Predictive Roles of Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Ki-67 in Pathologic Complete Response in an Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prospective Trial
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
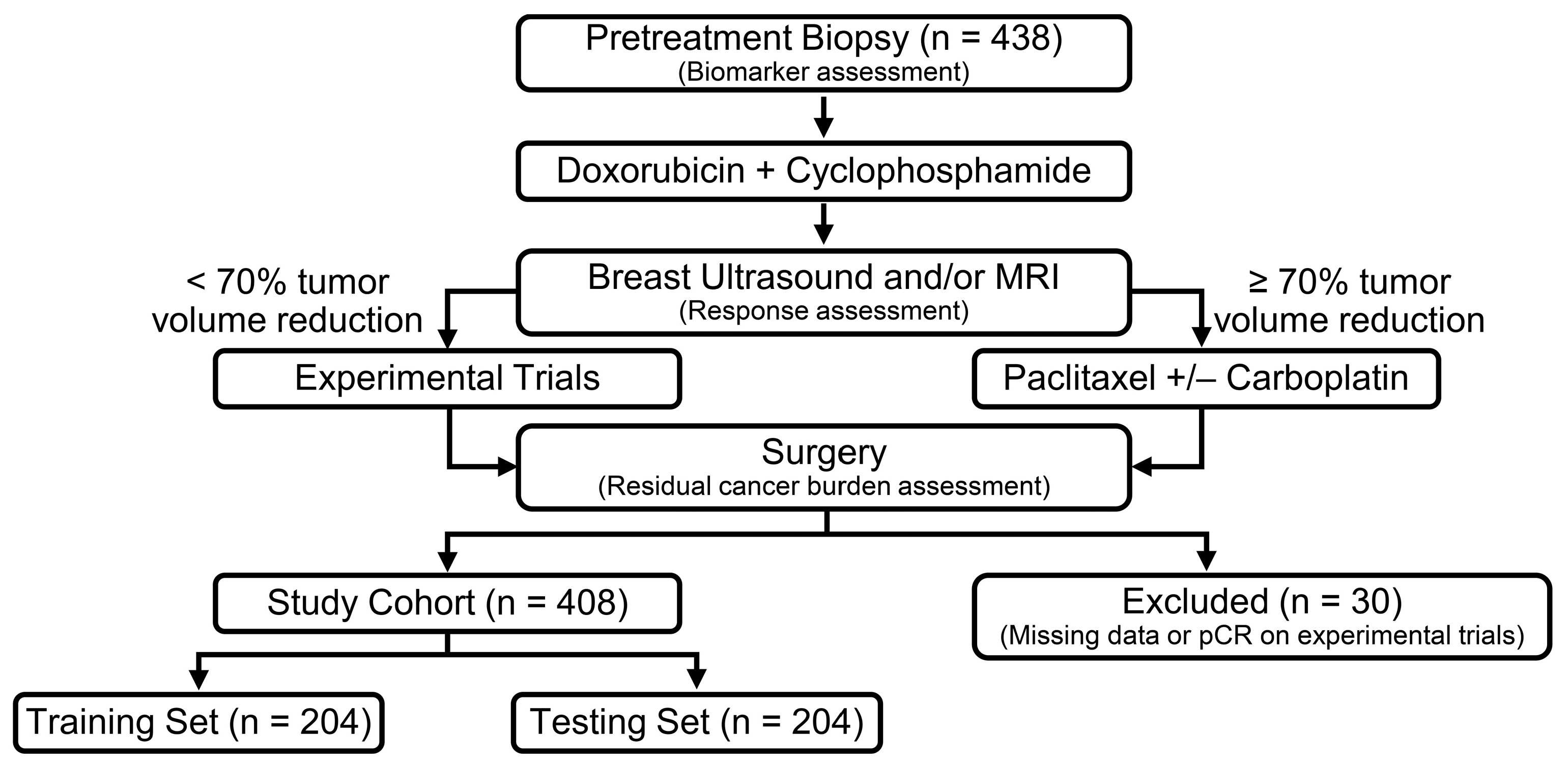
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Pathological Evaluation
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Characteristics
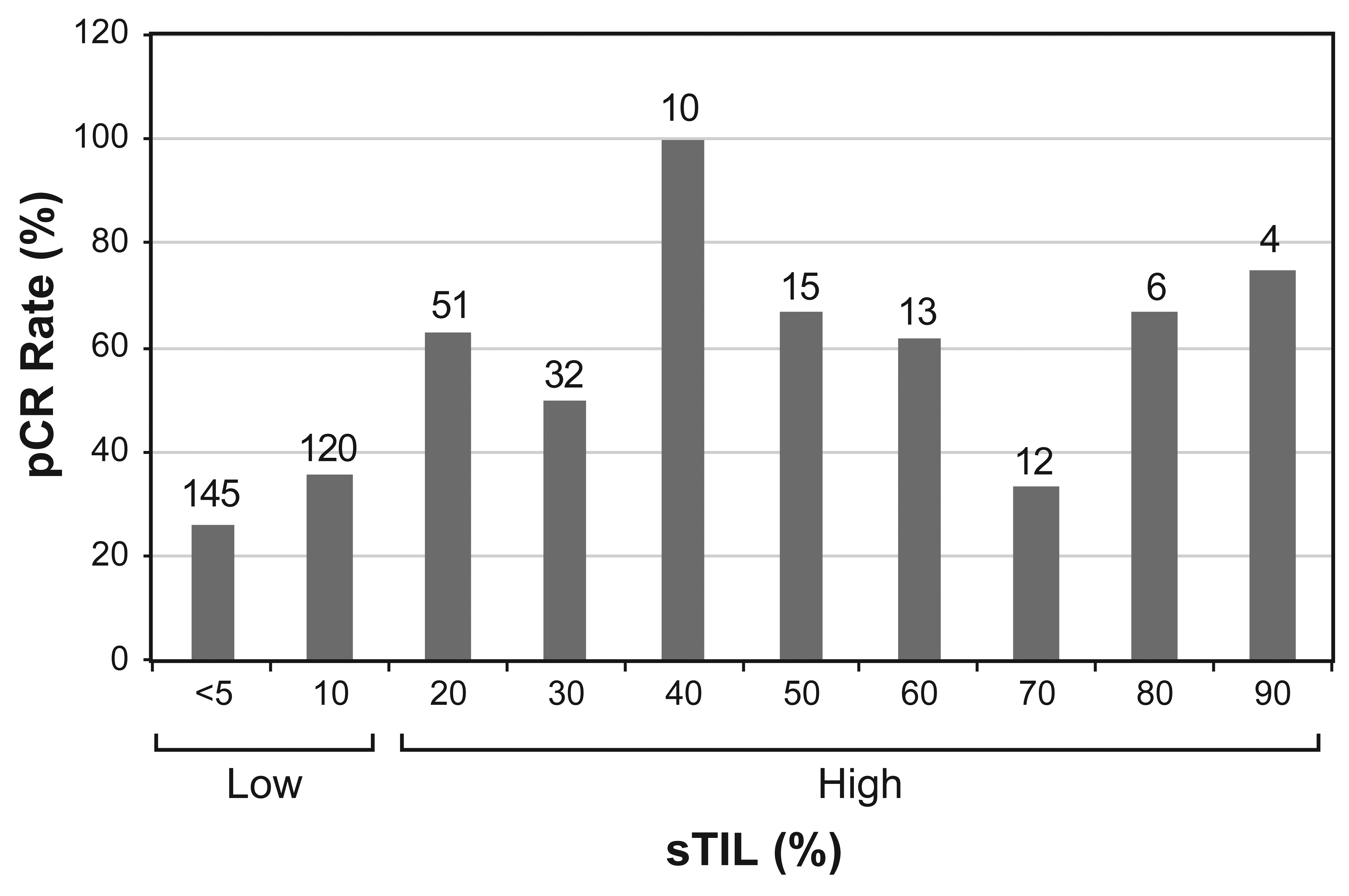
3.2. Predictors of pCR in Total, Low-sTIL and High-sTIL Patient Populations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanović, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; von Minckwitz, G.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Lederer, B.; Heppner, B.I.; Weber, K.E.; Budczies, J.; Huober, J.; Klauschen, F.; Furlanetto, J.; et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Tsuda, H.; Shimizu, C.; Yamamoto, S.; Shibata, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Hirata, T.; Yonemori, K.; Ando, M.; Tamura, K.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, S.; Salgado, R.; Gevaert, T.; Russell, P.A.; John, T.; Thapa, B.; Christie, M.; van de Vijver, K.; Estrada, M.V.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. Assessing Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Solid Tumors: A Practical Review for Pathologists and Proposal for a Standardized Method From the International Immunooncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 1: Assessing the Host Immune Response, TILs in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Ductal Carcinoma In Situ, Metastatic Tumor Deposits and Areas for Further Research. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieci, M.V.; Mathieu, M.C.; Guarneri, V.; Conte, P.; Delaloge, S.; Andre, F.; Goubar, A. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. International TILs Working Group 2014 The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Wang, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Drubay, D.; Adams, S.; Pruneri, G.; Francis, P.A.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Joensuu, H.; Dieci, M.V.; Badve, S.; Demaria, S.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis: A Pooled Individual Patient Analysis of Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieci, M.V.