The Epidemiological Pattern of Skin Cancer from 2011 to 2022 among the Population of the Aseer Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting and Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousef, H.; Alhajj, M.; Sharma, S. Anatomy, skin (integument), epidermis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, K.; Mehrmal, S.; Uppal, P.; Giesey, R.L.; Delost, G.R. The global burden of skin cancer: A longitudinal analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study, 1990–2017. JAAD Int. 2021, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losquadro, W.D. Anatomy of the skin and the pathogenesis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. 2017, 25, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, A.; He, Z.; Shen, X.; Dong, X.; Feng, J.; Lu, H. Global, regional and national incidence, mortality and disability-adjusted life-years of skin cancers and trend analysis from 1990 to 2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4905–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.H.; Mir, M.; Qian, L.; Baloch, M.; Khan, M.F.A.; Ngowi, E.E.; Wu, D.-D.; Ji, X.-Y. Skin cancer biology and barriers to treatment: Recent applications of polymeric micro/nanostructures. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 36, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Kramer, J.L.; Rowland, J.H.; Stein, K.D.; Alteri, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2017/cancer-facts-and-figures-2017.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Barton, V.; Armeson, K.; Hampras, S.; Ferris, L.K.; Visvanathan, K.; Rollison, D.; Alberg, A.J. Nonmelanoma skin cancer and risk of all-cause and cancer-related mortality: A systematic review. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Lallas, A.; Sotiriou, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Ioannides, D. Epidemiological trends in skin cancer. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A. Changing patterns in incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer. Epithel. Cell Biol. 1992, 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, D.M.; Ding, H.; Guy, G.P., Jr.; Watson, M.; Hartman, A.M.; Perna, F.M. Prevalence of sun protection use and sunburn and association of demographic and behaviorial characteristics with sunburn among US adults. