Simple Summary
The aim of our study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the on-site cytopathology advance report (OSCAR) procedure on breast FNA cytologic samples in our breast OSC during the first three years (April 2004 till March 2007) of its implementation. To this goal, we retrospectively analyzed a series of 1820 breast masses (1740 patients) radiologically classified according to the American College of Radiology (ACR) BI-RADS lexicon (67.6% being either BI-RADS 4 or 5), sampled by FNA and immediately diagnosed by cytomorphology. The on-site cytopathology advance report (OSCAR) procedure is a highly reliable diagnostic approach for breast masses, provided that it is performed by interventional cytopathologists in the multidisciplinary setting of a one-stop clinic (OSC). Besides dramatically limiting the rate of unsatisfactory specimens and diagnostic turnaround time, OSCAR is a highly efficient first-line approach. Diagnostic accuracy measures of the OSCAR procedure with their 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were the following: sensitivity (Se) = 97.4% (96.19–98.31); specificity (Sp) = 94.98% (92.94–96.56); positive predictive value (PPV) = 96.80% (95.48–97.81); negative predictive value (NPV) = 95.91% (94.02–97.33); positive likelihood ratio (LR+) = 19.39 (13.75–27.32); negative predictive ratio (LR−) = 0.03 (0.02–0.04), and; accuracy = 96.45% (95.42–97.31). The respective positive likelihood ratio (LR+) for each of the four categories of cytopathological diagnoses (with their 95% CI) which are malignant, suspicious, benign, and nondiagnostic were 540 (76–3827); 2.69 (1.8–3.96); 0.03 (0.02–0.04); and 0.37 (0.2–0.66), respectively.
Abstract
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology has been widely used for the diagnosis of breast cancer lesions with the objective of differentiating benign from malignant masses. However, the occurrence of unsatisfactory samples and false-negative rates remains a matter of concern. Major improvements have been made thanks to the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) in multidisciplinary and integrated medical settings such as one-stop clinics (OSCs). In these settings, clinical and radiological examinations are combined with a morphological study performed by interventional pathologists. The aim of our study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the on-site cytopathology advance report (OSCAR) procedure on breast FNA cytologic samples in our breast OSC during the first three years (April 2004 till March 2007) of its implementation. To this goal, we retrospectively analyzed a series of 1820 breast masses (1740 patients) radiologically classified according to the American College of Radiology (ACR) BI-RADS lexicon (67.6% being either BI-RADS 4 or 5), sampled by FNA and immediately diagnosed by cytomorphology. The clinicoradiological, cytomorphological, and histological characteristics of all consecutive patients were retrieved from the hospital computerized medical records prospectively registered in the central information system. Histopathological analysis and ultrasound (US) follow-up (FU) were the reference diagnostic tests of the study design. In brief, we carried out either a histopathological verification or an 18-month US evaluation when a benign cytology was concordant with the components of the triple test. Overall, histology was available for 1138 masses, whereas 491 masses were analyzed at the 18-month US-FU. FNA specimens were morphologically nondiagnostic in 3.1%, false negatives were observed in 1.5%, and there was only one false positive (0.06%). The breast cancer prevalence was 62%. Diagnostic accuracy measures of the OSCAR procedure with their 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were the following: sensitivity (Se) = 97.4% (96.19–98.31); specificity (Sp) = 94.98% (92.94–96.56); positive predictive value (PPV) = 96.80% (95.48–97.81); negative predictive value (NPV) = 95.91% (94.02–97.33); positive likelihood ratio (LR+) = 19.39 (13.75–27.32); negative predictive ratio (LR−) = 0.03 (0.02–0.04), and; accuracy = 96.45% (95.42–97.31). The respective positive likelihood ratio (LR+) for each of the four categories of cytopathological diagnoses (with their 95% CI) which are malignant, suspicious, benign, and nondiagnostic were 540 (76–3827); 2.69 (1.8–3.96); 0.03 (0.02–0.04); and 0.37 (0.2–0.66), respectively. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that the OSCAR procedure is a highly reliable diagnostic approach and a perfect test to select patients requiring core-needle biopsy (CNB) when performed by interventional cytopathologists in a multidisciplinary and integrated OSC setting. Besides drastically limiting the rate of nondiagnostic specimens and diagnostic turn-around time, OSCAR is an efficient and powerful first-line diagnostic approach for patient-centered care.
1. Introduction
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology of breast masses is a useful tool for the rapid differential diagnosis of breast masses. Its advantages are the absence of medical contraindications, the fact that it is minimally invasive, safe, reliable, cost-effective, and reduces turn-around time considerably, thus mitigating patient anxiety in anticipation of diagnostic results [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,].
Despite its many advantages, variable nondiagnostic rates and the occurrence of false-negative and false-positive results, mainly operator-dependent, remain a matter of concern. Owing to these limitations, the debate over the current place of FNA as compared to core-needle biopsy (CNB) still persists [,,,,]. CNB is now mandatory for the pre-operative diagnosis of patients with breast cancer for tumor grading and immunohistochemical evaluation of the prognostic biomarkers as well as other markers that could influence the primary treatment choice.
In view of the non-invasive nature of FNA, its quickness and low cost coupled with the high sensitivity and specificity rates in the diagnosis of breast masses, major efforts have been dedicated to improving its overall diagnostic performance in pathology practice. In this context, rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) has represented a key game changer, particularly in OSCs in which reducing turnaround time and mitigating patient anxiety are two major priorities.
Due to the time of processing, the use of CNBs only for patients with breast masses may delay the diagnosis if FNA is not immediately used. By contrast, in the setting of an OSC, FNA combined with ultrasound (US) guidance is very suitable for accurate and same-day diagnosis of breast masses. FNA not only minimizes the time to diagnosis but also significantly decreases unsatisfactory specimen rates. This has been made possible thanks to the application of ROSEs to FNA samples [,]. Studies show that having an interventional pathologist make an on-the-spot cytological evaluation is a crucial part of the highly efficient triple test [] and may sharply reduce unnecessary CNBs and surgery for benign lesions []. Our OSC for breast masses was opened in 2004 and is located in the outpatient clinic of the tertiary referral Gustave Roussy (GR) comprehensive cancer center (Villejuif, France). Data about the challenges and cost-effectiveness have been previously published [].
The goal of our retrospective study was first to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the OSCAR procedure in a large consecutive series of patients with breast masses examined during the first 3 years of our OSC. To this aim, we compared cytopathological diagnoses with corresponding histopathological examinations. Second, in cases showing concordant benign clinicoradiological results and cytopathological diagnoses, we examined the US characteristics of the breast masses after 18 months with a US follow-up (US-FU). Finally, we evaluated the rate of nondiagnostic specimens sampled by FNA and described the features of the breast masses whose cytomorphology were discordant with the histopathological findings.
2. Patients and Methods
A retrospective observational study was conducted in a consecutive series of 1820 breast masses from 1740 patients sampled by FNA. The analysis covered our first 3 y experience (5 April 2004 till 31 March 2007) at an OSC set up at the GR institution—a large cancer comprehensive center distinct from regional screening facilities.
2.1. Organization of the Breast One-Stop Clinic (OSC)
The objective of the OSC was to identify patients with asymptomatic (non-palpable) breast masses detected either by the French national breast cancer screening program launched in 2004 or through opportunistic screening or diagnostic mammography in symptomatic patients with palpable lumps. Patients were evaluated in a large-scale multidisciplinary outpatient breast clinic. Patients with pure microcalcifications without a breast mass detected by mammography were not sampled by FNA.
The requirements for setting up a dedicated breast cancer OSC [,] have already been described. In brief, a dedicated hotline is available for both patients and referring physicians to schedule appointments within the following week. According to a written protocol, a secretary asks for the results of patients’ mammography and/or breast US reports (tumor size and imaging characteristics) to determine ahead of time whether the patient will need to be seen first by a surgeon or an oncologist. Then, the institution sends by regular mail a leaflet describing the outpatient breast clinic, the medical staff, as well as the types of procedures they might undergo. Consultations and all diagnostic procedures are located in a dedicated facility of the OSC and are performed during a single visit once a week by four different medical breast specialists; namely, an oncologist, a surgeon, a radiologist, and an interventional pathologist skilled in FNA procedures and interpretation of cytomorphology. Lastly, a nurse navigator is fundamental to coordinate the entire diagnostic workup, including patient assistance and psychological support.
2.2. Patient Management in Our OSC
In our OSC, patients with breast lesions are evaluated by the triple test. This test entails a clinical breast assessment, a mammography and/or US evaluation (or re-evaluation if needed) to quantify the risk of malignancy of each lesion according to the American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) lexicon. If a breast mass is detected, an FNA is carried out. In such cases, a topical anesthetic patch is applied to the region of interest before sampling.
2.3. FNA Sampling and Cytopathological Diagnosis
In our study, the FNA-based cytological diagnosis of breast lesions was made by three rotating cytopathologists either freehand for large or advanced tumors during the first 2 years then with the systematic help of a radiologist for US guidance (Siemens Acuson S2000 Helx Evolution; 18 Hz probe, München, Germany). Samples were collected with 2 to 3 multidirectional aspirates using a 10 mL syringe connected with a 23- or a 25-gauge (25 mm in length) needle depending on the distance of the mass from the areola. Overall, it took 10 to 20 s to collect the specimens. Samples were then immediately spread onto single slides and quickly air-dried. Next, they were stained with a Romanowsky-derived rapid staining (Diff Quik®) for ROSE. This enabled us to obtain additional FNA sampling when the first two specimens were diagnostically inadequate. To streamline the diagnostic process, we did not carry out any special or immunohistochemical staining or cell block preparations. The cytomorphological interpretation was conducted by an interventional pathologist capable of interpreting clinicoradiological information without double microscopic examination. Afterwards, an immediate cytopathological written report of the diagnosis was delivered to the clinician. The OSCAR procedure is the process conducted by an interventional pathologist performing FNA of the mass, rapid staining of the cytological sample, and immediate delivering of a definitive diagnostic report to the clinician. Cytopathologic diagnoses were then categorized at that time according to a 4-tiered classification system (see Discussion), i.e., malignant, suspicious, benign, and nondiagnostic. Such classification was based on the cellular yield and composition of 6 or more cell clusters or on the presence of more than 10 intact bipolar cells per 10 medium-power fields (×200). Malignancy was diagnosed when the smears contained either pure malignant cells or a largely predominant population of tumor cells admixed with few benign-looking glandular cells. A diagnosis of suspicious cytology was rendered in the following cases: when occasional cells of atypical features were intermingled with predominant populations of benign-looking cells; when smears showed naked nuclei in the background but with large clusters of cells with irregular boundaries; when paucicellular smears contained areas of mucinous or necrotic stroma; and when papillary formations with or without atypical cells were present. A diagnosis of benign cytology was made when the smears revealed normal, hyperplastic, or apocrine cells, and/or when fluid contained only cellular debris. In addition, a benign cytology consistent with fibroadenoma was suggested when numerous naked nuclei were intermingled with collagen strands and with anastomosing clusters of benign or apocrine cells; moreover, fat necrosis—consisting of numerous macrophages, multinucleated cells, and necrotic debris—was also associated with benign cytology. A nondiagnostic cytology report was made when smears contained no glandular cells or only debris or hemorrhage. Any discordance between the ACR BI-RADS classification and the specific cytopathological diagnosis was discussed on-site by the team, and CNB was performed immediately.
