Role of Epiregulin in Lung Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Resistance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiological Role of EREG in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
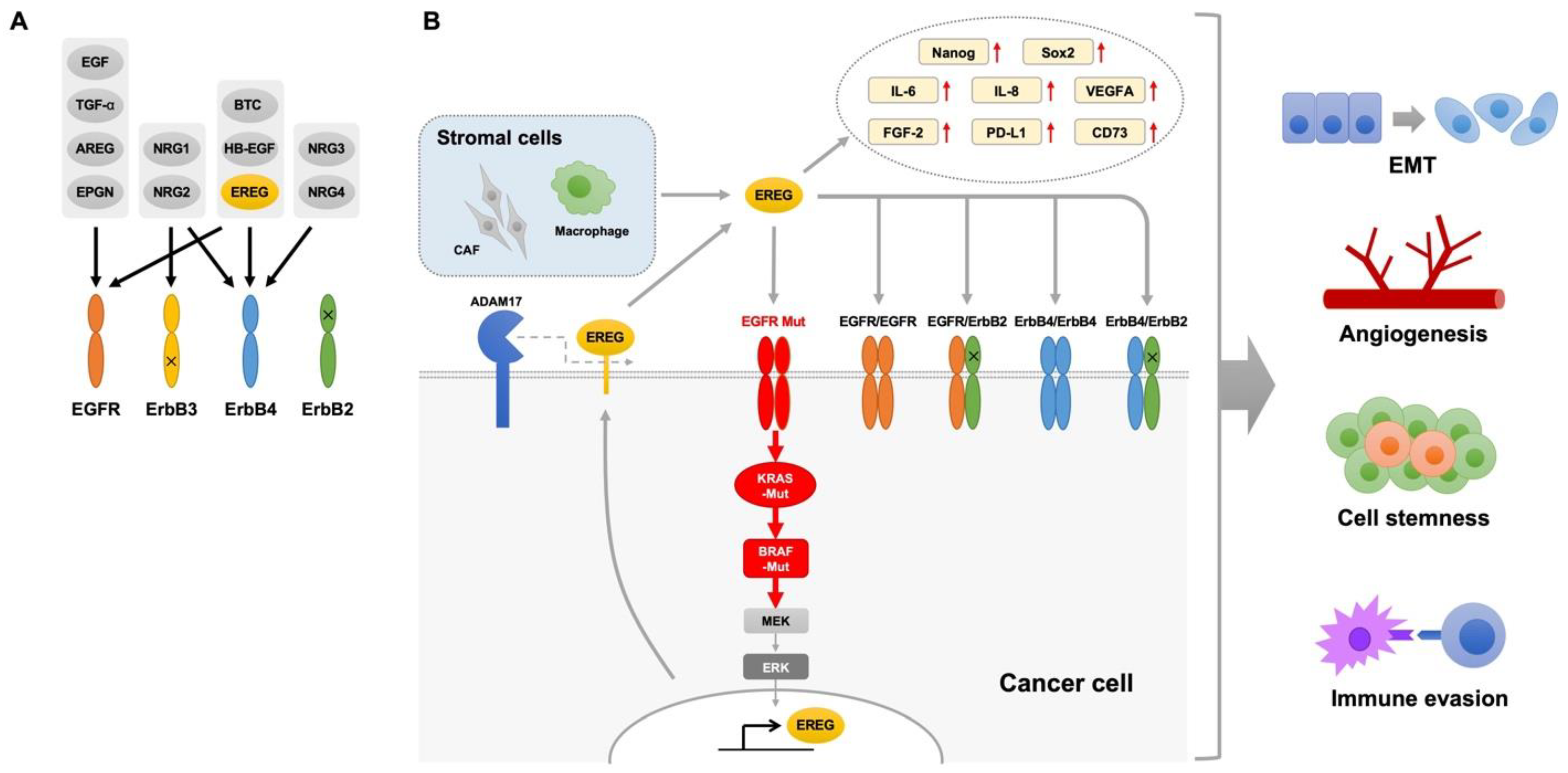
3. Oncogenic Roles of EREG in Lung Cancer
4. EREG in Oncogene-Driven NSCLC
5. EREG in the Tumor Microenvironment
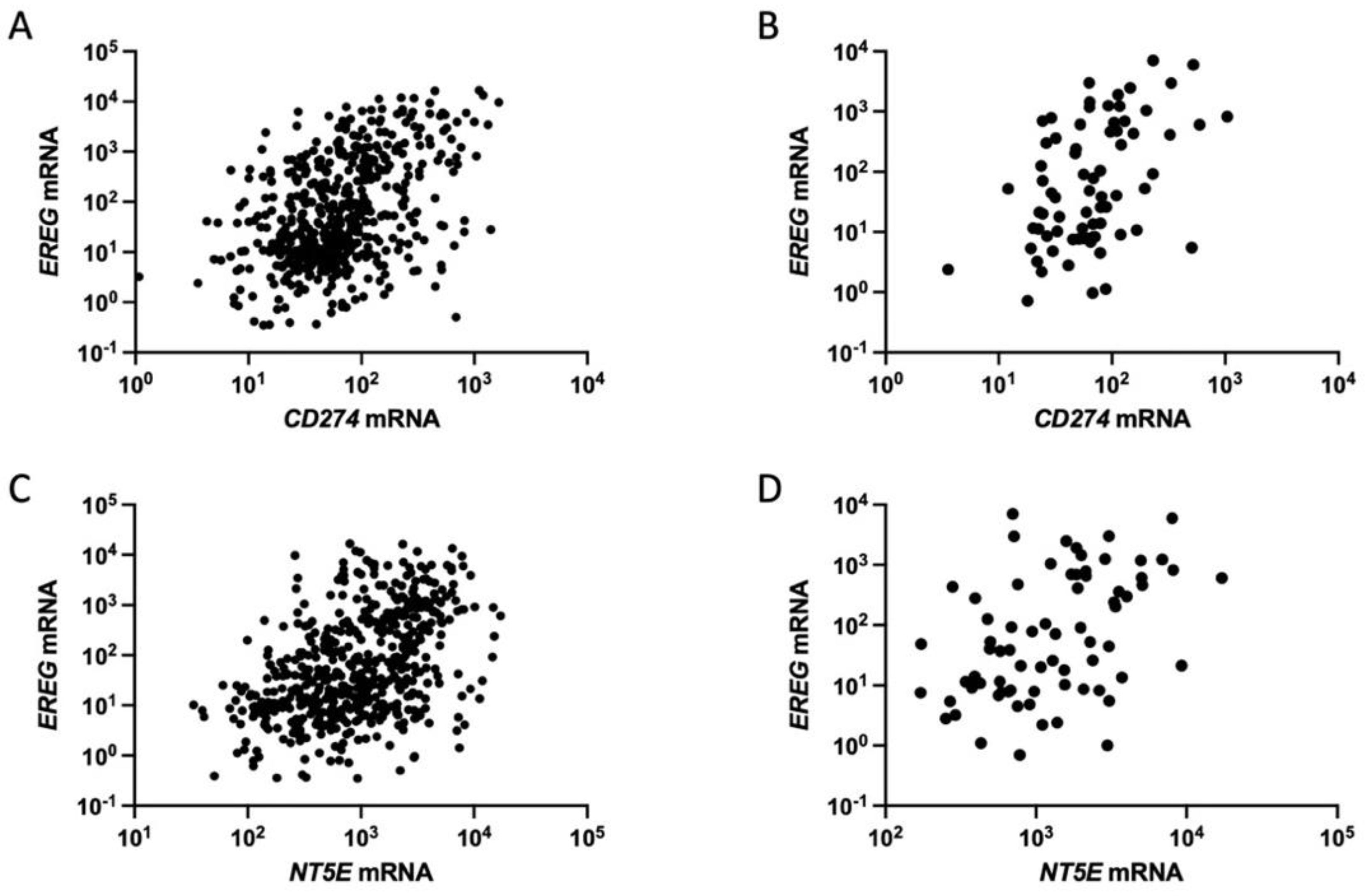
6. EREG for Immune Evasion
7. EREG and Resistance to Anticancer Drugs
8. Targeting EREG/EGFR Pathways
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, R.; Kirita, K.; Kuwata, T.; Umemura, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Fujii, S.; Yoh, K.; Kojima, M.; Niho, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; et al. Factors influencing the concordance of histological subtype diagnosis from biopsy and resected specimens of lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Boshoff, C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Juarez, M.; Serrano-Gomez, C.; Bote-de-Cabo, H.; Paz-Ares, L. Targeted therapy for lung cancer: Beyond EGFR and ALK. Cancer 2023, 129, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatabe, Y. Molecular pathology of non-small cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2024, 84, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, E.; Moraes, F.C.A.; Chavez, M.P.; Souza, M.E.C.; Rodrigues, A.; Ferreira, R.O.M.; Lopes, L.M.; Almeida, A.M.; Fernandes, M.R.; Santos, N. PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors plus Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone for Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cancers 2023, 15, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, K.; Ruiz, R.; Mas, L.; Pozza, D.H.; Vancini, M.; Silva Junior, J.A.; de Mello, R.A. Update in Immunotherapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Optimizing Treatment Sequencing and Identifying the Best Choices. Cancers 2023, 15, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris, M.G.; Johnson, B.E.; Berry, L.D.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.A.; Aronson, S.L.; Su, P.F.; et al. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA 2014, 311, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyasu, R.; Kakuto, S.; Miyadera, K.; Akita, T.; Kiritani, A.; Tsugitomi, R.; Amino, Y.; Uchibori, K.; Kitazono, S.; Yanagitani, N.; et al. Real-World Outcome Analysis of Patients With Stage IV NSCLC Treated With Tyrosine Kinase and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezawa, K.; Pirazzoli, V.; Arcila, M.E.; Nebhan, C.A.; Song, X.; de Stanchina, E.; Ohashi, K.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Spitzler, P.J.; Melnick, M.A.; et al. HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K. HER2-/HER3-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Treating Lung and Colorectal Cancers Resistant to EGFR Inhibitors. Cancers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zang, H.; Wen, Q.; Fan, S. AXL in cancer: A modulator of drug resistance and therapeutic target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamada, T.; Wang, R.; Tanimura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Araujo, L.H.; Boroni, M.; et al. AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, A.; Belugali Nataraj, N.; Lee, J.S.; Zhitomirsky, B.; Oren, Y.; Oster, S.; Lindzen, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Will, R.; Ghosh, S.; et al. AXL and Error-Prone DNA Replication Confer Drug Resistance and Offer Strategies to Treat EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2666–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Aminu, M.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Petranovic, M.; Saad, M.B.; Chen, P.; Qin, K.; Varghese, S.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; et al. Efficacy and clinicogenomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors alone or with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, G.; Helmink, B.A.; Sharma, P.; Wargo, J.A. Hallmarks of response, resistance, and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 2021, 184, 5309–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantini, E.; Maroni, G.; Del Re, M.; Tenen, D.G. EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abud, H.E.; Chan, W.H.; Jarde, T. Source and Impact of the EGF Family of Ligands on Intestinal Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 685665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.A.; Graves-Deal, R.; Pittelkow, M.R.; DuBois, R.; Cook, P.; Ramsey, G.W.; Bishop, P.R.; Damstrup, L.; Coffey, R.J. Auto- and cross-induction within the mammalian epidermal growth factor-related peptide family. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22817–22822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Carpenter, G.; Coffey, R.J. EGF receptor ligands: Recent advances. F1000Res 2016, 5, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riese, D.J., 2nd; Cullum, R.L. Epiregulin: Roles in normal physiology and cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Komurasaki, T.; Uchida, D.; Takayama, Y.; Isobe, T.; Okuyama, T.; Hanada, K. Epiregulin. A novel epidermal growth factor with mitogenic activity for rat primary hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7495–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Komurasaki, T.; Uchida, D.; Morimoto, S. Distribution of mRNA for human epiregulin, a differentially expressed member of the epidermal growth factor family. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, A.; Hammes, S.R. LH-Induced Steroidogenesis in the Mouse Ovary, but Not Testis, Requires Matrix Metalloproteinase 2- and 9-Mediated Cleavage of Upregulated EGF Receptor Ligands. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Weskamp, G.; Kelly, K.; Zhou, H.M.; Higashiyama, S.; Peschon, J.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P.; Blobel, C.P. Distinct roles for ADAM10 and ADAM17 in ectodomain shedding of six EGFR ligands. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.I.; Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J. ADAM17: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blobel, C.P. ADAMs: Key components in EGFR signalling and development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelly, M.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R.; Guarino, B.C.; Waterman, H.; Wang, L.M.; Lyass, L.; Alimandi, M.; Kuo, A.; Bacus, S.S.; Pierce, J.H.; et al. Epiregulin is a potent pan-ErbB ligand that preferentially activates heterodimeric receptor complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10496–10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Lin, X.; Li, G.; Han, N.; Du, J.; Fan, Z. Epiregulin promotes the migration and chemotaxis ability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 8450–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.S.; Cheng, X.; Pawlowski, J.E.; Wallace, A.R.; Ferrer, P.; Molloy, C.J. Epiregulin is a potent vascular smooth muscle cell-derived mitogen induced by angiotensin II, endothelin-1, and thrombin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, C. EGF receptor activation by GPCRs: An universal pathway reveals different versions. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 331, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.E.; Tan, T.C.; John, A.E.; Whatling, C.; McPheat, W.L.; Greaves, D.R. Fractalkine has anti-apoptotic and proliferative effects on human vascular smooth muscle cells via epidermal growth factor receptor signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, D.M.; Bessman, N.J.; Kiyatkin, A.; Salazar-Cavazos, E.; Byrne, P.O.; Moore, J.O.; Valley, C.C.; Ferguson, K.M.; Leahy, D.J.; Lidke, D.S.; et al. EGFR Ligands Differentially Stabilize Receptor Dimers to Specify Signaling Kinetics. Cell 2017, 171, 683–695.e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, P.D.; Panko, L.; Karp, P.; Lee, J.H.; Zabner, J. Differentiation of human airway epithelia is dependent on erbB2. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L175–L180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Gualano, R.C.; Hibbs, M.L.; Anderson, G.P.; Bozinovski, S. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling to Erk1/2 and STATs control the intensity of the epithelial inflammatory responses to rhinovirus infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9977–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arae, K.; Hirata, M.; Kurata, S.; Kamiya, S.; Taguchi, H. Mycoplasma pneumoniae induces interleukin-8 production via the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 55, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, E.K.; Foley, J.S.; Cheng, J.; Patel, A.S.; Drazen, J.M.; Tschumperlin, D.J. Bronchial epithelial compression regulates epidermal growth factor receptor family ligand expression in an autocrine manner. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 32, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, T.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Park, J.A.; Sunnarborg, S.W.; Horiuchi, K.; Blobel, C.P.; Drazen, J.M. TNF-alpha-converting enzyme/a disintegrin and metalloprotease-17 mediates mechanotransduction in murine tracheal epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, J.; Malvezzi, M.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Boffetta, P. Risk factors for lung cancer worldwide. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Leng, S.; Padilla, M.T.; Saxton, B.; Hutt, J.; Tessema, M.; Kato, K.; Kim, K.C.; Belinsky, S.A.; et al. Muc1 knockout potentiates murine lung carcinogenesis involving an epiregulin-mediated EGFR activation feedback loop. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xi, S.; Gara, S.K.; Shan, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; Shukla, V.; Wang, R.; Hoang, C.D.; Chen, H.; et al. Hookah Smoke Mediates Cancer-Associated Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Signatures in Human Respiratory Epithelial Cells. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kometani, T.; Yoshino, I.; Miura, N.; Okazaki, H.; Ohba, T.; Takenaka, T.; Shoji, F.; Yano, T.; Maehara, Y. Benzo[a]pyrene promotes proliferation of human lung cancer cells by accelerating the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2009, 278, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyaqoub, F.S.; Liu, Y.; Tao, L.; Steele, V.E.; Lubet, R.A.; Pereira, M.A. Modulation by bexarotene of mRNA expression of genes in mouse lung tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takagi, H.; Sugiura, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Wakamatsu, M.; Tsuritani, K.; Sato, Y. Gene expression analysis in the lung of the rasH2 transgenic mouse at week 4 prior to induction of malignant tumor formation by urethane and N-methylolacrylamide. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 40, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, K.Y.; Tseng, C.H.; Feng, P.H.; Sun, W.L.; Ho, S.C.; Lin, C.W.; Van Hiep, N.; Luo, C.S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Chen, T.T.; et al. 3-Nitrobenzanthrone promotes malignant transformation in human lung epithelial cells through the epiregulin-signaling pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 865–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaga, N.; Kaira, K.; Imai, H.; Shimizu, K.; Nakano, T.; Shames, D.S.; Girard, L.; Soh, J.; Sato, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; et al. Oncogenic KRAS-induced epiregulin overexpression contributes to aggressive phenotype and is a promising therapeutic target in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4034–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaga, N.; Tomizawa, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Imai, H.; Takahashi, G.; Kakegawa, S.; Ohtaki, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Kawashima, O.; Shames, D.S.; et al. Clinicopathological and biological significance of epiregulin expression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, S426–S427. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, X. Identification of PDL1-Related Biomarkers to Select Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients for PD1/PDL1 Inhibitors. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 7291586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Iwanaga, K.; Choi, K.C.; Wislez, M.; Raso, M.G.; Wei, W.; Wistuba, I.I.; Kurie, J.M. Intratumoral epiregulin is a marker of advanced disease in non-small cell lung cancer patients and confers invasive properties on EGFR-mutant cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, F.; Ye, T.; Lee, S.H.; Xu, J.; Jia, L.; Zeng, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, X.; et al. Epiregulin increases stemness-associated genes expression and promotes chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer via ERK signaling. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thogersen, V.B.; Sorensen, B.S.; Poulsen, S.S.; Orntoft, T.F.; Wolf, H.; Nexo, E. A subclass of HER1 ligands are prognostic markers for survival in bladder cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6227–6233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Feng, R.; Chen, B.; Zhou, J. EREG is a risk factor for the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1161835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeishi, H.; Higashikawa, K.; Hiraoka, M.; Fujimoto, S.; Mitani, Y.; Ohta, K.; Takechi, M.; Kamata, N. Expression of epiregulin, a novel epidermal growth factor ligand associated with prognosis in human oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.W.; Yang, L.Q.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.W.; Xu, L.H.; Fu, J.; Li, S.L.; Ge, X.Y. Epiregulin Promotes Lung Metastasis of Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3700–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Ju, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, G.; Liu, L.; et al. EREG-driven oncogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma exhibits higher sensitivity to Erlotinib therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10589–10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, S.; Hinohara, K.; Wang, L.; Nishimura, T.; Urushido, M.; Yachi, K.; Tsuda, M.; Tanino, M.; Kimura, T.; Nishihara, H.; et al. Epiregulin enhances tumorigenicity by activating the ERK/MAPK pathway in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Shu, X.; Sun, L.; Lou, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y. Tumor endothelial cells promote metastasis and cancer stem cell-like phenotype through elevated Epiregulin in esophageal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu, H.; Hashimoto, I.; Hiroshima, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Kano, K.; Takahashi, K.; Aoyama, T.; Yamada, T.; Tamagawa, H.; Ogata, T.; et al. Clinical Significance of EREG Gene Expression in Gastric Cancer Tissue After Curative Surgery. Anticancer. Res. 2022, 42, 3873–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yong, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Ding, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Feng, Z.; Wang, B. Elevated epiregulin expression predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Song, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. A TP53-associated immune prognostic signature for the prediction of the overall survival and therapeutic responses in pancreatic cancer. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kleeff, J.; Friess, H.; Wang, L.; Zimmermann, A.; Yarden, Y.; Buchler, M.W.; Korc, M. Epiregulin is Up-regulated in pancreatic cancer and stimulates pancreatic cancer cell growth. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Colby, J.K.; Rengel, R.C.; Fischer, S.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Klein, R.D. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in the mouse urinary bladder induces the expression of immune- and cell proliferation-related genes. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; He, H.W.; Sun, H.X.; Ren, K.H.; Shao, R.G. Dual knockdown of N-ras and epiregulin synergistically suppressed the growth of human hepatoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, M.; Bohrer, L.R.; Brady, N.J.; Chuntova, P.; Kemp, S.E.; Wardwell, C.T.; Nelson, A.C.; Schwertfeger, K.L. Epiregulin contributes to breast tumorigenesis through regulating matrix metalloproteinase 1 and promoting cell survival. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, D.; Jiang, X.; Nie, C. EREG is the core onco-immunological biomarker of cuproptosis and mediates the cross-talk between VEGF and CD99 signaling in glioblastoma. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qin, L.; Li, W.; Fei, F. MicroRNA-1179 targets Epiregulin (EREG) regulates the proliferation and metastasis of human multiple myeloma cells. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2023, 70, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minn, A.J.; Gupta, G.P.; Siegel, P.M.; Bos, P.D.; Shu, W.; Giri, D.D.; Viale, A.; Olshen, A.B.