Efficacy and Limitations of Flow Cytometry for the Rapid Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
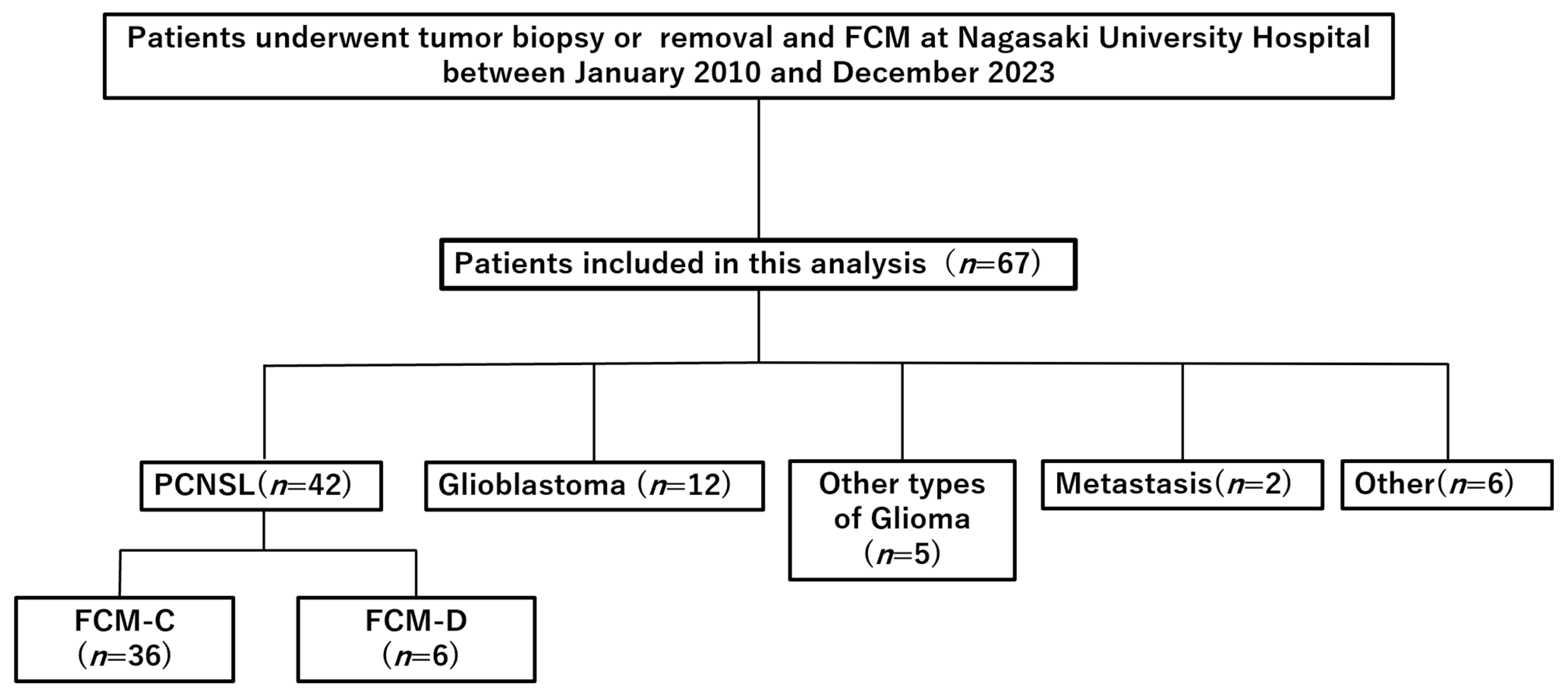
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Surgical Procedures and Tissue Handling
2.3. Flow Cytometry Protocol
2.4. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Clinical and Radiological Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of Flow Cytometry
3.3. Lymphocyte Subset Analysis
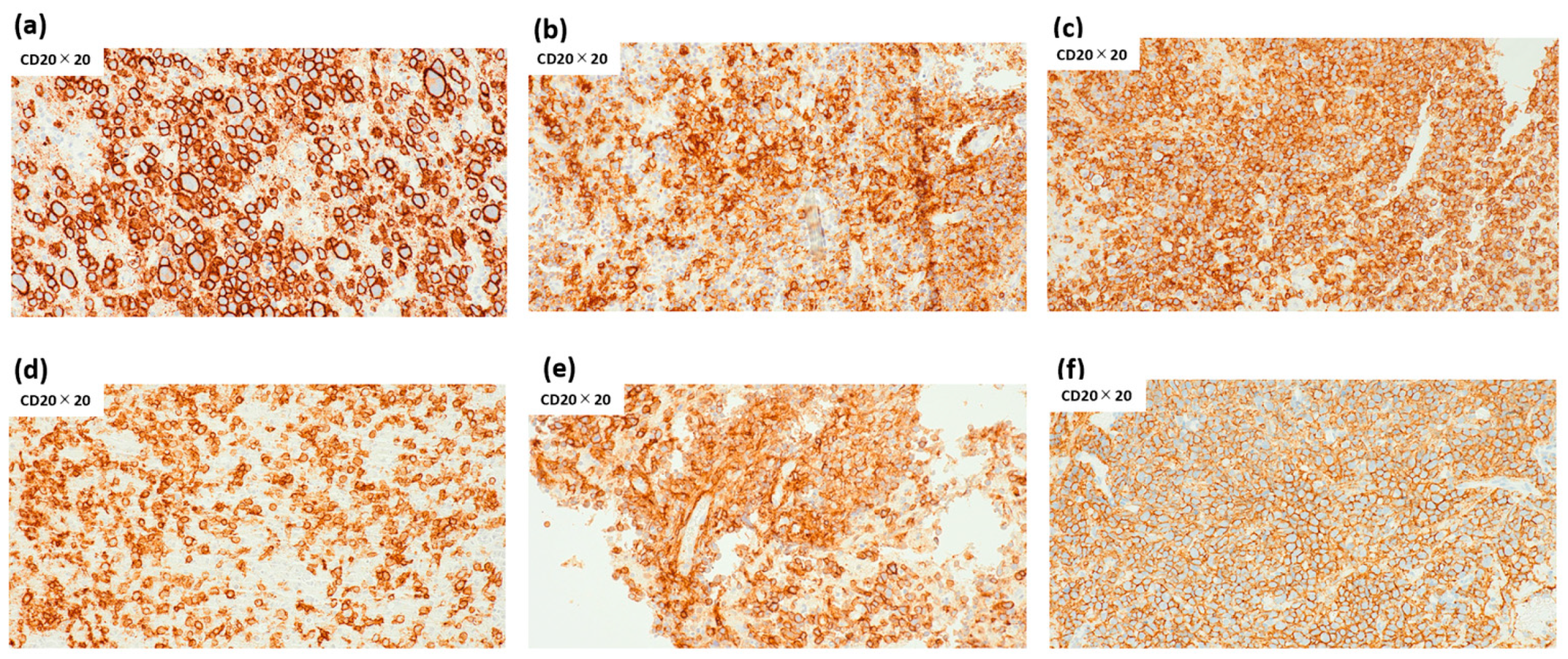
3.4. Histopathological Correlates of Discordant Cases
4. Discussion
4.1. Diagnostic Value of FCM
4.2. Discordant Cases and the Role of the Immune Microenvironment
4.3. Comparison with the Previous Literature
4.4. Clinical Implications
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCNSL | Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
| DLBCL | Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma |
| HD-MTX | High-Dose Methotrexate |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PET/CT | Positron Emission Tomograph/Computed Tomography |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| CXCL13 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 13 |
| FCM | Flow Cytometry |
| RPVI | Reactive Perivascular T-Cell Infiltration |
| FCM-D | Flow Cytometry Discordant |
| HE | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| KPS | Karnofsky Performance Status |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Calimeri, T.; Cwynarski, K.; Dietrich, J.; Grommes, C.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Illerhaus, G.; Makino, K.; Marturano, E.; Rubenstein, J.L.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauw, M.I.S.; Lucas, C.-H.G.; Ohgami, R.S.; Wen, K.W. Primary central nervous system lymphomas: A diagnostic overview of key histomorphologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic features. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Kato, T.; Hiu, T.; Imaizumi, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Niino, D.; Yamaguchi, S.; Baba, S.; Ujifuku, K.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Treatment of new-onset primary central nervous system lymphoma in elderly patients using RMPV chemotherapy: A single-institution experience. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 118, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, J.L.; Koshy, M.; Shaikh, H.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J. Age, gender, and racial differences in incidence and survival in primary CNS lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, M.; Brunn, A.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Terreni, M.R.; Ponzoni, M. Primary lymphoma of the central nervous system—A diagnostic challenge. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Li, W.