Real-World Presentation and Prognostic Effect of Allogeneic Blood Transfusion during the Intensive Induction Phase in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Chemotherapy Protocol and Treatment Response
2.4. Transfusion Events
2.5. Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Univariate Analysis for RFS and OS among Pediatric ALL Patients
3.3. Multivariate Analysis for RFS and OS among Pediatric ALL Patients
3.4. The Clinical Implication of Average FFP Transfusion among Pediatric ALL Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Remy, K.E.; Hall, M.W.; Cholette, J.; Juffermans, N.P.; Nicol, K.; Doctor, A.; Blumberg, N.; Spinella, P.C.; Norris, P.J.; Dahmer, M.K.; et al. Mechanisms of red blood cell transfusion-related immunomodulation. Transfusion 2018, 58, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.H.; Wu, K.H. Transfusion-related immunomodulation in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2019, 60, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opelz, G. Current relevance of the transfusion effect in renal transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1985, 17, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmohammadi, K.; Mahmoudi, T.; Jafari-Koshki, T.; Hassan, Z.M.; Pourfathollah, A.A. Immunomodulatory Effects of Blood Transfusion on Tumor Size, Metastasis, and Survival in Experimental Fibrosarcoma. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2018, 34, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.W.; Gao, L.; Stastka, P.; Cheney, M.C.; Mahabamunuge, J.; Torres Soto, M.; Ford, C.B.; Bryant, J.A.; Henn, M.R.; Hohmann, E.L. Fecal microbiota transplantation for the improvement of metabolism in obesity: The FMT-TRIM double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.I.; Patidar, G.K.; Lakshmy, R.; Makhija, N.; Talwar, S.; Hazarika, A. Effect of leukoreduction on transfusion-related immunomodulation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Transfus. Med. 2020, 30, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roets, M.; Sturgess, D.J.; Obeysekera, M.P.; Tran, T.V.; Wyssusek, K.H.; Punnasseril, J.E.J.; da Silva, D.; van Zundert, A.; Perros, A.J.; Tung, J.P.; et al. Intraoperative Cell Salvage as an Alternative to Allogeneic (Donated) Blood Transfusion: A Prospective Observational Evaluation of the Immune Response Profile. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720966265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, G.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Socioeconomic inequalities in cancer incidence and access to health services among children and adolescents in China: A cross-sectional study. Lancet 2022, 400, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.E.; Zantek, N.D.; Stanworth, S.J.; Parker, R.I.; Valentine, S.L.; Lehmann, L.E.; Josephson, C.D.; Bateman, S.T.; Luban, N.L.C. Recommendations on RBC Transfusion Support in Children with Hematologic and Oncologic Diagnoses from the Pediatric Critical Care Transfusion and Anemia Expertise Initiative. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 19 (9S Suppl. 1), S149–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, P.; Cox, C.V.; Moppett, J.P.; Blair, A. Parthenolide eliminates leukemia-initiating cell populations and improves survival in xenografts of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Pérez, J.C.; Colunga-Pedraza, P.R.; Gómez-Almaguer, D. Is the number of blood products transfused associated with lower survival in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia? Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, G.; Mao, S.T.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.F. Allogeneic blood transfusion in 163 children with acute lymphocytic leukemia (a STROBE-compliant article). Medicine 2019, 98, e14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colunga-Pedraza, J.E.; González-Llano, O.; González-Martinez, C.E.; Gómez-Almaguer, D.; Yáñez-Reyes, J.M.; Jiménez-Antolinez, V.; Colunga-Pedraza, P.R. Outpatient low toxic regimen with bortezomib in relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia in pediatrics and AYA patients: Single-center Mexican experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkayed, K.; Al Hmood, A.; Madanat, F. Prognostic effect of blood transfusion in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Res. 2013, 48, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, L.B.; Li, C.G.; Xu, L.H.; Liu, R.Y.; Chen, H.Q.; Ruan, Y.S.; Zhen, Z.J.; Li, C.K.; et al. Vincristine and Dexamethasone Pulses in Addition to Maintenance Therapy Among Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (GD-ALL-2008): An Open-label, Multicentre, Randomized, Phase Ⅲ Clinical Trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 869–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.Y.; Xu, H.G.; Luo, X.Q.; Mai, H.R.; Liao, N.; Yang, L.H.; Zheng, M.C.; Wan, W.Q.; Wu, X.D.; Liu, R.Y.; et al. Prognostic Value and Outcome for ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report from the South China Children’s Leukemia Group. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 797194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.Q.; Muench, M.O.; Jackman, R.P. Pathogen-reduced PRP blocks T-cell activation, induces Treg cells, and promotes TGF-β expression by cDCs and monocytes in mice. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5547–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberg, A.S.; Hancock, M.L.; Kunkel, K.D.; Rivera, G.K.; Crist, W.M. Transfusions and risk of failure in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 1994, 8, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Lelcu, T.; Bînă, A.M.; Dănilă, M.D.; Popoiu, C.M.; Aburel, O.M.; Arghirescu, S.T.; Borza, C.; Muntean, D.M. Assessment of Platelet Mitochondrial Respiration in a Pediatric Population: A Pilot Study in Healthy Children and Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Children 2021, 8, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melazzini, F.; Palombo, F.; Balduini, A.; De Rocco, D.; Marconi, C.; Noris, P.; Gnan, C.; Pippucci, T.; Bozzi, V.; Faleschini, M.; et al. Clinical and pathogenic features of ETV6-related thrombocytopenia with predisposition to acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winick, N.; Devidas, M.; Chen, S.; Maloney, K.; Larsen, E.; Mattano, L.; Borowitz, M.J.; Carroll, A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Impact of Initial CSF Findings on Outcome Among Patients with National Cancer Institute Standard- and High-Risk B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.Y.; Zhou, D.H.; Liao, X.Y.; Huang, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.G.; Weng, W.J.; Xu, L.H.; Fang, J.P. Prognostic value and outcome for acute lymphocytic leukemia in children with MLL rearrangement: A case-control study. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.Y.; Liao, X.Y.; He, Z.W.; Wu, R.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.H.; Zhou, D.H.; Fang, J.P. DNA index as prognostic factor in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the COG-TARGET database. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratei, R.; Basso, G.; Dworzak, M.; Gaipa, G.; Veltroni, M.; Rhein, P.; Biondi, A.; Schrappe, M.; Ludwig, W.D.; Karawajew, L. Monitoring treatment response of childhood precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the AIEOP-BFM-ALL 2000 protocol with multiparameter flow cytometry: Predictive impact of early blast reduction on the remission status after induction. Leukemia 2009, 23, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, L.; Claveau, M.; Tang, K.; Cameron, J.; Goulet, G. The association of age and adverse events of PEG-asparaginase in a pediatric tertiary care hospital: A retrospective review. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 110, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharia, P.; Swartz, M.D.; Bernhardt, M.B.; Chen, H.; Gramatges, M.M.; Lupo, P.J.; Brown, A.L.; Scheurer, M.E. Clinical and demographic factors contributing to asparaginase-associated toxicities in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, M.; Attarbaschi, A.; Haas, O.A.; Kastner, U.; Gadner, H.; Mann, G. Fresh frozen plasma contains free asparagine and may replace the plasma asparagine pool during L-ASP therapy. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, I.L.M.; Zuurbier, C.C.M.; Hutten, B.A.; van den Bos, C.; Schouten, A.Y.N.; Stokhuijzen, E.; van Ommen, C.H. Venous Thrombosis in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated on DCOG ALL-9 and ALL-10 Protocols: The Effect of Fresh Frozen Plasma. TH Open 2019, 3, e109–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Göttl, U.; Rath, B.; Binder, M.; Hassel, J.U.; Wolff, J.; Husemann, S.; Ritter, J. Inefficacy of fresh frozen plasma in the treatment of L-ASP-induced coagulation factor deficiencies during ALL induction therapy. Haematologica 1995, 80, 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, L.S.; Deevska, M.; Fernandez, C.V.; Dix, D.; Price, V.E.; Wang, H.; Parker, L.; Yhap, M.; Fitzgerald, C.; Barnard, D.R.; et al. The impact of prophylactic fresh-frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate on the incidence of central nervous system thrombosis and hemorrhage in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia receiving asparaginase. Blood 2009, 114, 5146–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, V.; Za, T.; Ciminello, A.; Betti, S.; Rossi, E. Haemostatic alterations induced by treatment with asparaginases and clinical consequences. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen, I.L.M.; Lauw, M.N.; Fiocco, M.; van der Sluis, I.M.; Pieters, R.; Middeldorp, S.; van de Wetering, M.D.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; van Ommen, C.H. Venous thromboembolism in a large cohort of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Risk factors and effect on prognosis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
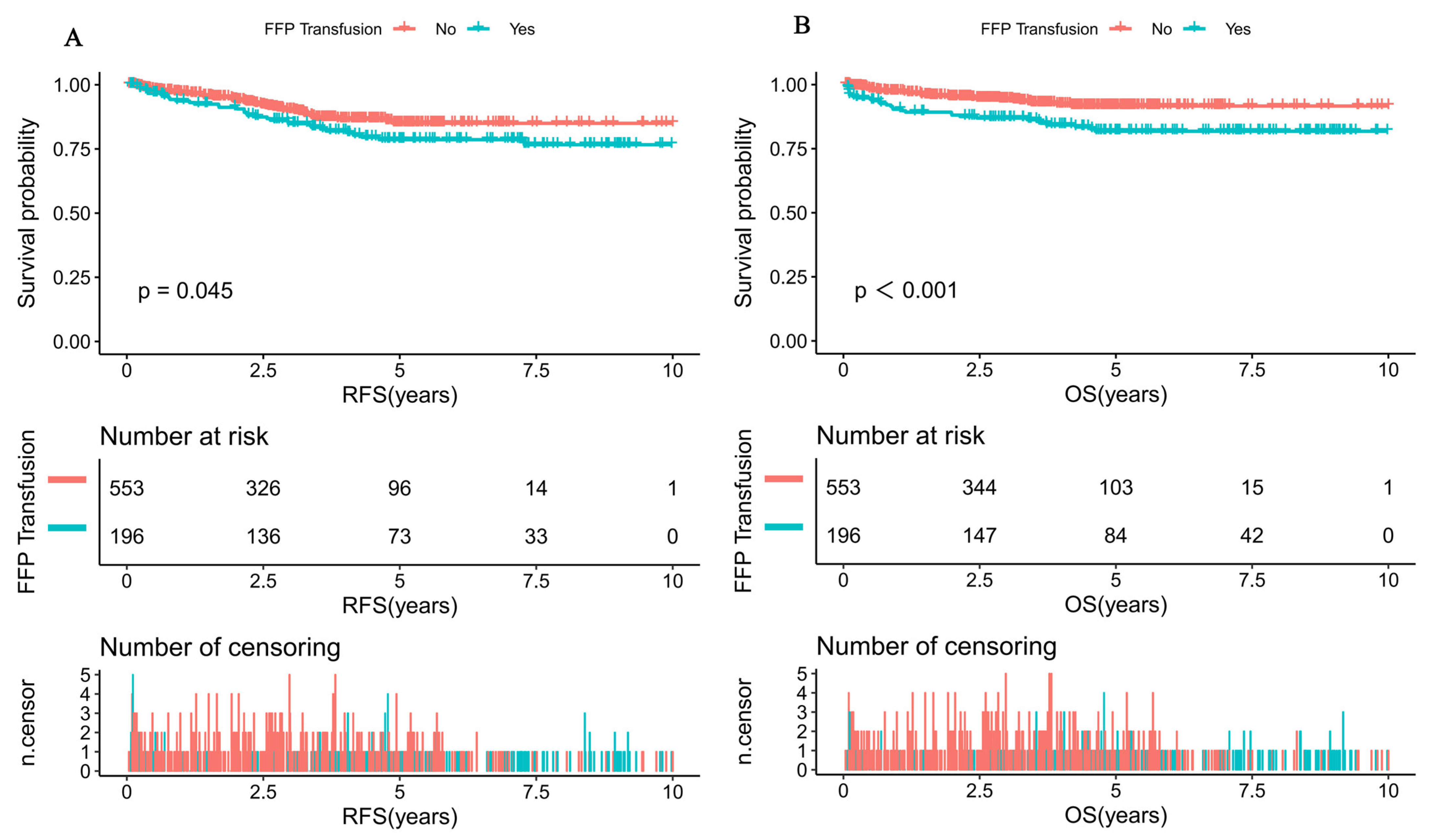

| Characteristics | Total | FFP Transfusion | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 553) | Yes (n = 196) | |||
| Gender, n (%) | 0.483 | |||
| Male | 462 (61.7%) | 337 (60.9%) | 125 (63.8%) | |
| Female | 287 (38.3%) | 216 (39.1%) | 71 (36.2%) | |
| Age (y), median (range) | 4.4 (0.4–14.9) | 4.1 (0.4–14.9) | 5.7 (1.0–14.7) | <0.001 |
| Age group (y) | <0.001 | |||
| <10 | 634 (84.6%) | 484 (87.5%) | 150 (76.5%) | |
| ≥10 | 115 (15.4%) | 69 (12.5%) | 46 (23.5%) | |
| Chemotherapy protocol, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| SCCLG-ALL-2016 Protocol | 340 (45.4%) | 247 (44.7%) | 162 (82.7%) | |
| GD-ALL-2008 Protocol | 409 (54.6%) | 306 (55.3%) | 34 (17.3%) | |
| Initial WBC (×109/L), median (range) | 9.3 (0.1–1095.0) | 9.6 (0.1–1095.0) | 8.6 (0.2–516.2) | 0.608 |
| WBC group, n(%) | 0.574 | |||
| <50 × 109/L | 610 (81.4%) | 453 (81.9%) | 157 (80.1%) | |
| ≥50 × 109/L | 139 (18.6%) | 100 (18.1%) | 39 (19.9%) | |
| Initial Hb (g/L), median (range) | 79.0 (24.0–172.0) | 78.0 (24.0–149.0) | 81.5 (28.0–172.0) | 0.136 |
