A Simple Frailty Score Predicts Survival and Early Mortality in Systemic AL Amyloidosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
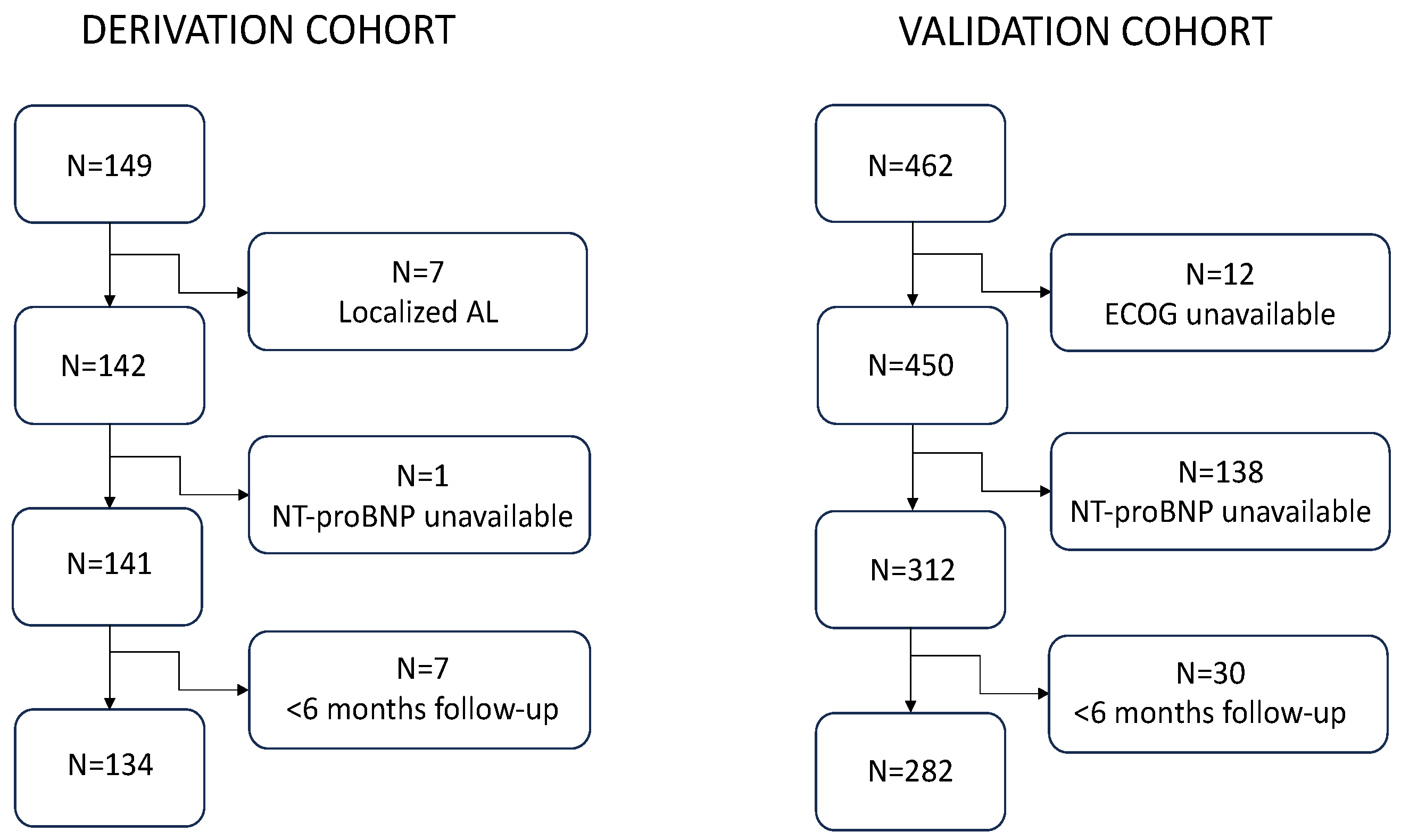
2.2. Patients
2.3. End-Points
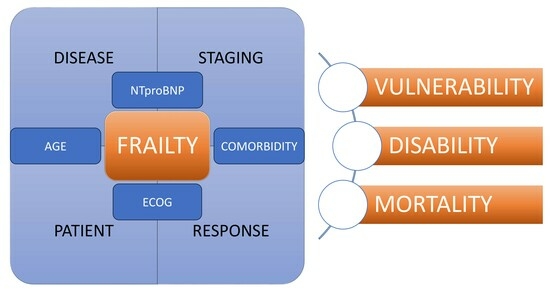
2.4. Variables
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Derivation Cohort
3.2. Validation Cohort
3.3. Comparison of Derivation and Validation Cohorts
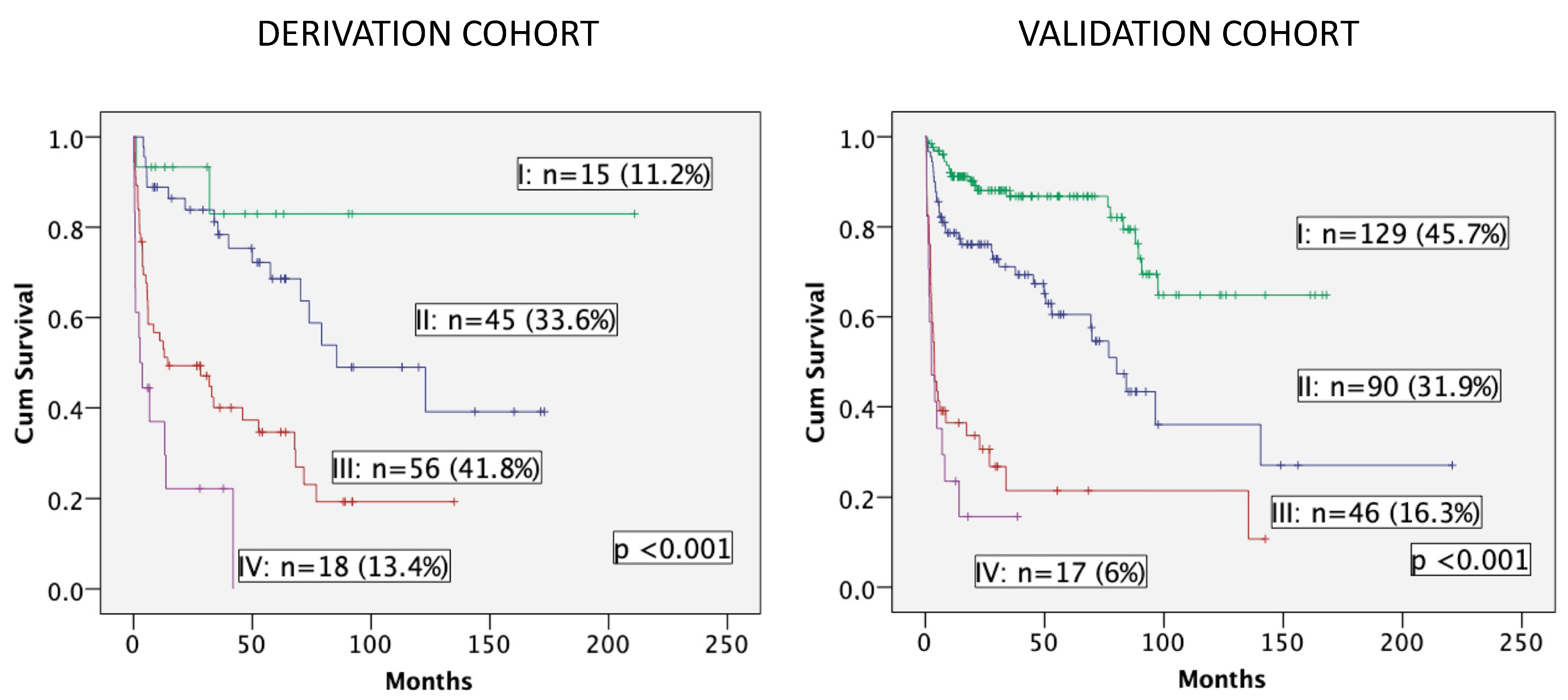
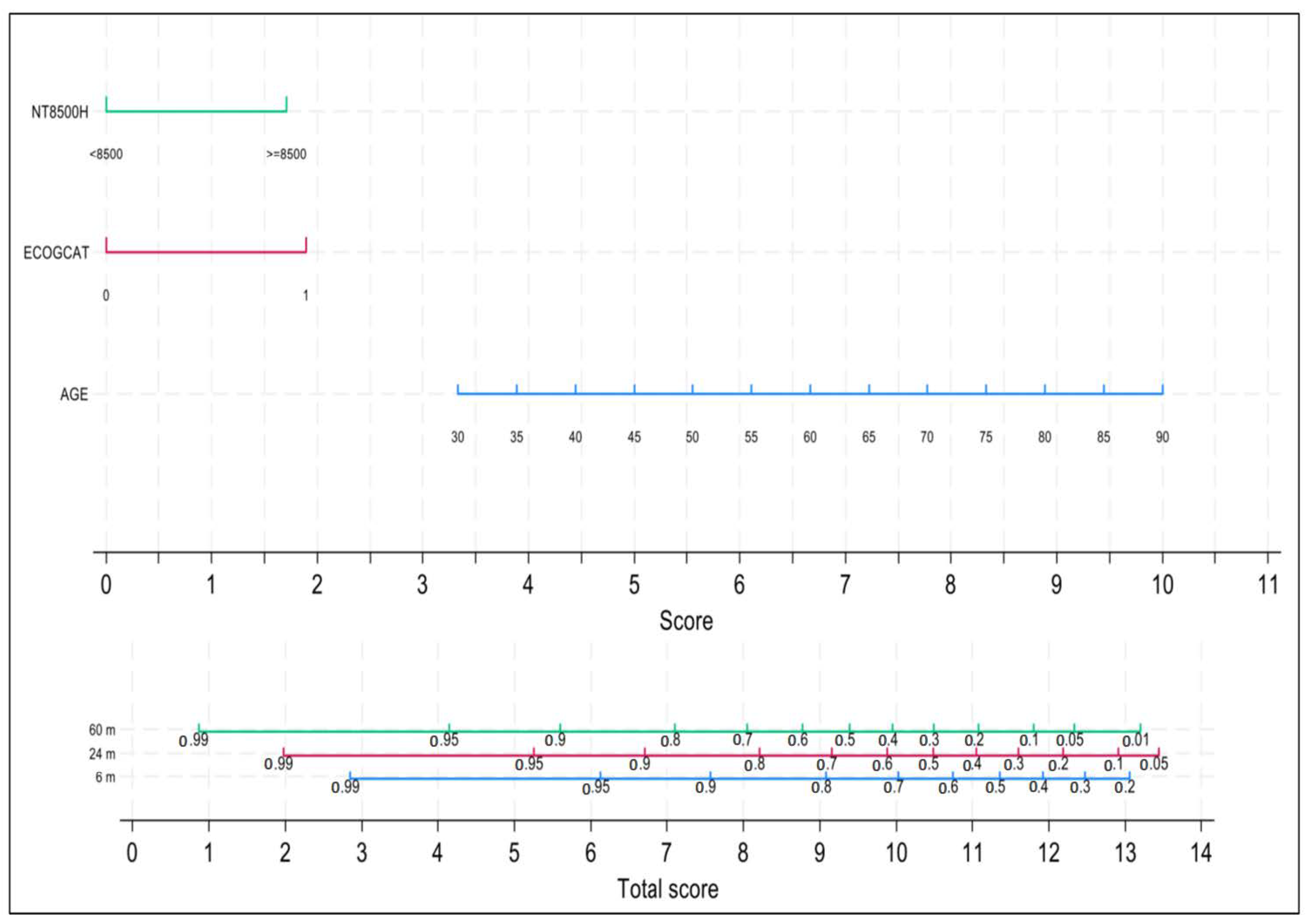
3.4. The Frailty Score
3.5. Ultra-Frail Patients
3.6. The Role of Comorbidity
3.7. Early Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merlini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Sanchorawala, V.; Schönland, S.O.; Palladini, G.; Hawkins, P.N.; Gertz, M.A. Systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.d.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Milani, P. Individualized Approach to Management of Light Chain Amyloidosis. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellqvist, U.; Cai, Q.; Hester, L.L.; Grövdal, M.; Börsum, J.; Rahman, I.; Ammann, E.M.; Hansson, M. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of light-chain amyloidosis in Sweden: A nationwide population-based study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 111, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.-A.; Tang, C.-H.; Goh, C.H.; Shen, S.-P.; Huang, K.-C.; Qiu, H.; Siggins, S.; Rothwell, L.A.; Liu, Y. A population-based cohort study of the epidemiology of light-chain amyloidosis in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staron, A.; Zheng, L.; Doros, G.; Connors, L.H.; Mendelson, L.M.; Joshi, T.; Sanchorawala, V. Marked progress in AL amyloidosis survival: A 40-year longitudinal natural history study. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Zhang, N.J.; Cherepanov, D.; Romanus, D.; Hughes, M.; Faller, D.V. Global epidemiology of amyloid light-chain amyloidosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, N.; Rodríguez-Lobato, L.G.; Cibeira, M.T.; Magnano, L.; Isola, I.; Rosiñol, L.; Bladé, J.; de Larrea, C.F. Bone marrow plasma cell infiltration in light chain amyloidosis: Impact on organ involvement and outcome. Amyloid 2018, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Vídriales, M.-B.; Pérez, J.J.; López-Berges, M.-C.; García-Sanz, R.; Ocio, E.M.; Heras, N.d.L.; Cuello, R.; de Coca, A.G.; Pardal, E.; et al. The clinical utility and prognostic value of multiparameter flow cytometry immunophenotyping in light-chain amyloidosis. Blood 2011, 117, 3613–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, G.Y.; Choi, J.