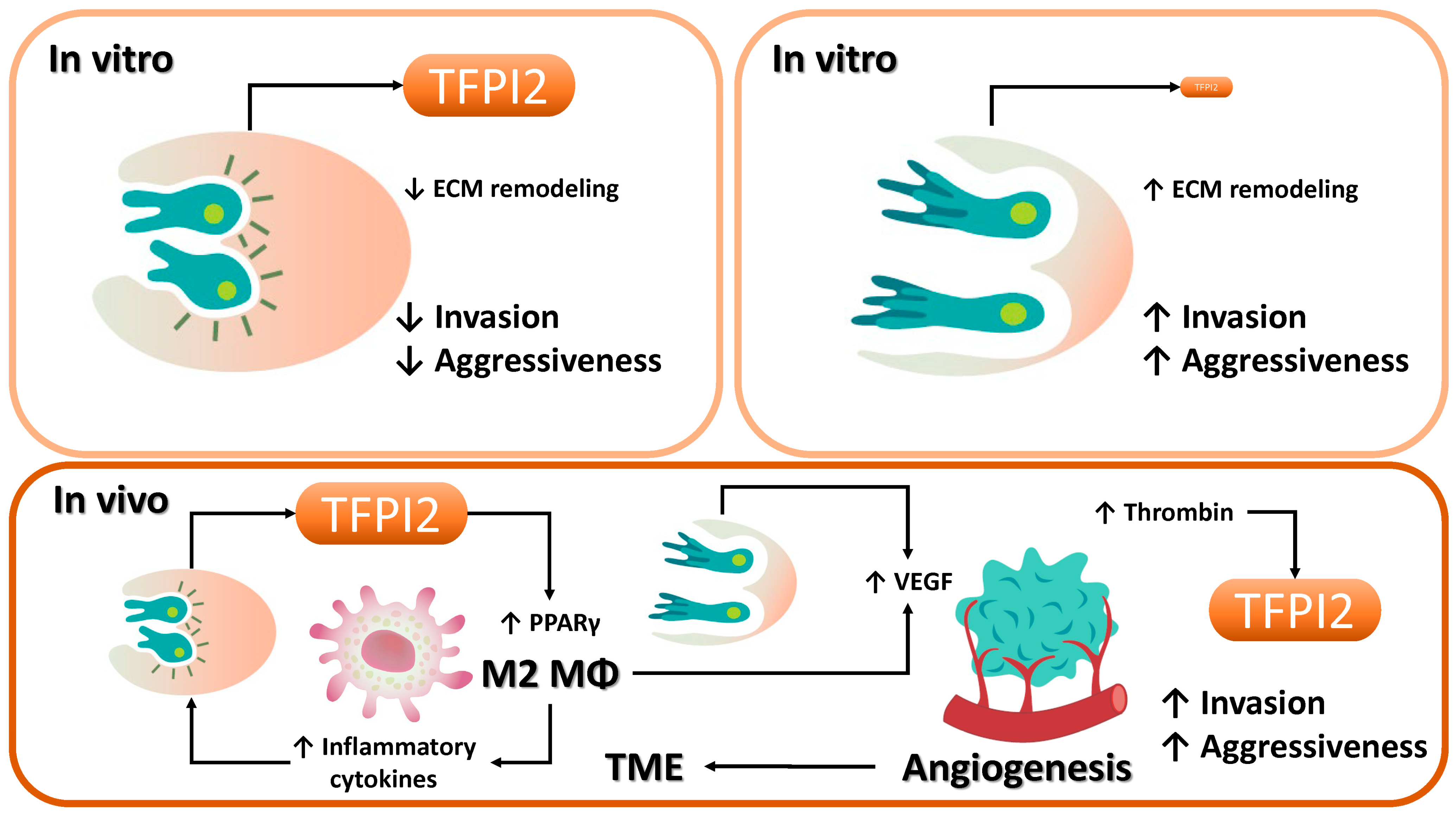
3.5.1. Tumor Suppressive Function of TFPI2
3.5.2. Tumor-Promoting Role of TFPI2
3.6. Impact of TFPI2 on Prognosis
3.6.1. Tissue TFPI2 Levels and Prognostic Significance
TFPI2 Expression in Ovarian, Endometrial, and Renal Cell Carcinomas
3.6.2. Serum TFPI2 Levels and Prognostic Significance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyagi, Y.; Koshikawa, N.; Yasumitsu, H.; Miyagi, E.; Hirahara, F.; Aoki, I.; Misugi, K.; Umeda, M.; Miyazaki, K. cDNA cloning and mRNA expression of a serine proteinase inhibitor secreted by cancer cells: Identification as placental protein 5 and tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2. J. Biochem. 1994, 116, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, H.S.; Foster, D.C.; Kisiel, W. Structure, function and biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Matsubara, S.; Imanaka, S. The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in the coagulation and fibrinolysis system. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2023, 49, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroney, S.A.; Mast, A.E. Expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor by endothelial cells and platelets. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2008, 38, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broze, G.J., Jr. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor and the revised theory of coagulation. Annu. Rev. Med. 1995, 46, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, K.; Ponnuraj, S.-M.; Kumar, Y.; Zaiss, A.K.; Bunce, M.W.; Camire, R.M.; Wu, L.; Evseenko, D.; Herschman, H.R.; Bajaj, M.S.; et al. Platelets contain tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 derived from megakaryocytes and inhibits fibrinolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 31647–31661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.P.; Sukhova, G.K.; Kisiel, W.; Foster, D.; Kehry, M.R.; Libby, P.; Schönbeck, U. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is a novel inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases with implications for atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierko, E.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Kisiel, W. The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in cancer biology. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2007, 33, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, B.; Yu, J.; Gao, W.; Pan, J.; Luo, X.; Shi, H. Conditional knockout of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in vascular endothelial cells accelerates atherosclerotic plaque development in mice. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Xie, J.; Dai, Y.; Han, H. TFPI2 suppresses the interaction of TGF-β2 pathway regulators to promote endothelial–mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Miyake, R.; Yamada, Y.; Kawaguchi, R.; Ootake, N.; Myoba, S.; Kobayashi, H. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2: A Novel Biomarker for Predicting Asymptomatic Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2022, 87, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, R.; Yamada, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Kawaguchi, R.; Ootake, N.; Myoba, S.; Kobayashi, H. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 as a serum marker for diagnosing asymptomatic venous thromboembolism in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer and positive D-dimer results. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 16, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, P.; Gu, W. TFPI-2 suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion through regulation of ERK signaling and interaction with actinin-4 and myosin-9. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Matsubara, S.; Yoshimoto, C.; Shigetomi, H.; Imanaka, S. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2: Current understanding, challenges, and future perspectives. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2023, 49, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Mysliwiec, M.; Tokajuk, A.; Kruszewska, J.; Politynska, B.; Jamroze, A.; Wojtukiewicz, A.M.; Tang, D.G.; Honn, K.V. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2)—An underappreciated partaker in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 1185–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Imanaka, S.; Matsubara, S.; Shigetomi, H.; Yoshimoto, C. Dual Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2—A Novel Serodiagnostic Marker for Ovarian Cancer—In Human Cancers. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 4, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Koizume, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoshihara, M.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, S.; Myoba, S.; Ohtake, N.; Kato, H.; Yokose, T.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is specifically expressed in ovarian clear cell carcinoma tissues in the nucleus, cytoplasm and extracellular matrix. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehana, T.; Kawaguchi, R.; Nishikawa, K.; Kawahara, N.; Yamada, Y.; Kimura, F. Investigating the efficacy of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 as a promising prognostic marker for ovarian cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Jikuya, R.; Myoba, S.; Tatenuma, T.; Noguchi, G.; Ueno, D.; Ito, Y.; Komeya, M.; Muraoka, K.; Yao, M.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TFPI2) is a potential serum biomarker for clear cell renal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Yamada, Y.; Kawaguchi, R.; Ootake, N.; Myoba, S.; Kimura, F. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2: A potential diagnostic marker for discriminating benign from malignant ovarian tumors. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2022, 48, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Maehana, T.; Yamanaka, S.; Miyake, R.; Kawahara, N.; Iwai, K.; Yamada, Y.; Kimura, F. Preoperative serum tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 level as a prognostic marker for endometrial cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 26, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uomoto, M.; Ota, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yumori, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Koizume, S.; Sato, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Myoba, S.; Ohtake, N.