Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Purpose
1.3. Overview of MPNs
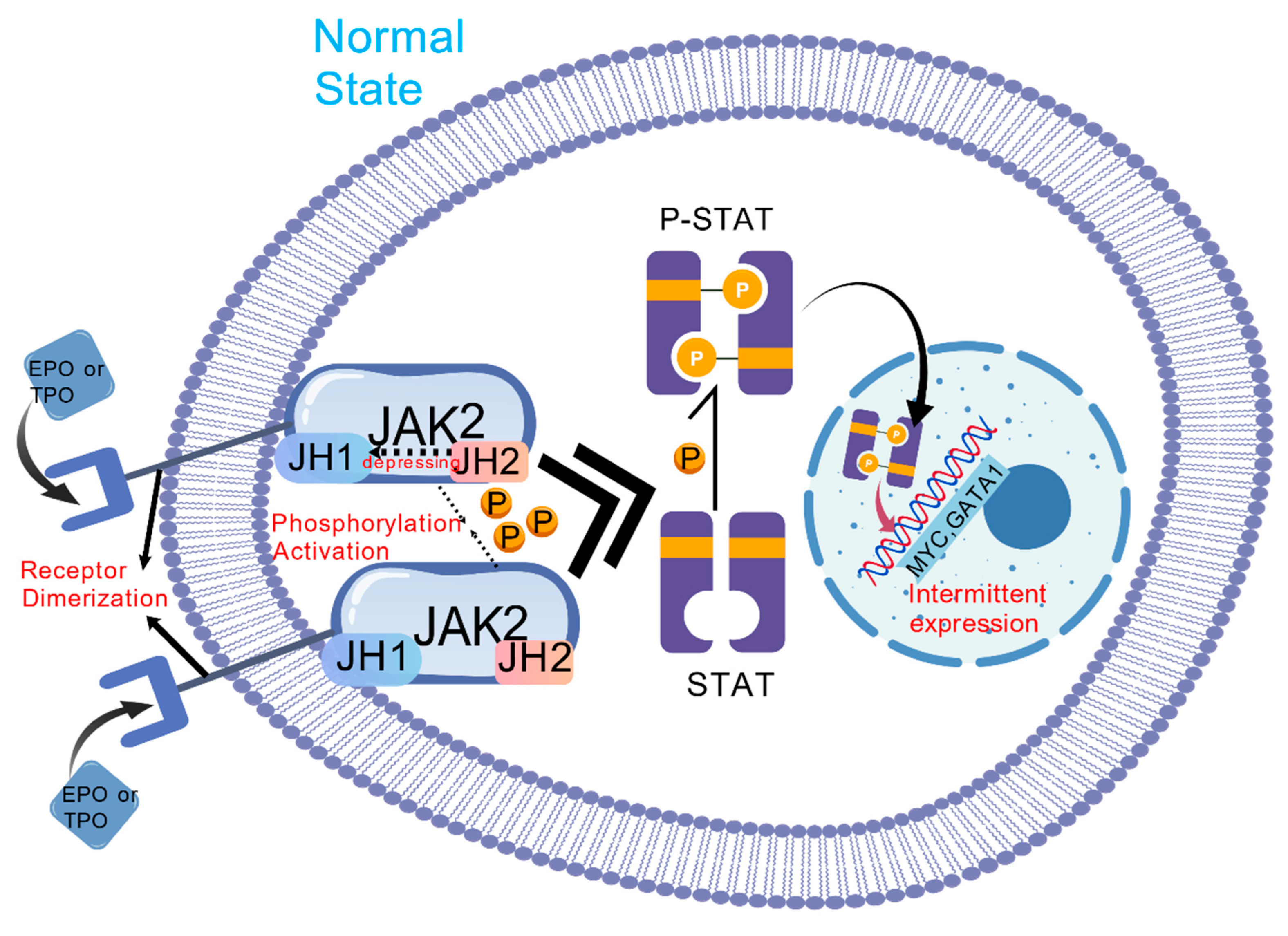
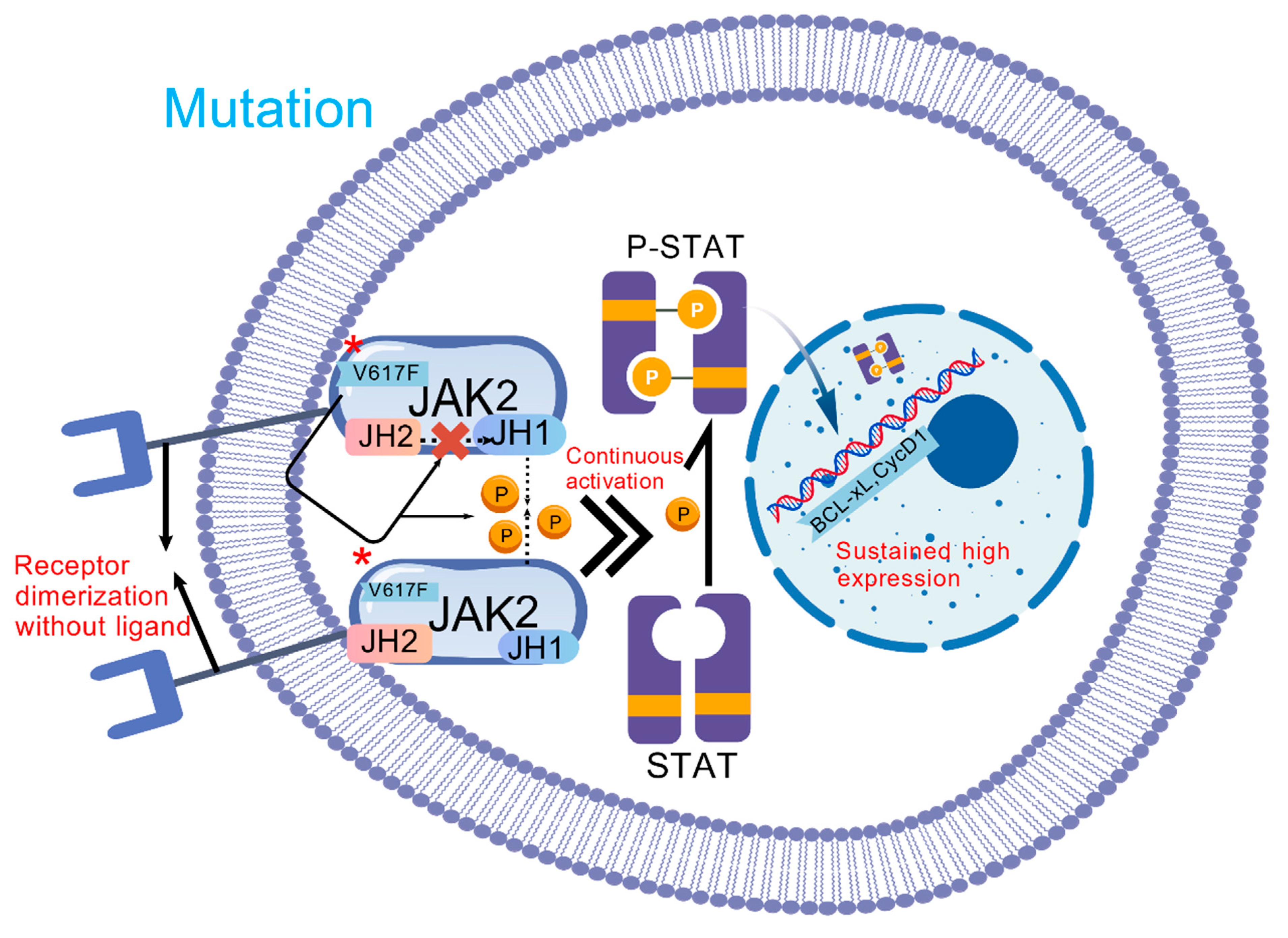
2. Pathogenesis and Molecular Mechanism
2.1. Clonal Hematopoiesis as a Precursor to MPNs
2.2. Driver Mutations
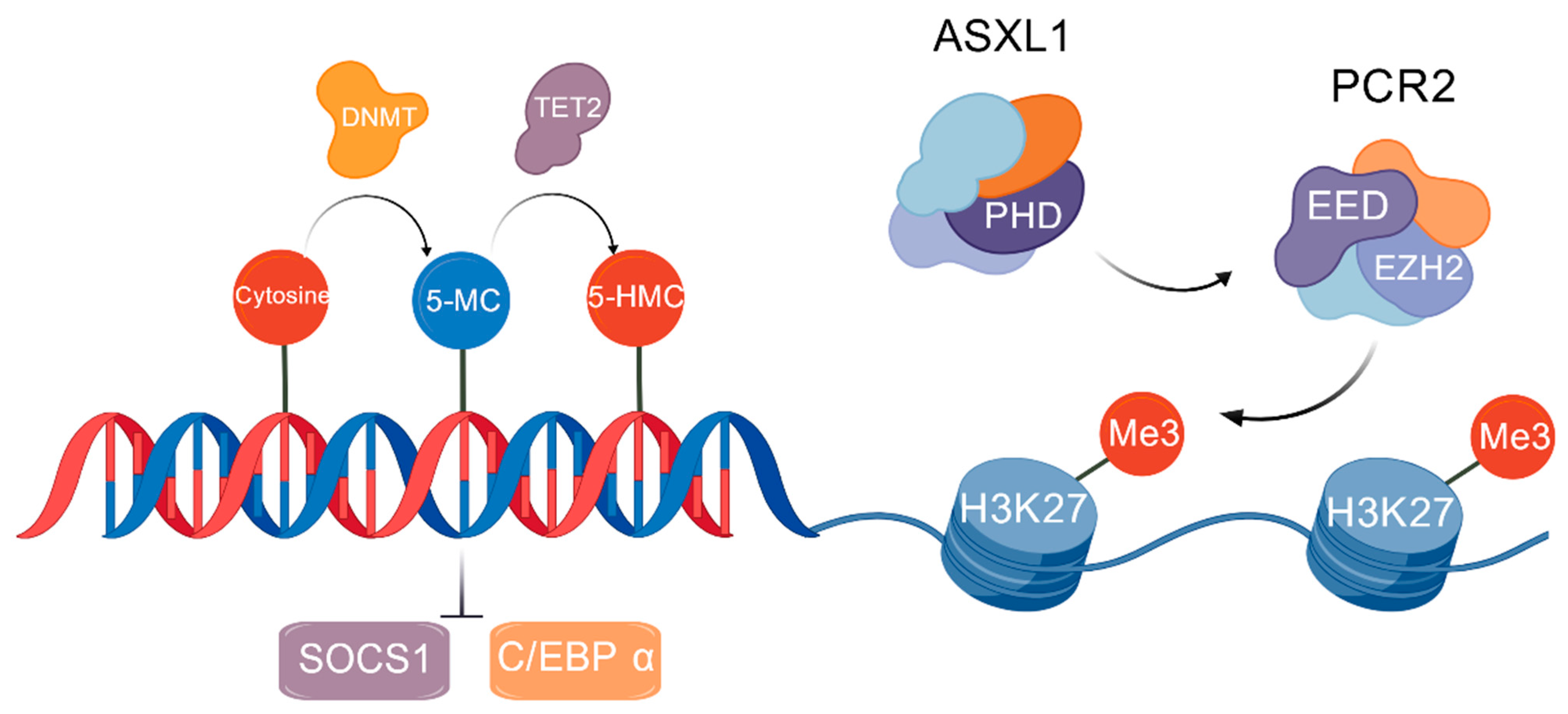
2.3. Epigenetic Changes
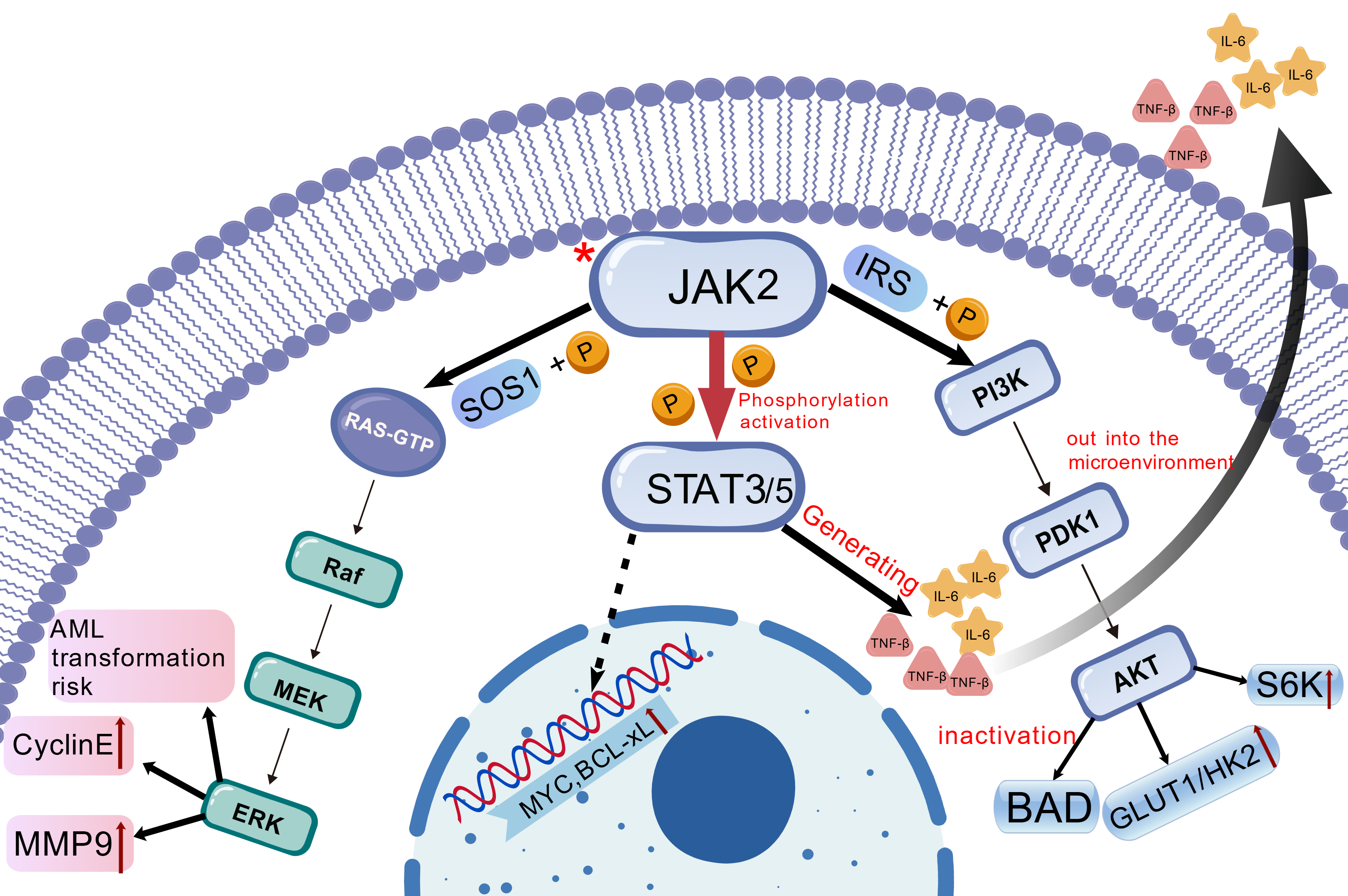
2.4. Dysregulation of Signaling Pathways
2.5. Nondriver Mutations
3. Diagnosis of MPN
3.1. PV
3.2. ET
3.3. MF
3.3.1. PMF
Pre-MF
Overt-PMF
Differential Diagnosis
3.3.2. SMF
4. Prognosis of MPN
4.1. Prognosis of PV
4.1.1. Thrombus Risk Stratification
4.1.2. Survival Prognosis Grouping
4.1.3. Post-PV Survival Prognosis Grouping
4.2. Prognosis of ET
4.2.1. Overall Survival Prognosis Judgment
4.2.2. Thrombotic Risk Prognosis Judgment
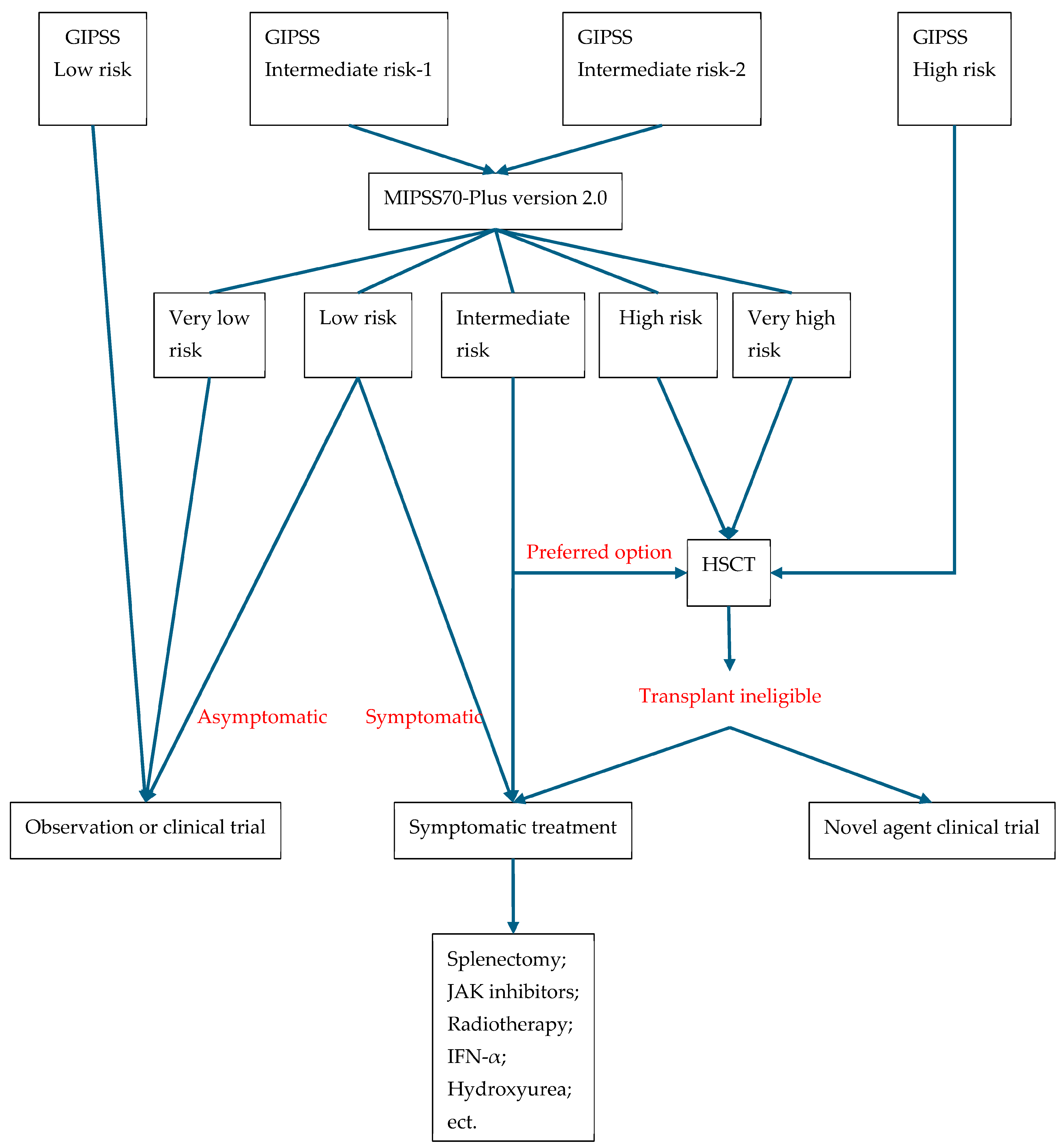
4.3. Prognosis of PMF
5. Treatment Modalities for MPN
5.1. PV
5.1.1. Traditional Treatment
5.1.2. New Treatments
5.2. ET
5.2.1. Risk-Adapted Therapy
5.2.2. Cytoreductive Treatment
5.2.3. Targeted Therapies
5.3. MF
5.3.1. Conventional Management
5.3.2. Novel Immunotherapies and Targeted Drugs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-HG | 2-Hydroxyglutarate |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| AP-1 | Activator Protein 1 |
| AS-PCR | Allele-specific PCR |
| ASXL1 | Additional Sex Combs Like 1 |
| AvWS | Acquired von Willebrand syndrome |
| BCL-XL | B-cell lymphoma-extra large |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| BMF | Bone marrow fibrosis |
| C/EBP α | CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Alpha |
| CALR | Calreticulin |
| CH | Clonal hematopoiesis |
| CHIP | Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential |
| CML | Chronic myeloid leukemia |
| CMML | Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia |
| CVF | Cardiovascular risk factor |
| DIPSS | Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System |
| DNMT3A | DNA Methyltransferase 3 Alpha |
| ELK1 | ETS Transcription Factor |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| ET | Essential Thrombocythemia |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 |
| GAS | Gamma-Interferon Activation Sequence |
| GATA1 | GATA Binding Protein 1 |
| GIPSS | Genetically inspired prognostic scoring system |
| GLUT1 | Glucose Transporter 1 |
| GTP | Guanosine Triphosphate |
| H3K27me3 | Histone H3 Lysine 27 Trimethylation |
| Hct | Hematocrit |
| HDAC2 | Histone Deacetylase 2 |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha |
| HK2 | Hexokinase 2 |
| HOXA9 | Homeobox A9 |
| HSCs | Hematopoietic stem cells |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| ICC | International Consensus Classification |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| IDH | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IPSET | International Prognostic Scoring System for Essential Thrombocythemia |
| IPSS | International Prognostic Scoring System |
| IRS | Insulin Receptor Substrate |
| IWG-PV | International Working Group for polycythemia vera |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JAK-STAT | Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| JH1 | JAK Homology 1 (Kinase domain) |
| JH2 | JAK Homology 2 (Pseudokinase domain) |
| LSD1 | lysine-specific demethylase |
| MCL-1 | Myeloid Cell Leukemia Sequence 1 |
| MDM2 | Murine double minute 2 |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells |
| MEK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MF | Myelofibrosis |
| MIPSS | Mutation-enhanced international prognostic systems |
| miR-146a | MicroRNA-146a |
| miR-155 | MicroRNA-155 |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| MPL | Myeloproliferative leukemia virus |
| MPNs | Myeloproliferative neoplasms |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| mTORC1 | mTOR Complex 1 |
| MYSEC-PM | Myelofibrosis secondary to polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia |
| NF-E2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| PB | Peripheral blood |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PEG | Pegylated interferon α |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate |
| PMF | Primary myelofibrosis |
| PRC2 | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 |
| Pre-MF | Prefibrotic MF |
| PV | Polycythemia vera |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| RAF | Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma |
| RAS | Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| Ropeg | Ropeginterferon alfa-2b |
| SHIP1 | SH2 Domain Containing Inositol 5′-Phosphatase 1 |
| SMF | Secondary myelofibrosis |
| SOCS1 | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 |
| SOS1 | Son of Sevenless Homolog 1 |
| SRSF2 | Serine and Arginine Rich Splicing Factor 2 |
| STAT3/STAT5 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3/5 |
| TET2 | Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 2 |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptor |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TP53 | Tumor Protein 53 |
| TPO-R | Thrombopoietin Receptor |
| U2AF1 | U2 Small Nuclear RNA Auxiliary Factor 1 |
| ULK1 | Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1 |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Verma, T.; Papadantonakis, N.; Peker Barclift, D.; Zhang, L. Molecular Genetic Profile of Myelofibrosis: Implications in the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Advancements. Cancers 2024, 16, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, J.; Garcia, J.S.; Mullally, A. Biology and therapeutic targeting of molecular mechanisms in MPNs. Blood 2023, 141, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, R.F. How I diagnose and treat essential thrombocythemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2023, 44, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Galán, I.; Martín, I.; Ferrer, B.