Simple Summary
Proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs, anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies (triple class drugs), and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) are promising myeloma treatments that have resulted in minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity and improvement in the bone marrow microenvironment. In the MASTER trial, a four-drug induction therapy, comprising triple-class drugs followed by ASCT, resulted in MRD negativity and long progression-free survival in patients with standard- and high-risk cytogenetics; however, it proved insufficient to overcome the poor outcomes in patients with ultra-high-risk chromosomal aberration (UHRCA). Hence, MRD negativity in autografts could signal positive clinical outcomes after ASCT. Additionally, high-risk myeloma cells lead to poor clinical outcomes owing to aggressive myeloma behavior as well as a poor bone marrow microenvironment. Thus, several new approaches for treating patients with MRD-positive UHRCA myeloma before and after ASCT are needed.
Abstract
Despite the development of anti-myeloma therapeutics, such as proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs, anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies, and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), multiple myeloma remains incurable. A trial treatment combining four drugs—daratumumab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone—followed by ASCT frequently results in minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity and prevents progressive disease in patients with standard- and high-risk cytogenetics; however, it is insufficient to overcome the poor outcomes in patients with ultra-high-risk chromosomal aberration (UHRCA). In fact, MRD status in autografts can predict clinical outcomes after ASCT. Therefore, the current treatment strategy might be insufficient to overcome the negative impact of UHRCA in patients with MRD positivity after the four-drug induction therapy. High-risk myeloma cells lead to poor clinical outcomes not only by aggressive myeloma behavior but also via the generation of a poor bone marrow microenvironment. Meanwhile, the immune microenvironment effectively suppresses myeloma cells with a low frequency of high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities in early-stage myeloma compared to late-stage myeloma. Therefore, early intervention might be key to improving clinical outcomes in myeloma patients. The purpose of this review is to improve clinical outcomes in patients with UHRCA by considering MRD assessment results and improvement of the microenvironment.
1. Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable hematologic malignancy, although the development of proteasome inhibitors (PIs), immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs), autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), and monoclonal antibody (MoAb) drugs has prolonged survival in patients [1]. Previously, we reviewed the literature regarding the total therapy strategy, including PIs, IMiDs, anti-CD38 MoAb, and ASCT, which not only induce a therapeutic effect on the myeloma cells but also improve the bone marrow microenvironment, including the enhancement of anti-myeloma immunological activity and the suppression of inhibitory anti-myeloma immunological effects [2,3]. Furthermore, it has recently been suggested that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity is a surrogate marker for prolonged survival [4,5]. In fact, several studies have shown that myeloma cells detected as MRD may develop drug resistance and affect the surrounding immune environment.
The Monoclonal Antibody-Based Sequential Therapy for Deep Remission in Multiple Myeloma (MASTER) trial, a phase II study, demonstrated that a four-drug combination of daratumumab (DARA), carfilzomib (CFZ), lenalidomide (LEN), and dexamethasone (DEX) (D-KRd) followed by ASCT and subsequent D-KRd consolidation therapy is effective for patients with newly diagnosed MM (NDMM). Once a patient entered an MRD surveillance (MRD-SURE) phase, after bone marrow samples tested MRD-negative twice consecutively, the treatment was discontinued [6]. In the MASTER study, MRD-SURE was achieved in most patients, and the survival outcome was excellent in patients with zero or one high-risk chromosomal aberration (HRCA). However, patients with two or more HRCAs, who were considered to have ultra-high-risk chromosomal aberrations (UHRCAs), not only had a low MRD negativity rate but also achieved MRD-SURE relapse in some cases. That is, the MASTER trial results suggest that other strategies are necessary for patients with UHRCAs, even if the total therapeutic strategy concerning the bone marrow microenvironment was performed and MRD negativity was achieved [6].
In this review, we discuss the treatment strategies for patients with MM and UHRCAs. Specifically, we analyze the clinical limitations of the MASTER trial in four parts: first, the genetic background of patients with UHRCAs; second, the necessity of MRD negativity in autografts; third, the method of MRD measurement; fourth, which strategies should be used moving forward to improve the prognosis of patients with UHRCAs. In particular, we discuss strategic therapies, including new targeted agents and preemptive interventions against high-risk smoldering MMs (SMMs) before they become UHRCAs.
2. Genetic Background of Patients with UHRCAs in the MASTER Trial
In the MASTER trial, the MRD negativity rate and survival time were lower in patients with UHRCAs than in the other chromosomal aberration (CA) groups. Of the 123 patients who participated in the MASTER trial, 24 (20%) were classified as having UHRCAs, including 83% with 1q21 gain or amplification (amp), 75% with deletion del(13q), 58% with del(17p), 54% with translocation t(4;14), and 17% with t(14;16). Herein, we discuss 1q21 gain or amp and del(17p), which were the most frequently observed chromosomal abnormalities in the MASTER trial [6]. Of the 20 patients with UHRCAs, 6 relapsed during treatment; all these patients had chromosome 1q21 aberrations and 5 had del(17p). These two CAs are occasionally detected as additional events for IgH chromosomal translocations or hyperdiploidy, which are considered an initial event for myelomagenesis and are identified less frequently in early-stage myelomas, such as monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and SMM, than in symptomatic myeloma [7]. In addition, these two CAs are associated with refractory myeloma cells after treatment with PIs and IMiDs [8]; an increasing incidence of these two CAs has also been reported in double refractory MM, which is refractory to both PIs and IMiDs [9].
The 1q21 gain and del(17p) aberrations reportedly exhibit genomic instability. Recently, NEIL1, which acts at a cell cycle checkpoint and is associated with DNA repair, was reported as a novel target of myeloma cells with 1q21 gain [10]. The incidence of 1q21 gain is positively correlated with del(13q) and t(4;14) and negatively correlated with t(11;14) [7]. A key reason for this is that +1q occurs as a secondary event, often in conjunction with other high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities and genomic complexity, complicating the search for the main drivers of outcomes and response to therapy.
There are various candidate target genes for 1q21 gain, such as CKS1B and MCL1 [11]. Overexpression of CKS1B induces an aggressive clinical course as it promotes myeloma cell growth by activating cyclin-dependent kinases [12,13], leading to upregulation of the STAT3 and MEK/ERK pathways [14]. Meanwhile, MCL1 is a member of the BCL2 family of anti-apoptotic proteins, with a genetic locus at 1q21 [15]. Upregulated MCL1 expression is highly correlated with the presence of +1q among patients with NDMM [16]. MCL1 dependency is also enhanced by IL-6 signaling within the bone marrow microenvironment [17]. 1q21 gain negatively correlates with the gene expression level of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3), a control protein of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, inducing refractoriness for IMiDs [18]. In the ENDURANCE trial, which directly compared the effectiveness of KRd and VRd for non-transplant-eligible NDMM, PFS was longer in the KRd group compared with the VRD group among patients with 1q21 gain and without 1q21 amp [19]. This finding indicates that CFZ improves the clinical outcome in patients with 1q21 gain compared to BOR. 1q21 gain also induces the JAK-STAT pathway, which reduces CD38 expression in myeloma cells [20]. Therefore, the efficacy of anti-CD38 MoAb may be relatively low in patients with 1q21 gain [21]. Meanwhile, anti-CD38 MoAb could contribute to myeloma cell death by not only binding to myeloma cells but also several immune cells, leading to reduced abundance of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells [22]. Therefore, anti-CD38 MoAb could be considered as induction therapy for NDMM even if 1q21 gain is present. Finally, 1q21 gain could be one of the causes of extramedullary disease (EMD) during relapse [23]. Thus, 1q21 gain is a CA that has recently received particular attention owing to its associations with poor prognosis and other HRCAs, which is called double-hit MM [24,25]. In a recent single-cell study, myeloma cells with 1q21 gain worsened the immune system by increasing the prevalence of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), decreasing the activity of effector NK cells and the gene burden of SLAMF7, leading to an aggravating immune microenvironment and the proliferation of myeloma cells [26].
Clinically, in patients with NDMM and 1q21 gain or amp, the response to bortezomib (BOR), LEN, and DEX (VRd) treatment is better than in patients without 1q21 gain or amp; however, the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) are shorter [27]. In addition, a retrospective study has reported poor prognosis for MM in patients with 1q21 gain at a cutoff value of 6% [28], although the cutoff of numerical abnormalities is generally defined as 8–20% [29], and a poor prognosis is determined when 1q21 gain is identified not only in the main clones but also in subclones [30]. In the FORTE trial, the PFS in patients with 1q21 gain was similar to that in those without 1q21 gain in the KRd followed by ASCT arm, whereas the PFS in patients with 1q21 gain was shorter than that in those without 1q21 gain in the KRd-only arm [31]. Thus, early ASCT could improve clinical outcomes in patients with 1q21 gain.
Del(17p) is observed in approximately 10% of patients with NDMM and in 50–70% of MM patients with EMD and plasma cell leukemia (PCL), implying that its frequency increases with disease progression [32,33,34]. TP53, a tumor suppressor gene, is located at 17p13 and is monoallelic in most patients with MM. p53 haploinsufficiency induces DNA repair failure, which is related to acquired point mutations in the other TP53 allele during disease progression. TP53 mutations are generally observed in patients with del(17p) and MM [35]. In particular, they are detected in approximately 33% of patients with del(17p) and NDMM, and approximately 50% of patients with del(17p) and relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM) [36,37]. The frequency of TP53 mutations is 5–8% in NDMM [36,38] and up to 25% in PCL [39,40]. In addition, mutant p53 usually has oncogenic functions, such as upregulation of the expression of C-MYC and genes encoding proteasome subunits [41], which can induce anticancer drug resistance [8,42,43,44]. Several new anti-myeloma agents have improved clinical outcomes in patients with del(17p) compared with old agents; however, no treatment has been reported to effectively treat MM in patients with del(17p). As a result, optimal treatment for patients with myeloma harboring del(17p) remains an unmet need [45]. Although therapeutics targeting TP53 are also being considered in the preclinical field [46], to date, they have not been applied clinically for patients with myeloma [47]. Therefore, we believe that early therapeutic intervention before the appearance of these numerical abnormalities is important for the prevention of myeloma development with UHRCA.
