Gene Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Glioblastoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
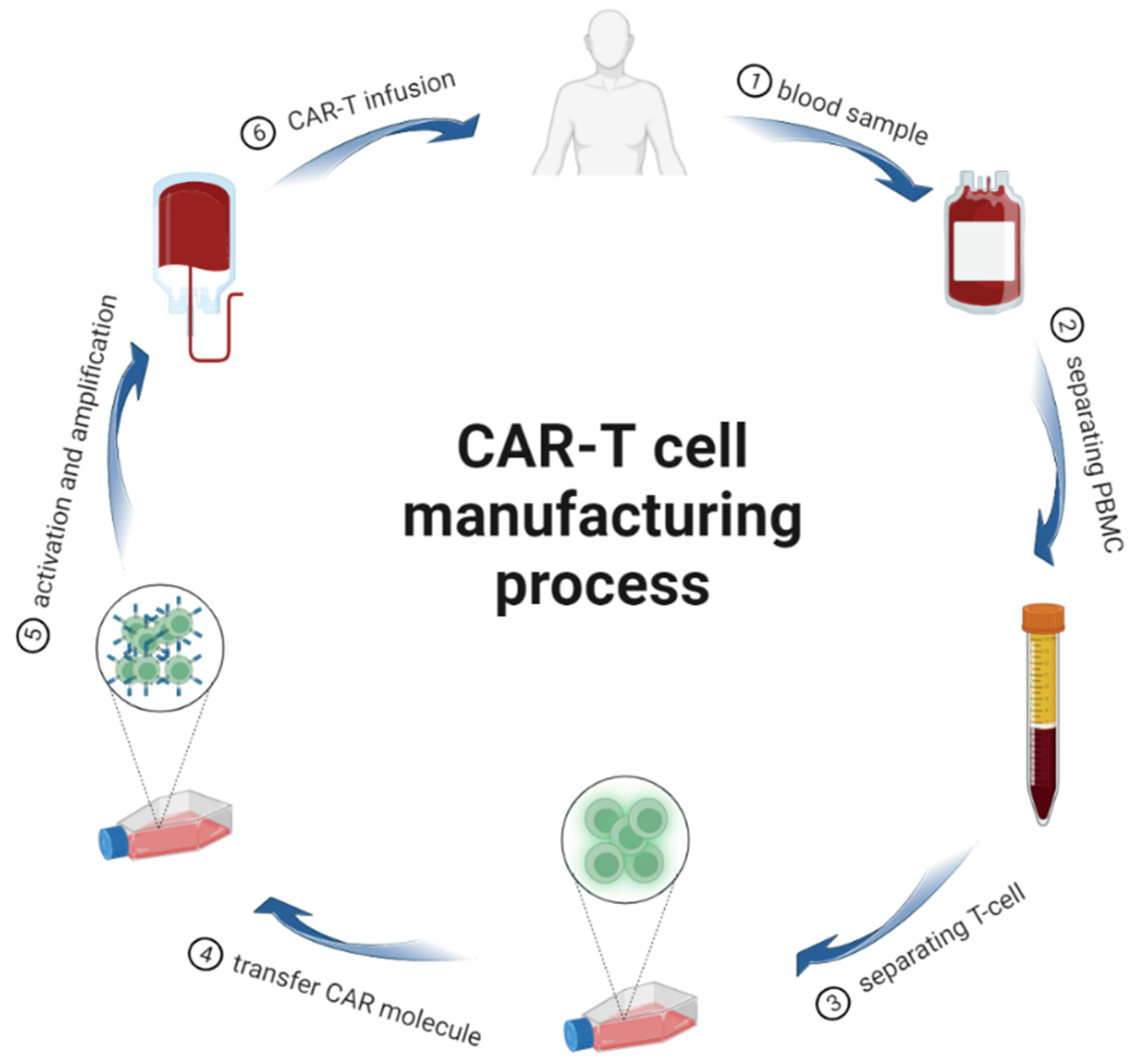
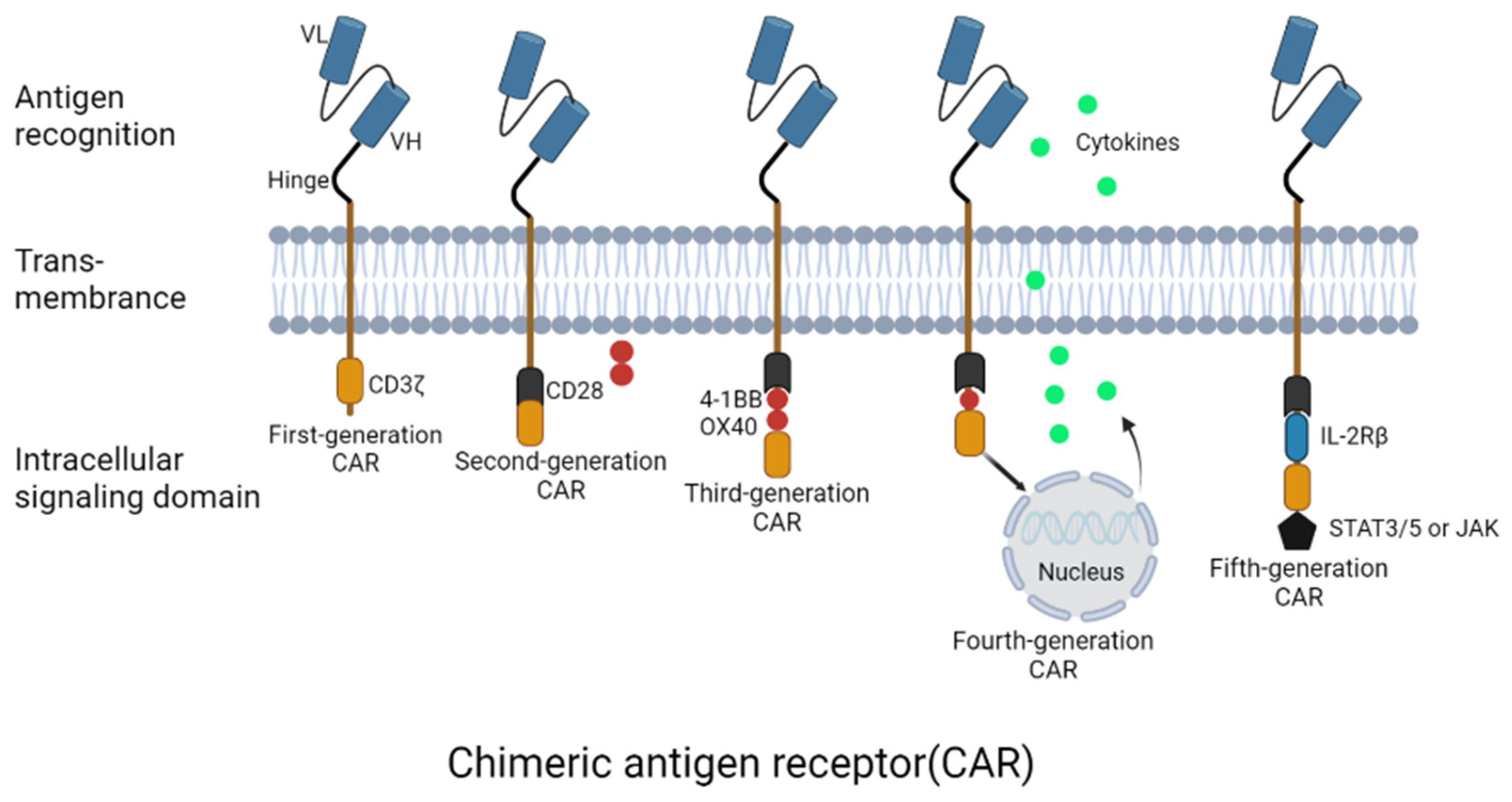
2. CAR-T Cells
3. CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematological Tumors
4. CAR-T Cell Therapy in GBM
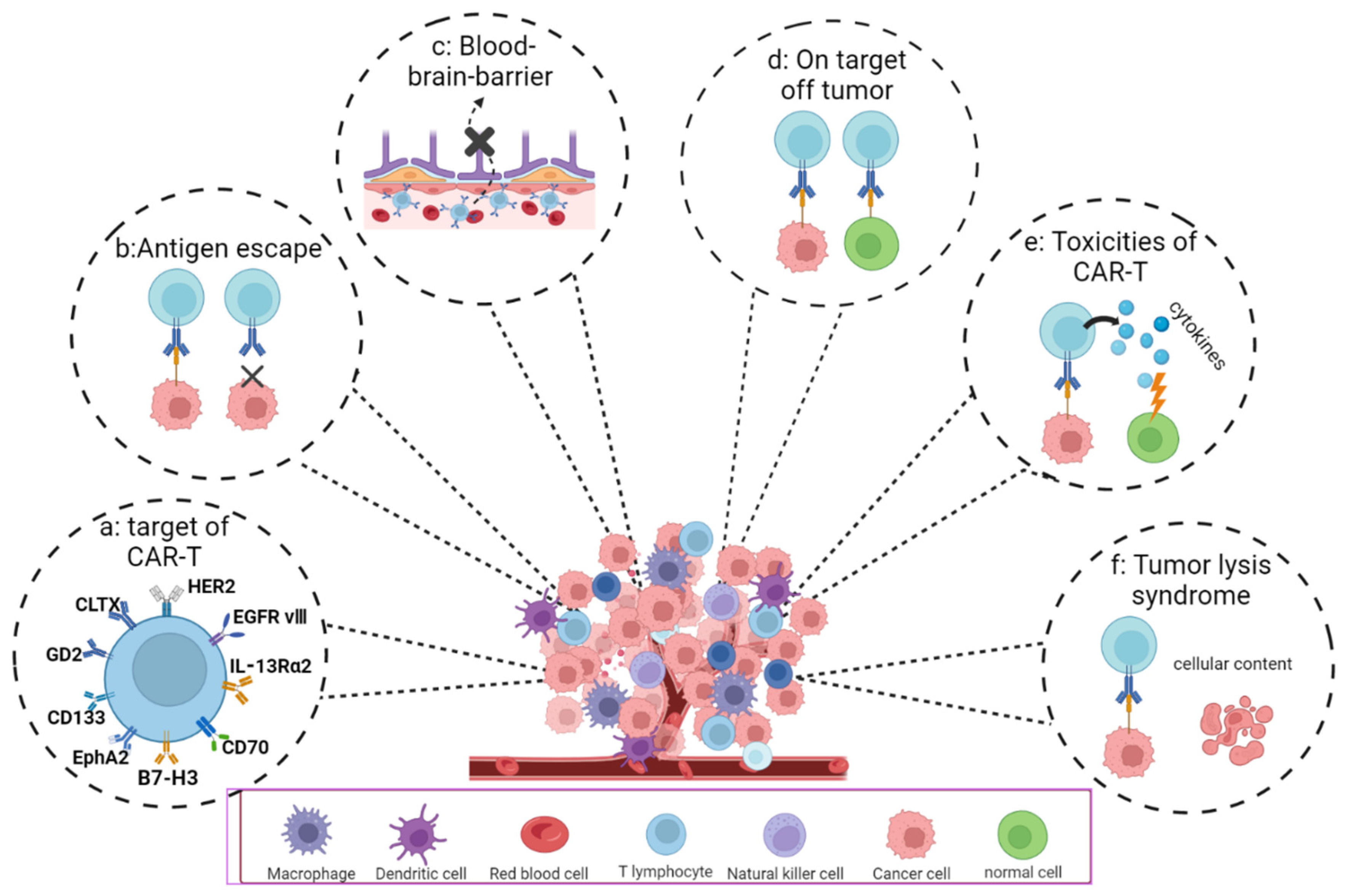
4.1. Potential Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for GBM
4.1.1. EGFR vIII
4.1.2. HER-2
4.1.3. IL-13Rα2
4.1.4. CD70
4.1.5. B7-H3
4.1.6. EphA2
4.1.7. CD133
4.1.8. GD2
4.1.9. Chlorotoxin (CLTX)
4.1.10. NKG2D
4.1.11. Some Promising Targets
4.2. Difficulties and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, S.; Tang, L.; Li, X.; Fan, F.; Liu, Z. Immunotherapy for glioma: Current management and future application. Cancer Lett. 2020, 476, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanov, G.S.; Dzhenkov, D.; Ghenev, P.; Iliev, B.; Enchev, Y.; Tonchev, A.B. Cell biology of glioblastoma multiforme: From basic science to diagnosis and treatment. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.M.; Cloughesy, T.F. Adult Glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Campian, J.L.; Clark, S.W.; Fabiano, A.J.; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2020, 18, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, A.L.; Schulte, J.D.; Okada, H.; Clarke, J.L. Current Advances in Immunotherapy for Glioblastoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, M.W.; Stupp, R.; Sonabend, A.M. Role of Resection in Glioblastoma Management. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 32, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ros, M.; De Gregorio, V.; Iorio, A.L.; Giunti, L.; Guidi, M.; de Martino, M.; Genitori, L.; Sardi, I. Glioblastoma Chemoresistance: The Double Play by Microenvironment and Blood-Brain Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labanieh, L.; Majzner, R.G.; Klysz, D.; Sotillo, E.; Fisher, C.J.; Vilches-Moure, J.G.; Pacheco, K.Z.B.; Malipatlolla, M.; Xu, P.; Hui, J.H.; et al. Enhanced safety and efficacy of protease-regulated CAR-T cell receptors. Cell 2022, 185, 1745–1763.e1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentjens, R.J.; Rivière, I.; Park, J.H.; Davila, M.L.; Wang, X.; Stefanski, J.; Taylor, C.; Yeh, R.; Bartido, S.; Borquez-Ojeda, O.; et al. Safety and persistence of adoptively transferred autologous CD19-targeted T cells in patients with relapsed or chemotherapy refractory B-cell leukemias. Blood 2011, 118, 4817–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westin, J.R.; Kersten, M.J.; Salles, G.; Abramson, J.S.; Schuster, S.J.; Locke, F.L.; Andreadis, C. Efficacy and safety of CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapies in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas: Observations from the JULIET, ZUMA-1, and TRANSCEND trials. Am. J. Hematol 2021, 96, 1295–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupp, S.A.; Kalos, M.; Barrett, D.; Aplenc, R.; Porter, D.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; Teachey, D.T.; Chew, A.; Hauck, B.; Wright, J.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, A.; Webster, R.M. The market for chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtane, K.; Elmariah, H.; Chung, C.H.; Abate-Daga, D. Adoptive cellular therapy in solid tumor malignancies: Review of the literature and challenges ahead. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, C.M.; Gedeon, P.C.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Verla, T.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.; Choi, B.D.; Fecci, P.E.; Sampson, J.H. Are BiTEs the “missing link” in cancer therapy? Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1008339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettini, F.; Barbao, P.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Galván, P.; Martínez, D.; Paré, L.; De Placido, S.; Prat, A.; Guedan, S. Identification of cell surface targets for CAR-T cell therapies and antibody-drug conjugates in breast cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Clubb, J.D.; Chen, Y.Y. Engineering CAR-T Cells for Next-Generation Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.; Rivière, I. The promise and potential pitfalls of chimeric antigen receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Frey, N.V.; Engels, B.; Barrett, D.M.; Shestova, O.; Ravikumar, P.; Cummins, K.D.; Lee, Y.G.; Pajarillo, R.; Chun, I.; et al. Antigen-independent activation enhances the efficacy of 4-1BB-costimulated CD22 CAR T cells. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, E.; Boucher, J.C.; Li, G.; Kotani, H.; Spitler, K.; Reid, K.; Cervantes, E.V.; Bulliard, Y.; Tu, N.; Lee, S.B.; et al. 4-1BB and optimized CD28 co-stimulation enhances function of human mono-specific and bi-specific third-generation CAR T cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramello, M.C.; Benzaïd, I.; Kuenzi, B.M.; Lienlaf-Moreno, M.; Kandell, W.M.; Santiago, D.N.; Pabón-Saldaña, M.; Darville, L.; Fang, B.; Rix, U.; et al. An immunoproteomic approach to characterize the CAR interactome and signalosome. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaap9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Feldman, S.A.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Black, M.A.; Morgan, R.A.; Wilson, W.H.; Rosenberg, S.A. Construction and preclinical evaluation of an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor. J. Immunother. 2009, 32, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feins, S.; Kong, W.; Williams, E.F.; Milone, M.C.; Fraietta, J.A. An introduction to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Universal CARs, universal T cells, and universal CAR T cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.M.; Li, Y.; Barz Leahy, A.; Barrett, D.M.; Teachey, D.T.; Callahan, C.; Fasano, C.C.; Rheingold, S.R.; DiNofia, A.; Wray, L.; et al. Humanized CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in CAR-Naive and CAR-Exposed Children and Young Adults With Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3044–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, S.R.; Velasco-Hernandez, T.; Gutierrez-Agüera, F.; Díaz, V.M.; Romecín, P.A.; Roca-Ho, H.; Sánchez-Martínez, D.; Tirado, N.; Baroni, M.L.; Petazzi, P.; et al. A novel and efficient tandem CD19- and CD22-directed CAR for B cell ALL. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022, 30, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xu, P.; Wang, E.; Zhou, M.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Lu, K.; Wang, C.; et al. Novel two-chain structure utilizing KIRS2/DAP12 domain improves the safety and efficacy of CAR-T cells in adults with r/r B-ALL. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 23, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, R.L.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.L.; Song, Y.P.; Yang, T.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Donor-derived CD19 CAR-T cell therapy of relapse of CD19-positive B-ALL post allotransplant. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Pan, J.; Deng, B.; Ling, Z.; Song, W.; Xu, J.; Duan, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Chang, A.H.; et al. Toxicity and effectiveness of CD19 CAR T therapy in children with high-burden central nervous system refractory B-ALL. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2021, 70, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcantara, M.; Tesio, M.; June, C.H.; Houot, R. CAR T-cells for T-cell malignancies: Challenges in distinguishing between therapeutic, normal, and neoplastic T-cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Eradication of T-ALL Cells by CD7-targeted Universal CAR-T Cells and Initial Test of Ruxolitinib-based CRS Management. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teachey, D.T.; Hunger, S.P. Anti-CD7 CAR T cells for T-ALL: Impressive early-stage efficacy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Jin, D.; Li, J.; et al. Naturally selected CD7 CAR-T therapy without genetic manipulations for T-ALL/LBL: First-in-human phase 1 clinical trial. Blood 2022, 140, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, D.; Fu, X.; Meng, H.; Nan, F.; Sun, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Li, X.; et al. Autologous Nanobody-Derived Fratricide-Resistant CD7-CAR T-cell Therapy for Patients with Relapsed and Refractory T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2830–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cen, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Leng, Y.; Ren, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. CAR T cells targeting CD99 as an approach to eradicate T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia without normal blood cells toxicity. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciocia, P.M.; Pule, M.A. Anti-CD1a CAR T cells to selectively target T-ALL. Blood 2019, 133, 2246–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battram, A.M.; Bachiller, M.; Lopez, V.; Fernández de Larrea, C.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Martín-Antonio, B. IL-15 Enhances the Persistence and Function of BCMA-Targeting CAR-T Cells Compared to IL-2 or IL-15/IL-7 by Limiting CAR-T Cell Dysfunction and Differentiation. Cancers 2021, 13, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Li, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z.; Jin, D.; Guo, T.; Kou, H.; Liu, L.; Tang, L.; et al. A bispecific CAR-T cell therapy targeting BCMA and CD38 in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidaway, P. Combining CAR T cells effective in RRMM. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.D.; Garfall, A.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Lancaster, E.; Vogl, D.T.; Weiss, B.M.; Dengel, K.; Nelson, A.; et al. B cell maturation antigen-specific CAR T cells are clinically active in multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Qin, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; et al. Claudin18.2-specific CAR T cells in gastrointestinal cancers: Phase 1 trial interim results. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, V.; Barber-Rotenberg, J.S.; Jung, I.Y.; Lacey, S.F.; Rech, A.J.; Davis, M.M.; Hwang, W.T.; Lal, P.; Carpenter, E.L.; Maude, S.L.; et al. PSMA-targeting TGFβ-insensitive armored CAR T cells in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, N.; Shi, J.; Qin, L.; Chen, A.; Tang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; He, B.; et al. IL-7 and CCL19-secreting CAR-T cell therapy for tumors with positive glypican-3 or mesothelin. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggs, L.; Cattaneo, G.; Dal, A.E.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Ferrone, S. CAR T Cell-Based Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 662064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Alizadeh, D.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Wagner, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; Blanchard, M.S.; Kilpatrick, J.; Simpson, J.; et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Asif, J.A.; Alam, M.K.; Slots, J. A bibliometric analysis of Periodontology 2000. Periodontology 2000 2020, 82, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, M.P.; Bartlett, N.L. CD19-targeted immunotherapies for treatment of patients with non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.H.; Shrestha, G.; Robison, R.A.; O’Neill, K.L. The expansion of targetable biomarkers for CAR T cell therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejo, T.; Yamamichi, A.; Almeida, N.D.; Goretsky, Y.E.; Okada, H. Tumor antigens in glioma. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 47, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F. Targeting Tumor-Associated Antigen: A Promising CAR-T Therapeutic Strategy for Glioblastoma Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 661606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Janczyk, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, A.; Shi, X.; Singh, S.; Facemire, L.; Kubow, K.; Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; et al. A cytoskeleton regulator AVIL drives tumorigenesis in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhu, H.; Ali-Osman, F.; Lo, H.W. EGFR and EGFRvIII undergo stress- and EGFR kinase inhibitor-induced mitochondrial translocalization: A potential mechanism of EGFR-driven antagonism of apoptosis. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawa, N.; Ekstrand, A.J.; James, C.D.; Collins, V.P. Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human glioblastomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8602–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrand, C.J.; Hale, L.P.; Batra, S.K.; Hill, M.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Kurpad, S.N.; McLendon, R.E.; Moscatello, D.; Pegram, C.N.; Reist, C.J.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies against EGFRvIII are tumor specific and react with breast and lung carcinomas and malignant gliomas. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moscatello, D.K.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Godwin, A.K.; Ramirez, G.; Gunn, G.; Zoltick, P.W.; Biegel, J.A.; Hayes, R.L.; Wong, A.J. Frequent expression of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in multiple human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5536–5539. [Google Scholar]
