Comparing Detection Schemes for Adversarial Images against Deep Learning Models for Cancer Imaging
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Declaration
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Models
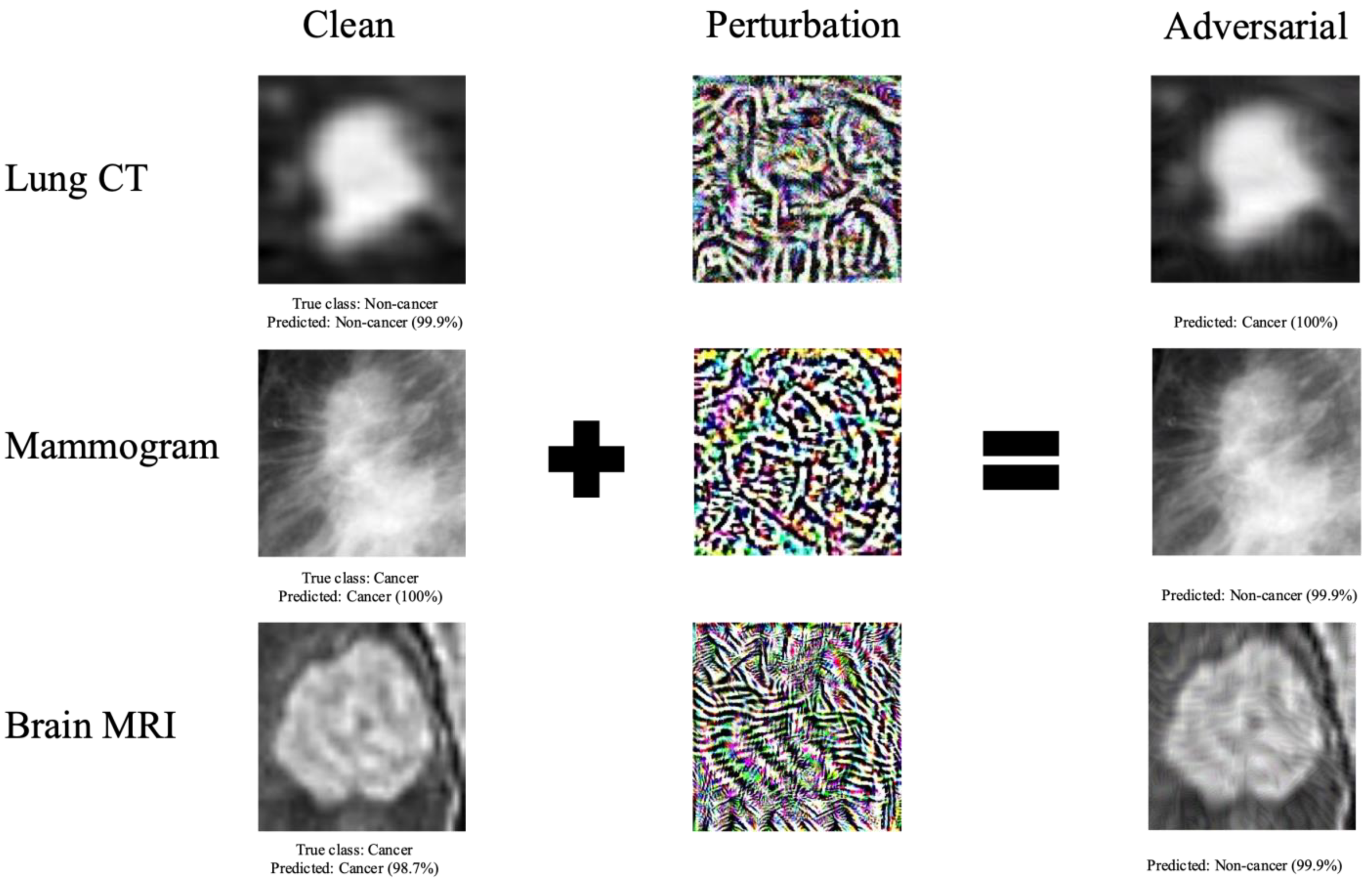
2.4. Adversarial Image Generation
2.5. Adversarial Detection
2.6. Comparison of Approaches on Improving Classification Accuracy
2.7. Code Availability
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, E.; Joel, M.Z.; Chang, H.Y.; Du, J.; Khanna, O.; Omuro, A.; Chiang, V.; Aneja, S. Comparison of radiomic feature aggregation methods for patients with multiple tumors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, H.; Koga, K.; Takemoto, K. Vulnerability of deep neural networks for detecting COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images to universal adversarial attacks. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, X. Deep learning for COVID-19 detection based on CT images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkus, Z.; Galimzianova, A.; Hoogi, A.; Rubin, D.L.; Erickson, B.J. Deep Learning for Brain MRI Segmentation: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesta, A.; Hossain, S.; Lin, M.; Aboian, M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Aneja, S. Comparing 3D, 2.5D, and 2D Approaches to Brain Image Auto-Segmentation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamens, S.; Dhunnoo, P.; Meskó, B. The state of artificial intelligence-based FDA-approved medical devices and algorithms: An online database. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, D. Robust Detection of Adversarial Attacks on Medical Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 1154–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Potnis, K.C.; Ross, J.S.; Aneja, S.; Gross, C.P.; Richman, I.B. Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer Screening: Evaluation of FDA Device Regulation and Future Recommendations. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, S.G.; Bowers, J.D.; Ito, J.; Zittrain, J.L.; Beam, A.L.; Kohane, I.S. Adversarial attacks on medical machine learning. Science 2019, 363, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaham, U.; Yamada, Y.; Negahban, S. Understanding adversarial training: Increasing local stability of supervised models through robust optimization. Neurocomputing 2018, 307, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6199. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, H.; Shi, R.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z. Adversarial Image Generation and Training for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.03243. [Google Scholar]
- Tabacof, P.; Valle, E. Exploring the Space of Adversarial Images. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.05328. [Google Scholar]
- Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.; Tsipras, D.; Vladu, A. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06083. [Google Scholar]
- Minagi, A.; Hirano, H.; Takemoto, K. Natural Images Allow Universal Adversarial Attacks on Medical Image Classification Using Deep Neural Networks with Transfer Learning. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortsova, G.; González-Gonzalo, C.; Wetstein, S.C.; Dubost, F.; Katramados, I.; Hogeweg, L.; Liefers, B.; van Ginneken, B.; Pluim, J.P.W.; Veta, M.; et al. Adversarial attack vulnerability of medical image analysis systems: Unexplored factors. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolidis, K.D.; Papakostas, G.A. A Survey on Adversarial Deep Learning Robustness in Medical Image Analysis. Electronics 2021, 10, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, M.Z.; Umrao, S.; Chang, E.; Choi, R.; Yang, D.X.; Duncan, J.S.; Omuro, A.; Herbst, R.; Krumholz, H.M.; Aneja, S. Using Adversarial Images to Assess the Robustness of Deep Learning Models Trained on Diagnostic Images in Oncology. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2022, 6, e2100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsipras, D.; Santurkar, S.; Engstrom, L.; Turner, A.; Madry, A. Robustness may be at odds with accuracy. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.12152. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, H.; Minagi, A.; Takemoto, K. Universal adversarial attacks on deep neural networks for medical image classification. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato III, S.G.; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.S.; Gimenez, F.; Hoogi, A.; Miyake, K.K.; Gorovoy, M.; Rubin, D.L. A curated mammography data set for use in computer-aided detection and diagnosis research. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6572. [Google Scholar]
- Kurakin, A.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Bengio, S. Adversarial examples in the physical world. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.02533. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M. Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolae, M.-I.; Sinn, M.; Tran, M.N.; Buesser, B.; Rawat, A.; Wistuba, M.; Zantedeschi, V.; Baracaldo, N.; Chen, B.; Ludwig, H. Adversarial Robustness Toolbox v1. 0.0. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01069. [Google Scholar]
- Kyono, T.; Gilbert, F.J.; van der Schaar, M. MAMMO: A Deep Learning Solution for Facilitating Radiologist-Machine Collaboration in Breast Cancer Diagnosis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.02661. [Google Scholar]
- Park, A.; Chute, C.; Rajpurkar, P.; Lou, J.; Ball, R.L.; Shpanskaya, K.; Jabarkheel, R.; Kim, L.H.; McKenna, E.; Tseng, J.; et al. Deep Learning–Assisted Diagnosis of Cerebral Aneurysms Using the HeadXNet Model. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, B.; Pezeshk, A.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Wang, X.; Drukker, K.; Cha, K.H.; Summers, R.M.; Giger, M.L. Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e1–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Niu, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bailey, J.; Lu, F. Understanding adversarial attacks on deep learning based medical image analysis systems. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 110, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari Laleh, N.; Truhn, D.; Veldhuizen, G.P.; Han, T.; van Treeck, M.; Buelow, R.D.; Langer, R.; Dislich, B.; Boor, P.; Schulz, V.; et al. Adversarial attacks and adversarial robustness in computational pathology. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Pan, D.; Zhu, D. Defending against adversarial attacks on medical imaging AI system, classification or detection? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13555. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Shih, F.Y.; Chang, I.C. Adaptive Image Reconstruction for Defense Against Adversarial Attacks. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2252022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shih, F.Y.; Roshan, U. Defense Against Adversarial Attacks Based on Stochastic Descent Sign Activation Networks on Medical Images. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2254005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Keenan, T.; Thavikulwat, A.T.; Lee, S.; Tang, Y.; Chew, E.Y.; Summers, R.M.; Lu, Z. Robust convolutional neural networks against adversarial attacks on medical images. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 132, 108923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinman, R.; Curtin, R.R.; Shintre, S.; Gardner, A.B. Detecting adversarial samples from artifacts. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.00410. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Erfani, S.M.; Wijewickrema, S.; Schoenebeck, G.; Song, D.; Houle, M.E.; Bailey, J. Characterizing adversarial subspaces using local intrinsic dimensionality. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02613. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.F.; Valdes, G.; Fuller, C.D.; Carpenter, C.M.; Morin, O.; Aneja, S.; Lindsay, W.D.; Aerts, H.; Agrimson, B.; Deville, C., Jr.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Radiation Oncology Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, S.; Chang, E.; Omuro, A. Applications of artificial intelligence in neuro-oncology. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.F.; Valdes, G.; Fuller, C.D.; Carpenter, C.M.; Morin, O.; Aneja, S.; Lindsay, W.D.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Agrimson, B.; Deville, C.; et al. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Radiation Oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Detection Accuracy (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGSM | PGD | BIM | |||||
| ε = 0.004 | ε = 0.008 | ε = 0.004 | ε = 0.008 | ε = 0.004 | ε = 0.008 | ||
| CT | DenseNet | 99.0 | 99.1 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 98.4 | 99.1 |
| Logistic Regression | 95.1 | 96.7 | 94.1 | 96.9 | 87.6 | 92.3 | |
| Random Forest | 93.9 | 96.2 | 90.6 | 95.8 | 81.2 | 89.1 | |
| ResNet | 99.3 | 99.3 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 99.3 | |
| SVM | 93.5 | 96.0 | 92.6 | 96.2 | 86.9 | 91.4 | |
| Mammogram | DenseNet | 99.7 | 100.0 | 99.9 | 100.0 | 98.7 | 100.0 |
| Logistic Regression | 70.4 | 83.8 | 75.6 | 84.2 | 69.8 | 83.0 | |
| Random Forest | 58.8 | 67.7 | 67.1 | 78.9 | 61.7 | 75.9 | |
| ResNet | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| SVM | 67.9 | 81.0 | 74.4 | 82.0 | 68.7 | 80.6 | |
| MRI | DenseNet | 90.0 | 94.4 | 80.5 | 93.5 | 75.8 | 91.7 |
| Logistic Regression | 95.1 | 95.3 | 93.9 | 95.3 | 87.0 | 95.3 | |
| Random Forest | 96.5 | 97.9 | 86.9 | 97.9 | 70.9 | 97.9 | |
| ResNet | 73.3 | 89.1 | 90.0 | 92.2 | 85.8 | 88.4 | |
| SVM | 84.1 | 84.1 | 83.9 | 84.1 | 81.3 | 84.1 | |
| Classification Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Adv Detection | Adv Training | Adv Detection + Training | |
| LIDC | 50.58 | 75.63 | 75.76 | 77.59 |
| Mammogram | 50.18 | 76.43 | 66.61 | 70.36 |
| MRI | 50.00 | 74.07 | 87.88 | 79.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joel, M.Z.; Avesta, A.; Yang, D.X.; Zhou, J.-G.; Omuro, A.; Herbst, R.S.; Krumholz, H.M.; Aneja, S. Comparing Detection Schemes for Adversarial Images against Deep Learning Models for Cancer Imaging. Cancers 2023, 15, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051548
Joel MZ, Avesta A, Yang DX, Zhou J-G, Omuro A, Herbst RS, Krumholz HM, Aneja S. Comparing Detection Schemes for Adversarial Images against Deep Learning Models for Cancer Imaging. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051548
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoel, Marina Z., Arman Avesta, Daniel X. Yang, Jian-Ge Zhou, Antonio Omuro, Roy S. Herbst, Harlan M. Krumholz, and Sanjay Aneja. 2023. "Comparing Detection Schemes for Adversarial Images against Deep Learning Models for Cancer Imaging" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051548
APA StyleJoel, M. Z., Avesta, A., Yang, D. X., Zhou, J.-G., Omuro, A., Herbst, R. S., Krumholz, H. M., & Aneja, S. (2023). Comparing Detection Schemes for Adversarial Images against Deep Learning Models for Cancer Imaging. Cancers, 15(5), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051548





