Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Sequential Use for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Real-Life Campus All Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
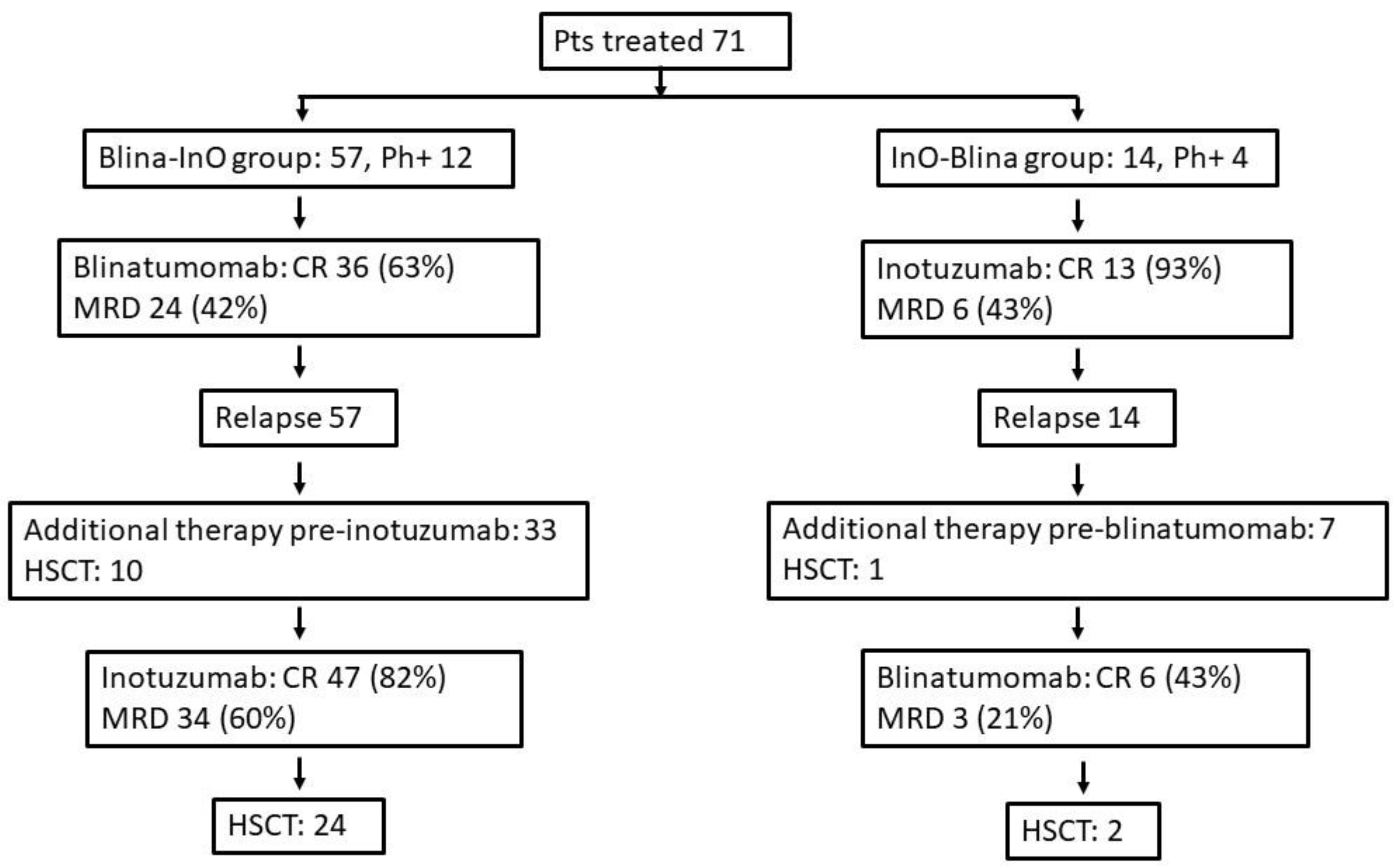
3. Results
3.1. Baselines Characteristics
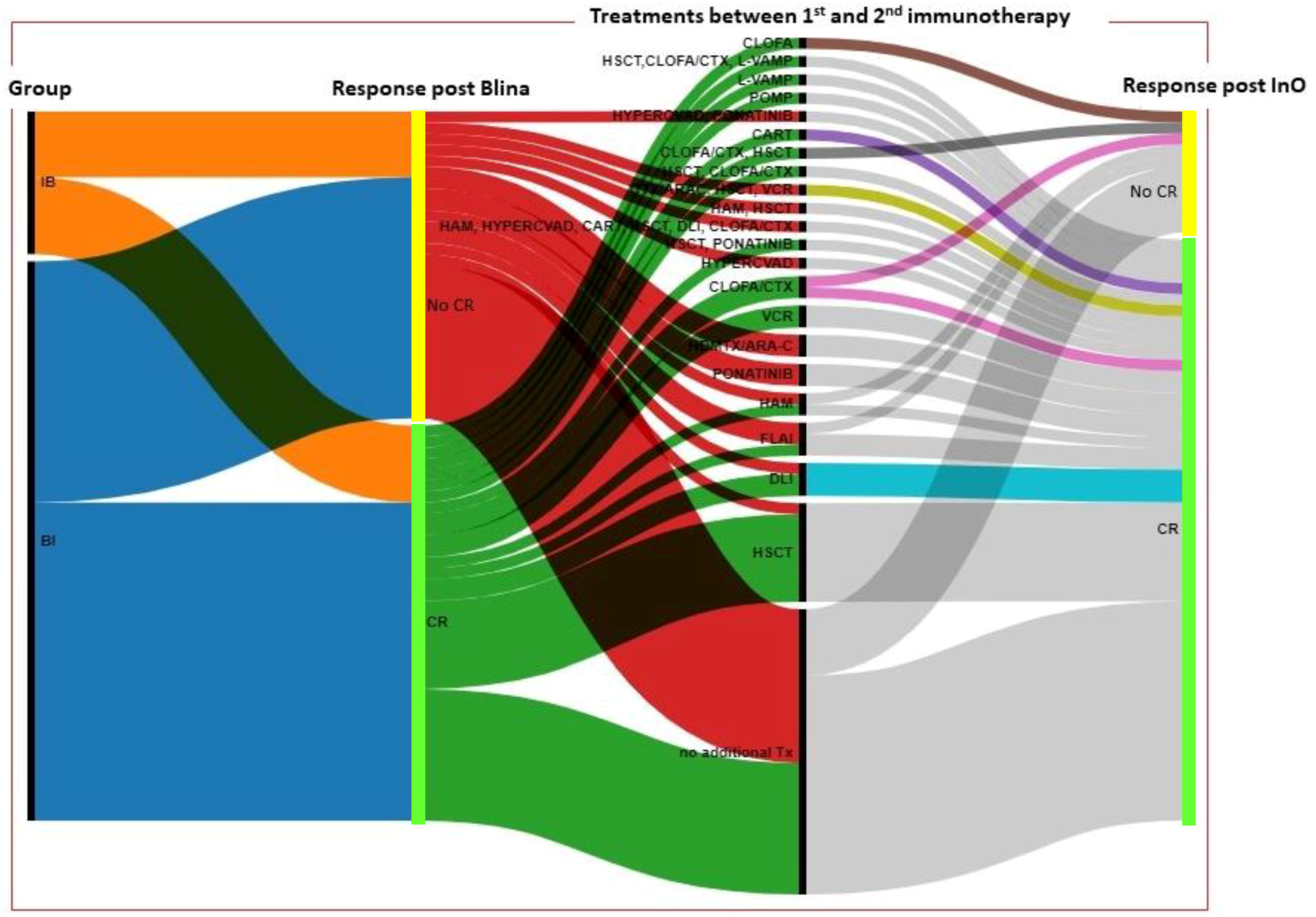
3.2. Response and outcome
3.3. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL). Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/alyl.html (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Bassan, R.; Bourquin, J.-P.; De Angelo, D.J.; Chiaretti, S. New approaches to the management of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3512–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökbuget, N.; Dombret, H.; Ribera, J.-M.; Fielding, A.K.; Advani, A.; Bassan, R.; Chia, V.; Doubek, M.; Giebel, S.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. International reference analysis of outcomes in adults with B-precursor Ph-negative relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.; Stein, A.; Gökbuget, N.; Fielding, A.K.; Schuh, A.C.; Ribera, J.-M.; Wei, A.; Dombret, H.; Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Martinelli, G.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gökbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Dombret, H.; Chevallier, P.; Ottmann, O.G.; Goekbuget, N.; Topp, M.S.; Fielding, A.K.; Sterling, L.R.; Benjamin, J.; Stein, A.S. Complete molecular and hematologic response in adult patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) Philadelphia chromosome–positive B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) following treatment with blinatumomab: Results from a phase 2 single-arm, multicenter study (ALCANTARA). Blood 2015, 126, 679. [Google Scholar]
- George, B.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.; Jain, N.; Thomas, X.; Kuramitsu, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Ohka, F.; Motomura, K.; Hara, M.; et al. Role of inotuzumab ozogamicin in the treatment of relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, G.; Piciocchi, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Papayannidis, C.; Lunghi, M.; Salutari, P.; Zappasodi, P.; Rambaldi, A.; Olivieri, A.; Cavallari, M.; et al. Gimema ALL2418: Interim Analysis of a Phase IIa Study of Feasibility and Effectiveness of Inotuzumab Ozogamicin in Adult Patients with B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Positive Minimal Residual Disease before Any Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 6119–6121. [Google Scholar]
