Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: A Population-Based Study in Italy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants and Data Sources
2.2. Variables and Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. A review of human carcinogens—Part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, S.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Dallari, B.; Barile, R.; Maisenti, F.; Rugarli, S.; Marinaccio, A.; Consonni, D.; Mensi, C. Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management. A Comprehensive Review, 1982–2024. Cancers 2024, 16, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plas, E.; Riedl, C.R.; Pflüger, H. Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis: Review of the literature and assessment of prognostic parameters. Cancer 1998, 83, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogg, J.B.; Fronzaroli, J.N.; Oliveira, P.; Bode, P.-K.; Lorch, A.; Issa, A.; Beyer, J.; Eberli, D.; Sangar, V.; Hermanns, T.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes in men with mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis: Analysis of published case-series data. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Guo, Z.; Song, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, A.; Yu, J.; et al. Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis. iMetaMed 2025, 1, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, A.; Nassiri, N.; Pearce, S.; Daneshmand, S. Testicular Mesothelioma: An Analysis of Epidemiology; Patient Outcomes; and Prognostic Factors. Urology 2019, 126, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, A.; Consonni, D.; Mensi, C.; Mirabelli, D.; Migliore, E.; Magnani, C.; Di Marzio, D.; Gennaro, V.; Mazzoleni, G.; Girardi, P.; et al. Association between asbestos exposure and pericardial and tunica vaginalis testis malignant mesothelioma: A case-control study and epidemiological remarks. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2020, 46, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dytor, T.B.; Verril, C.; Alizadeh, Y. Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis and epididymis. Diagn. Histopathol. 2023, 29, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recabal, P.; Rosenzweig, B.; Bazzi, W.M.; Carver, B.S.; Sheinfeld, J. Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: Outcomes Following Surgical Management Beyond Radical Orchiectomy. Urology 2017, 107, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnor, K.J.; Pavlisko, E.N.; Sporn, T.A.; Roggli, V.L. Mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 92, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.C.; Lange, P.H.; Takayama, T.K. Extensive palliative surgery for advanced mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis. Urology 2003, 62, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, C.; Giusiano, S.; Thiam, K.; Guinde, J.; Froudarakis, M.; Astoul, P. The necessity of a more aggressive initial surgical treatment in patients with mesothelioma of the testicular tunica vaginalis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2019, 47, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre; randomised; open-label; phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Perrone, F.; Greillier, L.; Tu, W.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Grosso, F.; Russo, G.L.; Florescu, M.; Mencoboni, M.; Morabito, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy in untreated advanced pleural mesothelioma in Canada, Italy, and France: A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Trama, A.; Capocaccia, R.; RARECARENet Working Group. Epidemiology of rare cancers and inequalities in oncologic outcomes. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, J.-Y.; Casali, P.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Seckl, M.J.; Gietema, J.; de Herder, W.W.; Caplin, M.; Klümpen, H.-J.; Glehen, O.; Wyrwicz, L.; et al. Management of patients with rare adult solid cancers: Objectives and evaluation of European reference networks (ERN) EURACAN. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 39, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, C.; Mensi, C.; Binazzi, A.; Marsili, D.; Grosso, F.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.P.; Ferrante, D.; Migliore, E.; Mirabelli, D.; Terracini, B.; et al. The Italian Experience in the Development of Mesothelioma Registries: A Pathway for Other Countries to Address the Negative Legacy of Asbestos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18; StataCorp LLC.: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Janes, S.M.; Alrifai, D.; Fennell, D.A. Perspectives on the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, N.; Bagrodia, A.; Baraban, E.; Fankhauser, C.D.; Ged, Y.M.S. Testicular Germ Cell Tumors: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, K.S.; Abdul-Muhsin, H.M.; Navaratnam, A.K.; Rose, K.M.; Stagg, J.; Ho, T.H.; Bryce, A.H.; Cheney, S.M.; Tyson, M.D.; Castle, E.P. Role of robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis: Case series and review of the literature. Can. J. Urol. 2019, 26, 9752–9757. [Google Scholar]