- Viana-Pereira, M.; Lopes, J.M.; Little, S.; Milanezi, F.; Basto, D.; Pardal, F.; Jones, C.; Reis, R.M. Analysis of EGFR overexpression, EGFR gene amplification and the EGFRvIII mutation in Portuguese high-grade gliomas. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Schaff, L.R.; Yan, D.; Thyparambil, S.; Tian, Y.; Cecchi, F.; Rosenblum, M.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Hembrough, T.; Lin, A.L. Characterization of MGMT and EGFR protein expression in glioblastoma and association with survival. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 146, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikstrand, C.J.; McLendon, R.E.; Friedman, A.H.; Bigner, D.D. Cell surface localization and density of the tumor-associated variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFRvIII. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4130–4140. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Choi, B.D.; Suryadevara, C.M.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Yang, S.; De Leon, G.; Sayour, E.J.; McLendon, R.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Healy, P.; et al. EGFRvIII-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells migrate to and kill tumor deposits infiltrating the brain parenchyma in an invasive xenograft model of glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.C.; Verdon, D.J.; Gracey, F.M.; Hughes-Parry, H.E.; Iliopoulos, M.; Watson, K.A.; Mulazzani, M.; Luong, K.; D’Arcy, C.; Sullivan, L.C.; et al. Novel high-affinity EGFRvIII-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells effectively eliminate human glioblastoma. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agliardi, G.; Liuzzi, A.R.; Hotblack, A.; De Feo, D.; Núñez, N.; Stowe, C.L.; Friebel, E.; Nannini, F.; Rindlisbacher, L.; Roberts, T.A.; et al. Intratumoral IL-12 delivery empowers CAR-T cell immunotherapy in a pre-clinical model of glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hu, X.; Feng, K.; Gao, R.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Corse, E.; Hu, Y.; Han, W.; et al. Temporal single-cell tracing reveals clonal revival and expansion of precursor exhausted T cells during anti-PD-1 therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, D.; Okazaki, I.M.; Maeda, T.K.; Maruhashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Arakaki, R.; Takemoto, T.; Ishimaru, N.; Okazaki, T. PD-1 agonism by anti-CD80 inhibits T cell activation and alleviates autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.D.; Yu, X.; Castano, A.P.; Darr, H.; Henderson, D.B.; Bouffard, A.A.; Larson, R.C.; Scarfò, I.; Bailey, S.R.; Gerhard, G.M.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 disruption of PD-1 enhances activity of universal EGFRvIII CAR T cells in a preclinical model of human glioblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ying, H.; Zeng, G.; Wheeler, C.J.; Black, K.L.; Yu, J.S. HER-2, gp100, and MAGE-1 are expressed in human glioblastoma and recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4980–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Salsman, V.S.; Kew, Y.; Shaffer, D.; Powell, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Grossman, R.G.; Heslop, H.E.; Gottschalk, S. HER2-specific T cells target primary glioblastoma stem cells and induce regression of autologous experimental tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Brawley, V.; Hegde, M.; Bielamowicz, K.; Kalra, M.; Landi, D.; Robertson, C.; Gray, T.L.; Diouf, O.; Wakefield, A.; et al. HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified Virus-Specific T Cells for Progressive Glioblastoma: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanza, N.A.; Johnson, A.J.; Wilson, A.L.; Brown, C.; Yokoyama, J.K.; Künkele, A.; Chang, C.A.; Rawlings-Rhea, S.; Huang, W.; Seidel, K.; et al. Locoregional infusion of HER2-specific CAR T cells in children and young adults with recurrent or refractory CNS tumors: An interim analysis. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaci, B.; Brown, C.E.; Binello, E.; Werbaneth, K.; Sampath, P.; Sengupta, S. Significance of interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2-targeted glioblastoma therapy. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debinski, W.; Gibo, D.M.; Hulet, S.W.; Connor, J.R.; Gillespie, G.Y. Receptor for interleukin 13 is a marker and therapeutic target for human high-grade gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, D.; Wong, R.A.; Gholamin, S.; Maker, M.; Aftabizadeh, M.; Yang, X.; Pecoraro, J.R.; Jeppson, J.D.; Wang, D.; Aguilar, B.; et al. IFNγ Is Critical for CAR T Cell-Mediated Myeloid Activation and Induction of Endogenous Immunity. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2248–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Young, J.S.; Solomaha, E.; Kanojia, D.; Lesniak, M.S.; Balyasnikova, I.V. A novel single-chain antibody redirects adenovirus to IL13Rα2-expressing brain tumors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, M.V.; Haas, A.R.; Beatty, G.L.; Albelda, S.M.; Levine, B.L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kalos, M.; June, C.H. T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors can cause anaphylaxis in humans. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Bai, Y.; An, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, X. IL-13Rα2 humanized scFv-based CAR-T cells exhibit therapeutic activity against glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Rodriguez, A.; Palmer, J.; Ostberg, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Wagner, J.R.; Aguilar, B.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Synold, T.W.; et al. Off-the-shelf, steroid-resistant, IL13Rα2-specific CAR T cells for treatment of glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Sagert, J.; Pham, M.T.; Will, M.; Henderson, D.; Tipton, K.; Iyer, S.; Lu, W.; Khan, K.B.; Hamana, L.; et al. CD70 is a potential target biomarker in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Histopathology 2022, 81, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held-Feindt, J.; Mentlein, R. CD70/CD27 ligand, a member of the TNF family, is expressed in human brain tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ge, H.; Long, Y.; Yang, C.; Chang, Y.E.; Mu, L.; Sayour, E.J.; De Leon, G.; Wang, Q.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. CD70, a novel target of CAR T-cell therapy for gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfrid, M.; Maich, W.T.; Shaikh, V.M.; Tatari, N.; Upreti, D.; Piyasena, D.; Subapanditha, M.; Savage, N.; McKenna, D.; Mikolajewicz, N.; et al. CD70 as an actionable immunotherapeutic target in recurrent glioblastoma and its microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, G.; Su, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, F. Enhancement of CD70-specific CAR T treatment by IFN-γ released from oHSV-1-infected glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2022, 71, 2433–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Yang, M.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Guo, G.; Tong, A.P.; et al. B7-H3 as a Novel CAR-T Therapeutic Target for Glioblastoma. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2019, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, W.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. Administration of B7-H3 targeted chimeric antigen receptor-T cells induce regression of glioblastoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, N.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Lu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, B.; et al. CXCL11-armed oncolytic adenoviruses enhance CAR-T cell therapeutic efficacy and reprogram tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2023, 31, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.Y.; Xiao, Z.; Su, M. Targeting EphA2 in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Q.J.; Fu, Z.; He, J.; Mao, M.; Yao, X.X.; Qin, Y.; Lan, X.; Zhang, L.; Miao, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. EPHA2 mediates PDGFA activity and functions together with PDGFRA as prognostic marker and therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Hu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Kang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Antitumor activity of the third generation EphA2 CAR-T cells against glioblastoma is associated with interferon gamma induced PD-L1. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1960728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ba, T.; Ho, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, G.