CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress RB-Null Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Mutant P53 Expression via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
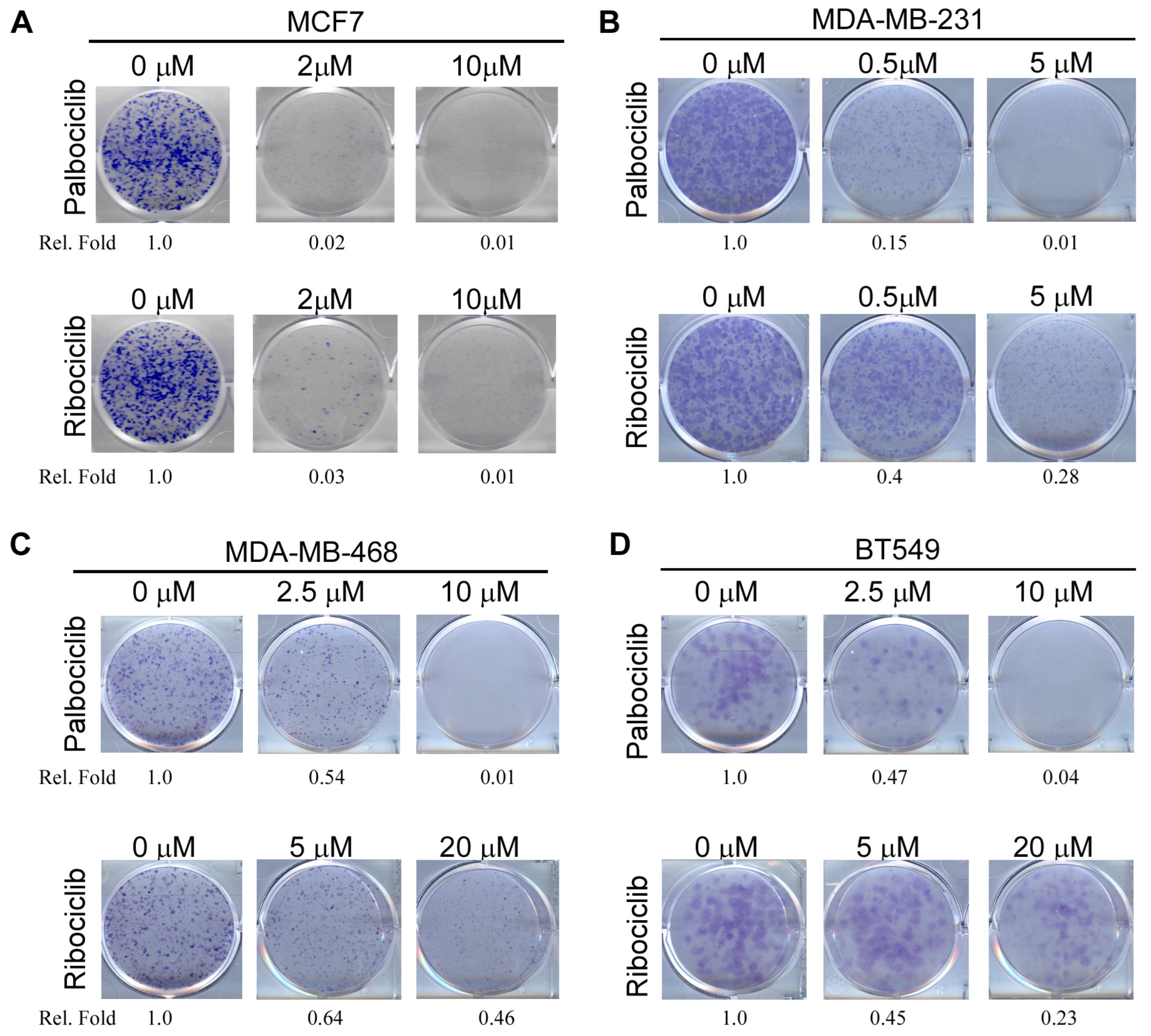
2.1. Both RB-Proficient and RB-Deficient Breast Cancer Cells Are Susceptible to CDK4/6 Inhibitors
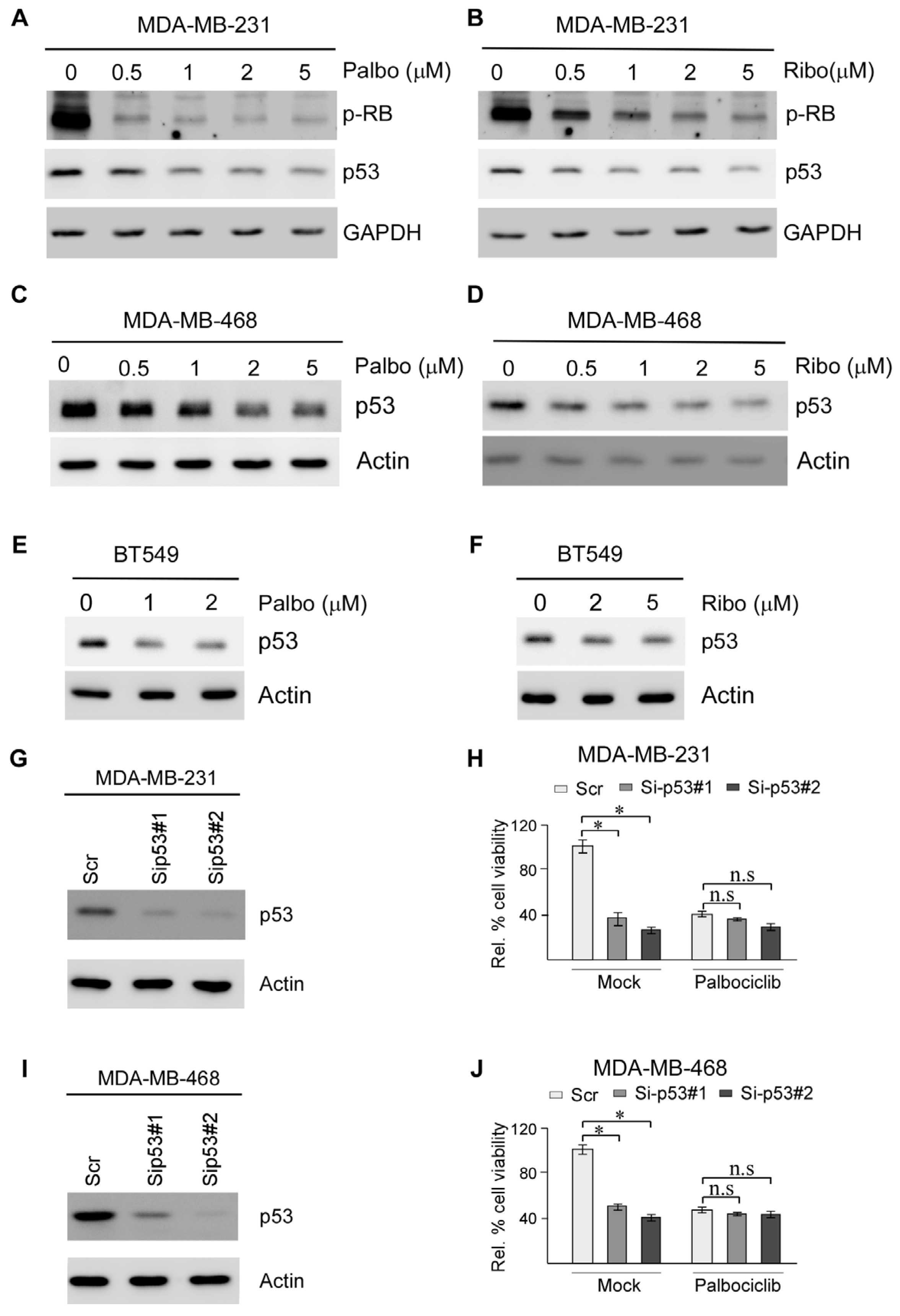
2.2. Suppression of Mutant p53 Expression Is Likely Responsible for CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppressing TNBC Cell Survival
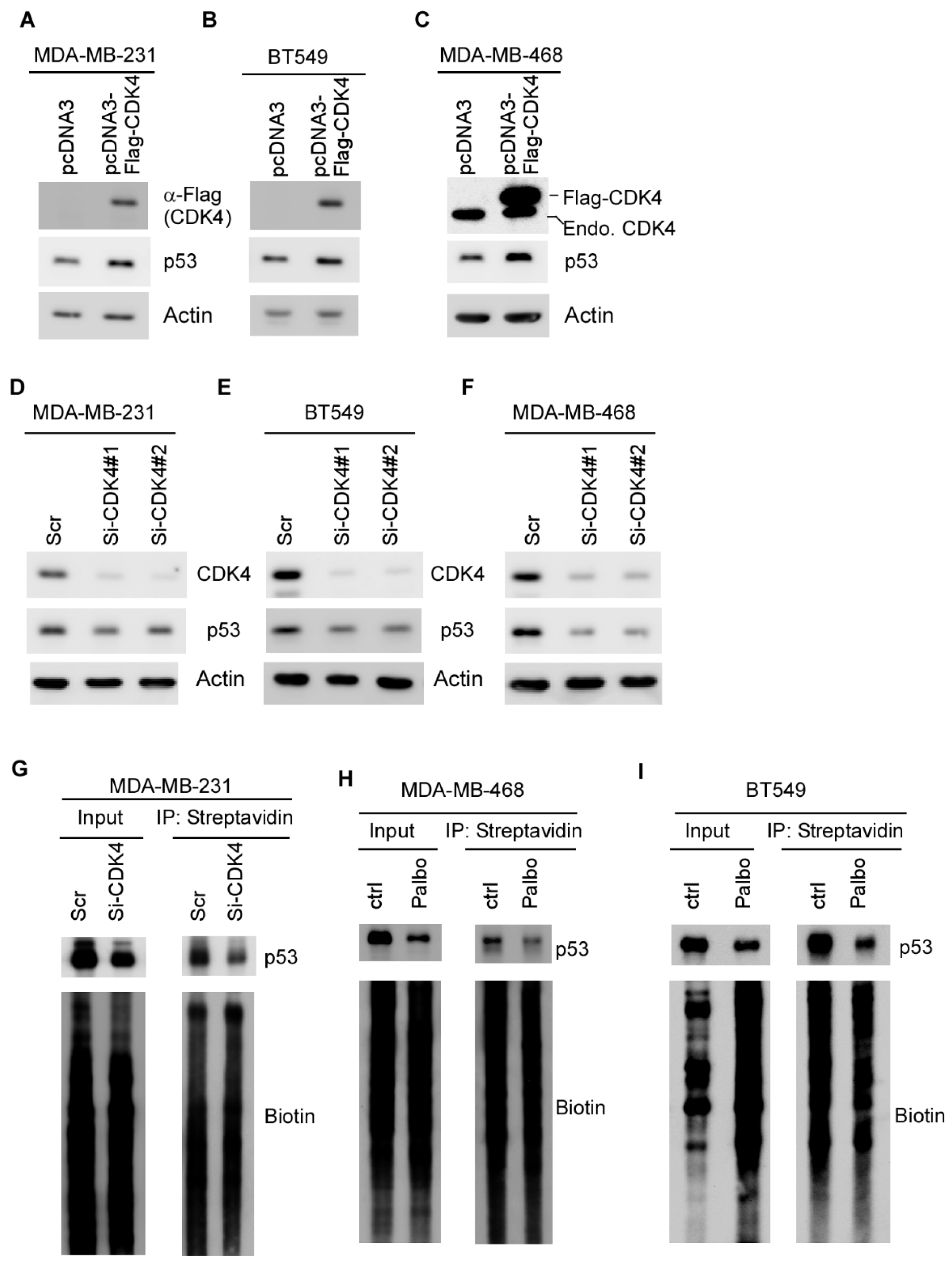
2.3. Mutant p53 Expression Is Regulated by CDK4 via mRNA Translation
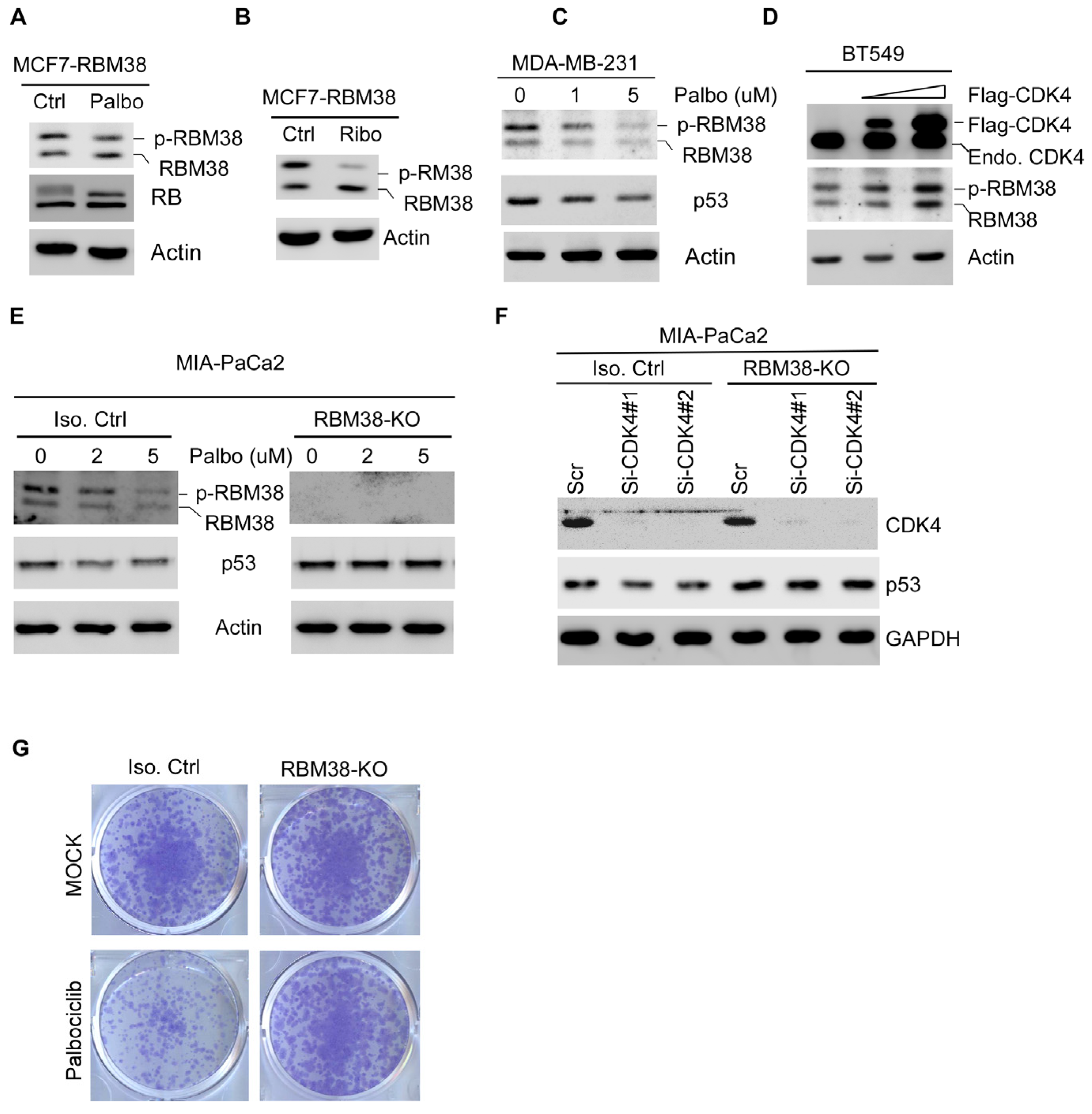
2.4. CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress Mutant p53 Expression and Cell Survival via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein
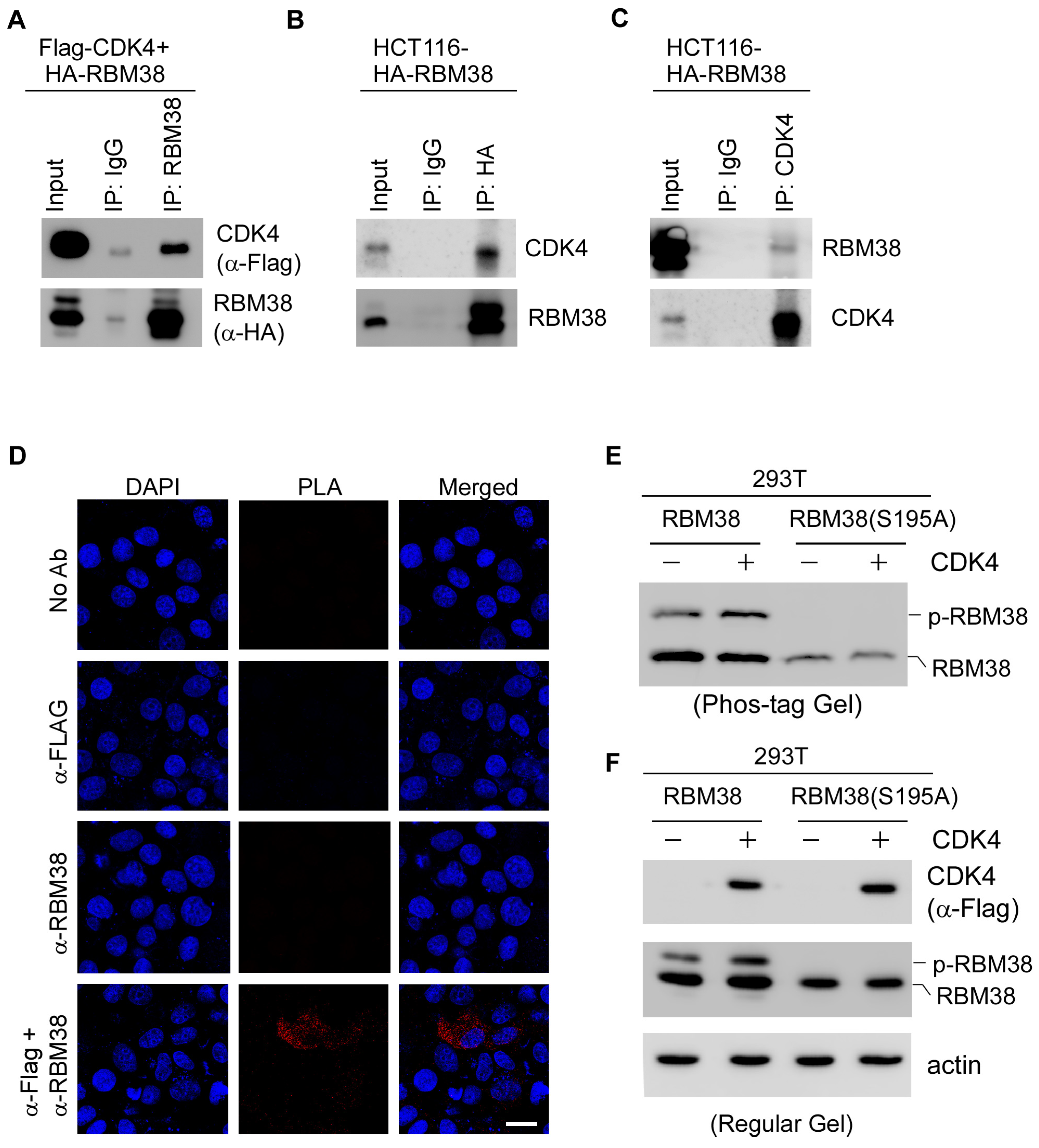
2.5. CDK4 Interacts with RBM38 and Mediates Phosphorylation of RBM38 at Serine 195
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Plasmids and Transient Transfection
4.4. SiRNA Transfection
4.5. Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
4.6. Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Click-It Assay Kit
4.8. Colony Formation Assay
4.9. CellTiter-Glo Viability Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fassl, A.; Geng, Y.; Sicinski, P. CDK4 and CDK6 kinases: From basic science to cancer therapy. Science 2022, 375, eabc1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Bergholz, J.S.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6 in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMichele, A.; Clark, A.S.; Tan, K.S.; Heitjan, D.F.; Gramlich, K.; Gallagher, M.; Lal, P.; Feldman, M.; Zhang, P.; Colameco, C.; et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD0332991) in Rb+ advanced breast cancer: Phase II activity, safety, and predictive biomarker assessment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Crown, J.P.; Lang, I.; Boer, K.; Bondarenko, I.M.; Kulyk, S.O.; Ettl, J.; Patel, R.; Pinter, T.; Schmidt, M.; et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickler, M.N.; Tolaney, S.M.; Rugo, H.S.; Cortés, J.; Diéras, V.; Patt, D.; Wildiers, H.; Hudis, C.A.