Real-World Study of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Long-Term Response to Regorafenib in the USA
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
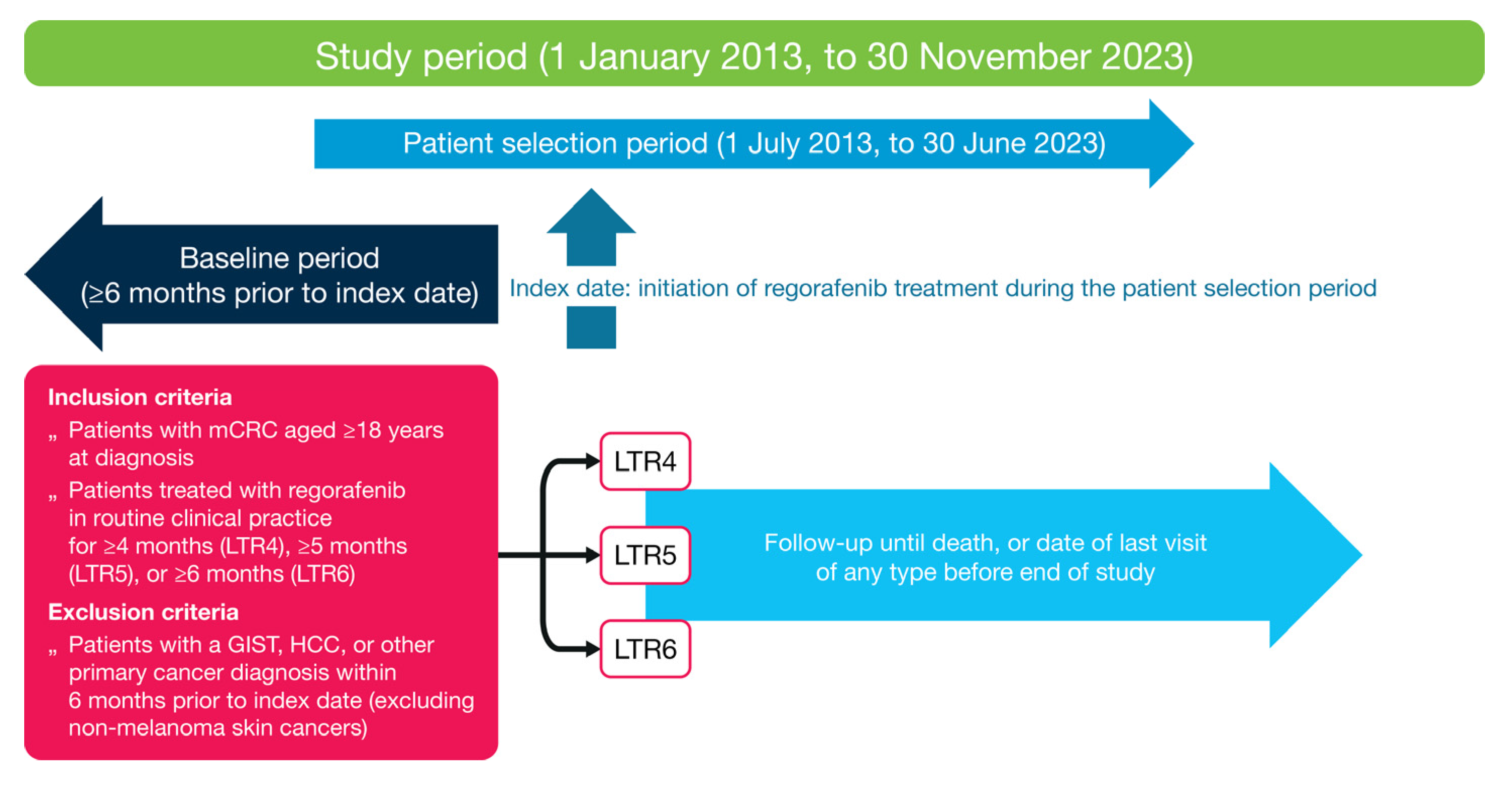
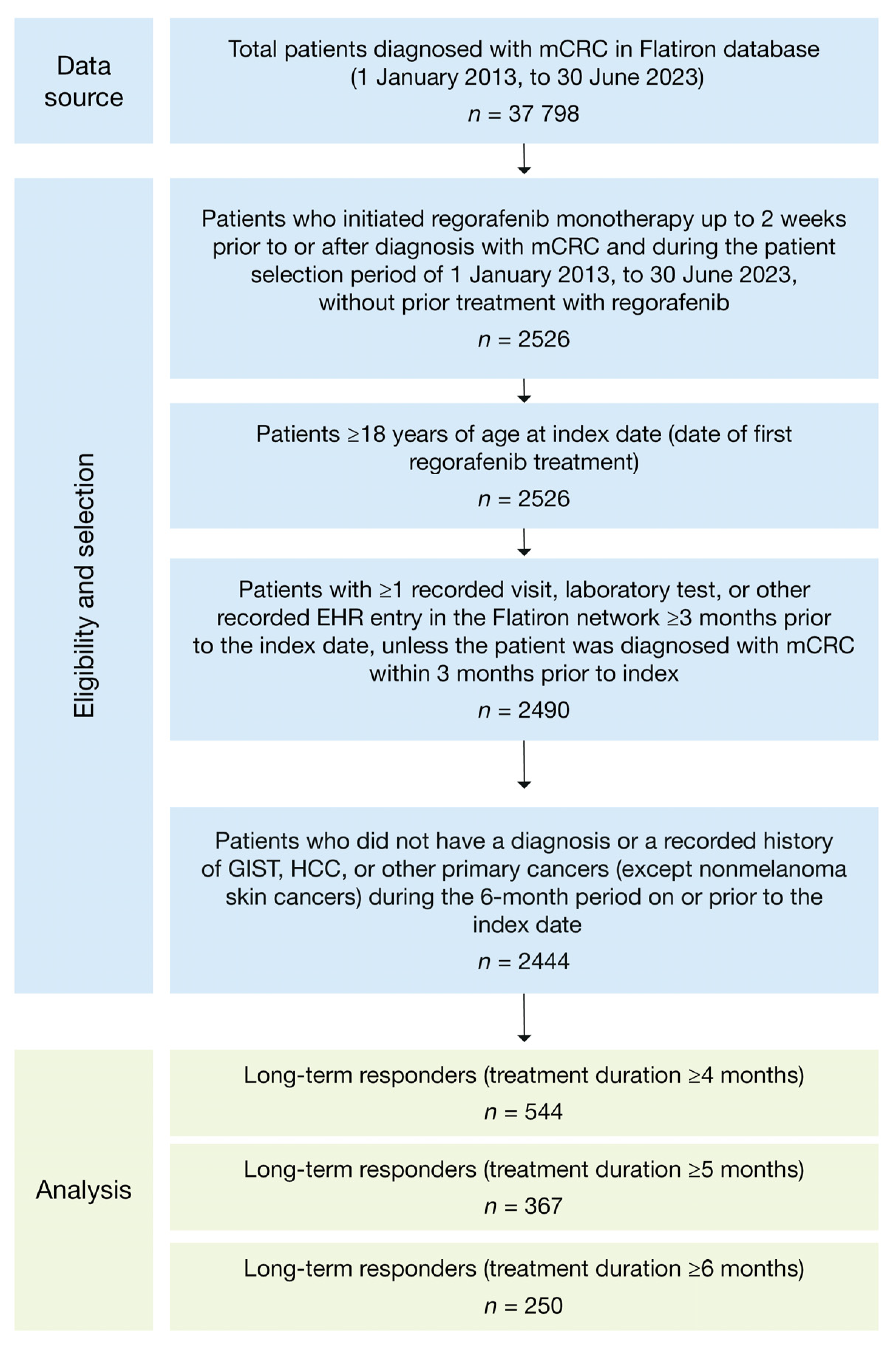
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Variables and Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Biomarkers
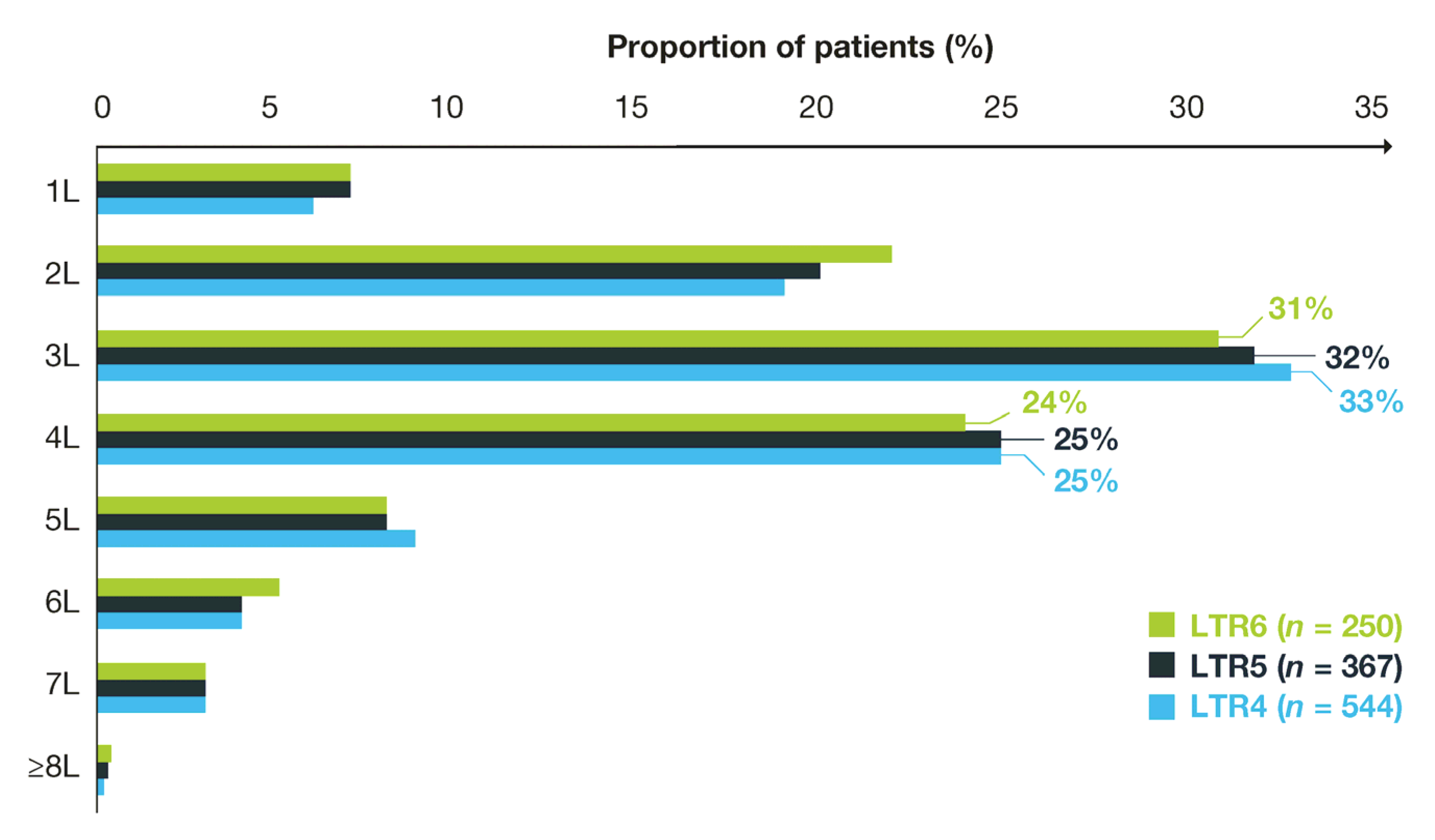
3.3. Treatment Duration and History
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Colorectal Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedesser, J.E.; Ebert, M.P.; Betge, J. Precision medicine for metastatic colorectal cancer in clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359211072703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Stivarga (Regorafenib) Full Prescribing Information; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Whippany, NJ, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/203085s011lbl.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Grothey, A.; Van, C.E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouche, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothey, A.; Falcone, A.; Humblet, Y.; Bouche, O.; Mineur, L.; Adenis, A.; Tabernero, J.; Yoshino, T.; Lenz, H.J.; Goldberg, R.; et al. Characteristics of patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) treated with regorafenib (REG) who had progression-free survival (PFS) >4 months (m): Subgroup analysis of the phase 3 CORRECT trial. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. S6), vi149–vi206, (abstract 516P). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Qin, S.; Huang, L.; Kalmus, J.; Xu, R.; Li, J. Subgroup analysis by progression-free survival (PFS) of Asian patients treated with regorafenib in the phase 3 CONCUR trial. Poster P-295. In Proceedings of the ESMO 19th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer, Barcelona, Spain, 28 June–1 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Martinelli, E.; Cascinu, S.; Sobrero, A.; Banzi, M.; Seitz, J.F.; Barone, C.; Ychou, M.; Peeters, M.; Brenner, B.