Impact of Diabetes and Metformin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 66 and Older: The Role of Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities † †
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Cohort
2.2. Exposure
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
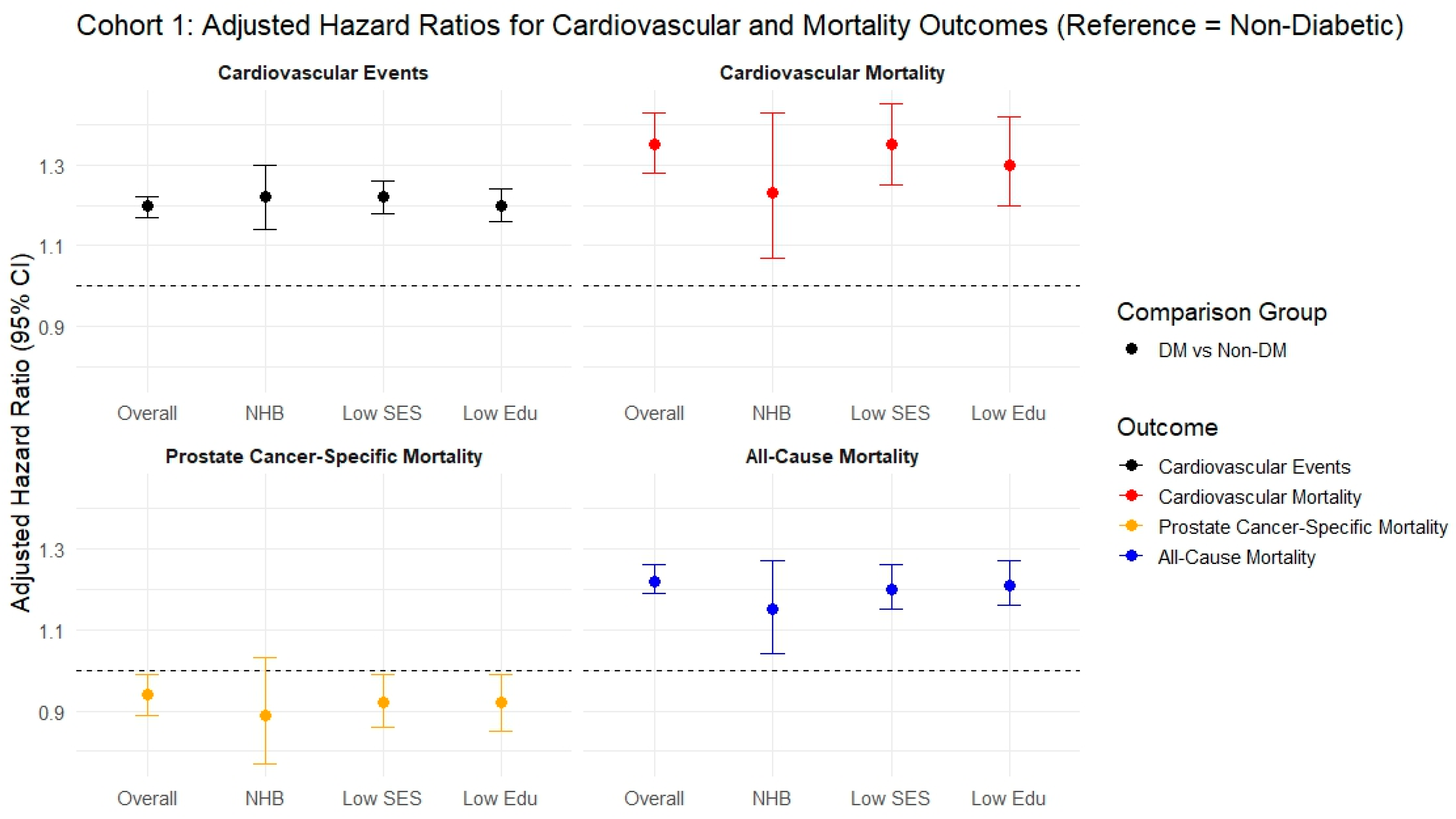
3.1. Cohort 1
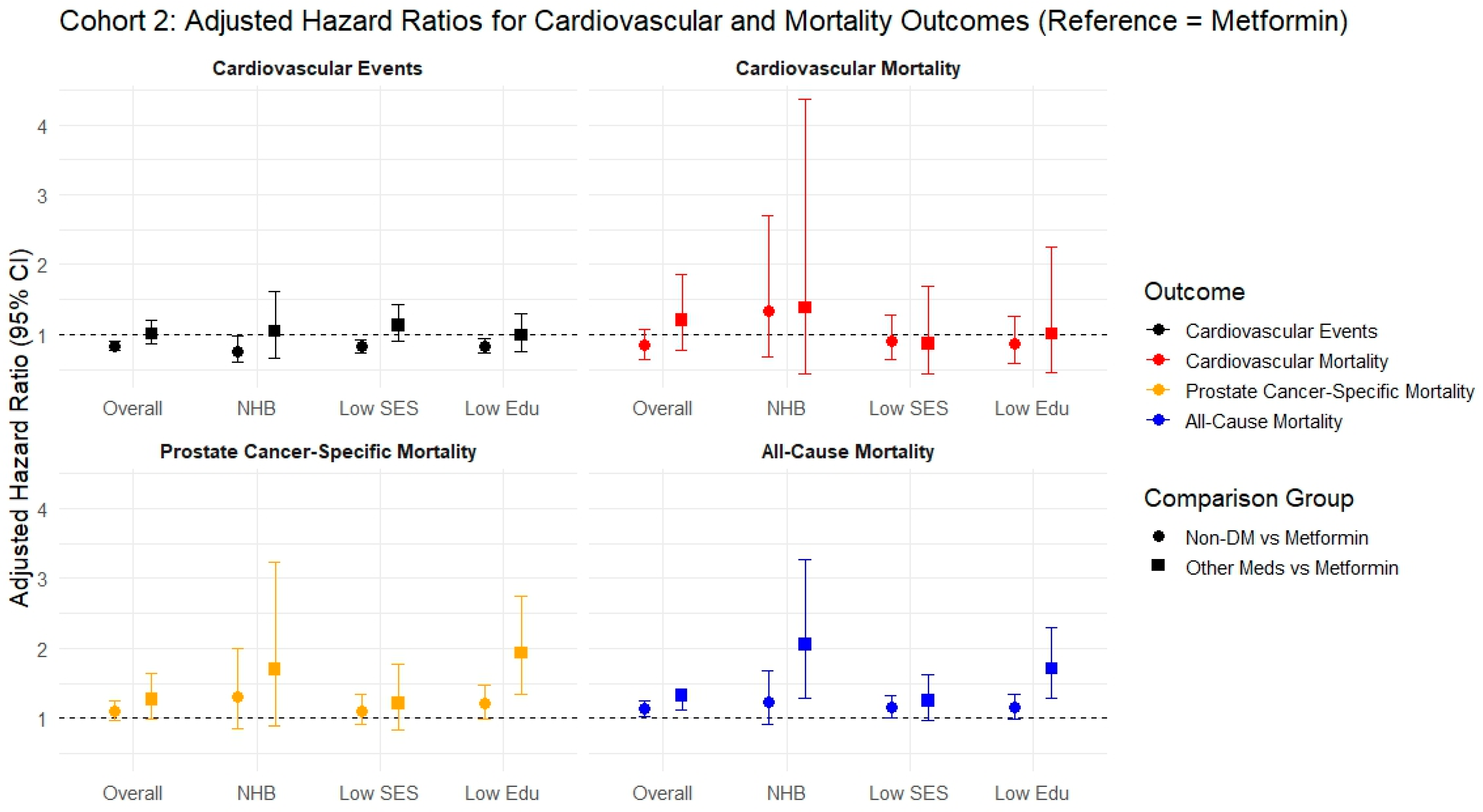
3.2. Cohort 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aHR | Adjusted Hazard Ratio |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| ADT | Androgen Deprivation Therapy |
| aOR | Adjusted Odds Ratio |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| CVE | Cardiovascular Event |
| CVm | Cardiovascular Mortality |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HLD | Hyperlipidemia |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IS | Ischemic Stroke |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| MetAb-Pro | Metformin and Abiraterone Study in Prostate Cancer |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| NHB | Non-Hispanic Black |
| NHW | Non-Hispanic White |
| PAD | Peripheral Artery Disease |
| PC | Prostate Cancer |
| PCsm | Prostate Cancer-Specific Mortality |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SDOH | Social Determinants of Health |
| SEER | Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results |
| SES | Socioeconomic Status |
| sHR | Subdistribution Hazard Ratio |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 |
References
- Drab, A.; Wdowiak, K.; Kanadys, W.; Zajączkowski, K.; Koczkodaj, P.; Religioni, U.; Borowska, M.; Łoś, M.; Lozano-Lorca, M. Diabetes Mellitus and Prostate Cancer Risk-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polesel, J.; Gini, A.; Maso, L.D.; Stocco, C.; Birri, S.; Taborelli, M.; Serraino, D.; Zucchetto, A. The impact of diabetes and other metabolic disorders on prostate cancer prognosis. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2016, 30, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Giovannucci, E.; Jeon, J.Y. Diabetes and mortality in patients with prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin, N.J.; Amin, S.B.; Verona, P.M.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Cook, C.B. Co-Existing Prostate Cancer And Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Patient Outcomes And Care. Endocr. Pract. 2017, 23, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Wittert, G. Androgens, diabetes and prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, F47–F62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, P.; Seth, L.; Patel, V.; Jiang, S.; Gopu, G.; Singh, R.; Stabellini, N.; Reddy, R.; Weintraub, N.L.; Harris, R.A.; et al. Understanding Cardiovascular Risk in Prostate Cancer: Role of Disparities, Diabetes, and Aging. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 26, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, B.; Weinstein, S.J.; Albanes, D.; Mondul, A.M. Metabolomic profile of prostate cancer-specific survival among 1812 Finnish men. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Song, M.; Preston, M.A.; Ma, W.; Hu, Y.; Pernar, C.H.; Stopsack, K.H.; Ebot, E.M.; Fu, B.C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The association of diabetes with risk of prostate cancer defined by clinical and molecular features. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nunzio, C.; Aronson, W.; Freedland, S.J.; Giovannucci, E.; Parsons, J.K. The correlation between metabolic syndrome and prostatic diseases. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.P.; Fradet, V.; Shayegan, B.; Duceppe, E.; Siemens, R.; Niazi, T.; Klotz, L.; Brown, I.; Chin, J.; Lavallee, L.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk in Men with Prostate Cancer: Insights from the RADICAL PC Study. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Miao, Q.; Ruan, H.; Zhang, X. Causes of Death Among Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 40 Years and Older in the United States. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 914875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Monteiro, O.; Chen, D.; Luo, Z.; Chi, K.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Long-term and short-term cardiovascular disease mortality among patients of 21 non-metastatic cancers. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 69, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.P.; Cirne, F.; Pinthus, J.H. Cardiovascular Risk in Prostate Cancer. Cardiol. Clin. 2024, 6, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chang, C.-P.; Dodson, M.W.; Deshmukh, V.; Newman, M.; Date, A.; Sanchez, A.; Lloyd, S.; Oneil, B.; Hashibe, M. Endocrine and metabolic diseases among survivors of prostate cancer in a population-based cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. 