-O.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.J.; Ju, E.-S.; Jeon, E.-S. Prognostic values of novel biomarkers in patients with AL amyloidosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visram, A.; Vachon, C.; Baughn, L.B.; Larson, D.; Smadbeck, J.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kapoor, P.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; et al. Family history of plasma cell disorders is associated with improved survival in MGUS, multiple myeloma, and systemic AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staron, A.; Connors, L.H.; Zheng, L.; Doros, G.; Sanchorawala, V. Race/ethnicity in systemic AL amyloidosis: Perspectives on disease and outcome disparities. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Schönland, S.; Merlini, G.; Milani, P.; Jaccard, A.; Bridoux, F.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Ravichandran, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Roeloffzen, W.; et al. The management of light chain (AL) amyloidosis in Europe: Clinical characteristics, treatment patterns, and efficacy outcomes between 2004 and 2018. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Burritt, M.F.; Therneau, T.M.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; et al. Serum Cardiac Troponins and N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide: A Staging System for Primary Systemic Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Colby, C.; Laumann, K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Leung, N.; Dingli, D.; et al. Revised Prognostic Staging System for Light Chain Amyloidosis Incorporating Cardiac Biomarkers and Serum Free Light Chain Measurements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Milani, P.; Gillmore, J.; Foli, A.; Lachmann, H.; Basset, M.; Hawkins, P.; Merlini, G.; Wechalekar, A.D. A European collaborative study of cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in upfront treatment of systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood 2015, 126, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schönland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kastritis, E.; et al. New Criteria for Response to Treatment in Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis Based on Free Light Chain Measurement and Cardiac Biomarkers: Impact on Survival Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wisniowski, B.; Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Merlini, G.; Schönland, S.; Veelken, K.; Hegenbart, U.; Geyer, S.M.; et al. Graded Cardiac Response Criteria for Patients with Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Basset, M.; Nuvolone, M.; Benigna, F.; Rodigari, L.; Lavatelli, F.; Foli, A.; Merlini, G.; Palladini, G. Indicators of profound hematologic response in AL amyloidosis: Complete response remains the goal of therapy. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Misra, A.; Gurskyte, L.; Kroi, F.; Verhoek, A.; Vermeulen, J.; Wechalekar, A.D. Assessing the prognostic utility of hematologic response for overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis: Results of a meta-analysis. Hematology 2023, 28, 2157581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Rapezzi, C.; Adler, Y.; Arad, M.; Basso, C.; Brucato, A.; Linhart, A. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis: A position statement of the ESCWorking Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Krsnik, I.; Gómez-Bueno, M.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Segovia-Cubero, J.; Huerta, A.; Salas, C.; Silvestre, R.; Sánchez, A.; Manso, M.; et al. AL Amyloidosis and Multiple Myeloma: A Complex Scenario in Which Cardiac Involvement Remains the Key Prognostic Factor. Life 2023, 13, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, A.; Bringhen, S.; Mateos, M.-V.; Larocca, A.; Facon, T.; Kumar, S.K.; Offidani, M.; McCarthy, P.; Evangelista, A.; Lonial, S.; et al. Geriatric assessment predicts survival and toxicities in elderly myeloma patients: An International Myeloma Working Group report. Blood 2015, 125, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, M.; Dold, S.M.; Ihorst, G.; Zober, A.; Möller, M.; Reinhardt, H.; Hieke, S.; Schumacher, M.; Wäsch, R. Geriatric assessment in multiple myeloma patients: Validation of the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) score and comparison with other common comorbidity scores. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facon, T.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Meuleman, N.; Belch, A.; Mohty, M.; Chen, W.-M.; Kim, K.; Zamagni, E.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Renwick, W.; et al. A simplified frailty scale predicts outcomes in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma treated in the FIRST (MM-020) trial. Leukemia 2020, 34, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stege, C.A.M.; van der Holt, B.; Dinmohamed, A.G.; Sonneveld, P.; Levin, M.-D.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Mellqvist, U.-H.; Waage, A.; Zweegman, S. Validation of the FIRST simplified frailty scale using the ECOG performance status instead of patient-reported activities. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1964–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, H.S.; Giri, S.; Wildes, T.M.; Balitsky, A.K.; McCurdy, A.; Pond, G.R.; Sivapathasundaram, B.; Seow, H. External validation of the FIRST trial’s simplified frailty score in a population-based cohort. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, P.; Vincent Rajkumar, S.; Merlini, G.; Kumar, S.; Gertz, M.A.; Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A. N-terminal fragment of the type-B natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) contributes to a simple new frailty score in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, H.; Brouwers, M.; Kouroukis, C.T.; Wildes, T.M. Comparison of frailty scores in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma: A review. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, H.; Wildes, T.M.; Vij, R.; Pianko, M.J.; Major, A.; Fiala, M.A. Dynamic frailty risk assessment among older adults with multiple myeloma: A population-based cohort study. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.; Jo, J.-C.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Song, K. Development of a new clinical index to easily assess frailty of elderly patients with multiple myeloma in Asian population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, H.L.; Sharpley, F.A. Frail Multiple Myeloma Patients Deserve More Than Just a Score. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyczyńska, A.; Krzempek, M.K.; Cortez, A.J.; Jurczyszyn, A.; Godlewska, K.; Ciepłuch, H.; Subocz, E.; Hałka, J.; de Nałęcz, A.K.; Wiśniewska, A.; et al. The Real-World Evidence on the Fragility and Its Impact on the Choice of Treatment Regimen in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Multiple Myeloma over 75 Years of Age. Cancers 2023, 15, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Sánchez, M.J.; Puerta, J.M.; Sáinz, J.; Chang, D.-Y.; Rodríguez, T.; López, P.; de Pablos, J.M.; Navarro, P.; de Veas, J.L.G.; et al. Trends in survival of multiple myeloma: A thirty-year population-based study in a single institution. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Campana, C.; Klersy, C.; Balduini, A.; Vadacca, G.; Perfetti, V.; Perlini, S.; Obici, L.; Ascari, E.; D’eril, G.M.; et al. Serum N-Terminal Pro–Brain Natriuretic Peptide Is a Sensitive Marker of Myocardial Dysfunction in AL Amyloidosis. Circulation 2003, 107, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, G.; Lousada, I.; Ando, Y.