CT-Guided vs. Navigational Bronchoscopic Biopsies for Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: A Single-Institution Retrospective Comparison
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
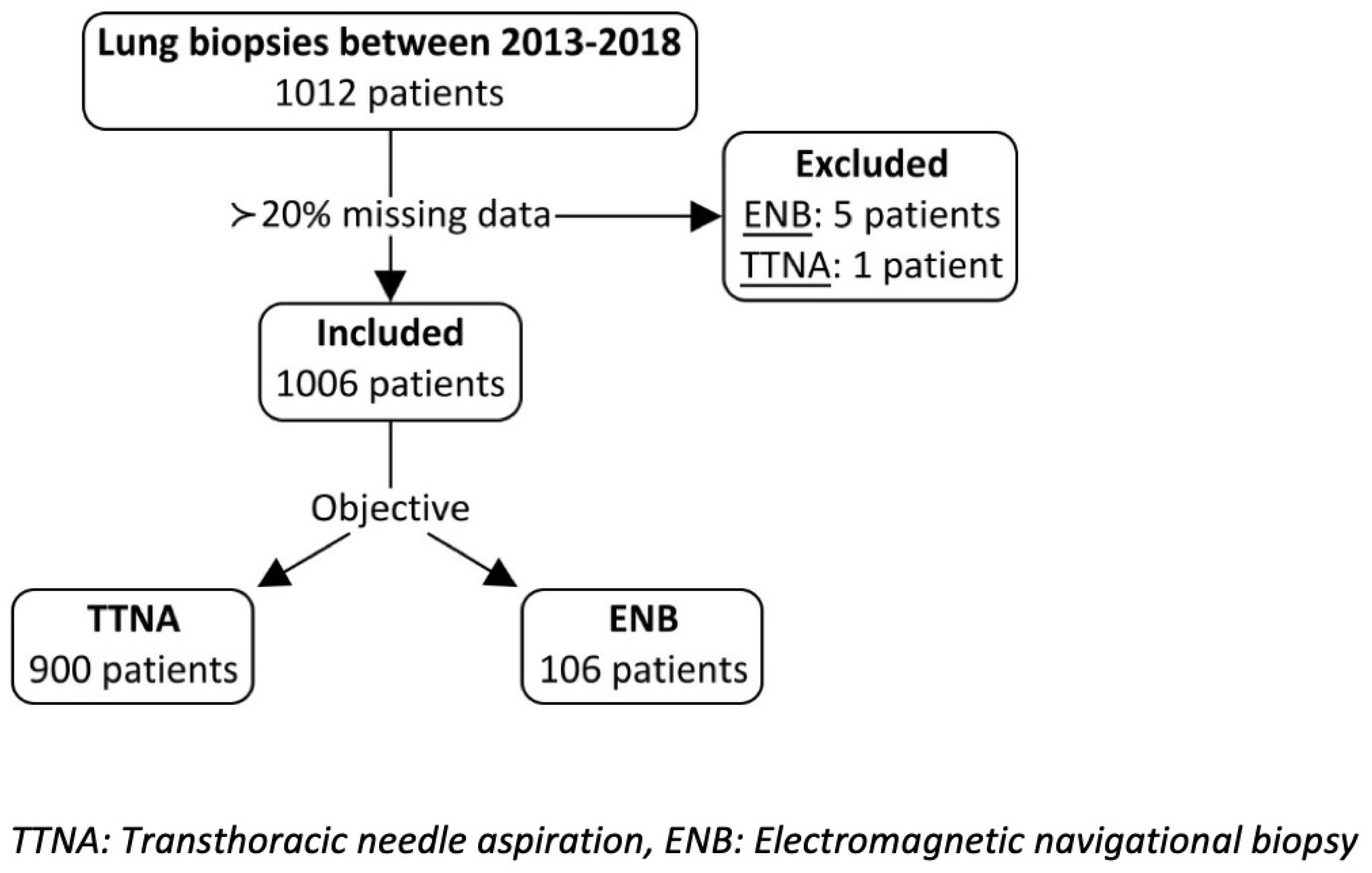
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Study Sample
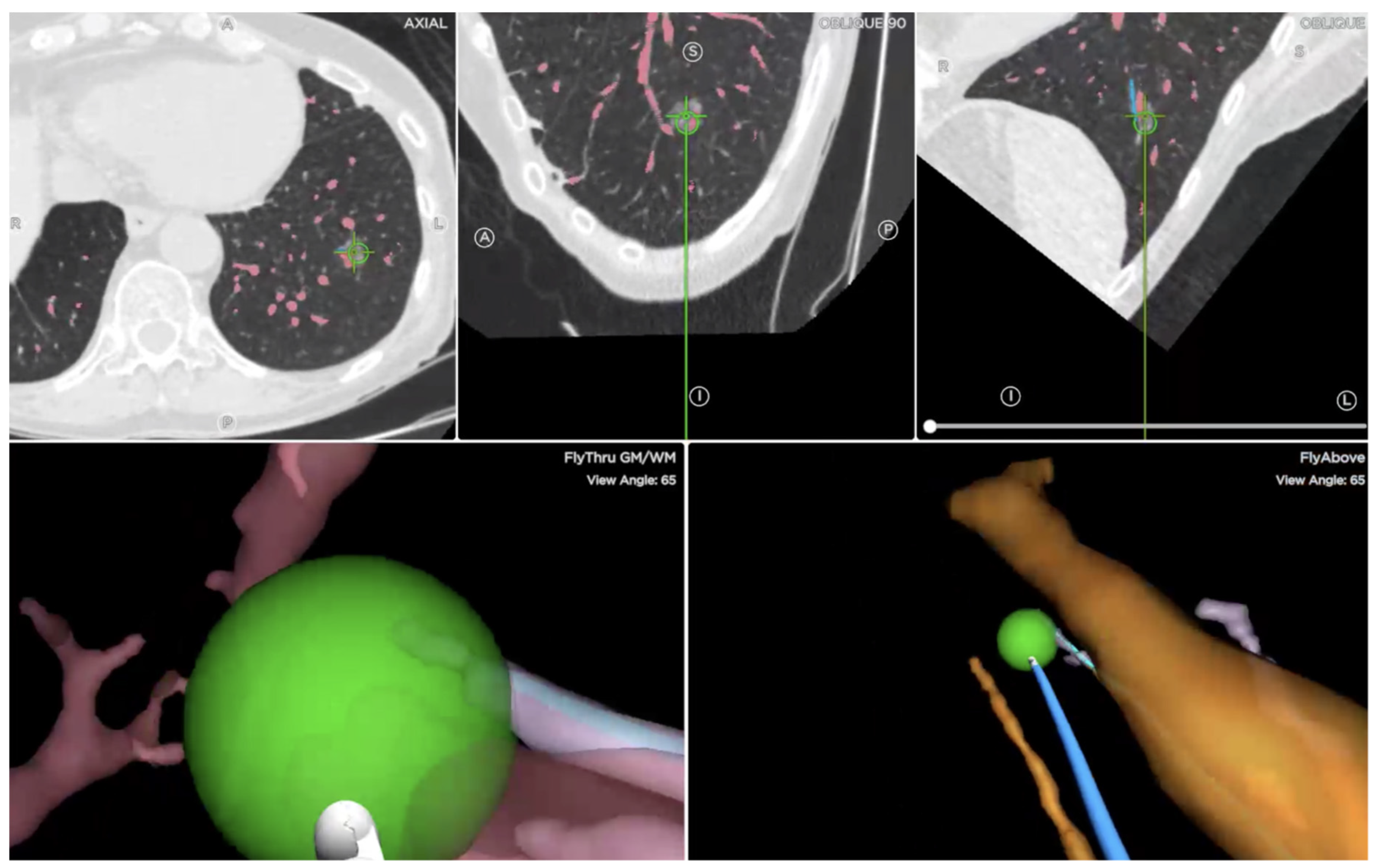
4.2. Procedure
4.3. Histopathology
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary of Abbreviations
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; Sicks, J.D. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, M.K.; Fletcher, J.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Lynch, W.R.; Midthun, D.E.; Naidich, D.P.; Ost, D.E. Evaluation of patients with pulmonary nodules: When is it lung cancer?: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest 2007, 132, 108s–130s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.P.; Mehta, A.C. Initial diagnosis of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest 2007, 132, 131s–148s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaklini, W.A.; Reinoso, M.A.; Gorin, A.B.; Sharafkaneh, A.; Manian, P. Diagnostic yield of fiberoptic bronchoscopy in evaluating solitary pulmonary nodules. Chest 2000, 117, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, J. Virtual Bronchoscopic Navigation (VBN) and Electromagnetic Navigation System. Kyobu Geka 2018, 71, 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, 25.0th ed.; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard, W. A Calculation of Effect Sizes. Allem. Psychom. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Lim, K.Y. Diagnostic Accuracy of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Lung Biopsies: A Multicenter Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraki, T.; Mimura, H.; Gobara, H.; Shibamoto, K.; Inoue, D.; Matsui, Y.; Kanazawa, S. Incidence of and risk factors for pneumothorax and chest tube placement after CT fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous lung biopsy: Retrospective analysis of the procedures conducted over a 9-year period. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Broemeling, L.D.; Morello, F.A.; Wallace, M.J.; Ahrar, K.; Madoff, D.C.; Murthy, R.; Hicks, M.E. Small (≤2-cm) subpleural pulmonary lesions: Short- versus long-needle-path CT-guided Biopsy—Comparison of diagnostic yields and complications. Radiology 2005, 234, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Harris, K. Bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S1047–S1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gex, G.; Pralong, J.A.; Combescure, C.; Seijo, L.; Rochat, T.; Soccal, P.M. Diagnostic yield and safety of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy for lung nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respiration 2014, 87, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, E.E.; Pritchett, M.A.; Nead, M.A.; Bowling, M.R.; Murgu, S.D.; Krimsky, W.S.; Murillo, B.A.; LeMense, G.P.; Minnich, D.J.; Bansal, S.; et al. Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy for Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions: One-Year Results of the Prospective, Multicenter NAVIGATE Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.; Ju, H.; Marshall, H.; Bowman, R.; Yang, I.; Ree, A.-M.; Saxon, C.; Fong, K.M. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy: A descriptive analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2012, 4, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, F. Advanced bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions. Respir. Investig. 2016, 54, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Dong, X.; Lei, P. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield and safety of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy for lung nodules. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 799–809. [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney, S.E.; O’Regan, K.N.; Mc Laughlin, P.D.; Crush, L.; Maher, M.M. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous biopsy of lung. Open Respir. Med. J. 2012, 6, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Yutaka, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Hamaji, M.; Motoyama, H.; Menju, T.; Aoyama, A.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Sonobe, M.; Date, H. Diagnostic yield of electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy: Results of initial 35 cases in a Japanese institute. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1615–S1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, L.; Robert, A.; Cottier, M.; Chambonniere, M.L.; Vergnon, J.M. Accuracy and feasibility of electromagnetic navigated bronchoscopy under nitrous oxide sedation for pulmonary peripheral opacities: An outpatient study. Respiration 2009, 78, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Kirbas, I.; Harman, A.; Ozyer, U.; Tore, H.G.; Aytekin, C.; Boyvat, F. CT-guided cutting needle lung biopsy using modified coaxial technique: Factors effecting risk of complications. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 70, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagami, T.; Terayama, K.; Yoshimatsu, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Miura, H.; Nishimura, T. Role of manual aspiration in treating pneumothorax after computed tomography-guided lung biopsy. Acta Radiol. 2009, 50, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, F.; Michel, P.; Latrabe, V.; Tunon de Lara, M.; Marthan, R. Pneumothoraces and chest tube placement after CT-guided transthoracic lung biopsy using a coaxial technique: Incidence and risk factors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiBardino, D.M.; Yarmus, L.B.; Semaan, R.W. Transthoracic needle biopsy of the lung. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7 (Suppl. S4), S304–S316. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.L.; Chu, C.M. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy: The initial experience in Hong Kong. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, D.; Scherpereel, A.; Leroy, S.; Bouchindhomme, B.; Faivre, J.-B.; Remy, J.; Ramon, P.; Marquette, C.-H. Electromagnetic navigation diagnostic bronchoscopy for small peripheral lung lesions. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wallace, M.J.; Cardella, J.F.; Kundu, S.; Miller, D.L.; Rose, S.C. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous needle biopsy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, L.M.; de Torres, J.P.; Lozano, M.D.; Bastarrika, G.; Alcaide, A.B.; Lacunza, M.M.; Zulueta, J.J. Diagnostic yield of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy is highly dependent on the presence of a Bronchus sign on CT imaging: Results from a prospective study. Chest 2010, 138, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Roknuggaman, M.; Han, W.S.; Kang, S.K.; Kang, M.-W. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy-Chungnam National University Hospital experience. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S717–S724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiboutot, J.; Lee, H.J.; Silvestri, G.A.; Chen, A.; Wahidi, M.M.; Gilbert, C.R.; Pastis, N.J.; Los, J.; Barriere, A.M.; Mallow, C.; et al. Study Design and Rationale: A Multicenter, Prospective Trial of Electromagnetic Bronchoscopic and Electromagnetic Transthoracic Navigational Approaches for the Biopsy of Peripheral Pulmonary Nodules (ALL IN ONE Trial). Contemp. Clin. Trials 2018, 71, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TTNA | ENB | Probability (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 900 (89.5) | 106 (10.5) | ------------------ | |
| Female sex (%) | 504 (56.0) | 56 (52.8) | 0534 | |
| Mean age (years) ± SD | 67.2 ± 11.2 | 68.3 ± 9.2 | 0.250 | |
| Diameter (mm) | Mean ± SD | 22.83 ± 15.34 | 17.03 ± 9.20 | <0.001 |
| Nodule diameter ≥ 2 cm n (%) | 499 (55.9) | 39 (38.2) | 0.001 | |
| SUV max | Mean ± SD | 6.97 ± 9.64 | 5.90 ± 10.33 | 0.314 |
| Nodule SUV max ≥ 2.5 n (%) | 629 (70.0) | 60 (63.8) | 0.213 | |
| Nodule location n (%) | LLL | 187 (20.8) | 10 (9.4) | 0.005 |
| Lingula | 16 (1.8) | 5 (4.7) | 0.061 | |
| LUL | 209 (23.2) | 32 (30.2) | 0.112 | |
| RLL | 172 (19.1) | 20 (18.9) | 0.952 | |
| RML | 44 (4.9) | 9 (8.5) | 0.116 | |
| RUL | 272 (30.2) | 30 (28.3) | 0.683 | |
| TTNA | ENB | Probability (p) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia n (%) | Local | 727 (99.2) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 | |
| Sedation | 6 (0.8) | 84 (84.8) | |||
| General | 0 (0.0) | 14 (15.2) | |||
| Use of fluoroscopy n (%) | --------- | 65 (61.3) | --------- | ||
| Use of ROSE n (%) | --------- | 0 (0.0) | --------- | ||
| Mean number of biopsies (± SD) | --------- | 5.35 (±2.62) | --------- | ||
| Number of patients with complications n (%) | 477 (53.0) | 20 (18.9) | <0.001 | ||
| Clavien-Dindo classification per patient with complications n (%) | Grade 1 | 403 (84.5) | 15 (75.0) | 0.264 | |
| Grade 2 | 0 (0.0) | 3 (15.0) | |||
| Grade 3a | 74 (15.5) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Grade 4a | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Grade 5 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Complication types n (%) Percentages represent % of complications from total complications | Air leak | 415 (87.0) | 1 (4.0) | <0.001 | |
