The Vimentin-Targeting Drug ALD-R491 Partially Reverts the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vimentin Interactome of Lung Cancer Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Antibodies and Cell Dyes
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Immunoflourescence
2.5. Live-Cell Imaging
2.6. Image Analysis
2.7. Tracking Cell Migration
2.8. Monitoring Nuclear Division
2.9. Proteomic Analysis Using Label-Free Quantification Mass Spectrometry
2.10. Protein Identification, Relative Quantification, Bioinformatic Functional Profiling and Interaction Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ALD-R491 Partially Reverses the Phenotypes of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
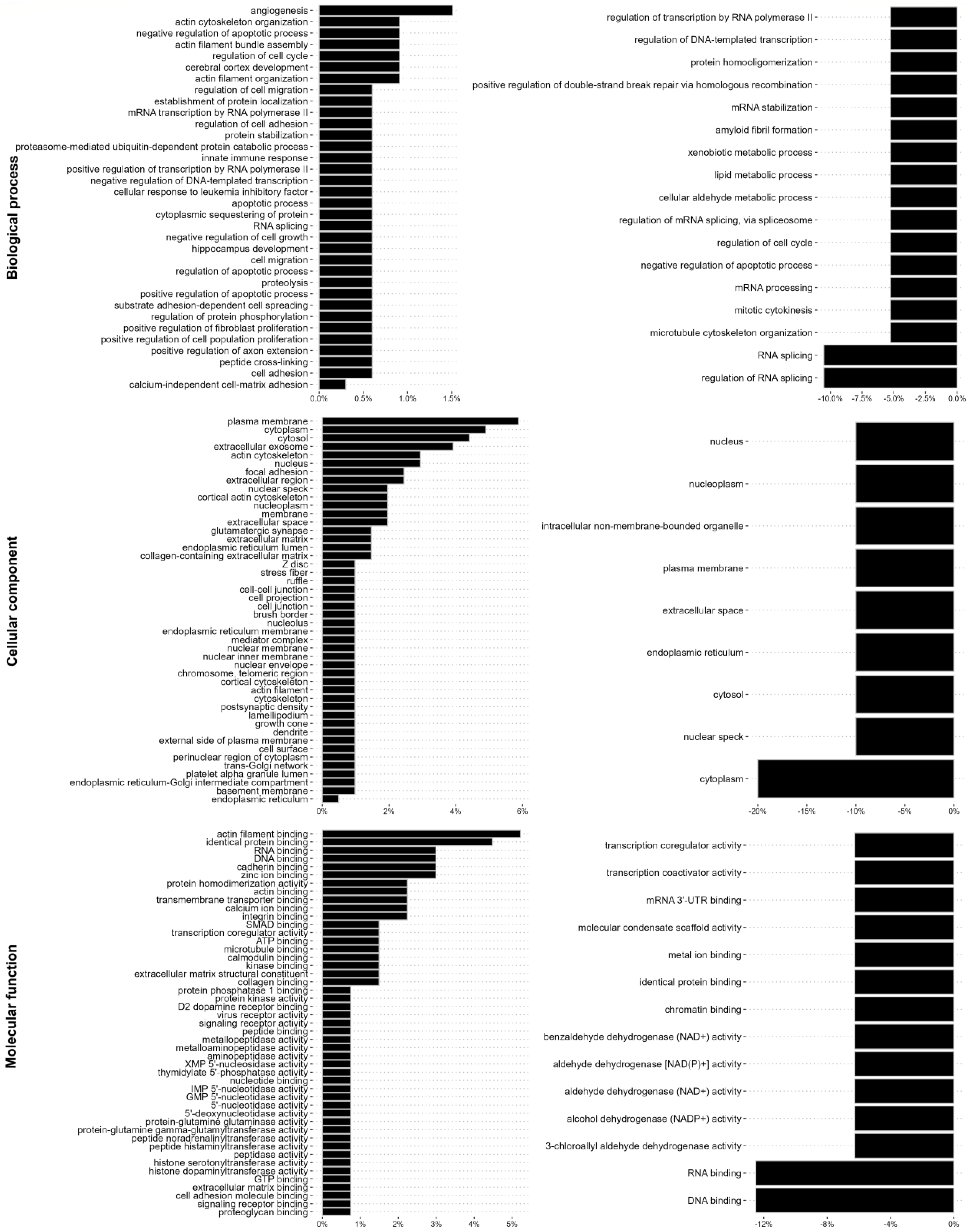
3.2. EMT-Increased Binding of Extracellular Matrix, Cell Motility, Cytokinesis, Cytoskeletal, and RNA-Binding Proteins to Vimentin, Is Partially Reversed by ALD-R491
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Usman, S.; Waseem, N.H.; Nguyen, T.K.N.; Mohsin, S.; Jamal, A.; Teh, M.T.; Waseem, A. Vimentin Is at the Heart of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Mediated Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and Definitions for Research on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menko, A.S.; Bleaken, B.M.; Libowitz, A.A.; Zhang, L.; Stepp, M.A.; Walker, J.L. A Central Role for Vimentin in Regulating Repair Function during Healing of the Lens Epithelium. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridge, K.M.; Eriksson, J.E.; Pekny, M.; Goldman, R.D. Roles of Vimentin in Health and Disease. Genes Dev. 2022, 36, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, F.; Peterson, M.K.; Araújo, H.C.; Lautenschläger, F.; Gad, A.K.B. Vimentin Diversity in Health and Disease. Cells 2018, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.G.; Kojima, S.; Goldman, R.D. Vimentin Induces Changes in Cell Shape, Motility, and Adhesion during the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovini, C.; Rossi, G.; Ciarrocchi, A. Approaches to Tumor Classification in Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2019, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuwa, T.; Ishii, G.; Nagai, K.; Yoshida, J.; Nishimura, M.; Hishida, T.; Neri, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Ochiai, A. Characteristic Immunophenotype of Solid Subtype Component in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 3943–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M.E.; Shumaker, D.K.; Ridge, K.M. The Role of Vimentin Intermediate Filaments in the Progression of Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berr, A.L.; Wiese, K.; dos Santos, G.; Koch, C.M.; Anekalla, K.R.; Kidd, M.; Davis, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Ridge, K.M. Vimentin