Methylation-Mediated Silencing of miR-124-3 Regulates LRRC1 Expression and Promotes Oral Cancer Progression
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Bisulfite Conversion of Genomic DNA
2.2. Bisulfite Pyrosequencing Assay
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse-Transcription PCR
2.5. 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine Treatment
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Transwell Cell Migration Assay
2.9. Western Blot Assay
2.10. Construction of Plasmid for Transient Transfection
2.11. Construction and Production of Lentiviral Vector
2.12. Construction of Luciferase Reporter Plasmids and Luciferase Activity Assay
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
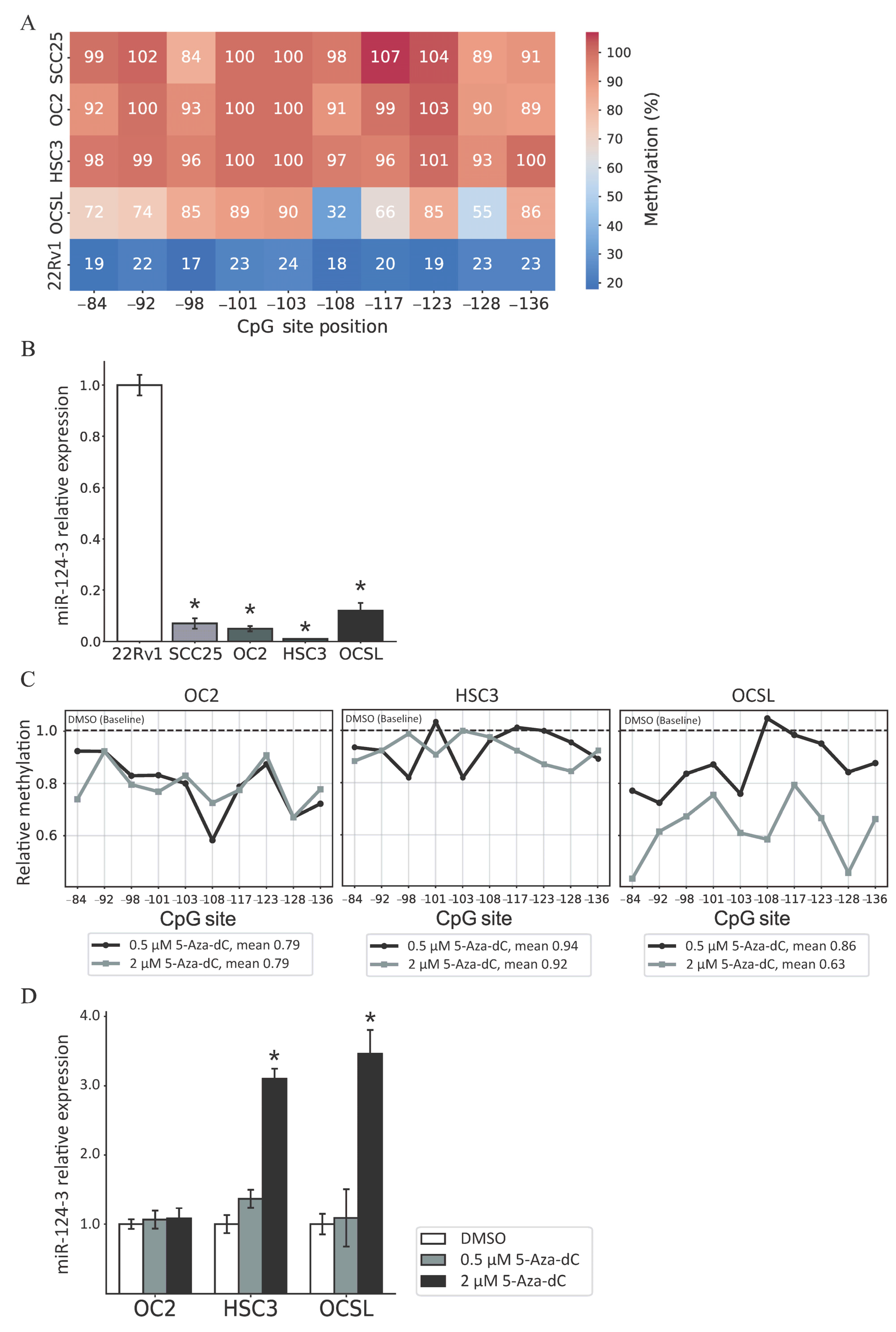
3.1. miR-124-3 Is Frequently Hypermethylated in OSCC Tissues
3.2. Regulation of miR-124-3 Expression by DNA Methylation
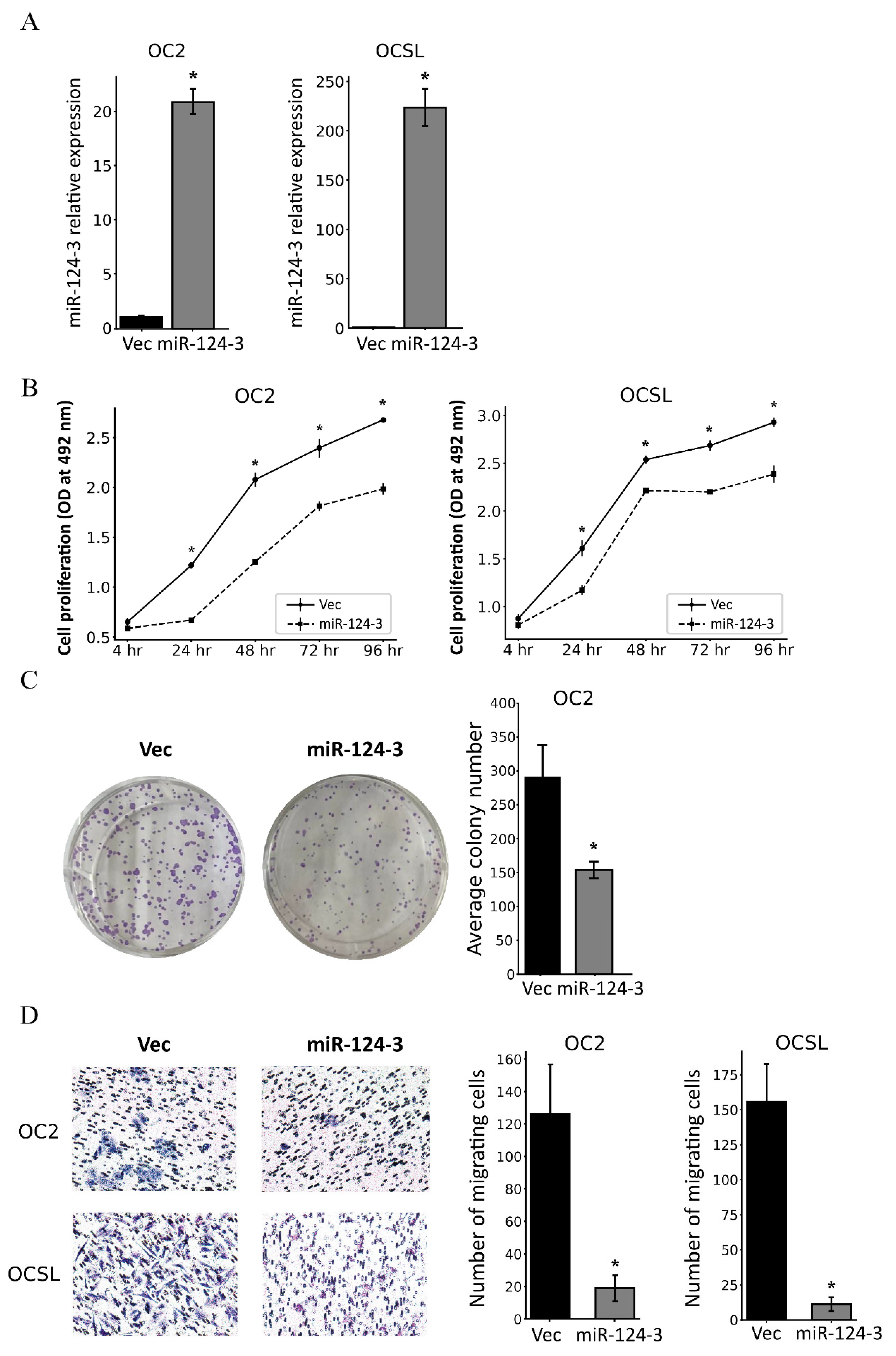
3.3. MiR-124-3 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of OSCC Cells
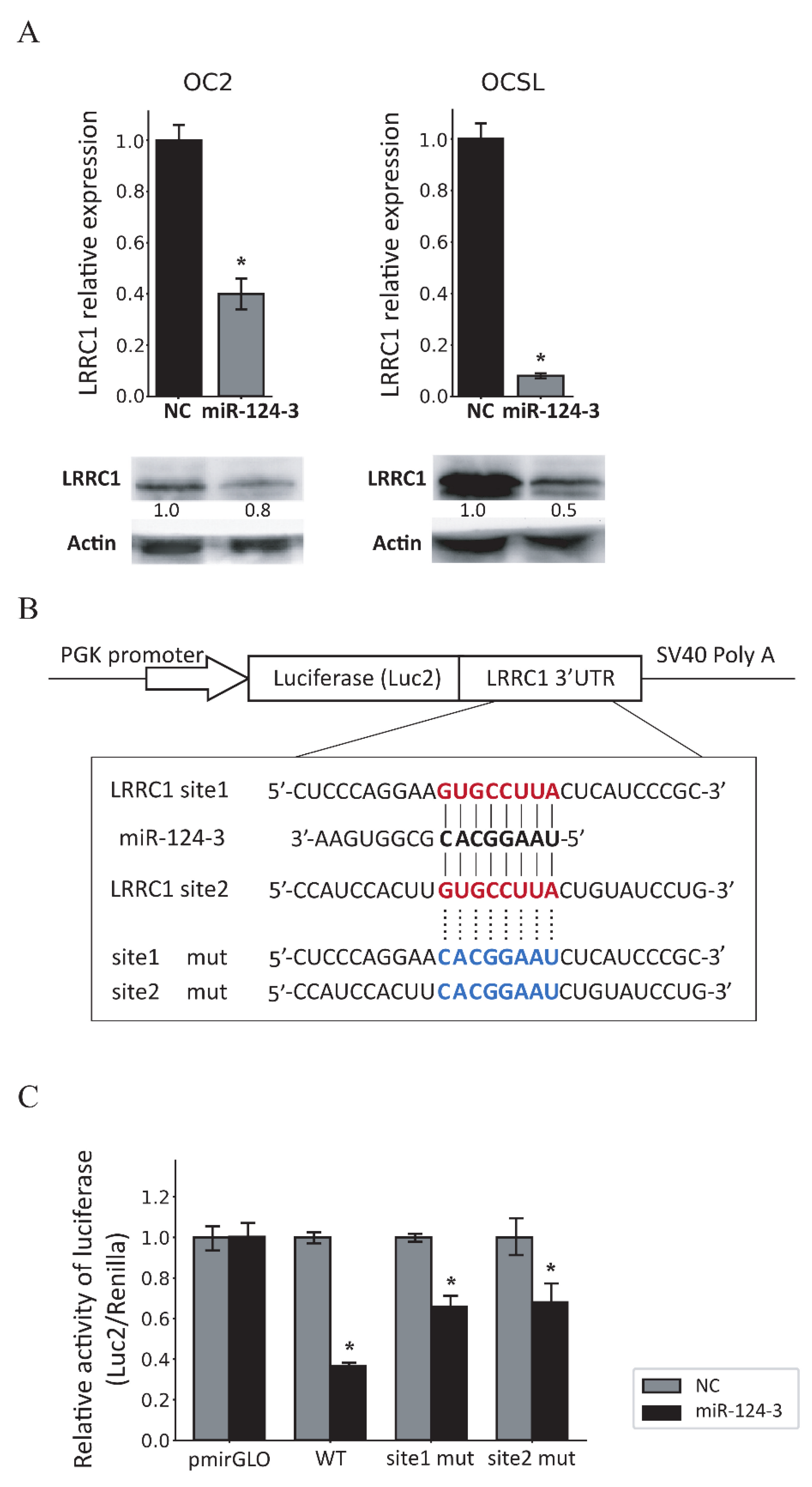
3.4. MiR-124-3 Downregulates LRRC1 Expression by Targeting Its 3′UTR
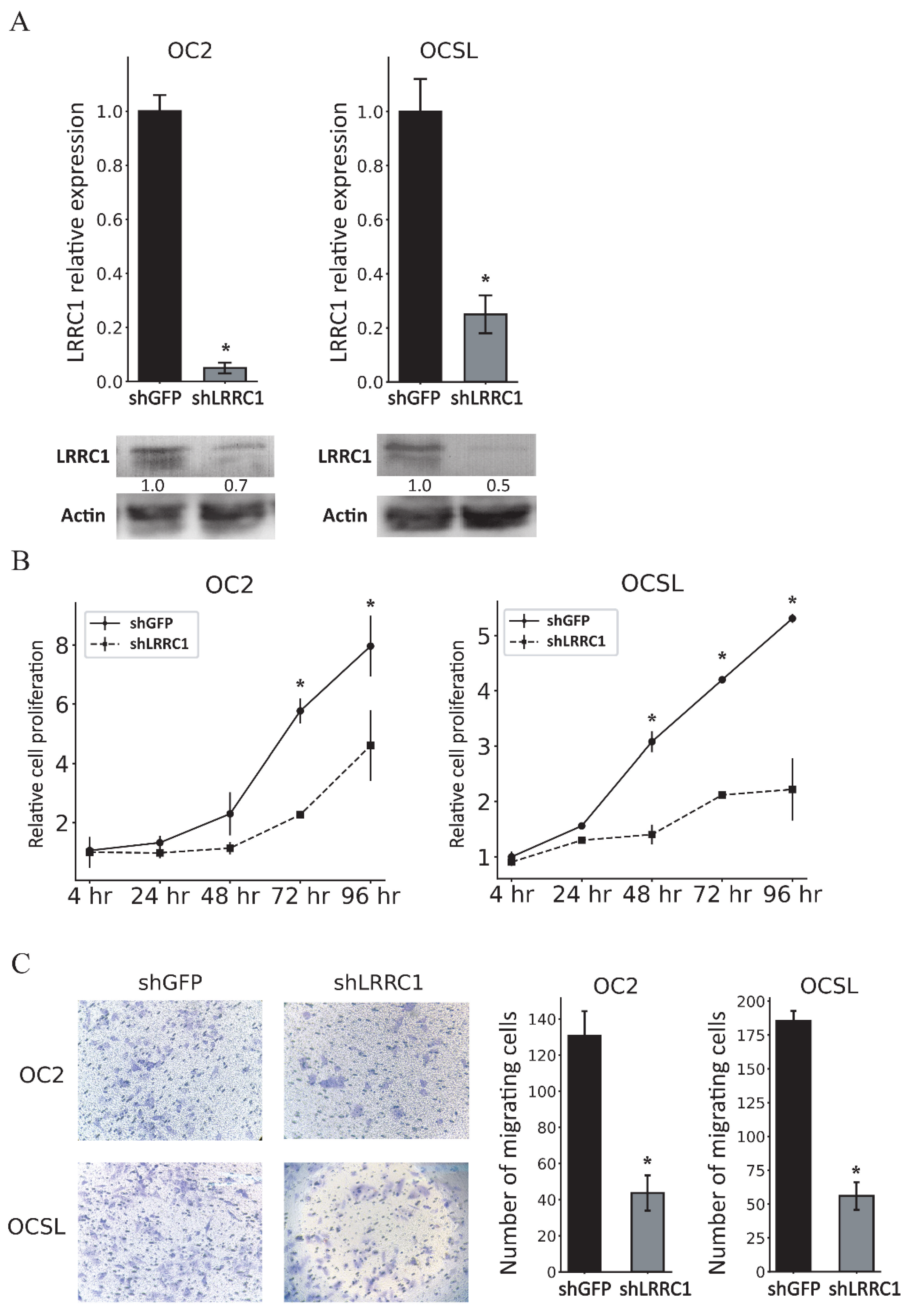
3.5. Knockdown of LRRC1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of OSCC Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badwelan, M.; Muaddi, H.; Ahmed, A.; Lee, K.T.; Tran, S.D. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Concomitant Primary Tumors, What Do We Know? A Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3721–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, E. Current concepts and future of noninvasive procedures for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma—A systematic review. Head Face Med. 2015, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chou, J.L.; Chan, M.