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Fineberg, S.; van den Eynden, G.; Ternes, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Pruneri, G.; D’Alfonso, T.M.; Demaria, S.; Castaneda, C.; et al. International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group on Breast Cancer Update on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer, including recommendations to assess TILs in residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy and in carcinoma in situ: A report of the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group on Breast Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spring, L.M.; Fell, G.; Arfe, A.; Trippa, L.; Greenup, R.; Reynolds, K.; Smith, B.L.; Moy, B.; Isakoff, S.J.; Parmigiani, G.; et al. Abstract GS2-03: Pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and impact on breast cancer recurrence and mortality, stratified by breast cancer subtypes and adjuvant chemotherapy usage: Individual patient-level meta-analyses of over 27,000 patients. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, GS2-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Kashiwagi, S.; Goto, W.; Takada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Hatano, T.; Takashima, T.; Tomita, S.; Motomura, H.; Ohsawa, M.; et al. Prediction of Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer by Subtype Using Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuhadra, N.; Sun, R.; Litton, J.K.; Rauch, G.M.; Yam, C.; Chang, J.T.; Seth, S.; Bassett, R.; Lim, B.; Thompson, A.M.; et al. Prognostic Impact of High Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Absence of Pathologic Complete Response in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Jonas, S.F.; Bataillon, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S.; Viale, G.; Lee, H.J.; Dieci, M.V.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.B.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, J.E.; Jung, K.H.; Gong, G.; Son, B.-H.; Ahn, S.-H.; Kim, S.-B. Intrinsic Prognostic Impact of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Systemically Untreated Patients With Early-stage Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Salgado, R.; Adams, S.; Pruneri, G.; Francis, P.A.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Joensuu, H.; Dieci, M.V.; Badve, S.; Demaria, S.; et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte stratification of prognostic staging of early-stage triple negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, C.; Yen, E.-Y.; Chang, J.T.; Bassett, R.L.; Alatrash, G.; Garber, H.; Huo, L.; Yang, F.; Philips, A.V.; Ding, Q.