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Grogan, M.; Comenzo, R.L. Rationale, application and clinical qualification for NT-proBNP as a surrogate end point in pivotal clinical trials in patients with AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaxman, I.; Kumar, S.K.; Buadi, F.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dingli, D.; Hwa, Y.; Dispenzieri, A. Outcomes among newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis patients with a very high NT-proBNP: Implications for trial design. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3604–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Sáinz, J.; Martínez-López, J.; Puerta, J.M.; Chang, D.Y.L.; Rodríguez, T.; Lahuerta, J.J. Early mortality in multiple myeloma: The time-dependent impact of comorbidity. A population-based study in 621 real-life patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, M.A. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: 2024 update on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, J.; Ravichandran, S.; Bomsztyk, J.; Cohen, O.; Foard, D.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Venneri, L.; Fontana, M.; Hawkins, P.N.; Gillmore, J.; et al. Limited utility of Mayo 2012 cardiac staging system for risk stratification of patients with advanced cardiac AL amyloidosis-analysis of a uniformly treated cohort of 1275 patients. Haematologica 2024, 142, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) ≥ 70 | 50 (37.3) |
| Median age | 64.5 (IQR 55–72.3) |
| Gender (male/female) | 71/63 (53/47) |
| ECOG PS 0–1 | 27 (20.1) |
| 2–4 | 107 (79.9) |
| CCI ≥ 3 | 76/130 (56.7) |
| Concurrent or previous MM | 26 (19.4) |
| Concurrent or previous WM | 4 (3) |
| Concurrent or previous cancer | 16/129 (12.4) |
| BMPC (biopsy) ≥ 10% | 101 (75.4) |
| Cytogenetic abnormalities (FISH) | 12/52 (23.1) |
| Involved FLC, lambda | 110/129 (85.3) |
| Heart involvement | 122 (91) |
| Revised Staging System 2012, stage 4 | 56/109 (51.4) |
| NT-proBNP ≥8500 ng/L | 54 (40.3) |
| ≥1800 ng/L | 99 (73.9) |
| LVEF < 45% | 25/127 (19.7) |
| Renal involvement | 63 (47) |
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 52/129 (40.3) |
| Proteinuria ≥ 3 g/24 h | 38/132 (28.8) |
| Renal stage 3 | 22/131 (16.8) |
| Hemoglobin < 120 g/L | 36/121 (29.8) |
| Platelets < 120 × 109/L | 6/120 (5) |
| LDH high | 56/117 (47.9) |
| Albumin < 35 g/L | 48/122 (39.3) |
| Beta2-microglobulin > 5 mg/L | 15/62 (24.2) |
| ASCT | 33 (24.6) |
| Heart transplant | 5 (3.7) |
| Variables | Derivation Cohort (n = 134) | Validation Cohort (n = 282) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGE | Mean (SD) | 64.4 (11.9) | 64.4 (11.6) | 0.970 |