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Tsou, Y.A.; Tsai, M.H.; et al. DNA methylation profiles and biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liouta, G.; Adamaki, M.; Tsintarakis, A.; Zoumpourlis, P.; Liouta, A.; Agelaki, S.; Zoumpourlis, V. DNA Methylation as a Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Predictive Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokovitch, L.; Maquet, C.; Crampon, F.; Taihi, I.; Roussel, L.M.; Obongo, R.; Virard, F.; Fervers, B.; Deneuve, S. Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors: State of the Art. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zil, E.R.; Baig, S.; Zaman, U.; Lucky, M.H. Human papilloma virus 16/18: Fabricator of trouble in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2024 Annual Report of Health Promotion Administration. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/List.aspx?nodeid=1070 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Baxter, E.; Windloch, K.; Gannon, F.; Lee, J.S. Epigenetic regulation in cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recillas-Targa, F. Cancer Epigenetics: An Overview. Arch. Med. Res. 2022, 53, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, M. DNA hypermethylation in disease: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 1141–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Li, C.; Yin, H.; Huang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Yu, M.; Lin, J.; Ding, L.; et al. The Mechanism of DNA Methylation and miRNA in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, D.; Lu, C. The SMART App: An interactive web application for comprehensive DNA methylation analysis and visualization. Epigenetics Chromatin 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildiyal, M.; Zamore, P.D. Small silencing RNAs: An expanding universe. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamlouche, F.; Yehya, A.; Zeid, Y.; Fakhereddine, H.; Fawaz, J.; Liu, Y.N.; Al-Sayegh, M.; Abou-Kheir, W. MicroRNAs as clinical tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in prostate cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 28, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, W.; Lu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Dong, Y. miR-124 regulates liver cancer stem cells expansion and sorafenib resistance. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.B.; Li, Q.L.; Hu, J.F.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.P.; Deng, L. miR-124 inhibits growth and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting ROCK1. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6543–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mei, Z.; Hu, H.B.; Zhang, X. The lncRNA MALAT1 contributes to non-small cell lung cancer development via modulating miR-124/STAT3 axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6679–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, B.; Zhou, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dong, B. miR-124 suppresses glioblastoma growth and potentiates chemosensitivity by inhibiting AURKA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani Asl, E.; Rasmi, Y.; Baradaran, B. MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses PD-L1 expression and inhibits tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer cells via modulating STAT3 signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 7071–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhong, H.; Jiao, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X.; Song, X.; Ying, B. MiR-124-3p inhibits the migration and invasion of Gastric cancer by targeting ITGB3. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ling, Z.; Hao, Y.; Pang, X.; Han, X.; Califano, J.A.; Shan, L.; Gu, X. MiR-124 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and its downstream signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25005–25020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, S.; Jones, A.V.; Hinsley, E.E.; Whawell, S.A.; Lambert, D.W. MicroRNA-124 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma motility by targeting ITGB1. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Gong, R.G.; Li, A.; Yang, S.; Cao, Y.T.; Wen, Y.M.; Wang, C.M.; Yi, X.Z. The expression profile of microRNAs in a model of 7,12-dimethyl-benz[a]anthrance-induced oral carcinogenesis in Syrian hamster. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Santoni, M.J.; Arsanto, J.P.; Jaulin-Bastard, F.; Le Bivic, A.; Marchetto, S.; Audebert, S.; Isnardon, D.; Adelaide, J.; Birnbaum, D.; et al. Lano, a novel LAP protein directly connected to MAGUK proteins in epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32051–32055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Dai, J.; Liu, R.; Han, Z.G. Aberrant upregulation of LRRC1 contributes to human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 4543–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Huang, Z. LRRC1 knockdown downregulates MACF1 to inhibit the malignant progression of acute myeloid leukemia by inactivating beta-catenin/c-Myc signaling. J. Mol. Histol. 2024, 55, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, X. YY1 and eIF4A3 are mediators of the cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma promoted by circ-ZNF609 by targeting miR-432-5p to regulate LRRC1. Aging 2021, 13, 25195–25212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidsley, R.; Zotenko, E.; Peters, T.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Risbridger, G.P.; Molloy, P.; Van Djik, S.; Muhlhausler, B.; Stirzaker, C.; Clark, S.J. Critical evaluation of the Illumina MethylationEPIC BeadChip microarray for whole-genome DNA methylation profiling. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Chang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, N.; Cui, J.; Gao, W.Q. Regulation and methylation of tumor suppressor miR-124 by androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constancio, V.; Nunes, S.P.; Henrique, R.; Jeronimo, C. DNA Methylation-Based Testing in Liquid Biopsies as Detection and Prognostic Biomarkers for the Four Major Cancer Types. Cells 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constancio, V.; Nunes, S.P.