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who progressed after standard therapy: Results of the large, single-arm, open-label phase IIIb CONSIGN study. Oncologist 2019, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.; Park, H.Y.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Bae, K.B. Complete response of MSI-high metastatic colon cancer following treatment with regorafenib: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 15, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callebout, E.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Laurent, S.; De Man, M.; Ferdinande, L.; Claes, K.B.M.; Van der Meulen, J.; Geboes, K.P. Long term response on regorafenib in non-V600E BRAF mutated colon cancer: A case report. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Kain, T.; Herman, J.; Seery, T. Durable response using regorafenib in an elderly patient with metastatic colorectal cancer: Case report. Cancer Manag. Res. 2015, 7, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Shinto, E.; Kajiwara, Y.; Mochizuki, S.; Okamoto, K.; Nishizawa, A.; Satoh, T.; Kishi, Y.; Ueno, H. Systemic steroid treatment can desensitize the skin reaction due to regorafenib in a recurrence colorectal cancer patient. Int. Cancer Conf. J. 2019, 8, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, M.; Falcone, R.; Mazzuca, F.; Archibugi, L.; Castaldi, N.; Botticelli, A.; Osti, M.F.; Marchetti, P. The role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in oligometastatic colorectal cancer: Clinical case report of a long-responder patient treated with regorafenib beyond progression. Medicine 2017, 96, e9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Manaka, D.; Kudo, R.; Kanai, S.; Mitsuoka, E.; Kanto, S.; Hamasu, S.; Konishi, S.; Nishitai, R. Metastatic colorectal cancer responsive to regorafenib for 2 