MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with Prognostic Potential
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Isolation of Total RNA from FFPE Samples
2.3. Isolation of Total RNA from Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytological Samples
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. Validation of RNA Sequencing Results by RT-qPCR Analysis
2.6. Reverse Transcription
2.7. Real-Time PCR
2.8. Reverse-Transcription PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
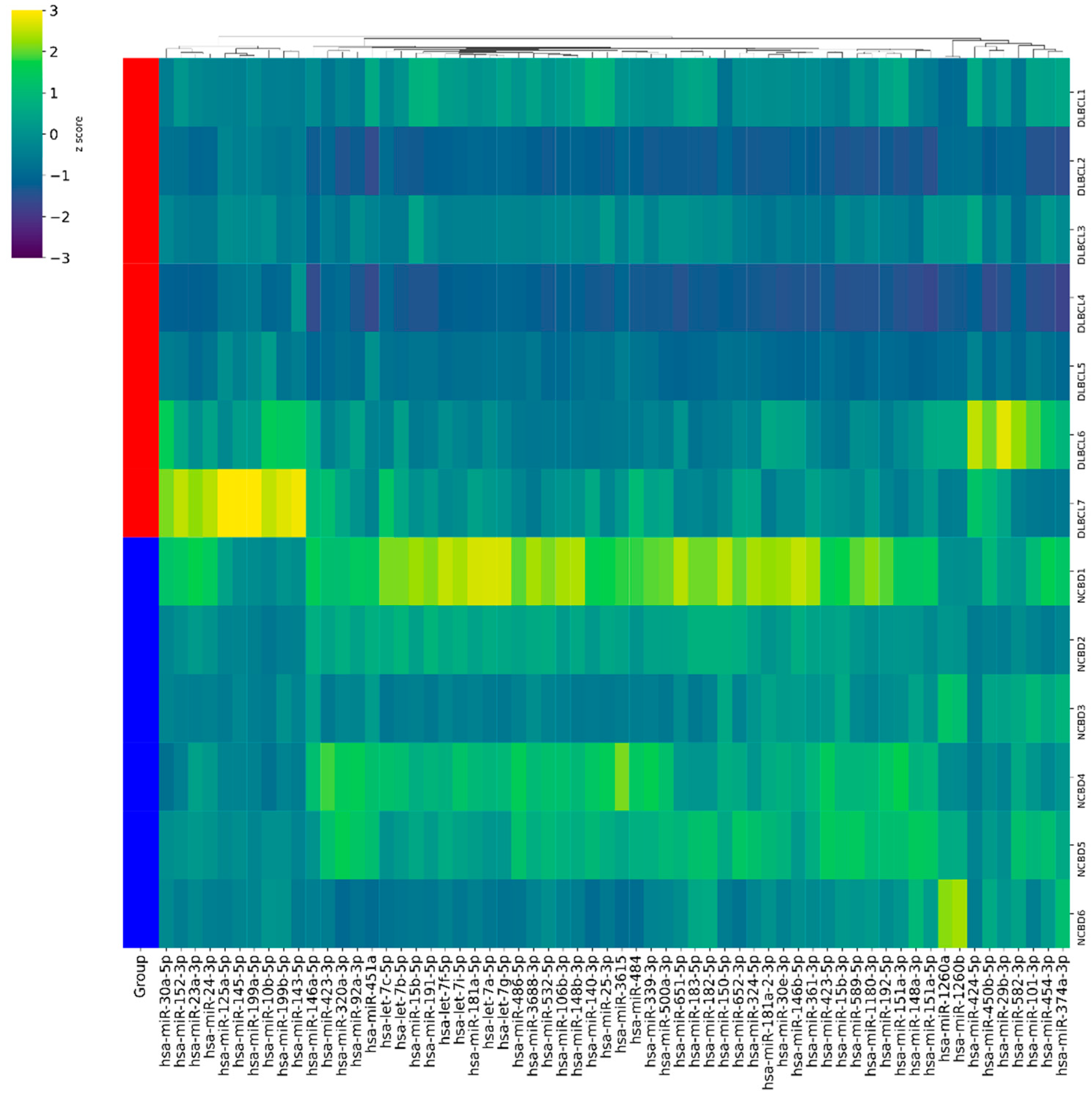
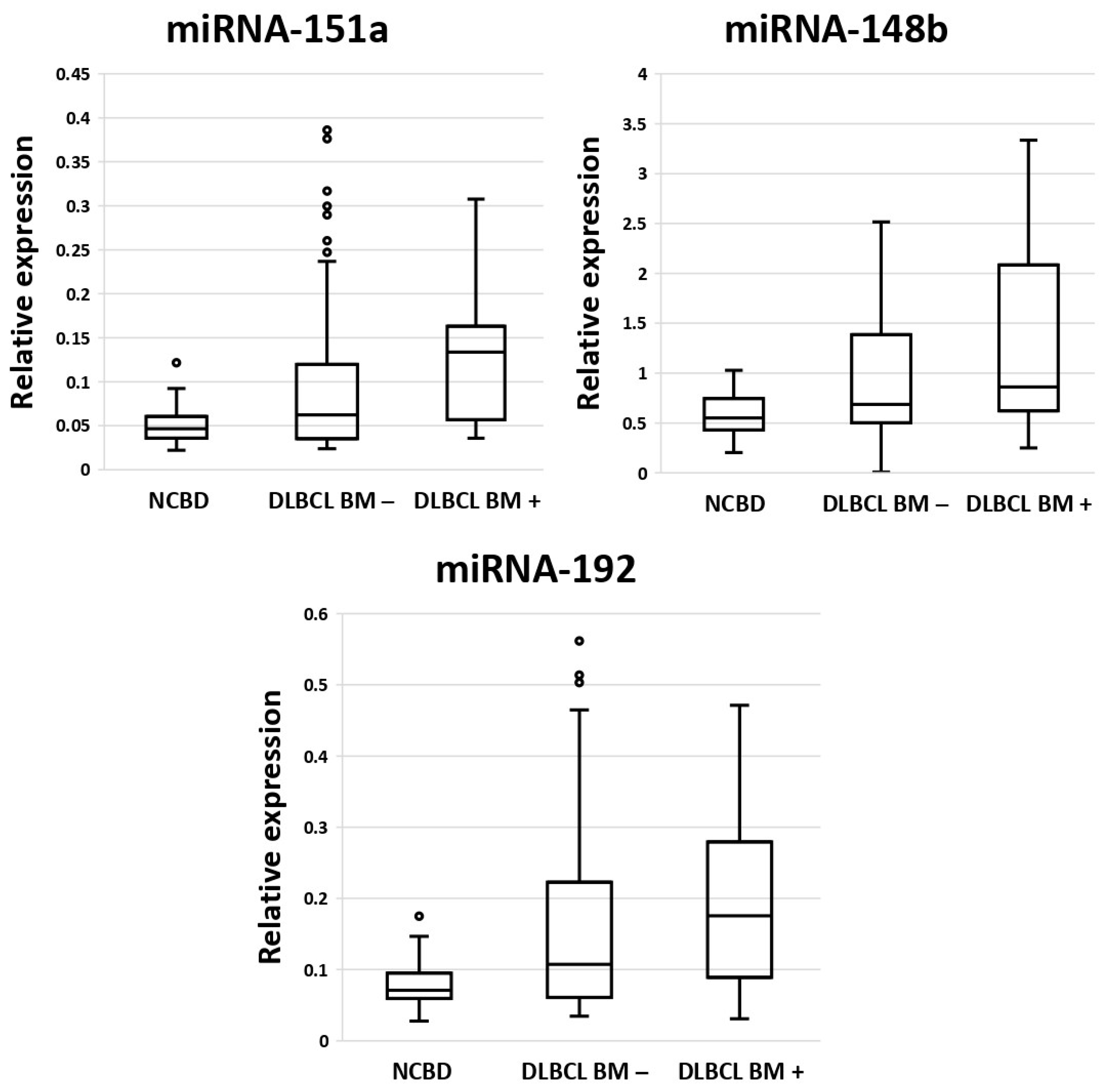
3.1. MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Bone Marrow Samples in Patients with DLBCL and Non-Cancerous Blood Diseases
3.2. Diagnostic Genetic Biomarkers in BM Samples of Patients with DLBCL or Non-Cancerous Blood Diseases
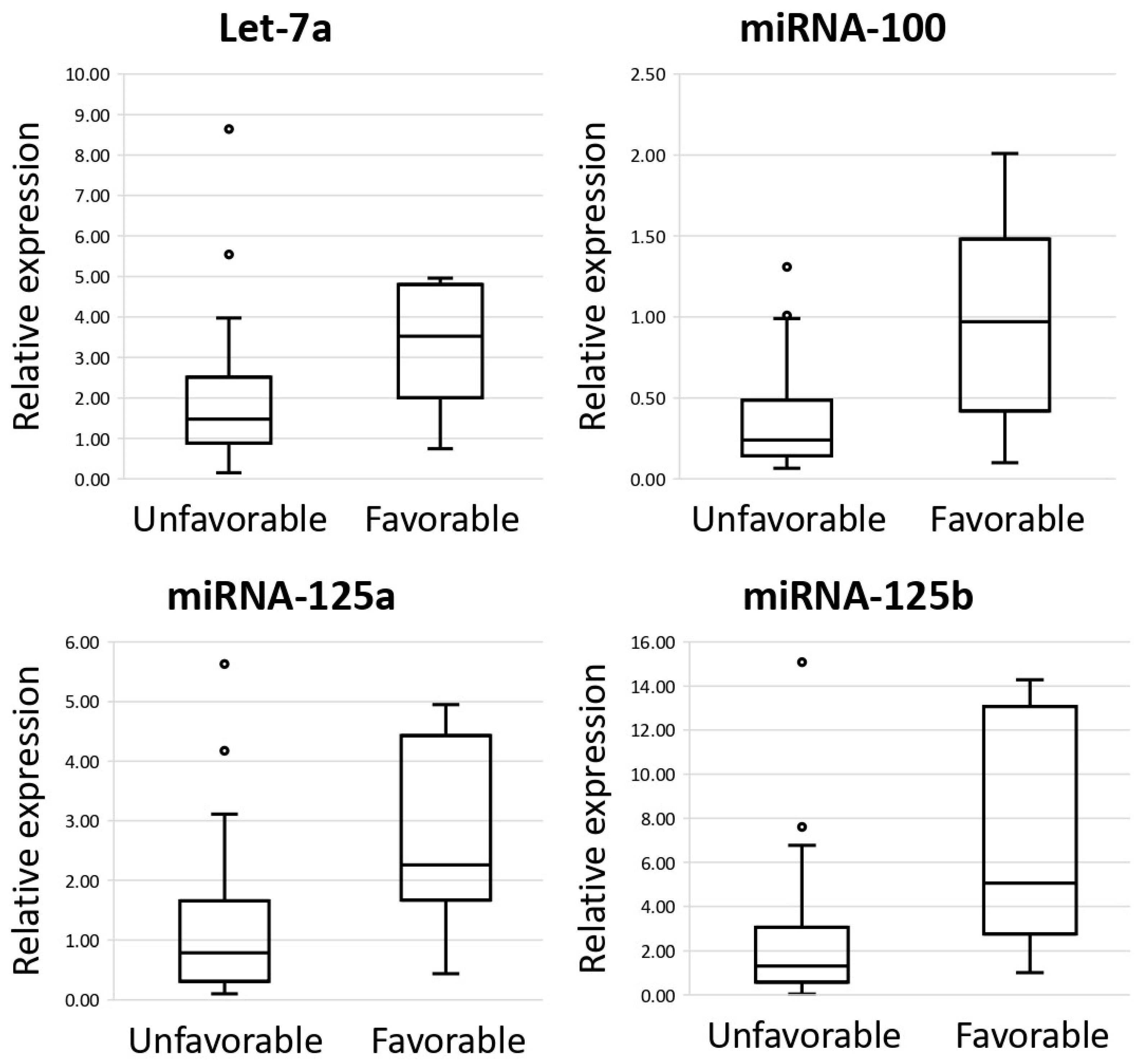
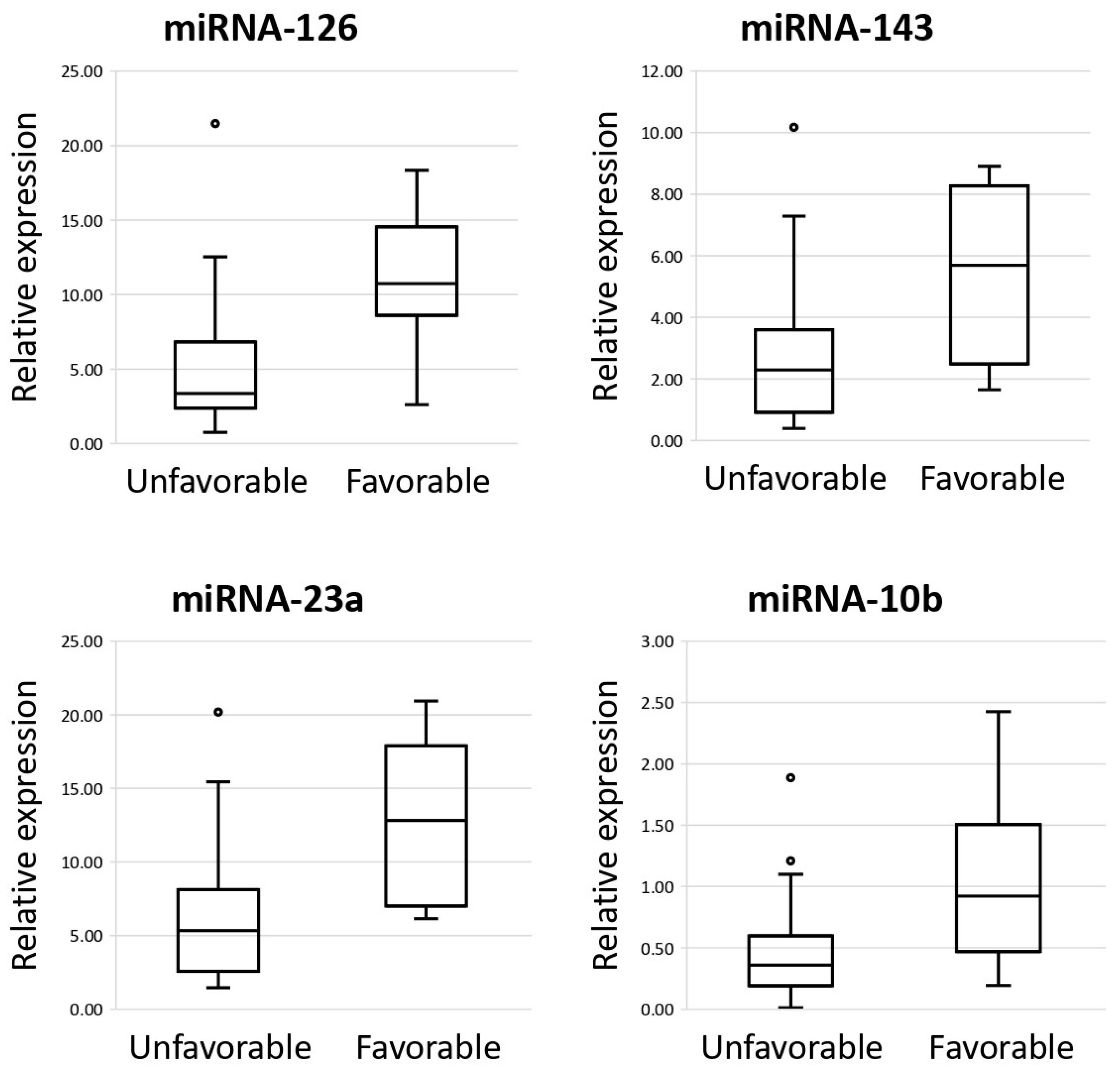
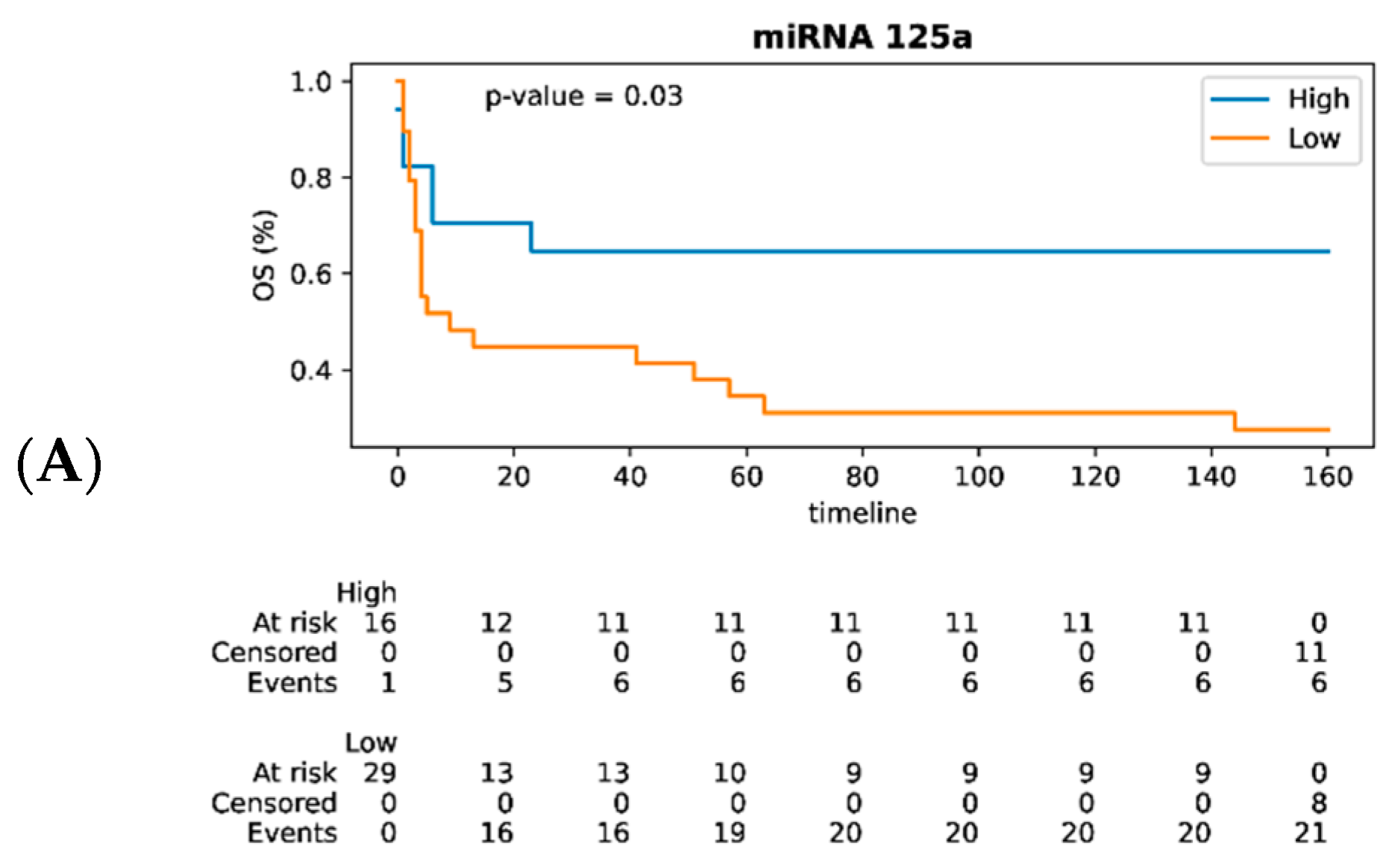
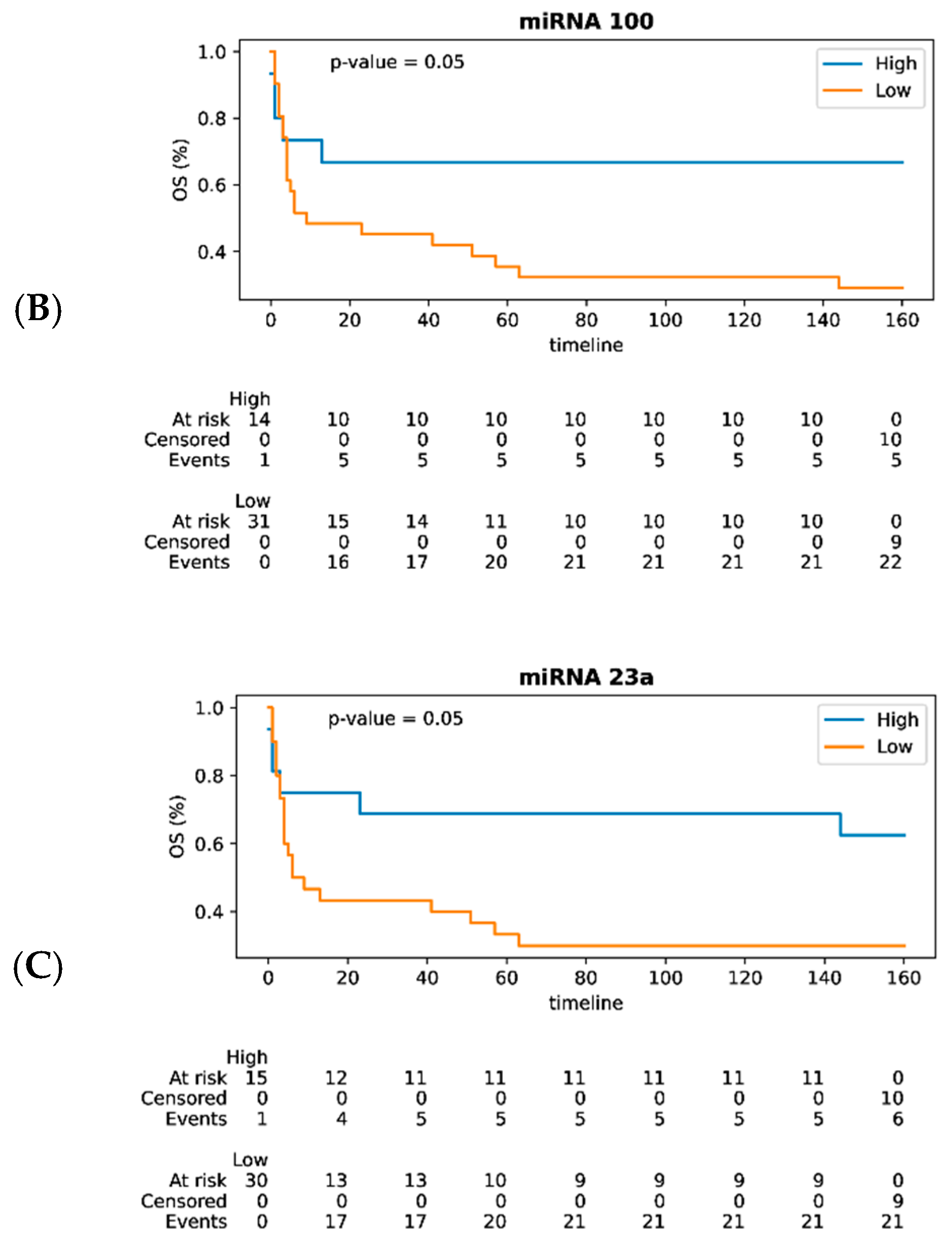
3.3. MiRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers of DLBCL in Lymph Nodes and Their Impact on Survival
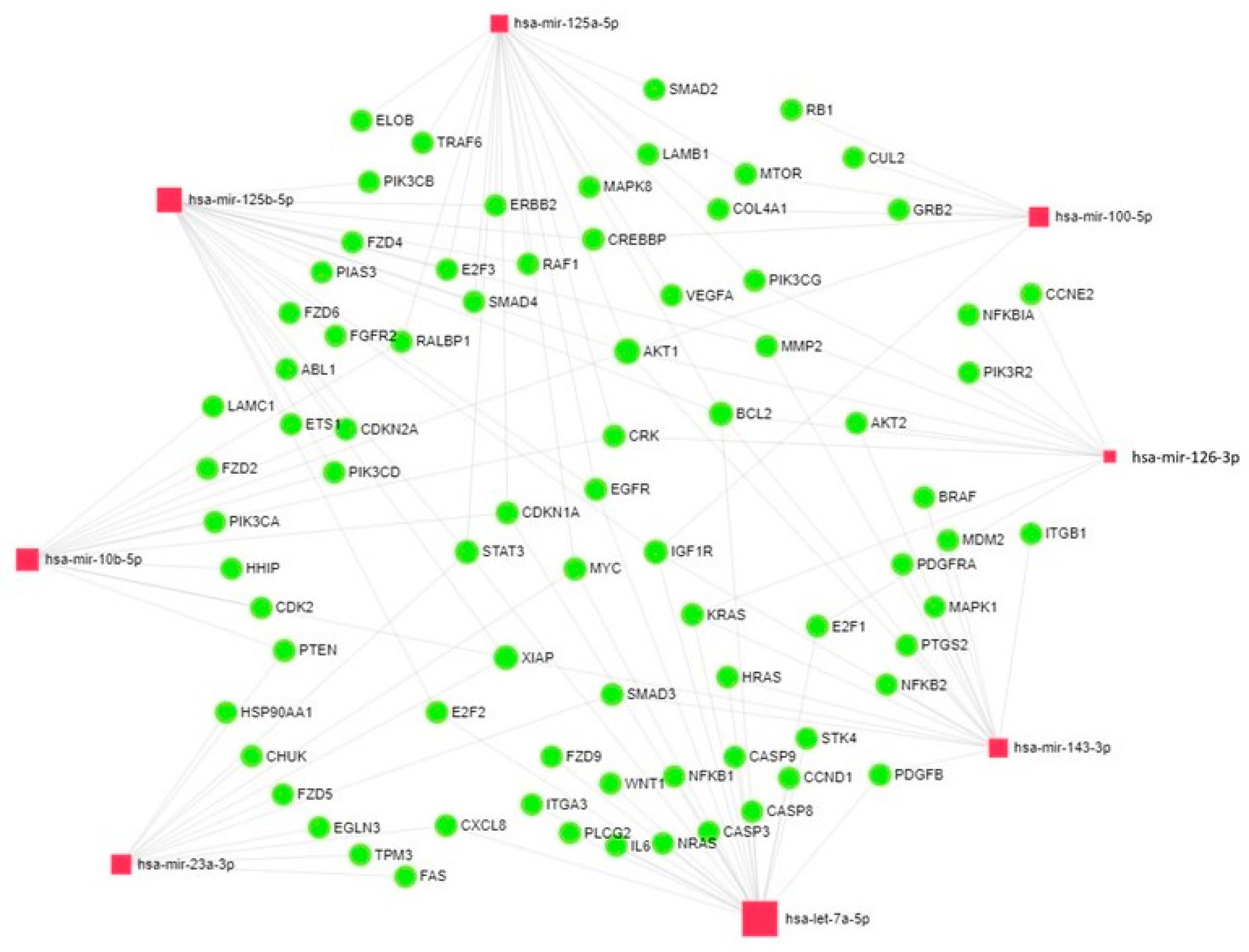
3.4. Analysis of the Network of Interactions of mRNAs and miRNAs in Lymph Nodes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Susanibar-Adaniya, S.; Barta, S.K. 2021 Update on Diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A review of current data and potential applications on risk stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hu, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Prognostic factors for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Clinical and biological factors in the rituximab era. Exp. Hematol. 2023, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, Z.; Xue, Q.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Shi, W. Identification of molecular subtypes and a novel prognostic model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on a metabolism-associated gene signature. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Leng, C. A glycolysis-related gene signatures in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma predicts prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1070777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, Y.; Pan, T.; Zeng, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, H. Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature: A New Method for Personalized Risk Assessment in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, L.; He, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Bai, B.; Huang, H. Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD)-Related Gene Signature Could Predict the Prognosis of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, S.; Lu, W.; Shi, J. A novel lipid metabolism-based risk model associated with immunosuppressive mechanisms in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yang, P.; Wang, F.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Lu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiu, B.; et al. Whole Transcriptome Data Analysis Reveals Prognostic Signature Genes for Overall Survival Prediction in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 648800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Hiraiwa, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Roncador, G.; Garcia, J.F.; et al. Artificial Neural Networks Predicted the Overall Survival and Molecular Subtypes of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Using a Pancancer Immune-Oncology Panel. Cancers 2021, 13, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liang, W.; He, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Lv, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, H. Immune microenvironment-related gene mapping predicts immunochemotherapy response and prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell. 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Ding, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Differential expression of miRNAs as biomarkers for predicting the outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20201551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedström, G.; Thunberg, U.; Berglund, M.; Simonsson, M.; Amini, R.M.; Enblad, G. Low expression of microRNA-129-5p predicts poor clinical outcome in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 97, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepshelovich, D.; Ram, R.; Uziel, O.; Kushnir, M.; Lithwick-Yanai, G.; Hoshen, M.; Feinmesser, M.; Bairey, O.; Lahav, M. MicroRNA signature is indicative of long-term prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2015, 39, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veryaskina, Y.A.; Titov, S.E.; Kovynev, I.B.; Pospelova, T.I.; Fyodorova, S.S.; Shebunyaeva, Y.Y.; Sumenkova, D.V.; Zhimulev, I.F. MicroRNA Expression Profile in Bone Marrow and Lymph Nodes in B-Cell Lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, C.X.; Xu, Y.L.; Ying, Y.; Mao, P. MicroRNA-148b enhances the radiosensitivity of non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma cells by promoting radiation-induced apoptosis. J. Radiat. Res. 2012, 53, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.R.; Li, X.; Jamieson, B.D.; Martínez-Maza, O. Overexpression of microRNAs from the miR-17-92 paralog clusters in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e20781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrabeiti-Etxebarria, A.; Bilbao-Aldaiturriaga, N.; Arzuaga-Mendez, J.; Martin-Arruti, M.; Cozzuto, L.; Gaafar, A.; Ruiz-Diaz, I.; Guerra, I.