4), 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chang, S.; Chang, Y.; Hsu, W.; Lin, C.; Kao, C. Risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with prostate cancer receiving injection therapy: A nationwide population-based propensity score-matched study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P.; Singh, A.; Higano, T.; Tilki, D.; Fleshner, N.; Nguyen, P.; Plummer, C.; Rivas, J.G.; Zhang, K.; Rendon, R.; et al. Addressing cardiovascular risks with a goal to prevent cardiovascular complications in patients undergoing antihormonal therapy for prostate cancer. Cardio-Oncology 2025, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.; Sasse, A.D.; Wagner, A.A.; Peixoto, G.; Kataguiri, A.; Neto, A.S.; Bianco, B.A.V.; Chang, P.; Pompeo, A.C.L.; Tobias-Machado, M. Cardiovascular events associated with androgen deprivation therapy in patients with prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Filippi, S.; Bianchi, N.; Dicuio, M.; Rastrelli, G.; Concetti, S.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M. Cardiovascular Risks of Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. World J. Mens. Health 2021, 39, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.P.; Zhang, N.; Misoi, M.; Gull, S.; Razouki, Z.; Gregg, J.; Giordano, S.H. Effect of metabolic syndrome on survival among patients with breast or prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 16), e22615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, P.; Datta, B.; Jiang, S.; Patel, V.; Seth, L.; Bhave, A.; Malik, S.; Nettles, D.; Gong, Y.; Fradley, M.; et al. Abstract 14915: Role of Diabetes and Diabetic Medication in Cardiovascular Events and Survival Among Older Men With Prostate Cancer on Androgen Deprivation Therapy: Longitudinal SEER Medicare Analysis. Circulation 2023, 148 (Suppl. 1), A14915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradin, J.; Kim, F.J.; Lu-Yao, G.L.; Storozynsky, E.; Kelly, W.K. Review of Cardiovascular Risk of Androgen Deprivation Therapy and the Influence of Race in Men with Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidar, A.; Yassin, A.; Saad, F.; Shabsigh, R. Effects of androgen deprivation on glycaemic control and on cardiovascular biochemical risk factors in men with advanced prostate cancer with diabetes. Aging Male 2007, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorram, A.A.; Pourasgharian, R.; Shams, A.S.; Toufani, S.; Mostafaei, M.; Khademi, R.; Daghayeghi, R.; Valifard, M.; Shahrokhi, M.; Seyedipour, S.; et al. Androgen deprivation therapy use and the risk of heart failure in patients with prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Heck, S.L.; Gulati, G. The Role of Cardioprotection in Cancer Therapy Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. Cardio Oncol. 2022, 4, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Keating, N.L.; Liu, P.-H.; O’mAlley, A.J.; Freedland, S.J.; Smith, M.R. Androgen-deprivation therapy and diabetes control among diabetic men with prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwata, J.L.; Dorff, T.B.; Schroeder, E.T.; E Gross, M.; Dieli-Conwright, C.M. A review of clinical effects associated with metabolic syndrome and exercise in prostate cancer patients. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016, 19, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrael, G.; Chehade, C.H.; Agarwal, N. Metformin in prostate cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2025, 26, 982–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Murphy, L.; James, N.D.; Sachdeva, A.; El-Taji, O.; Abdel-Aty, H.; I Adler, A.; Amos, C.; Attard, G.; Varughese, M.; et al. Metformin for patients with metastatic prostate cancer starting androgen deprivation therapy: A randomised phase 3 trial of the STAMPEDE platform protocol. Lancet Oncol. 2025, 26, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.A.; Hui, J.M.H.; Chan, J.S.K.; Liu, K.; Dee, E.C.; Ng, K.; Ng, C.F. Metformin use and mortality in Asian, diabetic patients with prostate cancer on androgen deprivation therapy: A population-based study. Prostate 2023, 83, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X. Effect of metformin on incidence, recurrence, and mortality in prostate cancer patients: Integrating evidence from real-world studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024, 28, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Pinthus, J.; Valle, F.; Piccoli, R.; Dusilek, C.; Duceppe, E.; Kann, A.; Fradet, V.; Shayegan, B.; Violette, P.; et al. Educational attainment and cardiovascular outcomes in prostate cancer: Observations from 3700 men in 6 countries in the RADICAL PC study. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45 (Suppl. 1), ehae666.3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Patel, V.; Stabellini, N.; Datta, B.; Nain, P.; Seth, L.; Kunhiraman, H.H.; Nettles, D.; Malik, S.; Patel, S.A.; et al. Rurality Status and Cardiovascular Events/Survival in Older Men With Prostate Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2025, 23, e247094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enewold, L.; Parsons, H.; Zhao, L.; Bott, D.; Rivera, D.R.; Barrett, M.J.; Warren, J.L. Updated Overview of the SEER-Medicare Data: Enhanced Content and Applications. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2020, 2020, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medicare Program—General Information. Available online: https://www.cms.gov/about-cms/what-we-do/medicare (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Cryer, D.R.; Nicholas, S.P.; Henry, D.H.; Mills, D.J.; Stadel, B.V. Comparative Outcomes Study of Metformin Intervention Versus Conventional Approach The COSMIC Approach Study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margel, D.; Urbach, D.R.; Lipscombe, L.L.; Bell, C.M.; Kulkarni, G.; Austin, P.C.; Fleshner, N. Metformin use and all-cause and prostate cancer-specific mortality among men with diabetes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Gibbs, B.B.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e347–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, K.; Perkins, C.; Cohen, R.; Morris, C.; Wright, W. Socioeconomic status and breast cancer incidence in California for different race/ethnic groups. Cancer Causes Control. 2001, 12, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Social Determinants of Health Database. In Content Last Reviewed June 2023; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ahrq.gov/sdoh/data-analytics/sdoh-data.html (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service (USDA-ERS). Rural-Urban Commuting Area (RUCA) Codes, ZIP Code File. Last updated 17 August 2020. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A Proportional Hazards Model for the Subdistribution of a Competing Risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, M.A.; Ebrahimi, R.; Hong, A.; Bobbili, P.; Desai, R.; Duh, M.S.; Gandhi, R.; Hanson, S.; Dufour, R.; Morgans, A.K. Risk of cardiovascular events following intermittent and continuous androgen deprivation therapy in patients with nonmetastatic prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 42, 447.e1–447.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellstadli, C.; Forster, R.B.; Myklebust, T.Å.; Bjørge, T.; Bønaa, K.H.; Helle, S.I.; Kvåle, R. Cardiovascular outcomes after curative prostate cancer treatment: A population-based cohort study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1121872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chi, K.-Y.; Lee, T.-N.; Hsiao, C.-L.; Chiang, C.-H.; Wang, Q.; Jang, A. Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes of prostate cancer patients receiving gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, zwae267, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chang, C.P.; Snyder, J.; Deshmukh, V.; Newman, M.; Date, A.; Hashibe, M. PD21-05 Cardiovascular Outcomes In A Population-Based Cohort Of Prostate Cancer Patients. J. Urol. 2023, 209, e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 19; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Valderas, J.M.; McFadden, E.C.; Bankhead, C.R.; Lavery, B.A.; Khan, N.F.; Stevens, R.J.; Keating, N.L. Keating. Outcomes of preexisting diabetes mellitus in breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. J. Cancer Surviv. 2017, 11, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; O’NEil, A.; Choi, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, X. Pre- and Post-diagnosis Diabetes as a Risk Factor for All-Cause and Cancer-Specific Mortality in Breast, Prostate, and Colorectal Cancer Survivors: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Doege, D.; Thong, M.S.; Koch-Gallenkamp, L.; Weisser, L.; Bertram, H.; Arndt, V. Diabetes mellitus in long-term survivors with colorectal, breast, or prostate cancer: Prevalence and prognosis. A population-based study. Cancer 2024, 130, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Bhave, A.; Kunhiraman, H.H.; Nahle, T.; Reddy, R.; Makram, O.; Nain, P.; Shah, V.; Swami, U.; Patel, S.A.; Esdaille, A.; et al. Cardiovascular risks in men with prostate cancer: A pragmatic, clinician-oriented review of risk stratification and management strategies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissei, B.G.; Ko, K.; Huang, A.; Lee, D.J.; Doucette, A.G.; Smith, A.M.; Wilcox, N.S.; Reibel, J.; Sun, L.; Agarwal, M.; et al. Social Determinants of Health Mediate Racial Disparities in Cardiovascular Disease in Men With Prostate Cancer. Cardio Oncol. 2024, 6, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahle, T.; Elsayed, O.M.M.; Shah, V.R.; Kunhiraman, H.H.; Farraj, S.A.; Nain, P.; Stabellini, N.; Al-Kindi, S.; Swami, U.; Ciuro, J.A.; et al. Socioeconomic position as a social determinant of health and its effect on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with prostate cancer: A SEER-Medicare based study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 5), 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florido, R.; Daya, N.R.; Ndumele, C.E.; Koton, S.; Russell, S.D.; Prizment, A.; Selvin, E. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Among Cancer Survivors: The Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Garmo, H.