Surgical Treatment of Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Current and Emerging Strategies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Medical Management of Tumor-Related Epilepsy: An Overview
3. Surgical Approaches for Tumor-Related Epilepsy: An Overview
4. Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Overview by Tumor Type
4.1. Long-Term Epilepsy-Associated Tumors
4.2. Infiltrating Gliomas
4.2.1. Low-Grade Infiltrating Gliomas
4.2.2. High-Grade Infiltrating Gliomas
4.3. Meningiomas
4.4. Cerebral Metastases
5. Seizure Outcome Classification
6. Surgical Resection and Seizure Outcomes
6.1. Surgery for Long-Term Epilepsy Associated Tumors
6.2. Surgery for Infiltrating Gliomas
6.2.1. Resection for Low-Grade Infiltrating Gliomas
6.2.2. Resection for High-Grade Infiltrating Gliomas
6.3. Surgery for Meningiomas
6.4. Surgery for Cerebral Metastases
7. Timing of Surgery
8. Seizure Control with Extended Lesionectomies
9. Adjunct Techniques
9.1. Electrocorticography-Guided Resective Surgery
9.2. Awake Mapping
10. Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT)
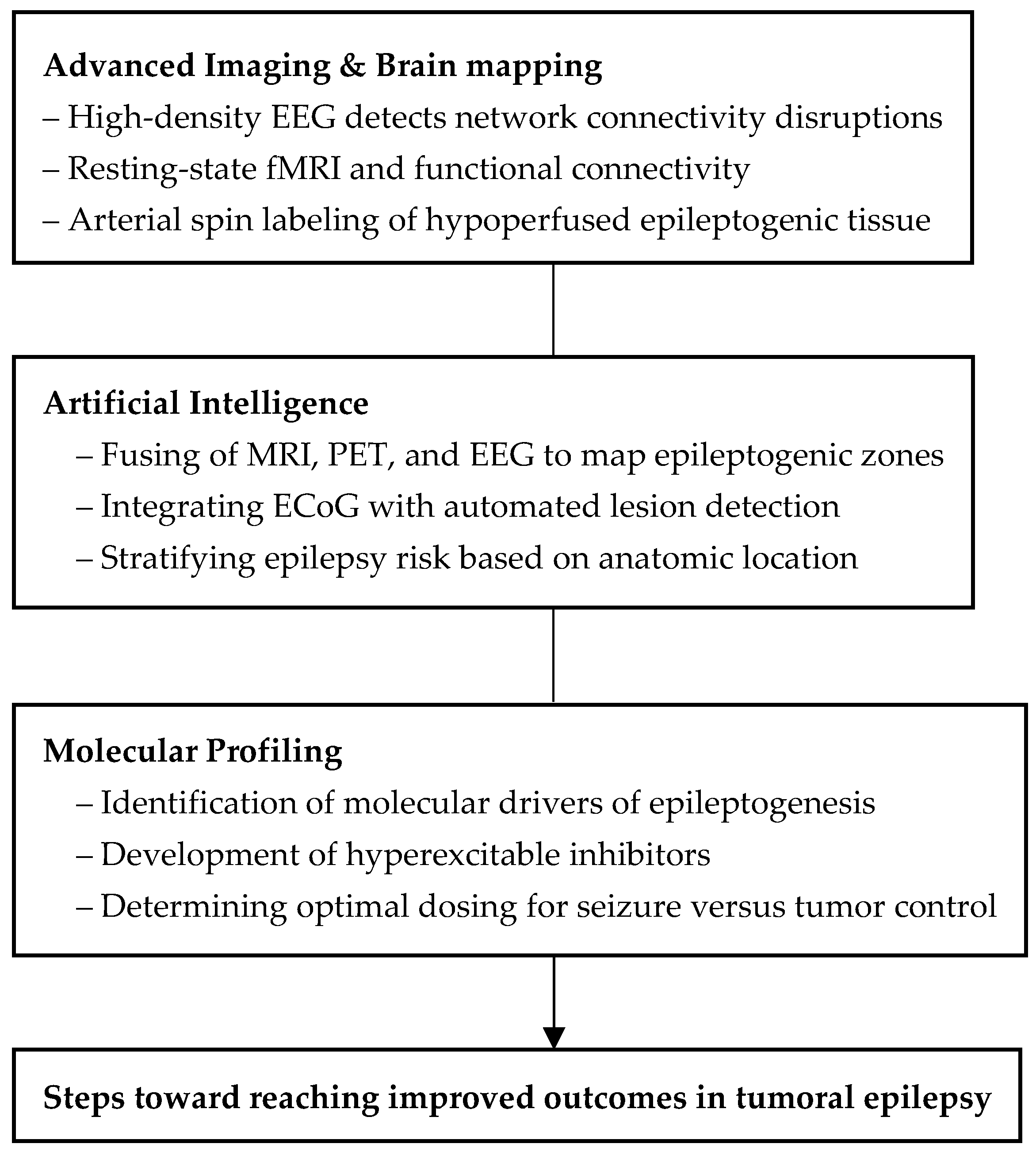
11. Developing Technologies
11.1. Augmenting Surgical Planning via Artificial Intelligence
11.2. Emerging Brain Mapping Techniques
11.3. Molecular Profiling in Predicting Epileptogenicity
12. Clinical Trials
12.1. Low- and High-Grade Gliomas
12.2. Meningioma
13. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ASM | Antiseizure Medication |
| ATL | Anterior Temporal Lobectomy |
| BTRE | Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DNET | Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor |
| DRE | Drug-Resistant Epilepsy |
| ECoG | Electrocorticography |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EOR | Extent of Resection |
| FCD | Focal Cortical Dysplasia |
| GNT | Glioneuronal Tumor |
| GTR | Gross Total Resection |
| HGG | High-Grade Glioma |
| IDHmut | IDH-Mutant |
| LEAT | Low-Grade Epilepsy-Associated Tumor |
| LGG | Low-Grade Glioma |
| LITT | Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy |
| MEG | Magnetoencephalography |
| nTMS | Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PRTE | Post-Radiation Treatment Effect |
| RANO | Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology |
| SMR | Supramaximal Resection |
| SRS | Stereotactic Radiosurgery |
| STR | Subtotal Resection |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Audrey, C.; Lim, K.S.; Ahmad Zaki, R.; Fong, S.L.; Chan, C.Y.; Sathis Kumar, T.; Narayanan, V.; Tan, C.T. Prevalence of seizures in brain tumor: A meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 187, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.F.; Christie, C.; Sullivan, J.E.; Garcia, P.A.; Tihan, T.; Gupta, N.; Berger, M.S.; Barbaro, N.M. Seizure control outcomes after resection of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor in 50 patients: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2010, 5, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, A.; Diosy, D. Seizures in children with dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors of the brain—A review of surgical outcomes across several studies. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2015, 31, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.R.; Clusmann, H.; von Lehe, M.; Niehusmann, P.; Becker, A.J.; Schramm, J.; Urbach, H. Simple and complex dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNT) variants: Clinical profile, MRI, and histopathology. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhof, M.; Vecht, C.J. Seizure characteristics and prognostic factors of gliomas. Epilepsia 2013, 54 (Suppl. 9), 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyken, C.; Blümcke, I.; Fimmers, R.; Urbach, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Schramm, J. Supratentorial gangliogliomas: Histopathologic grading and tumor recurrence in 184 patients with a median follow-up of 8 years. Cancer 2004, 101, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwell, D.G.; Garcia, P.A.; Berger, M.S.; Barbaro, N.M.; Chang, E.F. Long-term seizure control outcomes after resection of gangliogliomas. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.R.; Clusmann, H.; von Lehe, M.; Niehusmann, P.; Becker, A.J.; Schramm, J.; Urbach, H. The clinicopathological features of ganglioglioma with CD34 expression and BRAF mutation in patients with epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1022364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Si, Y.; Lei, D. Factors associated with preoperative and postoperative epileptic seizure in patients with cerebral ganglioglioma. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Audureau, E.; Blonski, M.; Sanai, N.; Bauchet, L.; Fontaine, D.; Mandonnet, E.; Dezamis, E.; Psimaras, D.; Guyotat, J.; et al. Epileptic seizures in diffuse low-grade gliomas in adults. Brain 2014, 137 Pt 2, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Sha, Z.Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, S.W.; Sang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.L.; Li, S.W.; et al. Seizure characteristics and outcomes in 508 Chinese adult patients undergoing primary resection of low-grade gliomas: A clinicopathological study. