Simple Summary
Approximately 20% of colorectal cancer (CRC) cases are diagnosed in individuals under 40, with a severe prognosis due to germline variant accumulation. Many of these variants have been classified as hereditary cancer causative, while others remain poorly researched. The identification of germline variants across different populations is critical for accurate prognosis, treatment, and follow-up. We aimed to identify and predict the functional implications of germline variants using whole-genome sequencing of a Tunisian pedigree with Lynch syndrome CRC risk. Two SNPs/indels were identified in genes with CRC association (MLH1 and PRH1-TAS2R14) and four in genes with non-CRC cancer association (PPP1R13B, LAMA5, FTO, and NLRP14). Three structural variants overlapped genes associated with non-CRC digestive cancer (RELN, IRS2, and FOXP1) and one overlapped RRAS2 with non-CRC cancer associations. This study provides further evidence of genetic predisposition according to the risk clustering of variants based on their functional implications and risk mechanisms within the same pedigree.
Abstract
Recently, worldwide incidences of young adult aggressive colorectal cancer (CRC) have rapidly increased. Of these incidences diagnosed as familial Lynch syndrome (LS) CRC, outcomes are extremely poor. In this study, we seek novel familial germline variants from a large pedigree Tunisian family with 12 LS-affected individuals to identify putative germline variants associated with varying risk of LS. Whole-genome sequencing analysis was performed to identify known and novel germline variants shared between affected and non-affected pedigree members. SNPs, indels, and structural variants (SVs) were computationally identified, and their oncological influence was predicted using the Genetic Association of Complex Diseases and Disorders, OncoKB, and My Cancer Genome databases. Of 94 germline familial variants identified with predicted functional impact, 37 SNPs/indels were detected in 28 genes, 2 of which (MLH1 and PRH1-TAS2R14) have known association with CRC and 4 others (PPP1R13B, LAMA5, FTO, and NLRP14) have known association with non-CRC cancers. In addition, 48 of 57 identified SVs overlap with 43 genes. Three of these genes (RELN, IRS2, and FOXP1) have a known association with non-CRC digestive cancers and one (RRAS2) has a known association with non-CRC cancer. Our study identified 83 novel, predicted functionally impactful germline variants grouped in three “variant risk clusters” shared in three familiarly associated LS groups (high, intermediate and low risk). This variant characterization study demonstrates that large pedigree investigations provide important evidence supporting the hypothesis that different “variant risk clusters” can convey different mechanisms of risk and oncogenesis of LS-CRC even within the same pedigree.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most frequent neoplasm worldwide, accounting for 8% of cancer-related deaths [1,2]. Pathogenetic variants in known high-penetrance cancer-risk-associated genes have been implicated in up to 8% of all CRC cases, where one in five (20%) cases of this type were diagnosed in under 40 year olds [3,4,5] compared to the average worldwide age at diagnosis of 65 [6]. Familial association (defined to be families with at least two affected members) appears in an estimated 35% of all CRC cases [7]. The most common familial CRC is Lynch syndrome (LS) [8,9]. The familial forms of CRC genetic predisposition have been correlated with germline mutations or epimutations in mismatch repair (MMR) genes such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 for nonpolyposis cases and in APC and MUTYH for Adenomatous colonic polyposis with recessive inheritance [4,5]. Despite the current knowledge of genetic predisposition in these hereditary forms of CRC (such as LS, Gardner syndrome, Juvenile polyposis coli, and others), much of the familial relationships and mechanisms of risk remain unexplained [10].
Genome-wide association via high throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies and the wide collection of variant functional predictive analytics, clouded applications, and databases are critical to the success of identifying new germline likely causative variants implicated in cancer predisposition. These powerful emerging tools help detect deleterious genomic changes in part responsible for the hereditary CRC development, diagnosis, predicted optimal treatment, and therefore long-term prognosis. Approximately 40% of patients with an inherited tumor syndrome exhibit a variant of uncertain significance, as revealed through sequencing analyses that examine germline variants involved in the production of truncated proteins and associated with alterations caused by hereditary pathologies at the germinal level [11]. These variants typically involve a single amino acid substitution, which cannot a priori be definitively classified as pathogenic or benign [12]. Conversely, synonymous nucleotide substitutions, which generally do not cause alterations in protein structure, have been found to be pathogenic in some instances, depending on their genomic location [13]. Additionally, variants appearing together in the same gene or different genes may coexist and co-segregated with the disease phenotype within a single family, potentially explaining the correlated predisposition risk of the family. In some cases, these variants contribute more significantly to cancer risk than classic pathogenic Mendelian variants, and when implicated in tumor predisposition, can cooperatively contribute to an increased risk of cancer development as low-risk alleles [14,15]. However, HTS studies have not covered all such cancers and therefore, it is highly likely that functionally pertinent variants and mutations and genes conveying predisposition to CRC and LS are yet to be discovered. This gap in the current knowledge of familial forms of CRC such as LS requires further clinical evaluation of hereditary CRCs supported by germline studies of familial cases [16].
In this study, we aim to identify, annotate, and computationally predict the functional implication of previously known and novel germline SNPs, indels, and structural variants using a whole-genome sequencing approach of a Tunisian large pedigree with three familiarly grouped members affected or at-risk to LS-CRC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample/Data Collection
An LS-affected, large-pedigree Tunisian family with 37 total and 12 known affected members was recruited for this study (Figure 1). Peripheral blood from 11 members (oval circled) was collected. Individual subjects’ clinical, environmental, and behavioral data were collected from medical records and personal interviews based on an interrogatory form conducted by the study personnel.
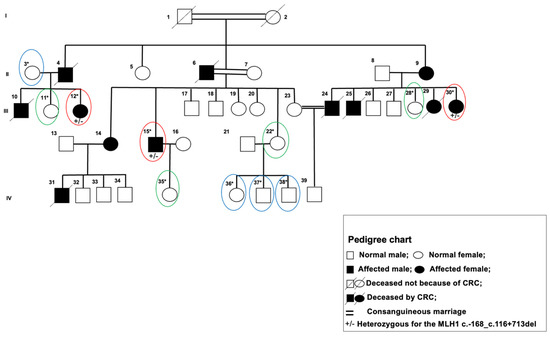
Figure 1.