2.4. Proposal to the Patient
On the same day and depending on the results of the multidisciplinary discussion, patients were either discharged and invited to a clinicoradiological follow up or advised on primary treatment. In the latter case, treatment decision-making was immediately shared with the patients in a second medical consultation session. In particular, when the triple test was concordant with a benign cytological diagnosis, the surgeon or the oncologist reassured the patient and prescribed a bi-annual US and/or mammography check-up to evaluate the lesion at an 18-month US-FU. At that time, if the US showed no changes in the lesion size and the BI-RADS category remained the same, the lesion was definitely classified as benign. On the other hand, if the triple test was concordant with a malignant or suspicious cytologic diagnosis, depending on the tumor size and the clinical and US axilla status, patients met either with a surgeon or with an oncologist to discuss whether to undergo primary surgery or neoadjuvant medical treatment. If they opted for surgery, prognostic and predictive biomarkers (ER, PgR, and HER2) were evaluated either on the pre-operative CNB performed the same day or later after lumpectomy. Instead, if patients opted for primary medical treatment, immediate CNB was performed for histopathological grading and assessment of biomarkers. Same day CNB was also systematic in several other cases. One case was when FNA yielded nondiagnostic samples; a second case was when there was a discrepancy between the clinicoradiological and cytomorphological results. Typical examples of the latter cases were when a patient presented with a BI-RADS 5 mass with a benign cytology or with a BI-RADS 3 mass with a malignant cytology; a third case was in patients presenting with large tumors eligible for neoadjuvant medical therapy; and a final case was when patients harbored centrally located tumors or bifocal lesions—cases for which breast conservative treatment with sentinel lymph node evaluation was usually precluded.
2.5. Histopathological Diagnosis
Histopathological examination without double reading was performed by senior breast pathologists either on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues obtained from US-guided CNB (14-Gauge) or on surgical specimens routinely cut and then stained with hematein and eosin. The 2012 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors was used then re-classified using the 2019 one [] for the purpose of our study. In this regard, when breast carcinomas contained more than one histological feature, only the main one was considered. When interpreting CNB or surgical samples, histopathologists had already been informed about patients’ clinicoradiological characteristics and cytopathological diagnoses. The non-operated patients either had refused surgery or were inoperable because their general status was insufficient for surgical intervention. As mentioned above, CNB was performed immediately after FNA when indicated, whereas surgery usually occurred within the following 4–6 weeks.
2.6. Data Collection
Clinical characteristics, imaging findings, and cytomorphological and histopathological diagnoses were prospectively recorded in our centralized hospital database storage system. The histopathological results and final tumor status revealed at the 18-month US-FU were extracted from the hospital computerized registered medical record. When the data from the US-FU were not available, a questionnaire was posted to patients who sent it back after completing the dates, the types of radiological examinations, and their relative results performed in the last 18 months.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean (standard deviation); categorical variables were expressed as frequencies (percentages) and compared between groups with a Fisher’s exact test. Diagnostic accuracy was calculated by assuming that the multiple breast masses present in each patient were independent. As measures of diagnostic accuracy are based on the assignment of true and false negatives and positives, the cytomorphological categories of suspicious and malignant were combined and nondiagnostic cases were excluded from the calculations. From there, sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), negative predictive value (NPV), positive predictive value (PPV), negative likelihood ratio (LR−), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), accuracy and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated for histopathology cytomorphologic assessments, US-FU, and overall cytomorphologic assessment, which combined histopathology and US-FU assessments. The 95% CIs for Se, Sp, and accuracy were calculated based on Clopper–Pearson, NPV, and PPV; 95% CI were calculated using standard logit, and LR− and LR+ with 95% CIs were calculated using the log method []. LR+ for each of the 4 categories of cytomorphologic diagnoses (with their 95% CI) were also computed [,]. Statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software R, version 4.0.4 [].
3. Results
3.1. Clinicoradiological Characteristics
Table 1 describes the clinicoradiological characteristics of 1740 patients harboring 1820 breast masses sampled by FNA. During the first two years, FNA samples of advanced and very large breast tumors were performed without US guidance. Then, all FNA samples were carried out under US guidance.

Table 1.
Clinicoradiologic characteristics of the 1740 patients with 1820 breast masses.
3.2. Study Flow Chart
Figure 1 illustrates the flow chart of the study.
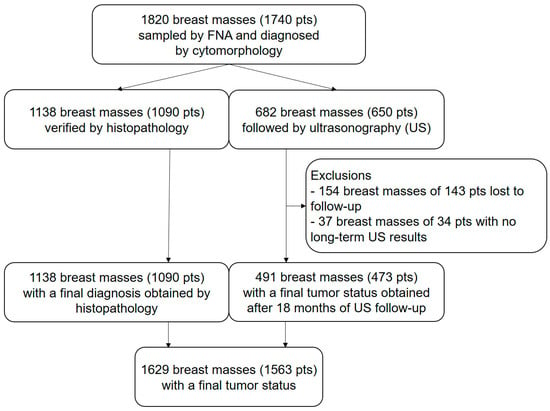
Figure 1.
Illustrates the study flow chart according to the STARD guidelines []. From an initial set of 1820 breast masses (1740 pts), US-FU data were lacking in 177 patients with 191 (10.5%) masses. Of the remaining 1629 breast masses, 1138 (62.5%) were verified by histopathology and 528 (29%) were evaluated at the 18-month US-FU. Final tumor status was therefore available for 1629 (89.5%) masses (1563 patients).
3.3. Cytomorphological Diagnoses
Table 2 shows the cytomorphological diagnoses of 1820 breast masses including the 191 with incomplete data.

Table 2.
Cytomorphologic diagnoses in 1820 breast masses and comparison with the group of 1629 masses with final tumor status obtained either by histopathology (Histo) or by the 18-month ultrasonography follow-up (US-FU).
In the group of 1629 breast masses, cytomorphological diagnoses were verified by histology in 1138 (69.8%) cases and by US-FU in 491 (30.1%) cases. Of the 1629 masses, 50.1% (816 cases) were cytologically malignant and concordant with histology in 98.4% (803/816) and with US-FU in 1.5% (12/816) of the cases, reaching an overall concordance rate of 99.9% (815/816); 9.3% (152 cases) were cytologically suspicious and histologically malignant in 80.2% (122/152 cases); 37.5% (611 cases) were cytologically benign and concordant with histology in 18.8% (115 cases) and with US-FU in 77.2% (472 cases), reaching an overall concordance rate of 96.1% (587/611); 3.1% (50 cases) were nondiagnostic, 18 of which (36%) turned out to be malignant after histological examination. False-negative and false-positive cytomorphological diagnoses were 1.5% (25/1629) and 0.06% (1/1629), respectively.
In the group of 177 patients with missing data, 3.1% (26/842) were malignant, 1.3% (2/154) were suspicious, 2.1% (160/771) were benign, and 5.7% (3/53) were nondiagnostic specimens for cytomorphological evaluation. No significant differences were found between the groups of 1629 and 1820 masses.
Table 3 displays the main clinicoradiological and histopathological characteristics of 228 breast masses histologically verified (the group with the missing data being excluded). Cytomorphology was suspicious in 152 cases, unsatisfactory in 50 cases, false negative in 25 cases, and false positive in 1 case. The mean age of patients was similar in the first three groups (59 years; range: 57–61). The mean size of breast masses was significantly smaller in the group of nondiagnostic specimens even though 96% (48/50) of FNA specimens were performed under US guidance. Similarly, 72% (18/25) of FNA samples were performed under US guidance in the group of false negatives. In both nondiagnostic and false-negative groups, breast masses were mainly classified as BI-RADS of intermediate (62% of BI-RADS 4; 31/50) and high (96% of BI-RADS 5; 24/25) risk.

Table 3.
Clinicoradiologic and histopathologic characteristics of 288 breast masses.
In the group of patients with suspicious cytomorphology (n = 152), the mean age was 57 years (+/− 13.4), the mean size of breast masses was 17.1 mm (+/− 15), and US-FNA was performed in 61.8% (94/152) of the cases. It comprised a first subgroup of 30 suspicious cases with either benign histology (n = 29) or with a (n = 1) reassuring 18-month US-FU. Sampling was performed under US guidance in 77% (23/30) of cases, and the results were categorized as BI-RADS 4 and BI-RADS 5 in 63.3% (19/30) and 20% (6/30) of the cases, respectively. Interestingly, the most frequent histological diagnoses were benign fibroadenomas (n = 9); papilloma (n = 9); adenosis (n = 3); and radial scar (n = 2). In the second subgroup of 122 suspicious cases with malignant histology, FNA was carried out under US guidance in only 59.8% (73/122) cases. In these latter cases, the rates of BI-RADS 4 and BI-RADS 5 were 33.6% (41/122) and 57.4% (70/122), respectively. Histopathology of the 122 cases showed 3 cases of pure ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of low (n = 1) and high (n = 2) nuclear grade, 99 cases of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) of grade I (n = 46), II (n = 31), III (n = 15), or unknown (n = 7), 18 cases of grade I invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), 1 case of malignant myoepithelioma, and 1case of a phyllode tumor of intermediate grade.
In the group of patients with nondiagnostic FNA specimens, histology showed 13 IDC of grade I (6 cases including 1 tubular carcinoma) or grade II (7 cases including 1 apocrine carcinoma), and 5 cases of ILC grade I.
In the group of patients with false-negative cytomorphology, histology showed 2 cases of pure DCIS of intermediate nuclear grade, 17 cases of grade I (including 5 tubular carcinomas) IDC and 3 IDC of grade II (including 1 mucinous adenocarcinoma), and 6 cases of ILC (1 grade I and 5 grade II).
The patient with a cytologically false-positive case corresponded to a 49-year-old woman presenting with a 20 mm BIRADS 4 left breast mass, which was sampled by free-hand FNA but then corrected by evaluation of the CNB.
