The Knowledge Gap in Gut Microbiome Characterization in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Scoping Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objectives
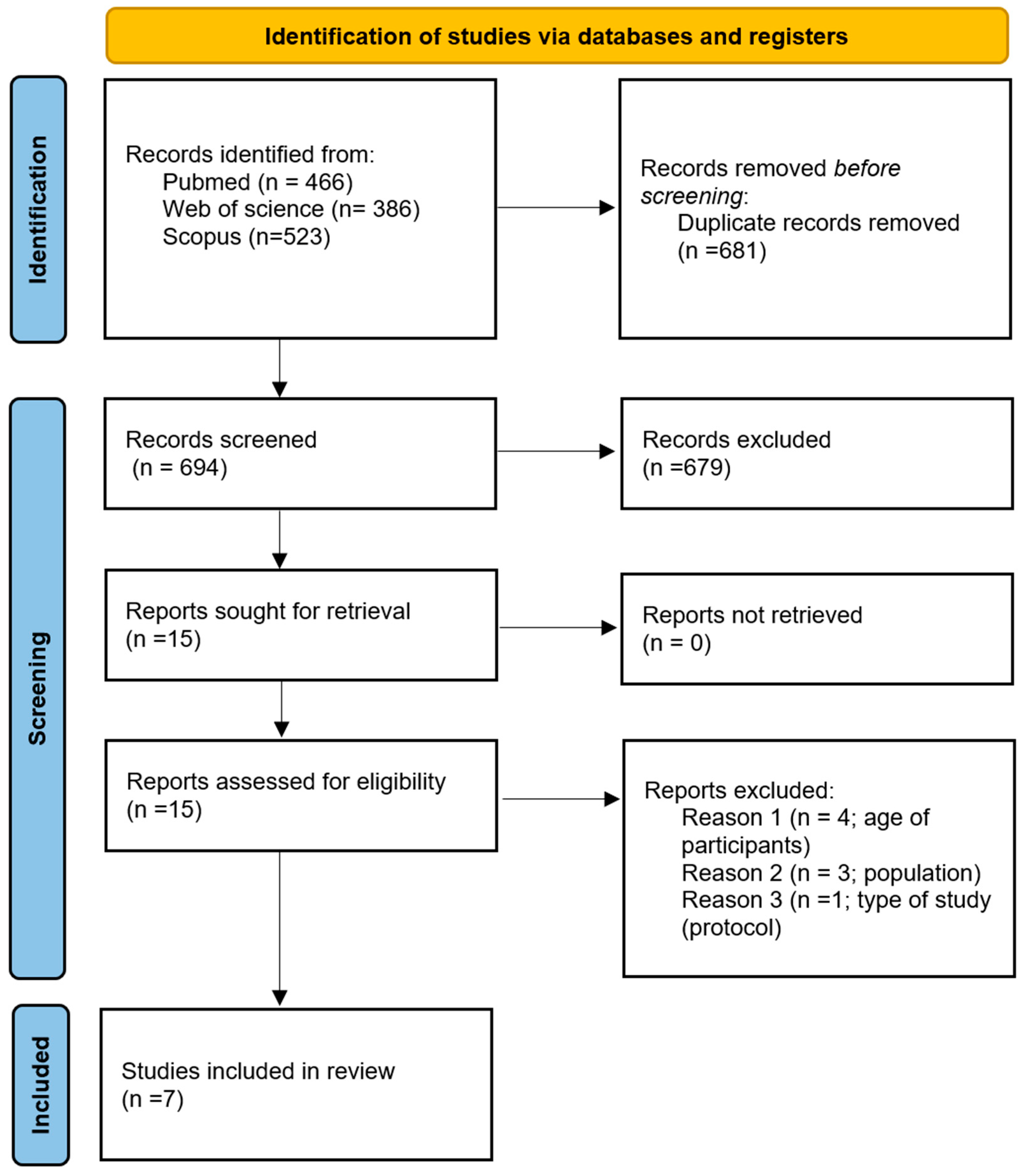
3. Methods
3.1. Eligibility Criteria
3.1.1. Participants
3.1.2. Concept
3.1.3. Context
3.1.4. Types of Sources
3.2. Search Strategy
3.3. Source of Evidence Screening and Selection
3.4. Data Extraction
3.5. Synthesis of Results
4. Results
4.1. Study and Sample Characteristics
4.2. Used Methodology
4.3. Gut Microbiota Diversity
4.4. Taxonomic Classification
4.5. Other Outcomes
5. Discussion
5.1. Gut Microbiota Diversity
5.2. Taxonomic Classification
5.3. Used Methodology
5.4. Knowledge Gaps and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Search Strategy
- MESH terms:
- MESH terms:
- Keywords in title/abstract:
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuik, F.E.; Nieuwenburg, S.A.; Bardou, M.; Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Bento, M.J.; Zadnik, V.; Pellisé, M.; Esteban, L.; Kaminski, M.F.; et al. Increasing Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Young Adults in Europe over the Last 25 Years. Gut 2019, 68, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Hayes, R.B.; Bray, F.; Weber, T.K.; Jemal, A. Global Patterns and Trends in Colorectal Cancer Incidence in Young Adults. Gut 2019, 68, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.E.; Hu, C.-Y.; You, Y.N.; Bednarski, B.K.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Skibber, J.M.; Cantor, S.B.; Chang, G.J. Increasing Disparities in the Age-Related Incidences of Colon and Rectal Cancers in the United States, 1975–2010. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.T.; Pai, R.K.; Rybicki, L.A.; Dimaio, M.A.; Limaye, M.; Jayachandran, P.; Koong, A.C.; Kunz, P.A.; Fisher, G.A.; Ford, J.M.; et al. Clinicopathologic and Molecular Features of Sporadic Early-Onset Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: An Adenocarcinoma with Frequent Signet Ring Cell Differentiation, Rectal and Sigmoid Involvement, and Adverse Morphologic Features. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraste, D.; Järås, J.; Martling, A. Population-based Analysis of Outcomes with Early-age Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett-Hartman, A.N.; Powers, J.D.; Chubak, J.; Corley, D.A.; Ghai, N.R.; McMullen, C.K.; Pawloski, P.A.; Sterrett, A.T.; Feigelson, H.S. Treatment Patterns and Survival Differ between Early-Onset and Late-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: The Patient Outcomes to Advance Learning Network. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercek, A.; Chatila, W.K.; Yaeger, R.; Walch, H.; Fernandes, G.D.S.; Krishnan, A.; Palmaira, L.; Maio, A.; Kemel, Y.; Srinivasan, P.; et al. A Comprehensive Comparison of Early-Onset and Average-Onset Colorectal Cancers. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Kleis, L.; Depetris-Chauvin, A.; Jaskulski, S.; Damerell, V.; Michels, K.B.; Gigic, B.; Nöthlings, U.; Panagiotou, G. Beneficial Microbiome and Diet Interplay in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2025, 17, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L.; Viaud, S.; Vétizou, M.; Daillère, R.; Merad, M.; Kroemer, G. Cancer and the Gut Microbiota: An Unexpected Link. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 271ps1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; Sukartini, N.; Nursyirwan, S.A.; Pribadi, R.R.; Maulahela, H.; Utari, A.P.; Muzellina, V.N.; Wiraatmadja, A.; Renaldi, K. Gut Microbiota Profiles in Early- and Late-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in the Future. Digestion 2021, 102, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saus, E.