Neurocognitive Adverse Events Related to Lorlatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Extraction
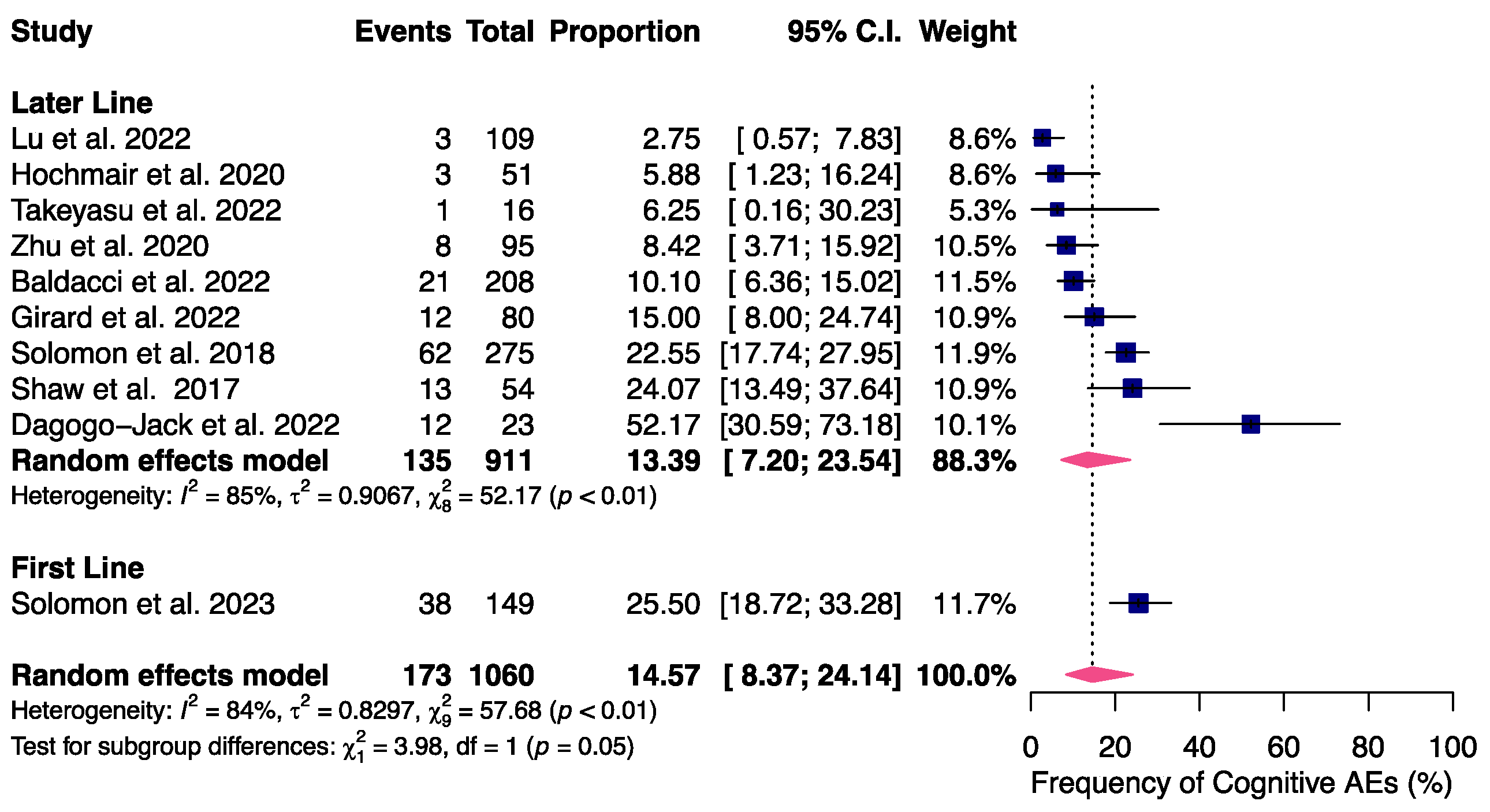
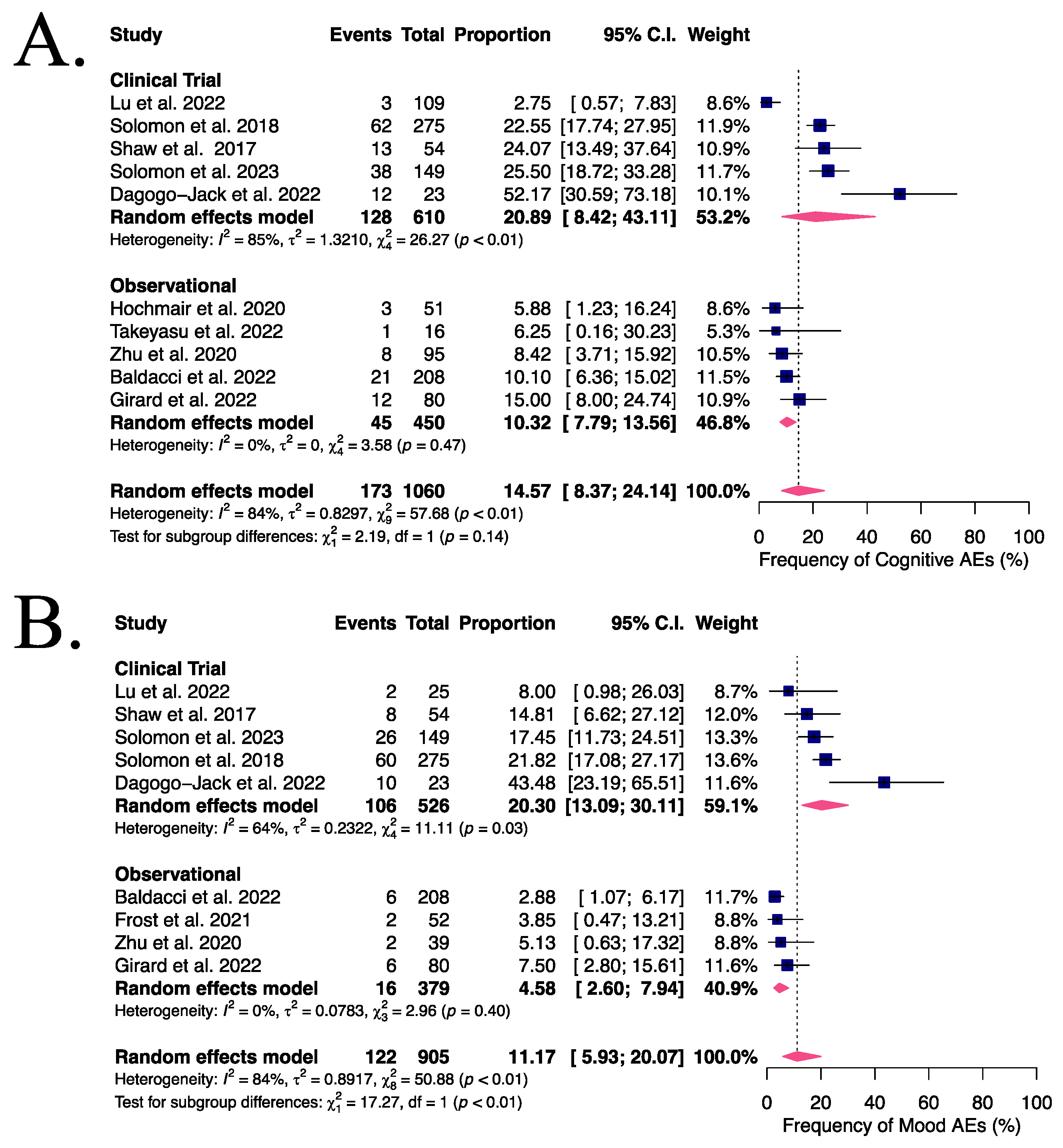
2.4. Endpoints and Subanalysis
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
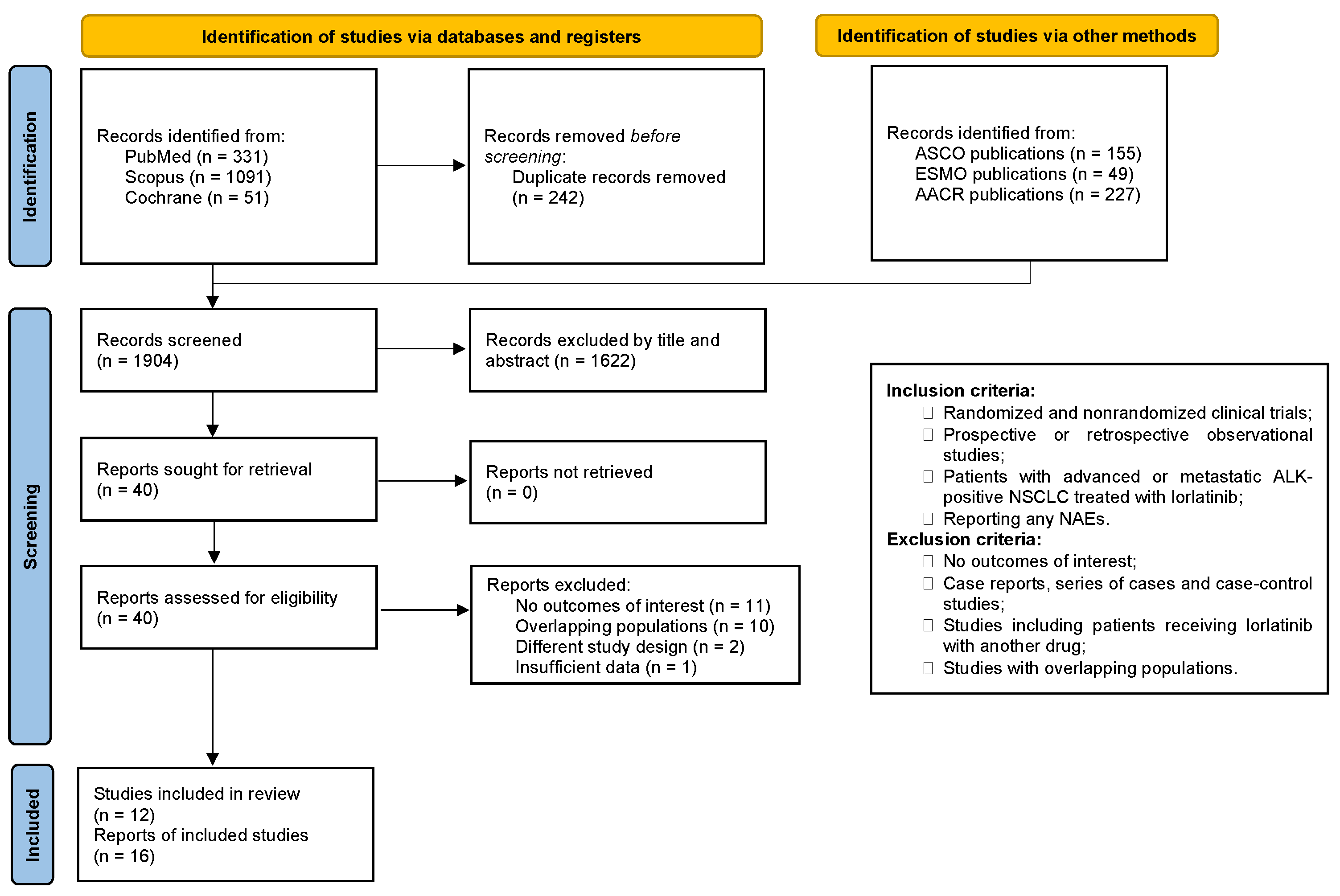
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies and Patients
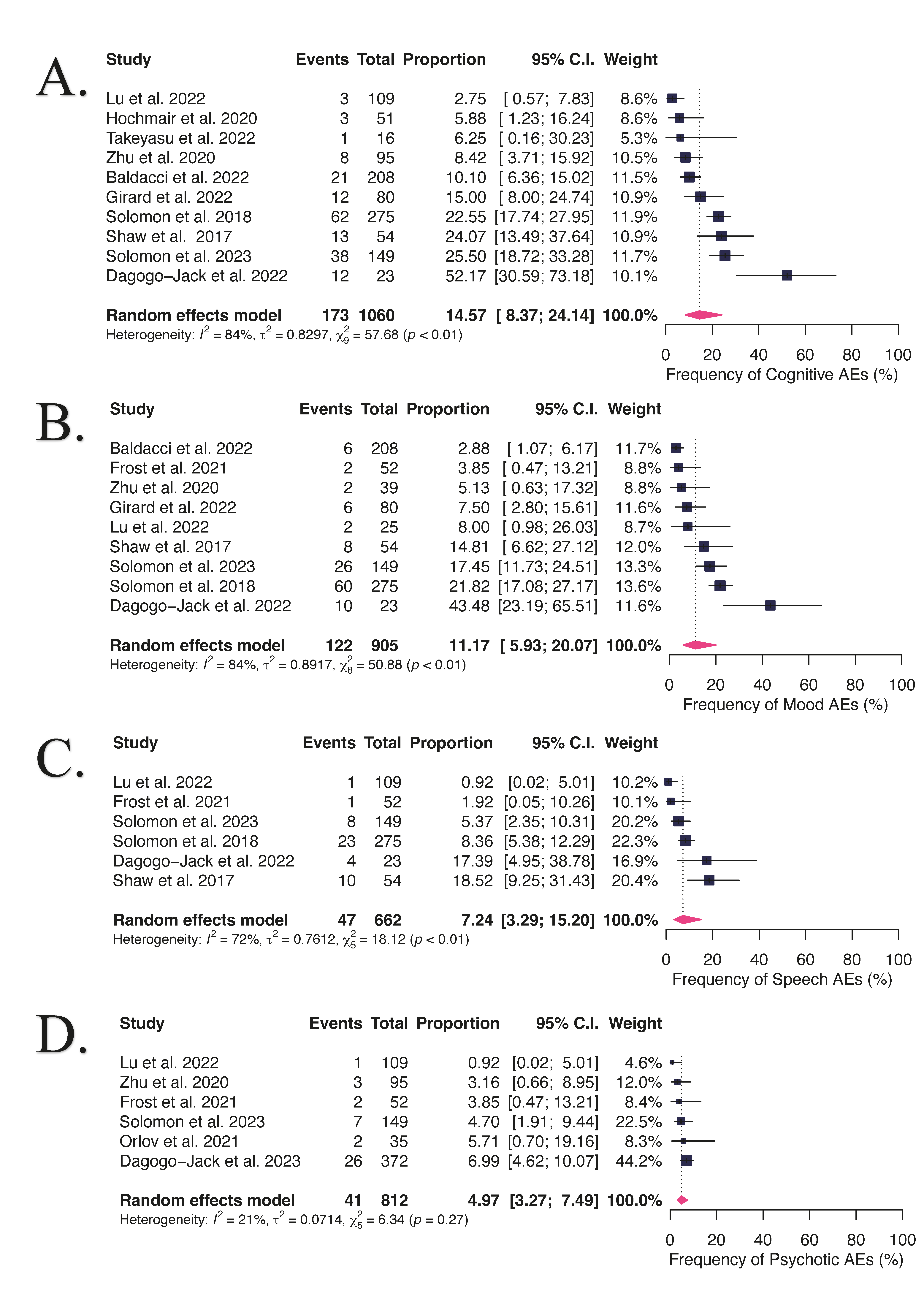
3.2. NAEs in Advanced or Metastatic ALK- or ROS1-Positive NSCLC Patients Receiving Lorlatinib
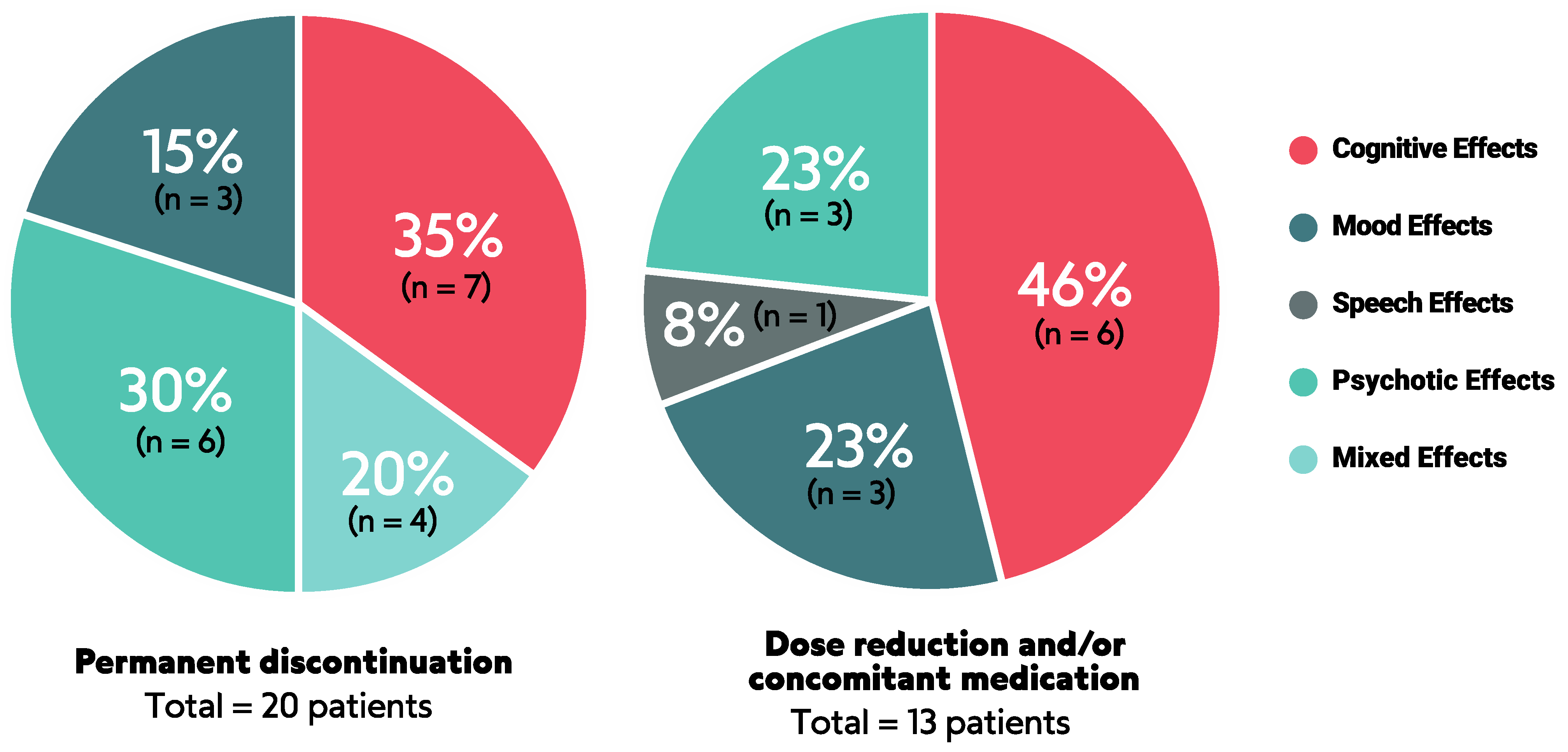
3.3. Management of NAEs
3.4. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.J.; Riely, G.J.; Shaw, A.T. Targeting ALK: Precision Medicine Takes on Drug Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The Function and Therapeutic Targeting of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clancy, J.S.; Li, S.; et al. ALK Resistance Mutations and Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Ignatius Ou, S.-H.; Liu, G.; Hayashi, H.; Bearz, A.; Penkov, K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Arrieta, O.; Jassem, J.; et al. Post Hoc Analysis of Lorlatinib Intracranial Efficacy and Safety in Patients With ALK-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer From the Phase III CROWN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Jassem, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Lorlatinib versus Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced, ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Analysis of Data from the Phase 3, Randomised, Open-Label CROWN Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Solomon, B.J.; Thurm, H.; Peltz, G.; Chioda, M.D.; Shaw, A.T. Clinical Management of Adverse Events Associated with Lorlatinib. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Abbattista, A.; Murphy, J.F.; Krulewicz, S.; Do, A.; Peterson, J.; Lin, J.J.; Gainor, J.F.; Messina, R.; Krueger, E.A.; et al. Factors Associated With Developing Neurocognitive Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Lorlatinib after Progression on Other Targeted Therapies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Stratmann, J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Mok, T.; Grizzard, M.; Goto, Y.; Felip, E.; Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M. A Pragmatic Guide for Management of Adverse Events Associated with Lorlatinib. Lung Cancer 2024, 191, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.B.; Costa, R.L.B.; Talamantes, S.M.; Kaplan, J.B.; Bhave, M.A.; Rademaker, A.; Miller, C.; Carneiro, B.A.; Mahalingam, D.; Chae, Y.K. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Selected Toxicities of Approved ALK Inhibitors in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22137–22146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cameron, L.B.; Hitchen, N.; Chandran, E.; Morris, T.; Manser, R.; Solomon, B.J.; Jordan, V. Targeted Therapy for Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD013453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J. Neurotoxicity of Cancer Therapies. Continuum 2020, 26, 1646–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, A. Cognitive Dysfunction among Cancer Survivors. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 90, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Barker, T.H.; Migliavaca, C.B.; Stein, C.; Colpani, V.; Falavigna, M.; Aromataris, E.; Munn, Z. Conducting Proportional Meta-Analysis in Different Types of Systematic Reviews: A Guide for Synthesisers of Evidence. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, G.; Rücker, G. Meta-Analysis of Proportions; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Baldacci, S.; Besse, B.; Avrillon, V.; Mennecier, B.; Mazieres, J.; Dubray-Longeras, P.; Cortot, A.B.; Descourt, R.; Doubre, H.; Quantin, X.; et al. Lorlatinib for Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the IFCT-1803 LORLATU Cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 166, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Oxnard, G.R.; Evangelist, M.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Lin, J.J.; Gainor, J.F.; Murphy, J.F.; Rabin, M.S.; Heist, R.S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Phase II Study of Lorlatinib in Patients With Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase–Positive Lung Cancer and CNS-Specific Relapse. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, N.; Christopoulos, P.; Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Stratmann, J.; Riedel, R.; Schaefer, M.; Alt, J.; Gütz, S.; Christoph, D.C.; Laack, E.; et al. Lorlatinib in Pretreated ALK- or ROS1-Positive Lung Cancer and Impact of TP53 Co-Mutations: Results from the German Early Access Program. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 175883592098055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N.; Galland-Girodet, S.; Avrillon, V.; Besse, B.; Duruisseaux, M.; Cadranel, J.; Otto, J.; Prevost, A.; Roch, B.; Bennouna, J.; et al. Lorlatinib for Advanced ROS1+ Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the IFCT-1803 LORLATU Study. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Fabikan, H.; Illini, O.; Weinlinger, C.; Setinek, U.; Krenbek, D.; Prosch, H.; Rauter, M.; Schumacher, M.; Wöll, E.; et al. Later-Line Treatment with Lorlatinib in ALK- and ROS1-Rearrangement-Positive NSCLC: A Retrospective, Multicenter Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J.; et al. Lorlatinib for Previously Treated ALK-Positive Advanced NSCLC: Primary Efficacy and Safety From a Phase 2 Study in People’s Republic of China. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlov, S.V.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Filippova, E.A.; Lozhkina, A.M.; Odintsova, S.V.; Sokolova, T.N.; Mitiushkina, N.V.; Tiurin, V.I.; Preobrazhenskaya, E.V.; Romanko, A.A.; et al. Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Lung Carcinomas Carrying Distinct ALK Translocation Variants: The Results of a Single-Center Study. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Lorlatinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with ALK or ROS1 Rearrangement: An International, Multicentre, Open-Label, Single-Arm First-in-Man Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.-C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in Patients with ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from a Global Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyasu, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Masuda, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shinno, Y.; Okuma, Y.; Goto, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohe, Y. Lorlatinib Versus Pemetrexed-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with ALK-Rearranged NSCLC Previously Treated with Alectinib. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, V.W.; Lin, Y.-T.; Kim, D.-W.; Loong, H.H.; Nagasaka, M.; To, H.; Ang, Y.L.-E.; Ock, C.-Y.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Ou, S.-H.I.; et al. An International Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib Through Early or Expanded Access Programs in Patients with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor–Refractory ALK-Positive or ROS1-Positive NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Teraoka, S.; Goto, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Nishio, M.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Matsumura, M.; Okura, M.; Peltz, G.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive NSCLC: Japanese Subgroup Analysis of CROWN. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.A.; Huat Tan, E.; Hayashi, H.; Seto, T.; Lin, C.-C.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Kim, D.-W.; Liu, G.; Abbattista, A.; Martini, J.-F.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib in Asian and Non-Asian Patients with ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Subgroup Analysis of a Global Phase 2 Trial. Lung Cancer 2022, 169, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Chiari, R.; Riely, G.J.; Besse, B.; Soo, R.A.; Kao, S.; Lin, C.-C.; Bauer, T.M.; Clancy, J.S.; et al. Lorlatinib in Advanced ROS1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 1–2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.M.; Shaw, A.T.; Johnson, M.L.; Navarro, A.; Gainor, J.F.; Thurm, H.; Pithavala, Y.K.; Abbattista, A.; Peltz, G.; Felip, E. Brain Penetration of Lorlatinib: Cumulative Incidences of CNS and Non-CNS Progression with Lorlatinib in Patients with Previously Treated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; Tang, Y.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis From a Study Comparing First-Line Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Mutation-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The Biology and Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remon, J.; Pignataro, D.; Novello, S.; Passiglia, F. Current Treatment and Future Challenges in ROS1- and ALK-Rearranged Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 95, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.-F.; Tai, Y.-H.; Gao, H.-J. ALK-Rearrangement in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikor, L.A.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. Genetic Alterations Defining NSCLC Subtypes and Their Therapeutic Implications. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Ren, S. Neurocognitive Adverse Events of Lorlatinib: On the Way to Precise Prediction? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, D.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, G. The Underlying Mechanisms of Lorlatinib Penetration across the Blood-Brain Barrier and the Distribution Characteristics of Lorlatinib in the Brain. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4350–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisi, M.; Fusaroli, M.; De Giglio, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Ardizzoni, A.; Raschi, E.; Gelsomino, F. Psychiatric Adverse Reactions to Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of Spontaneous Reports Submitted to the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Target. Oncol. 2022, 17, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutton, J.W.; Chen, H.; You, C.; Brodie, M.S.; Lasek, A.W. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Regulates Binge-like Drinking and Dopamine Receptor Sensitivity in the Ventral Tegmental Area. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Lasek, A.W. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Regulates Internalization of the Dopamine D2 Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 97, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Besse, B.; Felip, E.; Solomon, B.J.; Soo, R.A.; Bearz, A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Kao, S.; et al. Impact of Lorlatinib on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive or ROS1-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 144, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Iadeluca, L.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes from the Randomized Phase 3 CROWN Study of First-Line Lorlatinib versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2022, 174, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaekers, J.; Dijkstra, J.; van der Wekken, A.; Paats, M.; Broen, M.; Brandts, L.; Dingemans, A.