A pedigree of predisposition to colorectal cancer Lynch syndrome. I, II, III, IV the number of generations. * Sequenced subjects; Group 1 (high risk to LS group): subject and parent affected by LS-CRC, red circles; Group 2 (intermediate risk to LS): subject LS-CRC free and one of the parents is affected, green circles; Group 3 (low risk to LS): subject and both parents are LS-CRC free, blue circles.
Lynch syndrome status within this family was tested and confirmed during routine clinical work. The three patients collected from in the HRLS group were classified as meeting both the Amsterdam criteria II that have been established by the International Collaborative Group on HNPCC for assistance in identifying Lynch syndrome [17,18] and the original Bethesda guidelines [19]. Subsequent blood germline testing using PCR amplification and direct sequencing of the entire coding region and the exon–intron boundaries for MMR genes (MLH1, MSH2, and MSH6) [20,21] revealed a single deleterious germline alteration affecting the MLH1 gene (mutation c.-168_c.116 + 713 del). This corresponds to a 997 bp deletion that encompasses the entirety of exon 1, a portion of intron 1, and a section of the MLH1 promoter, and was observed in all subjects within the HRLS group who underwent germline testing.
Data summarized in Table 1 were recorded in a study database and maintained in a secure, private manner consistent with the Declaration of Helsinki and the permission of Salah Azaiz Institute Ethics Committee registration number: ISA/2016/02. All subjects were informed about the purposes of the study and consented in writing to participate in the study. The 11 subjects were stratified into three groups based on familial cancer status. The high risk to LS group (HRLS, Figure 1, red ovals) are affected subjects of the pedigree; intermediate risk to LS (IRLS, Figure 1, green ovals) includes CRC-free subjects that have at least one affected parent, and low risk to LS (LRLS, Figure 1, blue ovals) are those with no relatives affected in the subject’s immediate triplet (subject and both parents).

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the included family members.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
Genomic DNA was extracted from the 11 blood samples according to the manufacturer’s recommendation using a Flexigene DNA Whole Blood Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNA quality and quantity were assessed using a Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and electrophoresis migration in agarose gel 1%. The genomic DNA with good quality was subjected to library preparation prior to sequencing.
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
Libraries were prepared using Nextera XT kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA) and pair-end sequencing (2 × 300 base pairs) with the Miseq Reagent V3 kit (Illumina) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The Nextera enzyme mix was used to simultaneously fragment input DNA and tag with universal adapters in a single tube reaction. Library purification was performed by Agincourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, IN, USA) and Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Wilmington, DE, USA) was used for quantification and quality checking [22]. Libraries were sequenced using the Illumina NextSeq500 platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). A total of 1564.4 GB with 142.22 GB on average per sample of raw data was generated on the sequencer, resulting in a mean sequence coverage depth of 45.88-fold (range of 37.71- to 59.17-fold).
2.4. Bioinformatic Variant Analysis (BVA)
The full bioinformatics variant analysis (BVA) is described in Figure 2 and the Supplemental Material. We used a novel functional implicated variant pipeline created in our previous work on breast cancer [23], modified to account for the pedigree relationship between subjects and familial and thus the risk-related nature of the detected variants. Briefly, for each subject’s high-throughput sequencing (HTS) sequence, alignment, poor-quality read filtering, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions/deletions (indels), and structural variants (SVs) were called and variant quality score recalibration and filtering, annotation and removal of common and likely non-functional variants, and assessment of cancer-associated genes were performed.
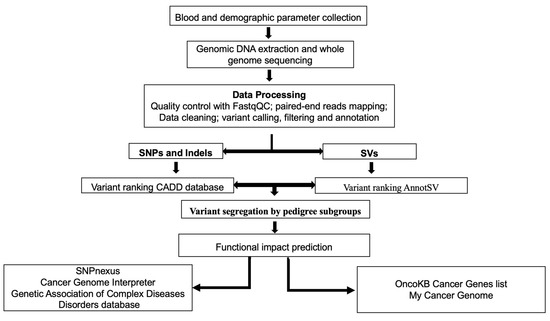
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the germline variant prioritization workflow. WGS: whole genome sequencing, QC: quality control, SNPs: single nucleotide polymorphisms, indels: insertions/deletions, SVs: structural variants, CADD: combined annotation dependent depletion, OncoKB: Oncology Knowledge Base.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characterization of the Pedigree Members
The large Tunisian pedigree (Figure 1) includes 39 members across four generations; 12 of them were diagnosed with LS CRC. In this study, 11 members’ (3 HRLS, 4 IRLS, and 6 LRLS) germline genomes were fully sequenced and their medical, environmental, and behavioral data were carefully analyzed. Individual and familial characterizations are described in Table 1. The HRLSs presented an average age of 48 ± 12.16 and BMI of 26.08 ± 3.11, IRLSs had an average age and BMI of 38.25 ± 17.63 and 26.77 ± 3.47, respectively, and the LRLSs had an average age and BMI of 35.50 ± 24.11 and 27.52 ± 2.64, respectively. Male sex distribution was 33.34% (1/3) HRLS, 0% (0/4) IRLS, and 50% (3/6) LRLS. Concerning lifestyle, 66.66% of HRLS recorded high brine and meat consumption, 100% of IRLS had a high fat consumption, and 75% of LRLS presented high meat and fat consumption. A total of 66.66% of HRLS were tobacco and alcohol users, 25% of IRLS were tobacco users, and 50% of LRLS were tobacco and alcohol users. A total of 66% of HRLS had hyperglycemia and hypertension, 75% of IRLS had hypertension and 50% had hyperglycemia, and 25% of LRLS had hypertension. An analysis of the clinical characteristics of each group found no statistically significant associations.