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Willis, J.R.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Gabaldón, T. Microbiome and Colorectal Cancer: Roles in Carcinogenesis and Clinical Potential. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 69, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, C.P.; Vieira, P.; Mendes-Rocha, M.; Pereira-Marques, J.; Ferreira, R.M.; Figueiredo, C. The Tissue-Associated Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabowei, G.; Gaddipati, G.N.; Mukhtar, M.; Alzubaidee, M.J.; Dwarampudi, R.S.; Mathew, S.; Bichenapally, S.; Khachatryan, V.; Muazzam, A.; Hamal, C.; et al. Microbiota Dysbiosis a Cause of Colorectal Cancer or Not? A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitay, E.L.; Krilaviciute, A.; Brenner, H. Systematic Review: Gut Microbiota in Fecal Samples and Detection of Colorectal Neoplasms. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Portela-Cidade, J.P.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Pimentel-Nunes, P. Role of Colonic Microbiota in Colorectal Carcinogenesis: A Systematic Review. Rev. Española Enfermedades Dig. 2015, 107, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhan, C.; Xu, H. Gut Microbiota Alterations in Colorectal Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequence Based on 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 195, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlo, L.-F.; Salcudean, A.; Sirli, R.; Iurciuc, S.; Herlo, A.; Nelson-Twakor, A.; Alexandrescu, L.; Dumache, R. Gut Microbiota Signatures in Colorectal Cancer as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in the Future: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharofa, J.; Apewokin, S.; Alenghat, T.; Ollberding, N.J. Metagenomic Analysis of the Fecal Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer Patients Compared to Healthy Controls as a Function of Age. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Porritt, K.; Pilla, B.; Jordan, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Shi, D.; Kong, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. Dysbiosis of Human Gut Microbiome in Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barot, S.V.; Sangwan, N.; Nair, K.G.; Schmit, S.L.; Xiang, S.; Kamath, S.; Liska, D.; Khorana, A.A. Distinct Intratumoral Microbiome of Young-Onset and Average-Onset Colorectal Cancer. eBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Tong, X.; Mei, W.-J.; Cheng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Han, K.; Yu, J.; Jie, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, S.; et al. Consistent Signatures in the Human Gut Microbiome of Old- and Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, D.; Trinh, J.Q.; Sharma, D.; Alsayid, M.; Bishehsari, F. Early-Onset Colon Cancer Shows a Distinct Intestinal Microbiome and a Host–Microbe Interaction. Cancer Prev. Res. 2023, 17, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Chang, Z.; Hu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Display Alternative Profiles in Patients with Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1036946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huo, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Tuersun, A.; Zhao, J.; et al. Dysbiosis of Human Tumor Microbiome and Aberrant Residence of Actinomyces in Tumor-Associated Fibroblasts in Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1008975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Liang, L.; Liu, G.