| Hb group | 0.097 | |||
| <70 g/L | 242 (32.3%) | 188 (34.0%) | 54 (27.6%) | |
| ≥70 g/L | 507 (67.7%) | 365 (66.0%) | 142 (72.4%) | |
| Initial PLT(×109/L), median (range) | 59.0 (2.0–634.0) | 59.0 (2.0–634.0) | 62.0 (8.0–417.0) | 0.953 |
| PLT group | 0.091 | |||
| <20 × 109/L | 116 (15.5%) | 93 (16.8%) | 23 (11.7%) | |
| ≥20 × 109/L | 633 (84.5%) | 460 (83.2%) | 173 (88.3%) | |
| Risk group, n (%) | 0.717 | |||
| SR | 154 (20.6%) | 110 (19.9%) | 44 (22.4%) | |
| IR | 331 (44.2%) | 248 (44.8%) | 83 (42.3%) | |
| HR | 264 (35.2%) | 195 (35.3%) | 69 (35.2%) | |
| Blood type | 0.220 | |||
| O | 302 (40.3%) | 227 (41.0%) | 75 (38.3%) | |
| A | 225 (30.0%) | 173 (31.3%) | 52 (26.5%) | |
| B | 179 (23.9%) | 122 (22.1%) | 57 (29.1%) | |
| AB | 43 (5.7%) | 31 (5.6%) | 12 (6.1%) | |
| Number of transfusions | <0.001 | |||
| No transfusions | 25 (3.3%) | 24 (4.3%) | 1 (0.5%) | |
| 1 to 10 transfusions | 555 (74.1%) | 439 (79.4%) | 116 (59.2%) | |
| 11 to 25 transfusions | 160 (21.4%) | 87 (15.7%) | 73 (37.2%) | |
| More than 25 transfusions | 9 (1.2%) | 3 (0.5%) | 6 (3.1%) | |
| Transfusion of blood products | ||||
| PRBCs (U), median (range) | 4.0 (0.0–25.5) | 3.0 (0.0–25.5) | 4.0 (0.0–21.0) | <0.001 |
| SDPs (U), median (range) | 1.0 (0.0–20.0) | 1.0 (0.0–20.0) | 1.0 (0.0–20.0) | 0.105 |
| Immunophenotype, n (%) | 0.126 | |||
| B | 681 (90.9%) | 509 (92.0%) | 172 (87.8%) | |
| T | 59 (7.9%) | 37 (6.7%) | 22 (11.2%) | |
| Biphenotypic | 9 (1.2%) | 7 (1.3%) | 2 (1.0%) | |
| CNSL, n (%) | 0.329 | |||
| Yes | 32 (4.3%) | 26 (4.7%) | 6 (3.1%) | |
| No | 717 (95.7%) | 527 (95.3%) | 190 (96.9%) | |
| BCR/ABL1 status, n (%) | 0.937 | |||
| Negative | 558 (94.6%) | 415 (94.5%) | 143 (94.7%) | |
| Positive | 32 (5.4%) | 24 (5.5%) | 8 (5.3%) | |
| KMT2A status, n (%) | 0.845 | |||
| Negative | 549 (96.8%) | 416 (96.7%) | 133 (97.1%) | |
| Positive | 18 (3.2%) | 14 (3.3%) | 4 (2.9%) | |
| ETV6/RUNX1 status, n (%) | 0.893 | |||
| Negative | 471 (83.2%) | 360 (83.3%) | 111 (82.8%) | |
| Positive | 95 (16.8%) | 72 (16.7%) | 23 (17.2%) | |
| Prednisone response, n (%) | 0.393 | |||
| PGR | 667 (90.1%) | 490 (89.6%) | 177 (91.7%) | |
| PPR | 73 (9.9%) | 57 (10.4%) | 16 (8.3%) | |
| D15 BM, n (%) | 0.062 | |||
| M1 | 492 (66.0%) | 374 (67.9%) | 118 (60.5%) | |
| M2/M3 | 254 (34.0%) | 177 (32.1%) | 77 (39.5%) | |
| D33 BM, n (%) | 0.085 | |||
| M1 | 707 (96.6%) | 532 (97.3%) | 175 (94.6%) | |
| M2/M3 | 25 (3.4%) | 15 (2.7%) | 10 (5.4%) | |
| D15 MRD, n (%) | 0.353 | |||
| <0.1% | 170 (30.0%) | 138 (29.2%) | 32 (34.0%) | |
| ≥0.1% | 396 (70.0%) | 334 (70.8%) | 62 (66.0%) | |
| D33 MRD, n (%) | 0.013 | |||
| <0.01% | 476 (81.8%) | 410 (83.5%) | 66 (72.5%) | |
| ≥0.01% | 106 (18.2%) | 81 (16.5%) | 25 (27.5%) | |