3.2. Variant Characterization of the Pedigree
3.2.1. SNPs and Indels
Before filtering, 7,836,438 SNPs and 2,039,903 indels were detected across the 11 genomes. A total of 23.63% (2,334,312 of 9,876,341) of all variants satisfied the low-frequency threshold (<0.01 AF 1000 G ALL and non-TCGA ExAC ALL) and 3.46% (80,905 of 2,334,312) of the variants demonstrated a probable deleterious function (CADD scaled score > 10). Subsequent annotation stratified the likely functionally implicated variants into coding (2824) and non-coding (78,081) variants. Lastly, filtering for variants predicted deleterious by having at least three of MutationTaster, PolyPhen V2, Provean, and SIFT resulted in 1961 coding and 9826 non-coding predicted deleterious variants. From the 1961 low-frequency, predicted functionally deleterious coding variants, 79 were found in all 11 sequenced individuals: 37 in all HRLS members, 27 in the IRLS group, and 15 in the LRLS. Of the 9826 non-coding filtered variants, all 9826 were found in members of at least one group; 4171 of the 9826 were found in each HRLS member, 2820 were found in every IRLS member, and 2835 in every LRLS member. In addition, 19 non-coding variants were exclusively detected only in a particular group of the pedigree: 2 variants exclusive to members in HRLS, 3 exclusives to IRLS, and 14 exclusives to LRLS, and 4 of these had a RegulomeDB Score < 4. Most of the detected non-coding variants were Intergenic (37,412) and found in all samples, whereas 30344 Intronic variants were found in all samples, and only 7 were found in samples in the same groups (Table 2).

Table 2.
Variants count for the whole pedigree subjects and shared variants by subjects under the same pedigree group with the functional annotation of noncoding variants according to ANNOVAR.
3.2.2. SNP and Indels with Evidence of Familial and Risk-Implicated Genes
Of the 83 variants identified in the cohort, 39 genes were identified containing at least one variant. PABPC3 had four variants (rs79397892, rs78826513, rs78552667, and rs80261016) found in all samples and one variant (rs201411821) found in all high and intermediate risk samples (HRLS and IRLS). Three of these five variants (rs78826513, rs201411821, and rs80261016) were classified as oncogenic driver variants according to SNPnexus (“Driver” as defined in the oncogenic classification by Cancer Genome Interpreter). KRT18 had four variants found in all samples, though none satisfied the oncogenic (or “Driver” predicted as tumor driver according to Cancer Genome Interpreter) threshold. One additional variant (rs201602708) located in MACF1 did not satisfy the oncogenic threshold. Five of the detected variants were in different genes that were previously described as common mutations in a collection of cancers. rs63750539 in the MLH1 gene has been described in several types of cancer including CRC and LS, rs373141354 in the PPP1R13B gene is associated with melanoma according to the Genetic Association of Complex Diseases database, rs551763507 in the LAMA5 gene is correlated to neuroblastoma, rs76670455 in NLRP14 gene to leukemia, and rs763119571 in TAS2R19 is also described in CRC according to the Cancer Genome Interpreter database. Concerning non-coding variants, four variants belonging to different genes (rs544153916 in PODN, rs116197074 in SCP2, and rs116526711 in MAML3) were noted only in samples from the LRLS group, and one of these variants rs115378978 in the FTO gene was previously associated with prostate cancer according to Disorders and SNPnexus databases (Table 3).

Table 3.
Classification of detected variants by gene and cancer impact according to pedigree groups.
3.2.3. Structural Variants (SVs)
A total of 11,171 SVs were found via smoove. Of the total SVs detected, their classifications were 4120 deletions, 194 duplications, 6560 breakends, and 297 inversions. Filtering for low-frequency novel variants resulted in 1122 deletions, 105 duplications, 5492 breakends, and 137 inversions. Filtering by highly likely functional (AnnotSV ranking > 3) resulted in 164 deletions, 17 duplications, 274 breakends, and 18 inversions. Finally, filtering for total length (>= 50 bp) resulted in 140 (of the 164) deletions. A familial analysis was performed to test sharing across study groups found, finding 154 breakends, 133 deletions, 4 duplications, and 13 inversions in each of the 11 subjects. A total of 35 shared breakends (23 shared within HRLS, 4 in IRLS, and 8 in LRLS) and 18 shared deletions (7 in HRLS, 4 in IRLS, and 7 in LRLS). Two duplications were shared by all members of LRLS and one inversion in IRLS and one inversion in LRLS. AnnotSV analysis for the SVs genomic location showed that 26 breakends and 17 deletions were intronic variants, but the 2 noted inversions were Transcript Start-Transcript End variants and the only detected duplication was an intronic variant (Table 4).

Table 4.
Variants count for the whole pedigree subjects and shared variants by subjects under the same pedigree group with variants location according to AnnotSV.
3.2.4. SVs with Risk-Implicated Genes
The 48 identified SVs were evaluated for functional prediction; the results showed that 43 SVs overlapped with genes with a probable functional impact, and 9 SVs overlapped with genes with an unlikely functional impact. Of these 43 SVs of probable impactful, 5 SVs overlapped with 4 genes with likely impact, 4 in the HRLS group (2 SVs in RELN, 1 each for FOXP1 and RRAS2 genes), and 1 in the IRLS group for the IRS2 gene previously associated with multiple cancers, including CRC according to OncoKB Cancer Genes list database. Two of the forty-three breakend SVs found in all members of the LRLS group had a potential impact on RELN, a gene correlated to several cancers including gastric cancer according to OncoKB Cancer Genes list database. One of the forty-three duplication SVs in all members of the IRLS group contains IRS2, a gene associated with esophageal, intestinal, stomach, and CRC cancers according to the My Cancer Genome database. One deletion SV in all members of LRLS impacts FOXP1, a gene correlated to several cancers including esophagogastric, gastrointestinal, and CRC in the My Cancer Genome database. Finally, one breakend SV found in all members of HRLS affects RRAS2, a gene associated with both breast and ovarian cancers according to the My Cancer Genome database (Table 5).

Table 5.
Classification of structural variants by gene and cancer impact according to pedigree groups.
4. Discussion
Several studies have examined the complex molecular heterogeneity of LS CRC in large families. The literature suggests that LS is caused by genetic and epigenetic variants sporadically found in genes, such as MMR (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM) associated with flat intra-mucosal neoplastic lesions [24,25]. However, a recent study by Binder et al. defined a third pathway for LS and showed the existence of two distinct genetic subtypes of the LS CRC [26]. These recent findings suggest that the risk and genesis of LS CRC may be caused by various multiply expressed functionally important “variant risk clusters” of germline mutations, each cluster independently associated with various pathways to carcinogenesis, and in a similar manner, each cluster may define both the type and degree of risk to LS CRC even within one large pedigree. The evidence of our results coupled with the broader collection of results in the literature supports such a working hypothesis.