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C. Impact of molecular profiling on the management of patients with myelofibrosis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 109, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Larson, D.R.; Finke, C.; Wassie, E.A.; Pieri, L.; Gangat, N.; Fjerza, R.; Belachew, A.A.; Lasho, T.L.; et al. Long-term survival and blast transformation in molecularly annotated essential thrombocythemia, polycythemia vera, and myelofibrosis. Blood 2014, 124, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, J.; Chatain, N.; Sofias, A.M.; Lammers, T.; Koschmieder, S. Progression of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Saeed, L.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Pardanani, A.; Gangat, N. Application of current prognostic models for primary myelofibrosis in the setting of post-polycythemia vera or post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2851–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensma, D.P.; Bejar, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Lindsley, R.C.; Sekeres, M.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ebert, B.L. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2015, 126, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Jasiakiewicz, J.; Greer, V.; Hindley, A.; McDowell, K.; Devlin, E.; Clarke, K.; Buckley, F.; Crean, C.; McGimpsey, J.; et al. Association between JAK2(V617F) variable allele frequency and risk of thrombotic events in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 2883–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Kao, H.W.; Kuo, M.C.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, Y.J.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, T.H.; Shih, L.Y. Genetic Evolution from Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms to Acute Myeloid Leukemia: An Analysis of Forty-Six Paired Samples. Blood 2023, 142, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, L.; Skov, V.; Larsen, M.K.; Boklund, T.I.; Andersen, M.; Kefala, M.; Knudsen, T.A.; Schjellerup Eickhardt-Dalbøge, C.; Stiehl, T.; Gudmand-Høyer, J.; et al. Case Report: First longitudinal study of a patient with CALR positive clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential developing into pre-fibrotic myelofibrosis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1176173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frawley, T.; O’Brien, C.P.; Conneally, E.; Vandenberghe, E.; Percy, M.; Langabeer, S.E.; Haslam, K. Development of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Assay to Detect Diagnostically Relevant Mutations of JAK2, CALR, and MPL in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2018, 22, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrao, R.D.; Wallweber, H.J.; Lupardus, P.J. Receptor-mediated dimerization of JAK2 FERM domains is required for JAK2 activation. eLife 2018, 7, e38089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainchenker, W.; Kralovics, R. Genetic basis and molecular pathophysiology of classical myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2017, 129, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.C.; Wang, S.X.; Li, F. Cytokines and Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Current Research Status from Mechanism to Clinic--Review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2024, 32, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangalia, J.; Massie, C.E.; Baxter, E.J.; Nice, F.L.; Gundem, G.; Wedge, D.C.; Avezov, E.; Li, J.; Kollmann, K.; Kent, D.G.; et al. Somatic CALR mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms with nonmutated JAK2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Obeng, E.A. Noncoding rules of survival: Epigenetic regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1273046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Han, R.; Gan, R. The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in Haematological Neoplasms. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shtylla, B.; Chou, T. Order-of-Mutation Effects on Cancer Progression: Models for Myeloproliferative Neoplasm. Bull. Math. Biol. 2024, 86, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, O.; Adli, M.; LaFave, L.M.; Gao, J.; Hricik, T.; Shih, A.H.; Pandey, S.; Patel, J.P.; Chung, Y.R.; Koche, R.; et al. ASXL1 mutations promote myeloid transformation through loss of PRC2-mediated gene repression. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A novel target for cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Labbaye, C. miR-146 and miR-155: Two Key Modulators of Immune Response and Tumor Development. Noncoding RNA 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivalioti, M.M.; Bartholdy, B.A.; Pradhan, K.; Bhagat, T.D.; Zintiridou, A.; Jeong, J.J.; Thiruthuvanathan, V.J.; Pujato, M.; Paranjpe, A.; Zhang, C.; et al. PU.1-Dependent Enhancer Inhibition Separates Tet2-Deficient Hematopoiesis from Malignant Transformation. Blood Cancer Discov. 2022, 3, 444–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Oetjen, K.A.; Wang, T.; Xu, H.; Abou-Ezzi, G.; Krambs, J.R.; Uttarwar, S.; Duncavage, E.J.; Link, D.C. TGF-β signaling in myeloproliferative neoplasms contributes to myelofibrosis without disrupting the hematopoietic niche. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.; Vasireddy, S.; Gowin, K.; Amaraneni, A. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Contemporary Review and Molecular Landscape. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusa, A.; Mouton, C.; Pecquet, C.; Herman, M.; Constantinescu, S.N. JAK2 V617F constitutive activation requires JH2 residue F595: A pseudokinase domain target for specific inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, G.; McMullin, M.F.; Mills, K. Molecular pathogenesis of the myeloproliferative neoplasms. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Carter-Su, C.; Myers, M.G., Jr.; Rui, L. SH2B1 enhances leptin signaling by both Janus kinase 2 Tyr813 phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2270–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebratu, Y.; Tesfaigzi, Y. How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenonos, K.; Kyprianou, K. RAS signaling pathways, mutations and their role in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 5, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Qi, J.; Babon, J.J.; Cao, L.; Fan, G.; Lang, J.; Zhang, J.; Mi, P.; Kobe, B.; Wang, F. The JAK-STAT pathway: From structural biology to cytokine engineering. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Verstovsek, S. Molecular pathways: Jak/STAT pathway: Mutations, inhibitors, and resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, G.N.; Li, W. HIF-1α pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, B.; Chen, Q. RAS signaling and immune cells: A sinister crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marneth, A.E.; Mullally, A. The Molecular Genetics of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a034876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, J.; Khalid, K.; Yadav, J.; Almanie, A.H.; Mehta, K.A.; Al Hennawi, H.; Boddeti, N.L.; Campos, V.Y.M.; Jean-Charles, G. JAK2 and TET2 Mutation in Polycythemia Vera. Cureus 2021, 13, e17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, E.; Trotti, C.; Vanni, D.; Casetti, I.C.; Pietra, D.; Sant’Antonio, E. The Genetic Basis of Primary Myelofibrosis and Its Clinical Relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, P.; Liu, D.; Ganesan, S.; Lauret, E.; Maslah, N.; Parietti, V.; Zhang, W.; Meignin, V.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Cassinat, B.; et al. Genomic and functional impact of Trp53 inactivation in JAK2V617F myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viny, A.D.; Levine, R.L. Genetics of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, M.M.; Rau, A.; Overkamp, M.; Flaadt, T.; Bonzheim, I.; Schürch, C.M.; Federmann, B.; Dirnhofer, S.; Fend, F.; Tzankov, A. Molecular Progression of Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Study on Sequential Bone Marrow Biopsies. Cancers 2021, 13, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslah, N.; Benajiba, L.; Giraudier, S.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Cassinat, B. Clonal architecture evolution in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: From a driver mutation to a complex heterogeneous mutational and phenotypic landscape. Leukemia 2023, 37, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque Paz, D.; Riou, J.; Verger, E.; Cassinat, B.; Chauveau, A.; Ianotto, J.C.; Dupriez, B.; Boyer, F.; Renard, M.; Mansier, O.; et al. Genomic analysis of primary and secondary myelofibrosis redefines the prognostic impact of ASXL1 mutations: A FIM study. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irino, T.; Uemura, M.; Yamane, H.; Umemura, S.; Utsumi, T.; Kakazu, N.; Shirakawa, T.; Ito, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kinoshita, K. JAK2 V617F-dependent upregulation of PU.1 expression in the peripheral blood of myeloproliferative neoplasm patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aujla, A.; Linder, K.; Iragavarapu, C.; Karass, M.; Liu, D. SRSF2 mutations in myelodysplasia/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Meira, A.; Norfo, R.; Wen, S.; Chédeville, A.L.; Rahman, H.; O’Sullivan, J.; Wang, G.; Louka, E.; Kretzschmar, W.W.; Paterson, A.; et al. Single-cell multi-omics identifies chronic inflammation as a driver of TP53-mutant leukemic evolution. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, T.; Thiele, J.; Gisslinger, H.; Finazzi, G.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Tefferi, A. The 2016 revision of WHO classification of myeloproliferative neoplasms: Clinical and molecular advances. Blood Rev. 2016, 30, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Khan, S.N.; Umair, M.; Khan, A.A.; Liu, X.; Khattak, A.A.; Yousafzai, Y.M. Development of a Real-Time qPCR Assay for Detection of Common MPL Mutations in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNS). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, V. Next Generation Sequencing in MPNs. Lessons from the Past and Prospects for Use as Predictors of Prognosis and Treatment Responses. Cancers 2020, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Barbui, T. Polycythemia vera: 2024 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, F.P.; Petrides, P.E. Congenital and acquired polycythemias. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2008, 105, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurlo, A.; Cattaneo, D.; Bucelli, C.; Baldini, L. New Perspectives on Polycythemia Vera: From Diagnosis to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Barbui, T. Essential thrombocythemia: 2024 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 697–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florena, A.M.; Tripodo, C.; Iannitto, E.; Porcasi, R.; Ingrao, S.; Franco, V. Value of bone marrow biopsy in the diagnosis of essential thrombocythemia. Haematologica 2004, 89, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncavage, E.J.; Bagg, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; DiNardo, C.D.; Godley, L.A.; Iacobucci, I.; Jaiswal, S.; Malcovati, L.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Patel, K.P.; et al. Genomic profiling for clinical decision making in myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 2228–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, G.; Viscovo, M. Cytomorphology of normal, reactive, dysmorphic, and dysplastic megakaryocytes in bone marrow aspirates. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43 (Suppl. S1), 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianelli, U.; Vener, C.; Raviele, P.R.; Moro, A.; Savi, F.; Annaloro, C.; Somalvico, F.; Radaelli, F.; Franco, V.; Deliliers, G.L. Essential thrombocythemia or chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis? A single-center study based on hematopoietic bone marrow histology. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combaluzier, S.; Quessada, J.; Abbou, N.; Arcani, R.; Tichadou, A.; Gabert, J.; Costello, R.; Loosveld, M.; Venton, G.; Berda-Haddad, Y. Cytological Diagnosis of Classic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms at the Age of Molecular Biology. Cells 2023, 12, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, M.M.; Tefferi, A. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: 2016 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, F.; Mora, B. Myelofibrosis. Blood 2023, 141, 1954–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Group of the Hematology Society of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of polycythemia vera (2022). Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2022, 43, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullin, M.F.; Harrison, C.N.; Ali, S.; Cargo, C.; Chen, F.; Ewing, J.; Garg, M.; Godfrey, A.; S, S.K.; McLornan, D.P.; et al. A guideline for the diagnosis and management of polycythaemia vera. A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Rumi, E.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Vaidya, R.; Cazzola, M.; Rambaldi, A.; et al. Survival and prognosis among 1545 patients with contemporary polycythemia vera: An international study. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Giorgino, T.; Mora, B.; Guglielmelli, P.; Rumi, E.; Maffioli, M.; Rambaldi, A.; Caramella, M.; Komrokji, R.; Gotlib, J.; et al. A clinical-molecular prognostic model to predict survival in patients with post polycythemia vera and post essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2726–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Thiele, J.; Girodon, F.; Rumi, E.; Carobbio, A.; Gisslinger, H.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Ruggeri, M.; Randi, M.L.; Gangat, N.; et al. A prognostic model to predict survival in 867 World Health Organization-defined essential thrombocythemia at diagnosis: A study by the International Working Group on Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2012, 120, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscocco, G.G.; Guglielmelli, P.; Gangat, N.; Rossi, E.; Mannarelli, C.; Betti, S.; Maccari, C.; Ramundo, F.; Jadoon, Y.; Gesullo, F.; et al. Clinical and molecular predictors of fibrotic progression in essential thrombocythemia: A multicenter study involving 1607 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Coltro, G.; Finke, C.M.; Loscocco, G.G.; Sordi, B.; Szuber, N.; Rotunno, G.; Pacilli, A.; et al. Mutation-enhanced international prognostic systems for essential thrombocythaemia and polycythaemia vera. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carobbio, A.; Ferrari, A.; Masciulli, A.; Ghirardi, A.; Barosi, G.; Barbui, T. Leukocytosis and thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, T.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; De Stefano, V.; Betti, S.; Rambaldi, A.; Rumi, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; et al. Practice-relevant revision of IPSET-thrombosis based on 1019 patients with WHO-defined essential thrombocythemia. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobbio, A.; Thiele, J.; Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Bertozzi, I.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Antonioli, E.; et al. Risk factors for arterial and venous thrombosis in WHO-defined essential thrombocythemia: An international study of 891 patients. Blood 2011, 117, 5857–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Finazzi, G.; Carobbio, A.; Thiele, J.; Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Bertozzi, I.; et al. Development and validation of an International Prognostic Score of thrombosis in World Health Organization-essential thrombocythemia (IPSET-thrombosis). Blood 2012, 120, 5128–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Wolf, D.; Sormann, S.; Forjan, E.; Schimetta, W.; Gisslinger, B.; Heibl, S.; Krauth, M.T.; Thiele, J.; Ruckser, R.; et al. Impact of platelets on major thrombosis in patients with a normal white blood cell count in essential thrombocythemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.F.; Li, H.Y.; Xue, F.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, R.C. Clinical evaluation of the revised International Prognostic Score of Thrombosis for essential thrombocythemia (IPSET-thrombosis) in a cohort of 746 Chinese adult patients. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2017, 38, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Cuevas, B.; Velez, P.; Noya, S.; Caballero-Navarro, G.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Carbonell, S.; Pérez-Encinas, M.; Gómez-Casares, M.T.; Pérez-López, R.; et al. Application of IPSET-thrombosis in 1366 Patients Prospectively Followed From the Spanish Registry of Essential Thrombocythemia. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A. Primary myelofibrosis: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerds, A.T.; Gotlib, J.; Ali, H.; Bose, P.; Dunbar, A.; Elshoury, A.; George, T.I.; Gundabolu, K.; Hexner, E.; Hobbs, G.S.; et al. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 1033–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.; Dupriez, B.; Pereira, A.; Passamonti, F.; Reilly, J.T.; Morra, E.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Mesa, R.A.; Demory, J.L.; Barosi, G.; et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2009, 113, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Cervantes, F.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Morra, E.; Rumi, E.; Pereira, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Pungolino, E.; Caramella, M.; Maffioli, M.; et al. A dynamic prognostic model to predict survival in primary myelofibrosis: A study by the IWG-MRT (International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment). Blood 2010, 115, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangat, N.; Caramazza, D.; Vaidya, R.; George, G.; Begna, K.; Schwager, S.; Van Dyke, D.; Hanson, C.; Wu, W.; Pardanani, A.; et al. DIPSS plus: A refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for primary myelofibrosis that incorporates prognostic information from karyotype, platelet count, and transfusion status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Rotunno, G.; Mudireddy, M.; Mannarelli, C.; Nicolosi, M.; Pacilli, A.; Pardanani, A.; Rumi, E.; Rosti, V.; et al. MIPSS70: Mutation-Enhanced International Prognostic Score System for Transplantation-Age Patients with Primary Myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Gangat, N.; Ketterling, R.P.; Pardanani, A.; Vannucchi, A.M. MIPSS70+ Version 2.0: Mutation and Karyotype-Enhanced International Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Nicolosi, M.; Mannelli, F.; Mudireddy, M.; Bartalucci, N.; Finke, C.