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; et al. microRNA sequencing for biomarker detection in the diagnosis, classification and prognosis of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Z.; Guan, M.; Liu, N.; Meng, F.; Wang, G. ASF1B Promotes Oncogenesis in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Other Cancer Types. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 731547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pon, J.R.; Marra, M.A. MEF2 transcription factors: Developmental regulators and emerging cancer genes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.H.; Chan, L.C.; Li, C.W.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.C. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol. Cell. 2019, 76, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Mao, H. High expression of fibronectin 1 indicates poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Role of Metastasis Suppressor KAI1/CD82 in Different Cancers. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 9924473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duch, P.; Díaz-Valdivia, N.; Ikemori, R.; Gabasa, M.; Radisky, E.S.; Arshakyan, M.; Gea-Sorlí, S.; Mateu-Bosch, A.; Bragado, P.; Carrasco, J.L.; et al. Aberrant TIMP-1 overexpression in tumor-associated fibroblasts drives tumor progression through CD63 in lung adenocarcinoma. Matrix Biol. 2022, 111, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, R.C.; Céspedes, A.G.; Conceição, M.P.F.; Oliveira, M.V.A.S.; Buron, A.; Rodrigues das Neves, D.; Moraes, F.A.; Gamarra, O.M.; Rodrigues de Bastos, D. Computational insights into CRISP3 downregulation in cervical cancer and its cervical lineages pattern. Precis. Clin. Med. 2024, 7, pbae016. [Google Scholar]
- Guimaraes, D.P.; Hainaut, P. TP53: A key gene in human cancer. Biochimie 2002, 84, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lu, J.; Wang, R.; Cao, W.; Xu, J. TOP2A promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma regulated by miR-144-3p. J Cancer 2022, 13, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lisio, L.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Gómez-López, G.; Rodríguez, M.E.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Mollejo, M.; Menárguez, J.; Martínez, M.A.; Alves, F.J.; Pisano, D.G.; et al. MicroRNA signatures in B-cell lymphomas. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Yang, C.; Han, X.L.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Zi, Y.M.; Li, J.D. MicroRNA-23a expression in paraffin-embedded specimen correlates with overall survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufayel, R.; Kadry, S. Expression of miR-23a by apoptotic regulators in human cancer: A review. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Dubey, R.; Saini, N. Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol. Cancer. 2010, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Liu, S.; Dai, K.; Jin, L.; He, T.; Pan, X.; Lai, Y. MicroRNA-23a/24-2/27a as a potential diagnostic biomarker for cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 8, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Feng, Y.G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y. microRNA-23a in Human Cancer: Its Roles, Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance. Cancers 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.Y.; Wong, D.K.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Estradiol induces apoptosis via activation of miRNA-23a and p53: Implication for gender difference in liver cancer development. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34941–34952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Wu, C.; Yin, B.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J.; Qiang, B.; Peng, X. cAMP response element-binding protein promotes gliomagenesis by modulating the expression of oncogenic microRNA-23a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15805–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkewich, J.L.; Hansen, J.; Klopfenstein, N.; Zhang, H.; Wood, C.; Boucher, A.; Hickman, J.; Muench, D.E.; Grimes, H.L.; Dahl, R. The miR-23a~27a~24-2 microRNA cluster buffers transcription and signaling pathways during hematopoiesis. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkewich, J.L.; Boucher, A.; Klopfenstein, N.; Baskar, R.; Kapur, R.; Dahl, R. The mirn23a and mirn23b microrna clusters are necessary for proper hematopoietic progenitor cell production and differentiation. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 59, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkewich, J.L.; Bikorimana, E.; Nguyen, T.; Klopfenstein, N.; Zhang, H.; Hallas, W.M.; Stayback, G.; McDowell, M.A.; Dahl, R. The mirn23a microRNA cluster antagonizes B cell development. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.Y.; Owens, K.S.; Rogers, J.H.; Mullenix, J.; Velu, C.S.; Grimes, H.L.; Dahl, R. MIR-23A microRNA cluster inhibits B-cell development. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 629–640.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-23a suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting the PAK6-LIMK1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Dai, J.; Tang, H.; Xu, T.; Yu, S.; Si, L.; Cui, C.; Sheng, X.; Chi, Z.; Mao, L.; et al. MicroRNA-23a-3p Inhibits Mucosal Melanoma Growth and Progression through Targeting Adenylate Cyclase 1 and Attenuating cAMP and MAPK Pathways. Theranostics 2019, 9, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Su, M.; Wu, L.