Recently, a second revision of the International Staging System 2 (R2-ISS) was developed using 16 randomized clinical trial datasets by the European Myeloma Network, although clinical trials on CD38-MoAb-containing initial treatments were not included [48]. 1q21 gain/amp and del(17p) were selected as poor prognostic factors in this new prognostic model, and the frequencies of 1q21 gain/amp and del(17p) were 78% and 42%, respectively, in the high-risk group. The median PFS and OS were significantly shorter, independent of whether the initial treatment used PIs and/or IMiDs and transplant eligibility. Thus, anti-CD38 MoAb, PIs, IMiDs, and ASCT are insufficient to overcome UHRCAs considering the results of the MASTER trial and the R2-ISS.
3. MRD in Autografts Might Predict Clinical Outcome
In the MASTER trial, the MRD negativity rate after D-KRd induction therapy was lower in patients with UHRCAs than in the other CA groups, indicating that the myeloma cells are more frequently contaminated in the former than in the latter [6]. In two clinical studies, the MRD status of the autograft correlated with the survival time after ASCT [49,50]. Therefore, we discuss the role of MRD eradication in autografts in achieving persistent MRD negativity, particularly in patients with UHRCAs. In the MASTER trial, consecutive MRD assessments after D-KRd induction, ASCT, and four or eight cycles of D-KRd consolidation were performed using bone marrow samples. Before PIs and IMiDs were available, the presence of MRD in autografts was not associated with subsequent survival [51]. However, we considered that the contamination of myeloma cells not affecting the clinical outcomes in several previous trials because the therapeutic efficacy of conventional cytotoxic induction treatments, such as vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, was inferior to the current induction therapy using novel agents [51,52,53,54].
In contrast, a single-center, retrospective analysis from Japan reported that the presence of MRD in autografts detected by next-generation sequencing (NGS) or real-time PCR predicts shorter OS and PFS after ASCT, and the lower levels of MRD in autografts are associated with longer OS and PFS [49]. In a retrospective study of patients with NDMM who underwent ASCT, those who achieved MRD negativity before ASCT had prolonged PFS compared with those who achieved MRD negativity after ASCT, suggesting that the achievement of earlier MRD negativity might be associated with a good response to induction therapy and that the incidence of MM cell contamination in the autograft might be lower in patients with MRD negativity before ASCT, leading to improved prognosis after ASCT [55]. Recently, two retrospective analyses employed next-generation flow cytometry (NGF) to reveal that MRD-negativity in autografts could predict long PFS and OS after ASCT [56,57]. Additionally, according to a retrospective analysis of MDACC, MRD-negativity was identified in patients treated with VRD induction therapy and without del17p and 1q21gain. MRD-negativity in autografts could predict long PFS and OS independent of induction therapy regimens [56]. While MRD-negativity in autografts could predict long PFS, the PFS in HRCA was short compared with non-HRCA, even in the patients with MRD-negativity in autografts [57]. Notably, the autograft MRD status could not be determined based on bone marrow samples, and the association of MRD status between autograft and peripheral blood samples was not analyzed in these two studies. Thus, the achievement of MRD negativity in autografts might be essential for longer OS and PFS, although the associated clinical significance has not yet been elucidated in large-scale prospective clinical trials in the era of novel agents.
Myeloma is generally distributed throughout the bone marrow. Therefore, residual myeloma cells may be present in untested bone marrow sites or extramedullary lesions, even when the tested bone marrow samples are MRD-negative [2,58,59,60,61]. Thus, a negative MRD status in bone marrow samples after induction therapy does not necessarily correspond to negative autografts, as MRD-positive autografts indicate the presence of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood [49,62]. Therefore, treatment strategies to eliminate MRD in the autograft include in vivo purging, which involves attacking CTCs using chemotherapy before mobilization, or ex vivo purging, which involves the positive selection of CD34-positive cells in the autograft. In several trials, ex vivo purging suppressed the contamination of myeloma cells in the autograft but did not improve survival time [53,63]. Hence, it is unlikely that a survival benefit from ex vivo purging will be achieved in the era of novel agents, considering that novel methods of ex vivo purging have not, to our knowledge, been studied on a large scale. Moreover, there is no evidence that a MoAb has been approved for in vivo purging following PI and IMiD approval.
The incidence of myeloma cell contamination in autografts is higher in patients with HRCAs, such as del(13q), even before PIs and IMiDs were available [64]. This was demonstrated by the FORTE trial, in which the MRD-positive rate before maintenance therapy in double-hit patients was lower than that in patients with a single HRCA regardless of the treatment group [65]. Thus, patients with UHRCAs may be more likely to have myeloma cells in their autografts than patients without UHRCAs. Accordingly, we consider that it is essential to reduce the tumor burden with intensive induction therapy to obtain MRD-negative autografts, especially in patients with UHRCAs. Moreover, given that a significant association has been reported between MRD in autografts and peripheral blood, following induction therapy, MRD assessment of the peripheral blood should be performed to monitor for CTCs and prevent myeloma cell contamination in autografts [50]. Indeed, some patients with negative MRD status in autografts test positive in the bone marrow [66]. As a result, MRD assessment of autograft specimens may be the most reliable method to confirm the MRD negativity of an autograft because the MRD positivity rate in autografts might be low even in patients with positive bone marrow samples [67].
4. Analyzing MRD Status: Optimal Sample and Device for UHRCA
According to the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) criteria, the CR criteria are focused on three biomarkers: levels of monoclonal (M) protein (products from myeloma cells), distribution of myeloma, and presence of myeloma cells in the bone marrow [4]. Although MRD assessment is currently focused primarily on myeloma cells in the bone marrow, it may be more useful to consider their presence throughout the entire body, particularly after achieving MRD negativity in the bone marrow [4,61,68]. This is important because the site of bone marrow aspiration is not indicative of myeloma in the body, given that myeloma has a partial, not diffuse, distribution [69,70]. Moreover, EMD can be observed at relapse after MRD negativity [71], suggesting that myeloma cells can be independent of the microenvironment or escape harmful microenvironments even if the myeloma cell burden is reduced below the cutoff level of MRD negativity as detected by NGS or NGF. Although the technology for MRD detection has developed over time, MRD negativity cannot be considered a sign of eradication of all myeloma cells [72,73,74]. Thus, intensive treatment should be continued for myeloma cells in patients with UHRCAs as they tend to relapse aggressively owing to changes in the beneficial microenvironment for myeloma cells with 1q21 CA and the incidence of EMD in patients with 1q21 amp and del(17p) [23,26,32,33].
In the MASTER trial, the MRD-negativity rate as the best response was similar among SRCA, HRCA, and UHRCA; meanwhile, the PFS in the UHRCA group was shorter than those in the other groups even when MRD-SURE was achieved [74]. However, MRD assessment was performed in bone marrow samples using NGF, and patients were neither tested for myeloma disease distribution using positron emission tomography/computerized tomography (PET/CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [69,75,76] nor for M-protein levels using mass spectrometry [77,78,79,80]. The IMWG criteria suggest combining MRD measurements using bone marrow samples with imaging MRD measurements, indicating the importance of MRD imaging to confirm the presence of extramedullary lesions [4]. Considering that myeloma cells in patients with UHRCAs frequently exhibit genomic instability and are prone to EMD complications, MRD should be analyzed using various strategies to confirm the achievement of true MRD negativity.
5. Early Treatment Intervention for Myeloma
Here, the clinical features and difficulty associated with treating ultra-high-risk patients are discussed. It is important that UHRCAs are identified as late-phase myeloma because ultra-high-risk myeloma has several acquired CAs with IgH translocation or hyperdiploidy in the majority of patients [7,9,81,82]. In fact, the frequency of 1q21 gain or del(17p) is higher in symptomatic MM and RRMM than in MGUS or SMM [69]. Concerning the immunological environment in the progression of myeloma disease, NK and T cell counts reportedly increase, while their function decreases with myeloma progression [83,84]. In addition, the immunological environment may be associated with MRD status [2,85]. More specifically, the TAM, erythroblast, Treg, memory B cell, and CD4+ T cell (especially CD27+) counts in the bone marrow of MRD-positive patients are significantly higher than those in the bone marrow of MRD-negative patients [85,86]. Effector Tregs, which strongly suppress immune activity for myeloma cells, exist at the bone marrow tumor site, the abundance of which does not differ significantly from that of the peripheral blood [87,88]. Meanwhile, the exhausted T cell count is higher, and the NK cell count is lower in the peripheral blood of MRD-positive patients than in MRD-negative patients who received ASCT followed by LEN maintenance therapy [89]. In addition, the expression of KIR2DS4, which activates immunity, is lower, whereas that of NKG2A, which suppresses immunity, is higher in MRD-negative patients than in MRD-positive patients [90]. Thus, improving the immune environment can contribute to the achievement of MRD-SURE, and eradicating residual myeloma cells can balance the immune environment. As the immune environment around myeloma cells is compromised in patients with 1q21 amp, including the proliferation of TAMs and a decrease in the number of active NK cells [26], early therapeutic intervention for myelomas with a possibility of developing UHRCAs could be key to improving clinical outcomes.