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, D.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. Integrated Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Distinct Gut-Microbiome-Derived Phenotypes in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Gut 2023, 72, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbirtseva, K.Y.; O’Toole, P.W. Healthy and Unhealthy Aging and the Human Microbiome. Annu. Rev. Med. 2025, 76, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Clooney, A.G.; Stanton, C.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing of Mock Microbial Populations- Impact of DNA Extraction Method, Primer Choice and Sequencing Platform. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bars-Cortina, D.; Ramon, E.; Rius-Sansalvador, B.; Guinó, E.; Garcia-Serrano, A.; Mach, N.; Khannous-Lleiffe, O.; Saus, E.; Gabaldón, T.; Ibáñez-Sanz, G.; et al. Comparison between 16S RRNA and Shotgun Sequencing in Colorectal Cancer, Advanced Colorectal Lesions, and Healthy Human Gut Microbiota. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzi, F.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; Manfreda, G.; Remondini, D.; Cesare, A.D. Comparison between 16S RRNA and Shotgun Sequencing Data for the Taxonomic Characterization of the Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Hul, M.V.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia Muciniphila in Overweight and Obese Human Volunteers: A Proof-of-Concept Exploratory Study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, L.; Termite, F.; Mignini, I.; Esposto, G.; Borriello, R.; Vitale, F.; Nicoletti, A.; Paratore, M.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Unraveling the Role of Fusobacterium Nucleatum in Colorectal Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Pathogenic Insights. Cancers 2025, 17, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, O.; Mankarious, M.; Yochum, G. Molecular Genetics of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 14, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethings-Behncke, C.; Coleman, H.G.; Jordao, H.W.T.; Longley, D.B.; Crawford, N.; Murray, L.J.; Kunzmann, A.T. Fusobacterium Nucleatum in the Colorectum and Its Association with Cancer Risk and Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2020, 29, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Ma, F.; Chen, Q.; Gou, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H. Construction of Size-Transformable Supramolecular Nano-Platform against Drug-Resistant Colorectal Cancer Caused by Fusobacterium Nucleatum. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Shibata, C.; Seimiya, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishibashi, R.; Kishikawa, T.; Tanaka, E.; Isagawa, T.; Takeda, N.; et al. Gut Bacteria-Derived Membrane Vesicles Induce Colonic Dysplasia by Inducing DNA Damage in Colon Epithelial Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 17, 745–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ji, S.; Su, D.; Zhao, Y.; Goncalves, V.B.E.; Xu, G.; Zhang, M. The Biofunction of Akkermansia Muciniphila in Intestinal-Related Diseases. Microbiome Res. Rep. 2024, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Collado, M.C.; Ben-Amor, K.; Salminen, S.; de Vos, W.M. The Mucin Degrader Akkermansia Muciniphila Is an Abundant Resident of the Human Intestinal Tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Derrien, M.; Isolauri, E.; de Vos, W.M.; Salminen, S. Intestinal Integrity and Akkermansia Muciniphila, a Mucin-Degrading Member of the Intestinal Microbiota Present in Infants, Adults, and the Elderly. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7767–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghfuri, E.; Gholizadeh, P. The Role of Akkermansia Muciniphila in Colorectal Cancer: A Double-Edged Sword of Treatment or Disease Progression? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, P.; Du, H.; Chu, W.; Sun, R.; Qin, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, F. Akkermansia Muciniphila Potentiates the Antitumor Efficacy of FOLFOX in Colon Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 725583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lv, J.; Guo, F.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiome Influences the Efficacy of PD-1 Antibody Immunotherapy on MSS-Type Colorectal Cancer via Metabolic Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.-Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y. Function of Akkermansia Muciniphila in Obesity: Interactions With Lipid Metabolism, Immune Response and Gut Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Jin, E.H.; Chung, G.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, S.; Han, K.-D.; Yang, S.Y. Association of Changes in Obesity and Abdominal Obesity Status with Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1208489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Ma, L.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, L. Prevalence of Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides Fragilis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1525609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Kong, C.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shi, D.; Li, X.; et al. Distinct Microbes, Metabolites, and the Host Genome Define the Multi-Omics Profiles in Right-Sided and Left-Sided Colon Cancer. Microbiome 2024, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, K.L.; Chan, A.T.; Izard, J.; Cassidy, A.; Rogers, G.B.; Rimm, E.B. Role of Dietary Flavonoid Compounds in Driving Patterns of Microbial Community Assembly. mBio 2019, 10, e01205-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.S.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, J.-S.; Ryu, S.W.; Yu, S.Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, J.; Jung, W.Y.; et al. Cell-Free Supernatant of Odoribacter Splanchnicus Isolated From Human Feces Exhibits Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 736343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, D.; Sun, D.; Zhou, Y. Gut Microbiome: New Biomarkers in Early Screening of Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDecker, L.; Coppedge, B.; Avelar-Barragan, J.; Karnes, W.; Whiteson, K. Microbiome Distinctions between the CRC Carcinogenic Pathways. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1854641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-L.; Zheng, Q.-F.; Wang, L.-Q.; Liu, Y. Bowel Preparation before Colonoscopy: Consequences, Mechanisms, and Treatment of Intestinal Dysbiosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shete, O.; Ghosh, T.S. Normal Gut Microbiomes in Diverse Populations: Clinical Implications. Annu. Rev. Med. 2025, 76, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population | Aim | Sample | Source of Microbiota Sample | Sequencing Methodology | Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yang et al. 2021 [23] | China | To evaluate the diagnostic value of gut microbiota for EoCRC patients | 185 EoCRC, 379 LoCRC, 217 young controls and 257 old controls. | Stools | 16S rRNA gene (all samples) and shotgun sequencing (200 samples, 50 from each group) | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, functional analysis, model construction (random forest). |