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, W.H. Behavioral factors associated with disease, injury, and death among men: Evidence and implications for prevention. J. Mens Stud. 2000, 9, 81–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddock, L.E.; Lu, S.E.; Bandera, E.V.; Rhoads, G.G.; Fine, J.; Paine, S.; Barnhill, R.; Berwick, M. Skin self-examination and long-term melanoma survival. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C. Epidemiology of skin cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Saudia Arabi. 2020. Available online: https://shc.gov.sa/Arabic/NCC/Activities/AnnualReports/Cancer%20Incidence%20Report%202020.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Alqahtani, W.S.; Almufareh, N.A.; Domiaty, D.M.; Albasher, G.; Alduwish, M.A.; Alkhalaf, H.; Almuzzaini, B.; Al-Marshidy, S.S.; Alfraihi, R.; Elasbali, A.M. Epidemiology of cancer in Saudi Arabia thru 2010–2019: A systematic review with constrained meta-analysis. AIMS Public Health 2020, 7, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Maghrabi, J.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.S.; Elhakeem, H.A. Pattern of skin cancer in Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2004, 25, 776–779. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dawsari, N.A.; Amra, N. Pattern of skin cancer among Saudi patients attending a tertiary care center in Dhahran, Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. A 20-year retrospective study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamdan, K.A.; Morad, N.A. Pattern of malignant skin tumors in Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Ann. Saudi Med. 1993, 13, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, R.M.; Bang, K.M. Skin cancer in blacks in the United States. Dermatol. Clin. 1988, 6, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenghi, M.; Puglisi, R.; Pontecorvi, G.; De Feo, A.; Carè, A.; Mattia, G. Sex and gender disparities in melanoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSalman, S.A.; Alkaff, T.M.; Alzaid, T.; Binamer, Y. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in Saudi Arabia: Single center experience. Ann. Saudi Med. 2018, 38, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufti, S.T. Pattern of skin cancer among Saudi patients who attended King AbdulAziz University Hospital between Jan 2000 and Dec 2010. J. Saudi Soc. Dermatol. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 16, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Triassi, M.; Mauriello, M.C.; Torre, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; De Vita, V.; Pastore, F.; D'Arco, V.; Monfrecola, G. Epidemiology of skin cancer: Role of some environmental factors. Cancers 2010, 2, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balducci, L. Epidemiology of cancer and aging. J. Oncol. Manag. 2005, 14, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albert, A.; Knoll, M.A.; Conti, J.A.; Zbar, R.I.S. Non-melanoma skin cancers in the older patient. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinikumpu, S.-P.; Jokelainen, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Huilaja, L. Skin cancers and their risk factors in older persons: A population-based study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanillas, P.; Alipanahi, B.; Furlotte, N.A.; Johnson, M.; Wilson, C.H.; Pitts, S.J.; Gentleman, R.; Auton, A. Disease risk scores for skin cancers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
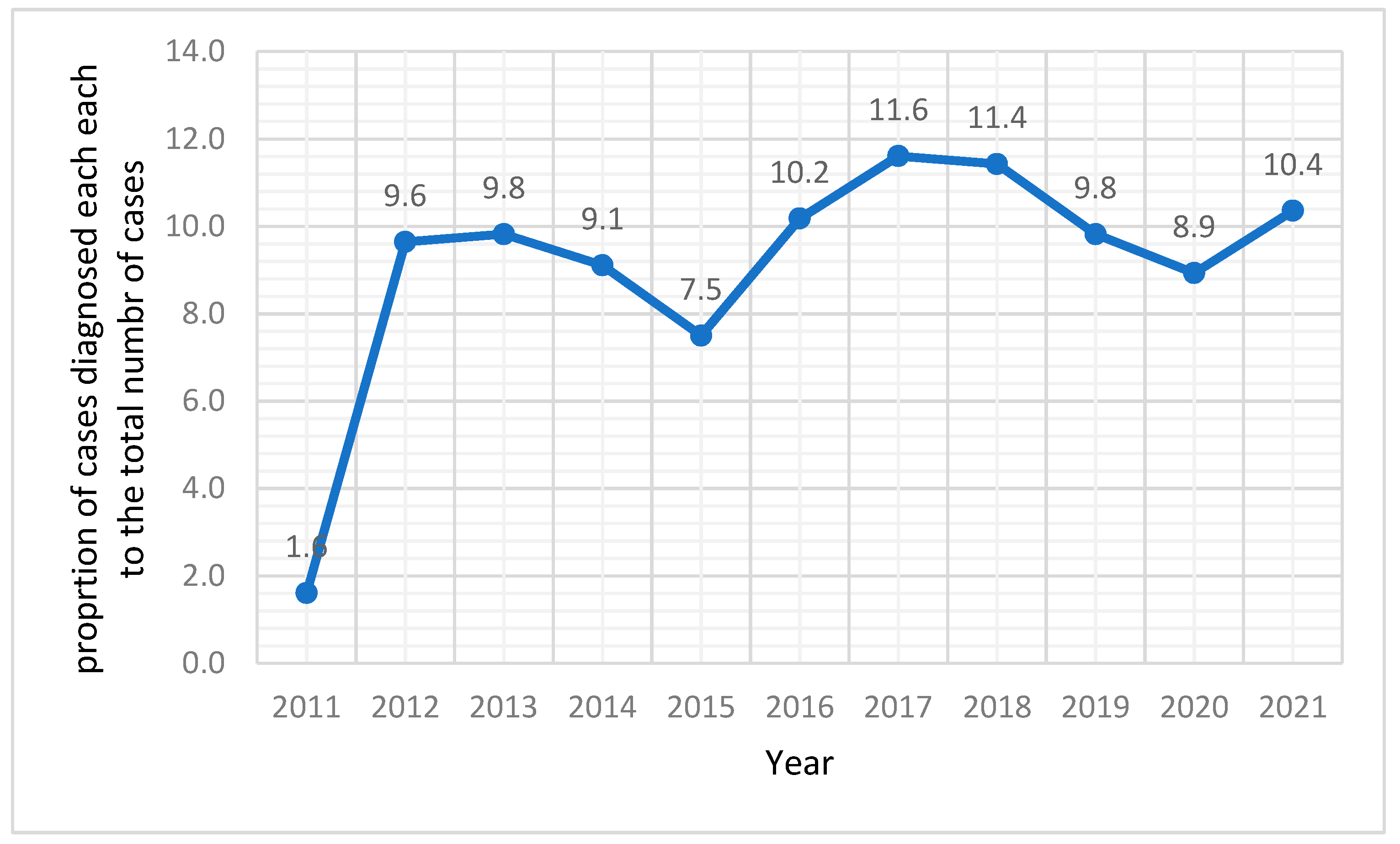
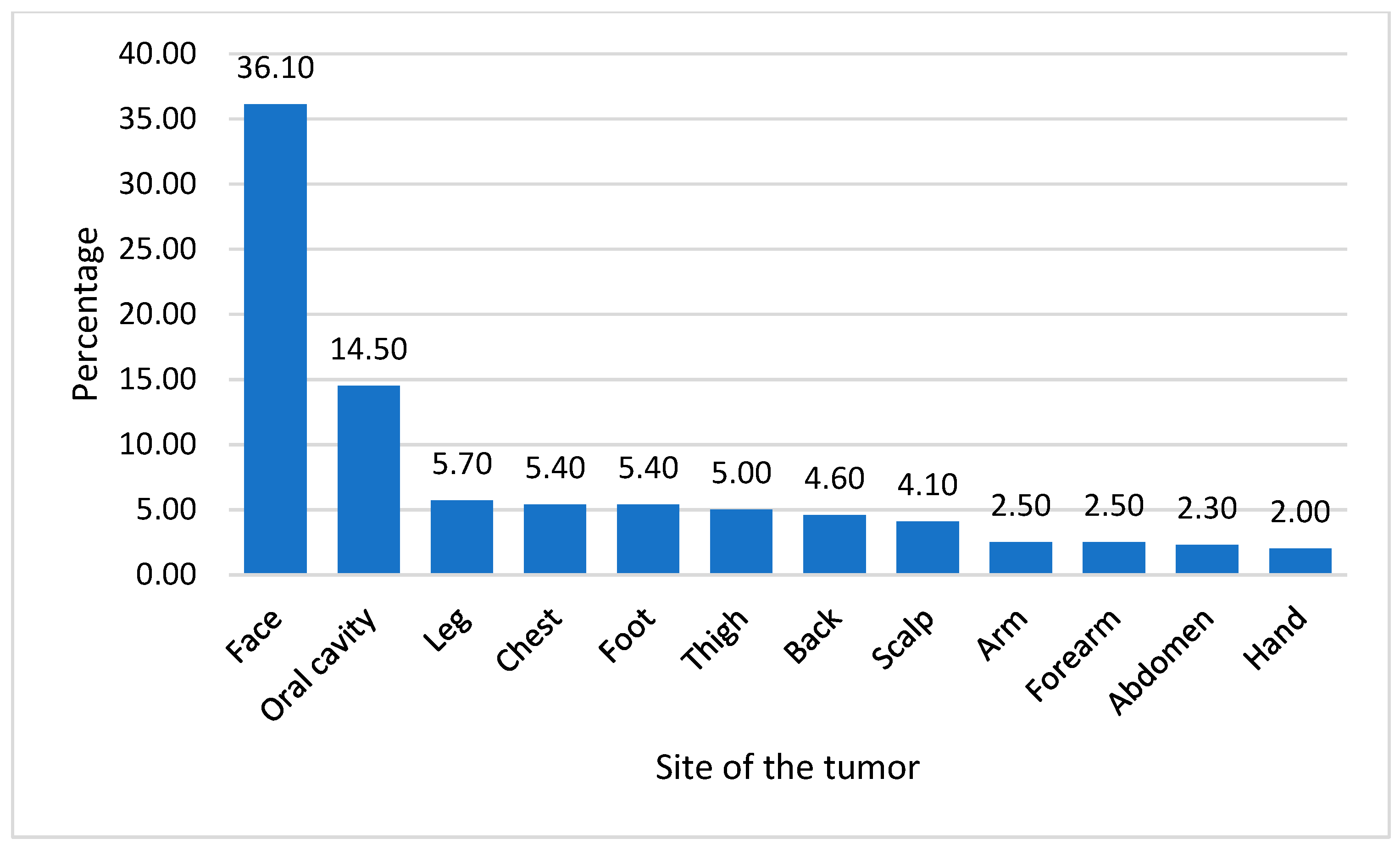
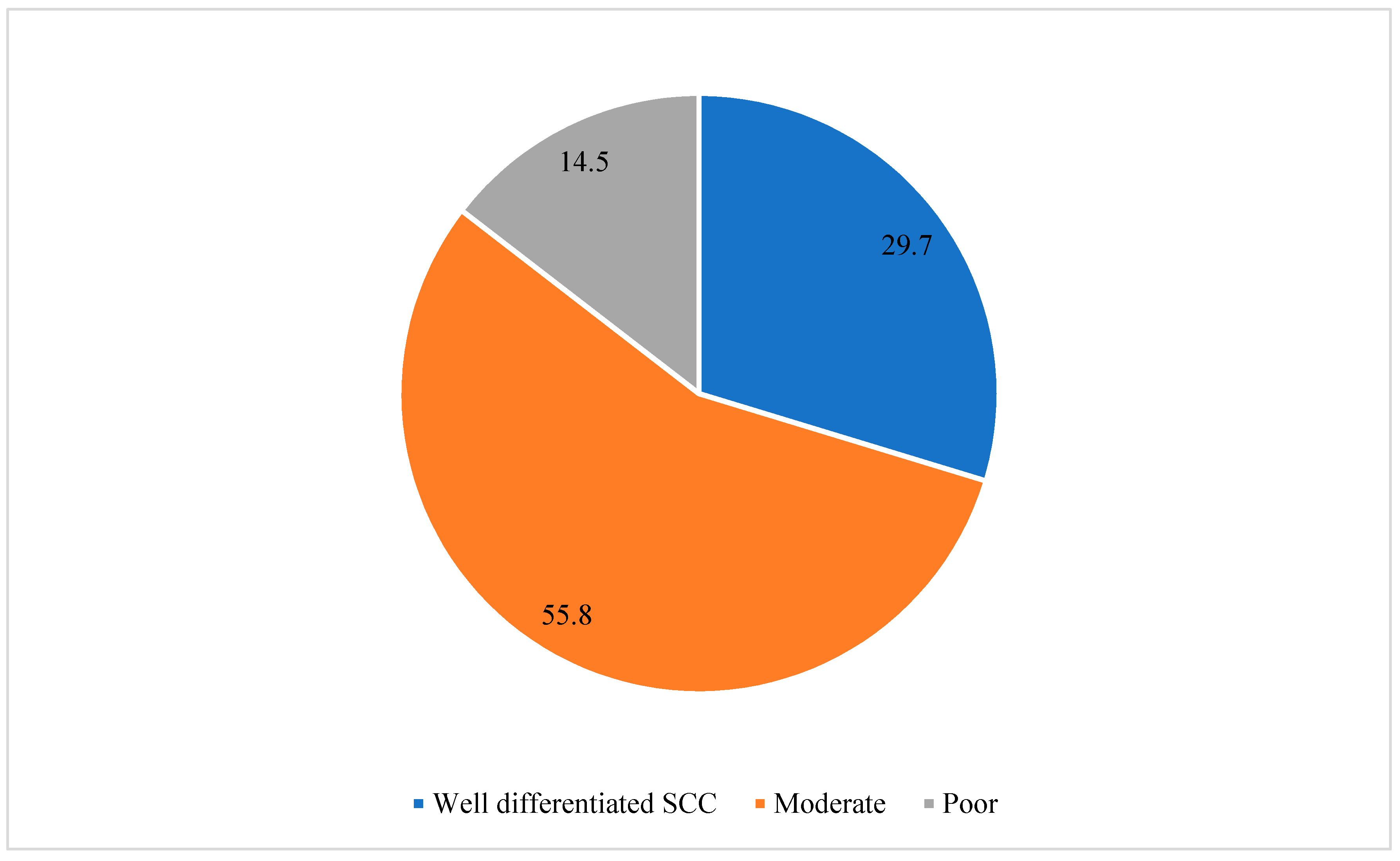
| Variable | Number | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age range (years) | ≤40 | 86 | 15.4 |
| 41–60 | 135 | 24.1 | |
| 61–80 | 232 | 41.4 | |
| >80 | 107 | 19.1 | |
| mean ± SD | 63.4 ± 21.3 | ||
| Sex | Male | 57 | 59.4 |
| Female | 39 | 40.6 | |
| Nationality | Saudi | 528 | 94.3 |
| Non-Saudi | 32 | 5.7 | |
| Source of the patient | Aseer Central Hospital | 487 | 87.0 |
| Other | 63 | 11.3 | |
| Unknown | 10 | 1.8 | |
| Skin cancer presentation | Skin lesion | 251 | 44.8 |
| Ulcer | 117 | 20.9 | |
| Use of immunosuppressive therapy | Yes | 8 | 1.4 |