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 as a serum biomarker for endometrial cancer: A single-center retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wu, D.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y. Downregulated DUXAP8 lncRNA impedes trophoblast cell proliferation and migration by epigenetically upregulating TFPI2 expression. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2023, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Xia, Z.; Hong, Y.; Ji, H.; Li, F.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Xin, H.; Tan, K.; Lian, Z. The TFPI2–PPARγ axis induces M2 polarization and inhibits fibroblast activation to promote recovery from post-myocardial infarction in diabetic mice. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierko, E.; Zimnoch, L.; Kozlowski, L.; Kisiel, W.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z. Immunohistochemical localization of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in human tumor tissue. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, K.; Yasumitsu, H.; Esaki, M.; Sawada, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Aoki, I.; Jin, M.; Miyagi, E.; Nakazawa, T.; Hirahara, F.; et al. Subcellular localization of PP5/TFPI-2 in human placenta: A possible role of PP5/TFPI-2 as an anti-coagulant on the surface of syncytiotrophoblasts. Placenta 2002, 23, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.; Goulding, D.A.; Ferreira, V.; Severs, N.J.; Lupu, F. Expression and localization of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in normal and atherosclerotic human vessels. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puttabyatappa, M.; Al-Alem, L.F.; Zakerkish, F.; Rosewell, K.L.; Brännström, M.; Curry, T.E., Jr. Induction of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 by hCG Regulates Periovulatory Gene Expression and Plasmin Activity. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Maiti, D.; Kisiel, W.; Duh, E.J. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is upregulated by vascular endothelial growth factor and suppresses growth factor-induced proliferation of endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Singer, R.H.; Gu, W. Localization of TFPI-2 in the nucleus modulates MMP-2 gene expression in breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Mohanam, S.; Puppala, A.; Rao, J.S. Regulation of ProMMP-1 and ProMMP-3 activation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2/matrix-associated serine protease inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 255, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Gondi, C.S.; Dinh, D.H.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Restoration of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2 in a Human Glioblastoma Cell Line Triggers Caspase-Mediated Pathway and Apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.-J.; Shi, H.-M.; Luo, X.-P.; Ma, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liang, W.; Mu, J.-G.; Li, J. Recombinant TFPI-2 enhances macrophage apoptosis through upregulation of Fas/FasL. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Zhou, C.; Hong, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, W.; Ji, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; et al. TFPI2 hypermethylation promotes diabetic atherosclerosis progression through the Ap2α/PPARγ axis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiology. 2025, 198, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, C.; Chatelain, N.; Delestre, M.; Susen, S.; Quesnel, B.; Juthier, F.; Jeanpierre, E.; Azzaoui, R.; Corseaux, D.; Breyne, J.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 gene methylation is associated with low expression in carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, e4–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, D.; Sun, F.; Liang, W.; Liu, R.; Shen, W.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Hu, R.; Liu, R.; et al. Over-expression of TFPI-2 promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability by inhibiting MMPs in apoE−/− mice. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, R.-L.; Luo, X.-P.; Shi, H.-M.; Ma, D.; Pan, J.-J.; Ni, H.-C. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2 Gene Polymorphisms Associate with Coronary Atherosclerosis in Chinese Population. Medicine 2015, 94, e1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z.; Hui, B.; Wang, J.; Qian, W.; Ge, Z.; et al. MiR-616-3p modulates cell proliferation and migration through targeting tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in preeclampsia. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, F.; Kong, H.; Xin, H. Overexpression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 attenuates trophoblast proliferation and invasion in preeclampsia. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Tao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ye, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y. Hypomethylation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in human placenta of preeclampsia. Thromb. Res. 2017, 152, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Lei, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Sun, M.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Q. DNA methylation landscape in pregnancy-induced hypertension: Progress and challenges. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2024, 22, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaszi, K.; Szabo, S.; Juhasz, K.; Kiraly, P.; Kocsis-Deak, B.; Hargitai, B.; Krenacs, T.; Hupuczi, P.; Erez, O.; Papp, Z.; et al. Increased placental expression of Placental Protein 5 (PP5)/Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) in women with preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome: Relevance to impaired trophoblast invasion? Placenta 2019, 76, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Sun, Y.; Benveniste, E.N. The transcription factors Sp1, Sp3, and AP-2 are required for constitutive matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene expression in astroglioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29130–29137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Ki, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Moon, A. Activating transcription factor 2 mediates matrix metalloproteinase-2 transcriptional activation induced by p38 in breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10487–10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Boyd, P.J.; Colgan, S.; Madri, J.A.; Haas, T.L. Transcriptional up-regulation of endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinase-2 in response to extracellular cues involves GATA-2. Mech. Signal Transduct. 