3.4. Diagnostic Accuracy Measures
Table 4 displays the different measures of diagnostic accuracy with corresponding 95% CIs for condensed cytomorphologic diagnosis with final tumor status in terms of sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative predictive ratio (LR−), and accuracy. As already mentioned (see Material and Methods), nondiagnostic specimens were excluded from analysis and suspicious diagnoses were grouped with malignant. From a total of 1579 cytomorphological diagnoses, 1094 and 485 were, respectively, verified by histology or US-FU. While sensitivity and specificity cannot be used on their own to estimate an individual’s probability of disease, likelihood ratios (LRs) provide a practical way of interpreting test results that can be translated to individual patients []. Table 4 illustrates positive likelihood ratios (LRs+) with 95% CIs according to the different categories of cytomorphology in the group of 1629 breast masses verified by either histology or an 18-month US-FU. In addition, disease prevalence within a population impacts predictive values. To avoid having to convert pre- and post-test probability to pre- and post-test odds, a Fagan’s nomogram [,] shows the post-test likelihood of malignancy as a function of pre-test probability (prevalence) of the OSCAR procedure in our series is illustrated in Figure 2.

Table 4.
Measures of diagnostic accuracy and corresponding confidence intervals for condensed cytomorphologic diagnosis with final tumor status.
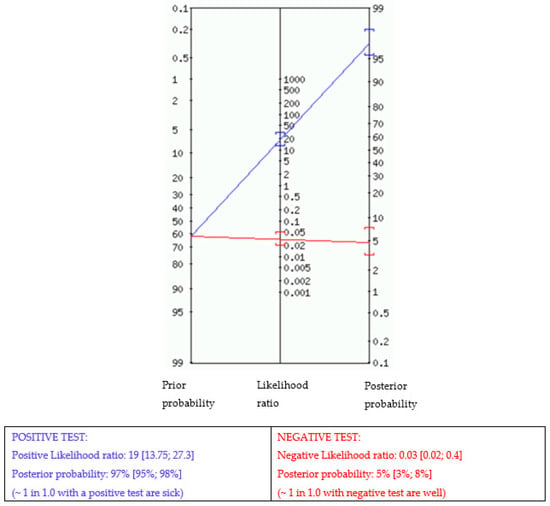
Figure 2.
Fagan nomogram. The nomogram displays the probability that a patient has the disease after a positive or negative test. Prior probability (odds): 62%.
4. Discussion
Our results underline the high diagnostic performance of the entire OSCAR procedure in patients with breast masses sampled by FNA and immediately interpreted by cytomorphology in the context of a multidisciplinary OSC setting. In addition, by facilitating consultations between the multidisciplinary team and patients, OSCAR enables clinicians to deliver definite cytopathological diagnosis to the patient within a single day, thereby streamlining the whole process of treatment decision making and reducing the levels of anxiety associated with long diagnostic waiting times. Furthermore, we showed that the OSCAR procedure can also reliably be considered as a rule in testing and identify patients with breast masses requiring CNB, thereby sparing many women the physical and emotional distress of unnecessary biopsies.
Diagnostic mammography and US assessments were categorized on the basis of the ACR BI-RADS lexicon which efficiently classifies the risk of malignancy in patients with breast diseases. Our study used the fourth edition of the system, which was published in 2003 []. In our series of 965 histologically malignant cases, 23% and 74% were classified as BI-RADS 4 and BI-RADS 5, respectively. Later versions of the system added mammographic aspects, measures of likelihood of malignancy, and management recommendations and subclassified BI-RADS 4 into BI-RADS 4A, 4B, and 4C categories [,]. However, although BI-RADS 4C and 5 breast lesions are associated with high risk of malignancy, they may also correspond to benign lesions [].
Performing FNA under US guidance is also known to be an important factor for enhancing diagnostic accuracy []. Not surprisingly, our study highlights that from 2004 to 2007, FNA under US guidance increased from 56.4% to 69%. This phenomenon was further confirmed in a 2016 study highlighting its increased popularity in tandem with the increased detection of small-sized breast masses thanks to national screening and more advanced imaging technologies [].
Our study lends support to earlier literature indicating the diagnostic efficiency of US-FNA for cytological diagnosis of breast masses. We confirm that achieving diagnostic accuracy is tightly dependent on the presence of an interventional pathologist. Indeed, our study has demonstrated that having a pathologist with skills in performing and interpreting FNA specimens can ensure a diagnostic accuracy equivalent to the quality assurance thresholds recommended for small tissue specimens (FNAC and CNB) by several international guidelines. Among these are the “Guidelines for cytology procedure and reporting on fine needle aspirates” [,] with measurements of likelihood ratios []; “European guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening” (section 5.5.3: Cytology/histology quality assurance) [] published in 2006; and “Guidelines for non-operative diagnostic procedures and reporting in breast cancer screening” (2nd edition; document G150) [] published in August 2021. Some authors have suggested that double reading selected cases by an expert cytopathologist might also be essential to improve cytodiagnostics and the quality of patient care []. However, we speculate that although this may be a useful tool at the beginning of a diagnostic learning curve, it might then slow down the entire diagnostic work-up.
Importantly, the OSCAR procedure resulted in low rates of nondiagnostic FNA specimens (3.1%), false negatives (1.5%), and false positives (0.06%). Factors influencing nondiagnostic FNA specimens include training, experience, and expertise in aspiration techniques [,,,,,,,], nature, size, and histotype of the lesion, as well as the number of passes [,,,,,,]. Moreover, a large systematic review and meta-analysis synthesizing evidence across different anatomic locations indicates that the application of ROSE, or lack thereof, is another critical factor influencing FNA diagnostic outcomes []. Importantly, lowering the rates of nondiagnostic preoperative FNA specimens not only guarantees fast and accurate diagnoses but also decreases the costs of the diagnostic workup [,] and increase its cost-effectiveness []. Accordingly, over the last decade, much effort has been dedicated to developing new guidelines to reduce the unsatisfactory/non diagnostic category rates of FNA samples [].
Regarding the factors contributing to the occurrence of false-negative and false-positive FNA cases, studies have shown that morphological difficulties associated with low-grade malignancies may play a key role. This was illustrated in our series of 25 cases of false-negative cases of breast masses comprising 14 IDC grade I (with 5 tubular carcinomas) and 6 cases of ILC (1 grade I and 5 grade II). Of note, only one case was classified as low risk (BI-RADS 3) by imaging. The BI-RADS 4 false-positive FNA case was fortunately further explored by CNB, and the patient was treated by conservative surgery. These false-negative and false-positive cases underline the critical role of the triple test. Discordance between the specimens and the imaging features led us to verify all the cases histologically. Indeed, of all the 152 cases diagnosed as suspicious by FNAC, 30 (19.7%) resulted as benign after histological examination (n = 29) or at the 18-month US-FU (n = 1). Moreover, whereas 5 cases (16.7%) were BI-RADS 3 and 19 cases (63.3%) were BI-RADS 4, 6 (20%) cases were BI-RADS 5. Of the 122 cases diagnosed as suspicious by cytomorphology (80.3%) and malignant by histology, 70 cases (57%) were BI-RADS 3, 41 cases (33.6%) were BI-RADS 4, and 7 cases (5.7%) were BI-RADS 5. Histologically, 3 were pure DCIS of low and high nuclear grade and 99 were IDC including 17 lobular, 11 tubular, 4 mucinous, 2 papillary, 3 metaplastic, 1 cribriform, and 1 apocrine type of carcinoma. These findings suggest that since most of these histotypes are associated with cytological difficulties [,,], they should be analyzed histologically after cytologic evaluation.
We used a 4-tiered system for reporting breast FNA cytomorphology instead of the 5-tiered system recommended by the National [], European [], American [], and international organizations [,]. Most organizations recommend the additional use of an “atypical” category because it maintains a high predictive value of cytological malignancy while retaining a high degree of diagnostic sensitivity. However, at the time of our study (2004–2007), the clinicians at our institution were reluctant to use this category, mainly because it could create confusion both for patients and for management. Nowadays, however, this category is progressively being incorporated in our routine practice. Despite the introduction of the atypical category, the interpretation of certain cytomorphological findings still remains challenging. Some problems of interpretation may also arise in some unclear cases of breast CNB specimens, particularly those categorized as uncertain malignant potential (B3) and atypical or undetermined (B4). Owing to the heterogeneous and complex nature of these lesions, there is always a risk of under- or overestimating the occurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ of low and intermediate nuclear grade, as well as fibroepithelial and papillary neoplasms [,,,,,,,,,,,,]. The diagnosis of cytological atypia may be challenging, and the morphological features of breast masses sampled by FNA or CNB do not always overlap. Accordingly, several studies have suggested using both approaches as sequential [] and complementary methods [,,,,,]. Future prospective studies based on the recent International Academy of Cytology (IAC) Yokohama System for Reporting Breast Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Cytopathology providing a more detailed definition, along with illustrations, of cytologic atypia [,,] are needed. It is also important to mention that management options have to take into account the considerable differences in practice between well-resourced and middle- or low-income countries, as detailed in the book explaining and illustrating the IAC Yokohama system [].
A unique and fundamental aspect of the OSCAR procedure is obviously the presence of an experienced and skilled interventional pathologist [,,,,] capable of both performing FNA preferentially under US guidance [,,,,] and delivering a swift diagnosis using rapid stains [,,,,,,]. On the other hand, some ROSE-based models performed by nonpathologists have been described. In these cases, a remote diagnosis is carried out by a pathologist using telecytology []. Although the latter method is cost-effective and, therefore, applicable in low-income settings, the presence of a pathologist is indisputably critical. Having a pathologist on-site gives the possibility to immediately discuss any type of difficulties, including discordance between clinical examination and/or imaging interpretation. Furthermore, having an in-house pathologist also gives the pathologist herself/himself the opportunity to interact with the whole clinicoradiological team in person and to participate in a “mini on-site” tumor board, if needed. This procedure is tremendously advantageous as it streamlines the entire diagnostic pathway, benefitting the overall care of patients.
Long waiting times for pre-operative assessments are physically and emotionally detrimental for patients. In conventional clinical settings, the excruciating waiting times needed to fix an appointment with a breast specialist, to have image-guided sampling, if needed, to receive a morphological diagnosis based on FNA and/or CNB, and to schedule further appointments to decide on a course of treatment are major sources of discomfort and anxiety for patients. The failure of the 2-week wait rule introduced in the UK [] by the Department of Health (Health Service Circular HCS 1998/242) prompted the development of rapid access breast specialist clinics [,,,] along with their corresponding recommended quality indicators []. In this context, the overarching goal of a breast OSC has been to reduce the waiting times of the entire process of the pre-operative assessment while maintaining a high level of diagnostic performance and minimal patient anxiety. This has been made possible by having a dedicated team of breast cancer specialists work in tandem to provide each patient with the best possible care in a minimal period of time. In our experience, we have seen that the logistics of such patient-centered organization is relatively sophisticated, requiring highly professional medical secretaries able to handle hotlines and nurse navigators able to assist patients throughout the entire course of the diagnostic pathway [].