| Variables | RFS | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p Value | HR (95%CI) | p Value | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Female | 0.7 (0.4, 1.1) | 0.113 | 0.9 (0.5, 1.4) | 0.542 |
| Age group | ||||
| <10 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥10 | 1.6 (0.9, 2.6) | 0.098 | 3.3 (2.0, 5.6) | <0.001 |
| Chemotherapy protocol | ||||
| GD-ALL-2008 Protocol | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| SCCLG-ALL-2016 Protocol | 0.3 (0.2, 0.5) | <0.001 | 0.0 (0.0, Inf) | 0.995 |
| WBC group | ||||
| <50 × 109/L | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥50 × 109/L | 2.4 (1.5, 3.8) | <0.001 | 2.3 (1.4, 4.0) | 0.002 |
| Hb group | ||||
| <70 g/L | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥70 g/L | 1.2 (0.7, 1.9) | 0.468 | 1.2 (0.7, 2.1) | 0.556 |
| PLT group | ||||
| <20 × 109/L | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥20 × 109/L | 0.5 (0.3, 0.8) | 0.008 | 0.6 (0.3, 1.1) | 0.108 |
| Risk group | ||||
| SR | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| IR | 1.0 (0.6, 1.7) | 0.937 | 1.6 (0.7, 3.4) | 0.229 |
| HR | 1.1 (0.6, 2.0) | 0.937 | 2.5 (1.2, 5.2) | 0.019 |
| Blood type | ||||
| O | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| A | 1.3 (0.8, 2.2) | 0.260 | 1.0 (0.6, 1.8) | 0.985 |
| B | 1.0 (0.6, 1.7) | 0.939 | 0.9 (0.5, 1.7) | 0.747 |
| AB | 1.0 (0.4, 2.5) | 0.943 | 0.5 (0.1, 2.0) | 0.302 |
| Number of transfusions | ||||
| No transfusions | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 1 to 10 transfusions | 1.0 (0.3, 3.1) | 0.945 | 1.8 (0.3, 13.4) | 0.548 |
| 11 to 25 transfusions | 1.3 (0.4, 4.4) | 0.643 | 3.9 (0.5, 28.6) | 0.187 |
| More than 25 transfusions | 1.1 (0.1, 10.7) | 0.926 | 6.3 (0.6, 69.6) | 0.133 |
| PRBCs (U), median (range) | 1.1 (1.0, 1.1) | 0.004 | 1.1 (1.0, 1.2) | <0.001 |
| SDPs (U), median (range) | 1.1 (1.0, 1.1) | 0.087 | 1.1 (1.0, 1.2) | 0.002 |
| FFP transfusion | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.5 (1.1, 2.4) | 0.047 | 2.4 (1.4, 3.9) | <0.001 |
| Immunophenotype | ||||
| B | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| T | 1.5 (0.7, 2.9) | 0.283 | 2.3 (1.2, 4.6) | 0.015 |
| Biphenotypic | 0.9 (0.1, 6.8) | 0.952 | 1.5 (0.2, 11.0) | 0.679 |
| CNSL | ||||
| Yes | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| No | 1.4 (0.3, 5.6) | 0.654 | 2.3 (0.3, 16.4) | 0.415 |
| BCR/ABL1 status | ||||
| Positive | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Negative | 0.8 (0.3, 2.7) | 0.764 | 1.8 (0.3, 13.3) | 0.550 |
| KMT2A status, n (%) | ||||
| Positive | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Negative | 9316259.7 (0.0, Inf) | 0.995 | 0.5 (0.1, 2.1) | 0.345 |
| ETV6/RUNX1 status | ||||
| Positive | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Negative | 1.9 (0.8, 4.8) | 0.172 | 1.2 (0.5, 3.1) | 0.718 |