2003, 278, 47785–47791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-H.; Wang, D.L. Nitric oxide inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression via the induction of activating transcription factor 3 in endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.C.; Brown, K.K.; Silvestre, M.J.; Willson, T.M.; Palinski, W.; Glass, C.K. Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ ligands inhibit development of atherosclerosis in LDL receptor–deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Chinetti, G.; Trottein, F.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B. The role of PPARs in atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Lai, B.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N. Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ (PPARγ) induces the gene expression of integrin αVβ5 to promote macrophage M2 polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 16572–16582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sorenson, A.L.; Poczobutt, J.; Amin, J.; Joyal, T.; Sullivan, T.; Crossno, J.T., Jr.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.M.; Nemenoff, R.A. Activation of PPARγ in myeloid cells promotes lung cancer progression and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, S. Activation of PPARγ suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting TLR4-dependent MAPK pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44572–44582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, C. PPARγ activation serves as therapeutic strategy against bladder cancer via inhibiting PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, A.; Ahmad, I. The role of PPARγ in prostate cancer development and progression. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Yip, Y.S.; Lim, E.K.Y.; Wahli, W.; Tan, N.S. PPARs and Tumor Microenvironment: The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Master Regulators in Tumor Stromal–Epithelial Crosstalk and Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Lv, X.; Cao, H.; Zou, Y.; You, J.; Luo, J.; Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Hypothermic oxygenated perfusion inhibits CLIP1-mediated TIRAP ubiquitination via TFPI2 to reduce ischemia—reperfusion injury of the fatty liver. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2588–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugler, W.E.; Karin, M. NF-κB and cancer—Identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pou, J.; Rebollo, A.; Piera, L.; Merlos, M.; Roglans, N.; Laguna, J.C.; Alegret, M. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 is induced by thrombin in human macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-G.; Malek, E.; Choi, S.H.; Ignatz-Hoover, J.J.; Driscoll, J.J. Novel therapies emerging in oncology to target the TGF-β pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ben, T.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.; Song, Y. Focal adhesion in the tumour metastasis: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Uomoto, M.; Koizume, S.; Sato, S.; Hoshino, D.; Yoshihara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tadokoro, H.; Myoba, S.; Ohtake, N.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 inhibits integrin β1 activation and focal adhesion formation and suppresses peritoneal ovarian cancer dissemination in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 736, 150890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaud, G.; Iochmann, S.; Guillon-Munos, A.; Brillet, B.; Petiot, S.; Seigneuret, F.; Touzé, A.; Heuzé-Vourc’h, N.; Courty, Y.; Lerondel, S.; et al. TFPI-2 silencing increases tumour progression and promotes metalloproteinase 1 and 3 induction through tumour-stromal cell interactions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K. The biological role of actinin-4 (ACTN4) in malignant phenotypes of cancer. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecci, A.; Ma, X.; Savoia, A.; Adelstein, R.S. MYH9: Structure, functions and role of non-muscle myosin IIA in human disease. Gene 2018, 664, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barai, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Das, A.; Saxena, N.; Sen, S. α-Actinin-4 drives invasiveness by regulating myosin IIB expression and myosin IIA localization. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs258581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Xie, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; et al. NudCL2 regulates cell migration by stabilizing both myosin-9 and LIS1 with Hsp90. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.-J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S. TMPRSS4 induces cancer cell invasion through pro-uPA processing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, H.Y.; Nam, E.-H.; Choi, M.-S.; Zhao, X.-F.; Hong, C.S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.-K. TMPRSS4 induces invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through upregulation of integrin 5 and its signaling pathways. Carcinog. 2010, 31, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. TMPRSS4, a type II transmembrane serine protease, as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, J.; Soejima, K.; Naoki, K.; Yasuda, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Yoda, S.; Nakayama, S.; Satomi, R.; Terai, H.; Ikemura, S.; et al. Methylation-induced downregulation of TFPI-2 causes TMPRSS4 overexpression and contributes to oncogenesis in a subset of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dissecting the roles of prosaposin as an emerging therapeutic target for tumors and its underlying mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Deng, F.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Mu, J.; Deng, S.; Ma, D. The interaction of the second Kunitz-type domain (KD2) of TFPI-2 with a novel interaction partner, prosaposin, mediates the inhibition of the invasion and migration of human fibrosarcoma cells. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, C.; Kang, M.; Zuo, G.; Niu, Z.; Ye, W.; Tian, B.; Cai, R. Integrative analyses of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq Reveal MITF as a Target Gene of TFPI-2 in MDA231 Cells. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margadant, C.