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-23a-3p influences the molecular mechanism of gastric cancer cells via CCL22/PI3K/Akt axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11277–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Qiu, G.B.; Fu, W.N. High microRNA-23a expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. Diagn Pathol. 2015, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. miR-23a-3p suppresses cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinomas by targeting FGF2 and correlates with a better prognosis: miR-23a-3p inhibits OSCC growth by targeting FGF2. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Lu, J.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Neilly, M.B.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19971–19976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, T. Expression and clinical significance of miR-23a and MTSS1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.M.; Mitrovic, Z.; Chan, W.C. Biological prognostic markers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Control. 2012, 19, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, K.R.; Morais, D.R.; Reis, S.T.; Viana, N.; Moura, C.; Florez, M.G.; Silva, I.A.; Dip, N.; Srougi, M. MicroRNA 100: A context dependent miRNA in prostate cancer. Clinics 2013, 68, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Lin, P.; Ma, X. miR-100 inhibits cell proliferation in mantle cell lymphoma by targeting mTOR. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Lin, S.; Dai, C.; Lu, Y.; Tian, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, S.; et al. Pooling-analysis for diagnostic and prognostic value of MiRNA-100 in various cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62703–62715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Guan, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y. Prognostic significance of microRNA-100 in solid tumors: An updated meta-analysis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2017, 10, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Gu, M.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, Z. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic microRNA biomarkers for survival outcome in laryngeal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y. Prognostic role of microRNA-100 in various carcinomas: Evidence from six studies. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 3067–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Guo, A.; Hong, Z.; Kuai, W. Upregulation of microRNA-100 predicts poor prognosis in patients with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Onco Targets Ther. 2012, 5, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Chi, J.; Taylor, S.; Tramonti, D.; Ballabio, E.; Palazzo, S.; Saunders, N.J.