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Zethelius, B.; Stattin, P.; Hagström, E.; Adolfsson, J.; Crawley, D. Association of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists for Prostate Cancer With Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Hypertension in Men With Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2225600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sebastiano, K.M.; Pinthus, J.H.; Duivenvoorden, W.C.M.; Mourtzakis, M. Glucose impairments and insulin resistance in prostate cancer: The role of obesity, nutrition and exercise. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, A.; Ghosh, S.; McGlynn, B.; Hollins, G. Prostate cancer, androgen deprivation therapy, obesity, the metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease: A review. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 35, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkat, S.; Pramanik, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P.; Sarkar, C.; Chakroborty, D. Cardiovascular Complications in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Potential Molecular Connections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, U.; Bank, S.; Jayawardana, M.W.; Bhowmik, J.; Redwig, F.; Jana, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Manna, E.; De, S.K.; Maiti, S.; et al. Insulin resistance in prostate cancer patients and predisposing them to acute ischemic heart disease. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZaim, I.; Al-Saidi, A.; Hammoud, S.H.; Darwiche, N.; Al-Dhaheri, Y.; Eid, A.H.; El-Yazbi, A.F. Thromboinflammatory Processes at the Nexus of Metabolic Dysfunction and Prostate Cancer: The Emerging Role of Periprostatic Adipose Tissue. Cancers 2022, 14, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, I.A.; Gallab, M.M.; Mohamed, D.A.; Hamdar, H.; Ibrahim, S.I.; Mohamed, A.; Abdelshafi, A.; Abd-ElGawad, M. Efficacy of metformin drug in preventing metabolic syndrome associated with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in prostate cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Oncol. 2024, 51, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, C.; Cafferty, F.H.; Vale, C.; Langley, R.E. Metformin as an adjuvant treatment for cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihervuori, V.J.; Talala, K.; Taari, K.; Lahtela, J.; Tammela, T.L.; Auvinen, A.; Raittinen, P.V.H.; Murtola, T.J. Antidiabetic Drugs and Prostate Cancer Prognosis in a Finnish Population-Based Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, D.; Hanni, S.; Serritella, A.V.; Fountzilas, C.; Michalek, J.; Hernandez, B.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Datta, P.; Romero, O.; Pillai, S.M.A.; et al. Utilizing metformin to prevent metabolic syndrome due to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT): A randomized phase II study of metformin in non-diabetic men initiating ADT for advanced prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonde, L.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Reddy, S.S.; McGill, J.B.; Berga, S.L.; Bush, M.; Chandrasekaran, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Galindo, R.J.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Developing a Diabetes Mellitus Comprehensive Care Plan-2022 Update. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 923–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Saad, F.; Sun, Y.; Malone, S.; Spratt, D.E.; Kishan, A.U.; Wallis, C.J.; Jia, A.Y.; Mohamad, O.; Swami, U.; et al. Effect of concomitant medications on treatment response and survival in non-metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer: Exploratory analysis of the SPARTAN trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 211, 114197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, N.; Ghosh, S.; Sanghera, K.P.; Ong, A.D.; Koul, R.; Dubey, A.; Ahmed, S.; Quon, H.; Yee, D.; Parliament, M.; et al. Metformin for Prevention of Anthropometric and Metabolic Complications of Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Patients Receiving Radical Radiotherapy: A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 115, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgans, A.K.; Chen, Y.; Jarrard, D.F.; Carducci, M.; Liu, G.; Eisenberger, M.; Plimack, E.R.; Bryce, A.; Garcia, J.A.; Dreicer, R.; et al. Association between baseline body mass index and survival in men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: ECOG-ACRIN CHAARTED E3805. Prostate 2022, 82, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.P.; Borchiellini, D.; Thamphya, B.; Guillot, A.; Paoli, J.-B.; Besson, D.; Hilgers, W.; Priou, F.; El Kouri, C.; Hoch, B.; et al. TAXOMET: A French Prospective Multicentric Randomized Phase II Study of Docetaxel Plus Metformin Versus Docetaxel Plus Placebo in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2021, 19, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, M.; Klingbiel, D.; Mey, U.; Winterhalder, R.; Rothermundt, C.; Gillessen, S.; von Moos, R.; Pollak, M.; Manetsch, G.; Strebel, R.; et al. Impact of Addition of Metformin to Abiraterone in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients With Disease Progressing While Receiving Abiraterone Treatment (MetAb-Pro): Phase 2 Pilot Study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, e323–e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghandour, R.; Elshal, A.M.; Ghobrial, F.; Elzaafarany, M.; Elbaiomy, M.A. Repurposing metformin as anticancer drug: Randomized controlled trial in advanced prostate cancer (MANSMED). Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 831.e1–831.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hu, H.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Cui, R.; Yi, L. The effect of metformin therapy on incidence and prognosis in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Yang, H.M.; Cao, L.M.; Yin, Y.; Shen, Y.M.; Zhu, W. Prognostic value of metformin in cancers: An updated meta-analysis based on 80 cohort studies. Medicine 2022, 101, e31799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopsack, K.H.; Ziehr, D.R.; Rider, J.R.; Giovannucci, E.L. Metformin and prostate cancer mortality: A meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2016, 27, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Sáez-Martínez, P.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; León-González, A.J.; Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Requena-Tapia, M.J.; López, M.; et al. Clinical, Cellular, and Molecular Evidence of the Additive Antitumor Effects of Biguanides and Statins in Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e696–e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knura, M.; Garczorz, W.; Borek, A.; Drzymała, F.; Rachwał, K.; George, K.; Francuz, T. The Influence of Anti-Diabetic Drugs on Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshua, A.M.; Armstrong, A.; Crumbaker, M.; Scher, H.I.; de Bono, J.; Tombal, B.; Hussain, M.; Sternberg, C.N.; Gillessen, S.; Carles, J.; et al. Statin and metformin use and outcomes in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with enzalutamide: A meta-analysis of AFFIRM, PREVAIL and PROSPER. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 170, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.E.; Armstrong, A.J.; de Bono, J.; Sternberg, C.N.; Ryan, C.J.; Scher, H.I.; Smith, M.R.; Rathkopf, D.; Logothetis, C.J.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Effects of metformin and statins on outcomes in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer: Secondary analysis of COU-AA-301 and COU-AA-302. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 170, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilusic, M.; Toney, N.J.; Donahue, R.N.; Wroblewski, S.; Zibelman, M.; Ghatalia, P.; Ross, E.A.; Karzai, F.; Madan, R.A.; Dahut, W.L.; et al. A randomized phase 2 study of bicalutamide with or without metformin for biochemical recurrence in overweight or obese prostate cancer patients (BIMET-1). Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, D.; Chandra, A.; Loda, M.; Gillett, C.; Cathcart, P.; Ben Challacombe, B.; Cook, G.; Cahill, D.; Olalla, A.S.; Cahill, F.; et al. Metformin and longevity (METAL): A window of opportunity study investigating the biological effects of metformin in localised prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bayrak, B.B.; Koroglu, P.; Bulan, O.K.; Yanardağ, R. Metformin protects against diabetes-induced heart injury and dunning prostate cancer model. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendryx, M.; Dong, Y.; Ndeke, J.M.; Luo, J.; Alpini, G.D. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor initiation and hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Dixon, D.L. The CANVAS Program: Implications of canagliflozin on reducing cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prostate Cancer—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Arnold, M.; Rutherford, M.J.; Bardot, A.; Ferlay, J.; Andersson, T.M.; Myklebust, T.Å.; Bray, F. Progress in cancer survival, mortality, and incidence in seven high-income countries 1995–2014 (ICBP SURVMARK-2): A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Non-Diabetic | Diabetic | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Characteristics | ||||
| Sample size | 150,647 | 102,271 (68%) | 48,376 (32%) | |
| Age at cancer diagnosis, median (IQR) | 72 (68–77) | 71 (68–76) | 73 (69–78) | <0.001 |
| Race/ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | 117,945 (78.3%) | 82,924 (81.1%) | 35,021 (72.4%) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 16,001 (10.6%) | 9523 (9.3%) | 6478 (13.4%) | |
| Hispanic | 9931 (6.6%) | 5792 (5.7%) | 4139 (8.6%) | |
| Other | 6770 (4.5%) | 4032 (3.9%) | 2738 (5.7%) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Single (Never married) | 8753 (5.8%) | 5935 (5.8%) | 2818 (5.8%) | |
| Married (including common law) | 71,950 (47.8%) | 49,973 (48.9%) | 21,977 (45.4%) | |
| Other # | 14,135 (9.4%) | 9152 (8.9%) | 4983 (10.3%) | |
| Unknown | 55,809 (37.0%) | 37,211 (36.4%) | 18,598 (38.4%) | |
| Socioeconomic status (SES), n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| High SES | 76,844 (51.0%) | 53,509 (52.3%) | 23,335 (48.2%) | |
| Low SES | 64,398 (42.7%) | 42,219 (41.3%) | 22,179 (45.8%) | |
| Unknown | 9405 (6.2%) | 6543 (6.4%) | 2862 (5.9%) | |