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Zamora, E.; et al. MONARCH 1, A Phase II Study of Abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6 Inhibitor, as a Single Agent, in Patients with Refractory HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5218–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldon, C.E.; Sergio, C.M.; Kang, J.; Muthukaruppan, A.; Boersma, M.N.; Stone, A.; Barraclough, J.; Lee, C.S.; Black, M.A.; Miller, L.D.; et al. Cyclin E2 Overexpression Is Associated with Endocrine Resistance but not Insensitivity to CDK2 Inhibition in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhees, F.; Demers, I.; Legemaate, D.; Jacobs, R.; Hoeben, A.; Kremer, B.; Speel, E.J. Exploring the antiproliferative effect of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and CDK4/6 inhibitors in human papillomavirus-positive and -negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2025, 66, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presti, D.; Quaquarini, E. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR and CDK4/6 Pathways in Endocrine Resistant HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer: Biological Mechanisms and New Treatments. Cancers 2019, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanabag, A.; Armand, J.; Son, E.; Yang, H.W. Targeting CDK4/6 in breast cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, S.; Li, Y. Breaking Cancer’s Momentum: CDK4/6 Inhibitors and the Promise of Combination Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, L.A.; Dees, E.C.; Sawyer, L.; Gatti, L.; Moore, D.T.; Collichio, F.; Ollila, D.W.; Sartor, C.I.; Graham, M.L.; Perou, C.M. The triple negative paradox: Primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2329–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagia, E.; Mahalingam, D.; Cristofanilli, M. The