Ultra-high-risk SMM, which has an 80% or greater chance of progressing to symptomatic myeloma within 2 years, should be treated as symptomatic myeloma according to the IMWG clinical guidelines [91,92]. In addition, high-risk SMM is defined as a 50% or greater chance of progressing to symptomatic myeloma within 2 years, and has been a target of population for clinical trials [93]. Treatment strategies for high-risk SMM have two goals: preventing progression to symptomatic myeloma and achievement of durable MRD negativity [94,95]. A phase II trial of KRd induction treatment followed by LEN maintenance therapy for 2 years was conducted for high-risk SMM [95]. Preliminary data showed a complete remission rate of 70.2%, a 2-year MRD-negative rate of 77.5%, and a 90-month MRD-negative rate of 39.2%, suggesting that this treatment does not achieve durable MRD negativity in approximately two in three patients. In the GEM-SECAR trial, KRD induction and consolidation therapies and ASCT followed by lenalidomide maintenance therapy, the complete response rate was 72% and the MRD-negative rate was 68% after completion of the consolidation therapy [96,97]. Moreover, the sustained MRD negativity rate was 25.6% even 2 years after LEN maintenance therapy was discontinued [98]. After 5 years, 94% of patients had survived without relapse, suggesting that intensive treatment strategies, including ASCT, contribute to the achievement of durable MRD negativity for high-risk SMM. The 5-year PFS from this trial was indirectly superior to that from the KRd-ASCT group in the FORTE trial for NDMM, whereas the MRD-negative rates were similar in patients treated with KRD-ASCT between the trials [99]. The difference in the PFS of the KRd-ASCT groups between these trials, regardless of similar MRD-negative rates, might be attributed to a poor microenvironment and higher myeloma cell aggressiveness in MM than in high-risk SMM. Finally, the ASCENT trial (NCT03289299)—a phase II clinical trial of D-KRd induction therapy followed by DR therapy as maintenance therapy for high-risk SMM [100]—reported a 3-year PFS of 89.9% and MRD-negativity rate of 84% [101]. DARA might also be promising for high-risk SMM, although direct comparisons have not been made between ASCT and DARA for high-risk SMM. Thus, for patients with high-risk SMM, combination chemotherapy, including ASCT, may be an important strategy not only to prevent progression to symptomatic myeloma but also to achieve durable MRD negativity, leading to prolonged PFS and OS and preventing secondary high-risk CAs, such as 1q21 gain/amp and del(17p).
Additionally, cytogenetic risk may be associated with the progression of myeloma cells. The percentage of patients with 1q21 amp, del(17p), t(4;14), or t(14;16) was 59% in the KRD-ASCT group in the FORTE trial [99]. The percentage of the KRd-ASCT group with HRCA, excluding 1q21 amp, in the GEM-SACER trial was lower than that of the FORTE trial (23% vs. 34%), and the number of UHRCA patients in the GEM-SACER trial was assumed to be lower because the frequency of 1q21amp and del(17p) was higher in patients with MM than in those with high-risk SMM [96,97]. Thus, the presence of HRCAs, especially acquired CAs, could be associated with a short survival time, even if a similar intensive treatment strategy is used. Moreover, the impact of MRD positivity may differ between high-risk SMM and MM. That is, the prognosis of patients with persistent MRD-positive disease may be better than that of patients with MM who lose MRD negativity [102,103]. It is, therefore, possible that early intervention for patients with high-risk SMM without UHRCAs can achieve long-term PFS without achieving MRD negativity. However, minimal residual myeloma cells can progress to UHRCA myeloma. As a result, the achievement of durable MRD negativity is essential for UHRCA or pre-UHRCA myelomas to prevent progression or recurrence.
6. Future Directions: Treatment Strategy for Patients with UHRCA Myeloma
In this section, we discuss treatment strategies for patients with UHRCAs considering the improved bone marrow microenvironment. We have demonstrated that inhibition of myeloma cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells, inhibition of angiogenesis, improvement of the immune environment, and improvement of bone formation are essential for the effective treatment of patients with myeloma. Therefore, a total therapeutic approach with PIs, IMiDs, anti-CD38MoAb, and ASCT is essential. The achievement of durable MRD negativity is key to improving clinical outcomes in UHRCA myeloma. Recently, the presence of CTCs, del(17p) and/or t(4;14), and T cells or NK cells with CD27 positivity were reported as predictors of MRD positivity [104]. As a result, CAs and the immune environment can be keys to developing effective treatments to achieve MRD negativity. In addition, it is essential to analyze the MRD status using not only NGF or NGS for bone marrow samples but also for peripheral blood samples, as well as imaging techniques and mass spectrometry to anticipate the possibility of EMD after treatment. Preventing myeloma cell contamination in autografts is also important, particularly in patients with UHRCAs. As a result, in vivo purging might represent effective treatment strategies, although sufficient evidence has not yet been reported for myeloma.
Prior to the development of novel agents, two large-scale trials were conducted to assess ex vivo purging using the CD34-positive selection method; however, definitive conclusions regarding the efficacy of ex vivo purging were not obtained [53,63]. Meanwhile, DECP (DEX, etoposide, cyclophosphamide, and cisplatin) and IEV (ifosphomide, epirubicin, and etopiside) were reported as effective in vivo purging regimens [64,105]. Additionally, a phase II trial with DARA in vivo purging is ongoing [106]. Moreover, it remains unclear whether it is more beneficial to continue with the same induction therapy after a positive MRD status is achieved or alter the treatment strategy. In fact, some patients who do not achieve an MRD-negative result after four cycles of induction therapy may achieve MRD negativity by continuing with a similar therapy. For example, in the FORTE study, the MRD-negative rate increased gradually after 4, 8, and 12 cycles of KRd [99]. In the U.S. phase II trial, after 4 cycles of KRd induction therapy, followed by ASCT, 4 cycles of KRd consolidation therapy, and 10 cycles of KRd maintenance therapy, the treatment response improved during continuous CFZ+LEN therapy [102]. Moreover, in the IFM2018-04 trial, a single-arm phase II trial, patients with HRCA were treated with six courses of D-KRd, ASCT, three courses of D-KRd as consolidation, an additional round of ASCT, followed by DR maintenance therapy for 2 years [103]. The MRD-negative rate after six courses of induction D-KRd was 50%, which is potentially superior to that after four courses of D-KRd in the MASTER study [6,103]. However, although this study included peripheral blood stem cell harvest (PBSCH) with high-dose cyclophosphamide plus G-CSF with or without plerixafor after six courses of initial D-KRd, the presence of several poor mobilizers prevented sufficient PBSC for the second ASCT in the interim analysis. Therefore, PBSCH was performed after three courses of D-KRd, after which PBSC could be collected for the second ASCT, considering the retrospective evidence that more than five cycles of LEN are associated with poor mobilization. As a result, a consensus has not been reached on the optimal number of induction therapy courses; however, LEN might be administered within four months to reduce the incidence of poor mobilization. Additionally, MRD monitoring could be repeated at short intervals, and the changing of therapy might be considered for improving the MRD status in autografts, although the evidence supporting this theory is not sufficient. Furthermore, PBSCH can be carried out because the autograft MRD status can be negative in patients with MRD positivity in the bone marrow and/or peripheral blood. The incidence of myeloma cell contamination in autografts is dependent on treatment response using M-protein; the incidence of contamination is 57%, 29%, and 6% in patients with partial response (PR), very good partial response (VGPR), and CR, respectively [50]. Therefore, we posit that a VGPR or better is necessary in UHRCA patients when considering risk reduction of myeloma cell contamination in autografts. In contrast, a change or intensification of induction therapy is reasonable for UHRCA patients with a partial or worse treatment response.
In patients with UHRCA, it may be necessary to alter the treatment strategy to eradicate minimal residual myeloma cells via a novel mechanism of action. For example, early administration of a BCMA-targeted agent to patients with MRD positivity might prevent the aggressive recurrence of the disease [107,108,109,110]. Subsequently, if MRD negativity is achieved, it would be suitable to perform PBSCH followed by ASCT. However, if MRD positivity persists despite treatment with an agent that has a novel mechanism of action, it remains unclear whether proceeding with PBSCH followed by ASCT directly or an alternative intensive re-induction therapy including cytotoxic agents, such as VTD-PACE (BOR, thalidomide, DEX, cisplatin, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide), will lead to a better outcome [111].
High-dose melphalan (MEL) may be effective regardless of the autograft MRD status, as it has a completely different mechanism of action from the antitumor drugs used in induction treatment [99,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119]. ASCT prolongs PFS in patients with MRD positivity but not in those with MRD negativity compared with VRd and KRd, suggesting that ASCT should be performed even if the MRD status is positive after intensive induction therapy; however, these results were observed in the analysis for all patients, not only those with HRCAs [99,119,120]. Meanwhile, tandem ASCT may improve clinical outcomes in patients with HRCAs [117,121].
Given that post-transplantation therapy has not been proven to be effective in entirely eliminating MRD [99,122], it remains controversial whether agents with novel modes of action or similar therapeutics that comprise post-transplantation therapy are more beneficial. LEN maintenance therapy until PD is a standard of care in post-transplantation settings. In the MRC-Myeloma XI and RV-MM-EMN-441 trials, LEN maintenance therapy improved the OS and PFS even after IMiDs containing induction therapy [116,123]. Additionally, in the GIMEMA MMY-3006 trial, VTD consolidation therapy improved the OS and PFS after VTD induction therapy followed by tandem ASCT [124]. However, therapeutics with alternative modes of action might be required because MRD negativity would not be achieved by repeating a similar short-term consolidation treatment with induction therapy. For instance, VRD consolidation did not improve PFS in MRD-positive patients after CVD induction therapy followed by ASCT or VMP (BOR, MEL, and prednisone) in the EMN02/HO95 trial [117]. In contrast, long-term maintenance therapy might be beneficial for conversion from MRD positivity to negativity [99,122]. In the FORTE trial, 2-year CFZ+LEN maintenance therapy increased the MRD conversion rate compared with LEN maintenance therapy alone, regardless of induction therapy of ASCT [99]. In the CASSIOPEIA2 trial, 2-year DARA maintenance therapy increased the MRD conversion rate in the VTD group but not in the D-VTD group [122]. In this second randomization of the FORTE trial, one-third of the patients who had never used LEN as induction and consolidation therapy were included. As a result, these patients did not receive LEN therapy prior to the LEN maintenance therapy. Therefore, long-term LEN-containing maintenance therapy, including LEN, which is a therapeutic with a new mode of action for the KCd (CFZ, cyclophosphamide, and DEX)/ASCT group, may increase the MRD negativity rate. Recently, among patients with UHRCA and primary plasma cell leukemia, the PFS in patients treated with twelve cycles of D-KRd +/− cyclophosphamide as consolidation followed by DR until PD as maintenance therapy in a single-arm phase II trial (the U.K. Optimum/Muknine Trial) was significantly longer than that of matched-paired patients treated with LEN maintenance therapy in the MRC Myeloma XI trial [125]. Thus, long-term post-transplantation treatment using a continuous multidrug combination or alternative agents may be essential to eradicating residual myeloma cells in MRD-positive patients.