- Lash, T.L.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Haneuse, S.; Rothman, K.J. Modern Epidemiology, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Iczkowski, K.A. Malignant Mesothelioma of Tunica Vaginalis Testis: Update for 2022. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2023, 30, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.J.; Sholl, L.M.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Schulte, S.; Wang, L.J.; Maclean, F.M.; Hirsch, M.S. Molecular and immunohistochemical characterisation of mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis. Histopathology 2022, 81, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.K.C.; Van Roo, J.; Kryvenko, O.N.; Ye, H.; McKenney, J.K.; Epstein, J.I. Mesothelioma of Uncertain Malignant Potential (MUMP) of the tunica vaginalis: Proposal for reclassification as “Complex Mesothelial Tumor of the Tunica Vaginalis”. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2024, 48, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanaroff, R.E.; Yang, S.R.; Tan, K.S.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Bodd, F.; Bowman, A.; Chang, J.; Offin, M.D.; Reiner, A.; Rekhtman, N.; et al. Correlation of Histologic Features with Gene Alterations in Pleural Mesothelioma. Mod. Pathol. 2025, 38, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Othus, M.; Palma, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Kurzrock, R. Designing Clinical Trials for Patients With Rare Cancers: Connecting the Zebras. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2025, 45, e100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Total Cases N (%) | Cases with Treatment Information N (%) | Cases Without Treatment Information N (%) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 104 (100) | 74 (100) | 30 (100) | |
| Age at diagnosis median (range) | 72 (17–92) | 72 (17–89) | 76 (40–92) | 0.16 |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | ||||
| <45 | 9 (9) | 8 (11) | 1 (3) | 0.13 |
| 45–64 | 21 (20) | 15 (20) | 6 (20) | |
| 65–74 | 32 (31) | 26 (35) | 6 (20) | |
| ≥75 | 42 (40) | 25 (34) | 17 (57) | |
| Period of diagnosis | ||||
| 1994–1998 | 10 (10) | 10 (14) | 0 | 0.04 |
| 1999–2004 | 23 (22) | 18 (24) | 5 (17) | |
| 2005–2010 | 24 (23) | 17 (23) | 7 (23) | |
| 2011–2016 | 28 (27) | 20 (27) | 8 (27) | |
| 2017–2021 | 19 (18) | 9 (12) | 10 (33) | |
| Morphology (ICD-O-3 code) | ||||
| Epithelioid (90523) | 54 (52) | 38 (51) | 16 (53) | 0.34 |
| Biphasic (90533) | 17 (16) | 15 (20) | 2 (7) | |
| Sarcomatoid (90513) | 6 (6) | 4 (5) | 2 (7) | |