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandoliya, K.R.; Thirunavu, V.; Ellis, E.; Dixit, K.; Tate, M.C.; Drumm, M.R.; Templer, J.W. Pre-operative predictors of post-operative seizure control in low-grade glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2024, 47, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bech, K.T.; Seyedi, J.F.; Schulz, M.; Poulsen, F.R.; Pedersen, C.B. The risk of developing seizures before and after primary brain surgery of low- and high-grade gliomas. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 169, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Hameed, N.U.F.; Qiu, T.; Zhuang, D.; Lu, J.; Wu, J. The Analysis of Risk Factors and Survival Outcome for Chinese Patients with Epilepsy with High-Grade Glioma. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, e947–e957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichana, K.L.; Parker, S.L.; Olivi, A.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. Long-term seizure outcomes in adult patients undergoing primary resection of malignant brain astrocytomas: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englot, D.J.; Magill, S.T.; Han, S.J.; Chang, E.F.; Berger, M.S.; McDermott, M.W. Seizures in supratentorial meningioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Magill, S.T.; Englot, D.J.; Baal, J.D.; Wagle, S.; Rick, J.W.; McDermott, M.W. Factors Associated with Pre- and Postoperative Seizures in 1033 Patients Undergoing Supratentorial Meningioma Resection. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazou, A.; Yassin, A.; Aljabali, A.S.; Al-Zamer, Y.S.; Alawajneh, M.; Al-Akhras, A.; AlBarakat, M.M.; Tashtoush, S.; Shammout, O.; Al-Horani, S.S.; et al. Predictors of early and late postoperative seizures in meningioma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2024, 47, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.H.; Morshed, R.A.; Chung, J.; Millares Chavez, M.A.; Sudhakar, V.; Saggi, S.; Avalos, L.N.; Gallagher, A.; Young, J.S.; Daras, M.; et al. Factors associated with preoperative and postoperative seizures in patients undergoing resection of brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, N.; Catalano, P.J.; Cagney, D.N.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Bubrick, E.J.; Wen, P.Y.; Aizer, A.A. Seizures Among Patients with Brain Metastases: A Population- and Institutional-level Analysis. Neurology 2021, 96, e1237–e1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberink, H.J.; Otte, W.M.; Blümcke, I.; Braun, K.P.J. Seizure outcome and use of antiepileptic drugs after epilepsy surgery according to histopathological diagnosis: A retrospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ling, M.; Fan, X. IDH1 mutation is associated with a higher preoperative seizure incidence in low-grade glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Seizure 2018, 55, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marku, M.; Rasmussen, B.K.; Belmonte, F.; Andersen, E.A.W.; Johansen, C.; Bidstrup, P.E. Postoperative epilepsy and survival in glioma patients: A nationwide population-based cohort study from 2009 to 2018. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 157, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Ambrogi, F.; Gay, L.; Gallucci, M.; Nibali, M.C.; Leonetti, A.; Puglisi, G.; Sciortino, T.; Howells, H.; Riva, M.; et al. Is supratotal resection achievable in low-grade gliomas? Feasibility, putative factors, safety, and functional outcome. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Ambrogi, F.; Gay, L.; Gallucci, M.; Conti Nibali, M.; Leonetti, A.; Puglisi, G.; Sciortino, T.; Howells, H.; Riva, M.; et al. Electrocorticography-Guided Resection Enhances Postoperative Seizure Freedom in Low-Grade Tumor-Associated Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2023, 92, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.S.; Zheng, S.F.; Wang, F.; Kang, D.Z.; Lin, Y.X. Surgery guided with intraoperative electrocorticography in patients with low-grade glioma and refractory seizures. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 128, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.M.; Drumm, M.R.; Rai, S.; Huang, J.; Tate, M.C.; Magill, S.T.; Templer, J.W. Patterns of Antiseizure Medication Use Following Meningioma Resection: A Single-Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, e392–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaios, E.J.; Maingi, S.; Batich, K.; Winter, S.F.; Dietrich, J.; Mullikin, T.; Floyd, S.R.; Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Reitman, Z.J.; Peters, K.B. Seizure risk factors and management approaches in patients with brain metastases. Neurooncol Pract. 2025, 12, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.R.; Johannsson, B.; Seyedi, J.F.; Halle, B.; Schulz, M.; Pedersen, C.B.; Kristensen, B.W.; Poulsen, F.R. The risk of developing seizures before and after surgery for brain metastases. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 193, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achrol, A.S.; Rennert, R.C.; Anders, C.; Soffietti, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Nayak, L.; Peters, S.; Arvold, N.D.; Harsh, G.R.; Steeg, P.S.; et al. Brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, F.; Lareida, A.; Terziev, R.; Grossenbacher, B.; Neidert, M.C.; Roth, P.; Poryazova, R.; Imbach, L.L.; Le Rhun, E.; Weller, M. Risk factors for the development of epilepsy in patients with brain metastases. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walbert, T.; Harrison, R.A.; Schiff, D.; Avila, E.K.; Chen, M.; Kandula, P.; Lee, J.W.; Le Rhun, E.; Stevens, G.H.J.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. SNO and EANO practice guideline update: Anticonvulsant prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, E.K.; Tobochnik, S.; Inati, S.K.; Koekkoek, J.A.F.; McKhann, G.M.; Riviello, J.J.; Rudà, R.; Schiff, D.; Tatum, W.O.; Templer, J.W.; et al. Brain tumor-related epilepsy management: A Society for Neuro-oncology (SNO) consensus review on current management. Neuro Oncol. 2024, 26, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.S.; Trinh, V.T.; Suki, D.; Graham, S.; Forman, A.; Weinberg, J.S.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Prabhu, S.S.; Heimberger, A.B.; Sawaya, R.; et al. A prospective randomized trial of perioperative seizure prophylaxis in patients with intraparenchymal brain tumors: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.B.; Templer, J.; Gerstner, E.R.; Wychowski, T.; Storstein, A.M.; Dixit, K.; Walbert, T.; Melnick, K.; Hrachova, M.; Partap, S.; et al. Discontinuation of Antiseizure Medications in Patients with Brain Tumors. Neurology 2024, 102, e209163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englot, D.J.; Berger, M.S.; Barbaro, N.M.; Chang, E.F. Factors associated with seizure freedom in the surgical resection of glioneuronal tumors. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonney, P.A.; Glenn, C.A.; Ebeling, P.A.; Conner, A.K.; Boettcher, L.B.; Cameron, D.M.; Battiste, J.D.; Sughrue, M.E. Seizure Freedom Rates and Prognostic Indicators After Resection of Gangliogliomas: A Review. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Nath, S.; Koziarz, A.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Ghayur, H.; Sourour, M.; Catana, D.; Nassiri, F.; Alotaibi, M.B.; Kameda-Smith, M.; et al. Biopsy Versus Subtotal Versus Gross Total Resection in Patients with Low-Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e762–e775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englot, D.J.; Berger, M.S.; Barbaro, N.M.; Chang, E.F. Predictors of seizure freedom after resection of supratentorial low-grade gliomas: A review. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.F.; Potts, M.B.; Keles, G.E.; Lamborn, K.R.; Chang, S.M.; Barbaro, N.M.; Berger, M.S. Seizure characteristics and control following resection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ius, T.; Pauletto, G.; Tomasino, B.; Maieron, M.; Budai, R.; Isola, M.; Cesselli, D.; Lettieri, C.; Skrap, M. Predictors of Postoperative Seizure Outcome in Low Grade Glioma: From Volumetric Analysis to Molecular Stratification. Cancers 2020, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, A.; Morokoff, A.; O’Brien, T.J.; Kwan, P. Postoperative seizure control in patients with tumor-associated epilepsy. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilinger, R.G.; Guo, L.; Sharma, A.; Volovetz, J.; Thompson, N.R.; Grabowski, M.; Lobbous, M.; Dhawan, A. Tumor-related epilepsy in high-grade glioma: A large series survival analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2024, 170, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritzelberger, J.; Gesmann, A.; Fuhrmann, I.; Brandner, S.; Welte, T.M.; Balk, S.; Eisenhut, F.; Dörfler, A.; Coras, R.; Adler, W.; et al. Time-dependent risk factors for epileptic seizures in glioblastoma patients: A retrospective analysis of 520 cases. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Glioma-related epilepsy in patients with diffuse high-grade glioma after the 2016 WHO update: Seizure characteristics, risk factors, and clinical outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 136, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drumm, M.R.; Wang, W.; Sears, T.K.; Bell-Burdett, K.; Javier, R.; Cotton, K.Y.; Webb, B.; Byrne, K.; Unruh, D.; Thirunavu, V.; et al. Postoperative risk of IDH-mutant glioma-associated seizures and their potential management with IDH-mutant inhibitors. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadot, R.; Khan, A.B.; Patel, R.; Goethe, E.; Shetty, A.; Hadley, C.C.; Bayley, J.C.; Harmanci, A.S.; Klisch, T.J.; Yoshor, D.; et al. Predictors of postoperative seizure outcome in supratentorial meningioma. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 137, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.M.; Wahood, W.; Akinduro, O.O.; Parney, I.F.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Chaichana, K.L. Four Independent Predictors of Postoperative Seizures After Meningioma Surgery: A Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 537–545.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepens, J.C.C.; van der Meer, P.B.; Dirven, L.; Vos, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Koekkoek, J.A.F. Seizure outcomes in patients with brain metastases and epilepsy: A systematic review on the efficacy of antitumor treatment and antiseizure medication. Neurooncol. Pract. 2024, 12, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easwaran, T.; Lion, A.; Vortmeyer, A.; Kingery, K.; Bc, M.D.; Raskin, J. Seizure freedom from recurrent insular low-grade glioma following laser interstitial thermal therapy. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.H.; Rasmussen, R. MR-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy in the treatment of brain tumors and epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogos, A.J.; Young, J.S.; Morshed, R.A.