Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classifying DLBCL
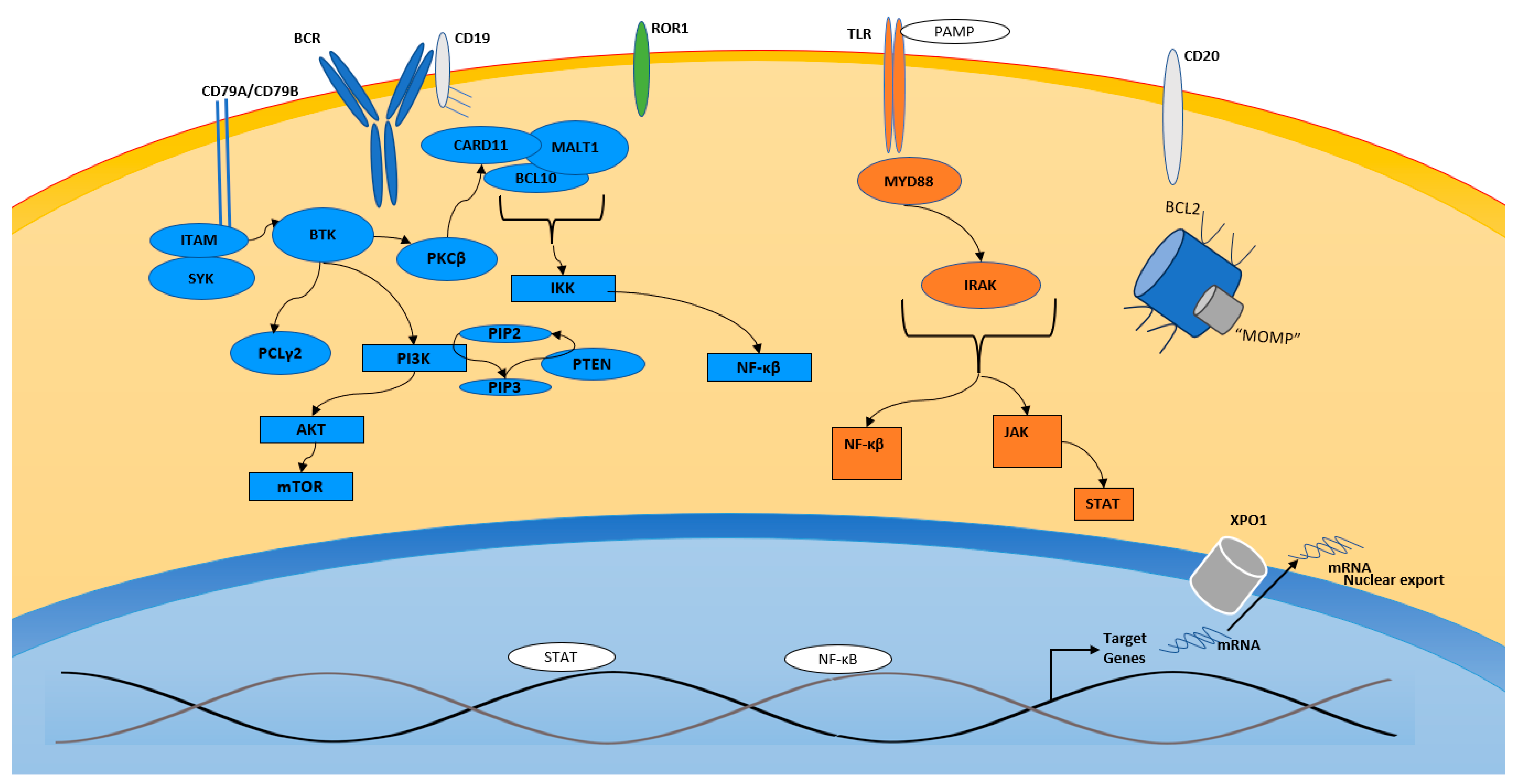
3. Molecular Pathway Targets
3.1. BCR Signaling in DLBCL
3.2. Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Pathways in DLBCL
3.3. PI3K-AKT-MTOR in DLBCL
3.4. BCL2 in DLBCL
3.5. XPO1
4. Surface Receptor Targets
5. Checkpoint Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hamadani, M.; Habermann, T.M.; Cerhan, J.R.; Macon, W.R.; Maurer, M.J.; Go, R.S. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtype distribution, geodemographic patterns, and survival in the US: A longitudinal analysis of the National Cancer Data Base from 1998 to 2011. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilly, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Sehn, L.H.; Friedberg, J.W.; Trněný, M.; Sharman, J.P.; Herbaux, C.; Burke, J.M.; Matasar, M.; Rai, S.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Briere, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Flinn, I.W.; Advani, R.; Sehn, L.H.; Diefenbach, C.; Kolibaba, K.; Press, O.W.; Salles, G.; Tilly, H.; Chen, A.I.; et al. Polatuzumab vedotin or pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Final results from a phase 2 randomised study (ROMULUS). Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e254–e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakonda, N.; Maerevoet, M.; Cavallo, F.; Follows, G.; Goy, A.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; Casasnovas, O.; Hamad, N.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Bakhshi, S.; et al. Selinexor in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (SADAL): A single-arm, multinational, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e511–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salles, G.; Duell, J.; González Barca, E.; Tournilhac, O.; Jurczak, W.; Liberati, A.M.; Nagy, Z.; Obr, A.; Gaidano, G.; André, M.; et al. Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): A multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caimi, P.F.; Ai, W.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Hamadani, M.; Hess, B.; Kahl, B.S.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Hahn, U.; Kim, W.S.; Fleury, I.; Laribi, K.; Bergua, J.M.; Bouabdallah, K.; Forward, N.; Bijou, F.; MacDonald, D.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin Combination for Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Corradini, P.; Iacoboni, G.; Khan, C.; Wróbel, T.; Offner, F.; Trněný, M.; et al. Glofitamab for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.A.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Mehta, A.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet 2020, 396, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.; Mous, R.; Clausen, M.R.; Johnson, P.; Linton, K.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Lewis, D.J.; Sureda Balari, A.; Cunningham, D.; Oliveri, R.S.; et al. Dose escalation of subcutaneous epcoritamab in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: An open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, M.A.; Ross, K.N.; Tamayo, P.; Weng, A.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Aguiar, R.C.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Angelo, M.; Reich, M.; Pinkus, G.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Mottok, A.; Ennishi, D.; Wright, G.W.; Farinha, P.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Kridel, R.; Barry, G.S.; Hother, C.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell of Origin Determined by Digital Gene Expression in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Noorani, M.; Lin, P.; Davis, R.E.; Neelapu, S.S.; Ma, L.; Ahmed, M.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Fowler, N.; et al. Double hit lymphoma: The MD Anderson Cancer Center clinical experience. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havranek, O.; Xu, J.; Köhrer, S.; Wang, Z.; Becker, L.; Comer, J.M.; Henderson, J.; Ma, W.; Man Chun Ma, J.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tonic B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.H.