| Type of Skin Cancer | Total | Age Range (Years) | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤40 | 41–60 | 61–80 | >80 | ||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | n | 230 | 13 | 64 | 101 | 52 | <0.001 |
| % | 41.07% | 5.70% | 27.80% | 43.90% | 22.60% | ||
| Basal cell carcinoma | n | 147 | 10 | 28 | 71 | 38 | |
| % | 26.25% | 6.80% | 19.00% | 48.30% | 25.90% | ||
| Vascular neoplasms | n | 39 | 7 | 15 | 15 | 2 | |
| % | 6.96% | 17.90% | 38.50% | 38.50% | 5.10% | ||
| Melanoma | n | 29 | 4 | 3 | 15 | 7 | |
| % | 5.18% | 13.80% | 10.30% | 51.70% | 24.10% | ||
| Cutaneous metastases | n | 30 | 5 | 11 | 10 | 4 | |
| % | 5.36% | 16.70% | 36.70% | 33.30% | 13.30% | ||
| Fibrous/fibrohistiocytic neoplasms | n | 9 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 1.61% | 55.60% | 44.40% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||
| Adnexal neoplasms | n | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | |
| % | 0.71% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 75.00% | 25.00% | ||
| Cutaneous neural neoplasms | n | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| % | 0.54% | 33.30% | 0.00% | 66.70% | 0.00% | ||
| Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | n | 60 | 37 | 9 | 11 | 3 | |
| % | 10.71% | 61.70% | 15.00% | 18.30% | 5.00% | ||
| B-cell lymphoma of the skin | n | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | |
| % | 0.54% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.00% | 0.00% | ||
| Mastocytosis | n | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| % | 1.07% | 66.70% | 16.70% | 16.70% | 0.00% | ||
| Type of Skin Cancer | Affected Body Part | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head and Neck | Upper Limb | Trunk | Pelvis | Lower Limb | |||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | n | 171 | 16 | 15 | 9 | 19 | <0.001 |
| % | 74.30% | 7.00% | 6.50% | 3.90% | 8.30% | ||
| Basal cell carcinoma | n | 122 | 5 | 13 | 0 | 7 | |
| % | 83.00% | 3.40% | 8.80% | 0.00% | 4.80% | ||
| Vascular neoplasms | n | 2 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 26 | |
| % | 5.10% | 17.90% | 10.30% | 0.00% | 66.70% | ||
| Melanoma | n | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 20 | |
| % | 17.20% | 13.80% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 69.00% | ||
