WEE1 Inhibitor Adavosertib Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer, Especially in Cases with p53 Mutations
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Patients
2.3. Immunohistochemistry for WEE1 Expression in Human CRC Tissue
2.4. Classification of Human CRC Tissue According to the p53 Mutation Status
2.5. WEE1 Expression Analysis Using the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) Cancer Genomics Browser
2.6. Cell Lines
2.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis of WEE1 Expression in CRC Cell Lines
2.8. In Vitro Adavosertib Effects on Cancer Cell Proliferation
2.9. In Vitro Adavosertib Effects on Cancer Cell Cycle
2.10. In Vitro Adavosertib Effects on Cancer Cell Apoptosis
2.11. Establishment of a CRC Orthotopic Transplantation Mouse Model and Adavosertib Treatment
2.12. Immunofluorescence Staining of Mouse Tumor Specimens
2.13. Immunohistochemistry Staining of Mouse Tumor Specimens
2.14. RNA Sequencing
2.15. Functional Enrichment Analysis and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
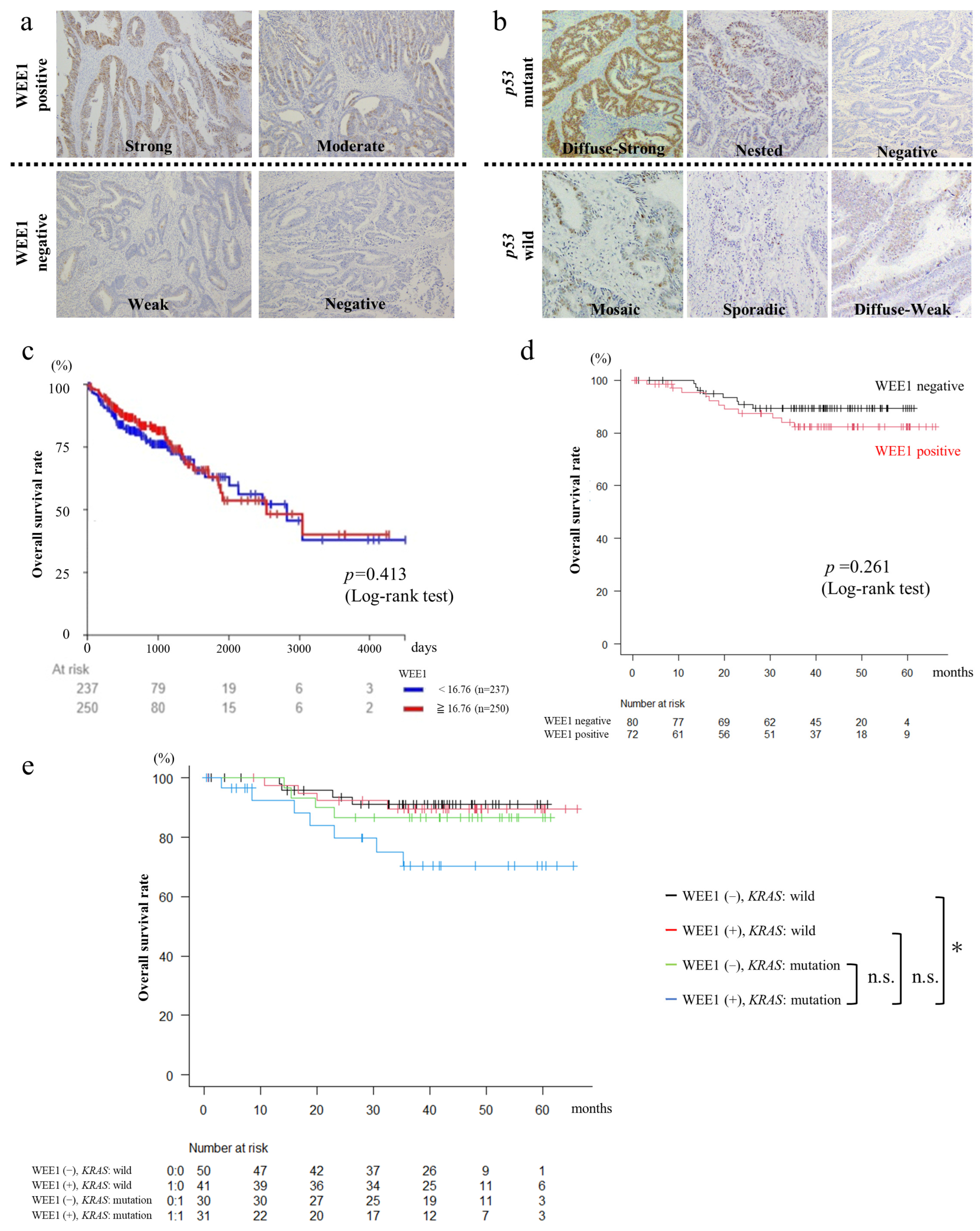
3.1. WEE1 Expression in Surgical CRC Specimens Is Not Correlated with CRC Clinicopathological Features
3.2. Patients with WEE1-Positive and KRAS-Mutated CRC Have Poor Prognosis
3.3. WEE1 Expression Tended to Be Higher in CRC Cell Lines than in Normal Colon Mucosa
3.4. WEE1 Inhibitor Suppresses CRC Cell Line Proliferation in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
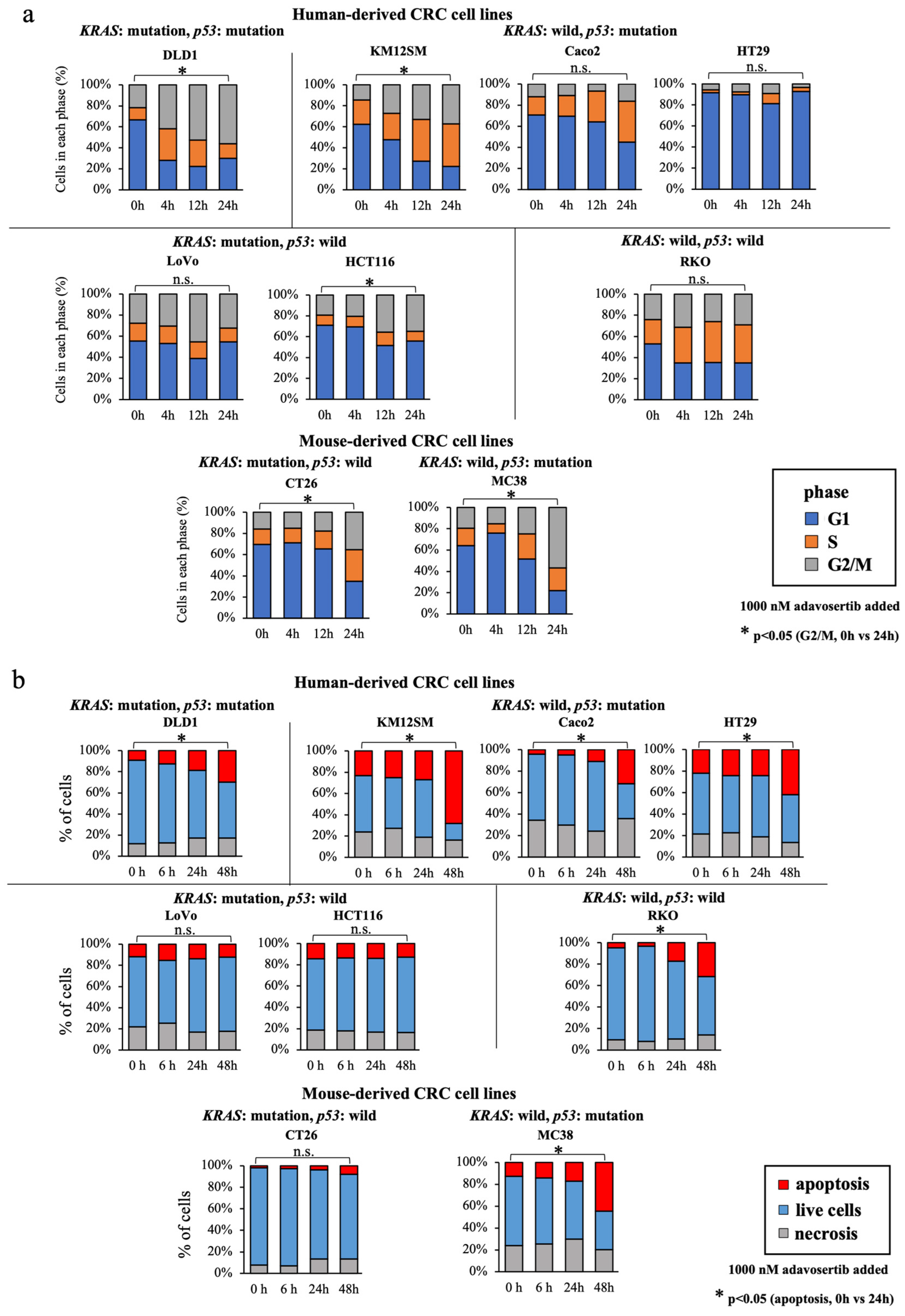
3.5. WEE1 Inhibitor Increases the G2/M-Phase Cell Percentage, Especially in KRAS-Mutated, p53-Mutated Cell Lines
3.6. WEE1 Inhibitor Increases Apoptosis in CRC Cell Lines, except in KRAS-Mutant, p53 Wild-Type Cell Lines
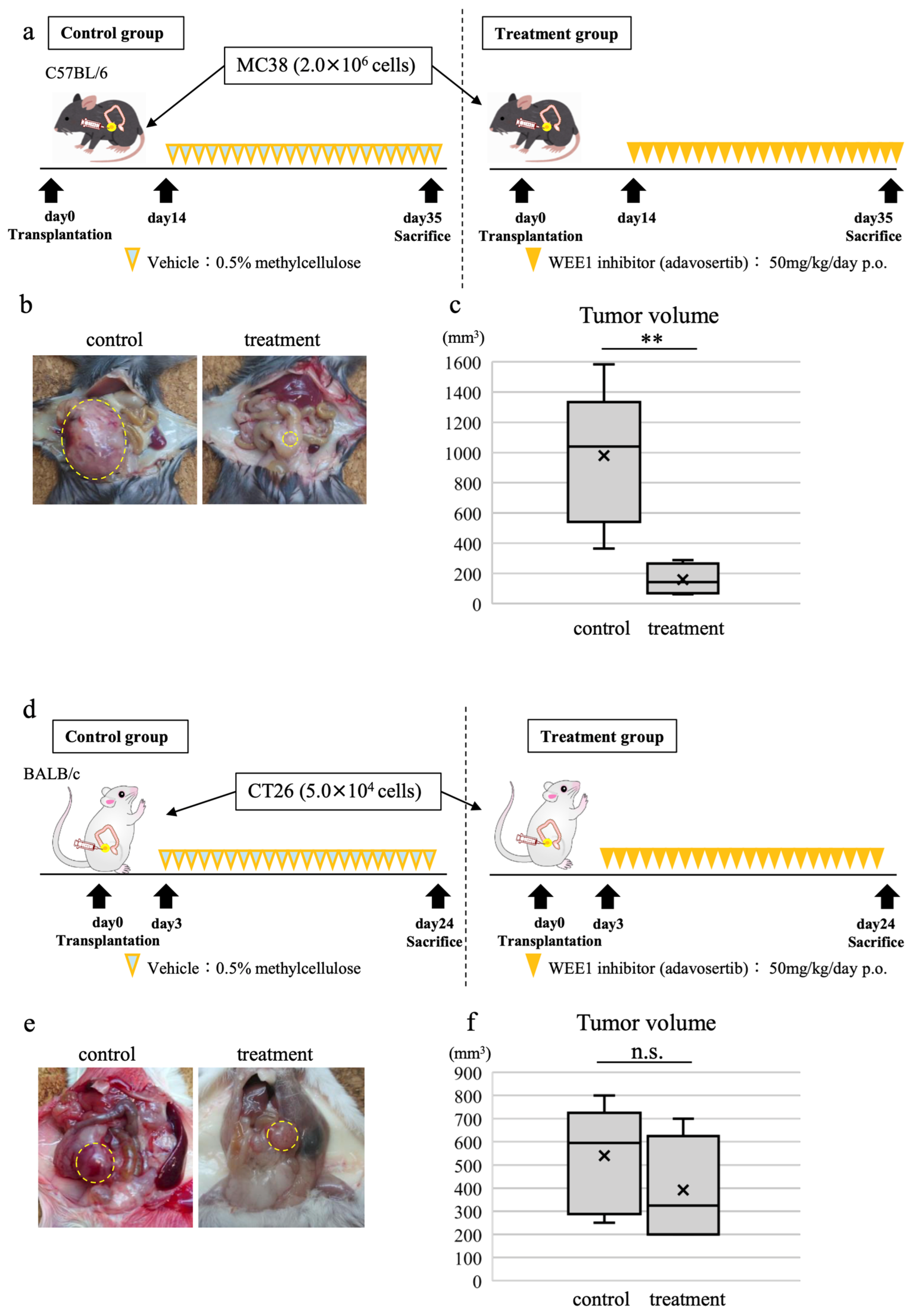
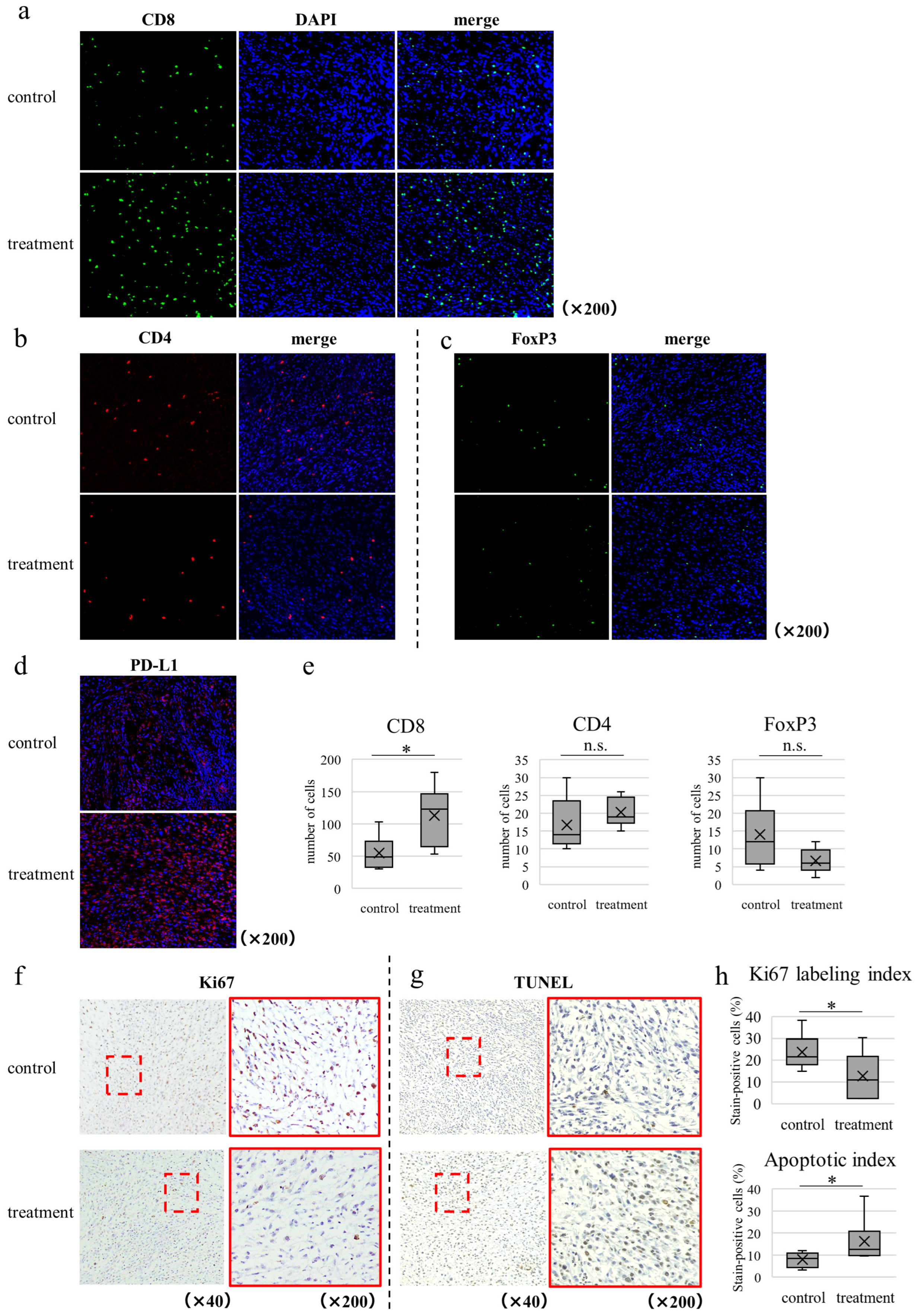
3.7. WEE1 Inhibitor Alone Induces Tumor Shrinkage, CD8-Positive T Cell Tumor Infiltration, and Tumor Cell Apoptosis in In Vivo CRC Model
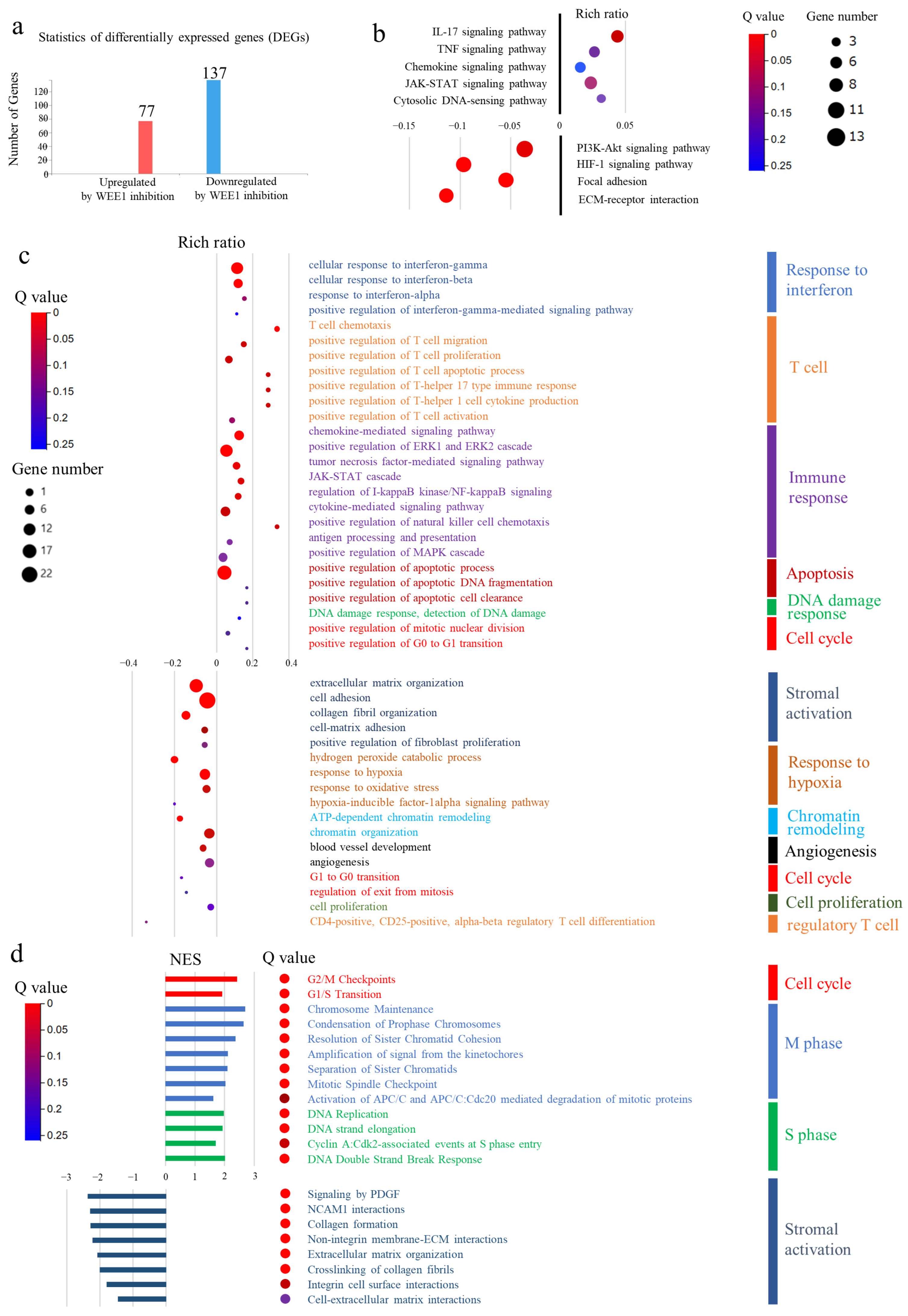
