Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping Using Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Whole-Slide Images in a Population-Based Cohort
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
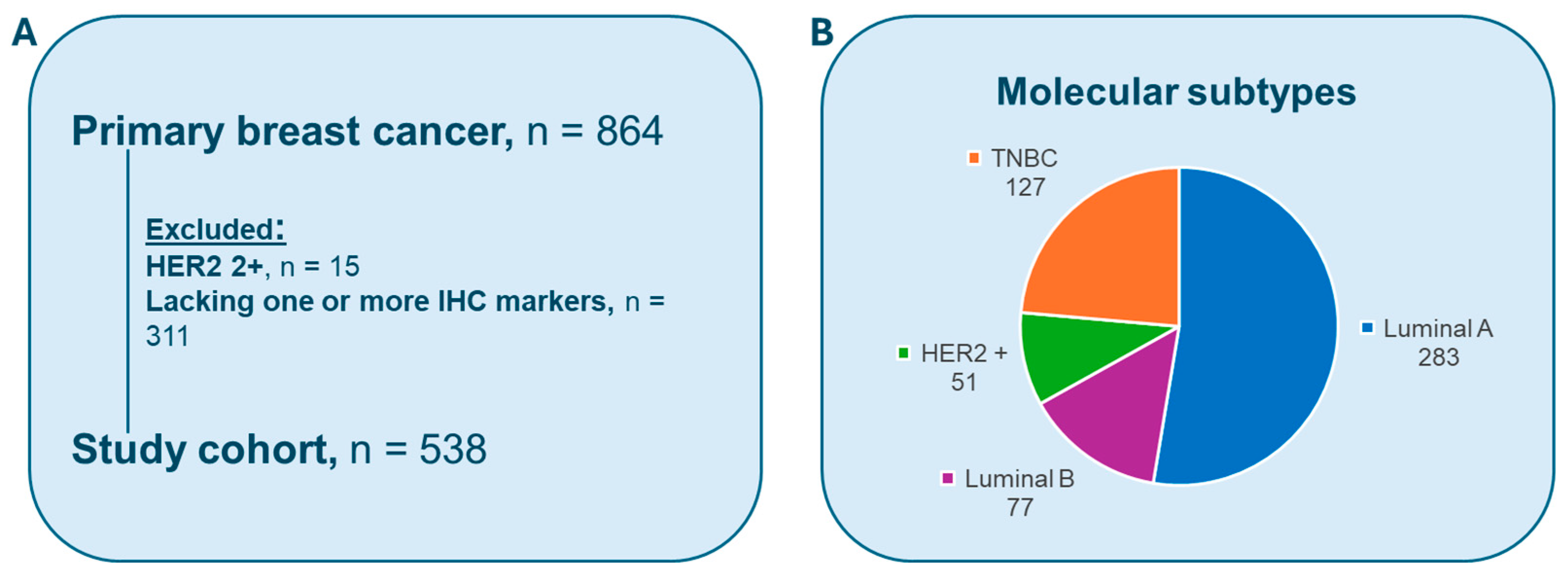
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
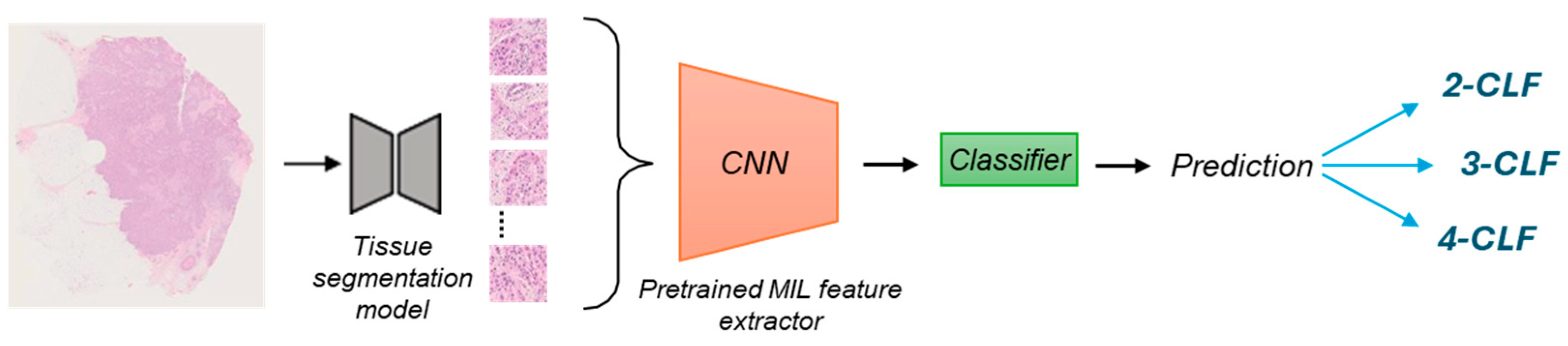
2.3. AI Model
2.3.1. Feature Extraction on the SBC Dataset
2.3.2. Retraining the Final Classifier
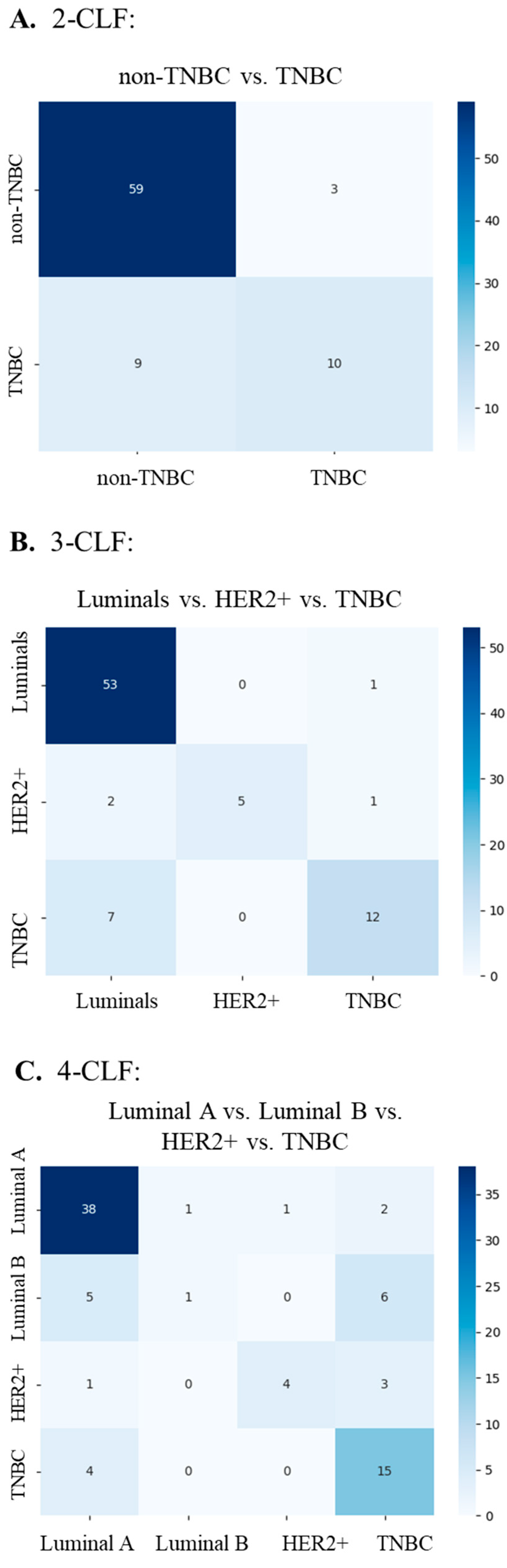
2.3.3. Performance Evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| BCNB | Breast Cancer Needle Biopsy |
| CLF | Classification tasks |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CV | Cross-Validation |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HER2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| ISH | In Situ Hybridization |
| LAR | Luminal Androgen Receptor |
| MAI | Mitotic Activity Index |
| MIL | Multiple Instance Learning |
| NBCG | Norwegian Breast cancer Group |
| PAM50 | Prediction Analysis of Microarray 50 |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| SBC | Stavanger Breast Cancer |
| TILs | Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| WSI | Whole Slide Image |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (Ed.) Breast Tumors; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 82–138. [Google Scholar]
- Cancer Genome Atlas, N. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.T.; Collyar, D.E.; Harris, L.N. Gene Expression Assays for Early-Stage Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: Understanding the Differences. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2017, 1, pkx008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habashy, H.O.; Powe, D.G.; Abdel-Fatah, T.M.; Gee, J.M.; Nicholson, R.I.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Ellis, I.O. A review of the biological and clinical characteristics of luminal-like oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Histopathology 2012, 60, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curigliano, G.; Burstein, H.J.; Gnant, M.; Loibl, S.; Cameron, D.; Regan, M.M.; Denkert, C.; Poortmans, P.; Weber, W.P.; Thurlimann, B.; et al. Understanding breast cancer complexity to improve patient outcomes: The St Gallen International Consensus Conference for the Primary Therapy of Individuals with Early Breast Cancer 2023. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 970–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleskandarany, M.A.; Ellis, I.O.; Rakha, E.A. Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer. In Precision Molecular Pathology of Breast Cancer; Khan, A., Ellis, I., Hanby, A., Cosar, E., Rakha, E., Kandil, D., Eds.; Molecular Pathology Library; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasjonalt Handlingsprogram Med Retningslinjer for Diagnostikk, Behandling og Oppfølging av Pasienter Med Brystkreft. Available online: https://nbcg.no/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/nasjonalt-handlingsprogram-for-pasienter-med-brystkreft-22.10.2021-17.-utgave.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- NordiQC. Available online: https://www.nordiqc.org/index.php (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Rewcastle, E.; Skaland, I.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Fykse, S.K.; Baak, J.P.A.; Janssen, E.A.M. The Ki67 Dilemma: Investigating Prognostic Cut-Offs and Inter-Platform Reproducibility for Automated Ki67 Scoring in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, C.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Shi, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, M. Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Breast Cancer Using Deep Learning on Primary Tumor Biopsy Slides. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 759007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilse, M.; Tomczak, J.; Welling, M. Attention-based Deep Multiple Instance Learning. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2127–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Macenko, M.; Niethammer, M.; Marron, J.S.; Borland, D.; Woosley, J.T.; Guan, X.; Schmitt, C.; Thomas, N.E. A method for normalizing histology slides for quantitative analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Boston, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, M.; Álvarez, P.M.; Cooper, L.A.D.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Deep Gaussian Processes for Classification with Multiple Noisy Annotators. Application to Breast Cancer Tissue Classification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 6922–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Pineda, E.; Adamo, B.; Galvan, P.; Fernandez, A.; Gaba, L.; Diez, M.; Viladot, M.; Arance, A.; Munoz, M. Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24 (Suppl. 2), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.; Yu, N.Y.; Johansson, A.; Ploner, A.; Hall, P.; Lindström, L.S.; Czene, K. Concordance of Immunohistochemistry-Based and Gene Expression-Based Subtyping in Breast Cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 5, pkaa087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Tarruella, S.; Del Monte-Millán, M.; Roche-Molina, M.; Jerez, Y.; Echavarria Diaz-Guardamino, I.; Herrero López, B.; Gamez Casado, S.