-M.; Hendriks, L. In-Depth Analysis of Lorlatinib-Related Neurocognitive Adverse Events in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 25, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study ID | Study Type | Country | N | Mutation | Sex | Smoking History | Asians | ECOG (>= 2) | CNS Disease n (%) | Brain RT n (%) | Median Follow-Up (mo) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALK | ROS1 | M | F | ||||||||||
| Baldacci et al., 2022 [22] | Ob | France | 208 | 208 | - | 91 | 117 | 64 | - | 48 | 160 (77) | 95 (46) | 23.3 |
| Dagogo-Jack et al., 2022 [23] | CT | USA | 23 | 23 | - | 13 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 23 (100) | 15 (65) | 16.8 |
| Frost et al., 2021 [24] | Ob | Germany | 52 | 37 | 15 | 24 | 28 | 18 | - | 13 | 36 (69) | - | 16.1 |
| Girard et al., 2022 [25] | Ob | France | 80 | - | 80 | 33 | 47 | 30 | - | 13 | 51 (64) | 27 (34) | 22.2 |
| Hochmair et al., 2020 [26] | Ob | Austria | 51 | 37 | 14 | 20 | 31 | 20 | - | - | 28 (55) | - | 24.8 |
| Lu et al., 2022 [27] | CT | China | 109 | 109 | - | 53 | 56 | 40 | 109 | 5 | 57 (52) | - | 8.4–11.4 * |
| Orlov et al., 2021 [28] | Ob | Russia | 35 | 35 | - | 16 | 19 | - | - | - | 27 (77) | - | 17.5 |
| Shaw et al., 2017 [29] | CT | Multicentric | 54 | 41 | 12 | 22 | 32 | - | 7 | 2 | 39 (72) | 27 (50) | 17.4 |
| Solomon et al., 2018 [30] | CT | Multicentric | 275 | 228 | 47 | 118 | 157 | - | 103 | 10 | 166 (60) | 103 (37) | 7.2 |
| Solomon et al., 2023 [8] | CT | Multicentric | 149 | 149 | - | 65 | 84 | 68 | 65 | 3 | 37 (25) | 8 (5) | 18.3 |
| Takeyasu et al., 2022 [31] | Ob | Japan | 16 | 16 | - | 8 | 8 | 7 | 16 | 2 | 11 (69) | - | 12.8 |
| Zhu et al., 2020 [32] | Ob | Multicentric | 95 | 76 | 19 | 40 | 55 | 21 | 76 | - | 77 (81) | - | 6.8 |