3.8. Comprehensive Gene Expression Analysis of Transplanted Tumors Using RNA Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nurse, P.; Thuriaux, P. Regulatory genes controlling mitosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics 1980, 96, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, K.L.; Nurse, P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature 1989, 342, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, C.J.; Backos, D.S.; Reigan, P. Targeting WEE1 Kinase in Cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, M. Cell cycle checkpoints and their inactivation in human cancer. Cell Prolif. 2000, 33, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcia, L.; Clemente-Ruiz, M.; Pierre-Elies, P.; Royou, A.; Milan, M. Selective Killing of RAS-Malignant Tissues by Exploiting Oncogene-Induced DNA Damage. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 119–131.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fikaris, A.J.; Lewis, A.E.; Abulaiti, A.; Tsygankova, O.M.; Meinkoth, J.L. Ras triggers ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated and Rad-3-related activation and apoptosis through sustained mitogenic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34759–34767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Arai, T.; Okada, M.; Nishibata, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakai, N.; Imagaki, K.; Ohtani, J.; Sakai, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; et al. MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tao, R.; Chang, W.; Li, R.; Xie, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Tao, K. Wee1 inhibition can suppress tumor proliferation and sensitize p53 mutant colonic cancer cells to the anticancer effect of irinotecan. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligmann, J.F.; Fisher, D.J.; Brown, L.C.; Adams, R.A.; Graham, J.; Quirke, P.; Richman, S.D.; Butler, R.; Domingo, E.; Blake, A.; et al. Inhibition of WEE1 Is Effective in TP53- and RAS-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Trial (FOCUS4-C) Comparing Adavosertib (AZD1775) With Active Monitoring. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3705–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, J.N.; Klomp, J.E.; Snare, K.R.; Hibshman, P.S.; Blake, D.R.; Kaiser, Z.D.; Gilbert, T.S.K.; Baldelli, E.; Pierobon, M.; Papke, B.; et al. The KRAS-regulated kinome identifies WEE1 and ERK coinhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy in KRAS-mutant pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiola, E.; Frapolli, R.; Tomanelli, M.; Valerio, R.; Iezzi, A.; Garassino, M.C.; Broggini, M.; Marabese, M. Wee1 inhibitor MK1775 sensitizes KRAS mutated NSCLC cells to sorafenib. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, E.; Nonami, A.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Sattler, M.; Nelson, E.; Cowens, K.; Christie, A.L.; Mitsiades, C.; et al. Identification of Wee1 as a novel therapeutic target for mutant RAS-driven acute leukemia and other malignancies. Leukemia 2015, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Linden, A.A.; Baturin, D.; Ford, J.B.; Fosmire, S.P.; Gardner, L.; Korch, C.; Reigan, P.; Porter, C.C. Inhibition of Wee1 sensitizes cancer cells to antimetabolite chemotherapeutics in vitro and in vivo, independent of p53 functionality. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreahling, J.M.; Gemmer, J.Y.; Reed, D.; Letson, D.; Bui, M.; Altiok, S. MK1775, a selective Wee1 inhibitor, shows single-agent antitumor activity against sarcoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.; Wilsker, D.; Ji, J.; Zlott, J.; Freshwater, T.; Kinders, R.J.; Collins, J.; Chen, A.P.; Doroshow, J.H.; Kummar, S. Phase I Study of Single-Agent AZD1775 (MK-1775), a Wee1 Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients With Refractory Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, G.I.; Holm, R.; Emilsen, E.; Rosnes, A.K.; Slipicevic, A.; Florenes, V.A. High expression of Wee1 is associated with poor disease-free survival in malignant melanoma: Potential for targeted therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrow, L.M.; Garimella, S.V.; Jones, T.L.; Caplen, N.J.; Lipkowitz, S. Identification of WEE1 as a potential molecular target in cancer cells by RNAi screening of the human tyrosine kinome. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 122, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipicevic, A.; Holth, A.; Hellesylt, E.; Trope, C.G.; Davidson, B.; Florenes, V.A. Wee1 is a novel independent prognostic marker of poor survival in post-chemotherapy ovarian carcinoma effusions. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.E.; De Witt Hamer, P.C.; Krawczyk, P.M.; Balaj, L.; Claes, A.; Niers, J.M.; Van Tilborg, A.A.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Geerts, D.; Kaspers, G.J.; et al. In silico analysis of kinase expression identifies WEE1 as a gatekeeper against mitotic catastrophe in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2010, 18, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, S.; Mogi, A.; Shitara, Y.; Kuwano, H. The clinical significance of Cyclin B1 and Wee1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, M.; Sharpe, R.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Gevensleben, H.; Hurd, M.S.; Shumway, S.D.; Toniatti, C.; Ashworth, A.; Turner, N.C. Forced mitotic entry of S-phase cells as a therapeutic strategy induced by inhibition of WEE1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.C.; Wu, F.; Li, W.T.; Zhu, X.J.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, B.L. Upregulation of WEE1 is a potential prognostic biomarker for patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4341–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeland, E.V.; Flatmark, K.; Nesland, J.M.; Florenes, V.A.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Boye, K. Expression and clinical significance of Wee1 in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12133–12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, E.; Xiao, R.; Wu, Y.; Lu, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. WEE1 inhibition induces anti-tumor immunity by activating ERV and the dsRNA pathway. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, Y. Evaluation of p53 Protein Overexpression by Immunohistochemistry―Study based on Gene Mutation Analysis. Niigata Igakukai Zassi 2016, 130, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yemelyanova, A.; Vang, R.; Kshirsagar, M.; Lu, D.; Marks, M.A.; Shih Ie, M.; Kurman, R.J. Immunohistochemical staining patterns of p53 can serve as a surrogate marker for TP53 mutations in ovarian carcinoma: An immunohistochemical and nucleotide sequencing analysis. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repecka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ’EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknaes, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.C.G.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Johannessen, B.; Bruun, J.; Danielsen, S.A.; Bjornslett, M.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Eknaes, M.; Lind, G.E.; et al. Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines―A resource for biomedical studies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Gowda, R.; Berg, A.; Neves, R.I.; Robertson, G.P. Identification of aurora kinase B and Wee1-like protein kinase as downstream targets of (V600E)B-RAF in melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modest, D.P.; Ricard, I.; Heinemann, V.; Hegewisch-Becker, S.; Schmiegel, W.; Porschen, R.; Stintzing, S.; Graeven, U.; Arnold, D.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; et al. Outcome according to KRAS-, NRAS- and BRAF-mutation as well as KRAS mutation variants: Pooled analysis of five randomized trials in metastatic colorectal cancer by the AIO colorectal cancer study group. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.M.; Bae, Y.H.; Koh, J.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.J. Mutational status of TP53 defines the efficacy of Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67526–67537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzu, O.F.; Gowda, R.; Sharma, A.; Noory, M.A.; Kardos, G.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Drabick, J.J.; Robertson, G.P. Identification of WEE1 as a target to make AKT inhibition more effective in melanoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Caeser, R.; Chavan, S.S.; Zhan, Y.A.; Chow, A.; Manoj, P.; Uddin, F.; Kitai, H.; Qu, R.; Hayatt, O.; et al. WEE1 inhibition enhances the antitumor immune response to PD-L1 blockade by the concomitant activation of STING and STAT1 pathways in SCLC. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.; Sainson, R.C. Regulation of the anti-tumour immune response by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 25, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel, E.E., III; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFbeta attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.B. The expanding role of WEE1. Cell Signal. 