Integrating Multi-Omics and Medical Imaging in Artificial Intelligence-Based Cancer Research: An Umbrella Review of Fusion Strategies and Applications
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Multimodal Data in Oncology
1.2. The Need for AI-Based Fusion
1.3. The Need for an Umbrella Review
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Leveraging PICOS Framework
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Quality Assessment Using AMSTAR 2.0
2.7. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Reviews
3.2. Summary of Umbrella Review
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment Using AMSTAR 2.0
3.4. Fusion Strategies Findings and Criticisms
3.5. Publicly Available Clinical and Multi-Omics Imaging Datasets
4. Discussion
4.1. Insights Across Cancer Types
4.2. Gaps & Challenges
4.3. Crosstalk Between AI and Clinical Base
4.4. Evaluation Metrics Used in Multi-Modal Fusion Studies
4.5. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Multimodal Cancer Modeling
4.6. Pipeline of Multi-Modal Cancer AI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.-Y.; Chung, H.W.; So, Y.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, E.J. Recent Updates of PET in Lymphoma: FDG and Beyond. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An Immeasurable Source of Knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, A68–A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Jian, J.; Meng, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Z. A Multi-Modal Deep Learning Framework for Pan-Cancer Prognosis. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.07016. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Deep Learning in Medical Image Registration: A Review. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 20TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Margolies, L.R.; Rothstein, J.H.; Fluder, E.; McBride, R.; Sieh, W. Deep learning to improve breast cancer detection on screening mammography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, N.; Diehn, M.; Bredel, M.; Kuo, M.D. Illuminating Radiogenomic Characteristics of Glioblastoma Multiforme through Integration of MR Imaging, Gene Expression, and DNA Copy Number Variation. Radiology 2014, 270, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, P.; Stringfield, O.; El-Hachem, N.; Bui, M.M.; Rios Velazquez, E.; Parmar, C.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Lambin, P.; Gillies, R.J.; et al. Defining the Biological Basis of Radiomic Phenotypes in Lung Cancer. eLife 2017, 6, e23421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobadersany, P.; Yousefi, S.; Amgad, M.; Gutman, D.A.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Velázquez Vega, J.E.; Brat, D.J.; Cooper, L.A.D. Predicting Cancer Outcomes from Histology and Genomics Using Convolutional Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2970–E2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayara, H.; Abdelbaky, I.; Chong, K.T. Recent omics-based computational methods for COVID-19 drug discovery and repurposing. Briefings Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Lu, M.Y.; Wang, J.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Mahmood, F. Synthetic Data in Machine Learning for Medicine and Healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.M.; Selvarajoo, K. Advancing drug-response prediction using multi-modal and -omics machine learning integration (MOMLIN): A case study on breast cancer clinical data. Briefings Bioinform. 2024, 25, Bbae300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hou, S.; Liu, S.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Y. Attention-based multimodal glioma segmentation with multi-attention layers for small-intensity dissimilarity. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivizakis, E.; Koutroumpa, N.-M.; Souglakos, J.; Karantanas, A.; Zervakis, M.; Marias, K. Radiotranscriptomics of non-small cell lung carcinoma for assessing high-level clinical outcomes using a machine learning-derived multi-modal signature. BioMed. Eng. Online 2023, 22, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Radua, J. Ten Simple Rules for Conducting Umbrella Reviews. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2018, 21, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, J.; Liao, T.; Pu, R.; Liu, S.; Peng, Y. A hybrid deep learning model for predicting molecular subtypes of human breast cancer using multimodal data. IRBM 2022, 43, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Moher, D.; Petticrew, M.; Stewart, L. An international registry of systematic-review protocols. Lancet 2011, 377, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardt, C.; Adams, M.B.; Owens, T.; Keitz, S.; Fontelo, P. Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2007, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A Critical Appraisal Tool for Systematic Reviews That Include Randomised or Non-randomised Studies of Healthcare Interventions, or Both. BMJ 2017, 358, J4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Hamel, C.; Wells, G.A.; Bouter, L.; Kristjansson, E.; Grimshaw, J.; Henry, D.; Boers, M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, P.; Milantoni, V.; Khalik, H.A.; Kay, J.; Slawaska-Eng, D.; Johnson, J.; de Sa, D. Evaluating the quality of systematic reviews of comparative studies in autograft-based anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the AMSTAR-2 tool: A systematic umbrella review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2024, 32, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Celotto, S.; Pizzol, D.; Gasevic, D.; Ji, M.; Barnini, T.; Solmi, M.; Stubbs, B.; Smith, L.; Sánchez, G.F.L.; et al. Metformin and health outcomes: An umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, E13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.; Savović, J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Caldwell, D.M.; Reeves, B.C.; Shea, B.; Davies, P.; Kleijnen, J.; Churchill, R. ROBIS: A new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 69, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. A survey on multi-omics-based cancer diagnosis using machine learning with the potential application in gastrointestinal cancer. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1109365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicora, G.; Vitali, F.; Dagliati, A.; Geifman, N.; Bellazzi, R. Integrated multi-omics analyses in oncology: A review of machine learning methods and tools. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuala, R.; Kushibar, K.; Garrucho, L.; Linardos, A.; Szafranowska, Z.; Klein, S.; Glocker, B.; Diaz, O.; Lekadir, K. Data synthesis and adversarial networks: A review and meta-analysis in cancer imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 84, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, C.; Broad, A.; Godson, L.; Clarke, E.; Westhead, D.; Treanor, D. Machine learning-based multimodal prognostic models integrating pathology images and high-throughput omic data for overall survival prediction in cancer: A systematic review. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.16876. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocka, M.; Wysocki, O.; Zufferey, M.; Landers, D.; Freitas, A. A systematic review of biologically-informed deep learning models for cancer: Fundamental trends for encoding and interpreting oncology data. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, F.; Codicè, F.; Caranzano, I.; Rollo, C.; Birolo, G.; Fariselli, P.; Pancotti, C. A Comprehensive Review of Deep Learning Applications with Multi-Omics Data in Cancer Research. Genes 2025, 16, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Kwon, H.; Jung, I. A review on multi-omics integration for aiding study design of large scale TCGA cancer datasets. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, G.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, S. Multi-OMICS approaches in cancer biology: New era in cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. Medcomm 2023, 4, E315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundova, D.; Rubin, M.A. Clinical application of advanced multi-omics tumor profiling: Shaping precision oncology of the future. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 920–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Garmire, L.X. More is better: Recent progress in multi-omics data integration methods. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, N.; Rao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Integration of multi-omics approaches in exploring intra-tumoral heterogeneity. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Laiouar-Pedari, S.; Kuntz, S.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Hekler, A.; Kather, J.N.; Gaiser, T.; Fröhling, S.; Brinker, T.J. Integration of deep learning-based image analysis and genomic data in cancer pathology: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 160, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirienko, M.; Gelardi, F.; Fiz, F.; Bauckneht, M.; Ninatti, G.; Pini, C.; Briganti, A.; Falconi, M.; Oyen, W.J.G.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; et al. Personalised PET Imaging in Oncology: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses to Guide the Appropriate Radiopharmaceutical Choice and Indication. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 52, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelaj, A.; Miskovic, V.; Zanitti, M.; Trovo, F.; Genova, C.; Viscardi, G.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Ferrara, R.; Rovati, L.; Leonetti, M.A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Biomarker Discovery in Immuno-Oncology: A Systematic Review. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, M.F.P.; Cormio, G.; Loizzi, V.; Maiorano, B.A. Artificial Intelligence in Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Predictive AI Models in Genomics, Radiomics, and Immunotherapy. AI 2025, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doykov, M.; Valkanov, S.; Khalid, U.; Gurung, J.; Kostov, G.; Hristov, B.; Uchikov, P.; Kraeva, M.; Kraev, K.; Doykov, D.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Augmented Advancements in the Diagnostic Challenges Within Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, Y.; Broughton, P.; Abdollahi, H.; Valafar, H.; Blenda, A.V. Integrating omics data and AI for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restini, F.C.F.; Torfeh, T.; Aouadi, S.; Hammoud, R.; Al-Hammadi, N.; Starling, M.T.M.; Sousa, C.F.P.M.; Mancini, A.; Brito, L.H.; Yoshimoto, F.H.; et al. AI tool for predicting MGMT methylation in glioblastoma for clinical decision support in resource limited settings. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.; Kather, J.N. A systematic analysis of deep learning in genomics and histopathology for precision oncology. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.S.; Tran, N.L.; Canoll, P.D.; Swanson, K.R.; Li, J. Knowledge-informed machine learning for cancer diagnosis and prognosis: A review. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 10008–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, R.F.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D.; Whiting, P.F.; Westwood, M.; Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Kleijnen, J.; Mallett, S.; PROBAST Group. PROBAST: A Tool to Assess the Risk of Bias and Applicability of Prediction Model Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Wolff, R.F.; Riley, R.D.; Whiting, P.F.; Westwood, M.; Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Kleijnen, J.; Mallett, S. PROBAST: A Tool to Assess Risk of Bias and Applicability of Prediction Model Studies: Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, W1–W33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute and National Human Genome Research Institute. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC). National Cancer Institute. 2024. Available online: https://proteomics.cancer.gov (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. National Cancer Institute. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Armato, S.G.; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) and Image Database Resource Initiative (IDRI): A Completed Reference Database of Lung Nodules on CT Scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.P. The Use of the Area under the ROC Curve in the Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B. Multivariable Prognostic Models: Issues in Developing Models, Evaluating Assumptions and Adequacy, and Measuring and Reducing Errors. Stat. Med. 1982, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, S.; Mittelstadt, B.; Russell, C. Counterfactual Explanations Without Opening the Black Box: Automated decisions and the GDPR. Harv. J. Law Technol. 2017, 31, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Jeong, W.; Lee, S.W. Explainable AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Methods, Applications, and Usability Challenges. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookkandi, K.; Nath, M.K. Robust Deep Neural Network for Classification of Diseases from Paddy Fields. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookkandi, K.; Nath, M.K.; Dash, S.S.; Mishra, M.; Blange, R. A Robust Lightweight Vision Transformer for Classification of Crop Diseases. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: Self-Adapting Framework for U-Net-Based Medical Image Segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, T.; Tao, X.; Li, L.; Xie, H.; Velásquez, J.D. A Survey of Multimodal Information Fusion for Smart Healthcare: Mapping the Journey from Data to Wisdom. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.K.; Sundararajan, K.; Mathivanan, S.; Thandapani, B. Analysis of breast cancer classification and segmentation techniques: A comprehensive review. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2025, 56, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Population | Cancer patients |
| Intervention | AI-based fusion of genomics and imaging |
| Comparator | None (overview of methods) |
| Outcome | Accuracy, interpretability, clinical value |
| Study Design | Systematic reviews or meta-analyses |
| Search Component | Keywords Used |
|---|---|
| Study Type (Query 1) | “systematic review” OR “systematic literature review” OR “literature review” OR “meta-analysis” |
| Omics Data (Query 2) | “multiomics” OR “genomics” OR “transcriptomics” OR “epigenomics” OR “methylation” |
| Medical Imaging (Query 3) | “imaging” OR “medical imaging” OR “radiomics” OR “MRI” OR “Magnetic Resonance Imaging” OR “CT” OR “Computed Tomography” OR “CT Scan” OR “Computed Tomography Scan” OR “PET” OR “Positron Emission Tomography” OR “histopathology” |
| Disease Focus (Query 4) | “cancer” OR “oncology” |