When PIs, IMiDs, and CD38 MoAbs are used as induction therapies without achieving deep treatment responses, agents with novel modes of action might be necessary to treat patients. For example, BCMA-targeting treatments, such as chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy (CART) and antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) [126], could be effective options in such cases. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that the novel BCMA-targeted CART and bispecific antibodies might be effective for patients with RRMM and triple-class refractory disease according to the subgroup analyses in a clinical trial [127]. If induction treatment cannot provide an adequate therapeutic response, conversion to BCMA-targeted agents might be an important therapeutic option to achieve MRD negativity at an early stage and in autografts. Indeed, BCMA-targeting CARTs have already been approved for RRMM [107,109], and several clinical trials on the efficacy of BCMA-targeting CARTs as a post-ASCT treatment (cilta-cel, CARTITUDE-2 trial (NCT04133636); bb2121, BMTCTN190 trial (NCT05032820), and CD19/BCMA CART (NCT03455972)) and belantamab mafodotin, a BCMA ADC (NCT04680468, NCT04876248) are ongoing (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical trials concerning BCMA-targeting therapy in post-transplantation settings.
The use of new molecules, such as G-protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D), in the treatment of patients with MRD positivity after BCMA-targeted therapy may be promising. GPRC5D is a relatively specific antigen expressed on the surface of myeloma cells [128]. Both BCMA and GPRC5D are expressed in most patients with MM, although there is no significant association between BCMA and GPRC5D expression [128]. In addition, BCMA and GPRC5D expression levels are independent of disease status and refractoriness to DARA [120]. Hence, anti-GPRC5D CART is expected to be effective for patients with MM that is refractory to anti-BCMA CART as GPRC5D is expressed on myeloma cells with HRCAs, such as t(4; 14), 1q21 gain, and del(13q), excluding t(11;14) [129,130], whereas BCMA expression is low in myeloma cells with HRCAs [131]. More recently, it has been reported that superior antitumor activity is achieved using dual CART targeting both BCMA and GPRC5D compared to using a treatment that combines anti-BCMA and -GPRC5D CARTs in a mouse model [132]. GPRC5D-targeting CART and bispecific antibodies have been investigated in RRMM but not post-ASCT settings.
Fc receptor-homolog 5 (FcRH5) is a novel surface protein on MM cells. FcRH5 has a genetic locus in the chromosomal breakpoint at 1q21, the expression of which is higher in patients with 1q21 gain than in those without it [133]. Cevostamab, a bispecific antibody targeting FcRH5, has been developed and has shown promising activity against myeloma in a phase I study [134].
Minimal residual myeloma cells have been reported to exhibit mechanisms to escape immune activity; therefore, immune checkpoint inhibitors are considered effective treatments [86]. Pembrolizumab—an anti-PD-1 MoAb—was effective but not tolerable for RRMM in the KEYNOTE-183 trial [135]. However, several anti-PD-1 MoAb-containing regimens as a post-ASCT treatment did not show significant efficacy and exhibited toxicity; therefore, these treatment approaches were withdrawn (pembrolizumab: NCT02331368, NCT02906332, and NCT02636010; nivolumab: NCT03292263). In contrast, SLAMF7 is overexpressed in most myeloma cells [136,137]. Post-ASCT treatment, including elotuzumab (ELO)—an anti-SLAMF7 MoAb—for enhancing the immunological activity of immune cells, especially NK cells, against myeloma cells was investigated [138,139,140]. ELO has been approved in combination with LEN or POM for RRMM [141,142]. ELO treatment post-ASCT has demonstrated improved tolerability and efficacy in several clinical trials (NCT02495922, NCT03168100, NCT03003728, NCT02420860, and NCT02655458) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Clinical trials concerning anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody- or elotuzumab-containing post-transplantation therapy.
Finally, donor immune attack might occur after allogeneic hematopoietic stem transplantation, such as up-front ASCT followed by reduced-intensity stem cell transplantation. The treatment algorithm that we have developed is presented in Figure 1.
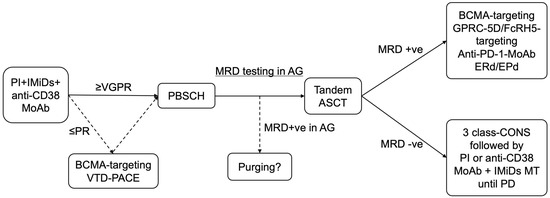
Figure 1.
Treatment algorithm for patients with UHRCA NDMM. PI, IMiDs, and anti-CD38 MoAb-containing induction therapy are preferable options, using a proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory drug, and anti-CD38 MoAb, for UHRCA NDMM considering its mode of action. If VGPR is not achieved by three courses of treatment including induction therapy, alternative therapy, such as BCMA-targeting therapy or conventional chemotherapy (VTD-PACE), might be suitable to improve treatment responses, including eradication of MRD. If the MRD status in the autograft is positive, in vivo or ex vivo purging might be challenging. Intensive post-transplantation treatment is key to achieving durable MRD negativity or preventing recurrence in patients with UHRCA myeloma. If the MRD negativity is achieved, 3-class-containing combination consolidation followed by PI plus IMiDs or anti-CD38 MoAb combined lenalidomide maintenance therapy is a preferable option. If the MRD status is positive, alternative therapeutics with a new mode of action might eradicate residual myeloma cells. BCMA, GPRC-5D, and FcRH5 are new therapeutic targets. Anti-PD-1 MoAbs might effectively attack minimal residual myeloma cells as immunological escape occurs in these cells via the expression of PD-1, leading to immunological tolerance. Elotuzumab and immunomodulatory drug combination therapy might effectively enhance the immunological activity and suppress soluble SLAMF-7, the gene expression of which increases in patients with 1q21 gain/amplification. MRD, minimal residual disease; PB, peripheral blood; BM, bone marrow; PI; proteasome inhibitor; IMiDs, immunomodulatory drugs; MoAb, monoclonal antibody; BCMA, B cell mature antigen; VTD-PACE, bortezomib, thalidomide, dexamethasone, cisplatin, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, plus etoposide; PBSCH, peripheral blood stem cell harvest; ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; AG, autograft; LEN, lenalidomide; MT, maintenance therapy; CONS, consolidation therapy; GPRC-5D, G-protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member D; FcRH5, Fc receptor-homolog 5; PD-1, programed death-1; MoAb, monoclonal antibody; ERd, elotuzumab, lenalidomide plus dexamethasone; EPd, elotuzumab, pomalidomide plus dexamethasone; PR, partial response; VGPR, very good partial response; PD, progressive disease.
7. Conclusions
The MASTER trial demonstrated that anti-CD38 MoAb, PI, and IMiDs induction therapy followed by ASCT could be effective, and treatment discontinuation could be possible in sustained MRD-negative NDMM patients without UHRCAs. However, a new treatment strategy is needed for NDMM patients with UHRCAs even if MRD negativity is achieved. For instance, MRD negativity in autograft could be associated with a long survival time, implying that purging might be one of the options for eliminating MRD in autograft. Sustained MRD negativity could be a key to long-term survival in patients with UHRCAs, and so MRD analysis using various strategies can be essential to confirm the true MRD negativity. Early treatment interventions might be essential to prevent disease progression and UHRCA acquisition. In the future, it will be critical to treat early-stage myelomas and develop therapeutics with new mechanisms of action with the goal of improving the microenvironment and preventing clonal evolution, leading to improved clinical outcomes in patients with myelomas who are candidates for UHRCA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.S.; writing—review and editing, S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
K.S. received personal fees from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Celgene, Ono Pharmaceutical Company, Sanofi K.K., and Bristol-Myers Squibb Co outside the submitted work; S.Y. reports grants from Kyowa Kirin, grants from Astella Pharma, grants from Chugai Pharma, grants from Mochida Pharma, grants from Lilly Pharma, grants from Takeda Pharma, grants from MDS Pharma, grants from Pfizer, grants from Dai Nippon Sumitomo Pharma, and grants from Ono Pharma outside the submitted work.