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Berger, M.S. Awake glioma surgery: Technical evolution and nuances. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englot, D.J.; Han, S.J.; Berger, M.S.; Barbaro, N.M.; Chang, E.F. Extent of surgical resection predicts seizure freedom in low-grade temporal lobe brain tumors. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, M.; Blümcke, I.; Aronica, E. Long-term epilepsy-associated tumors. Brain Pathol. 2012, 22, 350–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumcke, I.; Spreafico, R.; Haaker, G.; Coras, R.; Kobow, K.; Bien, C.G.; Pfäfflin, M.; Elger, C.; Widman, G.; Schramm, J.; et al. Histopathological Findings in Brain Tissue Obtained during Epilepsy Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, R.W.; Torok, M.R.; Gallegos, D.R.; Mulcahy-Levy, J.M.; Hoffman, L.M.; Liu, A.K.; Handler, M.H.; Hankinson, T.C. Pediatric Low Grade Ganglioglioma/Gangliocytoma: Epidemiology, treatments, and outcome analysis on 348 children from the SEER database. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.S.; Doan, N.; Gelsomino, M.; Shabani, S. Dysembryoplastic Neuroectodermal Tumor: An Analysis from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, 2004-2013. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Engelberts, N.H.; van der Ploeg, H.M.; Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité, D.G.; Aaronson, N.K.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Baaijen, H.; Vandertop, W.P.; Muller, M.; Postma, T.J.; et al. Epilepsy in low-grade gliomas: The impact on cognitive function and quality of life. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Wen, P.Y.; Hurwitz, S.; Black, P.; Kesari, S.; Drappatz, J.; Golby, A.J.; Wells, W.M., 3rd; Warfield, S.K.; Kikinis, R.; et al. Morphological characteristics of brain tumors causing seizures. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.M.; Drumm, M.R.; Rai, S.M.; Huang, J.; Tate, M.C.; Magill, S.T.; Templer, J.W. Long-term antiseizure medication use in patients after meningioma resection: Identifying predictors for successful weaning and failures. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 165, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, A.; Jalal, M.I.; Gupte, T.P.; Vetsa, S.; Vasandani, S.; Yalcin, K.; Marianayagam, N.; Blondin, N.; Corbin, Z.; McGuone, D.; et al. The clinical and genomic features of seizures in meningiomas. Neurooncol. Adv. 2023, 5 (Suppl. 1), i49–i57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs, F.L.; Brokinkel, C.; Adeli, A.; Sporns, P.B.; Hess, K.; Paulus, W.; Stummer, W.; Grauer, O.; Spille, D.C.; Brokinkel, B. Risk factors for preoperative seizures in intracranial meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2023, 67, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastall, M.; Wolpert, F.; Gramatzki, D.; Imbach, L.; Becker, D.; Schmick, A.; Hertler, C.; Roth, P.; Weller, M.; Wirsching, H.G. Survival of brain tumour patients with epilepsy. Brain 2021, 144, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Varlet, P.; Devaux, B.; Geha, S.; Badoual, M.; Deroulers, C.; Page, P.; Dezamis, E.; Daumas-Duport, C.; Roux, F.X. Diffuse low-grade oligodendrogliomas extend beyond MRI-defined abnormalities. Neurology 2010, 74, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. Imaging prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation in patients with glioma: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, Y.N.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Duffau, H. Awake surgery for WHO Grade II gliomas within “noneloquent” areas in the left dominant hemisphere: Toward a “supratotal” resection. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karschnia, P.; Young, J.S.; Dono, A.; Häni, L.; Sciortino, T.; Bruno, F.; Juenger, S.T.; Teske, N.; Morshed, R.A.; Haddad, A.F.; et al. Prognostic validation of a new classification system for extent of resection in glioblastoma: A report of the RANO resect group. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, B.F.; Dixit, K.; Kamson, D.O.; Horbinski, C.; Przybyla, D.J.; Tate, M.C.; Heimberger, A.B.; Lukas, R.V.; Templer, J.W. The excitatory milieu in glioma: Mechanisms and therapeutic avenues. Neuro Oncol. 2025, 27, 1932–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreatsoulas, D.; Damante, M.; Gruber, M.; Duru, O.; Elder, J.B. Supratotal Surgical Resection for Low-Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.; Choi, J.; Khalafallah, A.M.; Price, C.; Bettegowda, C.; Lim, M.; Gallia, G.; Weingart, J.; Brem, H.; Mukherjee, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of supratotal versus gross total resection for glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. Long-term outcomes after supratotal resection of diffuse low-grade gliomas: A consecutive series with 11-year follow-up. Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Still, M.E.H.; Roux, A.; Huberfeld, G.; Bauchet, L.; Baron, M.H.; Fontaine, D.; Blonski, M.; Mandonnet, E.; Guillevin, R.; Guyotat, J.; et al. Extent of Resection and Residual Tumor Thresholds for Postoperative Total Seizure Freedom in Epileptic Adult Patients Harboring a Supratentorial Diffuse Low-Grade Glioma. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, E332–E339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borger, V.; Hamed, M.; Ilic, I.; Potthoff, A.