CPSF3 Promotes Pre-mRNA Splicing and Prevents CircRNA Cyclization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2. Clinical Cancer Samples and Tissue Microarrays
2.3. Cells Culture and Plasmid Transfection
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. qRT-PCR
2.6. Dot Blot
2.7. Western Blot
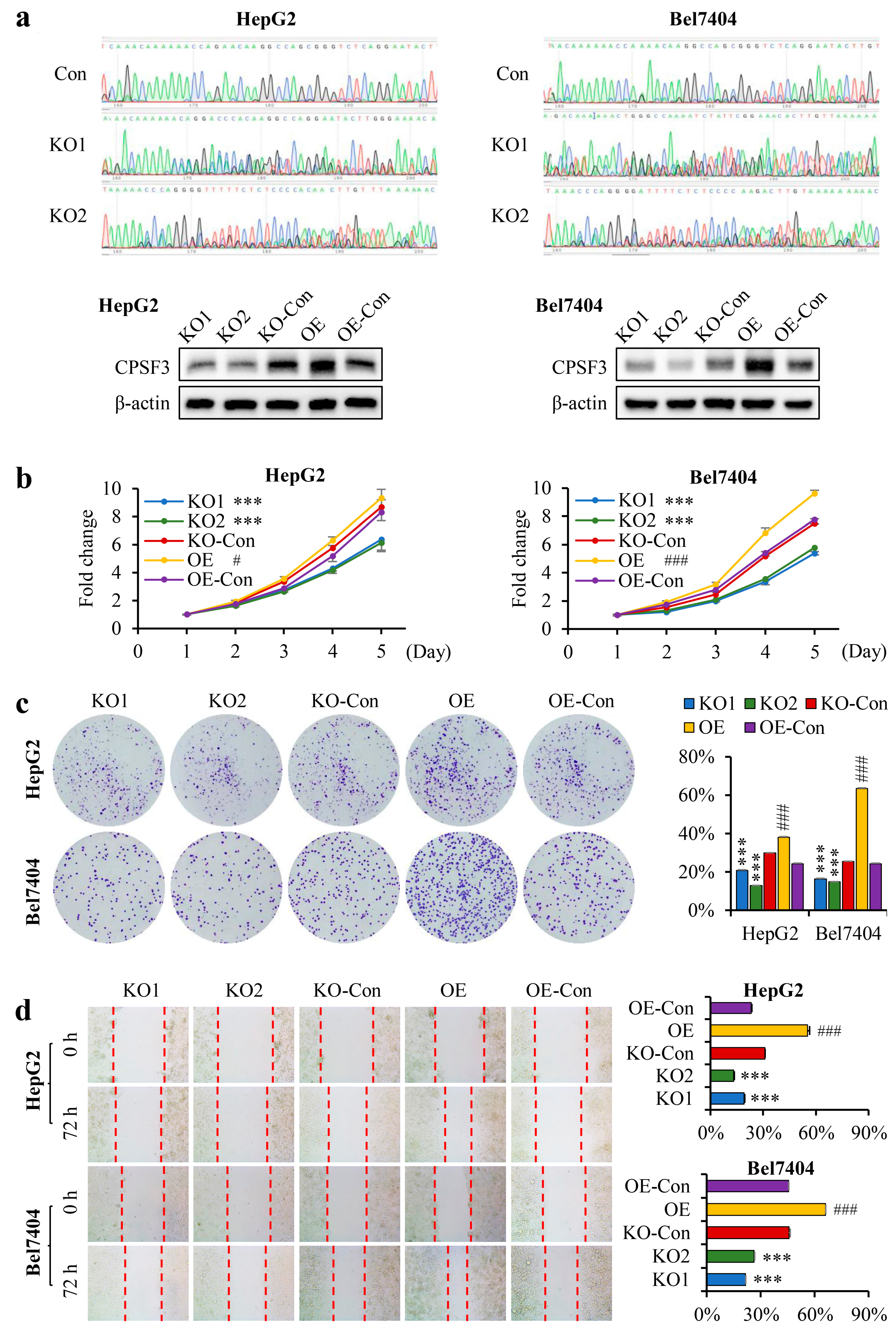
2.8. Cell Proliferation, Clone Formation, and Wound Healing Assays
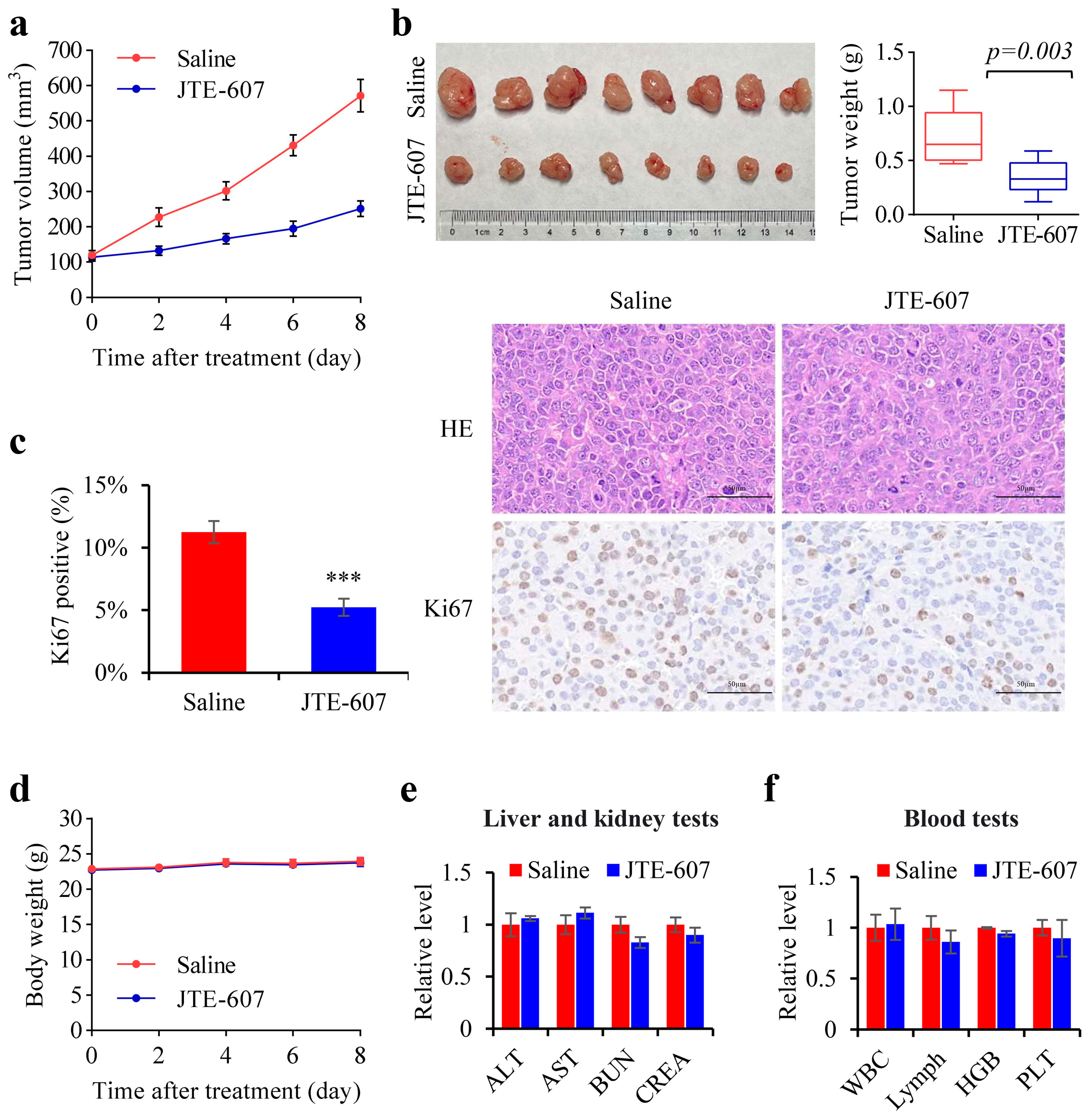
2.9. JTE-607 Studies
2.10. Xenograft Tumorigenic Assays
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
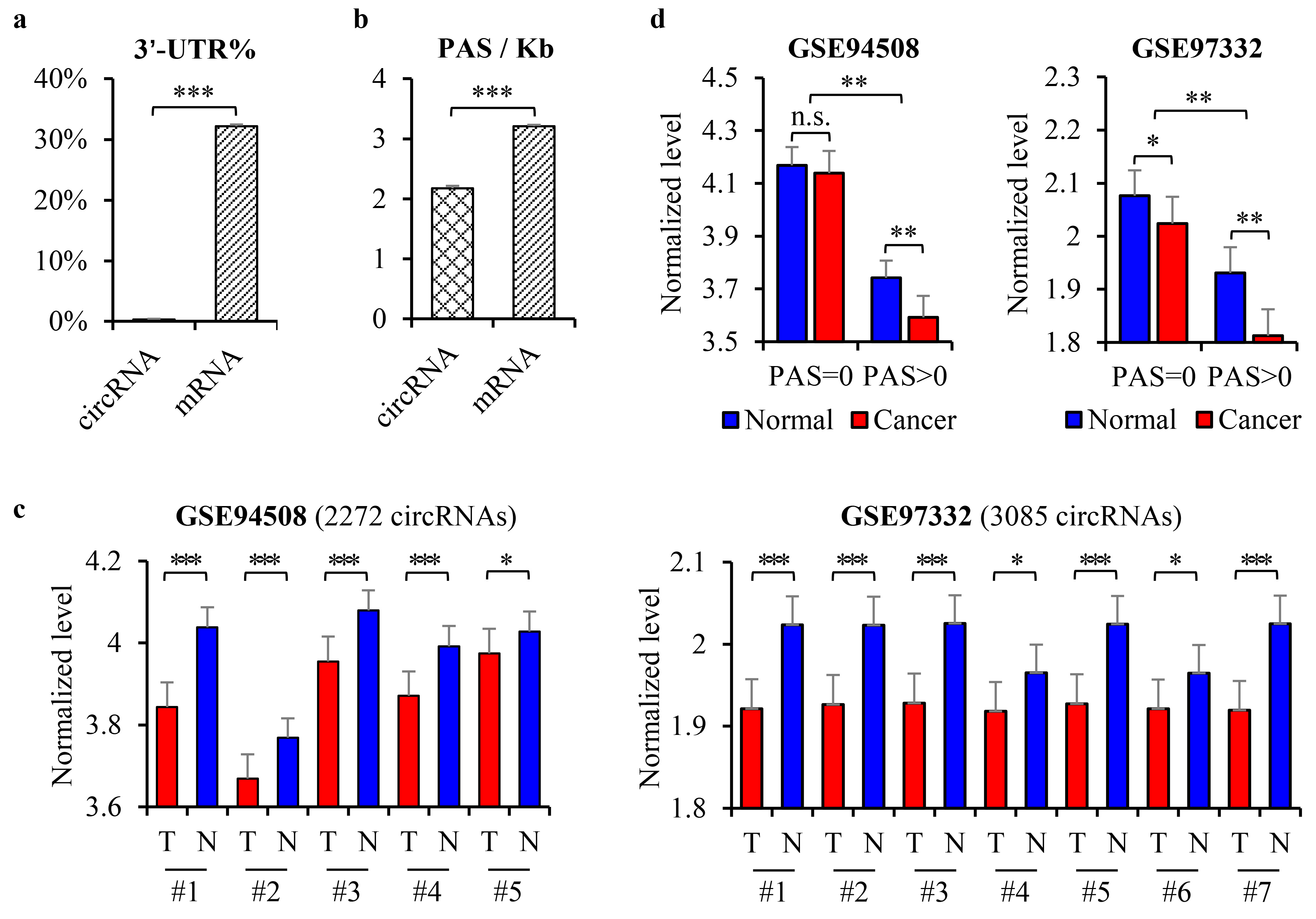
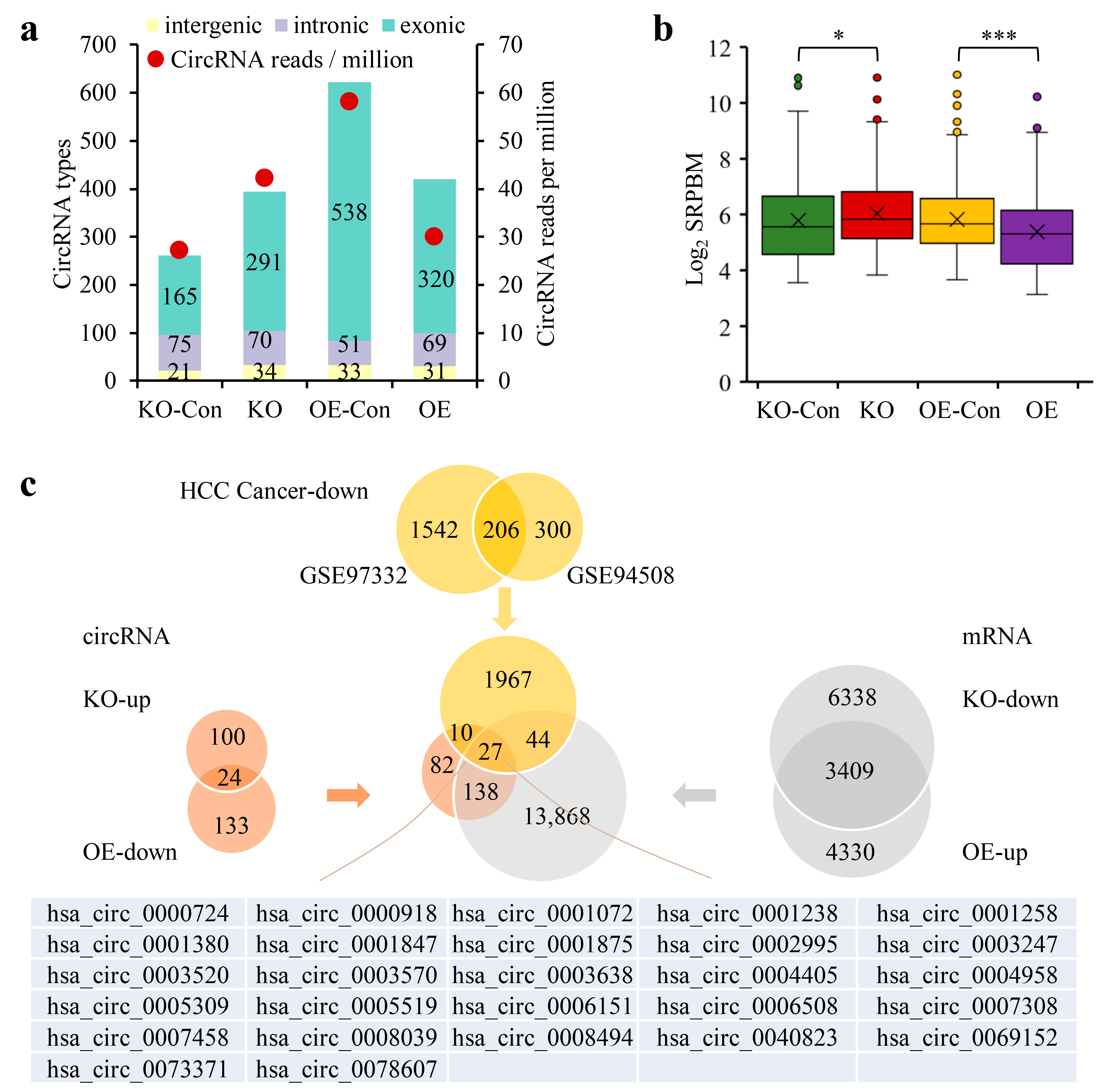
3.1. The Downregulation of CircRNAs in HCC Was Dependent on the PAS Sequence
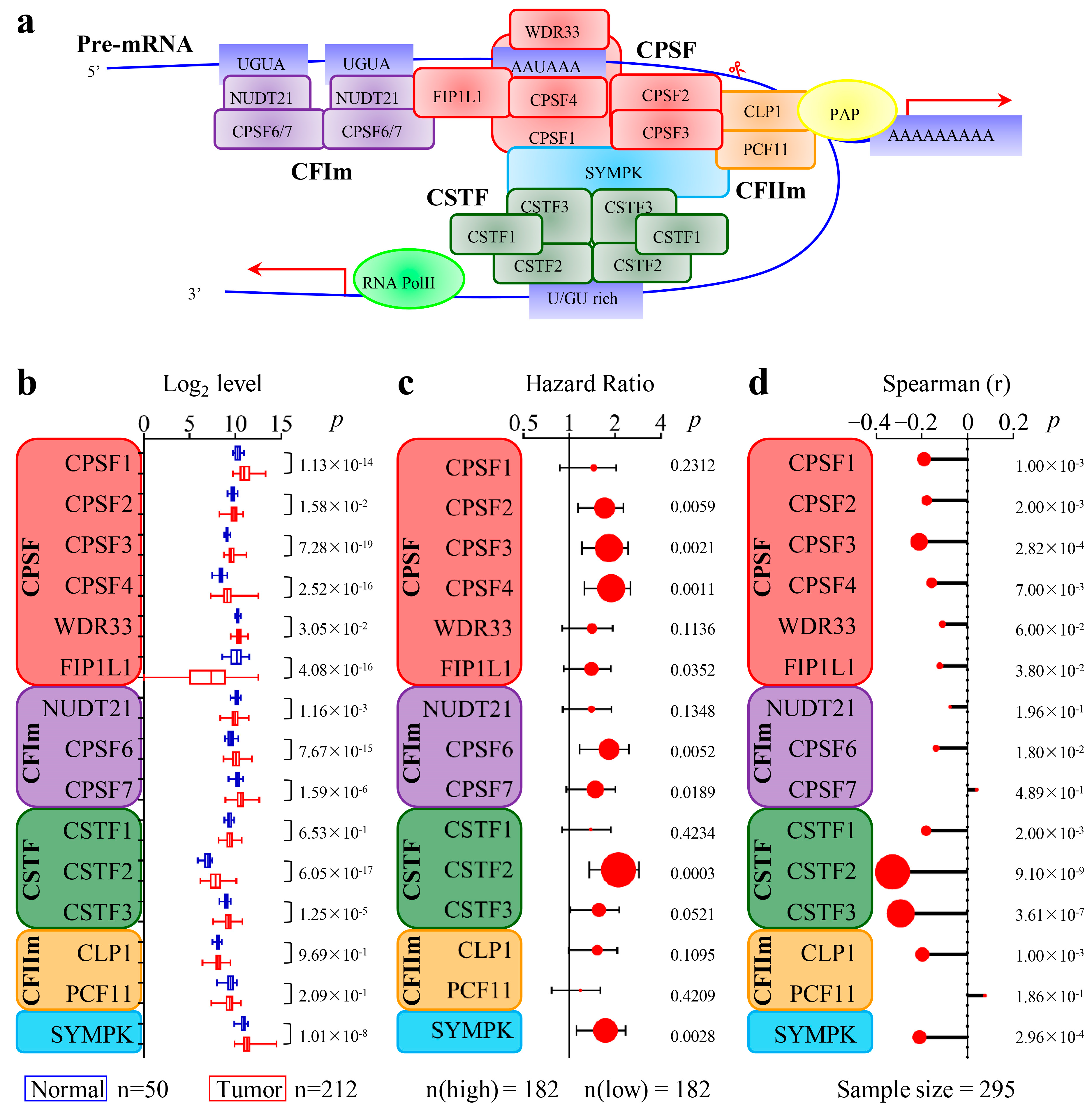
3.2. The 3′-End Formation Complex Was Associated with CircRNA Biogenesis and the Survival of HCC Patients
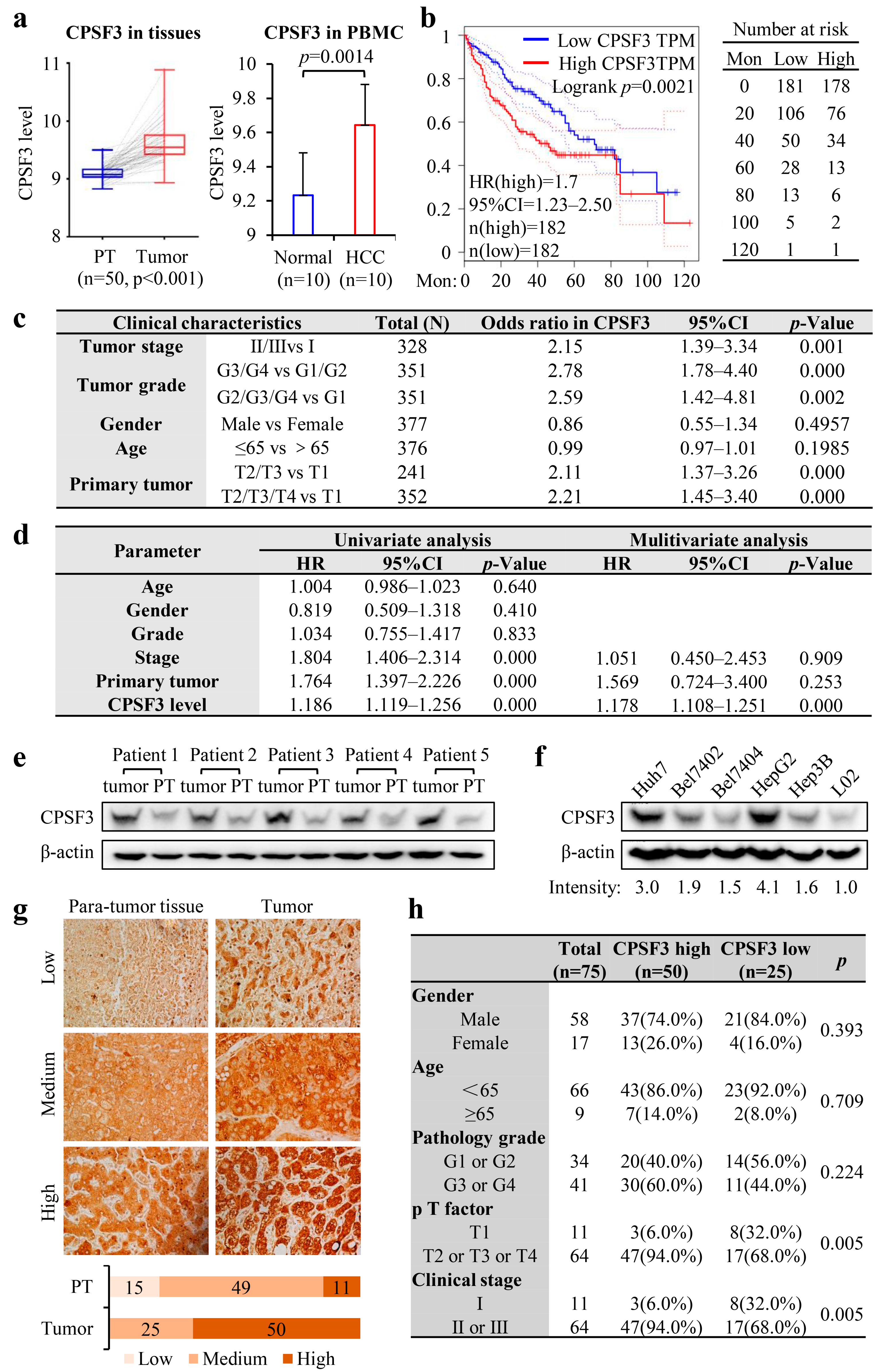
3.3. High Expression of CPSF3 Predicted Poor Prognosis in HCC Patients
3.4. CPSF3 Promoted the Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
3.5. The CPSF3 Protein and PAS Element Were Critical for CircRNA Cyclization