| Education status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| High school and above | 84,086 (55.8%) | 55,615 (54.4%) | 28,471 (58.9%) | |
| Below high school | 66,561 (44.2%) | 46,656 (45.6%) | 19,905 (41.1%) | |
| Rurality, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Rural | 20,568 (13.7%) | 14,617 (14.3%) | 5951 (12.3%) | |
| Urban | 130,054 (86.3%) | 87,637 (85.7%) | 42,417 (87.7%) | |
| Use of surgery, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No surgery | 76,608 (69.7%) | 51,155 (68.2%) | 25,453 (73.0%) | |
| Surgery | 33,287 (30.3%) | 23,875 (31.8%) | 9412 (27.0%) | |
| Use of radiotherapy, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No/Unknown radiation α | 68,398 (61.0%) | 47,239 (61.7%) | 21,159 (59.5%) | |
| Beam radiation | 32,619 (29.1%) | 21,442 (28.0%) | 11,177 (31.4%) | |
| Implanted radiation | 4961 (4.4%) | 3573 (4.7%) | 1388 (3.9%) | |
| Other | 6099 (5.4%) | 4279 (5.6%) | 1820 (5.1%) | |
| AJCC staging, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| I | 16,338 (10.8%) | 11,297 (11.0%) | 5041 (10.4%) | |
| II | 37,511 (24.9%) | 25,464 (24.9%) | 12,047 (24.9%) | |
| III | 5360 (3.6%) | 3935 (3.8%) | 1425 (2.9%) | |
| IV | 7215 (4.8%) | 4804 (4.7%) | 2411 (5.0%) | |
| Unknown | 84,223 (55.9%) | 56,771 (55.5%) | 27,452 (56.7%) | |
| Grade, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| 1 | 16,709 (11.1%) | 11,739 (11.5%) | 4970 (10.3%) | |
| 2 | 54,301 (36.0%) | 37,831 (37.0%) | 16,470 (34.0%) | |
| 3 | 65,646 (43.6%) | 43,969 (43.0%) | 21,677 (44.8%) | |
| 4 | 295 (0.2%) | 180 (0.2%) | 115 (0.2%) | |
| N/A | 13,696 (9.1%) | 8552 (8.4%) | 5144 (10.6%) | |
| ADT, n (%) | 30,618 (20.3%) | 19,191 (18.8%) | 11,427 (23.6%) | <0.001 |
| Past medical history at baseline | ||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 108,021 (71.7%) | 62,785 (61.4%) | 45,236 (93.5%) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 104,691 (69.5%) | 60,694 (59.3%) | 43,997 (90.9%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 34,860 (23.1%) | 15,953 (15.6%) | 18,907 (39.1%) | <0.001 |
| Any prior cardiovascular event, n (%) | 27,295 (18.1%) | 14,157 (13.8%) | 13,138 (27.2%) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral arterial disease, n (%) | 4112 (2.7%) | 1872 (1.8%) | 2240 (4.6%) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 13,307 (8.8%) | 7237 (7.1%) | 6070 (12.6%) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 5692 (3.8%) | 2731 (2.7%) | 2961 (6.1%) | <0.001 |
| Ischemic stroke, n (%) | 5454 (3.6%) | 2793 (2.7%) | 2661 (5.5%) | <0.001 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 10,726 (7.1%) | 4654 (4.6%) | 6072 (12.6%) | <0.001 |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Any cardiovascular event, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 80,515 (53.4%) | 60,974 (59.6%) | 19,541 (40.4%) | |
| Yes | 70,132 (46.6%) | 41,297 (40.4%) | 28,835 (59.6%) | |
| Peripheral arterial disease, n (%) | 19,415 (12.9%) | 10,707 (10.5%) | 8708 (18.0%) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 34,008 (22.6%) | 19,995 (19.6%) | 14,013 (28.9%) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 19,673 (13.1%) | 10,630 (10.4%) | 9043 (18.7%) | <0.001 |
| Ischemic stroke, n (%) | 18,264 (12.1%) | 10,488 (10.3%) | 7776 (16.1%) | <0.001 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 35,570 (23.6%) | 18,734 (18.3%) | 16,836 (34.8%) | <0.001 |
| CVE (Competing Risk = All-Cause Mortality) sHR (95% CI, p-Value) | |||||
| Overall | NHB | Low SES * | Low Edu # | ||
| Cohort 1 | Event/Total, person-year # | 40,197/109,895 429,629.7 | 4242/11,769 45,676.7 | 18,524/48,934 186,892.5 | 17,682/51,878 207,193.9 |
| Non-DM | Reference | ||||
| DM | 1.20 (1.17–1.22, p < 0.001) | 1.22 (1.14–1.30, p < 0.001) | 1.22 (1.18–1.26, p < 0.001) | 1.20 (1.16–1.24, p < 0.001) | |
| Cohort 2 | Event/Total, person-year # | 4036/9735 32,523.6 | 428/1021 3381.8 | 1896/4385 14,167.5 | 1863/4744 16,028.2 |
| Non-DM | 0.83 (0.77–0.90, p < 0.001) | 0.76 (0.60–0.97, p = 0.026) | 0.83 (0.73–0.93, p = 0.002) | 0.83 (0.73–0.94, p = 0.003) | |
| DM on metformin alone or metformin-based combination therapy (Reference) | |||||
| DM on other medications | 1.01 (0.86–1.20, p = 0.869) | 1.04 (0.66–1.62, p = 0.877) | 1.13 (0.90–1.42, p = 0.288) | 0.99 (0.75–1.29, p = 0.916) | |
| CVm (Competing risk = All-cause mortality except CVD mortality) sHR (95% CI, p-value) | |||||
| Overall | NHB | Low SES * | Low Edu # | ||
| Non-DM | Reference | ||||
| DM | 1.35 (1.28–1.43, p < 0.001) | 1.23 (1.07–1.43, p = 0.004) | 1.35 (1.25–1.45, p < 0.001) | 1.30 (1.20–1.42, p < 0.001) | |
| Cohort 2 | Event/Total, person-year # | 433/9735 32,523.6 | 57/1021 3381.8 | 226/4385 14,167.5 | 183/4744 16,028.2 |
| Non-DM | 0.84 (0.65–1.08, p = 0.181) | 1.34 (0.67–2.71, p = 0.408) | 0.91 (0.65–1.28, p = 0.596) | 0.86 (0.59–1.26, p = 0.448) | |
| DM on metformin alone or metformin-based combination therapy (Reference) | |||||
| DM on other medications | 1.20 (0.77–1.86, p = 0.415) | 1.38 (0.43–4.36, p = 0.588) | 0.87 (0.44–1.69, p = 0.675) | 1.01 (0.45–2.25, p = 0.983) | |
| PCsm (Competing risk = All-cause mortality except PCsm) sHR (95% CI, p-value) | |||||