-L.; Racz, A.; Schäfer, N.; Güresir, E.; Surges, R.; Herrlinger, U.; Vatter, H.; et al. Seizure outcome in temporal glioblastoma surgery: Lobectomy as a supratotal resection regime outclasses conventional gross-total resection. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 152, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, V.; Hamed, M.; Ilic, I.; Potthoff, A.L.; Racz, A.; Schäfer, N.; Güresir, E.; Surges, R.; Herrlinger, U.; Vatter, H.; et al. Seizure Outcome After Surgery for Insular High-Grade Glioma. World Neurosurg. 2021, 154, e718–e723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, M.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z. Risk factors and control of seizures in 778 Chinese patients undergoing initial resection of supratentorial meningiomas. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirsching, H.G.; Morel, C.; Gmür, C.; Neidert, M.C.; Baumann, C.R.; Valavanis, A.; Rushing, E.J.; Krayenbühl, N.; Weller, M. Predicting outcome of epilepsy after meningioma resection. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Helmy, A.; Huckey, H.; Mills, S.; Grant, R.; Hughes, D.; Marson, T.; Tangney, R.; Bulbeck, H.; Ali, U.; et al. RTID-10. Surgeons Trial of Prophylaxis for Epilepsy in Seizure Naïve Patients with Meningioma: A Randomized Controlled Trial (STOP ‘EM). Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22 (Suppl. 2), ii195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatiboglu, M.A.; Wildrick, D.M.; Sawaya, R. The role of surgical resection in patients with brain metastases. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufenkjian, K.; Lüders, H.O. Seizure Semiology: Its Value and Limitations in Localizing the Epileptogenic Zone. J. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Weingart, J.D.; Gallia, G.L.; Lim, M.; Brem, H.; Bettegowda, C.; Chaichana, K.L. Risk Factors for Preoperative Seizures and Loss of Seizure Control in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiacono, G.; Cirillo, C.; Chiarelli, F.; Verrotti, A. Focal Epilepsy Associated with Glioneuronal Tumors. ISRN Neurol. 2011, 2011, 867503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.; Bansal, S.; Chandra, P.S.; Suri, A.; Tripathi, M.; Sharma, M.C.; Sarkari, A.; Mahapatra, A.K. Ganglioglioma: Single-institutional experience of 24 cases with review of literature. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2016, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, S.; Morioka, T.; Mihara, F.; Gondo, K.; Fukui, M. Cerebral ganglioglioma with epilepsy: Neuroimaging features and treatment. Neurosurg. Rev. 2001, 24, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brainer-Lima, P.T.; Brainer-Lima, A.M.; Azevedo-Filho, H.R. Ganglioglioma: Comparison with other low-grade brain tumors. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2006, 64, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lee, B.L.; Joo, E.Y.; Seo, D.W.; Hong, S.B.; Hong, S.C.; Suh, Y.L.; Lee, M. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors in pediatric patients. Brain Dev. 2009, 31, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, D.I.; Ragheb, J.; Dunoyer, C.; Bhatia, S.; Olavarria, G.; Morrison, G. Surgical outcomes and seizure control rates after resection of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. Neurosurg. Focus 2005, 18, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, K.J.; Chae, J.H.; Lim, B.C.; Wang, K.C.; Park, S.H.; Phi, J.H. Satellite lesions of DNET: Implications for seizure and tumor control after resection. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 143, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baticulon, R.E.; Wittayanakorn, N.; Maixner, W. Low-grade glioma of the temporal lobe and tumor-related epilepsy in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2024, 40, 3085–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Pek, V.; Shlobin, N.A.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, A.; Ibrahim, G.M.; Hadjinicolaou, A.; Roessler, K.; Dudley, R.W.; Nguyen, D.K.; et al. Clinical utility of intraoperative electrocorticography for epilepsy surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, C.; Ius, T.; Verriello, L.; Budai, R.; Isola, M.; Valente, M.; Skrap, M.; Gigli, G.L.; Pauletto, G. Risk Factors for Intraoperative Seizures in Glioma Surgery: Electrocorticography Matters. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 40, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, B. Surgical treatment of long-term epilepsy-associated tumors guided by stereoelectroencephalography. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Zwarthoed, R.H.; Kilgallon, J.L.; Nawabi, N.L.; Jessurun, C.A.C.; Versyck, G.; Pruijn, K.P.; Fisher, F.L.; Larivière, E.; Solie, L.; et al. Effect of awake craniotomy in glioblastoma in eloquent areas (GLIOMAP): A propensity score-matched analysis of an international, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, J.; Manninen, P.; Valiante, T.; Venkatraghavan, L. The anesthetic considerations of intraoperative electrocorticography during epilepsy surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, S.A.; Rincon-Torroella, J.; Sattari, A.R.; Feghali, J.; Yang, W.; Kim, J.E.; Xu, R.; Jackson, C.M.; Mukherjee, D.; Lin, S.C.; et al. Awake Versus Asleep Craniotomy for Patients with Eloquent Glioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2024, 94, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, S.C.; Behrens, M.; Lortz, I.; Conradi, N.; Rauch, M.; Filipski, K.; Voss, M.; Kell, C.; Czabanka, M.; Forster, M.T. Neurocognitive Outcome and Seizure Freedom After Awake Surgery of Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 815733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youshani, A.S.; Heal, C.; Lee, J.X.; Younis, M.; Mohanraj, R.; Maye, H.; Bailey, M.; Coope, D.; D’Urso, P.I.; Karabatsou, K. Glioma-related epilepsy following low-grade glioma surgery. Neurooncol. Adv. 2024, 6, vdae127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Schwalb, J.M.; Rosenow, J.M.; McKhann, G.M.; Neimat, J.S. The American Society for Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery Position Statement on Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy for the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Neurosurgery 2022, 90, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedaya, A.A.; Hewitt, K.C.; Hu, R.; Epstein, C.M.; Gross, R.E.; Drane, D.L.; Willie, J.T. Open surgery or laser interstitial thermal therapy for low-grade epilepsy-associated tumors of the temporal lobe: A single-institution consecutive series. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 130, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Shao, X.; Sang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K. Magnetic resonance-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy vs. open surgery for drug-resistant mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: A propensity score matched retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkazemi, M.; Lo, Y.T.; Hussein, H.; Mammi, M.; Saleh, S.; Araujo-Lama, L.; Mommsen, S.; Pisano, A.; Lamba, N.; Bunevicius, A.; et al. Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy for the Treatment of Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023, 171, e654–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayan, M.; Mustafayev, T.Z.; Balmuk, A.; Mamidanna, S.; Kefelioglu, E.S.S.; Gungor, G.; Chundury, A.; Ohri, N.; Karaarslan, E.; Ozyar, E.; et al. Management of symptomatic radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery and clinical factors for treatment response. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2020, 38, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayan, M.; Mustafayev, T.Z.; Balmuk, A.; Mamidanna, S.; Kefelioglu, E.S.S.; Gungor, G.; Chundury, A.; Ohri, N.; Karaarslan, E.; Ozyar, E.; et al. Time to Steroid Independence After Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy vs Medical Management for Treatment of Biopsy-Proven Radiation Necrosis Secondary to Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis. Neurosurgery 2022, 90, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Revell, A.; Davis, K.A. Artificial intelligence in epilepsy—Applications and pathways to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeret, K.; Stumpo, V.; Staartjes, V.E.; Vasella, F.; Velz, J.; Marinoni, F.; Dufour, J.P.; Imbach, L.L.; Regli, L.; Serra, C.; et al. Topographic brain tumor anatomy drives seizure risk and enables machine learning based prediction. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 28, 102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walger, L.; Adler, S.; Wagstyl, K.; Henschel, L.; David, B.; Borger, V.; Hattingen, E.; Vatter, H.; Elger, C.E.; Baldeweg, T.; et al. Artificial intelligence for the detection of focal cortical dysplasia: Challenges in translating algorithms into clinical practice. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1093–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareček, R.; Říha, P.; Bartoňová, M.; Kojan, M.; Lamoš, M.; Gajdoš, M.; Vojtíšek, L.; Mikl, M.; Bartoň, M.; Doležalová, I.; et al. Automated fusion of multimodal imaging data for identifying epileptogenic lesions in patients with inconclusive magnetic resonance imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; You, G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Jiang, T.; Qiao, H. High-Density Electroencephalography Detects Spatiotemporal Abnormalities in Brain Networks in Patients with Glioma-Related Epilepsy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.A.; Lee, J.; Liu, H.L.; Allen, J.W.; Filippi, C.G.; Holodny, A.I.; Hsu, K.; Jain, R.; McAndrews, M.P.; Peck, K.K.; et al. Recommended Resting-State fMRI Acquisition and Preprocessing Steps for Preoperative Mapping of Language and Motor and Visual Areas in Adult and Pediatric Patients with Brain Tumors and Epilepsy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024, 45, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Chi, C.; Che, W.; Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, J.; et al. Lower-grade gliomas surgery guided by GRPR-targeting PET/NIR dual-modality image probe: A prospective and single-arm clinical trial. Theranostics 2024, 14, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampp, S.; Stefan, H.; Wu, X.; Kaltenhäuser, M.; Maess, B.; Schmitt, F.C.; Wolters, C.H.; Hamer, H.; Kasper, B.S.; Schwab, S.; et al. Magnetoencephalography for epileptic focus localization in a series of 1000 cases. Brain 2019, 142, 3059–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdoš, M.; Říha, P.; Kojan, M.; Doležalová, I.; Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Petr, J.; Rektor, I. Epileptogenic zone detection in MRI negative epilepsy using adaptive thresholding of arterial spin labeling data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Fayed, I.; Bachani, M.; Dowdy, T.; Jahanipour, J.; Khan, A.; Owotade, J.; Walbridge, S.; Inati, S.K.; Steiner, J.; et al. IDH-mutated gliomas promote epileptogenesis through d-2-hydroxyglutarate-dependent mTOR hyperactivation. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Judkins, J.; Thomas, C.; Wu, M.; Khoury, L.; Benjamin, C.G.; Pacione, D.; Golfinos, J.G.; Kumthekar, P.; Ghamsari, F.; et al. Mutant IDH1 and seizures in patients with glioma. Neurology 2017, 88, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Fan, X.; You, G. Significance of miR-1290 in glioblastoma patients with epilepsy. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomschik, M.; Horner, E.; Lang, A.; Mayer, F.; Czech, T.; Kasprian, G.; Pataraia, E.; Azizi, A.A.; Feucht, M.; Rössler, K.; et al. BRAF V600E Mutation in Ganglioglioma: Impact on Epileptogenicity and Implications for Surgical Strategy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e70136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, J.; Kim, H.; Han, S.; Lim, J.S.; Son, G.; Choi, J.; Park, B.O.; Heo, W.D.; et al. BRAF somatic mutation contributes to intrinsic epileptogenicity in pediatric brain tumors. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomschik, M.; Horner, E.; Lang, A.; Mayer, F.; Czech, T.; Kasprian, G.; Pataraia, E.; Azizi, A.A.; Feucht, M.; Rössler, K.; et al. 10311-ACT-19 A Global, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Phase 3 Study of Vorasidenib Versus Placebo in Patients with Adult-Type Diffuse Glioma with an Idh1/2 Mutation (Indigo): Updated Efficacy Results. Neurooncol. Adv. 2024, 6 (Suppl. 4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollon, T.C.; Pandian, B.; Adapa, A.R.; Urias, E.; Save, A.V.; Khalsa, S.S.S.; Eichberg, D.G.; D’Amico, R.S.; Farooq, Z.U.; Lewis, S.; et al. Near real-time intraoperative brain tumor diagnosis using stimulated Raman histology and deep neural networks. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.D.; Bulbeck, H.; Rooney, A.; Thompson, G.; Burns, J.; Robinson, T.; Vale, L.; Erridge, S.; Watts, C.; Grant, R. P18.39.A Seizure Prophylaxis in Glioma Surgery (Spring): A Multi-Centre, Unblinded, Randomised Trial. Neuro Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. 5), v106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, E.K.; Reiner, A.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Aaroe, A.E.; Cunningham, E.M.; Brown, J.G.; Bruno, F.; Diarte, J.; Haggiagi, A.; Harrison, R.A.; et al. RANO seizure working group-Tumor Related Epilepsy Assessment Tool (RANO-TREAT) to assess seizure control for glioma treatment trials and clinical practice. Neuro Oncol. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Choudhury, A.; Keough, M.B.; Seo, K.; Ni, L.; Kakaizada, S.; Lee, A.; Aabedi, A.; Popova, G.; Lipkin, B.; et al. Glioblastoma remodelling of human neural circuits decreases survival. Nature 2023, 617, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H. Brain connectomics applied to oncological neuroscience: From a traditional surgical strategy focusing on glioma topography to a meta-network approach. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Brain Tumor | Seizure Prevalence | Preoperative Seizure | Topography | Seizure Type | Preoperative Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNET | 83–100% [1] | 92–100% [2,3] | Temporal (66%) Frontal (20%) [4] | Bilateral tonic clonic (32%) Focal (76%) Focal to bilateral tonic–clonic (6%) [2] | Location within temporal lobe or insula [5] |
| Ganglioglioma | 66–97% [1] | 64–97% [6,7] | Temporal (79%) Frontal (12%) [6] | Focal (67%) Bilateral tonic–clonic (33%) [8] | Supratentorial location, temporal lobe involvement [9] |
| Infiltrating Low Grade Glioma | 57–68% [1] | 69–90% [10,11] | Frontal (48%) Temporal (41%) [12] | Focal (42%) Focal to bilateral tonic–clonic (37%) Other (21%) [12] | Hypertension, no comorbidity [13] |
| Infiltrating High Grade Glioma | 30–38% [1] | 22–24 [14,15] | Frontal (46%) Temporal (33%) Parietal (16%) [15] | Focal (37%) Bilateral tonic clonic (35%) [15] | Focal impaired seizure type, tumor size, hemorrhagic component [15] |
| Meningioma | 20–28% [1] | 12–76% [16] | Convexity (33%) Falx or parasagittal (38%) [17] | Focal (48%) Bilateral tonic–clonic or mixed (36%) Bilateral tonic clonic (10%) [18] | Male, absence of headache, peritumoral edema, non-skull base location [16] |
| Cerebral Metastases | 18–29% [1] | 10–24% [19,20] | Frontal (31%) Parietal (19%) Temporal (14%) Occipital (12%) Cerebellar (23%) [19] | Focal aware (32%) Focal impaired (18%) Bilateral tonic–clonic (39%) [20] | Frontal lobe location, melanoma diagnosis, KRAS mutation (in lung carcinoma), intratumoral hemorrhage, prior radiotherapy [19] |
| Antiseizure Medication | MOA/Target | Practical Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Levetiracetam | SV2A modulation | First-line agent; minimal drug–drug interactions; generally well tolerated; Monitor for mood changes (e.g., irritability) more commonly seen in setting of frontal lobe tumors |
| Lacosamide | Enhance slow inactivation of voltage-gated Na+ channels | Well tolerated; often tolerated with less side effects compared to LEV Monitor PR interval/risk of arrhythmias, dizziness, diplopia/ataxia at higher doses |