Although FNA may significantly improve the diagnostic pathway of patients with breast masses, its use remains a matter of debate. Indeed, the preference for CNB over FNA for breast lesions is still clearly stated in both the 2016 edition of the NHS Breast Screening Programme in the UK [] (4th edition, document number 49) and in the updated guidelines for non-operative diagnostic procedures in breast cancer screening published by the Royal College of Pathologists [] (document number G150, version number 2) in August 2021. FNA is only recommended for lymph node assessment. Yet, other organizations acknowledge the useful implementation of breast FNA, provided that skilled operators perform the procedure and experienced pathologists interpret the cytomorphologic features of FNA samples. Among these institutions are the NCCN [], ESMO [], EUSOMA [,], and the Japanese Breast Cancer Society []. In addition to reducing delays in diagnosis while ensuring diagnostic accuracy, some studies have suggested that OSCs might also contribute to easing the levels of patients’ anxiety while waiting for diagnosis [,]. The question of whether speedier diagnosis can actually lower women’s psychological distress and improve the overall care is still a matter of debate [,]. However, in our experience, most of our patients (80%) expressed high levels of satisfaction with the care we provided. Only a limited number of patients experienced anxiety, which was most likely associated with difficulties in establishing a good-quality relationship with their therapist [].
Our study did have some limitations. The most obvious limitation was the single center, observational and descriptive nature of our series [,]. Despite being prospectively registered in the central informatics system of our institution, its observational and retrospective aspects may have given rise to some bias and confounding factors [,,,]. Another limitation was that the cytomorphological diagnoses were reported according to a 4-tiered and not a 5-tiered classification system, as it is now recommended. A third and final limitation was that the study was not randomized since a subset of patients underwent only long-term (18-month) US-FU without histological assessment. The rationale behind the choice of a non-randomized study [] was to avoid ethical issues commonly associated with blinded studies.
Despite these limitations, our study has several strengths. These strengths included the large consecutive series of patients analyzed and its reporting, which was conducted according to published guidelines and specifications [,,,,,]. Another strength was that it was focused on patients with breast masses identified by mammography and US. By doing so, we eliminated confounding factors such as pure microcalcifications, architectural distortion, and asymmetries of breast imaging.
The main advantages of the OSCAR procedure are the possibility of triaging patients using a minimally invasive, rapid, safe, and low-cost technique identifying patients who are the best candidates for core needle biopsy. In addition, it significantly reduces the turn-around time for benign breast masses and therefore patients’ anxiety. On the other hand, this patient-centered approach needs a multidisciplinary oncoteam, and its main disadvantage is the need for an interventional pathologist able to deliver an immediate diagnosis based on cytology. Furthermore, this approach can only be performed in patients with breast masses.
Our findings indicate that the OSCAR procedure makes a very efficient approach for reaching a definitive diagnosis within a single day. Thanks to this procedure, we were also able to distinguish between women with malignant cytology who actually required CNB from those with benign cytology who were reassured and spared the physical and emotional distress of unnecessary CNB. We also demonstrated that the OSCAR procedure can be used as a rule-in test, as indicated by the main diagnostic indicators of performance. Similarly, we showed that it may also be used as a rule-out test. Indeed, at least in our study, we evidenced that the combination of clinical and radiological findings may facilitate the detection of discordance, a main indicator of CNB. Implementing the OSCAR procedure in a multidisciplinary OSC for breast masses enables clinicians to triage patients [,] adding a layer of confidence to the imaging features for patients requiring CNB. Decreasing the number of unnecessary CNB also has an important financial impact on the health care system []. The ideal setting to apply OSCAR is a breast referral/specialist clinic with a patient-centered pathway, a multidisciplinary team, and a tumor board, as recommended in the EUSOMA [,,,] and EUSOBI [,] guidelines. Undeniably, our internal results need to be verified prospectively and validated externally in other settings [] where the prevalence of breast cancer may differ significantly []. Finally, our data highlight time-saving aspects of our FNA-based cytomorphologic approach compared to CNB and suggest that the OSCAR procedure may be recommended as a triage test for indicating CNB in high-income countries and as an alternative approach to conventional diagnostic pathways in middle- or low-resource countries where the health system cannot afford the costs of CNB [,,,,] and infrastructures of histopathology laboratories [,].
5. Conclusions
Our study clearly shows that the OSCAR procedure is a highly reliable diagnostic approach and a perfect test to select patients requiring CNB when performed by interventional cytopathologists in a multidisciplinary setting. Additionally, it drastically reduces the percentage of nondiagnostic specimens and diagnostic turn-around time. Furthermore, it is an efficient and powerful first-line diagnostic approach for patient-centered care.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.B., S.D., S.C. and P.V.; methodology: C.E.C., Z.B. and S.C.; statistical analysis: C.E.C. and S.C.; resources: V.S., C.B., S.D., S.C. and P.V.; original draft preparation: P.V., Z.B., C.E.C. and S.C.; review and editing: V.S., C.E.C., R.S., M.-C.M., C.B., S.D., Z.B., J.-Y.S., S.C. and P.V.; supervision: S.C. and P.V.; project administration: Z.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gustave Roussy (protocol code IRB 2023-287, on 6 October 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
At the time of our study, the informed consent from patients was only based on oral approval.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Colleen Vrbin B.S. and Isabelle Borget Pharm. D., for their help and Paola Merolla for English language editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martin, H.E.; Ellis, E.B. Biopsy by Needle Puncture and Aspiration. Ann. Surg. 1930, 92, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, S.; Zajicek, J. Aspiration biopsy in diagnosis of palpable lesions of the breast. Critical review of 3479 consecutive biopsies. Acta Radiol. Ther. Phys. Biol. 1968, 7, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cornillot, M.; Verhaeghe, M.; Cappelaere, P.; Clay, A. Role of cytology by puncture in the diagnosis of breast neoplasms (2267 cytological examinations). Lille Med. 1971, 16, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreuzer, G.; Zajicek, J. Cytologic diagnosis of mammary tumors from aspiration biopsy smears. 3. Studies on 200 carcinomas with false negative or doubtful cytologic reports. Acta Cytol. 1972, 16, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zajdela, A.; Ghossein, N.A.; Pilleron, J.P.; Ennuyer, A. The value of aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of breast cancer: Experience at the Fondation Curie. Cancer 1975, 35, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnival, C.M.; Hocking, M.; Hughes, H.; Reid, M.; Blumgart, L. Aspiration cytology in breast cancer. Its relevance to diagnosis. Lancet 1975, 2, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsén, C. Breast disease. A clinical study with special reference to diagnostic procedures. Acta Chir. Scand. Suppl. 1975, 454, 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer, G.; Boquoi, E. Aspiration biopsy cytology, mammography and clinical exploration: A modern set up in diagnosis of tumors of the breast. Acta Cytol. 1976, 20, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.M.; Fitzharris, B.M.; Redding, W.H.; Williams, J.E.; Trott, P.A.; Powles, T.J.; Ford, H.T.; Gazet, J.C. Clinical examination, xeromammography, and fine-needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of breast tumours. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kline, T.S.; Joshi, L.P.; Neal, H.S. Fine-needle aspiration of the breast: Diagnoses and pitfalls. A review of 3545 cases. Cancer 1979, 44, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguid, H.; Wood, R.A.; Irving, A.D.; Preece, P.E.; Cuschieri, A. Needle aspiration of the breast with immediate reporting of material. Br. Med. J. 1979, 2, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bauermeister, D.E. The role and limitations of frozen section and needle aspiration biopsy in breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer 1980, 46, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardecki, T.M.; Hogbin, B.; Melcher, D.; Smith, R. Aspiration cytology in the preoperative management of breast cancer. Lancet 1980, 316, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Robinson, K. Aspiration cytology of the breast with immediate reporting: Initial experience with 1000 patients in a district general hospital. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 1991, 36, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Pilotti, S.; Rilke, F.; Delpiano, C.; Di Pietro, S.; Guzzon, A. Problems in fine-needle aspiration biopsy cytology of clinically or mammographically uncertain breast tumors. Tumori J. 1982, 68, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frable, W.J. Needle aspiration of the breast. Cancer 1984, 53, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Anderson, T.J.; Lamb, J.; Nixon, S.J.; Forrest, A.P.M. Fine needle aspiration cytology, in relationships to clinical examination and mammography in the diagnosis of a solid breast mass. Br. J. Surg. 1984, 71, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanow, R.M.; Galblum, L.; Canter, J.W. Fine needle aspiration in the diagnosis and management of solid breast lesions. Am. J. Surg. 1984, 148, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, L.W.; Davis, J.R.; Wiens, J.L.; Trego, D.C.; Dunnington, G.L. Accuracy of aspiration cytology in detecting breast cancer. Surgery 1984, 96, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg, N.J.; Caya, J.G.; Clowry, L. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast. A review of 321 cases with statistical evaluation. Acta Cytol. 1985, 29, 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, R.G.; Young, G.P.; Kaplan, M.J.; Bernhard, V.M.; Rosenberg, M.; Somers, D. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the management of solid breast tumors. Arch. Surg. 1985, 120, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, G.; Anderson, T.J.; Lamb, J.L.; Dixon, J.M. Fine-needle aspiration of breast cancer: Relationship of clinical factors to cytology results in 689 primary malignancies. Cancer 1986, 58, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannin, D.R.; Silverman, J.F.; Walker, C.; Pories, W.J. Cost-effectiveness of fine needle biopsy of the breast. Ann. Surg. 1986, 203, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, A.; Hajdu, S.I.; Wilhelmus, J.; Melamed, M.R.; Kinne, D. Preoperative aspiration cytology of breast tumors. Acta Cytol. 1986, 30, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Griffith, C.; Kern, W.; Mikkelsen, W. Needle aspiration cytologic examination in the management of suspicious lesions of the breast. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1986, 162, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.; Anderson, T.J.; Dixon, M.J.; Levack, P.A. Role of fine needle aspiration cytology in breast cancer screening. J. Clin. Pathol. 