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. First-in-Human Trial of EphA2-Redirected CAR T-Cells in Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma: A Preliminary Report of Three Cases at the Starting Dose. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 694941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Salim, S.K.; Tatari, N.; Bakhshinyan, D.; Singh, M.; Seyfrid, M.; Upreti, D.; Rentas, S.; Wong, N.; et al. The Rational Development of CD133-Targeting Immunotherapies for Glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 832–844.e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, M.D.; Read, K.A.; Sreekumar, B.K.; Oestreich, K.J. Ikaros Zinc Finger Transcription Factors: Regulators of Cytokine Signaling Pathways and CD4(+) T Helper Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Tang, J.; Jing, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhu, X.; Chi, T. IKZF3 deficiency potentiates chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting solid tumors. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, F.; Xu, H.; Ren, P.; Bai, F.; Niedermann, G.; Zhu, X. BAY 60-6583 Enhances the Antitumor Function of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells Independent of the Adenosine A2b Receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 619800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, K.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Jin, X.; Song, S.Y.; Kong, D.S.; Lee, J.I.; Jeon, J.W.; Kim, M.H.; Kang, B.G.; Jung, Y.; et al. Clinical and biological implications of CD133-positive and CD133-negative cells in glioblastomas. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2008, 88, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, S.; Haile, S.T.; Beinat, C.; Aalipour, A.; Alam, I.S.; Murty, T.; Shaffer, T.M.; Patel, C.B.; Graves, E.E.; Mackall, C.L.; et al. Intravital imaging reveals synergistic effect of CAR T-cells and radiation therapy in a preclinical immunocompetent glioblastoma model. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1757360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzner, R.G.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yeom, K.W.; Patel, S.; Chinnasamy, H.; Schultz, L.M.; Richards, R.M.; Jiang, L.; Barsan, V.; Mancusi, R.; et al. GD2-CAR T cell therapy for H3K27M-mutated diffuse midline gliomas. Nature 2022, 603, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Starr, R.; Chang, W.C.; Aguilar, B.; Alizadeh, D.; Wright, S.L.; Yang, X.; Brito, A.; Sarkissian, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; et al. Chlorotoxin-directed CAR T cells for specific and effective targeting of glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; An, C.; Zhu, H.; Wu, P.; Hu, W.; Qin, R.; Yao, D.; et al. NKG2D discriminates diverse ligands through selectively mechano-regulated ligand conformational changes. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.D.; Sun, L. Recent Advances in Molecular Mechanisms of the NKG2D Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Metais, J.Y.; Escudero, A.; Vela, M.; Valentín, J.; Vallcorba, I.; Leivas, A.; Torres, J.; Valeri, A.; Patiño-García, A.; et al. Memory T Cells Expressing an NKG2D-CAR Efficiently Target Osteosarcoma Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5824–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Sun, B.; Dai, H.; Li, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, X. T cells expressing NKG2D chimeric antigen receptors efficiently eliminate glioblastoma and cancer stem cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, H.; Look, T.; Roth, P.; Pascolo, S.; Sahin, U.; Lee, S.; Hale, B.D.; Snijder, B.; Regli, L.; Ravi, V.M.; et al. Multifunctional mRNA-Based CAR T Cells Display Promising Antitumor Activity Against Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenckhan, A.; Freytag, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Sauter, G.; Izbicki, J.R.; Gros, S.J. CAIX furthers tumour progression in the hypoxic tumour microenvironment of esophageal carcinoma and is a possible therapeutic target. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.R.; Liu, Y.S.; Lai, S.W.; Lin, H.J.; Shen, C.K.; Yang, L.Y.; Lu, D.Y. CAIX Regulates GBM Motility and TAM Adhesion and Polarization through EGFR/STAT3 under Hypoxic Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Dmitriev, P.; Sun, M.Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Indig, I.H.; et al. Targeting hypoxia downstream signaling protein, CAIX, for CAR T-cell therapy against glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, H.; Medina, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Indig, I.H.; Zhou, J.; Song, Q.; Dmitriev, P.; Sun, M.Y.; et al. Inhibition of PP2A with LB-100 Enhances Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy Against Glioblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, K.A.; Graves, S.A.; Buatti, J.M. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Theranostics for Treatment of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, L.; Feng, M.; Chen, X.; Hao, B.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cao, Y. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Promotes Angiogenesis of Glioblastoma Through Interacting With ITGB4 and Regulating NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 598377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann-Morvinski, D. Glioblastoma heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2014, 19, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, M.A.; Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Sidhu, S.S.; Moffat, J.; Swanton, C.; Singh, S.K. Intratumoral heterogeneity: Pathways to treatment resistance and relapse in human glioblastoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.H.; Watchmaker, P.B.; Simic, M.S.; Gilbert, R.D.; Li, A.W.; Krasnow, N.A.; Downey, K.M.; Yu, W.; Carrera, D.A.; Celli, A.; et al. SynNotch-CAR T cells overcome challenges of specificity, heterogeneity, and persistence in treating glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Lee, D.Y.; Eacret, J.S.; Ye, D.; June, C.H.; Minn, A.J. The immunostimulatory RNA RN7SL1 enables CAR-T cells to enhance autonomous and endogenous immune function. Cell 2021, 184, 4981–4995.e4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Limsakul, P.; Zhu, L.; Allen, M.; Pan, Y.; et al. Control of the activity of CAR-T cells within tumours via focused ultrasound. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1336–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.C.; Neelapu, S.S.; Giavridis, T.; Sadelain, M. Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.; Porter, D. Cytokine Release Syndrome with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, e123–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, R.M.; Frigault, M.J.; Fradley, M.G.; Jain, M.D.; Mahmood, S.S.; Awadalla, M.; Lee, D.H.; Zlotoff, D.A.; Zhang, L.; Drobni, Z.D.; et al. Cardiovascular Events Among Adults Treated With Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells (CAR-T). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrli, M.; Gallagher, K.; Chen, Y.B.; Leick, M.B.; McAfee, S.L.; El-Jawahri, A.R.; DeFilipp, Z.; Horick, N.; O’Donnell, P.; Spitzer, T.; et al. Single-center experience using anakinra for steroid-refractory immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Shang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic Potential of TNFα and IL1β Blockade for CRS/ICANS in CAR-T Therapy via Ameliorating Endothelial Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 623610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S.C.; Fehse, B.; Akyüz, N.; Geffken, M.; Wolschke, C.; Janson, D.; Gagelmann, N.; Luther, M.; Wichmann, D.; Frenzel, C.; et al. Molecular monitoring of T-cell kinetics and migration in severe neurotoxicity after real-world CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy. Haematologica 2022, 108, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halyabar, O.; Chang, M.H.; Schoettler, M.L.; Schwartz, M.A.; Baris, E.H.; Benson, L.A.; Biggs, C.M.; Gorman, M.; Lehmann, L.; Lo, M.S.; et al. Calm in the midst of cytokine storm: A collaborative approach to the diagnosis and treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and macrophage activation syndrome. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2019, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, P.J.; Roddie, C.; Bader, P.; Basak, G.W.; Bonig, H.; Bonini, C.; Chabannon, C.; Ciceri, F.; Corbacioglu, S.; Ellard, R.; et al. Management of adults and children receiving CAR T-cell therapy: 2021 best practice recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of ISCT and EBMT (JACIE) and the European Haematology Association (EHA). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2022, 33, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, D.