| Brivaracetam | High-affinity SV2A modulation | Similar interaction liability to LEV; consider if seizure free with LEV, but not tolerated due to mood side effects (~2/3 of patients report improved side effects) |
| Lamotrigine | Na+ channel blocking; decrease glutamate release | Slow titration required due to risk of rash/SJS/TEN; not for use as first-line agent given prolonged titration; good cognitive and mood profile Monitor for insomnia, dizziness/diplopia at higher doses |
| Valproic acid | Na+ channel blocking; T-type Ca2+ channel inhibition; GABA enhancement | Enzyme inhibition: CYP2C9 (strong); CYP2C19 (moderate); CYP3A4 (weak); UGT1A4/UGT2B7 (moderate) Monitor for hyperammonemia, transaminitis, thrombocytopenia and weight loss; Increased risk of thrombocytopenia with TMZ; May be an exclusion criterion for clinical trials Initial report of survival benefit in glioma not consistently reproduced |
| Clobazam | GABAA receptor agonist | Adjunct therapy, although positive seizure response may allow wean of other ASM(s); low doses may be sufficient; Monitor for fatigue (initial side effects often resolve within weeks) |
| Zonisamide | Na+ channel blocking; T-type Ca2+ channel inhibition | Avoid in patients with history of nephrolithiasis or sulfa allergies; Monitor for weight loss, cognitive slowing, and metabolic acidosis |
| Perampanel | AMPA antagonist | Adjunct therapy; anti-glutamatergic tumor benefit shown in animal models; Monitor for irritability, aggression, and dizziness |
| Eslicarbazepine | Enhance slow inactivation of voltage-gated Na+ channels | Not well studied in BTRE; Na+ channel mechanism similar to carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine without same degree of enzyme interactions [moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor; mild CYP3A4 inducer Monitor for hyponatremia, renal dysfunction, dizziness |
| Gabapentin, Pregabalin | α2δ subunit of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels | Minimal effect on CYPs; minimal drug-drug interactions |
| Avoid/limit with chemotherapy: Phenytoin, Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine, Primidone | Potent CYP induction | Enzyme induction reduces levels of oncologic agents (TMZ, TKIs, etc.) in addition to dexamethasone; Often listed as exclusion criteria for clinical trials |
| Rescue Benzodiazepines: intranasal Midazolam or Diazepam; PO clonazepam | GABAA receptor allosteric modulator | 1st-line for breakthrough seizures/status; intranasal are practical for outpatient use |
| Brain Tumor | Rate of Seizure Freedom † | Predictors of Postoperative Seizure Freedom | Predictors of Postoperative Seizures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glioneuronal Tumors | ‡ STR: 55% ‡ GTR: 87% [36] | GTR, focal to bilateral tonic–clonic seizures, seizure duration for <1 year, temporal lobe surgery, younger age [21,36] | Histopathology, concomitant cortical dysplasia, mesial temporal location [37] |
| Infiltrating Low Grade Glioma | STR: 49–60% GTR: 75–86% [38] | GTR, presurgical seizure control with ASMs, seizure duration for <1 year, frontal lobe location [12,39] | Focal seizures, preoperative seizures, mutational status, infiltrative pattern, histological subtype [12,39,40,41] |
| Infiltrating High Grade Glioma | STR/GTR: 26–77% [15,42] | GTR (if exclusively in temporal lobe), early seizure onset [43,44] | Temporal lobe location, preoperative epilepsy, molecular subtype [45,46] |
| Meningioma | ‡ STR/GTR: 69% [16] | GTR, well-defined tumor margins, lower WHO grade [47] | Male, postoperative neurological deficits, postoperative complications, preoperative seizures, motor cortex location, non-skull base location, recurrence [18,48] |
| Cerebral Metastases | § STR/GTR: 64% [49] | GTR (conflicting evidence) [19,31] | Checkpoint inhibitors, previous radiotherapy, older age, disease progression within CNS, parietal lobe, recurrence, multiple surgeries [19,29,31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalili, B.F.; Chojnacki, M.R.; Dixit, K.; Gururangan, K.; Horbinski, C.; Rosenow, J.M.; Hsieh, J.K.; Magill, S.T.; Tate, M.C.; Lukas, R.V.; et al. Surgical Treatment of Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Current and Emerging Strategies. Cancers 2025, 17, 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213539
Khalili BF, Chojnacki MR, Dixit K, Gururangan K, Horbinski C, Rosenow JM, Hsieh JK, Magill ST, Tate MC, Lukas RV, et al. Surgical Treatment of Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Current and Emerging Strategies. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213539
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalili, Bobak F., Michael R. Chojnacki, Karan Dixit, Kapil Gururangan, Craig Horbinski, Joshua M. Rosenow, Jason K. Hsieh, Stephen T. Magill, Matthew C. Tate, Rimas V. Lukas, and et al. 2025. "Surgical Treatment of Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Current and Emerging Strategies" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213539
APA StyleKhalili, B. F., Chojnacki, M. R., Dixit, K., Gururangan, K., Horbinski, C., Rosenow, J. M., Hsieh, J. K., Magill, S. T., Tate, M. C., Lukas, R. V., & Templer, J. W. (2025). Surgical Treatment of Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: Current and Emerging Strategies. Cancers, 17(21), 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213539