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.B.; Zuo, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, S.Z.; Yan, L.F.; et al. Differentiation between primary central nervous system lymphoma and atypical glioblastoma based on MRI morphological feature and signal intensity ratio: A retrospective multicenter study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 811197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, N.D.; Anh, N.N.; Minh, N.D.; Huyen, D.K.; Duc, N.M. Differentiation of glioblastoma and primary central nervous system lymphomas using multiparametric diffusion and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Biomed. Rep. 2023, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neska-Matuszewska, M.; Bladowska, J.; Sąsiadek, M.; Zimny, A. Differentiation of glioblastoma multiforme, metastases and primary central nervous system lymphomas using multiparametric perfusion and diffusion MR imaging of a tumor core and a peritumoral zone—Searching for a practical approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikova, H.; Koubska, E.; Weichet, J.; Klener, J.; Rulseh, A.; Liscak, R.; Vojtech, Z. Can morphological MRI differentiate between primary central nervous system lymphoma and glioblastoma? Cancer Imaging 2016, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Escoda, A.; Souza, L.; Vargas, M.I.; Thurnher, M.M.; Smirniotopoulos, J.G.; Castillo, M. Imaging of lymphomas involving the CNS: An update. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavazza, C.; Pellerino, A.; Ferrio, F.; Cistaro, A.; Soffietti, R.; Rudà, R. Primary CNS lymphomas: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3606970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Nakano, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Omura, T.; Shimizu, S.; Saito, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Narita, Y.; Kondo, A.; et al. Liquid biopsy of cerebrospinal fluid for MYD88 L265P mutation is useful for diagnosis of central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4702–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, D.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, W. Changes in cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 levels display better performance in predicting disease relapse than conventional magnetic resonance imaging in primary central nervous system lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorofchian, S.; Lu, G.; Zhu, J.J.; Duose, D.Y.; Windham, J.; Esquenazi, Y.; Ballester, L.Y. Detection of the MYD88 p.L265P mutation in the CSF of a patient with CNS lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Korfel, A.; Pfeiffer, S.; Kiewe, P.; Volk, H.