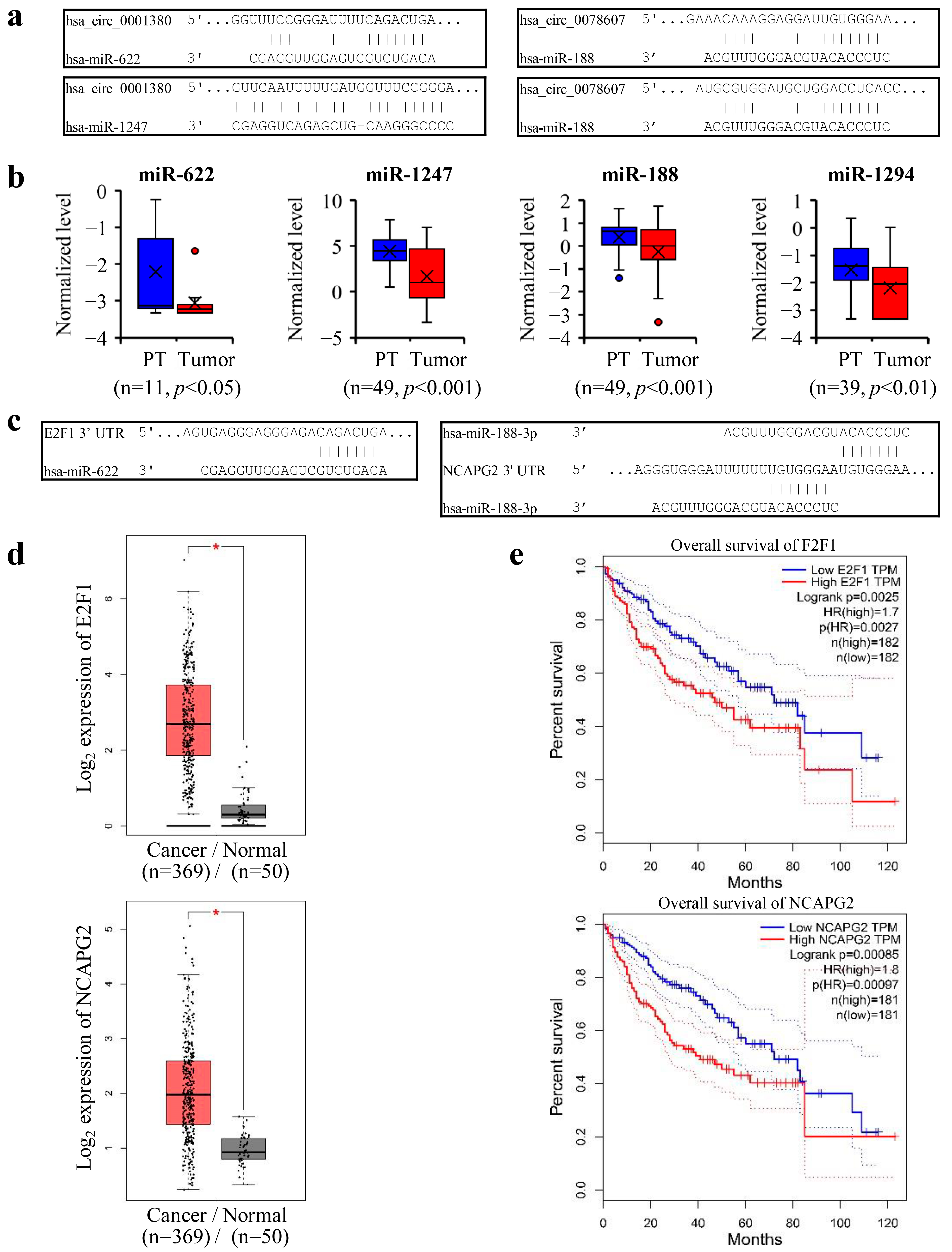
3.6. CPSF3 Promoted the Pre-mRNA Shift from CircRNA to Linear mRNA and Disrupted miRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing
3.7. Chemical Inhibition of CPSF3 by JTE-607 Inhibited the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Suppressed the Tumorigenicity in a Xenograft Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- El-Serag, H.B. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Sheng, C.; Huang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.H.; Cheng, Z.N.; Zhu, Q.B. MiR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Ding, J.; Li, D.; Yang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, Q. NUDT21 regulates 3’-UTR length and microRNA-mediated gene silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 410, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sheng, C.; Yin, Y.J.; Wen, S.; Yang, G.P.; Cheng, Z.N.; Zhu, Q.B. PABPC1 interacts with AGO2 and is responsible for the microRNA mediated gene silencing in high grade hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Tsang, F.H.; Ng, I.O. Non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular functions and pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q. Specific and sensitive detection of CircRNA based on netlike hybridization chain reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Zuo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, S.; et al. Cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 4 promotes colon cancer progression by transcriptionally activating hTERT. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Y.; Zhou, W.H.; Li, X.J.; Sun, M.; Ding, J.S.; Zhu, Q.B. Tandem DNAzyme for double digestion: A new tool for circRNA suppression. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilusz, J.E.; Sharp, P.A. Molecular biology. A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science 2013, 340, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enuka, Y.; Lauriola, M.; Feldman, M.E.; Sas-Chen, A.; Ulitsky, I.; Yarden, Y. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, Q. NUDT21 regulates circRNA cyclization and ceRNA crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, Q. Mechanisms Regulating Abnormal Circular RNA Biogenesis in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, C.; Goodall, G.J.; Shirokikh, N.E.; Preiss, T. Insights into the biogenesis and potential functions of exonic circular RNA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Green, M.R. From polyadenylation to splicing: Dual role for mRNA 3’ end formation factors. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Misra, A.; Ou, J.; Zhu, L.J.; Green, M.R. Global Promotion of Alternative Internal Exon Usage by mRNA 3’ End Formation Factors. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonemann, L.; Kuhn, U.; Martin, G.; Schafer, P.; Gruber, A.R.; Keller, W.; Zavolan, M.; Wahle, E. Reconstitution of CPSF active in polyadenylation: Recognition of the polyadenylation signal by WDR33. Genes. Dev. 2014, 28, 2381–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.G.; Beuth, B.; Taylor, I.A. Structure of a nucleotide-bound Clp1-Pcf11 polyadenylation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takagaki, Y.; Manley, J.L. RNA recognition by the human polyadenylation factor CstF. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.M.; Tatomer, D.C.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L.; Cherry, S.; Wilusz, J.E. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Steiniger, M.; Marzluff, W.F. A core complex of CPSF73, CPSF100, and Symplekin may form two different cleavage factors for processing of poly(A) and histone mRNAs. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hamilton, K.; Manley, J.L.; Shi, Y.; Walz, T.; Tong, L. Molecular basis for the recognition of the human AAUAAA polyadenylation signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1419–E1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Moore, C.L. On the Cutting Edge: Regulation and Therapeutic Potential of the mRNA 3’ End Nuclease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, W.; Guan, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y. CPSF3 is a promising prognostic biomarker and predicts recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.L.; Geng, J.W.; Zhang, Q.K.; Xu, Y.S.; Zhou, X.Z.; Huang, Z.; Shi, K.Q.; Pan, C.W.; Wu, J.M. LncRNA CASC9 interacts with CPSF3 to regulate TGF- signaling in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Yu, Y.P.; Shi, Y.K.; Nelson, J.B.; Luo, J.H. CSR1 induces cell death through inactivation of CPSF3. Oncogene 2009, 28, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, M.; Johnson, E.L.; Swamy, V.S.; Nersesian, L.E.; Corney, D.C.; Robinson, D.G.; Taylor, D.G.; Ambrus, A.M.; Jelinek, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Alternative polyadenylation factors link cell cycle to migration. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.T.; Lohmann, F.; Carbonneau, S.; Fazal, A.; Weihofen, W.A.; Gleim, S.; Salcius, M.; Sigoillot, F.; Henault, M.; Carl, S.H.; et al. CPSF3-dependent pre-mRNA processing as a druggable node in AML and Ewing’s sarcoma. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.Y.; Yao, T.; Chen, Q.Q.; Mo, X.Y.; Hu, Y.R.; Guo, J.M. Screening differential circular RNA expression profiles reveals hsa_ circ_ 0004018 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58405–58416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chen, M. CircPro: An integrated tool for the identification of circRNAs with protein-coding potential. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3314–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwecka, M.; Glazar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, M.; Guarnerio, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. A