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005, 436, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, B.E.; Frierson, H.F.; Conaway, M.R.; Seraj, J.M.; Harding, M.A.; Hampton, G.M.; Theodorescu, D. Profiling the evolution of human metastatic bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7813–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kobunai, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Konishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Matsuda, K.; Ishihara, S.; Nozawa, K.; Eshima, K.; et al. Prediction of liver metastasis after colorectal cancer using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of 10 genes. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.K.; Velmurugan, K.; Xiong, K.N.; Alexander, C.M.; Xiong, J.; Brooks, R. Epiregulin is required for lung tumor promotion in a murine two-stage carcinogenesis model. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. Cuproptosis: A new form of programmed cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J. Cuproptosis in lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaga, N.; Miura, Y.; Kasahara, N.; Sakurai, R. Targeting Oncogenic KRAS in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Rossi, G.; Minari, R.; Conti, A.; Friboulet, L.; Tiseo, M.; Planchard, D. BRAF in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Pickaxing another brick in the wall. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 66, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoshige, K.; Guo, M.; Tsuchiya, T.; Fukazawa, T.; Fink-Baldauf, I.M.; Stuart, W.D.; Naomoto, Y.; Nagayasu, T.; Maeda, Y. An EGFR ligand promotes EGFR-mutant but not KRAS-mutant lung cancer in vivo. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3894–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishii, K.; Ohashi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Makimoto, G.; Nakasuka, T.; Higo, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Kato, Y.; Kubo, T.; Rai, K.; et al. Triple therapy with osimertinib, bevacizumab and cetuximab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer with HIF-1alpha/TGF-alpha expression. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, T.; Yasuda, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Kuroda, A.; Arai, D.; Ishioka, K.; Ohgino, K.; Miyawaki, M.; Kawada, I.; Naoki, K.; et al. Activation of EGFR Bypass Signaling by TGFalpha Overexpression Induces Acquired Resistance to Alectinib in ALK-Translocated Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsumoto, F.; Fukagawa, S.; Miyata, K.; Nam, S.O.; Katsuda, T.; Miyahara, D.; Odawara, T.; Manabe, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Yasunaga, S.; et al. HB-EGF Is a Promising Therapeutic Target for Lung Cancer with Secondary Mutation of EGFR(T790M). Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regales, L.; Gong, Y.; Shen, R.; de Stanchina, E.; Vivanco, I.; Goel, A.; Koutcher, J.A.; Spassova, M.; Ouerfelli, O.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; et al. Dual targeting of EGFR can overcome a major drug resistance mutation in mouse models of EGFR mutant lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3000–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, I.; Shirasawa, S.; Iwamoto, R.; Okumura, K.; Tsunoda, T.; Nishioka, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Mekada, E.; Sasazuki, T. Involvement of deregulated epiregulin expression in tumorigenesis in vivo through activated Ki-Ras signaling pathway in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6886–6889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.C.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.Y.; Jung, M.; Park, S.N.; Yoon, D.Y. Epiregulin expression by Ets-1 and ERK signaling pathway in Ki-ras-transformed cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, N.; Wislez, M.; Zhang, J.; Iwanaga, K.; Dackor, J.; Hanna, A.E.; Kalyankrishna, S.; Cody, D.D.; Price, R.E.; Sato, M.; et al. High expression of ErbB family members and their ligands in lung adenocarcinomas that are sensitive to inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11478–11485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaga, N.; Shames, D.S.; Girard, L.; Peyton, M.; Larsen, J.E.; Imai, H.; Soh, J.; Sato, M.; Yanagitani, N.; Kaira, K.; et al. Knockdown of oncogenic KRAS in non-small cell lung cancers suppresses tumor growth and sensitizes tumor cells to targeted therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, M.; Bae, Y.K.; Han, C.