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin–TGF-β crosstalk in fibrosis, cancer and wound healing. Embo Rep. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Stamenkovic, I. Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-β and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Qian, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. PPARγ inhibition regulates the cell cycle, proliferation and motility of bladder cancer cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3724–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, M.S.; Stavik, B.; Sletten, M.; Tinholt, M.; Sandset, P.M.; Iversen, N.; Skretting, G. Indirect regulation of TFPI-2 expression by miR-494 in breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bove, A.M.; Simone, G.; Ma, B. Molecular Bases of VEGFR-2-Mediated Physiological Function and Pathological Role. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 599281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, S.; Kawase, C.; Altomare, D.A.; Morishige, K.; Hayashi, M.; Sawada, K.; Ito, K.; Terai, Y.; Nishio, Y.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, K.; Homma, S.; Satoh, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Abe, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Oki, A.; Tsunoda, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Nagasawa, T.; et al. Tissue factor expression as a possible determinant of thromboembolism in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Kostenko, S.; Sveinbjørnsson, B. The Role of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKAPKs) in Inflammation. Genes 2013, 4, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, P.; Huang, Z.; Dong, T.; Gui, Y.; Zhang, G. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2 Silencing Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Invasion in vitro. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, B.S.; Annunziata, C.M. NF-κB Signaling in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, H.; Vitale, S.G.; Kahramanoglu, I.; Della Corte, L.; Giampaolino, P.; Azemi, A.; Durmus, S.; Sal, V.; Tokgozoglu, N.; Bese, T.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic role of TFF3, Romo-1, NF-kB and SFRP4 as biomarkers for endometrial and ovarian cancers: A prospective observational translational study. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 306, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, G. Role of NF-κB pathway in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and its potential therapeutic implications. Aging 2023, 15, 11313–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Kajita, S.; Takahashi, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Tsuruta, T.; Saegusa, M. Transcriptional upregulation of HNF-1β by NF-κB in ovarian clear cell carcinoma modulates susceptibility to apoptosis through alteration in bcl-2 expression. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 95, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Guo, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Shan, W.; Zou, J.; Cao, Y.; et al. NLRC5 promotes endometrial carcinoma progression by regulating NF-κB pathway-mediated mismatch repair gene deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ween, M.P.; Oehler, M.K.; Ricciardelli, C. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein (TGFBI)/(βig-H3): A matrix protein with dual functions in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10461–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Volland, S.; Noskova, I.; Schramm, A.; Schweigerer, L.L.; Wilting, J. Keratoepithelin reverts the suppression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 by MYCN in human neuroblastoma: A mechanism to inhibit invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, M.; Foster, D.C.; Kisiel, W. Quantification and Characterization of Human Endothelial Cell–Derived Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduri, S.D.; Yanamandra, N.; Dinh, D.H.; Olivero, W.C.; Gujrati, M.; Foster, D.C.; Kisiel, W.; Rao, J.S. Physiological and chemical inducers of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in human glioma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, J.; Angel, P.; Schorpp-Kistner, M. AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117 Pt 25, 5965–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Jeon, H.; Akin, J.W.; Curry, T.E., Jr.; Jo, M. The FOS/AP-1 Regulates Metabolic Changes and Cholesterol Synthesis in Human Periovulatory Granulosa Cells. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xing, R.; Li, Q.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, B.; Li, X. Inhibition of the AP-1/TFPI2 axis contributes to alleviating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving blood–brain barrier integrity. Hum. Cell 2024, 37, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrouqi, A.; Pyrzynska, B.; Brat, D.J.; Van Meir, E.G. P14ARF Suppresses tumor-induced thrombosis by regulating the tissue factor pathway. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudurexiti, Y.; Gu, Z.; Chakma, K.; Hata, T.; Motoi, F.; Unno, M.; Horii, A.; Fukushige, S. Methylation-mediated silencing of the LIM homeobox 6 (LHX6) gene promotes cell proliferation in human pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, F.K.C.; Chan, D.W.; Liu, V.W.S.; Leung, T.H.Y.; Cheung, A.N.Y.; Ngan, H.Y.S. Increased Expression of PITX2 Transcription Factor Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Fard-Esfahani, P.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Fazeli, M.S.; Azadmanesh, K.; Zeinali, S.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. MiR-377 reverses cancerous phenotypes of pancreatic cells via suppressing DNMT1 and demethylating tumor suppressor genes. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, K.; Xi, M. MiR-494 Inhibits Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Growth by Targeting c-Myc. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Kong, X.; Xie, D.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, W.; Cui, J.; Du, Y.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; et al. Down-regulation of MicroRNA-494 via loss of SMAD4 increases FOXM1 and β-catenin signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 485–497.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, G.-H.; Teng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q. MicroRNA-494 promotes cancer progression and targets adenomatous polyposis coli in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Lin, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zou, B.