Landscape of Targeted Therapies in TNBC. Cancers 2020, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, P.K.; Villegas, A.G.; Cao, C.; Pinder-Schenck, M.; Chiappori, A.; Hou, W.; Zajac-Kaye, M.; Ivey, A.M.; Kaye, F.J. CDK4/6 inhibition stabilizes disease in patients with p16-null non-small cell lung cancer and is synergistic with mTOR inhibition. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 37352–37366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour-Leung, N.A.; Chen, X.; Bui, T.Y.; Jiang, Y.F.; Yang, D.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; McArthur, M.J.; Hunt, K.K.; Keyomarsi, K. Sequential Combination Therapy of CDK Inhibition and Doxorubicin Is Synthetically Lethal in p53-Mutant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney Eskiler, G.; Ozman, Z.; Haciefendi, A.; Cansaran-Duman, D. Novel combination treatment of CDK 4/6 inhibitors with PARP inhibitors in triple negative breast cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.S.; Barr, A.R.; Cutts, R.; Beaney, M.; Babina, I.; Sampath, D.; Giltnane, J.; Lacap, J.A.; Crocker, L.; Young, A.; et al. Single-Cell Dynamics Determines Response to CDK4/6 Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5561–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargonetti, J.; Prives, C. Gain-of-function mutant p53: History and speculation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, M.; Prives, C. p53: A tale of complexity and context. Cell 2024, 187, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, Z.I.; Abuhadra, N.; Goodyear, S.M.; Hobbs, E.A.; Kaempf, A.; Thompson, A.M.; Moulder, S.L. Impact of TP53 mutations in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. npj Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.; Synnott, N.C.; Crown, J.; Madden, S.F.; Duffy, M.J. Targeting mutant p53 with arsenic trioxide: A preclinical study focusing on triple negative breast cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 46, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Agostino, S.; Strano, S.; Emiliozzi, V.; Zerbini, V.; Mottolese, F.; Sacchi, A.; Blandino, G.; Piaggio, G. Gain of function of mutant p53: The mutant p53/NF-Y protein complex reveals an aberrant transcriptional mechanism of cell cycle regulation. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, T.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Kinoshita, I.; Hommura, F.; Morikawa, T.; Katoh, H.; Kawakami, Y. Cyclin D1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancers: Its association with altered p53 expression, cell proliferation and clinical outcome. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Zeng, S.X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T.J.; Zhou, F.; Cao, B.; Jung, J.H.; Del Sal, G.; Luo, S.W.; Lu, H. Mutant p53 Gains Its Function via c-Myc Activation upon CDK4 Phosphorylation at Serine 249 and Consequent PIN1 Binding. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.S.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Hernandez-Segura, A.; van Vliet, T.; Jongbloed, E.M.; Wilting, S.M.; Ohtani, N.; Jager, A.; Demaria, M. Pharmacological CDK4/6 inhibition reveals a p53-dependent senescent state with restricted toxicity. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e108946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.L.; Cho, S.J.; Chen, X.B. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 promotes p53 mRNA translation via phosphorylation of RNPC1. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2246–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Bhatt, T.; Dickler, M.; Giri, D.; Scaltriti, M.; Baselga, J.; Rosen, N.; Chandarlapaty, S. Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesch, A.M.; Hirsh, N.H.; Michmerhuizen, A.R.; Jungles, K.M.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Chandler, B.C.; Liu, M.; Lerner, L.M.; Nino, C.A.; Ward, C.; et al. RB expression confers sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization across breast cancer subtypes. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e154402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Dering, J.; Conklin, D.; Kalous, O.; Cohen, D.J.; Desai, A.J.; Ginther, C.; Atefi, M.; Chen, I.; Fowst, C.; et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.L.; Thangavel, C.; McClendon, A.K.; Reed, C.A.; Knudsen, E.S. Therapeutic CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer: Key mechanisms of response and failure. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4018–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.R.; Deshong, A.J.; Pelton, J.G.; Rubin, S.M. Phosphorylation-induced conformational changes in the retinoblastoma protein inhibit E2F transactivation domain binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16286–16293. [Google Scholar]
- Sriraman, A.; Dickmanns, A.; Najafova, Z.; Johnsen, S.A.; Dobbelstein, M. CDK4 inhibition diminishes p53 activation by MDM2 antagonists. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibra, D.; Xiong, S.; Moyer, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Qi, Y.; Su, X.; Kong, E.K.; Korkut, A.; Lozano, G. Mutant p53 protects triple-negative breast adenocarcinomas from ferroptosis in vivo. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibra, D.; Moyer, S.M.; Naggar, A.K.E.; Qi, Y.; Su, X.P.; Lozano, G. Triple-negative breast tumors are dependent on mutant p53 for growth and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308807120. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.S.; Chen, X.B. Characterization of Functional Domains Necessary for Mutant p53 Gain of Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14229–14238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewen, M.E. p53-dependent repression of cdk4 synthesis in transforming growth factor-beta-induced G1 cell cycle arrest. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1996, 128, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Khidekel, N.; Arndt, S.; Lamarre-Vincent, N.; Lippert, A.; Poulin-Kerstien, K.G.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Qasba, P.K.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C. A chemoenzymatic approach toward the rapid and sensitive detection of O-GlcNAc posttranslational modifications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 16162–16163. [Google Scholar]
- Chittavanich, P.; Saengwimol, D.; Sari, A.I.P.; Srimongkol, A.; Kaewkhaw, R. Protocol for quantifying N-Myc and global protein translation in neuroblastoma cells using click chemistry on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. STAR Protoc. 2024, 5, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cho, S.J.; Shu, L.; Yan, W.; Guerrero, T.; Kent, M.; Skorupski, K.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Translational repression of p53 by RNPC1, a p53 target overexpressed in lymphomas. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1528–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.H.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.J.; Turk, B.E. Homing in: Mechanisms of Substrate Targeting by Protein Kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, L.; Smolenski, A. Analysis of protein phosphorylation using Phos-tag gels. J. Proteom. 2022, 259, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J.; Park, J.; Asprer, K.J.; Doan, A.H. Updated Review Article: Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Impact, FDA Approval, and Resistance Pathways. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 39, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Wan, Y.; He, L.J.; Zheng, J.H.; Mei, Y.; Shi, J.F.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Z.Q.; Zhang, D.X. RBM38 in cancer: Role and mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Yan, W.; Chen, X. RNPC1, an RNA-binding protein and a target of the p53 family, is required for maintaining the stability of the basal and stress-induced p21 transcript. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2961–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, E.S.; Ren, C.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Sun, W.Q.; Kong, X.M.D.; Zhang, W.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Huang, E.; et al. Genetic Ablation of Promotes Lymphomagenesis in the Context of Mutant p53 by Downregulating PTEN. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohn, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. p63alpha and DeltaNp63alpha can induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and differentially regulate p53 target genes. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3193–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wen, K.; Nakajima, K.-i.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X. CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress RB-Null Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Mutant P53 Expression via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein. Cancers 2025, 17, 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203339
Zhang J, Wen K, Nakajima K-i, Shi Y, Chen X. CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress RB-Null Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Mutant P53 Expression via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203339
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jin, Kexin Wen, Ken-ichi Nakajima, Yang Shi, and Xinbin Chen. 2025. "CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress RB-Null Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Mutant P53 Expression via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203339
APA StyleZhang, J., Wen, K., Nakajima, K.-i., Shi, Y., & Chen, X. (2025). CDK4/6 Inhibitors Suppress RB-Null Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inhibiting Mutant P53 Expression via RBM38 RNA-Binding Protein. Cancers, 17(20), 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203339