| Overall | NHB | Low SES * | Low Edu # | ||
| Non-DM | Reference | ||||
| DM | 0.94 (0.89–0.99, p = 0.012) | 0.89 (0.77–1.03, p = 0.122) | 0.92 (0.86–0.99, p = 0.028) | 0.92 (0.85–0.99, p = 0.028) | |
| Cohort 2 | Event/Total, person-year # | 2078/9735 32,523.6 | 251/1021 3381.8 | 1001/4385 14,167.5 | 934/4744 16,028.2 |
| Non-DM | 1.09 (0.96–1.25, p = 0.188) | 1.31 (0.86–2.00, p =0.209) | 1.10 (0.91–1.34, p = 0.314) | 1.21 (0.98–1.48, p = 0.070) | |
| DM on metformin alone or metformin-based combination therapy Reference | |||||
| DM on other medications | 1.27 (0.99–1.64, p = 0.065) | 1.70 (0.89–3.24, p = 0.107) | 1.21 (0.83–1.77, p = 0.325) | 1.93 (1.35–2.75, p < 0.001) | |
| All-cause mortality (Cox) aHR (95% CI, p-value) | |||||
| Overall | NHB | Low SES * | Low Edu # | ||
| Non-DM | Reference | ||||
| DM | 1.22 (1.19–1.26, p < 0.001) | 1.15 (1.04–1.27, p = 0.005) | 1.20 (1.15–1.26, p < 0.001) | 1.21 (1.16–1.27, p < 0.001) | |
| Cohort 2 | Event/Total, person-year # | 3160/9734 40,838.6 | 399/1021 4262.2 | 1571/4385 18,046.4 | 1380/4744 19,643.2 |
| Non-DM | 1.13 (1.02–1.25, p = 0.025) | 1.23 (0.91–1.68, p = 0.183) | 1.15 (1.00–1.33, p = 0.056) | 1.15 (0.98–1.34, p = 0.083) | |
| DM on metformin alone or metformin-based combination therapy Reference | |||||
| DM on other medications | 1.33 (1.11–1.25, p = 0.002) | 2.05 (1.29–3.27, p = 0.002) | 1.25 (0.96–1.63, p = 0.095) | 1.71 (1.28–2.30, p < 0.001) | |
| Cohort 1 | ||||||||
| CVE | CVm | PCsm | All-Cause Mortality | |||||
| sHR (95% CI, p-Value) | aHR (95% CI, p-Value) | |||||||
| Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | |
| Race | p < 0.001 | DM + White: 1.17 (1.14–1.20, p < 0.001) DM + Black: 1.25 (1.18–1.33, p < 0.001) DM + Hispanic: 1.35 (1.25–1.46, p < 0.001) DM + Other: 1.33 (1.20–1.46, p < 0.001) | p = 0.543 | - | p = 0.179 | - | p = 0.229 | - |
| Age ≥ 75 | p < 0.001 | DM + Age < 75: 1.28 (1.24–1.32, p < 0.001) DM + Age ≥ 75: 1.10 (1.07–1.14, p < 0.001) | p < 0.001 | DM + Age < 75: 1.65 (1.51–1.79, p < 0.001) DM + Age ≥ 75: 1.21 (1.13–1.29, p < 0.001) | p = 0.002 | DM + Age < 75: 1.04 (0.96–1.12, p = 0.390) DM + Age ≥ 75: 0.89 (0.84–0.95, p < 0.001) | p < 0.001 | DM + Age < 75: 1.33 (1.27–1.39, p < 0.001) DM + Age ≥ 75: 1.16 (1.12–1.21, p < 0.001) |
| Rurality | p = 0.087 | - | p = 0.091 | - | p = 0.418 | p = 0.001 | DM + Rural: 1.32 (1.23–1.41, p < 0.001) DM + Urban: 1.21 (1.17–1.24, p < 0.001) | |
| Cohort 2 | ||||||||
| CVE | CVm | PCsm | All-Cause Mortality | |||||
| sHR (95% CI, p-Value) | aHR (95% CI, p-Value) | |||||||
| Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | Interaction | Stratification | |
| Race | p = 0.765 | - | p < 0.001 | Non-DM + White: 0.78 (0.58–1.05, p = 0.106) Non-DM + Black: 1.13 (0.55–2.32, p = 0.737) Non-DM + Hispanic: 1.06 (0.49–2.30, p = 0.883) Non-DM + Other: 0.87 (0.35–2.19, p = 0.769) DM on other + White: 1.55 (0.94–2.55, p = 0.084) DM on other + Black: 1.21 (0.37–3.94, p = 0.757) DM on other + Hispanic: (p < 0.001) † DM on other + Other: 0.57 (0.07–4.59, p = 0.593) | p = 0.725 | - | p = 0.244 | - |
| Age ≥ 75 | p = 0.001 | Non-DM + Age < 75: 0.86 (0.77–0.95, p = 0.005) Non-DM + Age ≥ 75: 0.79 (0.70–0.90, p = 0.001) DM on other + Age < 75: 1.17 (0.93–1.48, p = 0.174) DM on other + Age ≥ 75: 0.86 (0.68–1.10, p = 0.243) | p = 0.216 | - | p = 0.222 | - | p = 0.279 | - |
| Rurality | p = 0.002 | Non-DM + Rural: 0.80 (0.66–0.97, p = 0.021) Non-DM + Urban: 0.84 (0.77–0.92, p < 0.001) DM on other + Rural: 1.11 (0.78–1.59, p = 0.566) DM on other + Urban: 0.99 (0.82–1.20, p = 0.935) | p = 0.204 | - | p = 0.143 | - | p = 0.481 | - |
| Total | Non-DM | DM on Metformin Alone or Metformin-Based Combination Therapy | DM on Other Medication(s) ^ | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Characteristics | |||||
| Sample size | 14,938 | 12,071 (80.8%) | 2356 (15.8%) | 511 (3.4%) | |
| Age at cancer diagnosis, median (IQR) | 73 (69–78) | 73 (69–78) | 72 (69–77) | 74 (70–79) | <0.001 |
| Race/ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 11,850 (79.3%) | 9871 (81.8%) | 1648 (69.9%) | 331 (64.8%) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 1436 (9.6%) | 1069 (8.9%) | 276 (11.7%) | 91 (17.8%) | |
| Hispanic | 931 (6.2%) | 625 (5.2%) | 251 (10.7%) | 55 (10.8%) | |
| Other | 721 (4.8%) | 506 (4.2%) | 181 (7.7%) | 34 (6.7%) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | 0.61 | ||||
| Single (Never married) | 1016 (6.8%) | 824 (6.8%) | 157 (6.7%) | 35 (6.8%) | |
| Married (including common law) | 6468 (43.3%) | 5208 (43.1%) | 1048 (44.5%) | 212 (41.5%) | |
| Other # | 1442 (9.7%) | 1178 (9.8%) | 207 (8.8%) | 57 (11.2%) | |
| Unknown | 6012 (40.2%) | 4861 (40.3%) | 944 (40.1%) | 207 (40.5%) | |
| Socioeconomic status (SES), n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| High SES | 7354 (49.2%) | 6076 (50.3%) | 1077 (45.7%) | 201 (39.3%) | |
| Low SES | 6405 (42.9%) | 5067 (42.0%) | 1077 (45.7%) | 261 (51.1%) | |
| Unknown | 1179 (7.9%) | 928 (7.7%) | 202 (8.6%) | 49 (9.6%) | |
| Education status, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| High school and above | 8098 (54.2%) | 6506 (53.9%) | 1269 (53.9%) | 323 (63.2%) | |