| Kong et al. 2022 [29] | China | To characterize the interactions between gut microbiome, metabolites and microbial enzymes in EoCRC patients and evaluate their potential as non-invasive biomarkers for EoCRC. | Discovery cohort: 114 EoCRC, 130 LoCRC, 97 older controls and 100 young controls. Independent cohort: 24EoCRC, 22 LoCRC and 24 young controls. | Stools | Shotgun sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, metabolomic composition, functional analysis, model construction (random forest). |
| Xu et al. 2022 [28] | China | To identify microbial markers for EoCRC diagnosis and explore their potential roles in the tumor immune microenvironment and tumorigenesis. | 20 EoCRC, 19 LoCRC. Independent cohort: 78 CRC. | Tumor | 16S rRNA sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, network association, functional analysis, abundance of Actinomyces by FISH and correlation with immunohistochemistry. |
| Xiong et al. 2022 [27] | China | To explore whether there is an alternative gut microbiota profile in patients with EoCRC | 24EoCRC, 43 LoCRC and 31 young controls | Stools | 16S rRNA gene sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, functional analysis. |
| Qin et al. 2024 [25] | China | To address the question whether CRC signatures derived from old patients are valid in young patients | Guangzhou cohort: EoCRC 167 and 293 LoCRC. Fudan cohort: EoCRC 156, 241 LoCRC and 153 young controls. | Stools | Shotgun sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, functional analysis, model construction (random forest and LASSO logistic regression). |
| Adnan et al. 2024 [26] | USA | To investigate age-related differences in the gut microbiome of CRC patients and healthy individuals | CuratedMetagenomeData: 82 EoCRC; 1187 LoCRC and 125 young controls. Cancer Genoma Atlas: 15 EoCRC and 70 LoCRC. | CuratedMetagenomeData: Stools. Cancer Genoma Atlas: Tumor | Shotgun sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, functional analysis. |
| Barot et al. 2024 [24] | USA | To compare the tumor microbial profile of EoCRC with average-onset CRC and to assess its association with clinical factors | 136 EoCRC, 140 LoCRC and 276 adjacent non-malignant sample | Tumor | 16S rRNA sequencing | Diversity, taxonomic profiling, network analysis. |
| Measures | α Diversity | Measures | β Diversity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal microbiota | ||||
| Yang et al. [23] | Observed species (p = 4.12 × 10−8) |  | PCoA of weighted UniFrac distances and Permanova (p = 0.019) | ≠ |
| Kong et al. [29] | Breakaway estimates (p = 0.0074) |  | PCoA of Bray–Curtis distance and Permanova (p = 0.001) | ≠ |
| Xiong et al. [27] | Shannon index (p = 0.008)Simpson index (p = 0.011) |  | PCoA unweighted UniFrac distances and Permanova (p = 0.0001) | ≠ |
| Qin et al. [25] | Shannon index (p = 0.053 Fudan cohort; p = 1.7 × 10−5 Guangchou cohort) |  | PCoA of Bray–Curtis distance and Permanova (p = 0.46 Fudan cohort p = 0.012 Guangchou cohort) | ≠ |
 ) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients; the gray arrow (
) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients; the gray arrow ( ) reflects a decrease in EoCRC patients; and ≠ reflects a difference between groups. PCoA = Principal coordinate analysis.