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Lih, C.J.; Williams, P.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaswinkel, H.; Reth, M. Dual role of the tyrosine activation motif of the Ig-alpha protein during signal transduction via the B cell antigen receptor. Embo J. 1994, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, M.; Sabe, H.; Hata, A.; Inazu, T.; Homma, Y.; Nukada, T.; Yamamura, H.; Kurosaki, T. Tyrosine kinases Lyn and Syk regulate B cell receptor-coupled Ca2+ mobilization through distinct pathways. Embo J. 1994, 13, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamason, R.L.; McCully, R.R.; Lew, S.M.; Pomerantz, J.L. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations induce hyperactive signaling by disrupting autoinhibition by the PKC-responsive inhibitory domain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8240–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Brown, K.D.; Siebenlist, U.; Staudt, L.M. Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, P.; Erdmann, T.; Grondona, P.; Xu, W.; Schmitt, A.; Schürch, C.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Schönfeld, C.; Serfling, E.; Kramer, D.; et al. Targeting chronic NFAT activation with calcineurin inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2020, 135, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, I.W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Blum, K.A.; Ardeshna, K.M.; LaCasce, A.S.; Flowers, C.R.; Shustov, A.R.; Thress, K.S.; Mitchell, P.; Zheng, F.; et al. A phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy of fostamatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.M.; Shustov, A.; Essell, J.; Patel-Donnelly, D.; Yang, J.; Chen, R.; Ye, W.; Shi, W.; Assouline, S.; Sharman, J. An Open-label, Phase II Trial of Entospletinib (GS-9973), a Selective Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, e327–e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.J.; Kahl, B.S.; Vose, J.M.; de Vos, S.; Laughlin, M.; Flynn, P.J.; Rowland, K.; Cruz, J.C.; Goldberg, S.L.; Musib, L.; et al. Phase II study of enzastaurin, a protein kinase C beta inhibitor, in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontan, L.; Yang, C.; Kabaleeswaran, V.; Volpon, L.; Osborne, M.J.; Beltran, E.; Garcia, M.; Cerchietti, L.; Shaknovich, R.; Yang, S.N.; et al. MALT1 small molecule inhibitors specifically suppress ABC-DLBCL in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Ikegawa, M.; Ori, D.; Akira, S. Decoding Toll-like receptors: Recent insights and perspectives in innate immunity. Immunity 2024, 57, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, A.; Ejdeback, M.; Ludidi, P.L.; O’Neill, L.A.; Gay, N.J. Structural complementarity of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains in Toll-like receptors and the adaptors Mal and MyD88. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41443–41451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Karube, K.; Valera, A.; Colomer, D.; Enjuanes, A.; Colomo, L.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Giné, E.; Dlouhy, I.; Magnano, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P Mutations, But No Other Variants, Identify a Subpopulation of DLBCL Patients of Activated B-cell Origin, Extranodal Involvement, and Poor Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Zhu, S.; Li, T.; Wu, J.; Zang, G.; Lv, X.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, J.; Shao, Y.; Cui, J.; et al. A Dual TLR7/TLR9 Inhibitor HJ901 Inhibits ABC-DLBCL Expressing the MyD88 L265P Mutation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booher, R.N.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Patel, K.; Lunning, M.A.; Samson, M.E.S.; Atoyan, R.; Ma, A.W.; Xu, G.