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Freitas, R.; Oliveira, J.; Pousa, I.; Oliveira, J.; Soares, M.; Dias, C.G.; Dias, T.; et al. Early detection of the major male cancer types in blood-based liquid biopsies using a DNA methylation panel. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo-Silva, C.; Constancio, V.; Miranda-Goncalves, V.; Leite-Silva, P.; Salta, S.; Lobo, J.; Guimaraes, R.; Carvalho-Maia, C.; Gigliano, D.; Farinha, M.; et al. DNA methylation biomarkers accurately detect esophageal cancer prior and post neoadjuvant chemoradiation. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 8777–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Salta, S.; Palma de Sousa, S.; Pousa, I.; Oliveira, J.; Soares, M.; Rego, L.; Dias, T.; Rodrigues, J.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Methylation of Selected Genes Allows for Early Detection of the Major Cancers in Women. Cancers 2018, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Yoshida, T.; Enomoto, S.; Asada, K.; Tatematsu, M.; Ichinose, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Ushijima, T. DNA methylation of microRNA genes in gastric mucosae of gastric cancer patients: Its possible involvement in the formation of epigenetic field defect. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Gacem, R.; Ben Abdelkrim, O.; Ziadi, S.; Ben Dhiab, M.; Trimeche, M. Methylation of miR-124a-1, miR-124a-2, and miR-124a-3 genes correlates with aggressive and advanced breast cancer disease. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 4047–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Ropero, S.; Ballestar, E.; Fraga, M.F.; Cerrato, C.; Setien, F.; Casado, S.; Suarez-Gauthier, A.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Git, A.; et al. Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, E.E.; Bachman, K.E.; Myohanen, S.