| Total: | 1147 | 959 | 187 | 503 | 644 | 273 | 381 | 99 | 712 (62) | 275 (60) | - | ||
| Associated publications of main studies | |||||||||||||
| Author, Year | Related Study ID | Analysis Performed | |||||||||||
| Hayachi et al., 2023 [33] | Solomon et al., 2023 [8] | Subgroup analysis for ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Soo et al., 2022 [34] | Solomon et al., 2018 [30] | Subgroup analysis for ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Shaw et al., 2019 [35] | Shaw et al., 2017 [29], Solomon et al., 2018 [30] | Subgroup analysis for mutation profile | |||||||||||
| Bauer et al., 2020 [36] | Solomon et al., 2018 [30] | Subgroup analysis for CNS disease status | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Priantti, J.N.; Vilbert, M.; de Moraes, F.C.A.; Madeira, T.; de Lima Santiago, E.M.; Leighl, N.B.; Cavalcante, L.; Karim, N.F.A. Neurocognitive Adverse Events Related to Lorlatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142611
Priantti JN, Vilbert M, de Moraes FCA, Madeira T, de Lima Santiago EM, Leighl NB, Cavalcante L, Karim NFA. Neurocognitive Adverse Events Related to Lorlatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142611
Chicago/Turabian StylePriantti, Jonathan N., Maysa Vilbert, Francisco Cezar Aquino de Moraes, Thiago Madeira, Evair Moisés de Lima Santiago, Natasha B. Leighl, Ludimila Cavalcante, and Nagla F. Abdel Karim. 2024. "Neurocognitive Adverse Events Related to Lorlatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142611
APA StylePriantti, J. N., Vilbert, M., de Moraes, F. C. A., Madeira, T., de Lima Santiago, E. M., Leighl, N. B., Cavalcante, L., & Karim, N. F. A. (2024). Neurocognitive Adverse Events Related to Lorlatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(14), 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142611