| Not otherwise specified (90503) | 27 (26) | 17 (23) | 10 (33) | |
| Exposure evaluation | ||||
| Direct interview | 58 (56) | 43 (58) | 15 (50) | 0.65 |
| Indirect interview | 30 (29) | 21 (28) | 9 (30) | |
| None | 16 (15) | 10 (14) | 6 (20) | |
| Sources of asbestos exposure b | ||||
| Occupational | 56 (64) | 40 (63) | 16 (67) | 0.46 |
| Non-occupational | 3 (3) | 2 (3) | 1 (4) | |
| Familial | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | |
| Environmental | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | |
| Leisure-related | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | |
| Unexposed | 29 (33) | 22 (34) | 7 (29) | |
| Latency (years between first exposure and diagnosis—median (range)) | ||||
| Occupational | 54 (13–75) | 52 (13–75) | 54 (24–70) | 0.33 |
| Non-occupational (years) | ||||
| Familial | 51 | |||
| Environmental | 59 | |||
| Leisure-related | 32 |
| Variable | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 74 | 100 |
| Age at diagnosis, median (range) | 72 (17–89) | |
| Clinical presentation | ||
| Scrotal or testicular swelling/mass | 52 | 70 |
| Hydrocele or hemorrhagic hydrocele | 46 | 62 |
| Epididymitis/orchitis/other local inflammations a | 11 | 15 |
| Scrotal or inguinal hernia | 12 | 16 |
| Scrotal or inguinal pain | 17 | 23 |
| Other b | 7 | 10 |
| Distant Metastasis at diagnosis c | ||
| No | 64 | 87 |
| Yes | 10 | 14 |
| Variable | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 74 | 100 |
| Surgery | 74 | 100 |
| Orchi-funicolectomy | 58 | 78 |
| Orchi-funicolectomy + hemiscrotectomy and/or inguinal lymphadenectomy | 7 | 10 |
| Subtotal surgery a | 8 | 11 |
| Unknown | 1 | 1 |
| Surgery + adjuvant treatment(s) | ||
| Any adjuvant treatment | 15 | 20 |
| Adjuvant Radiotherapy | 2 | 3 |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy | 9 | 12 |
| Both | 4 | 5 |
| Variable | N | Deaths N (%) | Overall Survival, (Months) Median | Crude HR | 95% CI | Adjusted HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
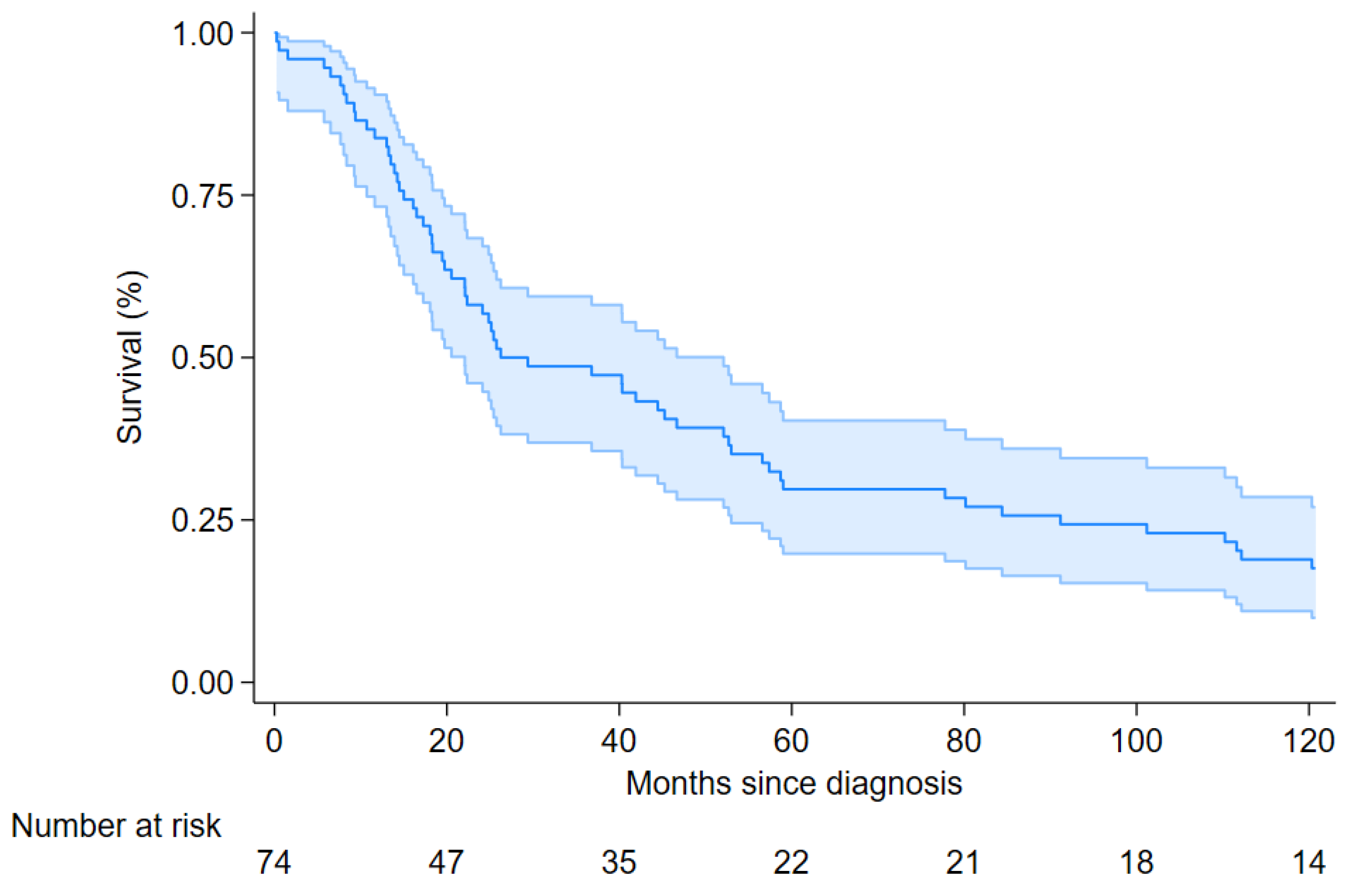
| Overall | 74 | 61 (82) | 26.2 (22.1–52.1) | ||||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | |||||||
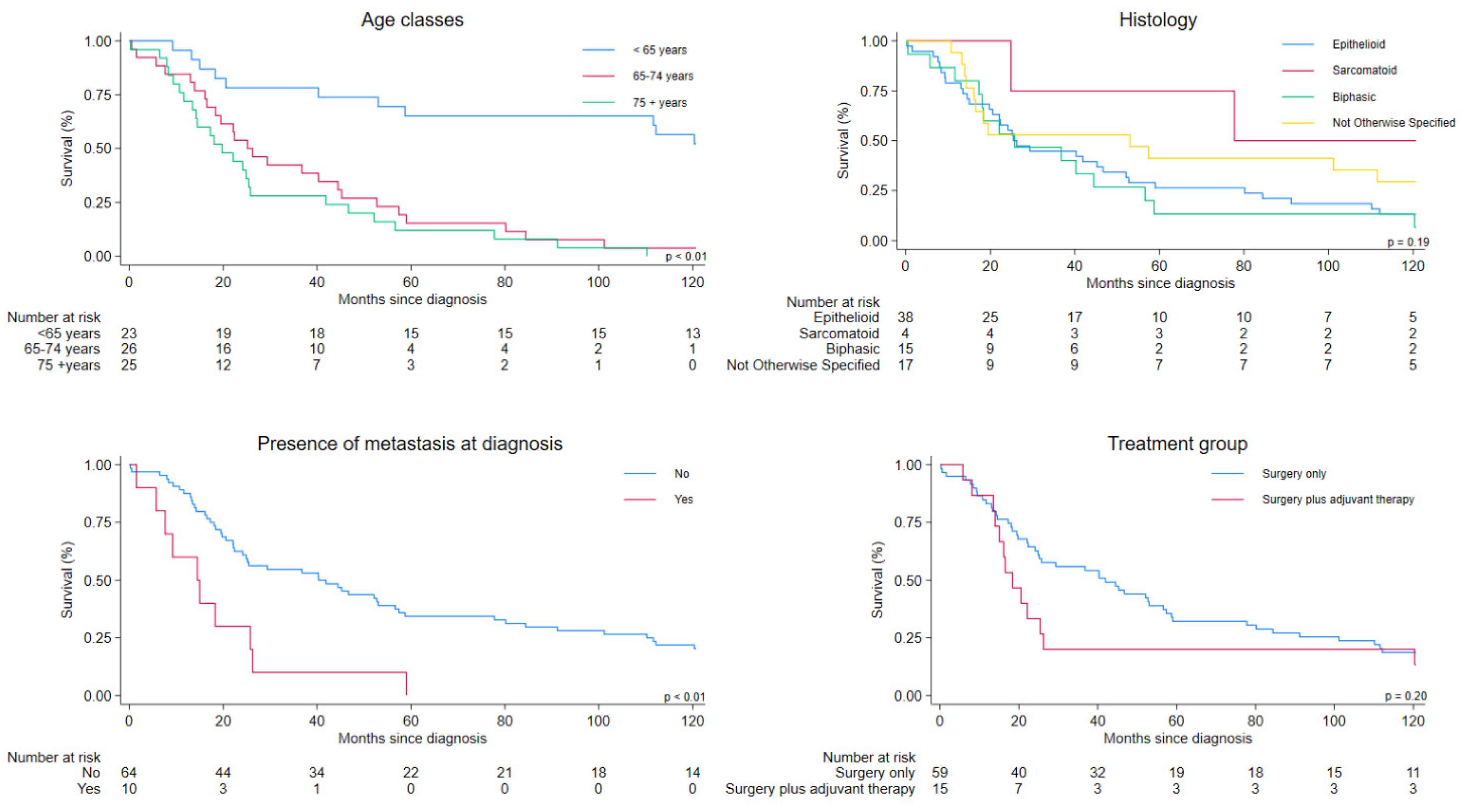
| <65 | 23 | 11 (48) | NC (NC- 53.0) | 1.00 | Reference | 1.00 | Reference |
| 65–74 | 26 | 25 (96) | 25.2 (16.5–44.5) | 4.97 | 2.32–10.64 | 6.69 | 2.77–16.14 |
| ≥75 | 25 | 25 (100) | 19.7 (13.5–25.8) | 6.70 | 3.07–14.60 | 10.50 | 4.16–26.50 |
| Period of diagnosis | |||||||
| 1994–1998 | 10 | 8 (80) | 13.3 (0.3–59.0) | 1.00 | Reference | 1.00 | Reference |
| 1999–2004 | 18 | 13 (72) | 25.4 (15.0–110.2) | 0.65 | 0.27–1.57 | 0.54 | 0.19–1.52 |