Is Required for Tumor Progression and Metastasis in a Mouse Model of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2074–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosibaty, Z.; Brustugun, O.T.; Zwicky Eide, I.J.; Tsakonas, G.; Grundberg, O.; De Petris, L.; McGowan, M.; Hydbring, P.; Ekman, S. Ras-Related Protein Rab-32 and Thrombospondin 1 Confer Resistance to the EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib by Activating Focal Adhesion Kinase in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ehrlicher, A.J.; Mahammad, S.; Fabich, H.; Jensen, M.H.; Moore, J.R.; Fredberg, J.J.; Goldman, R.D.; Weitz, D.A. The Role of Vimentin Intermediate Filaments in Cortical and Cytoplasmic Mechanics. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiu, Y.; Peränen, J.; Schaible, N.; Cheng, F.; Eriksson, J.E.; Krishnan, R.; Lappalainen, P. Vimentin Intermediate Filaments Control Actin Stress Fiber Assembly through GEF-H1 and RhoA. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Ding, L.; Burckhardt, C.J.; Lowery, J.; Zaritsky, A.; Sitterley, K.; Mota, A.; Costigliola, N.; Starker, C.G.; Voytas, D.F.; et al. Vimentin Intermediate Filaments Template Microtubule Networks to Enhance Persistence in Cell Polarity and Directed Migration. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 252–263.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho-Rato, L.S.; Parvanian, S.; Modi, M.K.; Eriksson, J.E. Vimentin at the Core of Wound Healing. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costigliola, N.; Ding, L.; Burckhardt, C.J.; Han, S.J.; Gutierrez, E.; Mota, A.; Groisman, A.; Mitchison, T.J.; Danuser, G. Vimentin Fibers Orient Traction Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Stefanovic, B. LARP6 Meets Collagen MRNA: Specific Regulation of Type I Collagen Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; Ding, I.; Norouzi, M.; McCulloch, C.A. Impact of Vimentin on Regulation of Cell Signaling and Matrix Remodeling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 869069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Warrington, S.J.; López-Guajardo, A.; Al Hennawi, K.; Cook, S.L.; Griffith, Z.D.J.; Symmes, D.; Zhang, T.; Qu, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. ALD-R491 Regulates Vimentin Filament Stability and Solubility, Cell Contractile Force, Cell Migration Speed and Directionality. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 926283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöding, B.; Herrmann, H.; Köster, S. Direct Observation of Subunit Exchange along Mature Vimentin Intermediate Filaments. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qu, Z.; Mo, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, R.; Shi, L. A Small Vimentin-Binding Molecule Blocks Cancer Exosome Release and Reduces Cancer Cell Mobility. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 627394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qu, Z.; Wu, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Mo, L.; Yao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, R. SARs of a Novel Series of S-Triazine Compounds Targeting Vimentin to Induce Methuotic Phenotype. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 214, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkasalias, T.; Alexeyenko, A.; Hennig, K.; Danielsson, F.; Lebbink, R.J.; Fielden, M.; Turunen, S.P.; Lehti, K.; Kashuba, V.; Madapura, H.S.; et al. RhoA Knockout Fibroblasts Lose Tumor-Inhibitory Capacity in Vitro and Promote Tumor Growth in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1413–E1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinevez, J.Y.; Perry, N.; Schindelin, J.; Hoopes, G.M.; Reynolds, G.D.; Laplantine, E.; Bednarek, S.Y.; Shorte, S.L.; Eliceiri, K.W. TrackMate: An Open and Extensible Platform for Single-Particle Tracking. Methods 2017, 115, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, S.H.; Evans, C.A.; Shaw, L.; Wong, C.H.; Connolly, J.; Griffiths, J.R.; Whetton, A.D.; Corfe, B.M. Proteomic Analyses of Intermediate Filaments Reveals Cytokeratin8 Is Highly Acetylated—Implications for Colorectal Epithelial Homeostasis. Proteomics 2008, 8, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.A.; Kim, H.R.; Macfarlane, S.C.; Nowicki, P.I.A.; Baltes, C.; Xu, L.; Widengren, J.; Lautenschläger, F.; Corfe, B.M.; Gad, A.K.B. Metastasising Fibroblasts Show an HDAC6-Dependent Increase in Migration Speed and Loss of Directionality Linked to Major Changes in the Vimentin Interactome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Hein, M.Y.; Luber, C.A.; Paron, I.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Accurate Proteome-Wide Label-Free Quantification by Delayed Normalization and Maximal Peptide Ratio Extraction, Termed MaxLFQ. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 2513–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwanhüusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global Quantification of Mammalian Gene Expression Control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.D.; Goode, R.J.A.; Huang, C.; Powell, D.R.; Schittenhelm, R.B. LFQ-Analyst: An Easy-To-Use Interactive Web Platform to Analyze and Visualize Label-Free Proteomics Data Preprocessed with MaxQuant. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, F.; Skogs, M.; Huss, M.; Rexhepaj, E.; O’Hurley, G.; Klevebring, D.; Pontén, F.; Gad, A.K.B.; Uhlén, M.; Lundberg, E. Majority of Differentially Expressed Genes Are Down-Regulated during Malignant Transformation in a Four-Stage Model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6853–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivaska, J.; Pallari, H.M.; Nevo, J.; Eriksson, J.E. Novel Functions of Vimentin in Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Ramos, G.; Bernardi, L.; Lauxen, I.; Filho, M.S.A.; Horwitz, A.R.; Lamers, M.L. Fibronectin Modulates Cell Adhesion and Signaling to Promote Single Cell Migration of Highly Invasive Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missirlis, D.; Haraszti, T.; Kessler, H.; Spatz, J.P. Fibronectin Promotes Directional Persistence in Fibroblast Migration through Interactions with Both Its Cell-Binding and Heparin-Binding Domains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odii, B.O.; Coussons, P. Biological Functionalities of Transglutaminase 2 and the Possibility of Its Compensation by Other Members of the Transglutaminase Family. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 714561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.; Kotsakis, P.; Johnson, T.S.; Chau, D.Y.S.; Ali, S.; Melino, G.; Griffin, M. Matrix Changes Induced by Transglutaminase 2 Lead to Inhibition of Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsukawa, H.; Furutani, Y.; Hitomi, K.; Kojima, S. Transglutaminase 2 Has Opposing Roles in the Regulation of Cellular Functions as Well as Cell Growth and Death. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, J.L.; Smith, T.C.; Fang, Z.; Takizawa, N.; Luna, E.J. Supervillin Reorganizes the Actin Cytoskeleton and Increases Invadopodial Efficiency. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hleihel, R.; El Hajj, H.; Wu, H.C.; Berthier, C.; Zhu, H.H.; Massoud, R.; Chakhachiro, Z.; El Sabban, M.; de The, H.; Bazarbachi, A. A Pin1/PML/P53 Axis Activated by Retinoic Acid in NPM-1c Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3090–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Shinde, D.N.N.; Reijnders, M.R.R.F.; Hauser, N.S.S.; Belmonte, R.L.L.; Wilson, G.R.R.; Bosch, D.G.G.M.; Bubulya, P.A.A.; Shashi, V.; Petrovski, S.; et al. De Novo Mutations in SON Disrupt RNA Splicing of Genes Essential for Brain Development and Metabolism, Causing an Intellectual-Disability Syndrome. Am. Soc. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.F.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Shi, P.C.; Li, H.Q.; Bai, J.; Song, J. KIF4A Facilitates Cell Proliferation via Induction of P21-Mediated Cell Cycle Progression and Promotes Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendeckel, U.; Karimi, F.; Al Abdulla, R.; Wolke, C. The Role of the Ectopeptidase APN/CD13 in Cancer. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirao, T.; Sekino, Y. General Introduction to Drebrin. In Drebrin; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; Volume 1006, pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, H.; Gleeson, J.G. Sun Proteins Enlighten Nuclear Movement in Development. Neuron 2009, 64, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Chang, R.; Zhu, L.; Feitelson, M.A.; Chen, Z. TMEM43 Promotes the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating VDAC1 through USP7 Deubiquitination. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.Y.; DeKelver, R.C.; Lo, M.C.; Nguyen, T.A.; Matsuura, S.; Boyapati, A.; Pandit, S.; Fu, X.D.; Zhang, D.E. SON Controls Cell-Cycle Progression by Coordinated Regulation of RNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, R.; Izquierdo, L.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Lozano, J.J.; Franco, M.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Roldan, F.L.; Llorens, M.; Ribal, M.J.; Mengual, L.; et al. Differential Gene Expression Profile between Progressive and de Novo Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Its Prognostic Implication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, A.; Schrecker, C.; Bon, D.; Friedrichs, N.; Bankov, K.; Wild, P.; Plotz, G.; Zeuzem, S.; Herrmann, E.; Hansmann, M.L.; et al. Downregulation of SPTAN1 Is Related to MLH1 Deficiency and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Farmer, S.M.; Wray, S. Drebrin Regulates Cytoskeleton Dynamics in Migrating Neurons through Interaction with CXCR4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2009493118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, V.; Paunu, K.; Kukkula, A.; Niva, S.; Junila, Y.; Toriseva, M.; Jokilehto, T.; Mäkelä, S.; Huhtaniemi, R.; Poutanen, M.; et al. Glucocorticoid Receptor-Induced Non-Muscle Caldesmon Regulates Metastasis in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.F.; Zhao, L.D.; Chen, Q.; Tang, D.X.; Chen, Q.Y.; Lu, H.F.; Cai, J.R.; Chen, Z. High ACTN1 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis, and ACTN1 Silencing Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Wiktorska, M.; Sacewicz-Hofman, I.; Boncela, J.; Lewiński, A.; Kowalska, M.A.; Niewiarowska, J. Filamin A Upregulation Correlates with Snail-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Cell Adhesion but Its Inhibition Increases the Migration of Colon Adenocarcinoma HT29 Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 359, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, M.S.Y.; Sy, S.M.H.; Leung, K.M.; Ching, Y.P.; Tipoe, G.L.; Man, C.; Dong, S.; Chen, J. SON Is a Spliceosome-Associated Factor Required for Mitotic Progression. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Öztürk, A.; Hicks, G.G. ALS-Associated FUS Mutations Result in Compromised FUS Alternative Splicing and Autoregulation. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Reed, R. FUS Functions in Coupling Transcription to Splicing by Mediating an Interaction between RNAP II and U1 SnRNP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8608–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Takanashi, K. FUS Interacts with Nuclear Matrix-Associated Protein SAFB1 as Well as Matrin3 to Regulate Splicing and Ligand-Mediated Transcription. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baechtold, H.; Kuroda, M.; Sok, J.; Ron, D.; Lopez, B.S.; Akhmedov, A.T. Human 75-KDa DNA-Pairing Protein Is Identical to the pro-Oncoprotein TLS/FUS and Is Able to Promote D-Loop Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34337–34342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.D.; Lazar, A.M.; Iskratsch, T.; Zhang, X.; Sheetz, M.P. Endoplasmic Spreading Requires Coalescence of Vimentin Intermediate Filaments at Force-Bearing Adhesions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.M.; Havel, L.S.; Koyen, A.E.; Konen, J.M.; Shupe, J.; Wiles, W.G.; David Martin, W.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Sica, G.; Gilbert-Ross, M.; et al. Vimentin Is Required for Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastasis via Heterotypic Tumor Cell-Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Interactions during Collective Invasion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Bai, Y.; Gunst, S.J. Silencing of P21-Activated Kinase Attenuates Vimentin Phosphorylation on Ser-56 and Reorientation of the Vimentin Network during Stimulation of Smooth Muscle Cells by 5-Hydroxytryptamine. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathje, L.S.Z.; Nordgren, N.; Pettersson, T.; Rönnlund, D.; Widengren, J.; Aspenström, P.; Gad, A.K.B. Oncogenes Induce a Vimentin Filament Collapse Mediated by HDAC6 That Is Linked to Cell Stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; Ding, I.; Lee, W.; Tanic, J.; Abbasi, S.; Arora, P.D.; Liu, R.S.; Patteson, A.E.; Janmey, P.A.; McCulloch, C.A. Vimentin Tunes Cell Migration on Collagen by Controlling Β1 Integrin Activation and Clustering. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs254359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Park, H.J.; Seong, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, C. Vimentin-Mediated Buffering of Internal Integrin Β1 Pool Increases Survival of Cells from Anoikis. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, W.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J.; Jia, L. Fibronectin 1 Promotes Melanoma Proliferation and Metastasis by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Regulating EMT. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 3207–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patteson, A.E.; Vahabikashi, A.; Pogoda, K.; Adam, S.A.; Mandal, K.; Kittisopikul, M.; Sivagurunathan, S.; Goldman, A.; Goldman, R.D.; Janmey, P.A. Vimentin Protects Cells against Nuclear Rupture and DNA Damage during Migration. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 4079–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Viedma-Poyatos, Á.; Navarro-Carrasco, E.; Martínez, A.E.; Pajares, M.A.; Pérez-Sala, D. Vimentin Filaments Interact with the Actin Cortex in Mitosis Allowing Normal Cell Division. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expression of SON in Lung Cancer—The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000159140-SON/cancer/lung+cancer#cptac_lung_ac (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Xiong, D.; Wu, Y.B.; Jin, C.; Li, J.J.; Gu, J.; Liao, Y.F.; Long, X.; Zhu, S.Q.; Wu, H.B.; Xu, J.J.; et al. Elevated FUS/TLS Expression Is Negatively Associated with E-Cadherin Expression and Prognosis of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Yin, R.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Lv, D.; Yang, K.; Geng, S.; Yang, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. ALDH3A1 Driving Tumor Metastasis Is Mediated by P53/BAG1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Espinoza, M.; Kim, M.; Ow, C.; Hutchins, E.J. Beyond Transcription: How Post-Transcriptional Mechanisms Drive Neural Crest EMT. Genesis 2024, 62, e23553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
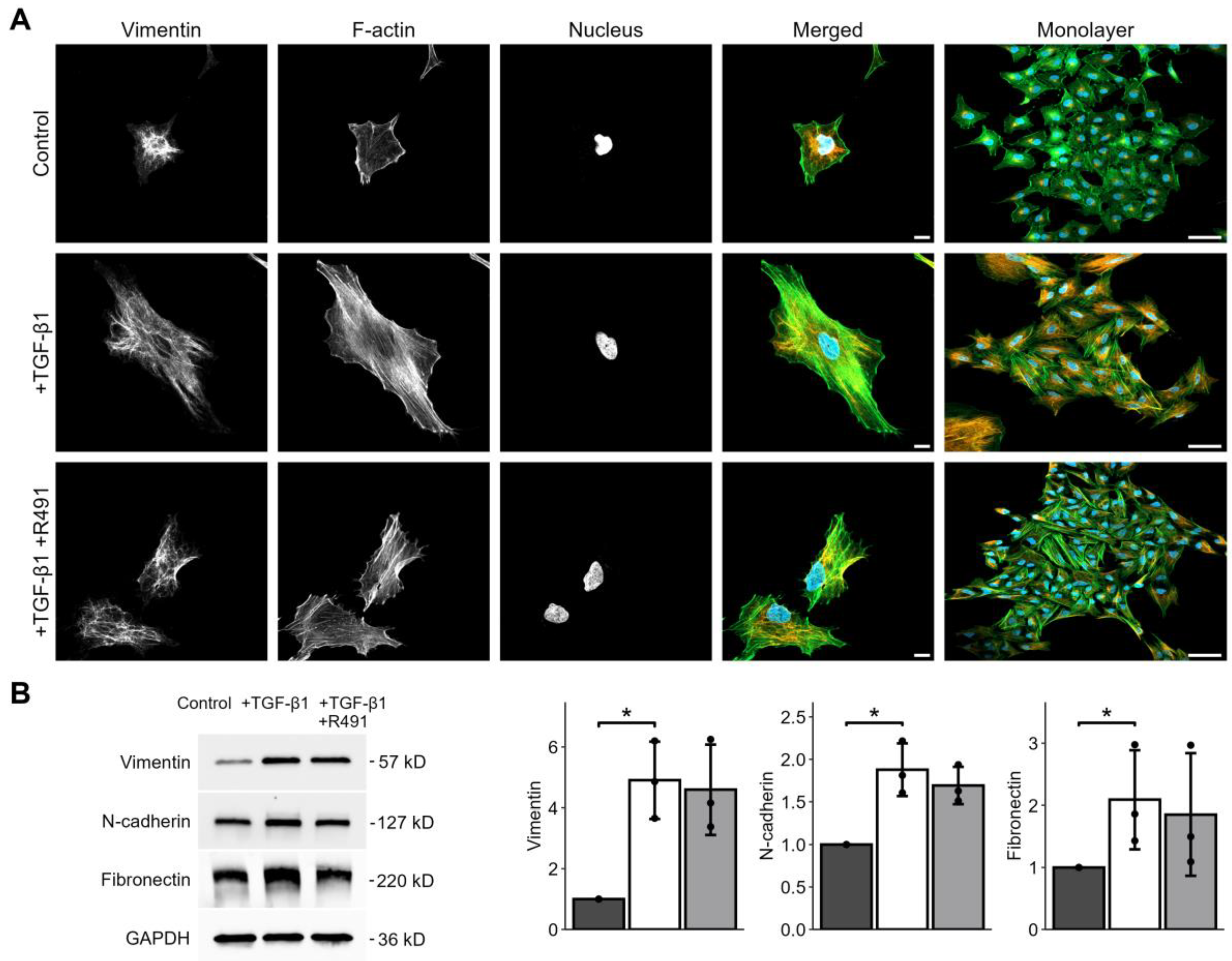
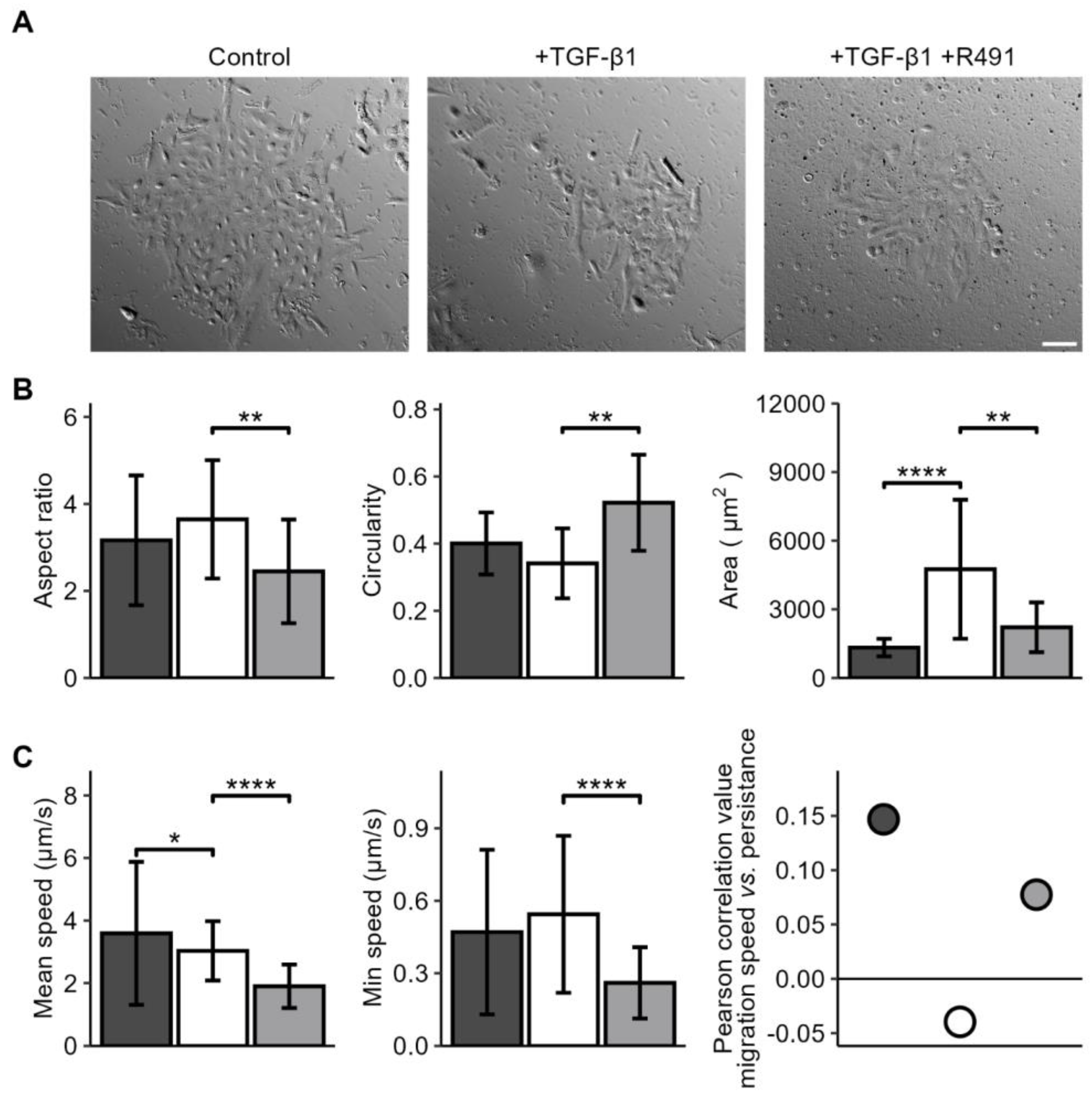
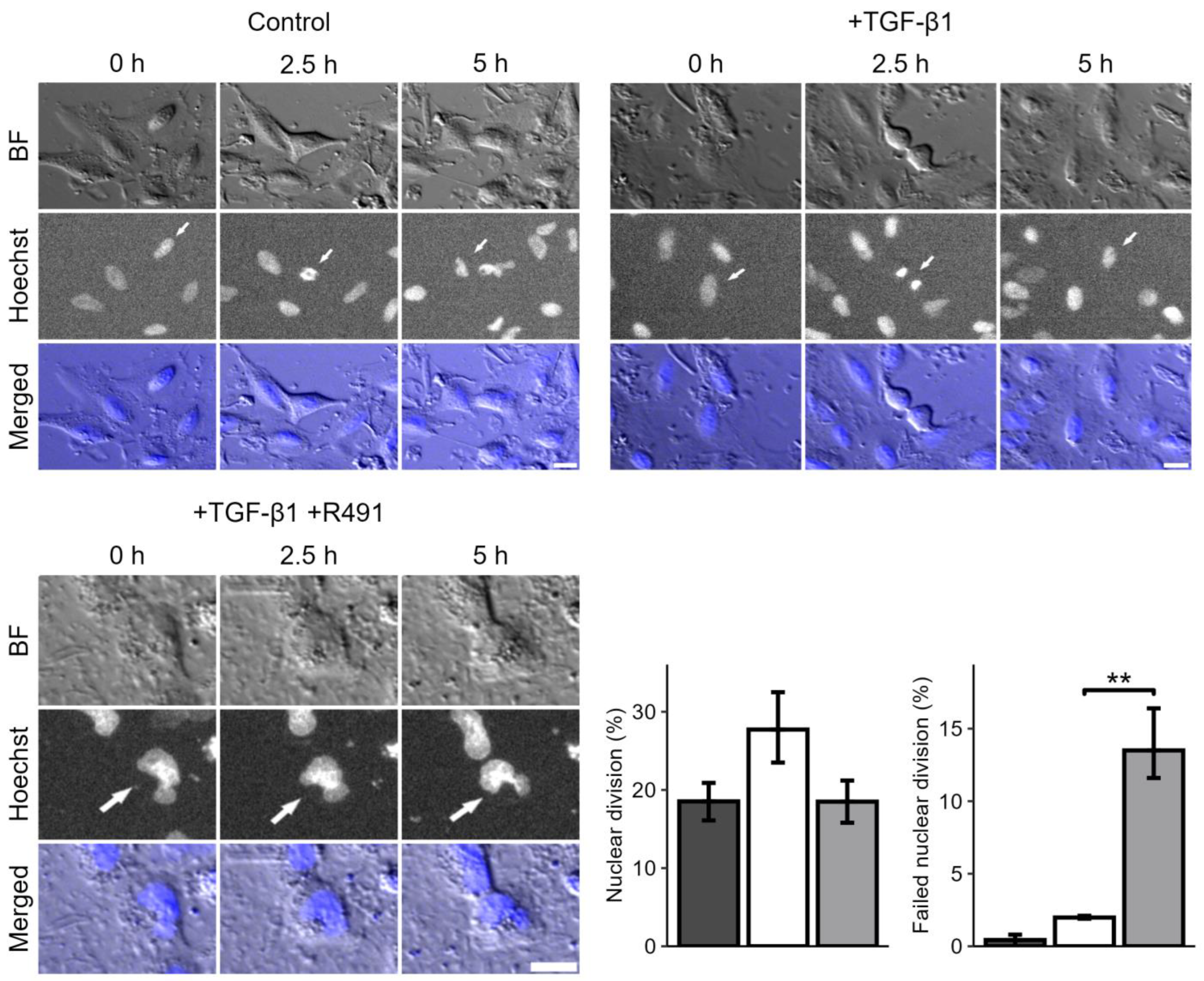
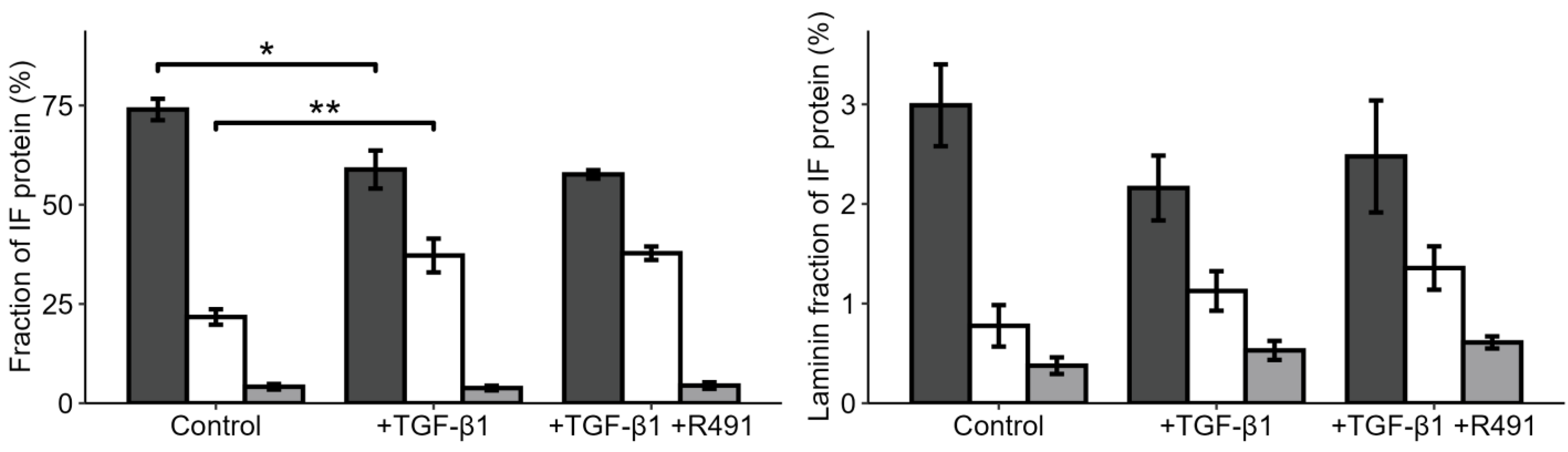
| Protein | Gene | Protein ID | Signalling Pathway | TGFβ1 vs. A549 Foldchange (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibronectin;Anastellin;Ugl-Y1;Ugl-Y2;Ugl-Y3 | FN1 | P02751 | Integrin, Collagen, Fibrin | 137.19 (3.09 × 10−13) |
| Transforming growth factor-β1-induced protein ig-h3 | TGF-Β1 | Q15582 | TGF-Β1, MAPK | 28.05 (1.33 × 10−10) |
| Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase 2 | TGM2 | P21980 | FN1, SPFN1, HSPB6 | 17.63 (2.09 × 10−18) |
| 5-nucleotidase | NT5E | P21589 | AMP- NAD- nucleotides | 6.92 (4.91 × 10−12) |
| Aminopeptidase N | ANPEP | P15144 | an aminopeptidase | 5.58 (1.06 × 10−7) |
| Neurabin-2 | PPP1R9B | Q96SB3 | F-actin, Rac, Dopamine D1 | 4.92 (0.000159) |
| Zinc finger protein 185 | ZNF185 | O15231 | * Wnt | 4.86 (4.95 × 10−10) |
| Drebrin 1 | DBN1 | Q16643 | * F-actin | 4.32 (1.88 × 10−10) |
| Caldesmon | CALD1 | E9PGZ1 | F-actin,, myosin, calmodulin | 4.08 (5.49 × 10−10) |
| SUN-domain-containing protein 2 | SUN2 | Q9UH99 | LINC complex | 3.92 (0.000905) |
| SON | SON | P18583 | TUBG1, KATNB1, AURKB | 3.78 (0.0034) |
| CTP synthase 1 | CTPS1 | A0A3B3IRI2 | CTP | 3.68 (3.42 × 10−5) |
| Bcl-2-associated transcription factor 1 | BCLAF1 | A0A3B3ITZ9 | CCND1 mRNA | 3.48 (0.00372) |
| Supervillin | SVIL | A0A6I8PIX7 | F-actin | 3.23 (0.000905) |