| Below high school | 6840 (45.8%) | 5565 (46.1%) | 1087 (46.1%) | 188 (36.8%) | |
| Rurality, n (%) | 0.70 | ||||
| Rural | 2549 (17.1%) | 2072 (17.2%) | 388 (16.5%) | 89 (17.4%) | |
| Urban | 12,388 (82.9%) | 9998 (82.8%) | 1968 (83.5%) | 422 (82.6%) | |
| Use of surgery, n (%) | 0.015 | ||||
| No surgery | 7616 (78.2%) | 6107 (77.9%) | 1223 (78.8%) | 286 (84.4%) | |
| Surgery | 2119 (21.8%) | 1737 (22.1%) | 329 (21.2%) | 53 (15.6%) | |
| Use of radiotherapy, n (%) | 0.012 | ||||
| No/Unknown radiation α | 5313 (53.8%) | 4309 (54.2%) | 808 (51.1%) | 196 (56.8%) | |
| Beam radiation | 3683 (37.3%) | 2914 (36.6%) | 636 (40.2%) | 133 (38.6%) | |
| Implanted radiation | 188 (1.9%) | >150 (>1.50%) + | 26 (1.6%) | <11 + | |
| Other | 696 (7.0%) | >570 (>7.0%) + | 111 (7.0%) | >13 (>3.5%) + | |
| AJCC Staging, n (%) | 0.43 | ||||
| I | 345 (2.3%) | 283 (2.3%) | 50 (2.1%) | 12 (2.3%) | |
| II | 2672 (17.9%) | 2121 (17.6%) | 452 (19.2%) | 99 (19.4%) | |
| III | 710 (4.8%) | 577 (4.8%) | 113 (4.8%) | 20 (3.9%) | |
| IV | 2103 (14.1%) | 1709 (14.2%) | 312 (13.2%) | 82 (16.0%) | |
| Unknown | 9108 (61.0%) | 7381 (61.1%) | 1429 (60.7%) | 298 (58.3%) | |
| Grade, n (%) | 0.004 | ||||
| 1 | 400 (2.7%) | 318 (2.6%) | 66 (2.8%) | 16 (3.1%) | |
| 2 | 2771 (18.6%) | 2245 (18.6%) | 448 (19.0%) | 78 (15.3%) | |
| 3 | 9652 (64.6%) | >7760 (>64.0%) + | >1560 (>66.0%) + | >320 (>63.0%) + | |
| 4 | 48 (0.3%) | >40 (>0.2%) + | <11 + | <11 + | |
| N/A | 2067 (13.8%) | 1700 (14.1%) | 275 (11.7%) | 92 (18.0%) | |
| Past medical history at baseline | |||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 11,446 (76.6%) | 8903 (73.8%) | 2074 (88.0%) | 469 (91.8%) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 10,784 (72.2%) | 8359 (69.2%) | 1989 (84.4%) | 436 (85.3%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 4211 (28.2%) | 3077 (25.5%) | 821 (34.8%) | 313 (61.3%) | <0.001 |
| Any prior cardiovascular event, n (%) | 3450 (23.1%) | 2654 (22.0%) | 594 (25.2%) | 202 (39.5%) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral arterial disease, n (%) | 559 (3.7%) | 411 (3.4%) | 106 (4.5%) | 42 (8.2%) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 1695 (11.4%) | 1328 (11%) | 277 (11.8%) | 90 (17.6%) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 784 (5.2%) | 574 (4.8%) | 153 (6.5%) | 57 (11.2%) | <0.001 |
| Ischemic stroke, n (%) | 731 (4.9%) | 545 (4.5%) | 144 (6.1%) | 42 (8.2%) | <0.001 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 1375 (9.2%) | 1011 (8.4%) | 248 (10.5%) | 116 (22.7%) | <0.001 |
| Outcomes | |||||
| Any cardiovascular event, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| No | 6901 (46.2%) | 5786 (47.9%) | 977 (41.5%) | 138 (27.0%) | |
| Yes | 8037 (53.8%) | 6285 (52.1%) | 1379 (58.5%) | 373 (73.0%) | |
| Peripheral arterial disease, n (%) | 2325 (15.6%) | 1762 (14.6%) | 438 (18.6%) | 125 (24.5%) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 3842 (25.7%) | 3018 (25%) | 632 (26.8%) | 192 (37.6%) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 2337 (15.6%) | 1752 (14.5%) | 451 (19.1%) | 134 (26.2%) | <0.001 |
| Ischemic stroke, n (%) | 2093 (14.0%) | 1613 (13.4%) | 380 (16.1%) | 100 (19.6%) | <0.001 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 4168 (27.9%) | 3117 (25.8%) | 797 (33.8%) | 254 (49.7%) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nain, P.; Makram, O.M.; Shah, V.; Hyma Kunhiraman, H.; Stabellini, N.; Datta, B.; Jiang, S.; Patel, V.; Seth, L.; Bhave, A.; et al. Impact of Diabetes and Metformin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 66 and Older: The Role of Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities †. Cancers 2025, 17, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172854
Nain P, Makram OM, Shah V, Hyma Kunhiraman H, Stabellini N, Datta B, Jiang S, Patel V, Seth L, Bhave A, et al. Impact of Diabetes and Metformin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 66 and Older: The Role of Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities †. Cancers. 2025; 17(17):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172854
Chicago/Turabian StyleNain, Priyanshu, Omar M. Makram, Viraj Shah, Harikrishnan Hyma Kunhiraman, Nickolas Stabellini, Biplab Datta, Stephanie Jiang, Vraj Patel, Lakshya Seth, Aditya Bhave, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Diabetes and Metformin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 66 and Older: The Role of Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities †" Cancers 17, no. 17: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172854
APA StyleNain, P., Makram, O. M., Shah, V., Hyma Kunhiraman, H., Stabellini, N., Datta, B., Jiang, S., Patel, V., Seth, L., Bhave, A., Malik, S. A., Gong, Y., Fradley, M. G., Leong, D. P., Harris, R. A., Hung, Y.-H., Lin, A. Y.-H., Weintraub, N. L., & Guha, A. (2025). Impact of Diabetes and Metformin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 66 and Older: The Role of Social Determinants of Health and Racial Disparities †. Cancers, 17(17), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172854