| Integration Approach (Query 5) | “fusion” OR “integration” |
| Artificial Intelligence Techniques (Query 6) | “AI” OR “artificial intelligence” OR “ML” OR “machine learning” OR “DL” OR “deep learning” OR “transfer learning” |
| Combined Search (Query-7) | (Query 1) AND (Query 2) AND (Query 3) AND (Query 4) AND (Query 5) AND (Query 6) |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Systematic reviews or meta-analyses | Original research studies only |
| Reviews that discuss AI/ML-based fusion of omics and imaging data | Reviews that does not used AI/ML methods on omics and imaging data |
| Reviews focusing on only omics or only imaging modalities having possibilities of fused together | Reviews on omics and medical imaging modalities on specific topics where fusion is not possible |
| Studies involving human cancer datasets | Studies involving non-human models or non-cancer conditions |
| Database Name | Count (No. of Article Found) |
|---|---|
| Scopus | 60 |
| PubMed | 66 |
| Web of Science (WoS) | Query-1 & Query-2 = 4744 Query-1 & Query-3 = 49,545 Query-1 & Query-6 = 29,382 Query 7 (All) = 45 |
| Dimensions.ai | Query-7 (All) Publications = 72 Datasets = 1 Grants = 2 Patents = 0 Clinical Trials = 1 Policy Documents = 0 Letters = 2 Total = 78 |
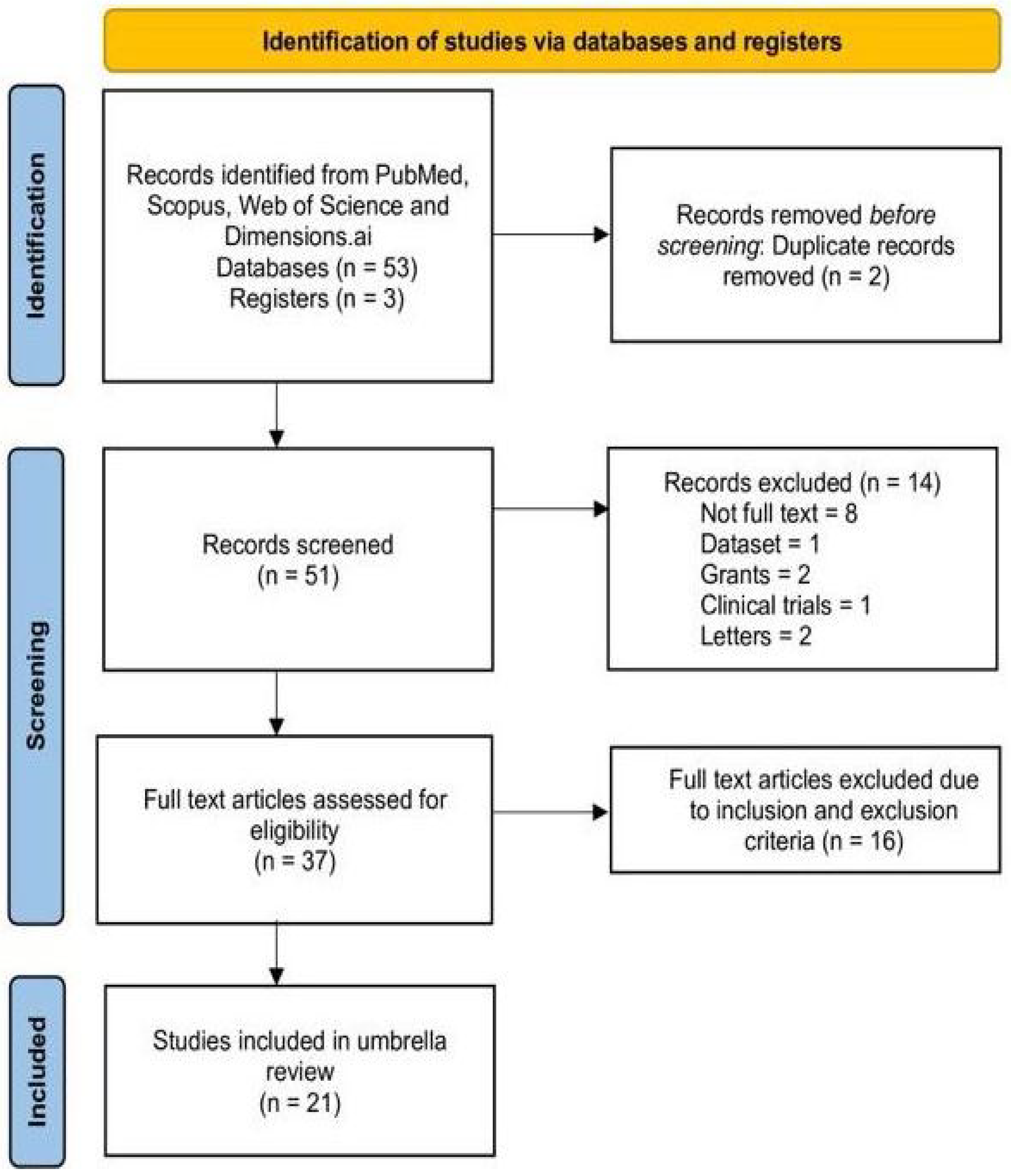
| After merging the databases and removing duplicates | 51 |
| Study ID | Author(s) | Title | DOI | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 [27] | Wang, Suixue; Wang, Shuling; Wang, Zhengxia | A survey on multi-omics-based cancer diagnosis using machine learning with the potential application in gastrointestinal cancer | 10.3389/fmed.2022.1109365 | 2023 |
| S2 [28] | Nicora, Giovanna; Vitali, Francesca; Dagliati, Arianna; Geifman, Nophar; Bellazzi, Riccardo | Integrated multi-omics analyses in oncology: a review of machine learning methods and tools | 10.3389/fonc.2020.01030 | 2020 |
| S3 [29] | Osuala, Richard; Kushibar, Kaisar; Garrucho, Lidia; Linardos, Akis; Szafranowska, Zuzanna; Klein, Stefan; Glocker, Ben; Diaz, Oliver; Lekadir, Karim | Data synthesis and adversarial networks: A review and meta-analysis in cancer imaging | 10.48550/arXiv.2107.09543 | 2023 |
| S4 [30] | Jennings, Charlotte; Broad, Andrew; Godson, Lucy; Clarke, Emily; Westhead, David; Treanor, Darren | Machine learning-based multimodal prognostic models integrating pathology images and high-throughput omic data for overall survival prediction in cancer: a systematic review | 10.48550/arXiv.2507.16876 | 2025 |
| S5 [31] | Wysocka, Magdalena; Wysocki, Oskar; Zufferey, Marie; Landers, Dónal; Freitas, André | A systematic review of biologically-informed deep learning models for cancer: fundamental trends for encoding and interpreting oncology data | 10.48550/arXiv.2207.00812 | 2023 |
| S6 [32] | Sartori, Flavio; Codicè, Francesco; Caranzano, Isabella; Rollo, Cesare; Birolo, Giovanni; Fariselli, Piero; Pancotti, Corrado | A Comprehensive Review of Deep Learning Applications with Multi-Omics Data in Cancer Research | 10.3390/genes16060648 | 2025 |
| S7 [33] | Han, Eonyong; Kwon, Hwijun; Jung, Inuk | A review on multi-omics integration for aiding study design of large scale TCGA cancer datasets | 10.1186/s12864-025-11925-y | 2025 |
| S8 [34] | Chakraborty, Sohini; Sharma, Gaurav; Karmakar, Sricheta; Banerjee, Satarupa | Multi-OMICS approaches in cancer biology: New era in cancer therapy | 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167120 | 2024 |
| S9 [35] | Chen, Chongyang; Wang, Jing; Pan, Donghui; Wang, Xinyu; Xu, Yuping; Yan, Junjie; Wang, Lizhen; Yang, Xifei; Yang, Min; Liu, Gong-Ping | Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases | 10.1002/mco2.315 | 2023 |
