Benign or Malignant? Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Bedside Histological Assessment of Melanocytic Lesions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- Benign nevi: Characteristic features of benign nevi included well-organized nests of melanocytes, uniform cell sizes, and minimal pleomorphism. The confocal images in DHE highlighted regular, evenly distributed nucleic acid staining within the nests and no increased mitotic activity. In RM, the nests appeared as well-circumscribed, highly reflective areas (Figure 1a–d).
- Melanoma: Characteristically, melanoma images exhibited significant architectural disarray, with irregular nests and melanocytes infiltrating the dermis and epidermis. There was notable cellular pleomorphism, with varied cell sizes and shapes. The presence of atypical melanocytes with prominent nucleoli and increased mitotic figures was evident. These features were more pronounced in DHE, where the acridine orange staining provided a contrast for nuclear abnormalities. RM revealed a disrupted and heterogeneous reflective pattern consistent with malignancy (Figure 1e–h).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babino, G.; Lallas, A.; Agozzino, M.; Alfano, R.; Apalla, Z.; Brancaccio, G.; Giorgio, C.M.; Fulgione, E.; Kittler, H.; Kyrgidis, A.; et al. Melanoma diagnosed on digital dermoscopy monitoring: A side-by-side image comparison is needed to improve early detection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, R.; Recule, F. Unusual Clinical Presentations of Malignant Melanoma: A review of clinical and histologic features with special emphasis on dermatoscopic findings. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, J.; Schuh, S. Noninvasive diagnosis in dermatology. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2017, 15, 999–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Swetter, S.M.; Menzies, A.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Scolyer, R.A. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet 2023, 402, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faldetta, C.; Kaleci, S.; Chester, J.; Ruini, C.; Ciardo, S.; Manfredini, M.; Guida, S.; Chello, C.; Cantisani, C.; Young, J.N.; et al. Melanoma clinicopathological groups characterized and compared with dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, C.; Marchetti, M.A.; Dusza, S.W.; Argenziano, G.; Braun, R.P.; Halpern, A.C.; Jaimes, N.; Kittler, H.J.; Malvehy, J.; Menzies, S.W.; et al. Validity and Reliability of dermoscopic criteria used to differentiate nevi from melanoma: A web-based international dermoscopy society study. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, C.; Marghoob, A.A. Discriminating Nevi from Melanomas: Clues and pitfalls. Dermatol. Clin. 2016, 34, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzak, J.M.; Xu, Y.G. Diagnosis and management of lentigo maligna: A review. Drugs Context 2015, 4, 212281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, C.C.W.; Lee, M.H.; Murad, F.G.; Waldman, A.H. Systematic review of the role of mohs micrographic surgery in the management of early-stage melanoma of the head and neck. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, E.; Perrot, J.L.; Labeille, B.; Cambazard, F.; Rubegni, P. Ex vivo confocal microscopy: An emerging technique in dermatology. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2018, 8, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvehy, J.; Perez-Anker, J.; Toll, A.; Pigem, R.; Garcia, A.; Alos, L.L.; Puig, S. Ex vivo confocal microscopy: Revolution in fast pathology in dermatology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragazzi, M.; Longo, C.; Piana, S. Ex Vivo (Fluorescence) confocal microscopy in surgical pathology: State of the art. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2016, 23, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, E.; Haouas, M.; Grivet, D.; Perrot, J.L. In vivo and ex vivo confocal microscopy for the management of a melanoma of the eyelid margin. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, F.F.; Laske, J.; Steininger, J.; Eberl, N.; Meier, F.; Beissert, S.; Hobelsberger, S. Ex vivo confocal microscopy speeds up surgical margin control of re-excised skin tumors and greatly shortens in-hospital stay. Cancers 2024, 16, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennassar, A.; Carrera, C.; Puig, S.; Vilalta, A.; Malvehy, J. Fast evaluation of 69 basal cell carcinomas with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Criteria description, histopathological correlation, and interobserver agreement. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, V.Q.; Dwyer, P.J.; Nehal, K.S.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Menaker, G.M.; Charles, C.; Jiang, S.B. Use of ex vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy during Mohs surgery for nonmelanoma skin cancers. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debarbieux, S.; Gaspar, R.; Depaepe, L.; Dalle, S.; Balme, B.; Thomas, L. Intraoperative diagnosis of nonpigmented nail tumours with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: 10 cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupp, M.; Illes, M.; Mentzel, J.; Simon, J.C.; Paasch, U.; Grunewald, S. Routine application of ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy with digital staining for examination of surgical margins in basal cell carcinomas. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, C.; Pampena, R.; Bombonato, C.; Gardini, S.; Piana, S.; Mirra, M.; Raucci, M.; Kyrgidis, A.; Pellacani, G.; Ragazzi, M. Diagnostic accuracy of ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy in Mohs surgery of basal cell carcinomas: A prospective study on 753 margins. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinasse, M.; Cinotti, E.; Grivet, D.; Labeille, B.; Prade, V.; Douchet, C.; Cambazard, F.; Thuret, G.; Gain, P.; Perrot, J.L. “En face” ex vivo reflectance confocal microscopy to help the surgery of basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 45, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.; Schubert, M.; Metzler, G.; Geppert, J.P.; Moehrle, M. Diagnostic accuracy of a new ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscope compared to H&E-stained paraffin slides for micrographic surgery of basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, K.; Fox, C.A.; Rossi, A.; Jain, M.; Cordova, M.; Dusza, S.W.; Ragazzi, M.; Gardini, S.; Moscarella, E.; Diaz, A.; et al. An international 3-center training and reading study to assess basal cell carcinoma surgical margins with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzel, J.; Stecher, M.M.; Paasch, U.; Simon, J.C.; Grunewald, S. Ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy with digital staining is able to map characteristic histopathological features and tissue reaction patterns of inflammatory skin diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e263–e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinem Bağcı, I.; Aoki, R.; Vladimirova, G.; Ergün, E.; Ruzicka, T.; Sárdy, M.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D. New-generation diagnostics in inflammatory skin diseases: Immunofluorescence and histopathological assessment using ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Ruini, C.; Mathemeier, L.; Bachmann, M.R.; Dietrich, A.; Ruzicka, T.; von Braunmuhl, T. Identification of ex-vivo confocal laser scanning microscopic features of melanocytic lesions and their histological correlates. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Krammer, S.; Ruini, C.; Ruzicka, T.; von Braunmühl, T. Correlation of histological and ex-vivo confocal tumor thickness in malignant melanoma. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Buttgereit, L.; Stärr, L.; Sattler, E.C.; French, L.E.; Deußing, M. Intraoperative PRO score assessment of actinic keratosis with FCF fast green-enhanced ex vivo confocal microscopy. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. A fast and effective option for tissue flattening: Optimizing time and efficacy in ex vivo confocal microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, e157–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Toll, A.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. Six steps to reach optimal scanning in ex vivo confocal microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nackenhorst, M.C.; Hummel, A.; Koeller, M.C.; Gollackner, B.; Regele, H. Fast green FCF improves depiction of extracellular matrix in ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy. Life 2024, 14, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Classifiation | Category | Subcategory | Number of Cases Included | Total (n = 130) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Common nevi | Junctional nevi | 13 | 76 |
| Dermal nevi | 9 | |||
| Compound nevi | 29 | |||
| Blue nevi | 4 | |||
| Dysplastic junctional nevi | 9 | |||
| Dysplastic compound nevi | 12 | |||
| Malignant | Lentigo maligna | 8 | 54 | |
| Superficial spreading melanoma in situ | 8 | |||
| Superficial spreading melanoma | 12 | |||
| Nodular melanoma | 6 | |||
| Acral melanoma, lentiginous subtype | 1 | |||
| Lentigo maligna melanoma | 6 | |||
| Spitz melanoma | 1 | |||
| Melanoma metastasis | 12 | |||
| Category | Characteristic Features | DHE Findings | RM Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign nevi |
|
|
|
| Malignant melanoma |
|
|
|
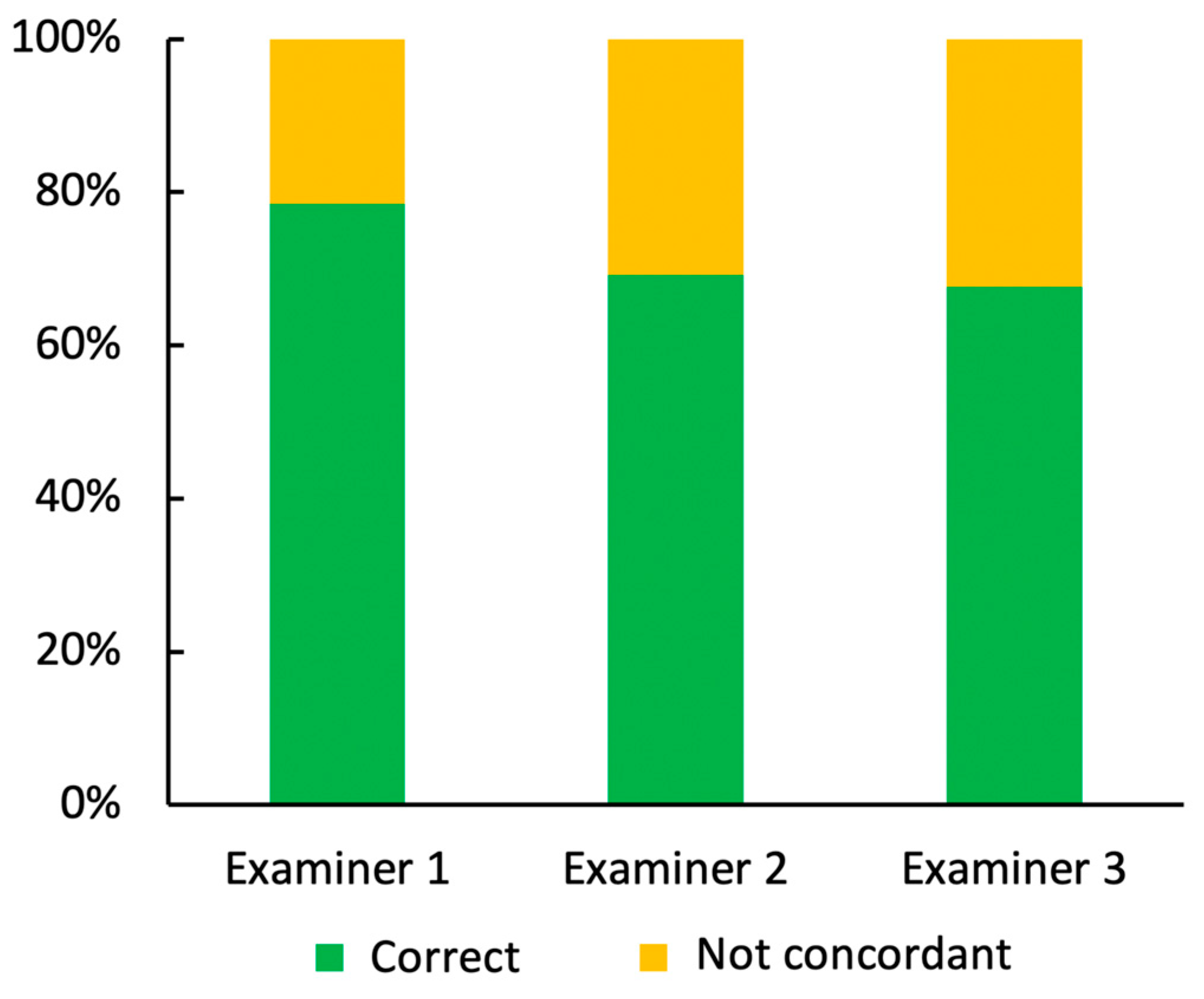
| Correctly Identified Lesions in Total | Correctly Identified Benign Lesions | Correctly Identified Malignant Lesions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Examiner 1 | 103 | 60 | 43 |
| Examiner 2 | 90 | 53 | 37 |
| Examiner 3 | 88 | 60 | 28 |
| Total number of lesions | 130 | 76 | 54 |
| All Examiners | Examiner 1 | Examiner 2 | Examiner 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical artifacts and image quality issues | 67 | 14 | 26 | 29 |
| Pigmentation and reflective signal interference | 25 | 5 | 13 | 7 |
| Confusion with inflammatory cells | 8 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Error cases in total | 109 | 28 | 40 | 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deußing, M.; Buttgereit, L.; Maurer, M.; Swarlik, A.; Stärr, L.; Ohlmann, A.; Kerl-French, K.; Flaig, M.; Sattler, E.C.; French, L.E.; et al. Benign or Malignant? Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Bedside Histological Assessment of Melanocytic Lesions. Cancers 2025, 17, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010151
Deußing M, Buttgereit L, Maurer M, Swarlik A, Stärr L, Ohlmann A, Kerl-French K, Flaig M, Sattler EC, French LE, et al. Benign or Malignant? Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Bedside Histological Assessment of Melanocytic Lesions. Cancers. 2025; 17(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeußing, Maximilian, Lisa Buttgereit, Michaela Maurer, Alisa Swarlik, Lara Stärr, Andreas Ohlmann, Katrin Kerl-French, Michael Flaig, Elke C. Sattler, Lars E. French, and et al. 2025. "Benign or Malignant? Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Bedside Histological Assessment of Melanocytic Lesions" Cancers 17, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010151
APA StyleDeußing, M., Buttgereit, L., Maurer, M., Swarlik, A., Stärr, L., Ohlmann, A., Kerl-French, K., Flaig, M., Sattler, E. C., French, L. E., & Hartmann, D. (2025). Benign or Malignant? Ex Vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Bedside Histological Assessment of Melanocytic Lesions. Cancers, 17(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17010151