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Expression of microRNAs in diffuse large B cell lymphoma is associated with immunophenotype, survival and transformation from follicular lymphoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S.; Shi, X.; Jiang, G.; Niu, S.; Ding, D. miR-125a-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration by targeting TAZ. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2019, 12, 3481–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiu, J.; Kang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J. miR-125a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer progression by targeting VEGFA. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5839–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lv, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. MiR-125a-5p suppresses bladder cancer progression through targeting FUT4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Feng, L.; He, J.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.G. MiR-125a-5p inhibits the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells and induces apoptosis by targeting GAB2. Math Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 6923–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yu, M.C.; Gao, G.L.; Liang, H.W.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.T.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Chen, X. MiR-125a-5p functions as a tumour suppressor in breast cancer by downregulating BAP1. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 8773–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, S.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Guo, Y.; Xu, R.R. MicroRNA-125a regulates proliferation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia through targeting NF-κB pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol Sci. 2019, 23, 3594–3601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Wang, G.; Gao, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, X. miR-125a-5p promotes gastric cancer growth and invasion by regulating the Hippo pathway. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e24078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, L.L.; Guan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zou, L. MicroRNA-125a/b-5p promotes malignant behavior in multiple myeloma cells and xenograft tumor growth by targeting DIS3. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Lu, J.; Schlanger, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.Y.; Fox, M.C.; Purton, L.E.; Fleming, H.H.; Cobb, B.; Merkenschlager, M.; et al. MicroRNA miR-125a controls hematopoietic stem cell number. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14229–14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhu, W.; Mei, L.; Lu, Z. Prognostic and clinicopathologic significance of MicroRNA-125a-5p in cancers: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, G.; Paciga, J.E.; Feldman, R.I.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Ma, X.L.; Shelley, S.A.; Jove, R.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Nicosia, S.V.; et al. AKT1/PKBalpha kinase is frequently elevated in human cancers and its constitutive activation is required for oncogenic transformation in NIH3T3 cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Ma, X.; Peng, P.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D.; Shen, K. Clinical and Expression Significance of AKT1 by Co-expression Network Analysis in Endometrial Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, Z.E.; Walton, Z.E.; Altman, B.J.; Hsieh, A.L.; Dang, C.V. MYC, Metabolism, and Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mak, V.C.; Cheung, L.W. Drugging IGF-1R in cancer: New insights and emerging opportunities. Genes. Dis. 2022, 10, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, O.T.; Aleksic, T.; Shah, K.A.; Han, C.; Mehanna, H.; Rapozo, D.C.; Sheard, J.D.; Goodyear, P.; Upile, N.S.; Robinson, M.; et al. IGF-1R expression is associated with HPV-negative status and adverse survival in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Larisch, S. Targeting XIAP for Promoting Cancer Cell Death-The Story of ARTS and SMAC. Cells 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Man, Q.W.; Huo, F.Y.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Li, S.R.; Wang, J.; Su, F.C.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. STAT3 pathway in cancers: Past, present, and future. MedComm 2022, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriv, O.I.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Delaney, A.D.; Lecault, V.; White, A.; Kent, D.; Marmolejo, L.; Heuser, M.; Berg, T.; Copley, M.; et al. Comprehensive microRNA expression profiling of the hematopoietic hierarchy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15443–15448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, M.; Schmitz, U.; Flamant, S.; Wong, J.J.; Bailey, C.G.; Ritchie, W.; Holst, J.; Rasko, J.E.J. Identifying microRNA determinants of human myelopoiesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Fu, C.; Guan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Li, B. Prognostic significance of miR-126 in various cancers: A meta-analysis. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrabeiti-Etxebarria, A.; Lopez-Santillan, M.; Santos-Zorrozua, B.; Lopez-Lopez, E.; Garcia-Orad, A. Systematic Review of the Potential of MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, L.; Vögler, O.; Sas-Barbeito, A.; Muncunill, J.; Ros, T.; Martínez, J.; Quintero-Duarte, A.; Ramos, R.; Asensio, V.J.