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; et al. GIPSS: Genetically inspired prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuykendall, A.T.; Talati, C.; Padron, E.; Sweet, K.; Sallman, D.; List, A.F.; Lancet, J.E.; Komrokji, R.S. Genetically inspired prognostic scoring system (GIPSS) outperforms dynamic international prognostic scoring system (DIPSS) in myelofibrosis patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameshek, W. The case for phlebotomy in polycythemia vera. Blood 1968, 32, 488–491. [Google Scholar]
- Ramundo, F.; Rossi, E.; Peris, K.; Pontecorvi, A.; Sani, G.; Betti, S.; Marietta, M.; De Stefano, V. Improving the management of Polycythemia Vera patients eligible for cytoreduction: Report of a multidisciplinary advisory board. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2025, 41, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, D.; Kremyanskaya, M.; Mascarenhas, J.; Hoffman, R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Polycythemia Vera: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioli, R.; Finazzi, G.; Specchia, G.; Cacciola, R.; Cavazzina, R.; Cilloni, D.; De Stefano, V.; Elli, E.; Iurlo, A.; Latagliata, R.; et al. Cardiovascular events and intensity of treatment in polycythemia vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Finazzi, M.C.; Finazzi, G. Front-line therapy in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood Rev. 2012, 26, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, L.R.; Balcerzak, S.P.; Berk, P.D.; Berlin, N.I.; Donovan, P.B.; Dresch, C.; Ellis, J.T.; Goldberg, J.D.; Landaw, S.A.; Laszlo, J.; et al. Influence of therapy on causes of death in polycythemia vera. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1981, 94, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Michiels, J.J.; Berneman, Z.; Schroyens, W.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Lindemans, J.; Neumann, H.A.; van Vliet, H.H. Platelet-mediated erythromelalgic, cerebral, ocular and coronary microvascular ischemic and thrombotic manifestations in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: A distinct aspirin-responsive and coumadin-resistant arterial thrombophilia. Platelets 2006, 17, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Smock, K.J.; Divgi, A.B. Polycythemia vera-associated acquired von Willebrand syndrome despite near-normal platelet count. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameshek, W. Some speculations on the myeloproliferative syndromes. Blood 1951, 6, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.A.; Tefferi, A. Thrombosis and haemorrhage in polycythaemia vera and essential thrombocythaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 128, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruchtman, S.M.; Mack, K.; Kaplan, M.E.; Peterson, P.; Berk, P.D.; Wasserman, L.R. From efficacy to safety: A Polycythemia Vera Study group report on hydroxyurea in patients with polycythemia vera. Semin. Hematol. 1997, 34, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barosi, G.; Tefferi, A.; Besses, C.; Birgegard, G.; Cervantes, F.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Griesshammer, M.; Harrison, C.; Hehlmann, R.; et al. Clinical end points for drug treatment trials in BCR-ABL1-negative classic myeloproliferative neoplasms: Consensus statements from European LeukemiaNET (ELN) and Internation Working Group-Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment (IWG-MRT). Leukemia 2015, 29, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstovsek, S.; Pemmaraju, N.; Reaven, N.L.; Funk, S.E.; Woody, T.; Valone, F.; Gupta, S. Real-world treatments and thrombotic events in polycythemia vera patients in the USA. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemmaraju, N.; Gerds, A.T.; Yu, J.; Parasuraman, S.; Shah, A.; Xi, A.; Kumar, S.; Scherber, R.M.; Verstovsek, S. Thrombotic events and mortality risk in patients with newly diagnosed polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia. Leuk. Res. 2022, 115, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiladjian, J.J.; Cassinat, B.; Chevret, S.; Turlure, P.; Cambier, N.; Roussel, M.; Bellucci, S.; Grandchamp, B.; Chomienne, C.; Fenaux, P. Pegylated interferon-alfa-2a induces complete hematologic and molecular responses with low toxicity in polycythemia vera. Blood 2008, 112, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, R.T. Interferon alfa: Effects of long-term treatment for polycythemia vera. Semin. Hematol. 1997, 34, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson, J.; Hasselbalch, H.; Bruserud, O.; Temerinac, S.; Brandberg, Y.; Merup, M.; Linder, O.; Bjorkholm, M.; Pahl, H.L.; Birgegard, G. A phase II trial of pegylated interferon alpha-2b therapy for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: Feasibility, clinical and biologic effects, and impact on quality of life. Cancer 2006, 106, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, R.T. Long-term effects of the treatment of polycythemia vera with recombinant interferon-alpha. Cancer 2006, 107, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Kantarjian, H.; Manshouri, T.; Luthra, R.; Estrov, Z.; Pierce, S.; Richie, M.A.; Borthakur, G.; Konopleva, M.; Cortes, J.; et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a yields high rates of hematologic and molecular response in patients with advanced essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5418–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewersdorf, J.P.; Giri, S.; Wang, R.; Podoltsev, N.; Williams, R.T.; Tallman, M.S.; Rampal, R.K.; Zeidan, A.M.; Stahl, M. Interferon alpha therapy in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunov, M.; Klisovic, R.B. Pegylated Interferons: Still a Major Player for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2025, 45, e473912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisà, E.; Cerrano, M.; Beggiato, E.; Benevolo, G.; Lanzarone, G.; Manzini, P.M.; Borchiellini, A.; Riera, L.; Boccadoro, M.; Ferrero, D. Can pegylated interferon improve the outcome of polycythemia vera patients? J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, X.W.; Li, Y.W.