- Badar, T.; Advani, A.S.; Liedtke, M.; Arslan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Aldoss, I.; Sienbenaller, C.; Schultz, E.; Hefazi, M.; Shallis, R.M.; et al. Clinical outcome with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after blinatumomab or inotuzumab ozogamicin in patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Real world experience. Biol. Blood Marrow. Transplant. 2020, 26, S101–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, T.; Szabo, A.; Wadleigh, M.; Liedtke, M.; Arslan, S.; Siebenaller, C.; Aldoss, I.; Schultz, E.; Hefazi, M.; Litzow, M.R.; et al. Real world outcomes of adult B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with inotuzumab ozogamicin. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 556–560.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.; Haddad, F.G.; Jain, N.; Sasaki, K.; Short, N.J.; Loghavi, S.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Jorgensen, J.; Khouri, I.; Kebriaei, P.; et al. Results of salvage therapy with mini-hyper-CVD and inotuzumab ozogamicin with or without blinatumomab in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Jain, N.; Haddad, F.G.; Welch, M.A.; Ravandi, F.; Kantarjian, H. The evolution of acute lymphoblastic leukemia research and therapy at MD Anderson over four decades. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsallab, M.; Ellithi, M.; Hempel, S.; Abdel-Azim, H.; Abou-El-Enein, M. Long-term response to autologous anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells in relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, J.-M.; Chiaretti, S. Modern management options for Ph+ ALL. Cancers 2022, 14, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökbuget, N.; Dombret, H.; Bonifacio, M.; Reichle, A.; Graux, C.; Faul, C.; Diedrich, H.; Topp, M.S.; Brüggemann, M.; Horst, H.-A.; et al. Blinatumomab for minimal residual disease in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, M.S.; Gökbuget, N.; Zugmaier, G.; Stein, A.S.; Dombret, H.; Chen, Y.; Ribera, J.; Bargou, R.C.; Horst, H.; Kantarjian, H.M. Long term survival of patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with blinatumomab. Cancer 2021, 12784, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Sasaki, K.; Short, N.J.; Ravandi, F.; Huang, X.; Khoury, J.D.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Jorgensen, J.; Khouri, I.F.; Kebriaei, P.; et al. Long-term follow-up of salvage therapy using a combination of inotuzumab ozogamicin and mini-hyper-CVD with or without blinatumomab in relapsed/refractory Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2021, 127, 2025–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegyes, D.; Jitaru, C.; Ghiaur, G.; Ciurea, S.; Hoelzer, D.