-D.; Cakiroglu, H.; Widmann, T.; Thiel, E. CXCL13 and CXCL12 in Central Nervous System Lymphoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5968–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debliquis, A.; Voirin, J.; Harzallah, I.; Maurer, M.; Lerintiu, F.; Drénou, B.; Ahle, G. Cytomorphology and flow cytometry of brain biopsy rinse fluid enables faster and multidisciplinary diagnosis of large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, F.E.; Foon, K.A. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood 2008, 111, 3941–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Inaba, T.; Shishido-Hara, Y.; Tsukamoto, T.; Mizutani, S.; Okamoto, T.; Tanigawa, S.; Yamanaka, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Konishi, E.; et al. Analysis of false-negative findings of the incomparable accuracy and swiftness of flow cytometric diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2023, 63, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, E.; Markopoulos, G.; Voulgaris, S.; Vartholomatos, G.; Alexiou, G.A. The role of intraoperative flow cytometry on intracranial tumor surgery: A scoping review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2025, 48, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Kusakabe, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Honda, T.; Kondo, T.; Kinnami, S.; et al. Reliable intraoperative diagnostic methods for PCNSL: Utility of combining intraoperative immunohistochemistry, cytology, and flow cytometry in achieving optimal treatment. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2025, 125, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordone, I.; Masai, S.; Carosi, M.; Vidiei, A.; Marchwsi, M.; Marino, M.; Tekera, S.; Pasquale, A.; Mengarelli, A.; Conti, L.; et al. Brain stereotactic biopsy flow cytometry for central nervous system lymphoma characterization: Advantages and pitfalls. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, R.; Chamberlain, M.; Ruby, E.; Hochberg, F.H. T-cell infiltration of primary CNS lymphoma. Neurology 1996, 46, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemersma, S.A.; Oudejans, J.J.; Vonk, M.J.; Dreef, E.J.; Prins, F.A.; Jansen, P.M.; Vermeer, M.H.; Blok, P.; Kibbelaar, R.E.; Muris, J.J.F.; et al. High numbers of tumour-infiltrating activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and frequent loss of HLA class I and II expression, are features of aggressive B-cell lymphomas of the brain and testis. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022; ISBN 978-92-832-4506-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meulen, M.; Bromberg, J.E.C.; Lam, K.H.; Dammers, R.; Langerak, A.W.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Kros, J.M.; van den Bent, M.J.; van der Velden, V.H.J. Flow cytometry shows added value in diagnosing lymphoma in brain biopsies. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zuo, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiao, B.; Zheng, J.; Cai, Z. Prognostic significance of the aggregative perivascular growth pattern of tumor cells in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, M.; Berger, F.; Chassagne-Clément, C.; Tinguely, M.; Jouvet, A.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Dell’Oro, S.; Terreni, M.R.; Doglioni, C.; Weis, J.; et al. Reactive perivascular T-cell infiltrate predicts survival in primary central nervous system B-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriyama, S.; Nitta, M.; Saito, N.; Hirano, M.; Tominaga, T. Intraoperative flow cytometry enables differentiation between PCNSL and glioblastoma. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e261–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Total (n = 42) | FCM-C (n = 36) | FCM-D (n = 6) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 71.5 (51–85) | 72.0 (51–85) | 66.5 (57–78) | 0.35 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 24 (57.1) | 21 (58.3) | 3 (50.0) | 1 |
| Needle biopsy, n (%) | 39 (92.9) | 34 (94.4) | 5 (83.3) | 0.38 |
| Preoperative KPS, median (range) | 50 (30–80) | 50 (30–80) | 40 (30–70) | 0.18 |
| Tumor number—single, n (%) | 24 (57.1) | 21 (58.3) | 3 (50.0) | 1 |
| Tumor number—multiple, n (%) | 18 (42.9) | 15 (41.7) | 3 (50.0) | 1 |
| MRI findings—homogeneous Gd enhancement, n (%) | 29 (69.0) | 25 (69.4) | 4 (66.7) | 1 |
| MRI findings—hemorrhage, n (%) | 17 (40.5) | 13 (36.1) | 4 (66.7) | 0.2 |
| MRI findings—calcification, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, H.; Hiu, T.; Kato, T.; Ueki, N.; Matsuo, A.; Yoshida, M.; Baba, S.; Ujifuku, K.; Yoshida, K.; Koike, H.; et al. Efficacy and Limitations of Flow Cytometry for the Rapid Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223646
Nakamura H, Hiu T, Kato T, Ueki N, Matsuo A, Yoshida M, Baba S, Ujifuku K, Yoshida K, Koike H, et al. Efficacy and Limitations of Flow Cytometry for the Rapid Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(22):3646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223646
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Hikaru, Takeshi Hiu, Takeharu Kato, Nozomi Ueki, Ayaka Matsuo, Michiharu Yoshida, Shiro Baba, Kenta Ujifuku, Koichi Yoshida, Hirofumi Koike, and et al. 2025. "Efficacy and Limitations of Flow Cytometry for the Rapid Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma" Cancers 17, no. 22: 3646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223646
APA StyleNakamura, H., Hiu, T., Kato, T., Ueki, N., Matsuo, A., Yoshida, M., Baba, S., Ujifuku, K., Yoshida, K., Koike, H., Hayashi, Y., Hasegawa, H., Ando, K., Yanagihara, K., Nakashima, M., Miyazaki, Y., & Matsuo, T. (2025). Efficacy and Limitations of Flow Cytometry for the Rapid Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers, 17(22), 3646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223646