| Protein PML | PML | P29590 | PML-NBs | 3.18 (0.000565) |
| Protein disulfide-isomerase A4 | PDIA4 | A0A499FI48 | * HSP, ERO1 | 2.85 (0.000398) |
| Transmembrane protein 43 | TMEM43 | Q9BTV4 | RNF26 | 2.62 (1.04 × 10−6) |
| Uncharacterised protein C17orf85 | C17orf85 | Q53F19 | mRNA | 2.58 (0.00418) |
| Thyroid-hormone-receptor-associated protein 3 | THRAP3 | A0A3B3ITZ9 | mRNA, DNA | 2.36 (0.00372) |
| Alpha-actinin-1 | ACTN1 | P12814 | F-actin | 2.25 (3.66 × 10−10) |
| LIM domain and actin-binding protein 1 | LIMA1 | Q9UHB6 | F-actin | 2.22 (0.000905) |
| Kinesin-like protein 14 | KIF14 | Q15058 | Tubulin, CDKN1B | 2.11 (0.00102) |
| Spectrin alpha chain, non-erythrocytic 1 | SPTAN1 | Q13813 | F-actin, Calmodulin | 2.06 (0.00151) |
| Filamin-A | FLNA | P21333 | F-actin, SEMA3A | 2.01 (9.05 × 10−6) |
| Protein | Gene | Protein ID | Signaling Pathway | TGFβ1 vs. A549 Fold Change (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein SON | SON | P18583 | TUBG1, KATNB1, AURKB | −4.89 (0.00156) |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase, dimeric NADP-preferring | ALDH3A1 | P30838 | Aldehyde substrates | −2.62 (0.00257) |
| RNA-binding protein FUS | FUS | P35637 | mRNA, DNA | −2.62 (0.00354) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosier, M.; Krstulović, A.; Kim, H.R.; Kaur, N.; Enakireru, E.M.; Symmes, D.; Dobra, K.; Chen, R.; Evans, C.A.; Gad, A.K.B. The Vimentin-Targeting Drug ALD-R491 Partially Reverts the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vimentin Interactome of Lung Cancer Cells. Cancers 2025, 17, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010081
Rosier M, Krstulović A, Kim HR, Kaur N, Enakireru EM, Symmes D, Dobra K, Chen R, Evans CA, Gad AKB. The Vimentin-Targeting Drug ALD-R491 Partially Reverts the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vimentin Interactome of Lung Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2025; 17(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosier, Marieke, Anja Krstulović, Hyejeong Rosemary Kim, Nihardeep Kaur, Erhumuoghene Mary Enakireru, Deebie Symmes, Katalin Dobra, Ruihuan Chen, Caroline A. Evans, and Annica K. B. Gad. 2025. "The Vimentin-Targeting Drug ALD-R491 Partially Reverts the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vimentin Interactome of Lung Cancer Cells" Cancers 17, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010081
APA StyleRosier, M., Krstulović, A., Kim, H. R., Kaur, N., Enakireru, E. M., Symmes, D., Dobra, K., Chen, R., Evans, C. A., & Gad, A. K. B. (2025). The Vimentin-Targeting Drug ALD-R491 Partially Reverts the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vimentin Interactome of Lung Cancer Cells. Cancers, 17(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010081