References
- Palumbo, A.; Anderson, K. Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nishiwaki, K.; Yano, S. Treatment Strategy for Multiple Myeloma to Improve Immunological Environment and Maintain MRD Negativity. Cancers 2021, 13, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nishiwaki, K.; Yano, S. Treatment Strategies Considering Micro-Environment and Clonal Evolution in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Criteria for Response and Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.C.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Anderson, K.C.; Neri, P.; Paiva, B.; Samur, M.; Dimopoulos, M.; Kulakova, M.; Lam, A.; Hashim, M.; et al. A Large Meta-Analysis Establishes the Role of MRD Negativity in Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5988–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.J.; Chhabra, S.; Medvedova, E.; Dholaria, B.R.; Schmidt, T.M.; Godby, K.N.; Silbermann, R.; Dhakal, B.; Bal, S.; Giri, S.; et al. Daratumumab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone with Minimal Residual Disease Response-Adapted Therapy in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 40, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, K.; Walker, B.; Kumar, S.K.; Spicka, I.; Moreau, P.; Martin, T.; Costa, L.J.; Richter, J.; Fukao, T.; Macé, S.; et al. Chromosomal 1q21 Abnormalities in Multiple Myeloma: A Review of Translational, Clinical Research, and Therapeutic Strategies. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, N.; Paramasivam, N.; Toprak, U.H.; Huebschmann, D.; Xu, J.; Uhrig, S.; Samur, M.; Bähr, S.; Fröhlich, M.; Mughal, S.S.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of Refractory Multiple Myeloma Reveals a Complex Mutational Landscape associated with Drug Resistance and Novel Therapeutic Vulnerabilities. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziccheddu, B.; Biancon, G.; Bagnoli, F.; De Philippis, C.; Maura, F.; Rustad, E.H.; Dugo, M.; Devecchi, A.; De Cecco, L.; Sensi, M.; et al. Integrative Analysis of the Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Double-Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, P.J.; An, O.; Chung, T.H.; Vaiyapuri, T.; Raju, A.; Hoppe, M.M.; Toh, S.H.M.; Wang, W.; Chan, M.C.; Fullwood, M.J.; et al. P53-NEIL1 Co-abnormalities Induce Genomic Instability and Promote Synthetic Lethality with Chk1 Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma Having Concomitant 17p13(Del) and 1q21(Gain). Oncogene 2022, 41, 2106–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamura, I. Gain/Amplification of Chromosome Arm 1q21 in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaughnessy, J. Amplification and Overexpression of CKS1B at Chromosome Band 1q21 Is Associated with Reduced Levels of P27 Kip1 and an Aggressive Clinical Course in Multiple Myeloma. Hematology 2005, 10, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Qi, X.; Trieu, Y.; Xu, W.; Reader, J.C.; Ning, Y.; Reece, D. Multiple Myeloma Patients with CKS1B Gene Amplification Have a Shorter Progression-Free Survival Post-autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 135, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Zangari, M.; Xu, H.; Cao, T.M.; Xu, C.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Over-Expression of CKS1B Activates Both MEK/ERK and JAK/STAT3 Signaling Pathways and Promotes Myeloma Cell Drug-Resistance. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.W.; Jabs, E.W.; Zhou, P.; Kozopas, K.M.; Hawkins, A.L.; Rochelle, J.M.; Seldin, M.F.; Griffin, C.A. Human and Mouse Chromosomal Mapping of the Myeloid Cell Leukemia-1 Gene: MCL1 Maps to Human Chromosome 1q21, a Region That Is Frequently Altered in Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Disease. Genomics 1994, 23, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samo, A.A.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; van Duin, M.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. MCL1 Gene Co-expression Module Stratifies Multiple Myeloma and Predicts Response to Proteasome Inhibitor-Based Therapy. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.A.; Matulis, S.M.; Conage-Pough, J.E.; Nooka, A.K.; Kaufman, J.L.; Lonial, S.; Boise, L.H. Bone Marrow Microenvironment–Derived Signals Induce Mcl-1 Dependence in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2017, 129, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.B.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Li, B.; Berg, D.; Lin, J.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Bahlis, N.J.; Moreau, P.; Richardson, P.G.; et al. Clinical Benefit of Ixazomib plus Lenalidomide-Dexamethasone in Myeloma Patients with Non-canonical NF-κB Pathway Activation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 105, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Jacobus, S.J.; Cohen, A.D.; Weiss, M.; Callander, N.; Singh, A.K.; Parker, T.L.; Menter, A.; Yang, X.; Parsons, B.; et al. Carfilzomib or Bortezomib in Combination with Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma without Intention for Immediate Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation (Endurance): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3, Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiya, D.; Liu, J.; Ohguchi, H.; Kurata, K.; Samur, M.K.; Tai, Y.T.; Adamia, S.; Ando, K.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C. The JAK-STAT Pathway Regulates CD38 on Myeloma Cells in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment: Therapeutic Implications. Blood 2020, 136, 2334–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Weinhold, N.; Schinke, C.; Thanedrarajan, S.; Rasche, L.; Sawyer, J.R.; Tian, E.; van Rhee, F.; Zangari, M. Daratumumab in High-Risk Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients: Adverse Effect of Chromosome 1q21 Gain/Amplification and GEP70 Status on Outcome. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Donk, N.W.C.J. Reprint of “Immunomodulatory Effects of CD38-Targeting Antibodies”. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stork, M.; Sevcikova, S.; Minarik, J.; Krhovska, P.; Radocha, J.; Pospisilova, L.; Brozova, L.; Jarkovsky, J.; Spicka, I.; Straub, J.; et al. Identification of Patients at High Risk of Secondary Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Development. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.A.; Mavrommatis, K.; Wardell, C.P.; Ashby, T.C.; Bauer, M.; Davies, F.; Rosenthal, A.; Wang, H.; Qu, P.; Hoering, A.; et al. A High-Risk, Double-Hit, Group of Newly Diagnosed Myeloma Identified by Genomic Analysis. Leukemia 2019, 33, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Lu, X.; Gong, Z.; Bassett, R.L.; Hu, S.; Konoplev, S.N.; Tang, G.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Khanlari, M.; et al. The Survival Impact of CKS1B Gains or Amplification Is Dependent on the Background Karyotype and TP53 Deletion Status in Patients with Myeloma. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirier, S.M.; Mallm, J.P.; Steiger, S.; Poos, A.M.; Awwad, M.H.S.; Giesen, N.; Casiraghi, N.; Susak, H.; Bauer, K.; Baumann, A.; et al. Subclone-Specific Microenvironmental Impact and Drug Response in Refractory Multiple Myeloma Revealed by Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.M.; Barwick, B.G.; Joseph, N.; Heffner, L.T.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Bernal, L.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; Gupta, V.A.; Jaye, D.L.; Wu, J.; et al. Gain of Chromosome 1Q Is Associated with Early Progression in Multiple Myeloma Patients Treated with Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, F.; Lu, G.; Srour, S.A.; Gaballa, S.; Lin, H.Y.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Honhar, M.; Stich, M.; Shah, N.D.; Bashir, Q.; et al. Outcome of Patients with Multiple Myeloma and CKS1B Gene Amplification after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Oliva, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Goldschmidt, H.; Rosinol, L.; Richardson, P.; Caltagirone, S.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Facon, T.; et al. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: A Report from International Myeloma Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, M.; Jauch, A.; Hielscher, T.; Bochtler, T.; Schönland, S.O.; Seckinger, A.; Hose, D.; Bertsch, U.; Neben, K.; Raab, M.S.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Cytogenetic Heterogeneity in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.; Ruggeri, M.; Aquino, S.; Giuliani, N.; Arigoni, M.; Gentile, M.; Olivero, M.; Vincelli, I.D.; Capra, A.; Mussatto, C.; et al. Impact of Gain and Amplification of 1q in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Patients Receiving Carfilzomib-Based Treatment in the Forte Trial. Blood 2020, 136, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billecke, L.; Murga Penas, E.M.; May, A.M.; Engelhardt, M.; Nagler, A.; Leiba, M.; Schiby, G.; Kröger, N.; Zustin, J.; Marx, A.; et al. Cytogenetics of Extramedullary Manifestations in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzetti, A.; Cerase, A.; Lotti, F.; Rossi, D.; Palumbo, A.; Petrucci, M.T.; Patriarca, F.; Nozzoli, C.; Cavo, M.; Offidani, M.; et al. Extramedullary Intracranial Localization of Multiple Myeloma and Treatment with Novel Agents: A Retrospective Survey of 50 Patients. Cancer 2012, 118, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Xu, Y.; An, G.; Sui, W.; Zou, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, F.; Hao, M.; Qiu, L. Features of Extramedullary Disease of Multiple Myeloma: High Frequency of P53 Deletion and Poor Survival: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 834 Cases. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodé, L.; Eveillard, M.; Trichet, V.; Soussi, T.; Wuillème, S.; Richebourg, S.; Magrangeas, F.; Ifrah, N.; Campion, L.; Traullé, C.; et al. Mutations in TP53 Are Exclusively Associated with Del(17p) in Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinhold, N.; Ashby, C.; Rasche, L.; Chavan, S.S.; Stein, C.; Stephens, O.W.; Tytarenko, R.; Bauer, M.A.; Meissner, T.; Deshpande, S.; et al. Clonal Selection and Double-Hit Events Involving Tumor Suppressor Genes Underlie Relapse in Myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, K.K.; Escure, G.; Demonchy, J.; Willaume, A.; Van de Wyngaert, Z.; Farhat, M.; Chauvet, P.; Facon, T.; Quesnel, B.; Manier, S. Deregulation and Targeting of TP53 Pathway in Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.A.; Mavrommatis, K.; Wardell, C.P.; Ashby, T.C.; Bauer, M.; Davies, F.E.; Rosenthal, A.; Wang, H.; Qu, P.; Hoering, A.; et al. Identification of Novel Mutational Drivers Reveals Oncogene Dependencies in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Heuck, C.; Mitchell, A.; Szymonifka, J.; Nair, B.; Hoering, A.; Alsayed, Y.; Waheed, S.; Haider, S.; Restrepo, A.; et al. Extramedullary Disease Portends Poor Prognosis in Multiple Myeloma and Is Over-represented in High-Risk Disease Even in the Era of Novel Agents. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanendrarajan, S.; Tian, E.; Qu, P.; Mathur, P.; Schinke, C.; van Rhee, F.; Zangari, M.; Rasche, L.; Weinhold, N.; Alapat, D.; et al. The Level of Deletion 17p and Bi-allelic Inactivation of TP53 Has a Significant Impact on Clinical Outcome in Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2017, 102, e364–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walerych, D.; Lisek, K.; Sommaggio, R.; Piazza, S.; Ciani, Y.; Dalla, E.; Rajkowska, K.; Gaweda-Walerych, K.; Ingallina, E.; Tonelli, C.; et al. Proteasome Machinery Is Instrumental in a Common Gain-of-Function Program of the p53 Missense Mutants in Cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, M.; Sive, J.I.; Allen, C.; Roddie, C.; Chavda, S.J.; Smith, D.; Blombery, P.; Jones, K.; Ryland, G.L.; Popat, R.; et al. Prevalence and Timing of TP53 Mutations in Del(17p) Myeloma and Effect on Survival. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakurta, A.; Ortiz, M.; Blecua, P.; Towfic, F.; Corre, J.; Serbina, N.V.; Flynt, E.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Palumbo, A.; et al. High Subclonal Fraction of 17p Deletion Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2019, 133, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, A.; Painuly, U.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Ketterling, R.P.; Kapoor, P.; Greipp, P.T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; et al. Impact of Acquired Del(17p) in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancman, G.; Tremblay, D.; Barley, K.; Barlogie, B.; Cho, H.J.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Moshier, E.; Parekh, S.; Chari, A. The Effect of Novel Therapies in High-Molecular-Risk Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 15, 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.M.R.; Gorzov, P.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Söderqvist, M.; Segerbäck, D.; Bergman, J.; Fersht, A.R.; Hainaut, P.; Wiman, K.G.; Bykov, V.J.N. PRIMA-1 Reactivates Mutant P53 by Covalent Binding to the Core Domain. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Bykov, V.J.N.; Ali, D.; Andrén, O.; Cherif, H.; Tidefelt, U.; Uggla, B.; Yachnin, J.; Juliusson, G.; Moshfegh, A.; et al. Targeting P53 In Vivo: A First-in-Human Study with P53-Targeting Compound APR-246 in Refractory Hematologic Malignancies and Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.; Cairns, D.A.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Wester, R.; Bertsch, U.; Waage, A.; Zamagni, E.; Mateos, M.V.; Dall’Olio, D.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; et al. Second Revision of the International Staging System (R2-ISS) for Overall Survival in Multiple Myeloma: A European Myeloma Network (EMN) Report Within the HARMONY Project. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3406–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, H.; Takezako, N.; Zheng, J.; Moorhead, M.; Carlton, V.E.H.; Kong, K.A.; Murata, R.; Ito, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Prognostic Value of Sequencing-Based Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Who Underwent Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, I.V.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Rousakis, P.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Panteli, C.; Orologas-Stavrou, N.; Kanellias, N.; Malandrakis, P.; Liacos, C.I.; Papaioannou, N.E.; et al. Aberrant Plasma Cell Contamination of Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Autografts, Assessed by Next-Generation Flow Cytometry, Is a Negative Predictor for Deep Response Post Autologous Transplantation in Multiple Myeloma; A Prospective Study in 199 Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszczuk-Gajda, A.; Feliksbrot-Bratosiewicz, M.; Król, M.; Snarski, E.; Drozd-Sokołowska, J.; Biecek, P.; Król, M.; Lewandowski, Z.; Peradzyńska, J.; Jędrzejczak, W.W.; et al. Influence of Clonal Plasma Cell Contamination of Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Autografts on Progression and Survival in Multiple Myeloma Patients after Autologous Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation in Long-Term Observation. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Yang, L.; Banihashemi, B.; Martin, L.; Halpenny, M.; Atkins, H.; Sabloff, M.; McDiarmid, S.A.; Huebsch, L.B.; Bence-Bruckler, I.; et al. Contaminating Tumour Cells in Autologous PBSC Grafts Do Not Influence Survival or Relapse Following Transplant for Multiple Myeloma or B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 43, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhis, J.H.; Bouko, Y.; Koscielny, S.; Bakkus, M.; Greinix, H.; Derigs, G.; Salles, G.; Feremans, W.; Apperley, J.; Samson, D.; et al. Relapse Risk after Autologous Transplantation in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Myeloma Is Not Related with Infused Tumor Cell Load and the Outcome Is Not Improved by CD34+ Cell Selection: Long Term Follow-Up of an EBMT Phase III Randomized Study. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanasami, U.; Kanteti, R.; Morelli, J.; Klekar, A.; Al-Olama, A.; Keating, C.; O’Connor, C.; Berkman, E.; Erban, J.K.; Sprague, K.A.; et al. Randomized Trial of Filgrastim versus Chemotherapy and Filgrastim Mobilization of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells for Rescue in Autologous Transplantation. Blood 2001, 98, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumelou, M.; Payssot, A.; Row, C.; Racine, J.; Lafon, I.; Bastie, J.N.; Chevreux, S.; Chrétien, M.L.; Maynadié, M.; Caillot, D.; et al. Early Achievement of Measurable Residual Disease Negativity in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma as Predictor of Outcome. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 197, e82–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasvolsky, O.; Milton, D.R.; Rauf, M.; Ghanem, S.; Masood, A.; Mohamedi, A.H.; Tanner, M.R.; Bashir, Q.; Srour, S.A.; Saini, N.; et al. Impact of Presence and Amount of Clonal Plasma Cells in Autografts Affect Outcomes in High-Risk Multiple Myeloma Patients Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Brown, S.; Devlin, S.M.; Dahi, P.B.; Landau, H.; Lahoud, O.B.; Scordo, M.; Shah, G.L.; Hassoun, H.; Hultcrantz, M.; et al. Stem Cell Autograft Minimal Residual Disease Negativity Improves Outcomes after Autotransplant for Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertamini, L.; D’Agostino, M.; Gay, F. MRD Assessment in Multiple Myeloma: Progress and Challenges. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2021, 16, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoja-Flores, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Puig, N.; Contreras-Sanfeliciano, T.; Pontes, R.; Corral-Mateos, A.; García-Sánchez, O.; Díez-Campelo, M.; Pessoa de Magalhães, R.J.; García-Martín, L.; et al. Blood Monitoring of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells by Next Generation Flow in Multiple Myeloma after Therapy. Blood 2019, 134, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, C.; Buisson, L.; Maheo, S.; Perrot, A.; Chretien, M.L.; Leleu, X.; Hulin, C.; Manier, S.; Hébraud, B.; Roussel, M.; et al. Myeloma MRD by Deep Sequencing from Circulating Tumor DNA Does Not Correlate with Results Obtained in the Bone Marrow. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2811–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.J.; Derman, B.A.; Bal, S.; Sidana, S.; Chhabra, S.; Silbermann, R.; Ye, J.C.; Cook, G.; Cornell, R.F.; Holstein, S.A.; et al. International Harmonization in Performing and Reporting Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma Trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moor, I.; Bacher, V.U.; Jeker, B.; Taleghani, B.M.; Mueller, B.U.; Keller, P.; Betticher, D.; Egger, T.; Novak, U.; Pabst, T. Peripheral Flow-MRD Status at the Time of Autologous Stem Cell Collection Predicts Outcome in Multiple Myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.K.; Vescio, R.; Schiller, G.; Ballester, O.; Noga, S.; Rugo, H.; Freytes, C.; Stadtmauer, E.; Tarantolo, S.; Sahebi, F.; et al. Purging of Autologous Peripheral-Blood Stem Cells Using CD34 Selection Does Not Improve Overall or Progression-Free Survival after High-Dose Chemotherapy for Multiple Myeloma: Results of a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, W.; Kopp, H.G.; Kanz, L.; Einsele, H. Myeloma Cell Contamination of Peripheral Blood Stem-Cell Grafts Can Predict the Outcome in Multiple Myeloma Patients after High-Dose Chemotherapy and Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 131, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Mina, R.; Rota-Scalabrini, D.; Galli, M.; Belotti, A.; Zamagni, E.; Bertamini, L.; Zambello, R.; Gamberi, B.; De Sabbata, G.; et al. Carfilzomib-Based Induction/Consolidation with or without Autologous Transplant (ASCT) Followed by Lenalidomide (R) or Carfilzomib-Lenalidomide (KR) Maintenance: Efficacy in High-Risk Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, S.; Landau, H.J.; Shah, G.L.; Scordo, M.; Dahi, P.; Lahoud, O.B.; Hassoun, H.; Hultcrantz, M.; Korde, N.; Lendvai, N.; et al. Stem Cell Mobilization and Autograft Minimal Residual Disease Negativity with Novel Induction Regimens in Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tageja, N.; Korde, N.; Kazandjian, D.; Panch, S.; Manasanch, E.; Bhutani, M.; Kwok, M.; Mailankody, S.; Yuan, C.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; et al. Combination Therapy with Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (KRd) Results in an Unprecedented Purity of the Stem Cell Graft in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Attal, M.; Caillot, D.; Macro, M.; Karlin, L.; Garderet, L.; Facon, T.; Benboubker, L.; Escoffre-Barbe, M.; Stoppa, A.M.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and [18 F]Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography at Diagnosis and before Maintenance Therapy in Symptomatic Patients with Multiple Myeloma Included in the IFM/DFCI 2009 Trial: Results of the IMAJEM Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillengass, J.; Usmani, S.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Durie, B.G.M.; Mateos, M.-V.; Lonial, S.; Joao, C.; Anderson, K.C.; García-Sanz, R.; Riva, E.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Recommendations on Imaging in Monoclonal Plasma Cell Disorders. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e302–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Gertz, M.A.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Fonseca, R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Offord, J.R.; Larson, D.R.; et al. Review of 1027 Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, L.; Alapat, D.; Kumar, M.; Gershner, G.; McDonald, J.; Wardell, C.P.; Samant, R.; Van Hemert, R.; Epstein, J.; Williams, A.F.; et al. Combination of Flow Cytometry and Functional Imaging for Monitoring of Residual Disease in Myeloma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.J.; Chhabra, S.; Medvedova, E.; Schmidt, T.M.; Dholaria, B.; Godby, K.N.; Silbermann, R.; Bal, S.; D’Souza, A.; Giri, S.; et al. Outcomes of MRD-Adapted Treatment Modulation in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Receiving Daratumumab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (Dara-KRd) and Autologous Transplantation: Extended Follow up of the Master Trial. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 7275–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; Orfao, A. New Criteria for Response Assessment: Role of Minimal Residual Disease in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2015, 125, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Child, J.A.; de Tute, R.M.; Davies, F.E.; Gregory, W.M.; Bell, S.E.; Szubert, A.J.; Navarro-Coy, N.; Drayson, M.T.; Feyler, S.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease Assessed by Multiparameter Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma: Impact on Outcome in the Medical Research Council Myeloma IX Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamagni, E.; Nanni, C.; Dozza, L.; Carlier, T.; Bailly, C.; Tacchetti, P.; Versari, A.; Chauvie, S.; Gallamini, A.; Gamberi, B.; et al. Standardization of 18 F-FDG–PET/CT According to Deauville Criteria for Metabolic Complete Response Definition in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belotti, A.; Ribolla, R.; Cancelli, V.; Villanacci, A.; Angelini, V.; Chiarini, M.; Giustini, V.; Facchetti, G.V.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Predictive Role of Diffusion-Weighted Whole-Body MRI (DW-MRI) Imaging Response According to MY-RADS Criteria after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Multiple Myeloma and Combined Evaluation with MRD Assessment by Flow Cytometry. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5859–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.L.; Puig, N.; Kristinsson, S.; Usmani, S.Z.; Dispenzieri, A.; Bianchi, G.; Kumar, S.; Chng, W.J.; Hajek, R.; Paiva, B.; et al. Mass Spectrometry for the Evaluation of Monoclonal Proteins in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: An International Myeloma Working Group Mass Spectrometry Committee Report. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langerhorst, P.; Noori, S.; Zajec, M.; De Rijke, Y.B.; Gloerich, J.; van Gool, A.J.; Caillon, H.; Joosten, I.; Luider, T.M.; Corre, J.; et al. Multiple Myeloma Minimal Residual Disease Detection: Targeted Mass Spectrometry in Blood vs Next-Generation Sequencing in Bone Marrow. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyasova, M.; McDonald, Z.; Taylor, P.; Gorospe, K.; Xu, X.; Yao, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Atenafu, E.G.; Piza, G.; et al. A Personalized Mass Spectrometry–Based Assay to Monitor M-Protein in Patients with Multiple Myeloma (EasyM). Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5028–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeykoon, J.P.; Murray, D.L.; Murray, I.; Jevremovic, D.; Otteson, G.E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Arendt, B.K.; Dasari, S.; Gertz, M.; Gonsalves, W.I.; et al. Implications of Detecting Serum Monoclonal Protein by MASS-Fix Following Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledergor, G.; Weiner, A.; Zada, M.; Wang, S.Y.; Cohen, Y.C.; Gatt, M.E.; Snir, N.; Magen, H.; Koren-Michowitz, M.; Herzog-Tzarfati, K.; et al. Single Cell Dissection of Plasma Cell Heterogeneity in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Myeloma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, E.M.; Deshpande, S.; Tytarenko, R.; Ashby, C.; Wang, Y.; Bauer, M.A.; Johnson, S.K.; Wardell, C.P.; Thanendrarajan, S.; Zangari, M.; et al. The Molecular Make up of Smoldering Myeloma Highlights the Evolutionary Pathways Leading to Multiple Myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavidij, O.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Sklavenitis-Pistofidis, R.; Cai, S.; Reidy, M.; Rahmat, M.; Flaifel, A.; Ferland, B.; Su, N.K.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Compromised Immune Microenvironment in Precursor Stages of Multiple Myeloma. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, D.; Zhou, W.; Xie, L. Cellular Interaction Analysis Characterizing Immunosuppressive Microenvironment Functions in MM Tumorigenesis from Precursor Stages. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 844604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Tsakirakis, N.; Malandrakis, P.; Vitsos, P.; Metousis, A.; Orologas-Stavrou, N.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Kanellias, N.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Pothos, P.; et al. Deep Phenotyping Reveals Distinct Immune Signatures Correlating with Prognostication, Treatment Responses, and MRD Status in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.; Cedena, M.T.; Puig, N.; Arana, P.; Vidriales, M.B.; Cordon, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Martín-Ramos, M.L.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring and Immune Profiling in Multiple Myeloma in Elderly Patients. Blood 2016, 127, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglietta, M.; Castella, B.; Mariani, S.; Coscia, M.; Godio, L.; Ferracini, R.; Ruggeri, M.; Muccio, V.; Omedé, P.; Palumbo, A.; et al. The Bone Marrow of Myeloma Patients Is Steadily Inhabited by a Normal-Sized Pool of Functional Regulatory T Cells Irrespective of the Disease Status. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh-Wakefield, F.; Kruzins, A.; McGuire, H.M.; Yang, S.; Bryant, C.; Fazekas de St Groth, B.; Nassif, N.; Byrne, S.N.; Gibson, J.; Brown, C.; et al. Mass Cytometry Discovers Two Discrete Subsets of CD39−Treg Which Discriminate MGUS from Multiple Myeloma. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, M.; Foureau, D.; Zhang, Q.; Robinson, M.; Wynn, A.S.; Steuerwald, N.M.; Druhan, L.J.; Guo, F.; Rigby, K.; Turner, M.; et al. Peripheral Immunotype Correlates with Minimal Residual Disease Status and Is Modulated by Immunomodulatory Drugs in Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Huang, B.; Li, J. Longitudinal Flow Cytometry Identified “Minimal Residual Disease” (MRD) Evolution Patterns for Predicting the Prognosis of Patients with Transplant-Eligible Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Updated Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 1, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Landgren, O.; Mateos, M.V. Smoldering Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2015, 125, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, M.V.; Kumar, S.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; González-Calle, V.; Kastritis, E.; Hajek, R.; De Larrea, C.F.; Morgan, G.J.; Merlini, G.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Risk Stratification Model for Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM). Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, P.; Engelhardt, M.; Caers, J.; Bolli, N.; Kaiser, M.; Van de Donk, N.; Terpos, E.; Broijl, A.; De Larrea, C.F.; Gay, F.; et al. European Myeloma Network Review and Consensus Statement on Smoldering Multiple Myeloma: How to Distinguish (and Manage) Dr. Jekyll and Mr Hyde. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, N.; Roschewski, M.; Zingone, A.; Kwok, M.; Manasanch, E.E.; Bhutani, M.; Tageja, N.; Kazandjian, D.; Mailankody, S.; Wu, P.; et al. Treatment with Carfilzomib-Lenalidomide-Dexamethasone with Lenalidomide Extension in Patients with Smoldering or Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Rodriguez Otero, P.; Gonzalez-Calle, V.; Gonzalez, M.S.; Oriol, A.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Paiva, B.; Ríos Tamayo, R.; Rosinol Dachs, L.; et al. Curative Strategy (GEM-CESAR) for High-Risk Smoldering Myeloma (SMM): Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (KRd) as Induction Followed by HDT-ASCT, Consolidation with Krd and Maintenance with Rd. Blood 2019, 134, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Martinez Lopez, J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Gonzalez-Calle, V.; Gonzalez, M.S.; Oriol, A.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Rios, R.; Rosinol, L.; Alvarez, M.A.; et al. Curative Strategy (GEM-CESAR) for High-Risk Smoldering Myeloma (SMM): Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (KRd) as Induction Followed by HDT-ASCT, Consolidation with Krd and Maintenance with Rd. Blood 2021, 138, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Martínez-López, J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; San-Miguel, J.; Gonzalez-Calle, V.; Gonzalez, M.S.; Oriol, A.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Rios, R.; Rosinol Dachs, L.; et al. Curative Strategy (GEM-CESAR) for High-Risk Smoldering Myeloma (SMM): Post-Hoc Analysis of Sustained Undetectable Measurable Residual Disease (MRD). Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Musto, P.; Rota-Scalabrini, D.; Bertamini, L.; Belotti, A.; Galli, M.; Offidani, M.; Zamagni, E.; Ledda, A.; Grasso, M.; et al. Carfilzomib with Cyclophosphamide and Dexamethasone or Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone plus Autologous Transplantation or Carfilzomib plus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone, Followed by Maintenance with Carfilzomib plus Lenalidomide or Lenalidomide Alone for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (Forte): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1705–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Badros, A.Z.; Laplant, B.; Dhakal, B.; Alsina, M.; Abonour, R.; Rosenbaum, C.A.; Bensinger, W.I.; Bhutani, M.; et al. Aggressive Smoldering Curative Approach Evaluating Novel Therapies (ASCENT): A Phase 2 Trial of Induction, Consolidation and Maintenance in Subjects with High Risk Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM): Initial Analysis of Safety Data. Blood 2020, 136, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Alsina, M.; Laplant, B.; Badros, A.Z.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Abonour, R.; Asmus, E.J.; Dhakal, B.; Rosenbaum, C.A.; Egan, D.; et al. Fixed Duration Therapy with Daratumumab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone for High Risk Smoldering Multiple Myeloma-Results of the Ascent Trial. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 1830–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.; Raje, N.S.; Vij, R.; Reece, D.; Berdeja, J.G.; Stephens, L.A.; McDonnell, K.; Rosenbaum, C.A.; Jasielec, J.; Richardson, P.G.; et al. Final Results of a Phase 2 Trial of Extended Treatment (Tx) with Carfilzomib (CFZ), Lenalidomide (LEN), and Dexamethasone (KRd) Plus Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation (ASCT) in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (NDMM). Blood 2016, 128, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzeau, C.; Perrot, A.; Hulin, C.; Manier, S.; Macro, M.; Caillot, D.; Karlin, L.; Decaux, O.; Jacquet, C.; Tiab, M.; et al. Daratumumab Carfilzomib Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone as Induction Therapy in High-Risk, Transplant-Eligible Patients with Newly Diagnosed Myeloma: Results of the Phase 2 Study IFM 2018–04. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Puig, N.; Cedena, M.T.; Goicoechea, I.; Perez, C.; Garcés, J.J.; Botta, C.; Calasanz, M.J.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Martin-Ramos, M.L.; et al. A Machine Learning Model Based on Tumor and Immune Biomarkers to Predict Undetectable MRD and Survival Outcomes in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella, E.; Madeo, D.; Albiero, E.; Roberti, S.; Castaman, G.; Elice, F.; Rodeghiero, F. Effect of DCEP Mobilizing Regimen in in Vivo Purging of PBSC Harvests in Multiple Myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrash, S.; Robinson, M.; Paul, B.; Norek, S.; Foureau, D.M.; Syfert, C.A.; Ndiaye, A.P.; Symanowski, J.T.; Robinson, J.; Bhutani, M.; et al. Phase II Trial of In Vivo Purging with Daratumumab in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. S1), 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, N.; Berdeja, J.