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, G. TFPI2AS1, a novel lncRNA that inhibits cell proliferation and migration in lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.L.; Ali, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Alosh, B.; Hayek, K.; Daaboul, M.F.; Winer, I.; Sarkar, F.H.; Ali-Fehmi, R. Comparative Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs and their Downstream mRNAs in Ovarian Cancer and its Associated Endome-triosis. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015, 7, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Camarillo, C.; Ruíz-García, E.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; la Cruz, O.N.H.-D.; Marchat, L.A.; Gallardo-Rincón, D. Deciphering the Long Non-Coding RNAs and MicroRNAs Coregulation Networks in Ovarian Cancer Development: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, E.S.; Tuck, D.; Richter, C.; Nallur, S.; Patel, R.M.; Schultz, V.; Hui, P.; Schwartz, P.E.; Rutherford, T.J.; Weidhaas, J.B. MicroRNA signatures differentiate uterine cancer tumor subtypes. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 118, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, E.; Dotan, Z.; Barshack, I.; Ben David, M.; Dov, A.; Tabak, S.; Zion, O.; Benjamin, S.; Benjamin, H.; Kuker, H.; et al. Accurate Molecular Classification of Renal Tumors Using MicroRNA Expression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, D.A.; Drula, R.; Ott, L.; Fabris, L.; Slaby, O.; Calin, G.A.; Pichler, M. Circulating Non-coding RNAs in Renal Cell Carcinoma—Pathogenesis and Potential Implications as Clinical Biomarkers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, M.S.; Ali, H.O.; Myklebust, C.F.; Sandset, P.M.; Stavik, B.; Iversen, N.; Skretting, G. Estrogen induced expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in MCF7 cells involves lysine-specific demethylase 1. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 443, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, B.C.; Song, S.J.; Park, J.I.; Chun, S.Y.; Cho, M.K. Expression of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitors during ovulation in rats: A relevance to the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Deng, X.; Zhong, J.; Wu, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, C. All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells and inhibiting angiogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Oura, S. Involvement of MAFB and MAFF in Retinoid-Mediated Suppression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z. A high-calcium environment induced ectopic calcification of renal interstitial fibroblasts via TFPI-2-DCHS1-ALP/ENPP1 axis to participate in Randall’s plaque formation. Urolithiasis 2024, 52, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.-L.; Li, W.-B.; Chen, L.-J.; Wang, W.; Ju, T.-F.; Yin, D.-L. Curcumin inhibits the invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by upregulating TFPI-2 to regulate ERK- and JNK-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, K.; Li, Y. Transcriptional Regulation during Aberrant Activation of NF-κB Signalling in Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Awasthee, N.; Rai, V.; Chava, S.; Gunda, V.; Challagundla, K.B. Long non-coding RNAs and nuclear factor-κB crosstalk in cancer and other human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Prabhakar, N.; Kumar, L.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Kar, S.; Malik, S.; Kumar, D.; Ruokolainen, J.; Negi, A.; Jha, N.K.; et al. Crosstalk between long noncoding RNA and microRNA in Cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2023, 46, 885–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ning, J.; Tang, Z.; He, Y.; Yao, L.-C.; Ye, L.; Wu, L. MicroRNA-23a acts as an oncogene in pancreatic carcinoma by targeting TFPI-2. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, V.; Savva-Bordalo, J.; Rei, M.; Liz-Pimenta, J.; Assis, J.; Pereira, D.; Medeiros, R. Plasma microRNA Environment Linked to Tissue Factor Pathway and Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: Prognostic Significance in Ovarian Cancer. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Shang, P.; Pan, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, D. Downregulation of microRNA-23a confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by upregulating tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 following luteolin pretreatment in rats. Chin. Med, J. 2023, 136, 866–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chan, Y.P.; Kwan, P.S.; Lee, T.K.; Yan, M.; Tang, K.H.; Ling, M.T.; Vielkind, J.R.; Guan, X.-Y.; Chan, K.W. MicroRNA-616 induces androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells by suppressing expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor TFPI-2. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; Che, R.; Wu, Y.; Wan, S.; Pei, J.; Yao, L.; Hua, X. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Trophoblast Cell Proliferation and Migration by Targeting TFPI2 in Preeclampsia. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 7927747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wan, S.; Zhao, X.; Gu, S.; Pei, J.; Wu, Y.; Han, Z.; Che, R.; Hua, X. Exosomal miR-195 in hUC-MSCs alleviates hypoxia-induced damage of trophoblast cells through tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2022, 70, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Dong, C.; Dong, Q. Circ_0015382 is associated with preeclampsia and regulates biological behaviors of trophoblast cells through miR-149-5p/TFPI2 axis. Placenta 2021, 108, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, V.; Bink, D.I.; Stanicek, L.; van Ingen, E.; Gimbel, T.; Hilderink, S.; Günther, S.; Nossent, A.Y.; Boon, R.A. MEG8 regulates Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 (TFPI2) expression in the endothelium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S. Long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 exerts oncogenic properties in glioblastoma by epigenetically silencing TFPI2 through EZH2 and LSD1. Aging 2019, 11, 3811–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, W.; Niu, X.; Ye, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, Y. The EZH2- H3K27me3-DNMT1 complex orchestrates epigenetic silencing of the wwc1 gene, a Hippo/YAP pathway upstream effector, in breast cancer epithelial cells. Cell. Signal. 