1987, 40, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Gartell, P.C.; Smallwood, J.A.; Herbert, A.; Royle, G.; Buchanan, R.; Taylor, I. Fine needle aspiration cytology of breast masses: An evaluation of its accuracy and reasons for diagnostic failure. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1987, 69, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen, C.; Poulsen, H.S.; Jensen, J.; Langfeldt, B.; Steenskov, V.; Frederiksen, P.; Jensen, O.M. Diagnostic reliability of combined physical examination, mammography, and fine-needle puncture (“triple-test”) in breast tumors: A prospective study. Cancer 1987, 60, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Lannin, D.R.; O’Brien, K.; Norris, H.T. The triage role of fine needle aspiration biopsy of palpable breast masses. Diagnostic accuracy and cost-effectiveness. Acta Cytol. 1987, 31, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Fornage, B.D.; Faroux, M.; Simatos, A. Breast masses: US-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Radiology 1987, 162, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Clarke, P.J.; Crucioli, V.; Dehn, T.C.B.; Lee, E.C.G.; Greenall, M.J. Reduction of the surgical excision rate in benign breast disease using fine needle aspiration cytology with immediate reporting. Br. J. Surg. 1987, 74, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; McGuire, M.; Nicholson, F.; Given, H.F. Aspiration cytology and its relevance to the diagnosis of solid tumors of the breast. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1987, 165, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, F.A.; Tinkoff, G.H.; Kline, T.S.; Neal, H.S. Final diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration biopsy for definitive operation in breast cancer. Am. J. Surg. 1987, 154, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrani, A.; Fulciniti, F.; Di Benedetto, G.; Zeppa, P.; Troncone, G.; Boscaino, A.; De Rosa, G.; Palombini, L. Fine-needle aspiration biopsies of breast masses. An additional experience with 1153 cases (1985 to 1988) and a meta-analysis. Cancer 1992, 69, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.; Butler, J.; Cobb, C. Fine-needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of primary breast cancer. Surgery 1988, 103, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azavedo, E.; Svane, G.; Auer, G. Stereotactic fine-needle biopsy in 2594 mammographically detected non-palpable lesions. Lancet 1989, 333, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, S.; Cecchini, S.; Grazzini, G.; Iossa, A.; Bartoli, D.; Cariaggi, M.P.; Bulgaresi, P. Positive predictive value of fine needle aspiration cytology of breast lesions. Acta Cytol. 1989, 33, 894–898. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, V.K.; Cramer, S.; Hood, M. Fine needle aspiration cytology in the management of palpable benign and malignant breast disease. Correlation with clinical and mammographic findings. Acta Cytol. 1989, 33, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, E.J.; Schuettke, C.M.; Ferrier, C.M.; Franzini, D.A.; Bland, K.I. Fine needle aspiration of breast masses. An analysis of 276 aspirates. Acta Cytol. 1989, 33, 613–619. [Google Scholar]
- Gelabert, H.; Hsiu, J.G.; Mullen, J.T.; Jaffe, A.H.; D’Amato, N.A. Prospective evaluation of the role of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis and management of patients with palpable solid breast lesions. Am. Surg. 1990, 56, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, P.; Waldron, D.; Mooney, E.; O’Brien, D.; McGuire, M.; Given, H.F. The role of aspiration cytologic examination in the diagnosis of carcinoma of the breast. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1991, 172, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atamdede, F.I.; Isaacs, J.H. The role of fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Gynecol. Oncol. 1993, 50, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotten, D.; Levaillant, J.M.; Leridon, H.; Letessier, A.; Sandres, M. Ultrasonographically guided fine needle aspiration cytology and core-needle biopsy in the diagnosis of breast tumors. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1993, 49, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneige, N. Fine-needle aspiration of the breast: A review of 1995 cases with emphasis on diagnostic pitfalls. Diagn. Cytopathol. 1993, 9, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Chen, R.; Ho, W. Intraoperative cytology: The use of Liu’s stain for immediate diagnosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi Chin. Med. J. Free China Ed. 1993, 51, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Sneige, N.; Fornage, B.D.; Saleh, G. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of nonpalpable breast lesions: Cytologic and histologic findings. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 102, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, S.; Bonardi, R.; Cariaggi, M.P. Performance of fine-needle aspiration cytology. of the breast-multicenter study of 23,063 aspirates in ten Italian laboratories. Tumori J. 1995, 81, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetto, J.; Pommier, R.; Schmidt, W.; Wachtel, M.; DuBois, P.; Jones, M.; Thurmond, A. Use of the “triple test” for palpable breast lesions yields high diagnostic accuracy and cost savings. Am. J. Surg. 1995, 169, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Stahl, R. Fine-needle aspiration of the breast. Pathology 1996, 4, 253–286. [Google Scholar]
- Purasiri, P.; Abdalla, M.; Heys, S.D.; Ah-See, A.K.; McKean, M.E.; Gilbert, F.; Needham, G.; Deans, H.E.; Eremin, O. A novel diagnostic index for use in the breast clinic. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 1996, 41, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, S.; Castelli, M.; Gattuso, P.; Kluskens, L.; Madsen, K.; Aranha, G. Fine-needle aspiration of 697 palpable breast lesions with histopathologic correlation. Surgery 1997, 122, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snead, D.; Vryenhoef, P.; Pinder, S.E.; Evans, A.; Wilson, A.R.M.; Blamey, R.W.; Elston, C.W.; Ellis, I.O. Routine audit of breast fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology specimens and aspirator inadequate rates. Cytopathology 1997, 8, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feichter, G.E.; Haberthür, F.; Gobat, S.; Dalquen, P. Breast cytology. Statistical analysis and cytohistologic correlations. Acta Cytol. 1997, 41, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, M.; Horiuchi, K.; Joy, N.; Haun, W.; Read, R.; Ratzer, E.; Fenoglio, M. Use of fine needle aspiration for solid breast lesions is accurate and cost-effective. Am. J. Surg. 1997, 174, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, F.; Riera, J.R.; Tojo, S.; Junco, P. Fine needle aspiration of breast masses. An analysis of 1398 patients in a community hospital. Acta Cytol. 1997, 41, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, S.; Del Turco, M.R.; Ambrogetti, D.; Bravetti, P.; Catarzi, S.; Morrone, D.; Cariaggi, M.P. Solid nonpalpable breast lesions: Success and failure of guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in a consecutive series of 2444 cases. Acta Radiol. 1997, 38, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.; Ray, S.; Layer, G. Immediate cytodiagnosis and imaging in the clinical management of discrete benign breast lesions. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1997, 79, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.H.; Ducatman, B.S. Fine needle aspiration of the breast. A probabilistic approach to diagnosis of carcinoma. Acta Cytol. 1998, 42, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardawi, I.M. Fine needle aspiration cytology vs. core biopsy in a rural setting. Acta Cytol. 1998, 42, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijanienko, J.; Côté, J.-F.; Thibault, F.; Zafrani, B.; Meunier, M.; Clough, K.; Asselain, B.; Vielh, P. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology of nonpalpable breast lesions: Institut Curie’s experience with 198 histologically correlated cases. Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1998, 84, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisio, R.; Cuccorese, C.; Accinelli, G.; Mano, M.P.; Bordon, R.; Fessia, L. Role of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in breast lesions: Analysis of a series of 4110 cases. Diagn. Cytopathol. 1998, 18, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Hosone, M.; Katayama, H.; Isobe, H.; Yanagida, Y.; Egami, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Asano, G. Rapid diagnosis at the outpatient clinic for breast tumors by fine needle aspiration cytology The utility. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 1998, 65, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boerner, S.; Fornage, B.D.; Singletary, E.; Sneige, N. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of nonpalpable breast lesions: A review of 1885 FNA cases using the National Cancer Institute-supported recommendations on the uniform approach to breast FNA. Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1999, 87, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaço, L.M.; de Lima, R.S.; Werner, B.; Torres, L.F.B. Value of fine needle aspiration in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Acta Cytol. 1999, 43, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmans, W.F.; Weg, N.; Gross, J.; Cangiarella, J.F.; Tata, M.; Mazzo, J.A.; Waisman, J. A prospective comparison of stereotaxic fine-needle aspiration versus stereotaxic core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of mammographic abnormalities. Cancer 1999, 85, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, A.; Jibril, J.A.; Squair, J.; Heys, S.D.; Ah-See, A.K.; Needham, G.; Gilbert, F.; Deans, H.E.; McKean, M.E.; Smart, L.M.; et al. The accuracy of “one-stop” diagnosis for 1110 patients presenting to a symptomatic breast clinic. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 1999, 44, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zanconati, F.; Bonifacio, D.; Falconieri, G.; Di Bonito, L. Role of fine-needle aspiration cytology in nonpalpable mammary lesions: A comparative cytohistologic study based on 308 cases. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2000, 23, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwun, B.; Settakorn, J.; Ya-In, C.; Wisedmongkol, W.; Rangdaeng, S.; Thorner, P. Effectiveness of fine-needle aspiration cytology of breast: Analysis of 2375 cases from northern Thailand. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2002, 26, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, R.; Bloom, K.; Reddy, V.B.; Kluskens, L.; Francescatti, D.; Dowlat, K.; Siziopikou, P.; Gattuso, P. Fine-needle aspiration of clinically suspicious palpable breast masses with histopathologic correlation. Am. J. Surg. 2002, 184, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshid, G.; Rush, G. The use of fine-needle aspiration cytology and core biopsy in the assessment of highly suspicious mammographic microcalcifications: Analysis of outcome for 182 lesions detected in the setting of a population-based breast cancer screening program. Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2003, 99, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.; Myrvold, K.; Lømo, J.; Anderssen, K.Y.; Skaane, P. Fine-needle aspiration cytology in nonpalpable mammographic abnormalities in breast cancer screening: Results from the breast cancer screening programme in Oslo 1996–2001. Breast 2003, 12, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; McKee, G.T.; Weir, M.M.; Tambouret, R.H.; Eichhorn, J.H.; Pitman, M.B. The negative predicative value of breast fine-needle aspiration biopsy: The Massachusetts General Hospital experience. Breast J. 2004, 10, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnappel, R.; Donk, M.v.D.; Holland, R.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Peterse, J.L.; Hendriks, J.H.C.L.; Peeters, P.H.M. Diagnostic accuracy for different strategies of image-guided breast intervention in cases of nonpalpable breast lesions. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.D.