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Liedtke, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Maus, M.V.; Turka, A.; et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-Cell Therapy bb2121 in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, L.D., Jr.; Shah, N.; Jagannath, S.; Berdeja, J.G.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.S.; Siegel, D.S.D.; Lin, Y.; Oriol, A.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel (Ide-Cel; bb2121), a BCMA-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy, in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Initial KarMMa Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdeja, J.G.; Madduri, D.; Usmani, S.Z.; Singh, I.; Zudaire, E.; Yeh, T.M.; Allred, A.J.; Olyslager, Y.; Banerjee, A.; Goldberg, J.D.; et al. Update of CARTITUDE-1: A Phase Ib/II Study of JNJ-4528, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA)-Directed CAR-T-Cell Therapy, in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.F.; Anderson, K.C.; Tai, Y.T. Targeting B Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) in Multiple Myeloma: Potential Uses of BCMA-Based Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, A.; Singh, P.P.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Hwa, Y.L.; Fonder, A.L.; et al. Efficacy of VDT PACE-Like Regimens in Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.E.; Ratain, M.J.; Williams, S.F.; Golick, J.A.; Beschorner, J.C.; Fullem, L.J.; Bitran, J.D. Plasma Pharmacokinetics of High-Dose Oral Melphalan in Patients Treated with Trialkylator Chemotherapy and Autologous Bone Marrow Reinfusion. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boros, L.; Peng, Y.M.; Alberts, D.S.; Asbury, R.F.; Goodman, T.L.; Penn, T.E.; Hickox, D.E. Pharmacokinetics of Very High-Dose Oral Melphalan in Cancer Patients. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 13, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, B.L.; Samuels, J.D.; Bitran, J.D. High-Dose Intravenous Melphalan: A Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Cavallo, F.; Gay, F.; Di Raimondo, F.; Ben Yehuda, D.; Petrucci, M.T.; Pezzatti, S.; Caravita, T.; Cerrato, C.; Ribakovsky, E.; et al. Autologous Transplantation and Maintenance Therapy in Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Oliva, S.; Petrucci, M.T.; Conticello, C.; Catalano, L.; Corradini, P.; Siniscalchi, A.; Magarotto, V.; Pour, L.; Carella, A.; et al. Chemotherapy plus Lenalidomide versus Autologous Transplantation, Followed by Lenalidomide plus Prednisone versus Lenalidomide Maintenance, in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A Randomised, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavo, M.; Gay, F.; Beksac, M.; Pantani, L.; Petrucci, M.T.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dozza, L.; van der Holt, B.; Zweegman, S.; Oliva, S.; et al. Autologous Haematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation versus Bortezomib–Melphalan–Prednisone, with or without Bortezomib–Lenalidomide–Dexamethasone Consolidation Therapy, and Lenalidomide Maintenance for Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (EMN02/HO95): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e456–e468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, M.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Hulin, C.; Leleu, X.; Caillot, D.; Escoffre, M.; Arnulf, B.; Macro, M.; Belhadj, K.; Garderet, L.; et al. Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone with Transplantation for Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Jacobus, S.J.; Weller, E.A.; Hassoun, H.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.S.; Medvedova, E.; McCarthy, P.L.; Libby, E.N.; Voorhees, P.M.; et al. Triplet Therapy, Transplantation, and Maintenance until Progression in Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Corre, J.; Robillard, N.; Hulin, C.; Chretien, M.L.; Dejoie, T.; Maheo, S.; Stoppa, A.M.; Pegourie, B.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease Negativity Using Deep Sequencing Is a Major Prognostic Factor in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, P.; Pasquini, M.C.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Fraser, R.; Fei, M.; Devine, S.M.; Efebera, Y.A.; Geller, N.; Horowitz, M.M.; Koreth, J.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of BMT CTN 0702 (STaMINA) of Postautologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (AutoHCT) Strategies in the Upfront Treatment of Multiple Myeloma (MM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Hulin, C.; Perrot, A.; Arnulf, B.; Belhadj, K.; Benboubker, L.; Béné, M.C.; Zweegman, S.; Caillon, H.; Caillot, D.; et al. Maintenance with Daratumumab or Observation Following Treatment with Bortezomib, Thalidomide, and Dexamethasone with or without Daratumumab and Autologous Stem-Cell Transplant in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (Cassiopeia): An Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, G.H.; Davies, F.E.; Pawlyn, C.; Cairns, D.A.; Striha, A.; Collett, C.; Hockaday, A.; Jones, J.R.; Kishore, B.; Garg, M.; et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance versus Observation for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (Myeloma XI): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavo, M.; Pantani, L.; Petrucci, M.T.; Patriarca, F.; Zamagni, E.; Donnarumma, D.; Crippa, C.; Boccadoro, M.; Perrone, G.; Falcone, A.; et al. Bortezomib-Thalidomide-Dexamethasone Is Superior to Thalidomide-Dexamethasone as Consolidation Therapy after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.F.; Hall, A.; Smith, I.; de Tute, R.M.; Roberts, S.; Ingleson, E.; Bowles, K.M.; Garg, M.; Lokare, A.; Messiou, C.; et al. Extended Intensified Post-ASCT Consolidation with Daratumumab, Bortezomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (Dara-VRd) for Ultra-High Risk (UHiR) Newly Diagnosed Myeloma (NDMM) and Primary Plasma Cell Leukemia (PPCL): The UK Optimum/Muknine Trial. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 1833–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Lee, H.C.; Badros, A.; Trudel, S.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Abdallah, A.O.; Callander, N.; Lendvai, N.; Sborov, D.; et al. Belantamab Mafodotin for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (DREAMM-2): A Two-Arm, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, L.D.; Shah, N.; Madduri, D.; Berdeja, J.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Oriol, A.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Harrington, K.; Staehr, M.; Masakayan, R.; Jones, J.; Long, T.J.; Ng, K.Y.; Ghoddusi, M.; Purdon, T.J.; Wang, X.; et al. GPRC5D Is a Target for the Immunotherapy of Multiple Myeloma with Rationally Designed CAR T Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkleij, C.P.M.; Broekmans, M.E.C.; van Duin, M.; Frerichs, K.A.; Kuiper, R.; de Jonge, A.V.; Kaiser, M.; Morgan, G.; Axel, A.; Boominathan, R.; et al. Preclinical Activity and Determinants of Response of the GPRC5DxCD3 Bispecific Antibody Talquetamab in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2196–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaniuk, J.; Gleiss, A.; Porpaczy, E.; Kainz, B.; Grunt, T.W.; Raderer, M.; Hilgarth, B.; Drach, J.; Ludwig, H.; Gisslinger, H.; et al. Overexpression of G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5D in the Bone Marrow Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckinger, A.; Delgado, J.A.; Moser, S.; Moreno, L.; Neuber, B.; Grab, A.; Lipp, S.; Merino, J.; Prosper, F.; Emde, M.; et al. Target Expression, Generation, Preclinical Activity, and Pharmacokinetics of the BCMA-T Cell Bispecific Antibody EM801 for Multiple Myeloma Treatment. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Larrea, C.; Staehr, M.; Lopez, A.V.; Ng, K.Y.; Chen, Y.; Godfrey, W.D.; Purdon, T.J.; Ponomarev, V.; Wendel, H.G.; Brentjens, R.J.; et al. Defining an Optimal Dual-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy Approach Simultaneously Targeting BCMA and GPRC5D to Prevent BCMA Escape–Driven Relapse in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020, 1, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Stagg, N.J.; Johnston, J.; Harris, M.J.; Menzies, S.A.; DiCara, D.; Clark, V.; Hristopoulos, M.; Cook, R.; Slaga, D.; et al. Membrane-Proximal Epitope Facilitates Efficient T Cell Synapse Formation by Anti-FcRH5/CD3 and Is a Requirement for Myeloma Cell Killing. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.D.; Harrison, S.J.; Krishnan, A.; Fonseca, R.; Forsberg, P.A.; Spencer, A.; Berdeja, J.G.; Laubach, J.P.; Li, M.; Choeurng, V.; et al. Initial Clinical Activity and Safety of BFCR4350A, a FcRH5/CD3 T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.V.; Blacklock, H.; Schjesvold, F.; Oriol, A.; Simpson, D.; George, A.; Goldschmidt, H.; Larocca, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Sherbenou, D.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (KEYNOTE-183): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e459–e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.T.; Dillon, M.; Song, W.; Leiba, M.; Li, X.F.; Burger, P.; Lee, A.I.; Podar, K.; Hideshima, T.; Rice, A.G.; et al. Anti-CS1 Humanized Monoclonal Antibody HuLuc63 Inhibits Myeloma Cell Adhesion and Induces Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in the Bone Marrow Milieu. Blood 2008, 112, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Mathew, S.O.; Vaidya, S.V.; Kumaresan, P.R.; Mathew, P.A. CS1 (CRACC, CD319) Induces Proliferation and Autocrine Cytokine Expression on Human B Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4672–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Boles, K.S.; Mathew, P.A. Molecular and Functional Characterization of a CS1 (CRACC) Splice Variant Expressed in Human NK Cells That Does Not Contain Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Switch Motifs. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2791–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassi, I.; Colonna, M. The Cytotoxicity Receptor CRACC (CS−1) Recruits EAT-2 and Activates the PI3K and Phospholipase Cγ Signaling Pathways in Human NK Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7996–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awwad, M.H.S.; Mahmoud, A.; Bruns, H.; Echchannaoui, H.; Kriegsmann, K.; Lutz, R.; Raab, M.S.; Bertsch, U.; Munder, M.; Jauch, A.; et al. Selective Elimination of Immunosuppressive T Cells in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2602–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Dimopoulos, M.; Palumbo, A.; White, D.; Grosicki, S.; Spicka, I.; Walter-Croneck, A.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Magen, H.; et al. Elotuzumab Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dytfeld, D.; Grosicki, S.; Moreau, P.; Takezako, N.; Hori, M.; Leleu, X.; LeBlanc, R.; Suzuki, K.; Raab, M.S.; et al. Elotuzumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).