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lyu, X.D. [Clinical Value of Detecting ABL Kinase Domain Mutations in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Based on High-Throughput Sequencing Technology]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2024, 32, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lanikova, L.; Kim, S.J.; Papadopoulos, N.; Meznarich, J.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Parsegov, B.; Prchal, J.F.; Prchal, J.T. Novel germline JAK2(R715T) mutation causing PV-like erythrocytosis in 3 generations. Amelioration by Ropeg-Interferon. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Griesshammer, M.; Palandri, F.; Egyed, M.; Benevolo, G.; Devos, T.; Callum, J.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Sivgin, S.; Bensasson, C.; et al. Ruxolitinib for the treatment of inadequately controlled polycythaemia vera without splenomegaly (RESPONSE-2): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.N.; Nangalia, J.; Boucher, R.; Jackson, A.; Yap, C.; O’Sullivan, J.; Fox, S.; Ailts, I.; Dueck, A.C.; Geyer, H.L.; et al. Ruxolitinib Versus Best Available Therapy for Polycythemia Vera Intolerant or Resistant to Hydroxycarbamide in a Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3534–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Martínez-Avilés, L.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Antelo, M.L.; Burgaleta, C.; Mata, M.I.; Xicoy, B.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Gómez-Casares, M.T.; et al. Busulfan in patients with polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia refractory or intolerant to hydroxyurea. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.; Harrison, C.; Forsyth, C.; Bennett, M.; Stevenson, W.; Hounsell, J.; Ratnasingam, S.; Ritchie, D.; Ross, D.M.; Grigg, A. Busulfan is effective second-line therapy for older patients with Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms intolerant of or unresponsive to hydroxyurea. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Thiele, J.; Passamonti, F.; Rumi, E.; Boveri, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Rodeghiero, F.; d’Amore, E.S.; Randi, M.L.; Bertozzi, I.; et al. Survival and disease progression in essential thrombocythemia are significantly influenced by accurate morphologic diagnosis: An international study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, G.; Caruso, V.; Marchioli, R.; Capnist, G.; Chisesi, T.; Finelli, C.; Gugliotta, L.; Landolfi, R.; Kutti, J.; Gisslinger, H.; et al. Acute leukemia in polycythemia vera: An analysis of 1638 patients enrolled in a prospective observational study. Blood 2005, 105, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Hakobyan, N.; Wang, J.C. Role of Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) Therapy in Philadelphia Negative Classic Myeloproliferative Neoplasm (MPN): Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstovsek, S.; Yu, J.; Scherber, R.M.; Verma, S.; Dieyi, C.; Chen, C.C.; Parasuraman, S. Changes in the incidence and overall survival of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms between 2002 and 2016 in the United States. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulard, O.; Mehta, J.; Fryzek, J.; Olivares, R.; Iqbal, U.; Mesa, R.A. Epidemiology of myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, and polycythemia vera in the European Union. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 92, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.N.; Bareford, D.; Butt, N.; Campbell, P.; Conneally, E.; Drummond, M.; Erber, W.; Everington, T.; Green, A.R.; Hall, G.W.; et al. Guideline for investigation and management of adults and children presenting with a thrombocytosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 352–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Tefferi, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Passamonti, F.; Silver, R.T.; Hoffman, R.; Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Hehlmann, R.; et al. Philadelphia chromosome-negative classical myeloproliferative neoplasms: Revised management recommendations from European LeukemiaNet. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, A.L.; Green, A.C.; Harrison, C.N. Essential thrombocythemia: Challenges in clinical practice and future prospects. Blood 2023, 141, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Pereira, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Arellano-Rodrigo, E.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Samah, A.; Griesshammer, M.; Kerguelen, A.; Andreasson, B.; et al. Antiplatelet therapy versus observation in low-risk essential thrombocythemia with a CALR mutation. Haematologica 2016, 101, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, B.; Tosetto, A.; Betti, S.; Soldati, D.; Petrucci, G.; Rossi, E.; Timillero, A.; Cavalca, V.; Porro, B.; Iurlo, A.; et al. A randomized double-blind trial of 3 aspirin regimens to optimize antiplatelet therapy in essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2020, 136, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, N.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Antman, E.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Clark, C.B.