years: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosso, F.; Lavacchi, D.; Fancelli, S.; Caliman, E.; Brugia, M.; Rossi, G.; Winchler, C.; Pillozzi, S.; Antonuzzo, L. Long-term response of more than 9 years to regorafenib in a heavily pretreated patient with metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2023, 34, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.D.; Pan, X.; Koufopoulou, M.; Arregui, M.; Wissinger, E.; Ostojic, H.; Pisa, F.; Peeters, M. Long-term response to regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): A systematic literature review (SLR). Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35 (Suppl. S1), S30–S31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, R.; Yau, T.C.; Ma, B.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinc, S.; Oruc, Z.; Urakci, Z.; Kalkan, Z.; Kaplan, M.A.; Kucukoner, M.; Isikdogan, A. Evaluation of factors predicting the effectiveness of regorafenib in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Eurasian J. Med. 2022, 54, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, J.; Lastraioli, E.; Tofani, L.; Petroni, G.; Antonuzzo, L.; Messerini, L.; Perrone, G.; Caputo, D.; Francesconi, M.; Amato, M.M.; et al. hERG1 and HIF-2alpha behave as biomarkers of positive response to bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmorino, F.; Salvatore, L.; Barbara, C.; Allegrini, G.; Antonuzzo, L.; Masi, G.; Loupakis, F.; Borelli, B.; Chiara, S.; Banzi, M.C.; et al. Serum LDH predicts benefit from bevacizumab beyond progression in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, E.; Sforza, V.; Cardone, C.; Capasso, A.; Nappi, A.; Martini, G.; Napolitano, S.; Rachiglio, A.M.; Normanno, N.; Cappabianca, S.; et al. Clinical outcome and molecular characterisation of chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer patients with long-term efficacy of regorafenib treatment. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaii-Saab, T.S.; Ou, F.S.; Ahn, D.H.; Boland, P.M.; Ciombor, K.K.; Heying, E.N.; Dockter, T.J.; Jacobs, N.L.; Pasche, B.C.; Cleary, J.M.; et al. Regorafenib dose-optimisation in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (ReDOS): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenis, A.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Paule, B.; Burtin, P.; Tougeron, D.; Wallet, J.; Dourthe, L.M.; Etienne, P.L.; Mineur, L.; Clisant, S.; et al. Survival, safety, and prognostic factors for outcome with regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard therapies: Results from a multicenter study (REBECCA) nested within a compassionate use program. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, E.; Puzzoni, M.; Ziranu, P.; Cremolini, C.; Lonardi, S.; Banzi, M.; Mariani, S.; Liscia, N.; Cinieri, S.; Dettori, M.; et al. Long term survival with regorafenib: REALITY (real life in Italy) trial—A GISCAD study. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2021, 20, e253–e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, T.C.; Charlton, M.E.; Schroeder, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Tolle, C.L.; Evers, B.M.; Mullett, T.W. Improving the quality of cancer care in community hospitals. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.D.L.; Oduyale, O.; Cao, Y. Overcoming racial and ethnic disparities in rectal cancer treatment. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e240018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepassi, A.; Li, M.; Zell, J.A.; Chan, A.; Saunders, I.M.; Mukamel, D.B. Rural-urban disparities in colorectal cancer screening, diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncologist 2024, 29, e431–e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | LTR4 a (n = 544) | LTR5 a (n = 367) | LTR6 a (n = 250) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender, n (%) | 309 (57) | 207 (56) | 141 (56) |
| Age Median (IQR), years ≤65, n (%) >65, n (%) | 66 (58–74) 271 (50) 273 (50) | 66 (58–74) 183 (50) 184 (50) | 66 (58–74) 124 (50) 126 (50) |