-X.; Dellarocca, S.; Modafferi, H.; et al. Preclinical Activity of IRAK4 Kinase Inhibitor CA-4948 Alone or in Combination with Targeted Therapies and Preliminary Phase 1 Clinical Results in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.D.; Baran, A.; Reagan, P.M.; Casulo, C.; Zent, C.; Evans, A.; Burack, R.; Williams, A.M.; Friedberg, J.W.; Barr, P.M. Efficacy of lenalidomide in high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, e33–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzig, T.E.; Vose, J.M.; Zinzani, P.L.; Reeder, C.B.; Buckstein, R.; Polikoff, J.A.; Bouabdallah, R.; Haioun, C.; Tilly, H.; Guo, P.; et al. An international phase II trial of single-agent lenalidomide for relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.C.; Perini, G.F.; Nastoupil, L.; Joergensen, J.M.; Bories, P.; Fontanet, B.; Zinzani, P.L.; Munoz, J.; Morillo Giles, D.; Carpio, C.; et al. Golcadomide (GOLCA) ± Rituximab (RTX) Demonstrates Durable Efficacy and Is Well Tolerated in Patients (pts) with Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma (R/R FL): Updated Results from the Phase 1/2 CC-99282-NHL-001 Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana, A.; Vera-Badillo, F.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Templeton, A.J.; Corrales-Sanchez, V.; Diez-Gonzalez, L.; Cuenca-Lopez, M.D.; Seruga, B.; Pandiella, A.; Amir, E. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway and survival in solid tumors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehama, T.; Dixon, J.E. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13375–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansal, I.; Sellers, W.R. The biology and clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Ebbs, A.; Pasparakis, M.; Van Dyke, T.; Basseres, D.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-dependent activation of mTORC1 complex involves phosphorylation of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) by IκB kinase α (IKKα). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25227–25240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Hawkes, E.; Verhoef, G.; Haioun, C.; Thye Lim, S.; Seog Heo, D.; Ardeshna, K.; Chong, G.; Haaber, J.; Shi, W.; et al. Single-agent activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition with copanlisib in patients with molecularly defined relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2184–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.A.; Jacobsen, E.; Feng, Y.; Freedman, A.; Hochberg, E.P.; LaCasce, A.S.; Armand, P.; Joyce, R.; Sohani, A.R.; Rodig, S.J.; et al. Everolimus in combination with rituximab induces complete responses in heavily pretreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2013, 98, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluck, R.M.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Green, D.R.; Newmeyer, D.D. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: A primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 1997, 275, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melani, C.; Lakhotia, R.; Pittaluga, S.; Phelan, J.D.; Huang, D.W.; Wright, G.; Simard, J.; Muppidi, J.; Thomas, C.J.; Ceribelli, M.; et al. Combination Targeted Therapy in Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2143–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, A.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.Y.; Godsey, A.; Liao, D. p53 SUMOylation promotes its nuclear export by facilitating its release from the nuclear export receptor CRM1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Huang, L.; Gu, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, H.; Chen, G.; Peng, Z.; Feng, Z. Expression of exportin-1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Immunohistochemistry and TCGA analyses. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kodali, D.; Rawal, A.; Ninan, M.J.; Patel, M.R.; Mesa, H.; Knapp, D.; Schnitzer, B.; Kratzke, R.A.; Gupta, P. Expression and phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 in B-cell lymphomas and reactive lymphoid tissues. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, J.M.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Farooq, U.; Feldman, T.; Ghesquieres, H.; Jurczak, W.; Linton, K.; Thieblemont, C.; et al. 3-Year Update from the Epcore NHL-1 Trial: Epcoritamab Leads to Deep and Durable Responses in Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Ku, M.; Hertzberg, M.; Huang, H.-Q.; Fox, C.P.; Zhang, H.