| S10 [36] | Akhoundova, Dilara; Rubin, Mark A. | Clinical application of advanced multi-omics tumor profiling: Shaping precision oncology of the future | 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.011 | 2022 |
| S11 [37] | Huang, Sijia; Chaudhary, Kumardeep; Garmire, Lana X. | More Is Better: Recent Progress in Multi-Omics Data Integration Methods | 10.3389/fgene.2017.00084 | 2017 |
| S12 [38] | Dong, Mengmeng; Wang, Liping; Hu, Ning; Rao, Yueli; Wang, Zhen; Zhang, Yu | Integration of multi-omics approaches in exploring intra-tumoral heterogeneity | 10.1186/s12935-025-03944-2 | 2025 |
| S13 [39] | Schneider, Lucas; Laiouar-Pedari, Sara; Kuntz, Sara; Krieghoff-Henning, Eva; Hekler, Achim; Kather, Jakob N.; Gaiser, Timo; Froehling, Stefan; Brinker, Titus J. | Integration of deep learning-based image analysis and genomic data in cancer pathology: A systematic review | 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.10.007 | 2022 |
| S14 [40] | Kirienko, Margarita; Gelardi, Fabrizia; Fiz, Francesco; Bauckneht, Matteo; Ninatti, Gaia; Pini, Cristiano; Briganti, Alberto; et al. | Personalised PET imaging in oncology: an umbrella review of meta-analyses to guide the appropriate radiopharmaceutical choice and indication | 10.1007/s00259-024-06882-9 | 2024 |
| S15 [41] | Prelaj, Arsela; Miskovic, V.; Zanitti, M.; Trovo, F.; Genova, C.; Viscardi, Giuseppe; Rebuzzi, S. E.; et al. | Artificial intelligence for predictive biomarker discovery in immuno-oncology: a systematic review | 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.125 | 2024 |
| S16 [42] | Maiorano, Mauro Francesco Pio; Cormio, Gennaro; Loizzi, Vera; Maiorano, Brigida Anna | Artificial Intelligence in Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Predictive AI Models in Genomics, Radiomics, and Immunotherapy | 10.3390/ai6040084 | 2025 |
| S17 [43] | Doykov, Mladen; Valkanov, Stanislav; Khalid, Usman; Gurung, Jasmin; Kostov, Gancho; Hristov, Bozhidar; Uchikov, Petar; et al. | Artificial Intelligence-Augmented Advancements in the Diagnostic Challenges Within Renal Cell Carcinoma | 10.3390/jcm14072272 | 2025 |
| S18 [44] | Ozaki, Yousaku; Broughton, Phil; Abdollahi, Hamed; Valafar, Homayoun; Blenda, Anna V. | Integrating Omics Data and AI for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis | 10.3390/cancers16132448 | 2024 |
| S19 [45] | Restini, Felipe Cicci Farinha; Torfeh, Tarraf; Aouadi, Souha; Hammoud, Rabih; Al-Hammadi, Noora; Starling, Maria Thereza Mansur; Sousa, Cecília Felix Penido Mendes; et al. | AI tool for predicting MGMT methylation in glioblastoma for clinical decision support in resource limited settings | 10.1038/s41598-024-78189-6 | 2024 |
| S20 [46] | Unger, Michaela; Kather, Jakob Nikolas | A systematic analysis of deep learning in genomics and histopathology for precision oncology | 10.1186/s12920-024-01796-9 | 2024 |
| S21 [47] | Mao, Lingchao; Wang, Hairong; Hu, Leland S.; Tran, Nhan L.; Canoll, Peter D.; Swanson, Kristin R.; Li, Jing | Knowledge-Informed Machine Learning for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Review | 10.1109/TASE.2024.3515839 | 2024 |
| ID | Cancer Types | Modalities (Omics + Imaging) | Fusion Type | AI Method | Tasks | Main Outcomes | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 [27] | Mixed | Multi-omics | Early | ML (integration) | Dx, Prognosis, Subtyping | Early proof of multi-omics value | Pre-DL era, shallow models |
| S2 [28] | Mixed oncology | Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Methylation | Early, Late, Hybrid | ML tools, pipelines | Prognosis, Biomarkers, Subtyping | Catalog of ML tools for oncology | Tool heterogeneity, limited validation |