2022, 94, 110310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelli Luserna di Rora, A.; Cerchione, C.; Martinelli, G.; Simonetti, G. A WEE1 family business: Regulation of mitosis, cancer progression, and therapeutic target. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, R.; Palazzo, L.; Della Monica, R.; Grieco, D. Fcp1-dependent dephosphorylation is required for M-phase-promoting factor inactivation at mitosis exit. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, H.; Nahse-Kumpf, V.; Larsen, M.S.; O’Hanlon, K.A.; Patzke, S.; Holmberg, C.; Mejlvang, J.; Groth, A.; Nielsen, O.; Syljuasen, R.G.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase suppression by WEE1 kinase protects the genome through control of replication initiation and nucleotide consumption. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 4226–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaek, C.R.; Petrosius, V.; Benada, J.; Erichsen, L.; Damgaard, R.B.; Sorensen, C.S. WEE1 kinase protects the stability of stalled DNA replication forks by limiting CDK2 activity. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, D.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.D. Hypoxia induces Wee1 expression and attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced endothelial damage in MS1 cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Homma, H.; Kaida, A.; Miura, M. WEE1 inhibition enhances sensitivity to hypoxia/reoxygenation in HeLa cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Su, H.; Jiang, J.; Yue, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; et al. WEE1 inhibition induces glutamine addiction in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Saqcena, M.; Foster, D.A. Synthetic lethality in KRas-driven cancer cells created by glutamine deprivation. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorai, T.; Pinto, J.T.; Denton, T.T.; Krasnikov, B.F.; Cooper, A.J.L. The metabolic importance of the glutaminase II pathway in normal and cancerous cells. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 644, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forment, J.V.; O’Connor, M.J. Targeting the replication stress response in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2018, 188, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.L.; Southgate, H.; Tweddle, D.A.; Curtin, N.J. DNA damage checkpoint kinases in cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2020, 22, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, J.D.; King, M.R. A syngeneic MC38 orthotopic mouse model of colorectal cancer metastasis. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2022, 7, bpac024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target Gene | Direction | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Human GAPDH | Forward | CCACCCATGGCAAATTCC |
| Reverse | TGATGGGATTTCCATTGATGAC | |
| Human WEE1 | Forward | GCTTGCCCTCACAGTGGTATG |
| Reverse | CCGAGGTAATCTACCCTGTCT | |
| Mouse GAPDH | Forward | GCCTCGTCCCGTAGACAAAA |
| Reverse | CCATTCTCGGCCTTGACTGT | |
| Mouse WEE1 | Forward | CCGGGGCTTGAGATACATACA |
| Reverse | CAGCATTTGGGATTGAGGTTCG |
| Features | WEE1 Negative (n = 81) | WEE1 Positive (n = 71) | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.4 ± 10.8 | 65.7 ± 12.8 | 0.157 | |
| Sex | Female | 29 (35.8) | 33 (46.5) | 0.181 |
| Male | 52 (64.2) | 38 (53.5) | ||
| Location | Right side colon | 30 (37.0) | 24 (33.8) | 0.678 |
| Left side colon | 51 (63.0) | 47 (66.2) | ||
| Histological type | tub1/2 | 74 (91.4) | 63 (88.7) | 0.588 |
| por/muc | 7 (8.6) | 8 (11.3) | ||
| Stage | I/II | 37 (45.7) | 39 (54.9) | 0.255 |
| III/IV | 44 (54.3) | 32 (45.1) | ||
| T | 1/2 | 23 (28.4) | 24 (33.8) | 0.472 |
| 3/4 | 58 (71.6) | 47 (66.2) | ||
| N | 0/1 | 38 (46.9) | 40 (56.3) | 0.246 |
| 2/3 | 43 (53.1) | 31 (43.7) | ||
| M | 0 | 65 (80.2) | 60 (84.5) | 0.493 |
| 1 | 16 (19.8) | 11 (15.5) | ||
| V | 0/1 | 71 (87.7) | 60 (84.5) | 0.575 |
| 2/3 | 10 (12.3) | 11 (15.5) | ||
| Gene | Status | WEE1 Negative (n = 81) | WEE1 Positive (n = 71) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KRAS | Wild type | 51 (63.0) | 40 (56.3) | 0.406 |
| Mutant | 30 (37.0) | 31 (43.7) | ||