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, W.-S.; Abdulhaq, H.; Townsend, W.; et al. Glofitamab plus gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (GemOx) versus rituximab-GemOx for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (STARGLO): A global phase 3, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet 2024, 404, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory aggressive large B cell lymphoma: A phase 1b/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyappan, S.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, T.M.; Walewski, J.; Cho, S.-G.; Jarque, I.; Iskierka-Jazdzewska, E.; Poon, M.; Oh, S.Y.; Inng Lim, F.L.W.; et al. Final Analysis of the Phase 2 ELM-2 Study: Odronextamab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, D.C.; Omori, S.A.; Rickert, R.C. Cd19-dependent activation of Akt kinase in B-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, D.A.; Lambert, N.; Caimi, P.F.; Merrill, M.; Pullarkat, P.; Godby, R.C.; Bond, D.A.; Wehmeyer, G.T.; Romancik, J.; Amoozgar, B.; et al. Tafasitamab and lenalidomide in large B-cell lymphoma: Real-world outcomes in a multicenter retrospective study. Blood 2023, 142, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, L.; Morley, N.J.; Rambaldi, A.; Mason, K.D.; Verhoef, G.; Furness, C.L.; Zhang, A.; Jung, A.S.; Cohan, D.; Franklin, J.L. Open-Label, phase 2 study of blinatumomab as second salvage therapy in adults with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Perales, M.A.; Kersten, M.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; McGuirk, J.; Pagel, J.M.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamdar, M.; Solomon, S.R.; Arnason, J.; Johnston, P.B.; Glass, B.; Bachanova, V.; Ibrahimi, S.; Mielke, S.; Mutsaers, P.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): Results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 2294–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshmanesh, A.H.; Porwit, A.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Tamm, K.P.; Grandér, D.; Lehmann, S.; Norin, S.; Shokri, F.; Rabbani, H.; et al. Orphan receptor tyrosine kinases ROR1 and ROR2 in hematological malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurgeon, S.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Barrientos, J.; De Vos, S.; Furman, R.; Patel, K.; Thompson, P.; Choi, M.Y.; Kallam, A.; et al. P1200: Zilovertamab Vedotin (Mk-2140) in Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (Nhl): Updated Results from the Phase 1 Waveline-001 Study. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e54506b2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, G.W.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; Gascoyne, R.D. CD30 expression in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A population-based study from British Columbia. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.D.; Sharman, J.P.; Oki, Y.; Advani, R.H.; Winter, J.N.; Bello, C.M.; Spitzer, G.; Palanca-Wessels, M.C.; Kennedy, D.A.; Levine, P.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin demonstrates objective responses in a phase 2 study of relapsed/refractory DLBCL with variable CD30 expression. Blood 2015, 125, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.P.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Gomez, F.; Luo, J.; Becker-Hapak, M.; Cashen, A.F.; Wagner-Johnston, N.D.; Maddocks, K.; Mosior, M.; Foster, M.; et al. Phase 1/dose expansion trial of brentuximab vedotin and lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2022, 139 (Suppl. 1), 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, G.J.; Long, A.J.; Iwai, Y.; Bourque, K.; Chernova, T.; Nishimura, H.; Fitz, L.J.; Malenkovich, N.; Okazaki, T.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Melnichenko, V.; Thieblemont, C.; Bouabdallah, K.; Tumyan, G.; Özcan, M.; Portino, S.; Fogliatto, L.; Caballero, D.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma (PMBCL): Data from the Keynote-013 and Keynote-170 Studies. Blood 2018, 132, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Santoro, A.; Gritti, G.; Brice, P.; Barr, P.M.; Kuruvilla, J.; Cunningham, D.; Kline, J.; Johnson, N.A.; Mehta-Shah, N.; et al. Nivolumab combined with brentuximab vedotin for R/R primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: A 3-year follow-up. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 5272–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, J.; Tumuluru, S.; Bao, R.; Leukam, M.; Venkataraman, G.; Phillip, J.; Fitzpatrick, C.; McElherne, J.; MacNabb, B.W.; Orlowski, R.; et al. PD-L1 gene alterations identify a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma harboring a T-cell–inflamed phenotype. Blood 2019, 133, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansell, S.M.; Minnema, M.C.; Johnson, P.; Timmerman, J.M.; Armand, P.; Shipp, M.A.; Rodig, S.J.; Ligon, A.H.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Reddy, N.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Patients Ineligible for or Having Failed Autologous Transplantation: A Single-Arm, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazama, R.; Miyoshi, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Miyawaki, K.; Nakashima, K.; Yoshida, N.; Kawamoto, K.; Yanagida, E.; Yamada, K.; Umeno, T.; et al. Combination of CD47 and signal-regulatory protein-α constituting the “don’t eat me signal” is a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2608–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, R.; Flinn, I.; Popplewell, L.; Forero, A.; Bartlett, N.L.; Ghosh, N.; Kline, J.; Roschewski, M.; LaCasce, A.; Collins, G.P.; et al. CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Rosen, S.T.; Helenowski, I.; Kline, J.; Larsen, A.; Colvin, J.; Winter, J.N.; van Besien, K.M.; Gordon, L.I.; Smith, S.M. A phase I/II trial of bortezomib combined concurrently with gemcitabine for relapsed or refractory DLBCL and peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Fanale, M.; Romaguera, J.; Fayad, L.; Fowler, N.; Copeland, A.; Samaniego, F.; Kwak, L.W.; Neelapu, S.; Wang, M.; et al. Phase II study of an AKT inhibitor MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 171, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Corradini, P.; Iacoboni, G.; Khan, C.; Wrobel, T.; Offner, F.; Trneny, M.; et al. Glofitamab in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and ≥2 prior therapies: Pivotal phase II expansion results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. 6), 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ghaderi, A.; Daneshmanesh, A.; Lehto, J.; Moshfegh, A.; Kokhaei, P.; Vågberg, J.; Olsson, E.; Löfberg, C.; Norström, C.C.; et al. Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Expresses ROR1 and a ROR1 Small Molecule Inhibitor (KAN0441571C) Induced Significant Apoptosis of Tumor Cells. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Martelli, M.; Trněný, M.; Liu, W.; Bolen, C.R.; Knapp, A.; Sahin, D.; Sellam, G.; Vitolo, U. A randomized, open-label, Phase III study of obinutuzumab or rituximab plus CHOP in patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: Final analysis of GOYA. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Chiappella, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Scott, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Jurczak, W.; Özcan, M.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Jin, J.; et al. ROBUST: A Phase III Study of Lenalidomide Plus R-CHOP Versus Placebo Plus R-CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients With ABC-Type Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Sehn, L.H.; Johnson, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Patti, C.; Belada, D.; Samoilova, O.; Suh, C.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Ibrutinib and Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone in Non-Germinal Center B-Cell Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offner, F.; Samoilova, O.; Osmanov, E.; Eom, H.S.; Topp, M.S.; Raposo, J.; Pavlov, V.; Ricci, D.; Chaturvedi, S.; Zhu, E.; et al. Frontline rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone with bortezomib (VR-CAP) or vincristine (R-CHOP) for non-GCB DLBCL. Blood 2015, 126, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Feugier, P.; Flinn, I.W.; Gasiorowski, R.; Greil, R.; Illés, Á.; Johnson, N.A.; Larouche, J.F.