These observations lead to the hypothesis that, in addition to the relatively well-characterized MMR deficiency in LS, other germline mutations or groups of mutations may contribute to the disruption of previously unassociated pathways, thus being associated with varying risks and oncogenesis of LS CRC. In this study, we investigated the germline mutational profiles of a large pedigree Tunisian family with Lynch syndrome-associated colorectal cancer using high throughput whole-genome sequencing. Subjects were grouped by familial cancer status into high, intermediate, and low risk to LS. Overall, we identified 94 germline variants, including 11 novel and rare cancer pathogenic variants previously described in cancer. Then, we clustered the identified germline variants according to the pedigree risk status into LRLS, IRLS, and HRLS groups.
The high-risk LS patients shared a missense mutation (rs63750539, p.Ala111Val) in MLH1 which is unlikely to be the cause of LS-CRC predisposition.
The MLH1 gene has been established as a causative gene for LS and presents the highest risk of CRC among individuals over 75 (46.6% of women and 51.4% of men) who are affected by the MLH1 variation. Rates range from 0% (at age 30) to 48.3% (at age 75) in females, and from 4.5% (at age 30) to 57.1% (at age 75) in males [22,23]. In another study, MLH1 variants were correlated with the highest risk of developing CRC in both heredity and sporadic cases [27]. Furthermore, two MLH1 5′UTR variants (c.-28A > G and c.-7C > T) were associated with early-onset CRC [28]. In addition, a cohort study reported that MLH1 is the most frequently mutated gene in early-onset sporadic CRC patients, exhibiting four pathogenic variations: c.C793T (p.R265C), c.C1029A (p.Y343X), c.C793T (p.R265C), and c.C1029A (p.Y343X) [29]. On the other hand, recent studies have found that promoter methylation of the MLH1 gene is prone to be silenced in CRC carcinogenesis pathways, and around 50% of MLH1-deficient tumors exhibit MLH1 promoter methylation [30]. Moreover, MLH1 promoter methylation in CRC cases was highly correlated with a BRAF V600E somatic mutation [31]. This variant was clinically classified as a hereditary sequence variant identified in disease-related genes directly affecting the clinical management of patients with LS-CRC [32]. To better understand the high risk effect on the pedigree, we investigated known driver mutations that are likely related to MMR deficiency. First, we investigated mutations in genes that play a key role in the adenoma–carcinoma model of CRC such as APC, KRAS, TP53, and binding/transactivated genes. We found the rs373141354 variant in the PPP1R13B gene (p.Gly866Arg), which assists TP53 activation during the cell apoptosis and lowers their ability shared by all subjects HRLS group [33]. Although TP53 is known to be rarely mutated in LS [34], our findings can be attributed to the high efficiency of TP53 in maintaining genomic integrity by arresting cells with mutated or damaged DNA in the G1 phase of the cell cycle to enable the repair mechanism or induce the apoptosis pathway [35]. The balance between cell cycle arrest and induced apoptosis depends on TP53 efficiency, which is related to the PPP1R13B activity identified in our research. Hence, we suggest that the variant rs373141354 (p.Gly866Arg) is associated with an increased risk of LS-CRC due to its low efficiency in cell cycle arrest.
Concerning the detected SVs overlapped with genes that have been previously correlated with different types of cancers, including digestive cancers, four shared SVs were found among HRLS subjects. Two SVs (7_103463079_103463080_BND_1 and 7_103463462_103463463_BND_1) were found to be related to the intronic region of the RELN gene, which has been correlated to several cancer risks including gastric cancer [36]. The large CpG islands are located at RELN promoter sites, and their transcriptional silence has been shown to be strongly controlled by promoter hypermethylation [37]. Consequently, a relationship between SVs and DNA methylation in cancer is speculated. Recent studies suggest that somatic copy number alterations in cancer are associated with DNA methylation [38], and numerous studies demonstrate that SVs may have a causal role in regulating CpG methylation [39,40]. Conversely, it is also possible that methylation could lead to SV imbalance by increasing DNA breaking [41,42]. Our observation enhances our growing understanding of the relationship between genetic (SVs) and epigenetic variation in cellular phenotype and the mechanism of gene regulation as well as the traits underlying the evolution of cancer with the presence of SVs in specific genome sites. The 71242366_71242638_DEL_1 deletion was noted in the FOXP1 gene. A large amount of substantial evidence has demonstrated that the tumor microenvironment is closely linked to the initiation, promotion, and progression of CRC through various mechanisms, such as immune suppression and the angiogenesis process [43]. Variation in FOXP3, an intracellular key molecule for Treg development and function, has been associated with a dysregulation in subverting antitumor immune responses and promoting tumor progression. The last SV detected, 11_14348706_14348707_BND_1, was related to the intronic region of the RRAS2 gene, which has previously been described in breast and ovarian cancers [44]. The role of LS in ovarian cancer was established and widely accepted, but the long-standing question of whether breast cancer should also be included under the umbrella of LS is still debated [45,46]. A recent study, consistent with other studies, shows that carriers of LS mutations tend to have earlier manifestations of breast cancer [47].
Regarding the IRLS group, a unique missense variant rs551763507 (p.Gly3688Glu) in the LAMA5 Laminin gene was identified in all subjects of the group. Based on Laminin’s function, these variants are not the most probable candidates to play a role in CRC susceptibility [48]. However, recent studies have identified LAMA5 in orthotropic metastases. The expression of Laminin 511 was associated with the upregulation of a set of genes regulating angiogenesis in TCGA data [48,49]. The Gordon group has demonstrated that the Laminin chains are localized within the vascular basement membrane on the basolateral surface of cancer cells, while colonic epithelial cells normally do not express vascular basement membrane Laminins. Consequently, the profound effect on vascular morphology and function upon LAMA5 mutation and inhibition of LAMA5 expression specifically by colon cancer cells indicates that cancer cell Laminin 511 deposition is important for colonic cells, promoting angiogenesis. Our results may suggest that inhibiting the production of vascular basement Laminins by tumor cells may serve as an efficient approach to prevent growth and the ability of tumor cells to regulate angiogenesis. Another novel variant was identified as an IRLS member as rs76670455 in the NLRP14 gene. NLRP14 has been described as a negative regulator of IFN responses. Interestingly, as inflammatory signaling pathways contribute to B cell lymphoma transformation, it is tempting to speculate that NLRP14 might contribute to cancer [50]. Another interesting aspect of NLR proteins is their expression in a panel of immune cells, notably myeloid cells and B cells, and their function as a negative regulator of inflammatory responses [51]. This differential expression of NLRP14 might be involved in the malignant transformation process. For the noted SVs in this HRLS pedigree group, only one variant was detected, the 13_110418067_110419056_DEL_1 in the intronic region of the IRS2 gene, which was shared by all IRLS subjects and has been described as related to several digestive cancers. Over-expression of IRS2 increases CRC cell adhesion to a similar extent as IGF-1 stimulation. Changes in adhesion, both increasing and decreasing, are important properties of metastasizing cancer cells and are involved in the invasion process, migration, and distant seeding of tumors [52]. In addition, it has been proven that the PI3K pathway is frequently dysregulated during CRC progression [53]. The TCGA Network demonstrated that high levels of IRS2 expression are mutually exclusive with IGF2 over-expression and with other mutations in the PI3K pathways in CRC. This suggests that the over-expression of IRS2 may be one mechanism by which the PI3K pathway could be dysregulated in CRC [54]. In summary, IRS2 appears to be a potential candidate as an oncogene driver, and the IGF1R-IRS2-PI3K axis could be an important therapeutic target in CRC.