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; Alvarez, E.; Cebollero, M.; et al. Correlation between breast cancer subtypes determined by immunohistochemistry and n-COUNTER PAM50 assay: A real-world study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 203, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Martin, C.; Silva-Rodriguez, J.; Kiraz, U.; Morales, S.; Janssen, E.A.M.; Naranjo, V. Uninformed Teacher-Student for hard-samples distillation in weakly supervised mitosis localization. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2024, 112, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivukoski, S.; Khan, U.; Ruusuvuori, P.; Latonen, L. Unstained Tissue Imaging and Virtual Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining of Histologic Whole Slide Images. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, M.I.; Song, B.; Taylor, C.; Vaske, C.J.; Benz, S.C.; Rabizadeh, S.; Soon-Shiong, P.; Szeto, C.W. A deep learning image-based intrinsic molecular subtype classifier of breast tumors reveals tumor heterogeneity that may affect survival. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaiminul Islam, M.; Huang, S.; Ajwad, R.; Chi, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P. An integrative deep learning framework for classifying molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2185–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, J.; Liao, T.; Pu, R.; Liu, S.; Peng, Y. A Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Predicting Molecular Subtypes of Human Breast Cancer Using Multimodal Data. Irbm 2022, 43, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, K.; Riaz, N.; Nielsen, T.O. Heterogeneity of triple negative breast cancer: Current advances in subtyping and treatment implications. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, U.; Rewcastle, E.; Fykse, S.K.; Lundal, I.; Gudlaugsson, E.G.; Skaland, I.; Soiland, H.; Baak, J.P.A.; Janssen, E.A.M. Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnstad, H.O.; Borgen, E.; Falk, R.S.; Lien, T.G.; Aaserud, M.; Sveli, M.A.T.; Kyte, J.A.; Kristensen, V.N.; Geitvik, G.A.; Schlichting, E.; et al. Prognostic value of PAM50 and risk of recurrence score in patients with early-stage breast cancer with long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnstad, H.O.; Blix, E.S.; Akslen, L.A.; Gilje, B.; Raj, S.X.; Skjerven, H.; Borgen, E.; Janssen, E.A.M.; Mortensen, E.; Brekke, M.B.; et al. Impact of Prosigna test on adjuvant treatment decision in lymph node-negative early breast cancer-a prospective national multicentre study (EMIT-1). ESMO Open 2024, 9, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ER | PR | HER2 | Proliferation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminal A | positive | positive | negative | low |