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Stupp, R.; Linette, G.P.; Posey, A.D., Jr.; June, C.H. CAR T-Cell Therapies in Glioblastoma: A First Look. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargett, T.; Ebert, L.M.; Truong, N.T.H.; Kollis, P.M.; Sedivakova, K.; Yu, W.; Yeo, E.C.F.; Wittwer, N.L.; Gliddon, B.L.; Tea, M.N.; et al. GD2-targeting CAR-T cells enhanced by transgenic IL-15 expression are an effective and clinically feasible therapy for glioblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Kuehle, J.; Dragon, A.C.; Galla, M.; Kloth, C.; Rudek, L.S.; Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Neyazi, B.; Moritz, T.; Meyer, J.; et al. Design and Characterization of an “All-in-One” Lentiviral Vector System Combining Constitutive Anti-G(D2) CAR Expression and Inducible Cytokines. Cancers 2020, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shou, P.; Smith, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Sun, C.; Porterfield Kren, N.; Michaud, D.; Ahn, S.; Vincent, B.; et al. Interleukin-23 engineering improves CAR T cell function in solid tumors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, L.; Bowman, R.L.; Tessier, J.; Klemm, F.; Handgraaf, S.M.; de Groot, M.; Quail, D.F.; Tillard, L.; Gadiot, J.; Huse, J.T.; et al. Dynamic changes in glioma macrophage populations after radiotherapy reveal CSF-1R inhibition as a strategy to overcome resistance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.; Wang, L.S.; Scholler, J.; Monslow, J.; Avery, D.; Newick, K.; O’Brien, S.; Evans, R.A.; Bajor, D.J.; Clendenin, C.; et al. Tumor-Promoting Desmoplasia Is Disrupted by Depleting FAP-Expressing Stromal Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.K.; Noguera-Ortega, E.; Xiao, Z.; Todd, L.; Scholler, J.; Song, D.; Liousia, M.; Lohith, K.; Xu, K.; Edwards, K.J.; et al. Monitoring Therapeutic Response to Anti-FAP CAR T Cells Using [18F]AlF-FAPI-74. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5330–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer Type | Target | Clinical Trial Phase | Main ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glioblastoma | EGFR vIII IL13Ra2 HER2 B7H3 CD70 GD2 MMP2 NKG2D | Phase I/Phase II Phase I Phase I Phase I/Phase II Phase I Phase I Not Applicable Phase I Phase I | NCT01454596 NCT04661384 NCT03500991 NCT04077866 NCT05366179 NCT05353530 ACTRN12622001514796 NCT05627323 NCT05131763 |
| Gastrointestinal cancers | Claudin 18.2 CEA IM92 | Phase I/Phase II Phase I/Phase II Early Phase I | NCT04404595 NCT05538195 NCT05275062 |
| Lung cancer | GD2 B7H3 EGFR | Early Phase I Early Phase I Early Phase I | NCT05620342 NCT05341492 NCT05060796 |
| Colorectal cance | CEA NKG2D | Phase I Phase I | NCT05240950 ChiCTR2100053018 |
| Malignant pleural diseases | IL13Ra2 | Phase I | NCT04119024 |
| Renal cancer | CAIX CD70 | Phase I Phase I | NCT04969354 NCT05420519 |
| HCC | glypican-3 | Phase I/Phase II | NCT05003895 |
| Ovarian cancer | Mesothelin B7H3 TAG72 | 0 Phase I/Phase II Phase I | ChiCTR2100042320 NCT05211557 NCT05225363 |
| Prostatic cancer | PSMA PSCA | Phase I Phase I | NCT05354375 NCT03873805 |
| Metastatic melanoma | IL13Ra2 | Phase I | NCT04119024 |
| Breast Cancer | Mesothelin MCU1 | Phase I Phase I/Phase II | NCT05623488 NCT02617134 |
| Pancreatic cancer | IM92 B7H3 Claudin18.2 | Early Phase I Phase I/Phase II Phase I/Phase II | NCT05275062 NCT05143151 NCT04404595 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Chen, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Qiu, S.; Jian, Z.; et al. Gene Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Glioblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082351
Wang C, Li Y, Gu L, Chen R, Zhu H, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Feng S, Qiu S, Jian Z, et al. Gene Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082351
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chaoqun, Yuntao Li, Lijuan Gu, Ran Chen, Hua Zhu, Xu Zhang, Yonggang Zhang, Shi Feng, Sheng Qiu, Zhihong Jian, and et al. 2023. "Gene Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Glioblastoma" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082351
APA StyleWang, C., Li, Y., Gu, L., Chen, R., Zhu, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Feng, S., Qiu, S., Jian, Z., & Xiong, X. (2023). Gene Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Glioblastoma. Cancers, 15(8), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082351