In connection with variants specific to LRLS, we noted rs763119571 in the TAS2R19 gene with a deleterious function. Previous research has shown the association of this variant with CRC risk [24]. Genetic variants in type 2 bitter taste receptors (TAS2R) may influence health-related outcomes and are expressed within the oral cavity [55,56], the gastrointestinal mucosa [57], and the lungs [58]. TAS2R variants are hypothesized to play roles in an individual’s food preferences [59] and the neutralization and expulsion of toxins from the colon/rectum [60], thereby influencing cancer risk. The last noted variant with the deleterious function was rs115378978 in the FTO gene. Different polymorphisms of the FTO gene have been consistently associated with obesity. However, recent genome studies reveal that genetic variants in this gene are associated not only with human adiposity and metabolic disorders but also with several cancers, including colorectal cancer, since they can activate several signaling and hormonal pathways to increase cancer incidence. The hormones included in this carcinogenesis process could be ghrelin, oxytocin, and Leptin. Hence, FTO polymorphisms could exert an influence on the hormonal balance and physiologic factors and might increase cancer risk [60]. The variants identified in FTO, TAS2R, and NLRP14 genes were correlated with lifestyle-related factors for cancer installation, which are expected to be found in cases belonging to the LRLS group who are CRC-free. No oncogenic impactful SVs were detected in the LRLS group, which may explain the low risk of these subjects developing LS CRC and the crucial role of these variants in heredity cancer development.
Our current findings clearly illustrate that subtle, familiarly grouped genetic factors underlying risk to LS CRC extend beyond the well-documented familial CRC syndrome genes. Our data suggest that comprehensive germline testing in all LS CRC patients will provide comprehensive results to identify substantially more opportunities for robust and accurate genetically driven cancer characterization and subsequent prevention than established in current practice. Moreover, the magnitude of developing secondary cancer (breast or ovarian) is still unknown. Hence, our study sheds light on the importance of risked grouped germline screening to identify secondary risks and even predict the site of metastases during CRC progression.
This study’s limitations include the lack of testing on all family members. On the other hand, given the limited studies on SV identification, the impact of the SVs found in our study was predicted based on the hypothesis and recent functional studies. Thus, further studies in many LS-CRC families are needed to confirm the effect of the 57 SVs identified in our study. In addition, despite the extensive advantages of whole-genome sequencing and data processing, there remain several gaps in the technology and analysis. For example, the restricted resolution is caused by limitations in the read depth related to the quality of aligned sequences; a higher depth provides a greater power to call and identify new variants [61]. However, our mixed pipeline generated for our WGS-specific study allows us to detect new and known coding and non-coding variants across the whole genome of the 11 sequenced individuals, greatly facilitating the germline profile evolution of LS-CRC pedigrees and opening new opportunities for cancer pedigree studies. The introduction of several commercially available multigene panels has tremendous promise for clinical use but simultaneously raises weaknesses such as clear criteria for selecting above average risk patients to undergo such clinical panel testing [62] and the optimal choice of the prescribed panel [63]. Several multigene panels are available for hereditary CRC and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has provided a useful protocol for predicting the appropriate panel according to the family history of patients to better optimize the patient care [64]. A limitation of our study is that not all members of the family were tested for the MLH1 gene variant (c.-168_c.116 + 713del) detected in the family. This may lead to the study being considered a population-based WGS investigation in the context of MLH1 carriers and non-carriers, potentially weakening our conclusions about genetic modifiers in LS.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed the germline landscape of a Tunisian family with a predisposition to LS CRC and identified a total of 94 germline variants affecting 39 genes, 6 of which have been previously described in cancer, and 57 SVs, 48 of which were related to 43 genes, with 4 of these genes categorized as oncogenes. According to the familial definition of LS risk in the pedigree members, we identified three “variant risk clusters” associated with the high, intermediate, and low LS CRC risk groups in the pedigree. The results showed that variants related to high-risk LS members may be causative of the disease, while other variants present in intermediate-risk members may develop LS through very different mechanistic disruptions and low-risk members with these variants may not develop LS at all. The application of HTS technology with such variant clustering for germline screening will efficiently provide further insights into the etiology of hereditary cancer and a huge opportunity to improve LS clinical suspicion. The significance of germline variants in cancer predisposition is still poorly explored, and this study contributes to filling this knowledge gap.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers15164074/s1, Section S1: Data Processing and Whole-Genome Mapping; Section S2: Variant Calling and Annotation; Section S2.1: SNPs and Indels; Section S2.2: Structural Variants; Section S2.3: Segregation in Pedigrees; Section S3: Variant Filtering; Section S3.1: SNPs and Indels; Section S3.2: Structural Variants; Section S4: Filtered Variants According to Cancer Relationship; Section S4.1: SNPs and Indels; Section S4.2: Structural Variants. References [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] are cited in the supplementary materials (References 1–28).