2018, 51, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chang, L.; Wang, S. EZH1-DNMT1 axis inhibits the expression of TFPI2 to promote osteogenic differentiation of periosteum-derived stem cells and accelerate fracture repair. Tissue Cell 2025, 93, 102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, K.; Nishimura, S.; Ninomiya, S.; Tujii, H.; Matsumori, Y.; Tsuchida, M.; Hosoi, M.; Koseki, K.; Wada, S.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Regulation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) expression by lysine-specific demethylase 1 and 2 (LSD1 and LSD2). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Vasilatos, S.N.; Yin, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Davidson, N.E.; Huang, Y. Restoration of TFPI2 by LSD1 inhibition suppresses tumor progression and potentiates antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 600, 217182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Guo, C.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, L. Lysine-specific demethylase 2 contributes to the proliferation of small cell lung cancer by regulating the expression of TFPI-2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhai, L.-L.; Chen, L.-J.; Yao, L.-C.; Wu, L.; Tang, Z.-G.; Ning, J.-Z. m6A RNA demethylase FTO promotes the growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through inhibiting TFPI-2. Epigenetics 2022, 17, 1738–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Mu, S.; Fan, R.; Wang, B.; Gao, W.; Kang, T. FTO overexpression expedites wound healing and alleviates depression in burn rats through facilitating keratinocyte migration and angiogenesis via mediating TFPI-2 demethylation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Han, Q.; Gong, L.; Zhan, X.; Li, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.; Wu, J.; et al. MBD3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through negative regulation of tumour suppressor TFPI2. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Min, J.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Gong, A.; Xu, M. MBD3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells by upregulating ACTG1 via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biol. Proced. Online 2024, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; He, J.; Li, J.; Feng, W.; Zhou, H.; Wei, H.; Zhou, M.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Peng, W.; et al. Methyl-CpG-binding domain 3 inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells via TGF-β/Smad signalling. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Guo, M.-Q.; Cui, Q.-K.; Yuan, H.; Fu, S.-J.; Liu, B.; Xie, F.; Qiao, W.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. PARP1 deficiency protects against hyperglycemia-induced neointimal hyperplasia by upregulating TFPI2 activity in diabetic mice. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, C.; Esteller, M. MicroRNAs and Epigenetics. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 135, 189–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, K.M.T.; Elliott, E.K.; Haupt, L.M.; Griffiths, L.R. Regulatory Mechanisms of Epigenetic miRNA Relationships in Human Cancer and Potential as Therapeutic Targets. Cancers 2020, 12, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, E.; Yui, Y.; Hattori, R.; Tanaka, M.; Inoue, R.; Aoyama, T.; Takimoto, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Miyahara, K.; Shizuta, Y.; et al. Tissue Factor pathway inhibitor-2 is a novel mitogen for vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5379–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Matsumura, M.; Kasai, K. Vascular smooth muscle cell activation by C-reactive protein. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 58, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, J.; Razuvaev, A.; Folkersen, L.; Roy, J.; Hedin, U. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is induced by fluid shear stress in vascular smooth muscle cells and affects cell proliferation and survival. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, S.; Lou, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liang, W.; Kong, D.; Ma, D.; Li, X. Changes of plasma and placental tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in women with preeclampsia and normal pregnancy. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e317–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yi, C.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Meng, X.; Mao, R.; Guo, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Downregulated TFPI2 Accelerates Skin Aging by Repressing the Cell Cycle through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/CDC6 Pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, M.M.; Spaans, F.; De Vos, P. Monocytes and Macrophages in Pregnancy and Pre-Eclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache, V.; Ciric, A.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Maltepe, E.; Milstone, D.S.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia and Trophoblast Differentiation: A Key Role for PPARγ. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercnik, M.H.; Schliefsteiner, C.; Fluhr, H.; Wadsack, C. Placental macrophages present distinct polarization pattern and effector functions depending on clinical onset of preeclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1095879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Jiménez, A.; Peón, A.N.; Terrazas, L.I. Alternatively Activated Macrophages in Types 1 and 2 Diabetes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 815953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orliaguet, L.; Dalmas, E.; Drareni, K.; Venteclef, N.; Alzaid, F. Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarization in Insulin Signaling and Sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, T.; Shimokado, A.; Sun, Y.; Akasaka, T.; Muragaki, Y. Diverse roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: From inflammatory biology to biomarker discovery. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 693083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Xiao, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Tie, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Ji, X. Ginsenoside Rg3 Mitigates Atherosclerosis Progression in Diabetic apoE–/– Mice by Skewing Macrophages to the M2 Phenotype. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louiselle, A.E.; Niemiec, S.M.; Zgheib, C.; Liechty, K.W. Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl. Res. 2021, 236, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Geng, X.; Hou, J.; Wu, G. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: Key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, N.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Sun, B. TFPI2 Promotes perivascular migration in an angiotropism model of melanoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 662434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Mysliwiec, M.; Matuszewska, E.; Sulkowski, S.; Zimnoch, L.; Politynska, B.; Wojtukiewicz, A.M.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Huang, Y.; Yan, X. TFPI-2 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer cells. Progres En Urol. 2021, 31, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Ge, A. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 suppresses the growth of thyroid cancer cells through by induction of apoptosis. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, e48–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Dunterman, M.; Guo, S.; Khan, F.; Liu, Y.; Taefi, E.; Bahrami, A.; Geula, C.; Hsu, W.-H.; Horbinski, C.; et al. Kunitz-type protease inhibitor TFPI2 remodels stemness and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1654–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaud, V.; Hisaka, T.; Monvoisin, A.; Bedin, C.; Balabaud, C.; Foster, D.C.; Desmoulière, A.; Kisiel, W.; Rosenbaum, J. Paradoxical pro-invasive effect of the serine proteinase inhibitor tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35565–35569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, W.; Seftor, E.A.; Petrovan, R.J.; Weiss, R.M.; Gruman, L.M.; Margaryan, N.V.; Seftor, R.E.B.; Miyagi, Y.; Hendrix, M.J.C. Differential role of tissue factor pathway inhibitors 1 and 2 in melanoma vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5381–5389. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yi, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. A vasculogenic mimicry prognostic signature associated with immune signature in human gastric cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, J.; Herlyn, M. Melanoma and the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Bengtson, C.; Razzokov, J.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Modifying the Tumour Microenvironment: Challenges and Future Perspectives for Anticancer Plasma Treatments. Cancers 2019, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y. Microglia Polarization from M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 815347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L. Shaping Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, K.V.; Pienta, K.J.; Amend, S.R. Cancer Cells and M2 Macrophages: Cooperative Invasive Ecosystem Engineers. Cancer Control. 2020, 27, 1073274820911058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, G.; Stavraka, C.; Adams, R.; Sayasneh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Montes, A.; Lacy, K.E.; Kristeleit, R.; Spicer, J.; Josephs, D.H.; et al. Macrophages in ovarian cancer and their interactions with monoclonal antibody therapies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 209, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yu, S.; Fei, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhai, L.; Sadhukhan, A.; Zhou, J. Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs): A Critical Activator In Ovarian Cancer Metastasis. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 8687–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; He, Y.; Peng, F.; Yang, J.; Yuan, C. Endometrial Cancer Cells Promote M2-Like Macrophage Polarization by Delivering Exosomal miRNA-21 under Hypoxia Condition. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9731049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Tumor-associated M2 macrophages in the immune microenvironment influence the progression of renal clear cell carcinoma by regulating M2 macrophage-associated genes. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1157861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Zhang, N.; Chen, M.; Ding, X. MDK promotes M2 macrophage polarization to remodel the tumour microenvironment in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shangguan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Xie, W. M2 macrophages secrete CXCL13 to promote renal cell carcinoma migration, invasion, and EMT. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Maehana, T.; Sugimoto, S.; Kawahara, N.; Iwai, K.; Yamada, Y.; Kimura, F. Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor-2 in Endometrial Clear Cell Carcinoma: A Single-center Retrospective Study. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2024, 43, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, J.; Iochmann, S.; Bléchet, C.; Hubé, F.; Régina, S.; Guyétant, S.; Lemarié, E.; Reverdiau, P.; Gruel, Y. Expression and methylation status of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ho, Y.; Sun, C.; Xia, G.; Ding, Q.; Gu, B. TFPI-2 expression is decreased in bladder cancer and is related to apoptosis. J. Buon. 2016, 21, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, C.L.; Wang, H.; McHugh, A.; Lattanzio, L.; Matin, R.; Harwood, C.; Syed, N.; Hatzimichael, E.; Briasoulis, E.; Merlano, M.; et al. Methylated Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 (TFPI2) DNA in Serum Is a Biomarker of Metastatic Melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, H.; He, H.; Zheng, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Ma, D.; Zhang, H. Low expression of TFPI-2 associated with poor survival outcome in patients with breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.-L.; Cai, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.-G. Correlation and prognostic significance of MMP-2 and TFPI-2 differential expression in pancreatic carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 682–691. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, Q.; Wan, K.