| p53 | Wild type | 12 (14.8) | 7 (9.9) | 0.357 |
| Mutant | 69 (85.2) | 65 (90.1) | ||
| BRAF | Wild type | 81 (100.0) | 66 (93.0) | 0.015 |
| Mutant | 0 (0.0) | 5 (7.0) | ||
| MSI | MSS | 78 (96.3) | 62 (87.3) | 0.041 |
| High MSI | 3 (3.7) | 9 (12.7) |
| CRC Cell Lines | p53 Status | KRAS Status | BRAF Status | MSI/MSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD1 | Mutant | Mutant | Wild type | MSI |
| KM12SM | Mutant | Wild type | Mutant | MSI |
| Caco2 | Mutant | Wild type | Wild type | MSS |
| HT29 | Mutant | Wild type | Mutant | MSS |
| HCT116 | Wild type | Mutant | Wild type | MSI |
| LoVo | Wild type | Mutant | Wild type | MSI |
| RKO | Wild type | Wild type | Mutant | MSI |
| CT26 | Wild type | Mutant | Wild type | MSS |
| MC38 | Mutant | Wild type | Wild type | MSI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ariyoshi, M.; Yuge, R.; Kitadai, Y.; Shimizu, D.; Miyamoto, R.; Yamashita, K.; Hiyama, Y.; Takigawa, H.; Urabe, Y.; Oka, S. WEE1 Inhibitor Adavosertib Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer, Especially in Cases with p53 Mutations. Cancers 2024, 16, 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183136
Ariyoshi M, Yuge R, Kitadai Y, Shimizu D, Miyamoto R, Yamashita K, Hiyama Y, Takigawa H, Urabe Y, Oka S. WEE1 Inhibitor Adavosertib Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer, Especially in Cases with p53 Mutations. Cancers. 2024; 16(18):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAriyoshi, Misa, Ryo Yuge, Yuki Kitadai, Daisuke Shimizu, Ryo Miyamoto, Ken Yamashita, Yuichi Hiyama, Hidehiko Takigawa, Yuji Urabe, and Shiro Oka. 2024. "WEE1 Inhibitor Adavosertib Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer, Especially in Cases with p53 Mutations" Cancers 16, no. 18: 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183136
APA StyleAriyoshi, M., Yuge, R., Kitadai, Y., Shimizu, D., Miyamoto, R., Yamashita, K., Hiyama, Y., Takigawa, H., Urabe, Y., & Oka, S. (2024). WEE1 Inhibitor Adavosertib Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer, Especially in Cases with p53 Mutations. Cancers, 16(18), 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183136