| Prednisone response | ||||
| PGR | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| PPR | 1.1 (0.6, 2.2) | 0.747 | 1.8 (0.9, 3.6) | 0.081 |
| D15 BM | ||||
| M1 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| M2/M3 | 2.0 (1.3, 3.1) | <0.001 | 2.1 (1.3, 3.5) | 0.002 |
| D33 BM | ||||
| M1 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| M2/M3 | 1.0 (0.2, 4.1) | 0.997 | 4.0 (1.6, 10.0) | 0.003 |
| D15 MRD | ||||
| <0.1% | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥0.1% | 1.4 (0.7, 2.8) | 0.349 | 2.4 (0.8, 7.1) | 0.103 |
| D33 MRD | ||||
| <0.01% | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥0.01% | 1.6 (0.8, 3.1) | 0.194 | 2.2 (0.9, 5.4) | 0.079 |
| Outcome | Variable | HR (95%CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFS | SCCLG-ALL-2016 Protocol | 0.3 (0.1, 0.5) | <0.001 |
| WBC ≥ 50 × 109/L | 2.3 (1.4, 3.7) | <0.001 | |
| PLT ≥ 20 × 109/L | 0.6 (0.4, 1.0) | 0.045 | |
| PRBCs | 1.0 (0.6, 1.6) | 0.937 | |
| FFP transfusion | 1.1 (1.0, 1.1) | 0.020 | |
| D15 BM | 1.7 (1.1, 2.6) | 0.014 | |
| OS | Age ≥10 y | 1.3 (0.7, 2.3) | 0.342 |
| WBC ≥ 50 × 109/L | 1.8 (1.0, 3.3) | 0.071 | |
| HR | 0.9 (0.4, 2.2) | 0.790 | |
| PRBCs | 1.1 (1.0, 1.2) | 0.153 | |
| SDPs | 1.0 (0.9, 1.1) | 0.788 | |
| FFP | 2.3 (1.2, 4.4) | 0.010 | |
| D15 BM | 2.1 (1.3, 3.6) | 0.005 | |
| D33 BM | 2.4 (0.8, 6.6) | 0.102 |
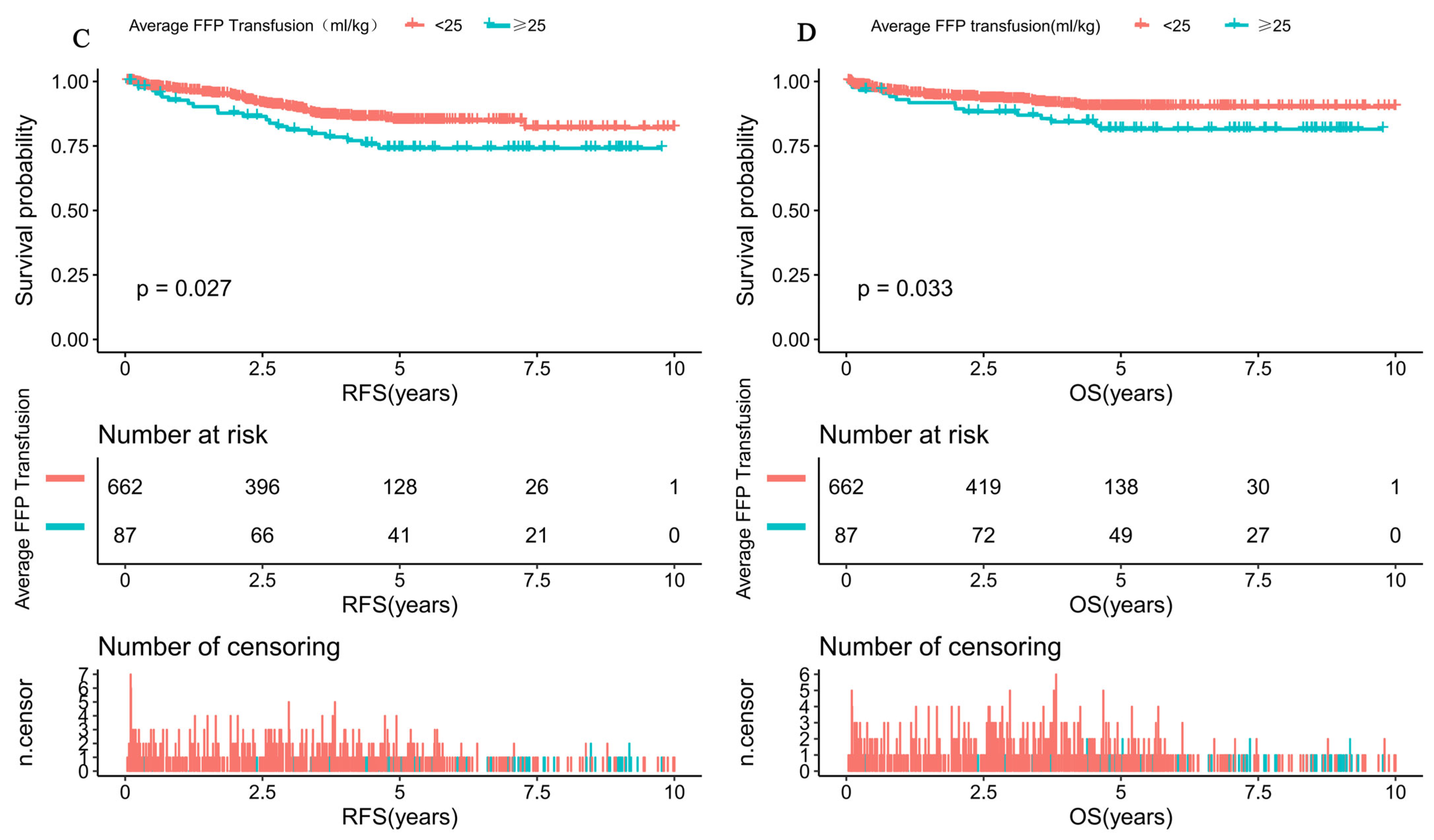
| Average FFP Transfusion | LogRR (95%CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| <25 mL/kg | 1.0 (1.0, 1.1) | 0.081 |
| ≥25 mL/kg | 1.2 (1.1, 1.3) | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, K.; Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Xu, H.; Fang, J.; Zhou, D. Real-World Presentation and Prognostic Effect of Allogeneic Blood Transfusion during the Intensive Induction Phase in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184462
Qiu K, Liao X, Li Y, Huang K, Xu H, Fang J, Zhou D. Real-World Presentation and Prognostic Effect of Allogeneic Blood Transfusion during the Intensive Induction Phase in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184462
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Kunyin, Xiongyu Liao, Yang Li, Ke Huang, Honggui Xu, Jianpei Fang, and Dunhua Zhou. 2023. "Real-World Presentation and Prognostic Effect of Allogeneic Blood Transfusion during the Intensive Induction Phase in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184462
APA StyleQiu, K., Liao, X., Li, Y., Huang, K., Xu, H., Fang, J., & Zhou, D. (2023). Real-World Presentation and Prognostic Effect of Allogeneic Blood Transfusion during the Intensive Induction Phase in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 15(18), 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184462