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.; et al. Screening for Prognostic microRNAs Associated with Treatment Failure in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Xu, L.; Zhong, J.H.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, F.Y. Clinical and prognostic significance of miR-155 and miR-146a expression levels in formalin-fixed/paraffin-embedded tissue of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, W.; Xie, X.; Jiang, J. Prognostic Significance of MiRNA in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DLBCL Without Bone Marrow Involvement | DLBCL with Bone Marrow Involvement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | Adjusted p-Value | Fold Change | Adjusted p-Value | |
| ASF1B | 1.18 | NS | 2.21 | 4 × 10−4 |
| CD82B | −1.05 | NS | 1.60 | NS |
| CRISP3 | 1.82 | 2 × 10−3 | 3.25 | NS |
| FN1 | 2.67 | 1 × 10−2 | 1.92 | NS |
| MEF2B | 1.43 | NS | 1.67 | NS |
| PD-L1 | 3.29 | 4.5 × 10−5 | 3.90 | 5 × 10−5 |
| TIMP1 | −2.48 | 5.05 × 10−9 | −2.58 | 4.9 × 10−4 |
| TOP2A | −2.62 | 6.8 × 10−5 | −2.58 | 6.2 × 10−4 |
| TP53 | −6.55 | 1.5 × 10−5 | −6.64 | 3 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veryaskina, Y.A.; Titov, S.E.; Kovynev, I.B.; Fyodorova, S.S.; Berezina, O.V.; Zhurakovskij, I.P.; Antonenko, O.V.; Demakov, S.A.; Demenkov, P.S.; Ruzankin, P.S.; et al. MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with Prognostic Potential. Cancers 2025, 17, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081300
Veryaskina YA, Titov SE, Kovynev IB, Fyodorova SS, Berezina OV, Zhurakovskij IP, Antonenko OV, Demakov SA, Demenkov PS, Ruzankin PS, et al. MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with Prognostic Potential. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081300
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeryaskina, Yuliya A., Sergei E. Titov, Igor B. Kovynev, Sofya S. Fyodorova, Olga V. Berezina, Igor P. Zhurakovskij, Oksana V. Antonenko, Sergei A. Demakov, Pavel S. Demenkov, Pavel S. Ruzankin, and et al. 2025. "MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with Prognostic Potential" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081300
APA StyleVeryaskina, Y. A., Titov, S. E., Kovynev, I. B., Fyodorova, S. S., Berezina, O. V., Zhurakovskij, I. P., Antonenko, O. V., Demakov, S. A., Demenkov, P. S., Ruzankin, P. S., Tarasenko, A. S., Pospelova, T. I., & Zhimulev, I. F. (2025). MicroRNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with Prognostic Potential. Cancers, 17(8), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081300