) reflects a decrease in EoCRC patients; and ≠ reflects a difference between groups. PCoA = Principal coordinate analysis.| Measures | α Diversity | Measures | β Diversity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal microbiota | ||||
| Yang et al. [23] | Shannon index (p = 8.88 × 10−5) |  | PCoA of Weighted UniFrac distances and Permanova (p = 0.001) | ≠ |
| Kong et al. [29] | Breakaway estimates (p = 0.0788) | = | Not available | |
| Xiong et al. [27] | Shannon index (p = 0.007) Simpson index (p = 0.013) |  | PCoA unweighted UniFrac distances and Permanova (p = 0.0001) | ≠ |
| Qin et al. [25] | Observed species (p = 0.13) Shannon index (p = 0.42) | = | PCoA of Bray–Curtis distance and Permanova (p = 0.15) | = |
| Tumor microbiota | ||||
| Xu et al. [28] | Chao1 index (p = 0.002), ACE index (p = 0.003), Shannon index (p = 0.063), Simpson index (p = 0.673), Pielou-e index (p = 0.354) |  | PCoA of unweighted (p = 0.051) and Jaccard (p = 0.003) UniFrac distances and Permanova | ≠ |
| Barot et al. [24] | Shannon index (p = 1.5 × 10−5) |  | PCoA of Bray–Curtis distance and Permanova (p = 0.013) | ≠ |
 ) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients; the gray arrow (
) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients; the gray arrow ( ) reflects a decrease in EOCRC patients; = means no difference; and ≠ means a difference between groups. PCoA = Principal coordinate analysis.
) reflects a decrease in EOCRC patients; = means no difference; and ≠ means a difference between groups. PCoA = Principal coordinate analysis.| Bacteria | Study (Statistical Significance) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fecal microbiota | ||
| Flavonifractor plautii |  | Yang et al. (LDA score p < 0.01), Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [23,29]. |
| Bacteroides vulgatus |  | Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [29] |
| Bacteroides cellulositycus |  | Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [29] |
| Parabacteroides sp CT06 |  | Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [29] |
| Vibrio_qinghalensis |  | Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [29] |
| Odoribacter splanchnicus |  | Kong et al. (LDA score p < 0.05) [29] |
| Fusobacteria |  | Xiong et al. (LDA score p < 0.001) [27] |
| Akkermansia muciniphila |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
| Bacteroides fragilis |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
| Bacteroides cellulolyticus |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
| Eubacterium siraem |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
| Erysipelatochlostridium ramosum |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
| Oscillibbacter sp. CAG.241 |  | Adnan et al. [26] |
| Enterocloster boltoes |  | Adnan et al. (MLR p < 0.05) [26] |
 ) reflects an increase in EoCRC. LDA = linear discriminant analysis. MLR = multivariable linear regression.
) reflects an increase in EoCRC. LDA = linear discriminant analysis. MLR = multivariable linear regression.| Bacteria | Study (Statistical Significance) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fecal microbiota | ||
| Fusobacteria |  | Xiong et al. (LDA score p < 0.001) [27] |
| Tumor microbiota | ||
| Actinomyces |  | Xu et al. (LDA p < 0.05) [28] |
| Akkermansia |  | Barot et al. (p = 4.1 × 10−2) [24] |
| Bacteroides |  | Barot et al. (p = 4.1 × 10−2) [24] |
 ) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients. LDA = linear discriminant analysis.
) reflects an increase in EoCRC patients. LDA = linear discriminant analysis.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes de Sousa, R.; Guerreiro, C.S.; Santos, I.; Cravo, M. The Knowledge Gap in Gut Microbiome Characterization in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Scoping Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111863
Gomes de Sousa R, Guerreiro CS, Santos I, Cravo M. The Knowledge Gap in Gut Microbiome Characterization in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Scoping Review. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111863
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes de Sousa, Rita, Catarina Sousa Guerreiro, Inês Santos, and Marília Cravo. 2025. "The Knowledge Gap in Gut Microbiome Characterization in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Scoping Review" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111863
APA StyleGomes de Sousa, R., Guerreiro, C. S., Santos, I., & Cravo, M. (2025). The Knowledge Gap in Gut Microbiome Characterization in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Scoping Review. Cancers, 17(11), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111863