| Median (IQR) | 64.5 (55–72.2) | 65 (56–73) | - | |
| ≥70, n (%) | 50 (37.3) | 100 (35.5) | 0.744 | |
| ECOG PS | 0 | 0 (0) | 65 (23) | <0.001 |
| 1 | 27 (20.1) | 132 (46.8) | <0.001 | |
| 2 | 57 (42.5) | 54 (19.1) | <0.001 | |
| 3 | 44 (32.8) | 29 (10.3) | <0.001 | |
| 4 | 6 (4.5) | 2 (0.7) | <0.001 | |
| (≥2, n (%) | 107 (79.9) | 85 (30.1) | <0.001 | |
| NT-proBNP | Mean (SD) | 8919 (12,139) | 4987.6 (7594.8) | <0.001 |
| Median (IQR) | 6265 (1607.2–10,702.8) | 1958.5 (473.8–5828.5) | - | |
| (≥8500 ng/L, n (%) | 54 (40.3) | 50 (17.7) | <0.001 | |
| Univariate Analysis | Cox Regression Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age, years | 1.05 | 1.03–1.08 | <0.001 | 1.06 | 1.03–1.08 | <0.001 |
| ECOG PS, <2 vs. ≥2 | 2.90 | 1.33–6.33 | 0.008 | 2.56 | 1.16–5.67 | 0.020 |
| NT-proBNP, <8500 vs. ≥8500 ng/L | 2.57 | 1.61–4.11 | <0.001 | 2.34 | 1.45–3.77 | <0.001 |
| Nco, <5 vs. ≥5 | 2.46 | 1.39–4.33 | 0.002 | |||
| CCI, <3 vs. ≥3 | 1.98 | 1.18–3.33 | 0.010 | |||
| LVEF, ≥45 vs. <45% | 1.99 | 1.14–3.48 | 0.016 | |||
| eGFR, ≥60 vs. <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1.88 | 1.15–3.01 | 0.011 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ríos-Tamayo, R.; Lecumberri, R.; Cibeira, M.T.; González-Calle, V.; Alonso, R.; Domingo-González, A.; Landete, E.; Encinas, C.; Iñigo, B.; Blanchard, M.-J.; et al. A Simple Frailty Score Predicts Survival and Early Mortality in Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091689
Ríos-Tamayo R, Lecumberri R, Cibeira MT, González-Calle V, Alonso R, Domingo-González A, Landete E, Encinas C, Iñigo B, Blanchard M-J, et al. A Simple Frailty Score Predicts Survival and Early Mortality in Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091689
Chicago/Turabian StyleRíos-Tamayo, Rafael, Ramón Lecumberri, María Teresa Cibeira, Verónica González-Calle, Rafael Alonso, Amalia Domingo-González, Elena Landete, Cristina Encinas, Belén Iñigo, María-Jesús Blanchard, and et al. 2024. "A Simple Frailty Score Predicts Survival and Early Mortality in Systemic AL Amyloidosis" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091689
APA StyleRíos-Tamayo, R., Lecumberri, R., Cibeira, M. T., González-Calle, V., Alonso, R., Domingo-González, A., Landete, E., Encinas, C., Iñigo, B., Blanchard, M.-J., Alejo, E., Krsnik, I., Gómez-Bueno, M., Garcia-Pavia, P., Segovia-Cubero, J., Rosiñol, L., Lahuerta, J.-J., Martínez-López, J., & Bladé, J. (2024). A Simple Frailty Score Predicts Survival and Early Mortality in Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Cancers, 16(9), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091689