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, J.H.; Juhng, S.W.; Choi, C. Analysis of fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast: A review of 1297 cases and correlation with histologic diagnoses. Acta Cytol. 2004, 48, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorianakou, P.; Fiaccavento, S.; Zagorianakou, N.; Makrydimas, G.; Stefanou, D.; Agnantis, N.J. FNAC: Its role, limitations and perspective in the preoperative diagnosis of breast cancer. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgaresi, P.; Cariaggi, P.; Ciatto, S.; Houssami, N. Positive predictive value of breast fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in combination with clinical and imaging findings: A series of 2334 subjects with abnormal cytology. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 97, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentine, B.D.; Staymates, B.; Rabadi, M.; Barstis, J.; Black, A.; Cancer Committee of the Henry Mayo Newhall Memorial Hospital. The reliability of fine-needle aspiration biopsy as the initial diagnostic procedure for palpable masses: A 4-year experience of 730 patients from a community hospital-based outpatient aspiration biopsy clinic. Cancer 2006, 107, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Tanabe, M.; Momiyama, N.; Chishima, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Nozawa, A.; Sasaki, T.; Kitamura, H.; Shimada, H. False-positive and false-negative cases of fine-needle aspiration cytology for palpable breast lesions. Breast Cancer 2007, 14, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwun, B.; Thorner, P. Fine needle aspiration for evaluation of breast masses. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 19, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocjan, G.; Bourgain, C.; Fassina, A.; Hagmar, B.; Herbert, A.; Kapila, K.; Kardum-Skelin, I.; Kloboves-Prevodnik, V.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Koutselini, H.; et al. The role of breast FNAC in diagnosis and clinical management: A survey of current practice. Cytopathology 2008, 19, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, E.; Mariotto, R.; Remo, A.; Reghellin, D.; Dalfior, D.; Falsirollo, F.; Bonetti, F. Is there still a role for fine-needle aspiration cytology in breast cancer screening? Experience of the Verona Mammographic Breast Cancer Screening Program with real-time integrated radiopathologic activity (1999–2004). Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2008, 114, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pogačnik, A.; Strojan Fležar, M.; Rener, M. Ultrasonographically and stereotactically guided fine-needle aspiration cytology of non-palpable breast lesions: Cyto-histological correlation. Cytopathology 2008, 19, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.; Moatamed, N.; Fimbres, A.M.; Salami, N.; Lim, S.; Apple, S.K. A retrospective study of the diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration for breast lesions and implications for future use. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2008, 36, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feoli, F.; Paesmans, M.; Van Eeckhout, P. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast: Impact of experience on accuracy, using standardized cytologic criteria. Acta Cytol. 2008, 52, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsir, A.; Rapkiewicz, A.; Cangiarella, J. Current utilization of breast FNA in a cytology practice. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2009, 37, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-L.; Chang, T.-W. Can concurrent core biopsy and fine needle aspiration biopsy improve the false negative rate of sonographically detectable breast lesions? BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooistra, B.; Wauters, C.; Strobbe, L.; Wobbes, T. Preoperative cytological and histological diagnosis of breast lesions: A critical review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2010, 36, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A. Core needle biopsy versus fine needle aspiration biopsy in breast—A historical perspective and opportunities in the modern era. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, B.; Wauters, C.; Wobbes, T.; Strobbe, L. Conclusiveness of fine needle aspiration in 2419 histologically confirmed benign and malignant breast lesions. Breast 2011, 20, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, P.-L.; Liu, T.-J.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Lin, H.-P.; Lu, C.-F.; Yao, M.-S.; Chen, C.-L. Rapid staining and immediate interpretation of fine-needle aspiration cytology for palpable breast lesions: Diagnostic accuracy, mammographic, ultrasonographic and histopathologic correlations. Acta Cytol. 2011, 55, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Tsuchiya, S.-I.; Koshikawa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Mibuchi, K.; Nonaka, Y.; Ito, S.; Higuchi, H.; Nagao, M.; Higaki, K.; et al. Evaluation of inadequate, indeterminate, false-negative and false-positive cases in cytological examination for breast cancer according to histological type. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, B.; Crocetti, E.; Bianchi, S.; Catarzi, S.; Risso, G.G.; Bulgaresi, P.; Piscioli, F.; Scialpi, M.; Ciatto, S.; Houssami, N. Accuracy of needle biopsy of breast lesions visible on ultrasound: Audit of fine needle versus core needle biopsy in 3233 consecutive samplings with ascertained outcomes. Breast 2012, 21, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.J.; Heffron, C.C.; Rothwell, J.R.; Loftus, B.M.; Jeffers, M.; Geraghty, J.G. Fine needle aspiration cytology in symptomatic breast lesions: Still an important diagnostic modality? Breast J. 2012, 18, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Masood, S. The value of fine needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis and prognostic assessment of palpable breast lesions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2012, 40, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, T.; Tsuchiya, S.-I.; Watarai, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Harada, O.; Yanagihara, K.; Iida, S.; Yamashita, K.; Haga, S.-S.; Uchida, E. Roles of fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2012, 19, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, S.; Iacco, A.; Riggs, T.; Kestenberg, W.; Keidan, R. An analysis of fine needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy in clinically palpable breast lesions: A report on the predictive values and a cost comparison. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Sehgal, S.; Ghosh, S.; Aggarwal, D.; Shukla, P.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.; Singh, S. Histopathological correlation of atypical (C3) and suspicious (C4) categories in fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 2013, 965498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Rosa, M.; Kraemer, D.F.; Smotherman, C.; Mohammadi, A. Comparative cost-effectiveness of fine needle aspiration biopsy versus image-guided biopsy, and open surgical biopsy in the evaluation of breast cancer in the era of affordable care act: A changing landscape. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aker, F.; Gümrükçü, G.; Onomay, B.; Erkan, M.; Gürleyik, G.; Kiliçoğlu, G.; Karagüllü, H. Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of breast cancer a single-center retrospective study from Turkey with cytohistological correlation in 733 cases. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ly, A.; Arpin, R.; Ahmed, Q.; Brachtel, E. Breast fine needle aspiration continues to be relevant in a large academic medical center: Experience from Massachusetts General Hospital. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, K.L.; Bassett, L.W.; Apple, S.K. Upgrade rates of high-risk breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: A single-institution experience and literature review. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mišković, J.; Zorić, A.; Mišković, H.R.; Šoljić, V. Diagnostic value of fine needle aspiration cytology for breast tumors. Acta Clin. Croat. 2016, 55, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Farras Roca, J.A.; Tardivon, A.; Thibault, F.; El Khoury, C.; Alran, S.; Fourchotte, V.; Marck, V.; Alépée, B.; Sigal, B.; de Rycke, Y.; et al. Diagnostic performance of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of nonpalpable breast lesions in a multidisciplinary setting: The institut curie’s experience. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 147, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Salibay, C.; Elatre, W.; Naritoku, W.Y.; Ma, Y.; Martin, S.E.; Wang, T. Performance of breast fine needle aspiration as an initial diagnostic tool: A large academic hospital experience. Cytopathology 2022, 33, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombini, L.; Fulciniti, F.; Vetrani, A.; de Rosa, G.; Benedetto, G.D.; Zeppa, P.; Troncone, G. Fine-needle aspiration biopsies of breast masses. A critical analysis of 1956 cases in 8 years (1976–1984). Cancer 1988, 61, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, E.; Pinder, S.E. Pre-operative diagnosis of breast cancer in screening: Problems and pitfalls. Pathology 2009, 41, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Souers, R.J.; Tabbara, S.O.; Natale, K.E.; Nguyen, L.N.; Booth, C.N. Breast fine-needle aspiration practice in 2019: Results of a College of American Pathologists National Survey. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennerstam, R.B.; Franzén, B.S.H.; Wiksell, H.O.T.; Auer, G.U. Core-needle biopsy of breast cancer is associated with a higher rate of distant metastases 5 to 15 years after diagnosis than FNA biopsy. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, X.; Chang, Y.; Sun, G.; Thabane, L. A sensitivity and specificity comparison of fine needle aspiration cytology and core needle biopsy in evaluation of suspicious breast lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast 2017, 31, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, P.; Duffy, S.W.; Sinnatamby, R.; Wallis, M.G.; Barter, S.; Gaskarth, M.; O’Neill, A.; Caldas, C.; Brenton, J.D.; Forouhi, P.; et al. One-stop diagnostic breast clinics: How often are breast cancers missed? Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Witt, B.L.; Lopez-Calderon, L.E.; Layfield, L.J. The influence of rapid onsite evaluation on the adequacy rate of fine-needle aspiration cytology: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 139, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torous, V.F.; Lopez, S.H.; Xu, C.; Sweeney, B.J.; Pitman, M.B. Performance of rapid on-site evaluation in breast fine-needle aspiration biopsies: Identifying areas of diagnostic challenge. Acta Cytol. 2022, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, G.; Pilotti, S.; de Yoldi, G.C.; Viganotti, G.; Fariselli, G.; Lepera, P.; Moglia, D. Diagnostic efficacy of physical examination, mammography, fine needle aspiration cytology (triple-test) in solid breast lumps: An analysis of 1708 consecutive cases. Tumori J. 1990, 76, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaloge, S.; Bonastre, J.; Borget, I.; Garbay, J.-R.; Fontenay, R.; Boinon, D.; Saghatchian, M.; Mathieu, M.-C.; Mazouni, C.; Rivera, S.; et al. The challenge of rapid diagnosis in oncology: Diagnostic accuracy and cost analysis of a large-scale one-stop breast clinic. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 66, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Marotti, L.; Bianchi, S.; Biganzoli, L.; Claassen, S.; Decker, T.; Frigerio, A.; Goldhirsch, A.; Gustafsson, E.; Mansel, R.; et al. The requirements of a specialist Breast Centre. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3579–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Cataliotti, L.; Costa, A.; Knox, S.; Marotti, L.; Rutgers, E.; Beishon, M. European Breast Cancer Conference manifesto on breast centres/units. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 72, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.; Sasano, H.; Wu, Y. WHO Classifcation of Tumours Editorial Board: Breast Tumours; WHO classifcation of tumours series; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019.