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B. Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberg, L.O.; Edenberg, H.J. Epigenetics of gene expression in human hepatoma cells: Expression profiling the response to inhibition of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rayyan, N.; Litchfield, L.M.; Ivanova, M.M.; Radde, B.N.; Cheng, A.; Elbedewy, A.; Klinge, C.M. 5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine and trichostatin A increase COUP-TFII expression in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yin, S.; Liang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; Fu, Z.; Shen, C.; Han, Y.; et al. Function of microRNA-124 in the pathogenesis of cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Mu, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Liu, W.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-193a reduces cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells via targeting LRRC1. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| (A) For Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip Assay | ||
| Patients | ||
| Characteristics | (n = 23) | |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 50.6 ± 7.6 | |
| Pathological Stage | n | % |
| P1 | 3 | 13.0% |
| P2 | 5 | 21.8% |
| P3 | 8 | 34.8% |
| P4 | 7 | 30.4% |
| (B) For Pyrosequencing Assay | ||
| Patients | ||
| Characteristics | (n = 18) | |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 54.5 ± 10.9 | |
| Pathological Stage | n | % |
| P1 | 3 | 16.7% |
| P2 | 5 | 27.8% |
| P3 | 6 | 33.3% |
| P4 | 4 | 22.2% |
| Probe | UCSC RefGene Group | Mean Δβ | Discrimination Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | (95% CI) | p | ||||
| cg08737296 | TSS1500 | 0.14 | 0.91 | (0.82, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg02650317 | TSS1500 | 0.22 | 0.88 | (0.77, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg02065637 | TSS1500 | 0.30 | 0.94 | (0.87, | 1.00) | <0.0001 |