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gale, R.P. Switching from salvage chemotherapy to immunotherapy in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Rev. 2023, 59, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-N.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. CD19 CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Factors affecting toxicities and long-term efficacies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.V.; Shaw, P.A.; Hexner, E.O.; Pequignot, E.; Gill, S.; Luger, S.M.; Mangan, J.K.; Loren, A.W.; Perl, A.E.; Maude, S.L.; et al. Optimizing Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaldi, A.; Huguet, F.; Zak, P.; Cannell, P.; Tran, Q.; Franklin, J.; Topp, M.S. Blinatumomab consolidation and maintenance therapy in adults with relapsed/refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R.; Bassan, R.; Vitale, A.; Elia, L.; Piciocchi, A.; Puzzolo, M.-C.; Canichella, M.; Viero, P.; Ferrara, F.; Lunghi, M.; et al. Dasatinib blinatumomab for Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaretti, S.; Bassan, R.; Vitale, A.; Elia, L.; Piciocchi, A.; Viero, P.; Ferrara, F.; Lunghi, M.; Fabbiano, F.; Bonifacio, M.; et al. Forty months update of the GIMEMA LAL2116 (D-ALBA) protocol and ancillary LAL2217 study for newly diagnosed adult Ph+. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Jain, N.; Huang, X.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Banerjee, P.; Rezvani, K.; Jiang, X.; Kim, K.H.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; et al. Ponatinib and blinatumomab for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A US, single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e24–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassan, R.; Chiaretti, S.; Della Starza, I.; Spinelli, O.; Santoro, A.; Elia, L. Preliminary results of the GIMEMA LAL2317 sequential chemotherapy-blinatumomab front-line trial for newly diagnosed adult Ph-negative B-lineage ALL patients. EHA Libr. 2021, 324522, S114. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbour, E.; Short, N.J.; Senapati, J.; Jain, N.; Huang, X.; Daver, N.; Di Nardo, C.D.; Pemmaraju, N.; Wierda, W.; Garcia-Manero, G.; et al. Mini-hyper-CVD plus inotuzumab ozogamicin, with or without blinatumomab, in the subgroup of older patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-negative B-cell acute lymphocytic leukaemia: Long-term results of an open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e433–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissel, N.; Huguet, F.; Graux, C.; Hicheri, Y.; Chevallier, P.; Kim, R.; Balsat, M.; Leguay, T.; Hunault, M.; Maury, S.; et al. Frontline consolidation with blinatumomab for high-risk philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic adult patients. Early results from the Graall-2014- QUEST Phase 2. Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, T.; Szabo, A.; Dinner, S.; Liedtke, M.; Burkart, M.; Shallis, R.M.; Yurkiewicz, I.R.; Kuo, E.; Khan, M.A.; Balasubramanian, S.; et al. Sequencing of novel agents in relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Blinatumomab and inotuzumab ozogamicin may have comparable efficacy as first or second novel agent therapy in relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2021, 127, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelo, D.J.; Advani, A.S.; Marks, D.I.; Stelljes, M.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gökbuget, N.; Jabbour, E.; Merchant, A.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Outcomes by disease burden. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, M.; Papayannidis, C.; Lussana, F.; Fracchiolla, N.; Annunziata, M.; Sica, S.; Delia, M.; Foà, R.; Pizzolo, G.; Chiaretti, S. Real-World Multicenter Experience in Tumor Debulking Prior to Blinatumomab Administration in Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 804714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Blina/InO Group | No. 57 | InO/Blina Group | No. 14 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—median (range) pre Blina | 33 (15–64) * | Age—median (range) pre InO | 41.5 (22–64) * |
| Male/female | 34/23 | Male/female | 10/4 |
| ECOG n° (%) pre Blina | ECOG n° (%) pre InO | ||
| 0 | 33 | 0 | 8 |
| 1 | 21 | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Treatments pre-Blina—median (range) | 2 (1–8) | Treatments pre-InO—median (range) | 3 (1–9) |
| Previous HSCT—n° (%) | 24/57 (42%) | Previous HSCT—n° (%) | 3/14 (21%) |
| WBC (×109/L)—median (range) pre Blina | 4.8 (0.7–98) | WBC (×109/L)—median (range) pre InO | 6.3 (1–101) |
| WBC (×109/L)—median (range) pre InO | 5.4 (1.3–101.4) | WBC (×109/L)—median (range) pre Blina | 5.3 (34) |
| Bone marrow blast median % (range) pre Blina | 40 (0–100) | Bone marrow blast median % (range) pre Ino | 64 (2–90) |
| Bone marrow blast median % (range) pre InO | 50 (0–90) | Bone marrow blast median % (range) pre Blina | 34 (0–90) |
| Ph+—n° (%) | 12/57 (21%) | Ph+—n° (%) | 4/14 (29%) |
| Extramedullary involvement—n° (%) pre Blina | 5/57 (9%) | Extramedullary involvement—n° (%) pre InO | 1/14 (7%) |