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Patti, C.; et al. A phase 2 study of venetoclax plus R-CHOP as first-line treatment for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzig, T.E.; Tobinai, K.; Rigacci, L.; Ikeda, T.; Vanazzi, A.; Hino, M.; Shi, Y.; Mayer, J.; Costa, L.J.; Bermudez Silva, C.D.; et al. Adjuvant everolimus in high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Final results from the PILLAR-2 randomized phase III trial. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Drug | Mechanism of Action (MOA) | ORR in Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL |
|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib [23] | BTK inhibitor | 20/80 (25%) —ABC DLBCL 14/38 (37%) —GCB DLBCL 1/20 (5%) |
| Fostamatinib [30] | SYK inhibitor | 2/68 (3%) |
| Entospletinib [31] | SYK inhibitor | 0/43 (0%) |
| Enzastaurin [32] | PKCβ inhibitor | 8/55 (15%) freedom from progression following 4 cycles |
| Lenalidomide [39] | NF-κβ inhibitor/CELMoD | 30/108 (28%) |
| Bortezomib + Gemcitabine [79] | Down-regulates NF-κβ | 1/16 (6%) |
| Copanlisib [47] | PI3K inhibitor | 13/67 (19%) |
| MK2206 [80] | AKT inhibitor | 0/9 (0%) |
| Everolimus + Rituximab [48] | mTOR inhibitor | 9/24 (38%) |
| Venotoclax [52] | BCL2 inhibitor | 6/34 (18%) |
| Selinexor [5] * | XPO1 inhibitor | 36/127 (28%) |
| Glofitamab [81] * | CD20XCD3 bispecific antibody | 54/107 (50%) |
| Epcoritamab [13] * | CD20XCD3 bispecific antibody | 15/22 (68%) |
| Tafasitamab + Lenalidomide [6] * | anti-CD19 | 48/80 (60%) |
| Loncastuximab tesirine [7] * | CD19 antibody–drug conjugate | 70/145 (48%) |
| Blinatumomab [63] | CD19/CD3 bispecific antibody | 15/41 (37%) |
| Axicabtagene ciloleucel [10] * | CD-19 CAR-T cell | 83/101 (82%) |
| Tisagenlecleucel [11] * | CD-19 CAR T-cell | 48/93 (52%) |
| Lisocabtagene Maraleucel [12] * | CD-19 CAR T-cell | 186/256 (73%) |
| Polatuzumab vedotin + bendamustine/rituximab [4] * | CD79 antibody–drug conjugate | 60/106 (57%) |
| Zilovertamab vedotin [82] | ROR-1 antibody–drug conjugate | 3/5 (6%) |
| Brentuximab-vedotin (BV) [70] | CD30 antibody–drug conjugate | 21/48 (44%) |
| BV + Lenalidomide + Rituximab [8] * | CD30 antibody–drug conjugate with NF-κβ inhibitor | 71/112 (64%) |
| Nivolumab [76] | PD-1 inhibitor | 3/87 (3%) |
| Magrolimab + Rituximab [78] | CD47 inhibitor | 6/15 (40%) |
| First-Line Trial | Comparison | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pola-R-CHP [2] | Standard R-CHOP | 2-year PFS 76.7% vs. 70.2%. No OS benefit | |
| Obin-CHOP [83] | Standard R-CHOP | No PFS or OS benefit | |
| R2-CHOP [84] | Standard R-CHOP | No PFS or OS benefit | - included patients with ABC-DLBCL |
| Ibrutinib-R-CHOP [85] | Standard R-CHOP | Worsened EFS, PFS, and OS | - included patients with non-GCB DLBCL - patients younger than 60 showed improved EFS, PFS, and OS |
| Bortezomib-R-CHP [86] | Standard R-CHOP | No difference in PFS or OS | |
| Venetoclax + R-CHOP [87] | Standard R-CHOP in GOYA trial [83] | Improved PFS (HR 0.61) No OS benefit | - increased hematologic grade 3/4 adverse events |
| R-Chemo followed by 1 yr of everolimus [88] | R-chemo followed by 1 yr of placebo | No difference in EFS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiss, J.; Carty, S.A.; Karimi, Y.H. Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Cancers 2025, 17, 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142314
Weiss J, Carty SA, Karimi YH. Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Cancers. 2025; 17(14):2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142314
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiss, Jonathan, Shannon A. Carty, and Yasmin H. Karimi. 2025. "Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)" Cancers 17, no. 14: 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142314
APA StyleWeiss, J., Carty, S. A., & Karimi, Y. H. (2025). Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Cancers, 17(14), 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142314