Author Contributions
M.B.: participated in study concept and design, carried out the study, and managed all project study participants who aided with experiments, patient consenting and charts, data review, statistical analysis, and manuscript preparation. A.A.M.: data analysis and processing, sequencing alignment, variant calling, and manuscript editing. A.M.: patient recruitment and clinical data acquisition. B.B.-Z.: original idea and study concept. P.J.T.: project principal investigation, original idea, study concept and design, guided overall study analysis, bioinformatics and statistical analysis, discussion of results, and review and editing of the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by funding provided by the Center for Biomedical Informatics, School of Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All subject investigations conformed to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and have been performed with permission of the study protocol approved by the ethics committee of Salah Azaiz Institute (SAI), under the same’s Ethics Committee registration number (#ISA/2019/04).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank all blood donors who participated in the present study. We express our thanks to Ikram Sghaier for reviewing the manuscript and Hushan Yang and Chun Wang for their excellent assistance with experiments, discussion of results, and suggested ideas for consideration.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Guillén-Ponce, C.; Lastra, E.; Lorenzo-Lorenzo, I.; Martín Gómez, T.; Morales Chamorro, R.; Sánchez-Heras, A.B.; Serrano, R.; Soriano Rodríguez, M.C.; Soto, J.L.; Robles, L. SEOM Clinical Guideline on Hereditary Colorectal Cancer (2019). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods—Ferlay—2019—International Journal of Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijc.31937 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Ahnen, D.J.; Wade, S.W.; Jones, W.F.; Sifri, R.; Mendoza Silveiras, J.; Greenamyer, J.; Guiffre, S.; Axilbund, J.; Spiegel, A.; You, Y.N. The Increasing Incidence of Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Call to Action. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurgelun, M.B.; Kulke, M.H.; Fuchs, C.S.; Allen, B.A.; Uno, H.; Hornick, J.L.; Ukaegbu, C.I.; Brais, L.K.; McNamara, P.G.; Mayer, R.J.; et al. Cancer Susceptibility Gene Mutations in Individuals With Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlDubayan, S.H.; Giannakis, M.; Moore, N.D.; Han, G.C.; Reardon, B.; Hamada, T.; Mu, X.J.; Nishihara, R.; Qian, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Inherited DNA-Repair Defects in Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colorectal Cancer—Risk Factors and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/colorectal-cancer/risk-factors-and-prevention (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Concordant and Discordant Familial Cancer: Familial Risks, Proportions and Population Impact—Frank—2017—International Journal of Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijc.30583 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Umar, A.; Boland, C.R.; Terdiman, J.P.; Syngal, S.; de la Chapelle, A.; Rüschoff, J.; Fishel, R.; Lindor, N.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Hamelin, R.; et al. Revised Bethesda Guidelines for Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (Lynch Syndrome) and Microsatellite Instability. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A. The 2019 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina Pabón, M.A.; Babiker, H.M. A Review Of Hereditary Colorectal Cancers. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Valentin, M.; Nakken, S.; Tubeuf, H.; Vodak, D.; Ekstrøm, P.O.; Nissen, A.M.; Morak, M.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Martins, A.; Møller, P.; et al. Identification of Genetic Variants for Clinical Management of Familial Colorectal Tumors. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngal, S.; Fox, E.A.; Li, C.; Dovidio, M.; Eng, C.; Kolodner, R.D.; Garber, J.E. Interpretation of Genetic Test Results for Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal CancerImplications for Clinical Predisposition Testing. JAMA 1999, 282, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Aberrant Splicing Due to Missense or Silent Mutations in the APC Gene—Aretz—2004—Human Mutation—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/humu.20087 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Nolano, A.; Medugno, A.; Trombetti, S.; Liccardo, R.; De Rosa, M.; Izzo, P.; Duraturo, F. Hereditary Colorectal Cancer: State of the Art in Lynch Syndrome. Cancers 2023, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Low-Risk MSH3 and MSH2 Variant Alleles with Lynch Syndrome: Probability of Synergistic Effects—Duraturo—2011—International Journal of Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijc.25824 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Rahman, N. Realizing the Promise of Cancer Predisposition Genes. Nature 2014, 505, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasen, H.F.A.; Watson, P.; Mecklin, J.; Lynch, H.T. New Clinical Criteria for Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC, Lynch Syndrome) Proposed by the International Collaborative Group on HNPCC. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasen, H.F.A.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Meera Khan, P.; Lynch, H.T. The International Collaborative Group on Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colorectal Cancer (ICG-HNPCC). Dis. Colon Rectum 1991, 34, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Boland, C.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Henson, D.E.; Srivastava, S.; Jass, J.R.; Khan, P.M.; Lynch, H.; Smyrk, T.; Perucho, M.; et al. A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer Syndrome: Meeting Highlights and Bethesda Guidelines. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Frankel, W.; Panescu, J.; Lockman, J.; Sotamaa, K.; Fix, D.; Comeras, I.; La Jeunesse, J.; Nakagawa, H.; Westman, J.A.; et al. Screening for Lynch Syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer) among Endometrial Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7810–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol, V.; Castells, A.; Andreu, M.; Castellví-Bel, S.; Alenda, C.; Llor, X.; Xicola, R.M.; Rodríguez-Moranta, F.; Payá, A.; Jover, R.; et al. Accuracy of Revised Bethesda Guidelines, Microsatellite Instability, and Immunohistochemistry for the Identification of Patients With Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer. JAMA 2005, 293, 1986–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, E.; Agoti, C.N.; Ngoi, J.M.; de Laurent, Z.R.; Gitonga, J.; Cotten, M.; Phan, M.V.T.; Nokes, D.J.; Delwart, E.; Sanders, E.; et al. Complete Genome Sequences of Dengue Virus Type 2 Strains from Kilifi, Kenya. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01566-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbirou, M.; Miller, A.A.; Gafni, E.; Mezlini, A.; Zidi, A.; Boley, N.; Tonellato, P.J. Evaluation of CfDNA as an Early Detection Assay for Dense Tissue Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadova, A.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M.; Bläker, H.; Kloor, M. CTNNB1-Mutant Colorectal Carcinomas with Immediate Invasive Growth: A Model of Interval Cancers in Lynch Syndrome. Fam. Cancer 2016, 15, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Three Molecular Pathways Model Colorectal Carcinogenesis in Lynch Syndrome—Ahadova—2018—International Journal of Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijc.31300 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Binder, H.; Hopp, L.; Schweiger, M.R.; Hoffmann, S.; Jühling, F.; Kerick, M.; Timmermann, B.; Siebert, S.; Grimm, C.; Nersisyan, L.