| S3 [29] | Mixed cancers | CT, MRI, PET, WSI pathology (no omics) | Late | GANs, adversarial DL | Data synthesis, Detection | GANs boost imaging analysis | Publication bias, limited clinical use |
| S4 [30] | Mixed tumors | Multi-omics tumor profiling | Hybrid | Clinical ML pipelines | Precision oncology | Framework for clinical precision medicine | Costly, early-stage |
| S5 [31] | Mixed | Multi-omics (knowledge-informed encoding) | Hybrid | Biologically-informed DL | Dx, Prog. | Improves interpretability | High computational cost |
| S6 [32] | Mixed pathology | Genomics + Histopathology | Hybrid | DL (CNNs) + ML | Dx, Prognosis | Pathogenomics fusion improves accuracy | Reproducibility concerns |
| S7 [33] | Gastrointestinal + mixed | Genomics, Transcriptomics, Epigenomics | Early, Hybrid | ML, DL (survey) | Diagnosis, Subtyping | Multi-omics, single-omics for Dx | Retrospective data, preprocessing heterogeneity |
| S8 [34] | Mixed diseases | Multi-omics | Early | ML, DL | Disease analysis (Dx, Prog.) | Disease-specific multi-omics patterns | Not cancer-only |
| S9 [35] | Immuno-oncology | Genomics, Transcriptomics (+ some radiomics) | Hybrid | AI biomarker pipelines | Biomarker discovery | Predictive IO biomarkers found | Risk of bias, endpoint variation |
| S10 [36] | Mixed (PET) | PET radiomics (umbrella review) | Late | Radiomics + ML | Dx, Staging, Response | PET guides radiotracer choice | PET-only, heterogeneous studies |
| S11 [37] | Ovarian cancer | Genomics, Radiomics, CT/MRI, Immunotherapy | Hybrid | ML, DL | Dx, Prognosis, Tx response | Strong performance across modalities | Heterogeneous, small cohorts |
| S12 [38] | RCC | Genomics + CT/MRI | Hybrid | AI, ML | Diagnosis, Risk stratification | AI augments RCC workflows | Limited external validation |
| S13 [39] | Mixed oncology | Multi-omics + Radiomics/Pathomics | Hybrid | AI, ML | Dx, Prognosis | Fusion > single-modality | Lack of prospective studies |
| S14 [40] | Glioblastoma | Epigenomics (MGMT methylation) + MRI | Hybrid | ML, DL | Biomarker prediction (MGMT) | Accurate non-invasive MGMT prediction | Bias risks identified |
| S15 [41] | Mixed | Multi-omics + Clinical + Radiology/Pathology | Hybrid | Knowledge-informed ML | Dx, Prognosis | Improves interpretability | Limited benchmarks |
| S16 [42] | Mixed | Multi-omics (therapy focus) | Hybrid | ML methods | Therapy stratification | Personalized therapy potential | Harmonization challenges |
| S17 [43] | Mixed | Histopathology WSI + Omics | Hybrid | ML, DL survival models | Survival prediction | Fusion > unimodal for OS | Preprint, small external validation |
| S18 [44] | Mixed | Large-scale multi-omics | Early, Hybrid | Deep learning | Classification, Prognosis | Effective across TCGA | No prospective validation |
| S19 [45] | Mixed | Multi-omics (TCGA datasets) | Hybrid | ML + statistical frameworks | Study design, integration | Provides framework guidance | Not validated clinically |
| S20 [46] | Mixed | Genomics + Transcriptomics (ITH) | Hybrid | ML integration | Heterogeneity analysis | Fusion captures ITH patterns | Small datasets |
| S21 [47] | Mixed | Histopathology + Omics | Hybrid | ML, DL | Survival analysis | Multimodal survival | No benchmarks |
| ID | Protocol Registered | Search Adequacy | Exclusions Justified | RoB of Included | Meta-Analytic Methods | Publication Bias | Critical Domains Met (0–7) | Overall Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S2 | N | Y | N | N | NA | NA | 1 | Critically low |
| S3 | NR | Y | PN | Y | NA | NA | 3 | Low |
| S4 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S5 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S6 | NR | Y | PN | Y | NA | NA | 3 | Low |
| S7 | N | Y | N | N | NA | NA | 1 | Critically low |