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Kahi, C.J.; Laine, L.; et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 Expert Consensus Document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: A focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation 2010, 122, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.J.; Scott, L.M.; Buck, G.; Wheatley, K.; East, C.L.; Marsden, J.T.; Duffy, A.; Boyd, E.M.; Bench, A.J.; Scott, M.A.; et al. Definition of subtypes of essential thrombocythaemia and relation to polycythaemia vera based on JAK2 V617F mutation status: A prospective study. Lancet 2005, 366, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Natelson, E.; Rice, L. Successful long-term treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms with combination of hydroxyurea and anagrelide. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S2), S300–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adda, M.; Micheletti, M.; Drera, M.; Ferrari, S.; Rossi, G. The combined use of hydroxyurea and anagrelide allows satisfactory hematologic control in patients with chronic myeloproliferative disorders and thrombocytosis: A report on 13 patients with poor tolerance to hydroxyurea monotherapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 2216–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliotta, L.; Besses, C.; Griesshammer, M.; Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Coll, R.; Smith, J.; Abhyankar, B.; Birgegård, G. Combination therapy of hydroxycarbamide with anagrelide in patients with essential thrombocythemia in the evaluation of Xagrid(R) efficacy and long-term safety study. Haematologica 2014, 99, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Prchal, J.T.; Rambaldi, A.; Berenzon, D.; Yacoub, A.; Harrison, C.N.; McMullin, M.F.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Ewing, J.; et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of interferon-α vs hydroxyurea in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2022, 139, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiatt, J.B.; Sandborg, H.; Garrison, S.M.; Arnold, H.U.; Liao, S.Y.; Norton, J.P.; Friesen, T.J.; Wu, F.; Sutherland, K.D.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; et al. Inhibition of LSD1 with Bomedemstat Sensitizes Small Cell Lung Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Blockade and T-Cell Killing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4551–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienhoff, H.Y., Jr.; Gill, H. Bomedemstat as an investigative treatment for myeloproliferative neoplasms. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerlocher, G.M.; Oppliger Leibundgut, E.; Ottmann, O.G.; Spitzer, G.; Odenike, O.; McDevitt, M.A.; Röth, A.; Daskalakis, M.; Burington, B.; Stuart, M.; et al. Telomerase Inhibitor Imetelstat in Patients with Essential Thrombocythemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, T.; Zeiser, R. The role of the MDM2/p53 axis in antitumor immune responses. Blood 2024, 143, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallis, R.M.; Podoltsev, N.A. Emerging agents and regimens for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Bacigalupo, A. 2021 Update on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for myelofibrosis: A review of current data and applications on risk stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perram, J.; Ross, D.M.; McLornan, D.; Gowin, K.; Kröger, N.; Gupta, V.; Lewis, C.; Gagelmann, N.; Hamad, N. Innovative strategies to improve hematopoietic stem cell transplant outcomes in myelofibrosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Pereira, A.; Kröger, N.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Finke, J.; Beelen, D.; de Witte, M.; Wilson, K.; Platzbecker, U.; Sengeloev, H.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in older myelofibrosis patients: A study of the chronic malignancies working party of EBMT and the Spanish Myelofibrosis Registry. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, J.B.; Beuscart, J.B.; Robin, M.; Mohty, M.; Barraco, F.; Chevallier, P.; Marchand, T.; Rubio, M.T.; Charbonnier, A.; Blaise, D.; et al. Splenectomy before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: A French nationwide study. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Zine, M.; Chevret, S.; Meignin, V.; Munoz-Bongrand, N.; Moatti, H.; Xhaard, A.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Peffault de Latour, R.; Sarfati, E.; et al. The Impact of Splenectomy in Myelofibrosis Patients before Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017, 23, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverelli, N.; Mauff, K.; Kröger, N.; Robin, M.; Beelen, D.; Beauvais, D.; Chevallier, P.; Mohty, M.; Passweg, J.; Rubio, M.T.; et al. Impact of spleen size and splenectomy on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: A retrospective analysis by the chronic malignancies working party on behalf of European society for blood and marrow transplantation (EBMT). Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, N.; Sbianchi, G.; Sirait, T.; Wolschke, C.; Beelen, D.; Passweg, J.; Robin, M.; Vrhovac, R.; Helbig, G.; Sockel, K.; et al. Impact of prior JAK-inhibitor therapy with ruxolitinib on outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: A study of the CMWP of EBMT. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3551–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Porcher, R.; Orvain, C.; Bay, J.O.; Barraco, F.; Huynh, A.; Charbonnier, A.; Forcade, E.; Chantepie, S.; Bulabois, C.; et al. Ruxolitinib before allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation in patients with myelofibrosis on behalf SFGM-TC and FIM groups. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 1888–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Silverstein, M.N.; Noël, P. Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia. Semin. Oncol. 1995, 22, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.; Mesa, R.; Barosi, G. New and old treatment modalities in primary myelofibrosis. Cancer J. 2007, 13, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Trillos, A.; Gaya, A.; Maffioli, M.; Arellano-Rodrigo, E.; Calvo, X.; Díaz-Beyá, M.; Cervantes, F. Efficacy and tolerability of hydroxyurea in the treatment of the hyperproliferative manifestations of myelofibrosis: Results in 40 patients. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Waltzman, R.; Stalbovskaya, V.; McQuitty, M.; Hunter, D.S.; Levy, R.; Knoops, L.; et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Mesa, R.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Schroeder, G.; Silverstein, M.N. Splenectomy in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia: A single-institution experience with 223 patients. Blood 2000, 95, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudireddy, M.; Gangat, N.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Ashrani, A.A.; Pardanani, A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Tefferi, A. Early thrombotic events and preemptive systemic anticoagulation following splenectomy for myelofibrosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, E235–E238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, R.A.; Begna, K.H.; Al-Kali, A.; Hogan, W.J.; Litzow, M.R.; Pardanani, A.; Tefferi, A. Momelotinib treatment-emergent neuropathy: Prevalence, risk factors and outcome in 100 patients with myelofibrosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, S.; Regimbeau, M.; Jego, G.; Garrido, C.; Girodon, F.; Hermetet, F. Heat Shock Proteins and PD-1/PD-L1 as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancers 2020, 12, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, X. Cytokines frequently implicated in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cytokine X 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, L.; Li Volti, G.; Giallongo, C.; Spampinato, M.; Barbagallo, I.; Di Rosa, M.; Romano, A.; Avola, R.; Tibullo, D.; Palumbo, G.A. The Role of Inflammation and Inflammasome in Myeloproliferative Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, M.; Mitrović-Ajtić, O.; Beleslin-Čokić, B.; Djikić, D.; Subotički, T.; Diklić, M.; Leković, D.; Gotić, M.; Mossuz, P.; Čokić, V.P. TLR4 and RAGE conversely mediate pro-inflammatory S100A8/9-mediated inhibition of proliferation-linked signaling in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandrán, J.C.; Lasry, A.; Aifantis, I. The Role of Inflammation in the Initiation and Progression of Myeloid Neoplasms. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023, 4, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.A.C.; Fowles, J.S.; Zhou, A.; Oh, S.T. Inflammatory Pathophysiology as a Contributor to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira, A.B.A.; Kong, T.; Snyder, S.C.; Fulbright, M.C.; Fisher, D.A.C.; Starczynowski, D.T.; Oh, S.T. In vivo ablation of NF-κB cascade effectors alleviates disease burden in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2024, 143, 2414–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremyanskaya, M.; Kuykendall, A.T.; Pemmaraju, N.; Ritchie, E.K.; Gotlib, J.; Gerds, A.; Palmer, J.; Pettit, K.; Nath, U.K.; Yacoub, A.; et al. Rusfertide, a Hepcidin Mimetic, for Control of Erythrocytosis in Polycythemia Vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstovsek, S.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Mascarenhas, J.; Perkins, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Mohan, S.R.; Scott, B.L.; Woszczyk, D.; Koschmieder, S.; García-Delgado, R.; et al. BOREAS: A global, phase III study of the MDM2 inhibitor navtemadlin (KRT-232) in relapsed/refractory myelofibrosis. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 4059–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waibel, M.; Solomon, V.S.; Knight, D.A.; Ralli, R.A.; Kim, S.K.; Banks, K.M.; Vidacs, E.; Virely, C.; Sia, K.C.; Bracken, L.S.; et al. Combined targeting of JAK2 and Bcl-2/Bcl-xL to cure mutant JAK2-driven malignancies and overcome acquired resistance to JAK2 inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemmaraju, N.; Somervaille, T.C.P.; Palandri, F.; Harrison, C.; Komrokji, R.S.; Perkins, A.; Ayala Diaz, R.M.; Lavie, D.; Tomita, A.; Feng, Y.; et al. Addition of navitoclax to ruxolitinib for patients with myelofibrosis with progression or suboptimal response. Blood Neoplasia 2025, 2, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Risk Factor | Score | Risk Level | Median OS/Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very-high-risk karyotype a | 2 | Low risk: 0 point | 26.4 |
| Unfavorable karyotype b | 1 | Intermediate risk-1: 1 point | 8 |
| Absence of CALR type 1-like mutation | 1 | Intermediate risk-2: 2 points | 4.2 |
| ASXL1 mutation | 1 | High risk: 3 or more points | 2 |
| SRSF2 mutation | 1 | ||
| U2AF2 Q157 mutation | 1 |
| Therapeutic Agent | Mechanism of Action | Clinical Trial Status | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV | Rusfertide | Inhibits iron transport into the bloodstream, thereby suppressing erythropoiesis | International Phase II REVIVE trial |
| MF | navtemadlin (KRT-232) | Inhibits murine double minute 2 (MDM2), leading to reactivation of p53 tumor suppressor function | Phase III BOREAS trial |
| Navitoclax | Functions as a BCL-2 homology 3 (BH3) mimetic; binds to pro-survival BCL-2 family proteins, disrupts their interaction with pro-apoptotic factors, and promotes apoptosis of malignant MF cells | Phase II REFINE trial |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Shao, R.; Yan, J.; Chen, W.; Shi, X. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs). Cancers 2025, 17, 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193142
Ma X, Zhou Z, Gu S, Guo Y, Zhou T, Shao R, Yan J, Chen W, Shi X. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs). Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193142
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xinyu, Zhibo Zhou, Shuyu Gu, Yan Guo, Tianqing Zhou, Ruonan Shao, Jinsong Yan, Wei Chen, and Xiaofeng Shi. 2025. "Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs)" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193142
APA StyleMa, X., Zhou, Z., Gu, S., Guo, Y., Zhou, T., Shao, R., Yan, J., Chen, W., & Shi, X. (2025). Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs). Cancers, 17(19), 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193142