| Pneumothorax | 411 (86) | 1 (4.0) | <0.001 | ||
| Bleeding | 111 (23.3) | 7 (28.0) | 0.227 | ||
| Other | Total | 1 (0.2) | 17 (68.0) | <0.001 | |
| Cough | 1 (0.2) | 11 (44.0) | --------- | ||
| Bradycardia | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | --------- | ||
| Desaturation | 0 (0.0) | 6 (24.0) | --------- | ||
| Intervention required per patient n (%) | Total | 82 (17.2) | 6 (30.0) | <0.001 | |
| Chest tube | 74 (90.2) | 0 (0.0) | --------- | ||
| Aspiration | 8 (9.8) | 1 (16.7) | --------- | ||
| Other | Total | 0 (0.0) | 5 (83.3) | --------- | |
| Oxygen | 0 (0.0) | 3 (50.0) | --------- | ||
| Naloxone | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) | --------- | ||
| Advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) | --------- | ||
| Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Positive Predictive Value (%) | Negative Predictive Value (%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT-guided TTNA | <2 cm | 63.0 | 75.0 | 95.4 | 19.6 | 64.3 |
| ≥2 cm | 87.4 | 46.2 | 94.7 | 25.0 | 84.0 | |
| Overall | 77.5 | 61.5 | 95.0 | 22.5 | 75.9 | |
| ENB | <2 cm | 34.4 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 40.0 | 54.3 |
| ≥2 cm | 56.3 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 41.7 | 66.7 | |
| Overall | 40.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 40.0 | 57.1 | |
| CT Guided TTNA | ENB | Probability (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathology | Negative | 180 (20.0) | 58 (54.7) | <0.001 |
| Positive | 624 (69.3) | 47 (44.3) | ||
| Inadequate specimen | 96 (10.7) | 1 (0.9) | ||
| Other | 120 (19.2) | 9 (19.1) | ||
| Sensitivity for cancer patients | 80.3 | 39.5 | ------------------ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudry, F.A.; Thivierge-Southidara, M.; Molina, J.C.; Farooqui, S.M.; Hussain, S.T.; Libermen, M. CT-Guided vs. Navigational Bronchoscopic Biopsies for Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: A Single-Institution Retrospective Comparison. Cancers 2023, 15, 5258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215258
Chaudry FA, Thivierge-Southidara M, Molina JC, Farooqui SM, Hussain ST, Libermen M. CT-Guided vs. Navigational Bronchoscopic Biopsies for Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: A Single-Institution Retrospective Comparison. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215258
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudry, Fawad Aleem, Maureen Thivierge-Southidara, Juan Carlos Molina, Samid M. Farooqui, Syed Talal Hussain, and Moishe Libermen. 2023. "CT-Guided vs. Navigational Bronchoscopic Biopsies for Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: A Single-Institution Retrospective Comparison" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215258
APA StyleChaudry, F. A., Thivierge-Southidara, M., Molina, J. C., Farooqui, S. M., Hussain, S. T., & Libermen, M. (2023). CT-Guided vs. Navigational Bronchoscopic Biopsies for Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: A Single-Institution Retrospective Comparison. Cancers, 15(21), 5258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215258