| Cutaneous metastases | n | 7 | 0 | 19 | 1 | 3 | |
| % | 23.30% | 0.00% | 63.30% | 3.30% | 10.00% | ||
| Fibrous/fibrohistiocytic neoplasms | n | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| Adnexal neoplasms | % | 22.20% | 44.40% | 11.10% | 0.00% | 22.20% | |
| n | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Cutaneous neural neoplasms | % | 75.00% | 0.00% | 25.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | |
| n | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | ||
| % | 0.00% | 0.00% | 66.70% | 0.00% | 100.00% | ||
| Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | n | 7 | 9 | 24 | 3 | 17 | |
| % | 11.70% | 15.00% | 40.00% | 5.00% | 28.30% | ||
| B-cell lymphoma of the skin | n | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 66.70% | 33.30% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||
| Mastocytosis | n | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| % | 0.00% | 33.30% | 66.70% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||
| Total | 321 (57.3%) | 48 (8.6%) | 83 (14.8%) | 13 (2.3%) | 95 (17.0%) | ||
| Type of Skin Cancer | Sub Type | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Invasive squamous cell carcinoma | 144 | 25.7 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen’s ds) | 27 | 4.8 | |
| Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma | 7 | 1.3 | |
| Unknown squamous cell carcinoma | 45 | 8 | |
| Basal cell carcinoma | Nodular basal cell carcinoma | 141 | 25.2 |
| Superficial basal cell carcinoma | 2 | 0.4 | |
| Morpheaform basal cell carcinoma | 2 | 0.4 | |
| Fibroepithelial basal cell carcinoma (fibroepithelioma of Pinkus) | 1 | 0.2 | |
| Infundibulocystic basal cell carcinoma | 1 | 0.2 | |
| Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | Mycosis fungoides | 86.7 | 52 |
| ENKL | 1.7 | 1 | |
| Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified | 1.7 | 1 | |
| Subcutaneous-panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma | 1.7 | 1 | |
| Primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disease | 5 | 3 | |
| Unspecified | 3.3 | 2 | |
| Vascular neoplasm | Kaposi sarcoma | 92.3 | 36 |
| Angiosarcoma | 5.1 | 2 | |
| Malignant glomus tumours | 2.6 | 1 | |