| cg04927004 | TSS1500 | 0.11 | 0.85 | (0.72, | 0.97) | <0.0001 |
| cg15699267 | TSS1500 | 0.26 | 0.90 | (0.80, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg20277905 | TSS200 | 0.16 | 0.89 | (0.80, | 0.98) | <0.0001 |
| cg19267861 | TSS200 | 0.25 | 0.91 | (0.82, | 1.00) | <0.0001 |
| cg03387135 | TSS200 | 0.18 | 0.85 | (0.73, | 0.97) | <0.0001 |
| cg01052879 | TSS200 | 0.16 | 0.89 | (0.79, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg18627360 | TSS200 | 0.13 | 0.90 | (0.81, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg15028514 | TSS200 | 0.15 | 0.90 | (0.80, | 0.99) | <0.0001 |
| cg06660530 | Body | 0.16 | 0.87 | (0.77, | 0.97) | <0.0001 |
| cg18772588 | Body | 0.20 | 0.86 | (0.75, | 0.97) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, S.-W.; Liao, X.-H.; Wu, S.-H.; Li, Y.-F.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Lu, Y.-C.; Tai, C.-K. Methylation-Mediated Silencing of miR-124-3 Regulates LRRC1 Expression and Promotes Oral Cancer Progression. Cancers 2025, 17, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071136
Liao S-W, Liao X-H, Wu S-H, Li Y-F, Chen P-Y, Wang Y-L, Lu Y-C, Tai C-K. Methylation-Mediated Silencing of miR-124-3 Regulates LRRC1 Expression and Promotes Oral Cancer Progression. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071136
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Shin-Wei, Xiao-Hui Liao, Shao-Huang Wu, Yu-Fen Li, Pin-Yi Chen, Yi-Ling Wang, Yin-Che Lu, and Chien-Kuo Tai. 2025. "Methylation-Mediated Silencing of miR-124-3 Regulates LRRC1 Expression and Promotes Oral Cancer Progression" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071136
APA StyleLiao, S.-W., Liao, X.-H., Wu, S.-H., Li, Y.-F., Chen, P.-Y., Wang, Y.-L., Lu, Y.-C., & Tai, C.-K. (2025). Methylation-Mediated Silencing of miR-124-3 Regulates LRRC1 Expression and Promotes Oral Cancer Progression. Cancers, 17(7), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071136