| Race, n (%) White Black or African American Asian Other Unknown | 349 (64) 73 (13) 15 (3) 81 (15) 26 (5) | 243 (66) 47 (13) 10 (3) 51 (14) 16 (4) | 167 (67) 30 (12) 4 (2) 38 (15) 11 (4) |
| Region, n (%) Midwest Northeast South West Unknown | 59 (11) 84 (15) 244 (45) 80 (15) 77 (14) | 39 (11) 60 (16) 158 (43) 55 (15) 55 (15) | 21 (8) 37 (15) 111 (44) 39 (16) 42 (17) |
| Stage at initial CRC diagnosis, n (%) 0/I II III IV Unknown | 16 (3) 85 (16) 164 (30) 261 (48) 18 (3) | 12 (3) 53 (14) 119 (32) 170 (46) 13 (4) | 11 (4) 43 (17) 83 (33) 104 (42) 9 (4) |
| ECOG PS, n (%) 0/1 2–4 Unknown/missing | 366 (67) 64 (12) 114 (21) | 251 (68) 48 (13) 68 (19) | 170 (68) 31 (12) 49 (20) |
| Sidedness of tumor, n (%) b Left Right Other/missing | 356 (65) 152 (28) 36 (7) | 249 (68) 95 (26) 23 (6) | 176 (70) 62 (25) 12 (5) |
| Sites of metastases, n (%) c Liver ± other sites Non-liver only Missing | 333 (61) 209 (38) 2 (<1) | 212 (58) 153 (42) 2 (<1) | 138 (55) 110 (44) 2 (1) |
| Practice type, n (%) Academic Community Academic and community | 53 (10) 476 (88) 15 (3) | 35 (10) 319 (87) 13 (4) | 27 (11) 213 (85) 10 (4) |
| Received prior bevacizumab treatment, n (%) | 367 (67) | 231 (63) | 149 (60) |
| Received prior fluorouracil treatment, n (%) | 431 (79) | 280 (76) | 190 (76) |
| Initiated regorafenib treatment between 2013 and 2018, n (%) | 219 (40) | 148 (40) | 98 (39) |
| Initiated regorafenib treatment between 2019 and 2022, n (%) | 325 (60) | 219 (60) | 152 (61) |
| Biomarker/ Laboratory Test | LTR4 (n = 544) | LTR5 (n = 367) | LTR6 (n = 250) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDH levels, n (%) Low: <300 IU/L High: ≥300 IU/L Unknown/missing Within normal reference range a Within abnormal reference range a Unknown/missing | 74 (14) 34 (6) 436 (80) 62 (11) 44 (8) 438 (81) | 56 (15) 20 (5) 291 (79) 49 (13) 26 (7) 292 (80) | 36 (14) 14 (6) 200 (80) 33 (13) 16 (6) 201 (80) |
| Median CEA levels (IQR), ng/mL b | 36 (8–152) | 32 (8–139) | 29 (7–108) |