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Heterogeneity of Colorectal Tumours Arising in Lynch Syndrome. J. Pathol. 2017, 243, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.K.; Jenkins, M.A.; Dowty, J.G.; Antoniou, A.C.; Lee, A.; Giles, G.G.; Buchanan, D.D.; Clendenning, M.; Rosty, C.; Ahnen, D.J.; et al. Prevalence and Penetrance of Major Genes and Polygenes for Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2017, 26, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesson, L.B.; Packham, D.; Kwok, C.-T.; Nunez, A.C.; Ng, B.; Schmidt, C.; Fields, M.; Wong, J.W.H.; Sloane, M.A.; Ward, R.L. Lynch Syndrome Associated with Two MLH1 Promoter Variants and Allelic Imbalance of MLH1 Expression. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wang, M.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Tsai, W.-S.; You, J.-F.; Chen, C.-C.; Liu, H.-L.; Chiang, J.-M. Pathogenic Germline Mutations of DNA Repair Pathway Components in Early-Onset Sporadic Colorectal Polyp and Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikenboom, E.L.; van der Werf–’t Lam, A.-S.; Rodríguez-Girondo, M.; Van Asperen, C.J.; Dinjens, W.N.M.; Hofstra, R.M.W.; Van Leerdam, M.E.; Morreau, H.; Spaander, M.C.W.; Wagner, A.; et al. Universal Immunohistochemistry for Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 58,580 Colorectal Carcinomas. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e496–e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.I.O.; Domingos, T.A.; Kupper, B.E.C.; De Brot, L.; Aguiar Junior, S.; Carraro, D.M.; Torrezan, G.T. Amplicon-Based NGS Test for Assessing MLH1 Promoter Methylation and Its Correlation with BRAF Mutation in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 130, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.A.; Spurdle, A.B.; Plazzer, J.-P.; Greenblatt, M.S.; Akagi, K.; Al-Mulla, F.; Bapat, B.; Bernstein, I.; Capellá, G.; den Dunnen, J.T.; et al. Application of a 5-Tiered Scheme for Standardized Classification of 2,360 Unique Mismatch Repair Gene Variants in the InSiGHT Locus-Specific Database. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prognostic Values of Apoptosis-Stimulating P53-Binding Protein 1 and 2 and Their Relationships with Clinical Characteristics of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients: A Retrospective Study|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40880-016-0169-0 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Kloth, M.; Ruesseler, V.; Engel, C.; Koenig, K.; Peifer, M.; Mariotti, E.; Kuenstlinger, H.; Florin, A.; Rommerscheidt-Fuss, U.; Koitzsch, U.; et al. Activating ERBB2/HER2 Mutations Indicate Susceptibility to Pan-HER Inhibitors in Lynch and Lynch-like Colorectal Cancer. Gut 2016, 65, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P53 Polymorphic Variants at Codon 72 Exert Different Effects on Cell Cycle Progression—Pim—2004—International Journal of Cancer—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijc.11548 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Jamshidi, M.; Mohammadi Pour, S.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.-R. Single Nucleotide Variants Associated with Colorectal Cancer Among Iranian Patients: A Narrative Review. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2020, 13, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sharma, R.P.; Costa, R.H.; Costa, E.; Grayson, D.R. On the Epigenetic Regulation of the Human Reelin Promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Bunn, P.; Jin, C.; Little, P.; Zhabotynsky, V.; Perou, C.M.; Hayes, D.N.; Chen, M.; Lin, D.-Y. The Association between Copy Number Aberration, DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Tumor Samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Lappalainen, T.; Montgomery, S.B.; Buil, A.; Ongen, H.; Yurovsky, A.; Bryois, J.; Giger, T.; Romano, L.; Planchon, A.; et al. Passive and Active DNA Methylation and the Interplay with Genetic Variation in Gene Regulation. eLife 2013, 2, e00523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Wen, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, J.; Lam, B.A.; Mills, R.E.; Stranger, B.E.; Lee, C.; Setlur, S.R. Association of CNVs with Methylation Variation. npj Genom. Med. 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Harris, R.A.; Cheung, S.W.; Coarfa, C.; Jeong, M.; Goodell, M.A.; White, L.D.; Patel, A.; Kang, S.-H.; Shaw, C.; et al. Genomic Hypomethylation in the Human Germline Associates with Selective Structural Mutability in the Human Genome. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Kucherlapati, M.; Hadjipanayis, A.; Pantazi, A.; Bristow, C.A.; Lee, E.A.; Mahadeshwar, H.S.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Global Impact of Somatic Structural Variation on the DNA Methylome of Human Cancers. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motz, G.T.; Coukos, G. The Parallel Lives of Angiogenesis and Immunosuppression: Cancer and Other Tales. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordiev, M.; Shigapova, L.H.; Brovkina, O.; Enikeev, R.F.; Druzhkov, M.; Nikitin, A.; Shagimardanova, E.; Gusev, O. Lynch Syndrome-Associated Hereditary Mutations Cause Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Results from Russian Heredetary Oncogenomics Project. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovkina, O.I.; Shigapova, L.; Chudakova, D.A.; Gordiev, M.G.; Enikeev, R.F.; Druzhkov, M.O.; Khodyrev, D.S.; Shagimardanova, E.I.; Nikitin, A.G.; Gusev, O.A. The Ethnic-Specific Spectrum of Germline Nucleotide Variants in DNA Damage Response and Repair Genes in Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patients of Tatar Descent. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Is Breast Cancer a Part of Lynch Syndrome?|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/bcr3241 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Nikitin, A.G.; Chudakova, D.A.; Enikeev, R.F.; Sakaeva, D.; Druzhkov, M.; Shigapova, L.H.; Brovkina, O.I.; Shagimardanova, E.I.; Gusev, O.A.; Gordiev, M.G. Lynch Syndrome Germline Mutations in Breast Cancer: Next Generation Sequencing Case-Control Study of 1,263 Participants. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Use of Multigene-Panel Identifies Pathogenic Variants in Several CRC-Predisposing Genes in Patients Previously Tested for Lynch Syndrome—Hansen—2017—Clinical Genetics—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/cge.12994 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Gordon-Weeks, A.; Lim, S.Y.; Yuzhalin, A.; Lucotti, S.; Vermeer, J.A.F.; Jones, K.; Chen, J.; Muschel, R.J. Tumour-Derived Laminin A5 (LAMA5) Promotes Colorectal Liver Metastasis Growth, Branching Angiogenesis and Notch Pathway Inhibition. Cancers 2019, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Lee, A.; Sitharam, R.; Kesner, J.; Rabadan, R.; Shapira, S.D. Germ-Cell-Specific Inflammasome Component NLRP14 Negatively Regulates Cytosolic Nucleic Acid Sensing to Promote Fertilization. Immunity 2017, 46, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, K.; Becker, E.; Kienes, I.; Sowa, A.; Postma, Y.; Gloria, Y.C.; Weber, A.N.R.; Kufer, T.A. The NLR Family Pyrin Domain–Containing 11 Protein Contributes to the Regulation of Inflammatory Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, K.; Gassmann, P.; Enns, A.; Korb, T.; Hemping-Bovenkerk, A.; Hölzen, J.; Haier, J. Organ-Specific Metastatic Tumor Cell Adhesion and Extravasation of Colon Carcinoma Cells with Different Metastatic Potential. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Wang, T.-L.; Samuels, Y.; Bardelli, A.; Cummins, J.M.; DeLong, L.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Willson, J.K.V.; et al. Mutations in a Signalling Pathway. Nature 2005, 436, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRS2 Is a Candidate Driver Oncogene on 13q34 in Colorectal Cancer—Day—2013—International Journal of Experimental Pathology—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iep.12021 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Diószegi, J.; Llanaj, E.; Ádány, R. Genetic Background of Taste Perception, Taste Preferences, and Its Nutritional Implications: A Systematic Review. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmanov, A.A.; Beauchamp, G.K. Taste Receptor Genes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternini, C. Taste Receptors in the Gastrointestinal Tract. IV. Functional Implications of Bitter Taste Receptors in Gastrointestinal Chemosensing. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G457–G461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, D.A.; Wang, W.C.H.; McIlmoyle, E.L.; Robinett, K.S.; Schillinger, R.M.; An, S.S.; Sham, J.S.K.; Liggett, S.B. Bitter Taste Receptors on Airway Smooth Muscle Bronchodilate by Localized Calcium Signaling and Reverse Obstruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A.; Rock, C.L. The Influence of Genetic Taste Markers on Food Acceptance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozengurt, E. Taste Receptors in the Gastrointestinal Tract. I. Bitter Taste Receptors and α-Gustducin in the Mammalian Gut. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G171–G177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whole-Genome Sequencing of Synchronous Thyroid Carcinomas Identifies Aberrant DNA Repair in Thyroid Cancer Dedifferentiation—Paulsson—2020—The Journal of Pathology—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://pathsocjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/path.5359 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- NCCN Guidelines Insights: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Version 2.2019 in: Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Volume 17 Issue 9 (2019). Available online: https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/17/9/article-p1032.xml (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Syngal, S.; Brand, R.E.; Church, J.M.; Giardiello, F.M.; Hampel, H.L.; Burt, R.W. ACG Clinical Guideline: Genetic Testing and Management of Hereditary Gastrointestinal Cancer Syndromes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 223–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Kalady, M.F.; Pearlman, R.; Stanich, P.P. Hereditary Colorectal Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. 2022, 36, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Long-Read Alignment with Burrows–Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional Annotation of Genetic Variants from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A Global Reference for Human Genetic Variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K.; Ward, M.; Sherry, S.T. DbSNP: A Database of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of Protein-Coding Genetic Variation in 60,706 Humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderman, M.D.; Paudyal, C.; Shakeel, M.; Kelley, W.; Bashir, A.; Gelb, B.D. NPSV: A Simulation-Driven Approach to Genotyping Structural Variants in Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, R.M.; Chiang, C.; Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. LUMPY: A Probabilistic Framework for Structural Variant Discovery. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Layer, R.M.; Faust, G.G.; Lindberg, M.R.; Rose, D.B.; Garrison, E.P.; Marth, G.T.; Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. SpeedSeq: Ultra-Fast Personal Genome Analysis and Interpretation. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.S.; Quinlan, A.R. Duphold: Scalable, Depth-Based Annotation and Curation of High-Confidence Structural Variant Calls. GigaScience 2019, 8, giz040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoffroy, V.; Herenger, Y.; Kress, A.; Stoetzel, C.; Piton, A.; Dollfus, H.; Muller, J. AnnotSV: An Integrated Tool for Structural Variations Annotation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3572–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A General Framework for Estimating the Relative Pathogenicity of Human Genetic Variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster Evaluates Disease-Causing Potential of Sequence Alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A Method and Server for Predicting Damaging Missense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN Web Server: A Tool to Predict the Functional Effect of Amino Acid Substitutions and Indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting Amino Acid Changes That Affect Protein Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DbNSFP v3.0: A One-Stop Database of Functional Predictions and Annotations for Human Nonsynonymous and Splice-Site SNVs—Liu—2016—Human Mutation—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/humu.22932 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg v4: Systematic Mining of Putative Causal Variants, Cell Types, Regulators and Target Genes for Human Complex Traits and Disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D877–D881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of Functional Variation in Personal Genomes Using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birney, E.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Dutta, A.; Guigó, R.; Gingeras, T.R.; Margulies, E.H.; Weng, Z.; Snyder, M.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; et al. Identification and Analysis of Functional Elements in 1% of the Human Genome by the ENCODE Pilot Project. Nature 2007, 447, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.L.; Brand, H.; Karczewski, K.J.; Zhao, X.; Alföldi, J.; Francioli, L.C.; Khera, A.V.; Lowther, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; Wang, H.; et al. A Structural Variation Reference for Medical and Population Genetics. Nature 2020, 581, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscanoa, J.; Sivapalan, L.; Gadaleta, E.; Dayem Ullah, A.Z.; Lemoine, N.R.; Chelala, C. SNPnexus: A Web Server for Functional Annotation of Human Genome Sequence Variation (2020 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W185–W192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.G.; Barnes, K.C.; Bright, T.J.; Wang, S.A. The Genetic Association Database. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamborero, D.; Rubio-Perez, C.; Deu-Pons, J.; Schroeder, M.P.; Vivancos, A.; Rovira, A.; Tusquets, I.; Albanell, J.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J.; et al. Cancer Genome Interpreter Annotates the Biological and Clinical Relevance of Tumor Alterations. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Phillips, S.; Kundra, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Rudolph, J.E.; Yaeger, R.; Soumerai, T.; Nissan, M.H.; et al. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO.17.00011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home—My Cancer Genome. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).