- MedCalc Software Ltd. Diagnostic Test Evaluation Calculator. Version 22.007. Available online: https://www.medcalc.org/calc/diagnostic_test.php (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Simel, D.L.; Samsa, G.P.; Matchar, D.B. Likelihood ratios with confidence: Sample size estimation for diagnostic test studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1991, 44, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centor, R.M. Estimating confidence intervals of likelihood ratios. Med. Decis. Mak. 1992, 12, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Cohen, J.F.; Korevaar, D.A.; Altman, D.G.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Hooft, L.; Irwig, L.; Levine, D.; Reitsma, J.B.; de Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015 guidelines for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbin, C.M. Recommendations for reporting measures of diagnostic accuracy. Cytopathology 2023, 34, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, T. Nomogram for Bayes’ theorem [carta]. N. Eng. J. Med. 1975, 293, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Diagnostic tests 4: Likelihood ratios. Bmj 2004, 329, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reporting and Data Systems. American College of Radiology. Available online: https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/Bi-Rads (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013. Available online: https://radiologyassistant.nl/breast/bi-rads/bi-rads-for-mammography-and-ultrasound-2013 (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Farras Roca, J.A.; Tardivon, A.; Thibault, F.; Rouzier, R.; Klijanienko, J. Correlation of ultrasound, cytological, and histological features of 110 benign BI-RADS categories 4C and 5 nonpalpable breast lesions. The Institut Curie’s experience. Cancer Cytopathol. 2021, 129, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.; Ellis, I.O.; Zakhour, H.D.; Wilson, A.R. Guidelines for cytology procedures and reporting on fine needle aspirates of the breast. Cytopathology 1994, 5, 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Wells, C. Assessment of accuracy in breast cytology. Cytopathology 2001, 12, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.; Blackham, R. Is there a better way to assess performance in breast cytology? Cytopathology 2001, 12, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Screening at IARC. International Agency for Research on Cancer. World Health Organization. Available online: https://screening.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- The Royal College of Pathologists. Available online: https://www.rcpath.org (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Kuijpers, C.C.; Visser, M.; Sie-Go, D.M.D.S.; de Leeuw, H.; de Rooij, M.J.; van Diest, P.J.; Jiwa, M. Improved cytodiagnostics and quality of patient care through double reading of selected cases by an expert cytopathologist. Virchows Arch. 2015, 466, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, S.; Sneige, N. Specimen adequacy and false-negative diagnosis rate in fine-needle aspirates of palpable breast masses. Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1998, 84, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Lamb, J.; Anderson, T. Fine needle aspiration of the breast: Importance of the operator. Lancet 1983, 322, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.R.; Foster, R.S.; Papillo, J. Fine needle aspiration of the breast. Importance of the aspirator. Acta Cytol. 1987, 31, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M.; Rodgers, R.P.; Hales, M.S.; Gonzales, J.M.; Ljung, B.M.; Beckstead, J.H.; Bottles, K.; Miller, T.R. Influence of training and experience in fine-needle aspiration biopsy of breast. Receiver operating characteristics curve analysis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1987, 111, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Coghill, S. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast: Factors affecting sensitivity. Cytopathology 1991, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, B.M.; Drejet, A.; Chiampi, N.; Jeffrey, J.; Goodson, W.H., 3rd; Chew, K.; Moore, D.H., 2nd; Miller, T.R. Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy is determined by physician training in sampling technique. Cancer Cytopathol. Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2001, 93, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, E.D.; Fajardo, L.L.; Caudry, D.J.; Sneige, N.; Frable, W.J.; Berg, W.A.; Tocino, I.; Schnitt, S.J.; Connolly, J.L.; Gatsonis, C.A.; et al. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions in a multicenter clinical trial: Results from the radiologic diagnostic oncology group V. Radiology 2001, 219, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.R.; Ljung, B.M. Teaching and learning FNA biopsy: An update for the modern audience. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019, 127, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.A.; Ham, E.K. Fine needle aspiration cytology of palpable breast lesions. Acta Cytol. 1997, 41, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennes, D.; Naylor, B.; Rebner, M. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the breast. Influence of the number of passes and the sample size on the diagnostic yield. Acta Cytol. 1990, 34, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Manfrin, E.; Falsirollo, F.; Remo, A.; Reghellin, D.; Mariotto, R.; Dalfior, D.; Piazzola, E.; Bonetti, F. Cancer size, histotype, and cellular grade may limit the success of fine-needle aspiration cytology for screen-detected breast carcinoma. Cancer Cytopathol. A J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2009, 117, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Howard, K.; Hall, B.J.; Layfield, L.J. The comparative effectiveness of fine-needle aspiration cytology sampling policies: A simulation study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Kordy, M. Mathematical modelling can predict adequacy rates and needle passes for fine needle aspiration cytology with rapid on-site evaluation. Cytopathology 2015, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabb, N.S.; Boulos, F.I.; Chakhachiro, Z.; Abbas, J.; Abdul-Karim, F.W. Inconclusive or erroneous fine-needle aspirates of breast with adequate and representative material: A cytologic/histologic study. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borget, I.; Vielh, P.; Leboulleux, S.; Allyn, M.; Iacobelli, S.; Schlumberger, M.; de Pouvourville, G. Assessment of the cost of fine-needle aspiration cytology as a diagnostic tool in patients with thyroid nodules. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 129, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukkinen, K.; Kivisaari, L.; Heikkilä, P.S.; Von Smitten, K.; Leidenius, M. Unsuccessful preoperative biopsies, fine needle aspiration cytology or core needle biopsy, lead to increased costs in the diagnostic workup in breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 2008, 47, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Walker, B.S.; Cohen, M.B. When is rapid on-site evaluation cost-effective for fine-needle aspiration biopsy? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, J.N.; Nigam, J.S.; Rath, A.; Pradeep, I. Insufficient/inadequate category in breast cytology: Are the standardized guidelines of rapid on-site evaluation available to reduce its rate? Diagn. Cytopathol. 2023, 51, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orell, S.R.; Miliauskas, J. Fine needle biopsy cytology of breast lesions: A review of interpretative difficulties. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2005, 12, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, G.; Ma, T.K.; Lui, P.C.; Ng, D.C.; Yu, A.M.; Vong, J.S.; Niu, Y.; Chaiwun, B.; Lam, W.W.; Tan, P.H. Fine needle aspiration cytology of papillary lesions of the breast: How accurate is the diagnosis? J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Fine-Needle Aspiration of Breast Workshop Subcommittees. Unif. Approach Breast Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy. Diagn. Cytopathol. 1997, 16, 295–311. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A.S.; Schmitt, F.; Vielh, P. IAC standardized reporting of breast fine-needle aspiration biopsy cytology. Acta Cytol. 2017, 61, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.S.; Raymond, W.A.; Rickard, M.; Arnold, L.; Brachtel, E.F.; Chaiwun, B.; Chen, L.; Di Bonito, L.; Kurtycz, D.F.I.; Lee, A.H.S.; et al. The International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System for Reporting Breast Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Cytopathology: Introduction and Overview, in The International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System for Reporting Breast Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Cytopathology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Orell, S. Radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion—A problem in the diagnostic work-up of screen-detected breast lesions. Cytopathology 1999, 10, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.; Mak, A. A prospective study of the diagnostic accuracy of cytological criteria in the FNAB diagnosis of breast papillomas. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2007, 35, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, E.M.L.; Chan, S.-K.; Vong, J.S.L.; Lui, P.C.W.; Chan, A.W.H.; Ma, T.K.F.; Ang, M.A.; Law, B.K.B.; Tan, P.-H.; Tse, G.M. Predictors of invasion in needle core biopsies of the breast with ductal carcinoma in situ. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, J.G.; Longton, G.M.; Carney, P.A.; Geller, B.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Nelson, H.D.; Pepe, M.S.; Allison, K.H.; Schnitt, S.J.; et al. Diagnostic concordance among pathologists interpreting breast biopsy specimens. JAMA 2015, 313, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Aleskandarany, M.A.; Hodi, Z.; Lee, A.H.S.; Pinder, S.E.; Ellis, I.O. Diagnostic concordance of breast pathologists: Lessons from the National health service breast screening programme pathology external quality assurance scheme. Histopathology 2017, 70, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-N.; Li, J.; Wong, S.-I.; Tsang, J.Y.S.; Ni, Y.-B.; Chen, J.; Tse, G.M. Atypical aspirates of the breast: A dilemma in current cytology practice. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinder, S.; Shaaban, A.; Deb, R.; Desai, A.; Gandhi, A.; Lee, A.; Pain, S.; Wilkinson, L.; Sharma, N. NHS Breast Screening multidisciplinary working group guidelines for the diagnosis and management of breast lesions of uncertain malignant potential on core biopsy (B3 lesions). Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rageth, C.J.; O’flynn, E.A.M.; Pinker, K.; Kubik-Huch, R.A.; Mundinger, A.; Decker, T.; Tausch, C.; Dammann, F.; Baltzer, P.A.; Fallenberg, E.M.; et al. Second International Consensus Conference on lesions of uncertain malignant potential in the breast (B3 lesions). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandenBussche, C.J.; Khouri, N.; Sbaity, E.; Tsangaris, T.N.; Vang, R.; Tatsas, A.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Argani, P. Borderline atypical ductal hyperplasia/low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ on breast needle core biopsy should be managed conservatively. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Gary, M.T. Core needle biopsy diagnosis of fibroepithelial lesions of the breast: A diagnostic challenge. Pathology 2020, 52, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamidi, S.K.; Li, J.J.X.; Aphivatanasiri, C.; Chow, M.B.C.Y.; Chan, R.C.K.; Ng, J.K.M.; Tsang, J.Y.; Tse, G.M. Papillary lesions of the breast: A systematic evaluation of cytologic parameters. Cancer Cytopathol. 2021, 129, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Gary, M.T. Papillary Lesions of the Breast–Review and Practical Issues. In Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Elfgen, C.; Leo, C.; Kubik-Huch, R.A.; Muenst, S.; Schmidt, N.; Quinn, C.; McNally, S.; van Diest, P.J.; Mann, R.M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; et al. Third International Consensus Conference on lesions of uncertain malignant potential in the breast (B3 lesions). Virchows Arch. 2023, 483, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, M.W.; Sidawy, M.K.; Sanchez, M.A.; Stahl, R.E.; Goldfischer, M. Current issues in breast cytopathology. Pathol. Patterns Rev. 2000, 113 (Suppl. S1), S49–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennison, G.; Anand, R.; Makar, S.H.; Pain, J.A.; Frcs, G.D.; Frcs, R.A.; Frcs, S.H.M.; Frcs, J.A.P. A prospective study of the use of fine-needle aspiration cytology and core biopsy in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast J. 2003, 9, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Ashida, K. Possible intervention of insulin, cyclic AMP, and glucocorticoids in protein-sparing action of dietary carbohydrate in rats. J. Nutr. 1975, 105, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.d.A.; Gobbi, H.; de L Rezende, C.A.; Gouvêa, A.P.; de Lucena, C.E.; Reis, J.H.; Costa e Silva, S.Z. A comparision of aspiration cytology and core needle biopsy according to tumor size of suspicious breast lesions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2008, 36, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.J.; Al-Mubarak, G.; Homer, M.J.; Goldkamp, A.; Samenfeld-Specht, M.; Lee, Y.; Logvinenko, T.; Rothschild, J.G.; Graham, R.A. A modified triple test for palpable breast masses: The value of ultrasound and core needle biopsy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustova, P.; Klijanienko, J. Value of combined use of fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy in palpable breast tumors performed by pathologist: Institut curie experience. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2020, 48, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Singh, D.; Mehan, A.; Paul, P.; Puri, N.; Gupta, P.; Syed, A.; Rao, S.; Chowdhury, N.; Ravi, B. Accuracy of the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama system of breast cytology reporting for fine needle aspiration biopsy of the breast in a dedicated breast care setting. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2021, 49, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, J.S.; Miller, T.R.; Goodson, W.H.; Hunt, T.K.; Hohn, D.C. Fine-needle aspiration of palpable breast masses: A program for staged implementation. Arch. Surg. 1983, 118, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohs, H.K. Starting Out: The Interventional Cytopathologist: A New Clinician/Pathologist Hybrid. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 90, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Coghill, S.; Powis, S. Audit of diagnostic accuracy of FNA cytology specimens taken by the histopathologist in a symptomatic breast clinic. Cytopathology 1991, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coghill, S.; Brown, L. Why Pathologists Should Take Needle Aspiration Specimens; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 6, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abele, J.S. The case for pathologist ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Cancer 2008, 114, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, D. Cytopathologist-performed ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and core-needle biopsy: A prospective study of 500 consecutive cases. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2008, 36, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, D. Value of cytopathologist-performed ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration as a screening test for ultrasound-guided core-needle biopsy in nonpalpable breast masses. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2009, 37, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, H.T.; Cibas, E.S.; Kraft, A.O.; Jiang, X.; Foo, W.-C.; Sanchez, M.A.; Powers, C.N. Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Practice Patterns. AJSP Rev. Rep. 2018, 23, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bellevicine, C.; Vigliar, E.; Malapelle, U.; Pisapia, P.; Conzo, G.; Biondi, B.; Vetrani, A.; Troncone, G. Cytopathologists can reliably perform ultrasound-guided thyroid fine needle aspiration: A 1-year audit on 3715 consecutive cases. Cytopathology 2016, 27, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Burton, L.G.; Stanley, M.W.; Horwitz, C.A. Application of a modified Diff-Quik stain to fine needle aspiration smears: Rapid staining with improved cytologic detail. Acta Cytol. 1987, 31, 954–955. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.F.; Frable, W.J. The use of the Diff-Quik stain in the immediate interpretation of fine-needle aspiration biopsies. Diagn. Cytopathol. 1990, 6, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschowitz, S.L.; Mandell, D.; Nieberg, R.K.; Carson, K. The alcohol-fixed Diff-Quik stain. A novel rapid stain for the immediate interpretation of fine needle aspiration specimens. Acta Cytol. 1994, 38, 499–501. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Alvarez, I.I. Ultrafast Papanicolaou stain. An alternative preparation for fine needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol. 1995, 39, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ammanagi, A.; Dombale, V.; Patil, S.S. On-site toluidine blue staining and screening improves efficiency of fine-needle aspiration cytology reporting. Acta Cytol. 2012, 56, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewer, E.; Schmitt, A.M. Ultrafast toluidine blue staining for rapid on-site evaluation of cytological smears. Acta Cytol. 2020, 64, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummidi, S.; Shankaralingappa, A.; Sharmila, V. Applicability of On-Site Evaluation of Cervical Cytology Smears Stained with Toluidine Blue to Reduce Unsatisfactory Results. Acta Cytol. 2022, 66, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, L.N.; Layfield, L.J.; Schmidt, R.L. Cost-effectiveness of rapid on-site evaluation of the adequacy of FNA cytology samples performed by nonpathologists. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.; Govindarajulu, S.; Shere, M.; Braddon, F.; Curran, G.; Greenwood, R.; Sahu, A.K.; Cawthorn, S.J. Referral patterns, cancer diagnoses, and waiting times after introduction of two week wait rule for breast cancer: Prospective cohort study. Bmj 2007, 335, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, M.R.; Conte, J.; Fadel, D.A.; Raia, C.; Forte, F.; Ahern, K.; Smith, M.; ElSayeh, D.; Buchbinder, S. Improving access to breast health services with an interdisciplinary model of care. Breast J. 2008, 14, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliski, C.; McGahan, C.E.; Liberto, C.M.; Broughton, S.; Ellard, S.; Taylor, M.; Bates, J.; Lai, A. Influence of nurse navigation on wait times for breast cancer care in a Canadian regional cancer center. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 207, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKevitt, E.C.; Dingee, C.K.; Leung, S.-P.; Brown, C.J.; Van Laeken, N.Y.; Lee, R.; Kuusk, U. Reduced time to breast cancer diagnosis with coordination of radiological and clinical care. Cureus 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biganzoli, L.; Marotti, L.; Hart, C.D.; Cataliotti, L.; Cutuli, B.; Kühn, T.; Mansel, R.E.; Ponti, A.; Poortmans, P.; Regitnig, P.; et al. Quality indicators in breast cancer care: An update from the EUSOMA working group. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breast Screening: Clinical Guidelines for Screening Assessment. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/567600/Clinicalguidance_for_breast__cancer_screening__assessment_Nov_2016.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- The Royal College of Pathologists. Cancer Datasets and Tissue Pathways. Available online: https://www.rcpath.org/profession/guidelines/cancer-datasets-and-tissue-pathways.html# (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Bevers, T.B.; Helvie, M.; Bonaccio, E.; Calhoun, K.E.; Daly, M.B.; Farrar, W.B.; Garber, J.E.; Gray, R.; Greenberg, C.C.; Greenup, R. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis, version 3.2018, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 1362–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rubio, I.T.; Zackrisson, S.; Senkus, E.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1194–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bick, U.; Trimboli, R.M.; Athanasiou, A.; Balleyguier, C.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Bernathova, M.; Borbély, K.; Brkljacic, B.; Carbonaro, L.A.; Clauser, P.; et al. Image-guided breast biopsy and localisation: Recommendations for information to women and referring physicians by the European Society of Breast Imaging. Insights Into Imaging 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, R.; Honma, N.; Ogiya, A.; Kozuka, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, M.; Horiguchi, S.-I.; Ito, Y.; Mukai, H. The Japanese Breast Cancer Society clinical practice guidelines for pathological diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2016, 23, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, J.; Leblanc, M.; Elgbeili, G.; Cordova, M.J.; Marin, M.-F.; Brunet, A. The mental health impacts of receiving a breast cancer diagnosis: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, C.J.; Carpenter, K.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Evidence-based strategies to reduce suicide mortality among patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M.; McCrone, S.H. Psychological distress associated with the diagnostic phase for suspected breast cancer: Systematic review. J. Adv. Nurs. 2010, 66, 2372–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocken, P.; Prins, J.B.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.; van der Heijden, H.F. The faster the better?—A systematic review on distress in the diagnostic phase of suspected cancer, and the influence of rapid diagnostic pathways. Psycho-Oncol. 2012, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinon, D.; Dauchy, S.; Charles, C.; Fasse, L.; Cano, A.; Balleyguier, C.; Mazouni, C.; Caron, H.; Vielh, P.; Delaloge, S. Patient satisfaction with a rapid diagnosis of suspicious breast lesions: Association with distress and anxiety. Breast J. 2018, 24, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. An overview of clinical research: The lay of the land. Lancet 2002, 359, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. Descriptive studies: What they can and cannot do. Lancet 2002, 359, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. Bias and causal associations in observational research. Lancet 2002, 359, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Factor, R.E. Understanding sources of bias in diagnostic accuracy studies. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.; Gersbach, E.; Yang, X.J.; Rohan, S.M. Differential diagnosis of renal tumors with clear cytoplasm: Clinical relevance of renal tumor subclassification in the era of targeted therapies and personalized medicine. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Walker, B.S.; Cohen, M.B. Verification and classification bias interactions in diagnostic test accuracy studies for fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015, 123, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, K.F.; Grimes, D.A. Blinding in randomised trials: Hiding who got what. Lancet 2002, 359, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Hall, B.J.; Wilson, A.R.; Layfield, L.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology for parotid gland lesions. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Hunt, J.P.; Hall, B.J.; Wilson, A.R.; Layfield, L.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of frozen section for parotid gland lesions. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Cook, J.B.; Affolter, K.E.; Factor, R.E.; Hall, B.J.; Narra, K.K.; Witt, B.L.; Layfield, L.J. Methods specification for diagnostic test accuracy studies in fine-needle aspiration cytology: A survey of reporting practice. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, J.E.; March, J.K.; Cohen, M.B.; Schmidt, R.L. A survey of the prevalence and impact of reporting guideline endorsement in pathology journals. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 148, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Irwig, L.; Craig, J.; Glasziou, P. Comparative accuracy: Assessing new tests against existing diagnostic pathways. Bmj 2006, 332, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Ende, J.; Moreira, J.; Basinga, P.; Bisoffi, Z. The trouble with likelihood ratios. Lancet 2005, 366, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Taylor, C.; Ramirez, A.-J.; Palmieri, C.; Gunnarsson, U.; Schmoll, H.J.; Dolci, S.M.; Ghenne, C.; Metzger-Filho, O.; Skrzypski, M.; et al. Role of the multidisciplinary team in breast cancer management: Results from a large international survey involving 39 countries. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héquet, D.; Huchon, C.; Baffert, S.; Alran, S.; Reyal, F.; Nguyen, T.; Combes, A.; Trichot, C.; Alves, K.; Berseneff, H.; et al. Preoperative clinical pathway of breast cancer patients: Determinants of compliance with EUSOMA quality indicators. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souadka, A.; Houmada, A.; Souadka, A. Multidisciplinary team meeting as a highly recommended EUSOMA criteria evaluating the quality of breast cancer management between centers. Breast Off. J. Eur. Soc. Mastology 2021, 60, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biganzoli, L.; Battisti, N.M.L.; Wildiers, H.; McCartney, A.; Colloca, G.; Kunkler, I.H.; Cardoso, M.-J.; Cheung, K.-L.; de Glas, N.A.; Trimboli, R.M.; et al. Updated recommendations regarding the management of older patients with breast cancer: A joint paper from the European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists (EUSOMA) and the International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG). Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e327–e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.; Trimboli, R.M.; Athanasiou, A.; Balleyguier, C.; Baltzer, P.A.; Bick, U.; Herrero, J.C.; Clauser, P.; Colin, C.; Cornford, E.; et al. Breast ultrasound: Recommendations for information to women and referring physicians by the European Society of Breast Imaging. Insights Into Imaging 2018, 9, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwig, L.; Bossuyt, P.; Glasziou, P.; Gatsonis, C.; Lijmer, J. Designing studies to ensure that estimates of test accuracy are transferable. Bmj 2002, 324, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. Uses and abuses of screening tests. Lancet 2002, 359, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daramola, A.O.; Odubanjo, M.O.; Obiajulu, F.J.; Ikeri, N.Z.; Banjo, A.A. Correlation between fine-needle aspiration cytology and histology for palpable breast masses in a Nigerian tertiary health institution. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 2015, 742573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkonge, K.M.; Rogena, E.A.; Walong, E.O.; Nkonge, D.K. Cytological evaluation of breast lesions in symptomatic patients presenting to Kenyatta National Hospital, Kenya: A retrospective study. BMC Women’s Health 2015, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibikunle, D.E.; Omotayo, J.A.; Ariyibi, O.O. Fine needle aspiration cytology of breast lumps with histopathologic correlation in Owo, Ondo State, Nigeria: A five-year review. Ghana Med. J. 2017, 51, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.S. Cytopathology in low medical infrastructure countries: Why and how to integrate to capacitate health care. Clin. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, K.E.; Bird, P.; Sturgis, C.D. Concordance of breast fine needle aspiration cytology interpretation with subsequent surgical pathology: An 18-year review from a single sub-Saharan African institution. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.A.; Stahl, R.E. Fine–needle aspiration biopsy of the breast. Cancer 2008, 114, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.A.; Burga, A.M.; Ljung, B.M. Primum Non Nocere; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 745–747. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).