| Blina cycles—median (range) InO cycles—median (range) | 2 (1–9) 2 (1–6) | InO cycles—median (range) Blina cycles—median (range) | 2 (1–4) 1.5 (1–4) |
| Toxicity G3/4—n° (%) after Blina | 15/57 (26%) | Toxicity G3/4—n° (%) after InO | 3/14 (21%) |
| Hematological | 3 | Hematological | 1 |
| Extrahematological | 12 | Extrahematological | 2 |
| Neurological | 4 | Hepatic | 1 |
| Infectious AEs—n° (%) | 17/57 (31%) | Infectious AEs—n° (%) after InO | 4/14 (28%) |
| Toxicity G3/4—n° (%) after InO | 12/57 (21%) | Toxicity G3/4—n° (%) after Blina | 3/14 (21%) |
| Hematological | 9 | Hematological | 1 |
| Extrahematological | 3 | Extrahematological | 2 |
| 1 CMV enterocolitis, 1 sacroiliitis, 1 hepatic | Pulmonary thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis | ||
| Infectious AEs—n° (%) after InO | 21/57 (37%) | Infectious AEs—n° (%) after Blina | 4/14 (28%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fracchiolla, N.S.; Sciumè, M.; Papayannidis, C.; Vitale, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Annunziata, M.; Giglio, F.; Salutari, P.; Forghieri, F.; Lazzarotto, D.; et al. Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Sequential Use for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Real-Life Campus All Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184623
Fracchiolla NS, Sciumè M, Papayannidis C, Vitale A, Chiaretti S, Annunziata M, Giglio F, Salutari P, Forghieri F, Lazzarotto D, et al. Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Sequential Use for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Real-Life Campus All Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184623
Chicago/Turabian StyleFracchiolla, Nicola Stefano, Mariarita Sciumè, Cristina Papayannidis, Antonella Vitale, Sabina Chiaretti, Mario Annunziata, Fabio Giglio, Prassede Salutari, Fabio Forghieri, Davide Lazzarotto, and et al. 2023. "Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Sequential Use for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Real-Life Campus All Study" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184623
APA StyleFracchiolla, N. S., Sciumè, M., Papayannidis, C., Vitale, A., Chiaretti, S., Annunziata, M., Giglio, F., Salutari, P., Forghieri, F., Lazzarotto, D., Lunghi, M., Imovilli, A., Scappini, B., Bonifacio, M., Dargenio, M., Gurrieri, C., Todisco, E., Defina, M., Del Principe, M. I., ... Curti, A. (2023). Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Sequential Use for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Real-Life Campus All Study. Cancers, 15(18), 4623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184623