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Lv, X. The methylation of SDC2 and TFPI2 defined three methylator phenotypes of colorectal cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röbeck, P.; Franzén, B.; Cantera-Ahlman, R.; Dragomir, A.; Auer, G.; Jorulf, H.; Jacobsson, S.P.; Viktorsson, K.; Lewensohn, R.; Häggman, M.; et al. Multiplex protein analysis and ensemble machine learning methods of fine needle aspirates from prostate cancer patients reveal potential diagnostic signatures associated with tumour grade. Cytopathology 2023, 34, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Parker, A.R.; Fukushima, N.; Miyagi, Y.; A Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Eshleman, J.R.; Goggins, M. Epigenetic inactivation of TFPI-2 as a common mechanism associated with growth and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2005, 24, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, E.; Arakawa, N.; Sakamaki, K.; Yokota, N.R.; Yamanaka, T.; Yamada, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nagao, S.; Hirashima, Y.; Kasamatsu, Y.; et al. Validation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 as a specific biomarker for preoperative prediction of clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, J.; Kirkin, V.; Steffen, A.; Hegen, M.; Weih, D.; Tomarev, S.; Wilting, J.; Sleeman, J.P. Differential in vivo and in vitro expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and VEGF-D in tumors and its relationship to lymphatic metastasis in immunocompetent rats. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Holle, A.W.; Young, J.L.; Spatz, J.P. In vitro cancer cell–ECM interactions inform in vivo cancer treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Quan, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, B.; Guo, G. Immune Cell Infiltration of the Primary Tumor Microenvironment Predicted the Treatment Outcome of Chemotherapy with or Without Bevacizumab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 581051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, F.; Yin, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.-H. Influence of Tumor Immune Infiltration on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapeutic Efficacy: A Computational Retrospective Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 685370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosińska-Kaczyńska, K. Placental Syndromes—A New Paradigm in Perinatology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Search Mode | The Keyword and Search Term Combinations |
|---|---|
| Search term 1 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 OR TFPI2 |
| Search term 2 | Ovarian cancer OR Gynecological cancer |
| Search term 3 | Clear cell carcinoma |
| Search term 4 | Tumor suppression OR Suppressor |
| Search term 5 | Tumor promotion OR Promoter |
| Search term 6 | Hyperglycemia |
| Search term 7 | Atherosclerosis |
| Search | Search term 1 |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 2 | |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 3 | |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 4 | |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 5 | |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 6 | |
| Search term 1 AND Search term 7 |
| Type of Cancer | Ref. | Number of Patients | Tissue | Serum | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ovarian cancer | [17] | 142 | Fifty-two of seventy-seven ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) tumors (67.5%) exhibited TFPI2 protein expression in at least one of the nuclear, cytoplasmic, or extracellular matrix compartments, whereas all other histological subtypes (n = 65) were TFPI2-negative. | No significant correlation was observed between immunohistochemical findings and five-year survival rates. | |
| Among 11 OCCC cell lines, four demonstrated TFPI2 expression in the nuclear, cytoplasmic, or extracellular matrix fractions; four were positive exclusively in the extracellular matrix; and three were entirely negative. | |||||
| [18] | 256 | Serum TFPI2 levels were quantified in 109 serous carcinomas, 66 clear cell carcinomas, and 81 cases of other histological subtypes. | In clear cell carcinoma, patients with serum TFPI2 levels ≥ 255 pg/mL exhibited significantly poorer progression-free survival (PFS) compared to those with lower levels. Among non-clear cell carcinoma cases, patients with serum TFPI2 levels ≥201 pg/mL had significantly reduced overall survival (OS) relative to those with levels below this threshold. | ||
| Endometrial cancer | [21] | 207 | A serum TFPI2 concentration ≥ 177 pg/mL was identified as an adverse prognostic marker. | ||
| [22] | 328 | Immunohistochemical analysis of 105 endometrial carcinoma cases revealed TFPI2 positivity in 39 cases (37.1%), with no significant variation in expression across histological subtypes. | Serum TFPI2 levels increased in parallel with disease progression and were significantly elevated in high-risk histological variants compared to low-risk types. | A serum TFPI2 level ≥ 191 pg/mL was associated with poor prognosis. | |
| [174] | 55 | TFPI2 expression was evaluated via immunohistochemistry in 13 endometrial clear cell carcinoma cases and 42 cases of other histological subtypes. All 13 clear cell carcinoma cases exhibited TFPI2 positivity, whereas 11 cases (26.2%) among the other histological subtypes showed expression. | |||
| Renal cell carcinoma | [19] | No significant difference was detected in TFPI2 mRNA expression between malignant and normal tissues. | Serum TFPI2 levels were assessed in 42 patients with localized disease, 12 with metastatic disease, and 241 healthy controls using a cutoff value of 170 pg/mL. TFPI2 levels were significantly higher in patients with metastatic disease compared to those with localized disease and correlated with tumor grade but not with tumor size. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, H.; Shigetomi, H.; Imanaka, S. Reassessing the Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 in Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Lesions. Cancers 2025, 17, 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091447
Kobayashi H, Shigetomi H, Imanaka S. Reassessing the Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 in Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Lesions. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091447
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Hiroshi, Hiroshi Shigetomi, and Shogo Imanaka. 2025. "Reassessing the Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 in Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Lesions" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091447
APA StyleKobayashi, H., Shigetomi, H., & Imanaka, S. (2025). Reassessing the Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 in Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Lesions. Cancers, 17(9), 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091447