| S8 | NR | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S9 | NR | Y | PN | PN | NA | NA | 2 | Low |
| S10 | NR | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 | Moderate |
| S11 | NR | Y | PN | Y | NA | NA | 3 | Low |
| S12 | N | N | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S13 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S14 | N | PN | N | N | PN | PN | 1 | Critically low |
| S15 | NR | Y | PN | PN | Y | Y | 4 | Low |
| S16 | N | Y | PN | PN | NA | NA | 2 | Low |
| S17 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S18 | N | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S19 | NR | PN | N | N | NA | NA | 0 | Critically low |
| S20 | N | PN | N | N | PN | PN | 1 | Critically low |
| S21 | NR | Y | PN | Y | NA | NA | 3 | Low |
| Dataset | Data Modalities | Cancer/Population Coverage | Typical Use (Research Scope) | Access Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) [50] | Genomics, Transcriptomics, Epigenomics, Clinical data | 33+ tumor types (11,000+ patients) | Biomarker discovery, Survival analysis, Multi-omics fusion | Open (controlled data for germline variants) |
| TCIA (The Cancer Imaging Archive) [51] | CT, MRI, PET, Histopathology (WSI) | Linked cohorts to TCGA; multiple disease-specific collections | Radiomics, image-based deep learning, segmentation, multimodal studies with TCGA | Open access (after registration) |
| CPTAC (Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium) [52] | Proteomics + genomics + transcriptomics + imaging for specific cancers | Breast, colon, ovarian, endometrial, lung, etc. | Proteogenomics; linking omics with imaging and clinical outcomes | Open (some controlled-access biospecimen data) |
| UK Biobank [53] | MRI, CT, whole-body imaging, genomics, lifestyle/clinical phenotypes | Population-scale cohort (500,000+ participants) | Imaging-genomics association, early disease detection, longitudinal studies | Approved application required |
| SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) [54] | Clinical + demographic survival registry | US cancer registry covering >47% of population | Population-level outcomes, epidemiology, survival modeling | Open (controlled limited datasets) |
| Multi-Institutional Radiomics Repositories (e.g., RIDER, LIDC-IDRI, NSCLC-Radiomics, ACRIN) [55] | CT, PET/CT, radiology images with segmentation labels | Lung cancer, NSCLC, COPD, etc. | Radiomics feature extraction, segmentation benchmarking, multimodal validation | Open access |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marouf, A.A.; Rokne, J.G.; Alhajj, R. Integrating Multi-Omics and Medical Imaging in Artificial Intelligence-Based Cancer Research: An Umbrella Review of Fusion Strategies and Applications. Cancers 2025, 17, 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223638
Marouf AA, Rokne JG, Alhajj R. Integrating Multi-Omics and Medical Imaging in Artificial Intelligence-Based Cancer Research: An Umbrella Review of Fusion Strategies and Applications. Cancers. 2025; 17(22):3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223638
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarouf, Ahmed Al, Jon George Rokne, and Reda Alhajj. 2025. "Integrating Multi-Omics and Medical Imaging in Artificial Intelligence-Based Cancer Research: An Umbrella Review of Fusion Strategies and Applications" Cancers 17, no. 22: 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223638
APA StyleMarouf, A. A., Rokne, J. G., & Alhajj, R. (2025). Integrating Multi-Omics and Medical Imaging in Artificial Intelligence-Based Cancer Research: An Umbrella Review of Fusion Strategies and Applications. Cancers, 17(22), 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223638