circular twist on microRNA regulation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1401–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Wong, C.C.; Lee, J.M.; Fan, D.N.; Au, S.L.; Ng, I.O. Sequential alterations of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma development and venous metastasis. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lu, P.; Shi, W.; Sun, G.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. MiR-622 functions as a tumor suppressor and directly targets E2F1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.Y.; Lu, H.P.; Li, J.D.; Chen, G.; He, R.Q.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhou, X.G.; Rong, M.H.; Yang, L.H.; He, W.Y.; et al. Clinical Implication of E2F Transcription Factor 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Song, X.; Lu, Z.; et al. NCAPG2 overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through activating the STAT3 and NF-kappaB/miR-188-3p pathways. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shan, G. CircRNA in cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett. 2021, 505, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Ji, H.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; He, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, Q. CPSF3 Promotes Pre-mRNA Splicing and Prevents CircRNA Cyclization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164057
Huang Y, Ji H, Dong J, Wang X, He Z, Cheng Z, Zhu Q. CPSF3 Promotes Pre-mRNA Splicing and Prevents CircRNA Cyclization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(16):4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164057
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ying, Haofei Ji, Jiani Dong, Xueying Wang, Zhilin He, Zeneng Cheng, and Qubo Zhu. 2023. "CPSF3 Promotes Pre-mRNA Splicing and Prevents CircRNA Cyclization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 16: 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164057
APA StyleHuang, Y., Ji, H., Dong, J., Wang, X., He, Z., Cheng, Z., & Zhu, Q. (2023). CPSF3 Promotes Pre-mRNA Splicing and Prevents CircRNA Cyclization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 15(16), 4057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164057