| Cutaneous metastasis | Breast origin | 43.3 | 13 |
| Colonic origin | 13.3 | 4 | |
| Paget’s disease | 10 | 3 | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 6.7 | 2 | |
| Metastatic lymphoma | 6.7 | 2 | |
| Head and neck cancer | 3.3 | 1 | |
| Unknown cutaneous metastasis | 13.3 | 4 | |
| Leukaemia cutis | 3.3 | 1 | |
| Malignant melanoma | Acral lentiginous melanoma | 2 | 0.4 |
| Lentigo maligna melanoma | 2 | 0.4 | |
| Superficial spreading melanoma | 1 | 0.2 | |
| Congenital melanocytic nevus | 1 | 0.2 | |
| Unknown melanoma | 5 | 0.9 | |
| Nodular melanoma | 18 | 3.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Algarni, A.M.; Alshehri, H.S.; Al Zomia, A.S.; Alhifthi, M.A.; Lahiq, L.A.; Al Fae, F.M.; Alwadie, A.M.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.; Al Amri, F.S.; Tobeigei, F.H. The Epidemiological Pattern of Skin Cancer from 2011 to 2022 among the Population of the Aseer Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Cancers 2023, 15, 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184612
Algarni AM, Alshehri HS, Al Zomia AS, Alhifthi MA, Lahiq LA, Al Fae FM, Alwadie AM, Al-Qahtani SA, Al Amri FS, Tobeigei FH. The Epidemiological Pattern of Skin Cancer from 2011 to 2022 among the Population of the Aseer Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184612
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlgarni, Abdullah Mohammed, Hamza Salim Alshehri, Ahmed Saad Al Zomia, Mohammed Abdulrahman Alhifthi, Lama Ali Lahiq, Faisal Mohammed Al Fae, Awad Mohammed Alwadie, Shuruq Abdullah Al-Qahtani, Faisal Suhaim Al Amri, and Faisal Hassan Tobeigei. 2023. "The Epidemiological Pattern of Skin Cancer from 2011 to 2022 among the Population of the Aseer Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184612
APA StyleAlgarni, A. M., Alshehri, H. S., Al Zomia, A. S., Alhifthi, M. A., Lahiq, L. A., Al Fae, F. M., Alwadie, A. M., Al-Qahtani, S. A., Al Amri, F. S., & Tobeigei, F. H. (2023). The Epidemiological Pattern of Skin Cancer from 2011 to 2022 among the Population of the Aseer Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Cancers, 15(18), 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184612