| Luminal B | positive | any | any | high |
| HER2-positive | negative | negative | overexpressed | - |
| TNBC | negative | negative | negative | - |
| Classification Tasks | Description |
|---|---|
| Two-class task (2-CLF) | Non-TNBC TNBC |
| Three-class task (3-CLF) | Luminals (Luminal A and B) HER2-positive TNBC |
| Four-class task (4-CLF) | Luminal A Luminal B HER2-positive TNBC |
| Task | AUC | Accuracy | F1 Score | Precision | Recall | Learning Rate | Weight Decay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-CLF | 0.823 ± 0.040 | 0.833 ± 0.015 | 0.824 ± 0.017 | 0.823 ± 0.018 | 0.833 ± 0.015 | 0.01 | 1 × 10−6 |
| 3-CLF | 0.834 ± 0.037 | 0.795 ± 0.034 | 0.770 ± 0.046 | 0.761 ± 0.063 | 0.795 ± 0.034 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 4-CLF | 0.790 ± 0.026 | 0.642 ± 0.043 | 0.601 ± 0.045 | 0.587 ± 0.056 | 0.642 ± 0.043 | 0.01 | 1 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiraz, U.; Fernandez-Martin, C.; Rewcastle, E.; Gudlaugsson, E.G.; Skaland, I.; Naranjo, V.; Morales-Martinez, S.; Janssen, E.A.M. Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping Using Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Whole-Slide Images in a Population-Based Cohort. Cancers 2025, 17, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193234
Kiraz U, Fernandez-Martin C, Rewcastle E, Gudlaugsson EG, Skaland I, Naranjo V, Morales-Martinez S, Janssen EAM. Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping Using Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Whole-Slide Images in a Population-Based Cohort. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193234
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiraz, Umay, Claudio Fernandez-Martin, Emma Rewcastle, Einar G. Gudlaugsson, Ivar Skaland, Valery Naranjo, Sandra Morales-Martinez, and Emiel A. M. Janssen. 2025. "Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping Using Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Whole-Slide Images in a Population-Based Cohort" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193234
APA StyleKiraz, U., Fernandez-Martin, C., Rewcastle, E., Gudlaugsson, E. G., Skaland, I., Naranjo, V., Morales-Martinez, S., & Janssen, E. A. M. (2025). Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping Using Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Whole-Slide Images in a Population-Based Cohort. Cancers, 17(19), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193234