| BRAF mutation status, n (%) Positive Negative Unknown/missing | 20 (4) 335 (62) 189 (35) | 13 (4) 223 (61) 131 (36) | 10 (4) 146 (58) 94 (38) |
| KRAS mutation status, n (%) Positive Negative Unknown/missing | 134 (25) 107 (20) 303 (56) | 89 (24) 80 (22) 198 (54) | 55 (22) 63 (25) 132 (53) |
| MMR/MSI status, n (%) MSS dMMR/MSI-H Unknown/missing | 379 (70) 9 (2) 156 (29) | 253 (69) 6 (2) 108 (29) | 168 (67) 6 (2) 76 (30) |
| Treatment Duration/ History Variable | LTR4 (n = 544) | LTR5 (n = 367) | LTR6 (n = 250) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median time to discontinuation of regorafenib treatment (95% CI), a months | 6.0 (5.7–6.3) | 7.4 (7.0–7.9) | 9.3 (8.6–10.1) |
| Median follow-up time from index date (IQR), months | 10.7 (7.2–17.2) | 13.0 (8.1–20.2) | 14.6 (9.9–22.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, R.D.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lunacsek, O.; Pisa, F.; Ostojic, H.; Peeters, M. Real-World Study of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Long-Term Response to Regorafenib in the USA. Cancers 2025, 17, 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193196
Kim RD, Pan X, Zhang Y, Lunacsek O, Pisa F, Ostojic H, Peeters M. Real-World Study of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Long-Term Response to Regorafenib in the USA. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193196
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Richard D., Xiaoyun Pan, Yiqiao Zhang, Orsolya Lunacsek, Federica Pisa, Helene Ostojic, and Marc Peeters. 2025. "Real-World Study of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Long-Term Response to Regorafenib in the USA" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193196
APA StyleKim, R. D., Pan, X., Zhang, Y., Lunacsek, O., Pisa, F., Ostojic, H., & Peeters, M. (2025). Real-World Study of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Long-Term Response to Regorafenib in the USA. Cancers, 17(19), 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193196