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, S.S.; Han, J.Y. Oncogenic KRAS promotes growth of lung cancer cells expressing SLC3A2-NRG1 fusion via ADAM17-mediated shedding of NRG1. Oncogene 2022, 41, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, B.; Lu, F.; Stribbling, S.M.; Grieve, A.G.; Ryan, A.J.; Freeman, M. iRhom2 regulates ERBB signalling to promote KRAS-driven tumour growth of lung cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.I.; Alhayyani, S.; McLeod, L.; Yu, L.; Alanazi, M.; Deswaerte, V.; Tang, K.; Jarde, T.; Smith, J.A.; Prodanovic, Z.; et al. ADAM17 selectively activates the IL-6 trans-signaling/ERK MAPK axis in KRAS-addicted lung cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chan, K.I.; Kwok, H.F.; Tam, K.Y. Novel Therapeutic Anti-ADAM17 Antibody A9(B8) Enhances EGFR-TKI-Mediated Anticancer Activity in NSCLC. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufert, C.; Becker, C.; Tureci, O.; Waldner, M.J.; Backert, I.; Floh, K.; Atreya, I.; Leppkes, M.; Jefremow, A.; Vieth, M.; et al. Tumor fibroblast-derived epiregulin promotes growth of colitis-associated neoplasms through ERK. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westendorp, F.; Karpus, O.N.; Koelink, P.J.; Vermeulen, J.L.M.; Meisner, S.; Koster, J.; Buller, N.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Muncan, V.; van den Brink, G.R. Epithelium-derived Indian Hedgehog restricts stromal expression of ErbB family members that drive colonic tumor cell proliferation. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1628–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Dai, W.; Chen, T.; Luo, L.; Zeng, J.; Mi, K.; Lang, J.; Cao, B. Epiregulin confers EGFR-TKI resistance via EGFR/ErbB2 heterodimer in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2596–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia-Terrassa, T.; Jolly, M.K. Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a036905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition---A Hallmark of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Hallm. 2013, 1, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhan, H. Communication between EMT and PD-L1 signaling: New insights into tumor immune evasion. Cancer Lett. 2020, 468, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Ten Dijke, P.; Kostidis, S.; Giera, M.; Hornsveld, M. TGFbeta-induced metabolic reprogramming during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2103–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokizaki, S.; Podyma-Inoue, K.A.; Matsumoto, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Ibi, H.; Uchida, S.; Iwabuchi, S.; Harada, H.; Hashimoto, S.; et al. Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signals suppresses tumor formation by regulation of tumor microenvironment networks. Cancer Sci. 2023, 115, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Hashemi, F.; Zarrabi, A.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Sharifzadeh, S.O.; Soleymani, L.; Daneshi, S.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. New insight towards development of paclitaxel and docetaxel resistance in cancer cells: EMT as a novel molecular mechanism and therapeutic possibilities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorieff, A.; Liu, Y.; Inanlou, M.R.; Khomchuk, Y.; Wrana, J.L. Yap-dependent reprogramming of Lgr5(+) stem cells drives intestinal regeneration and cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Davis, A.K.; Xin, M.; Walz, G.; Tian, W.; Zheng, Y. CDC42 controlled apical-basal polarity regulates intestinal stem cell to transit amplifying cell fate transition via YAP-EGF-mTOR signaling. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Suzuki, M.; Natori, O.; Kato, A.; Matsubara, K.; Jau Chen, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Funahashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; et al. LGR5-positive colon cancer stem cells interconvert with drug-resistant LGR5-negative cells and are capable of tumor reconstitution. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Autocrine epiregulin activates EGFR pathway for lung metastasis via EMT in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25251–25263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.D. Regulation of PD-L1: A novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumimoto, H.; Takano, A.; Teramoto, K.; Daigo, Y. RAS-Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signal Is Required for Enhanced PD-L1 Expression in Human Lung Cancers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Lin, Z.; Peng, P.; Wang, J.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, L.; Sheng, J.; et al. KRAS mutation-induced upregulation of PD-L1 mediates immune escape in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, Y.; Sunaga, N. Role of Immunotherapy for Oncogene-Driven Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, J.; Divisekera, U.; Duret, H.; Sparwasser, T.; Teng, M.W.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73-deficient mice have increased antitumor immunity and are resistant to experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Longhi, M.S.; Robson, S.C.; Stagg, J. The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: Novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yao, F.; Davis, P.F.; Tan, S.T.; Hall, S.R.R. CD73, Tumor Plasticity and Immune Evasion in Solid Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Negrao, M.V.; Reuben, A.; Federico, L.; Diao, L.; McGrail, D.; Nilsson, M.; Robichaux, J.; Munoz, I.G.; Patel, S.; et al. Characterization of the Immune Landscape of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Identifies CD73/Adenosine Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Target. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lee, T.; He, Y.; Raman, R.; Irizarry, A.; Martin, M.L.; Giaccone, G. The regulation of CD73 in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 170, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, E.; McGlinchey, K.; Wang, J.; Martin, P.; Ching, S.L.; Floc’h, N.; Kurasawa, J.; Starrett, J.H.; Lazdun, Y.; Wetzel, L.; et al. Anti-PD-L1 and anti-CD73 combination therapy promotes T cell response to EGFR-mutated NSCLC. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e142843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Sun, D.; Song, P.; Shi, L.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Circular RNA circ_ASAP2 regulates drug sensitivity and functional behaviors of cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells by the miR-330-3p/NT5E axis. Anticancer. Drugs 2021, 32, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Paknahad, M.H.; Nemati, M.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Rajabi, A.; Shojaie, L.; Mirzaei, H. Dysregulated expression and functions of microRNA-330 in cancers: A potential therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, R.; Elkharti, M.; Ge, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.Z. The homeostatic malfunction of a novel feedback pathway formed by lncRNA021545, miR-330-3p and epiregulin contributes in hepatocarcinoma progression via mediating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 2492–2525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, I.; Kundra, R.; Mastrogiacomo, B.; Tran, T.N.; Sikina, L.; Mazor, T.; Li, X.; Ochoa, A.; Zhao, G.; Lai, B.; et al. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Takeuchi, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Yamada, T. Ligand-triggered resistance to molecular targeted drugs in lung cancer: Roles of hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor ligands. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.L.; Haderk, F.; Bivona, T.G. Allosteric SHP2 inhibitors in cancer: Targeting the intersection of RAS, resistance, and the immune microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, S.; Elhassan, R.M.; Hou, X.; Fang, H. Strategies to overcome drug resistance using SHP2 inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3908–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurupi, R.; Floros, K.V.; Jacob, S.; Chawla, A.T.; Cai, J.; Hu, B.; Puchalapalli, M.; Coon, C.M.; Khatri, R.; Crowther, G.S.; et al. Pharmacologic Inhibition of SHP2 Blocks Both PI3K and MEK Signaling in Low-epiregulin HNSCC via GAB1. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Dai, Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Huang, X.; Pu, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Epiregulin reprograms cancer-associated fibroblasts and facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via JAK2-STAT3 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Long, Q.; Fu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Fu, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Lam, E.W.; et al. Targeting epiregulin in the treatment-damaged tumor microenvironment restrains therapeutic resistance. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4941–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, M.L.; Minond, D. Recent Advances in ADAM17 Research: A Promising Target for Cancer and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9673537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Ying, X.W.; Zhou, H.B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.C.; Yan, J.P.; Jing, Y.T.; Yang, Y. Lentivirus-mediated disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 RNA interference reversed the acquired resistance to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Jiang, T.; Duan, D.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Ni, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of Lethal Skin Toxicities Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors and Related Treatment Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 804212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Muhsin, M.; Kirkpatrick, P. Cetuximab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auf, G.; Jabouille, A.; Delugin, M.; Guerit, S.; Pineau, R.; North, S.; Platonova, N.; Maitre, M.; Favereaux, A.; Vajkoczy, P.; et al. High epiregulin expression in human U87 glioma cells relies on IRE1alpha and promotes autocrine growth through EGF receptor. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, C.; Jin, Y.H.; You, Z.; Qiong, Q.; Jun, Z. Prognostic value of amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNA expression in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55890–55899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Iijima, M.; Kado, Y.; Mizohata, E.; Inoue, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Doi, H.; Shibasaki, Y.; Kodama, T. Construction and characterization of functional anti-epiregulin humanized monoclonal antibodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, M.; Anai, M.; Kodama, T.; Shibasaki, Y. Epiregulin-blocking antibody inhibits epiregulin-dependent EGFR signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | No. of Subjects | Survival | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCLC (stage I–III) | Protein | 356 | OS | NA | [51] |
| NSCLC (stage IA) | mRNA | 244 | OS | 1.62 (1.07–2.48) | [47] |
| NSCLC | mRNA | 998 | DFS & OS | NA | [52] |
| Lung adenocarcinoma | mRNA | 119 | DFS OS | 2.33 (1.03–5.28) 8.71 (1.90–39.8) | [49] |
| mRNA | 462 | OS | 1.588 (NA) | [42] | |
| mRNA | 520 | OS | NA | [50] | |
| Bladder cancer | mRNA | 73 | OS | NA | [53] |
| Cervical cancer | mRNA | 304 | OS | 3.26 (2.03–5.21) | [54] |
| OSCC | mRNA | 30 | OS | NA | [55] |
| SACC | Protein | 72 | MFS & OS | NA | [56] |
| HNSCC | Protein | 80 | OS | NA | [57] |
| Glioblastoma | Protein | 73 | OS | NA | [58] |
| Esophageal cancer | Protein | 120 | OS | NA | [59] |
| Gastric cancer | mRNA | 253 | OS | NA | [60] |
| Protein | 550 | OS | 1.763 (1.235–2.480) | [61] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | mRNA | NA | OS | NA | [62] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunaga, N.; Miura, Y.; Masuda, T.; Sakurai, R. Role of Epiregulin in Lung Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers 2024, 16, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040710
Sunaga N, Miura Y, Masuda T, Sakurai R. Role of Epiregulin in Lung Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040710
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunaga, Noriaki, Yosuke Miura, Tomomi Masuda, and Reiko Sakurai. 2024. "Role of Epiregulin in Lung Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Resistance" Cancers 16, no. 4: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040710
APA StyleSunaga, N., Miura, Y., Masuda, T., & Sakurai, R. (2024). Role of Epiregulin in Lung Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers, 16(4), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040710