| 2005–2010 | 17 | 11 (65) | 41.9 (19.7 -NC) | 0.49 | 0.20–1.21 | 0.46 | 0.17–1.23 |
| 2011–2016 | 20 | 20 (100) | 22.3 (14.5–80.2) | 0.97 | 0.43–2.21 | 0.69 | 0.27–1.76 |
| 2017–2021 | 9 | 9 (100) | 40.3 (11.6–53.0) | 1.13 | 0.43–2.97 | 0.96 | 0.33–2.76 |
| Morphology | |||||||
| Epithelioid (90523) | 38 | 33 (87) | 25.4 (19.7–46.7) | 1.00 | Reference | 1.00 | Reference |
| Biphasic (90533) | 15 | 14 (93) | 25.7 (11.6–44.5) | 1.18 | 0.63–2.21 | 1.72 | 0.85–3.45 |
| Sarcomatoid (90513) | 4 | 2 (50) | 77.8 (25.9-NC) | 0.33 | 0.08–1.39 | 0.36 | 0.08–1.59 |
| NOS (90503) | 17 | 12 (71) | 53.0 (14.2-NC) | 0.65 | 0.34–1.27 | 1.25 | 0.60–2.61 |
| Presence of metastasis at diagnosis | |||||||
| No | 64 | 51 (78) | 40.3 (22.3–56.6) | 1.00 | Reference | 1.00 | Reference |
| Yes | 10 | 10 (100) | 14.5 (1.6–25.8) | 3.09 | 1.53–6.24 | 1.91 | 0.85–4.26 |
| Treatment group | |||||||
| Surgery only | 59 | 48 (81) | 41.9 (24.1–56.6) | 1.00 | Reference | 1.00 | Reference |
| Surgery plus adjuvant therapy | 15 | 13 (87) | 18.3 (13.5–25.4) | 1.50 | 1.53–6.24 | 2.54 | 1.25–5.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceresoli, G.L.; Stella, S.; Dallari, B.; Perduri, R.; Storchi, C.; Vimercati, L.; Piro, S.; Giovannetti, L.; Fedeli, U.; Casotto, V.; et al. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: A Population-Based Study in Italy. Cancers 2025, 17, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193249
Ceresoli GL, Stella S, Dallari B, Perduri R, Storchi C, Vimercati L, Piro S, Giovannetti L, Fedeli U, Casotto V, et al. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: A Population-Based Study in Italy. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193249
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeresoli, Giovanni Luca, Simona Stella, Barbara Dallari, Riccardo Perduri, Cinzia Storchi, Luigi Vimercati, Sara Piro, Lucia Giovannetti, Ugo Fedeli, Veronica Casotto, and et al. 2025. "Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: A Population-Based Study in Italy" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193249
APA StyleCeresoli, G. L., Stella, S., Dallari, B., Perduri, R., Storchi, C., Vimercati, L., Piro, S., Giovannetti, L., Fedeli, U., Casotto, V., Migliore, E., Stura, A., Genova, C., Benfatto, L., Larese Filon, F., D’Agostin, F., Cozzi, I., Angelillo, I. F., Spata, E., ... Mensi, C. (2025). Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis: A Population-Based Study in Italy. Cancers, 17(19), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193249