-Q.; et al. Immune Phenotype and Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5365–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Dowsett, M.; McShane, L.M.; Allison, K.H.; Allred, D.C.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology; College of American Pathologists Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of american pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Huo, L.; Koenig, K.B.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kuerer, H.M.; Bedrosian, I.; Buzdar, A.U.; Symmans, W.F.; Crow, J.R.; et al. Which threshold for ER positivity? A retrospective study based on 9639 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.H.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Dowsett, M.; McKernin, S.E.; Carey, L.A.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hayes, D.F.; Lakhani, S.R.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Estrogen and progesterone receptor testing in breast cancer: ASCO/CAP guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1346–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmans, W.F.; Wei, C.; Gould, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Walls, A.; Bousamra, A.; Ramineni, M.; Sinn, B.; et al. Long-Term Prognostic Risk After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Associated With Residual Cancer Burden and Breast Cancer Subtype. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symmans, W.F.; Peintinger, F.; Hatzis, C.; Rajan, R.; Kuerer, H.; Valero, V.; Assad, L.; Poniecka, A.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikov, W.M.; Berry, D.A.; Perou, C.M.; Singh, B.; Cirrincione, C.T.; Tolaney, S.M.; Kuzma, C.S.; Pluard, T.J.; Somlo, G.; Port, E.R.; et al. Impact of the addition of carboplatin and/or bevacizumab to neoadjuvant once-per-week paclitaxel followed by dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide on pathologic complete response rates in stage II to III triple-negative breast cancer: CALGB 40603 (Alliance). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikov, W.M.; Polley, M.-Y.; Twohy, E.; Perou, C.M.; Singh, B.; Berry, D.A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Somlo, G.; Port, E.R.; Ma, C.X.; et al. CALGB (Alliance) 40603: Long-term outcomes (LTOs) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) +/− carboplatin (Cb) and bevacizumab (Bev) in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). JCO 2019, 37, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Long-term outcomes for neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer: Meta-analysis of individual patient data from ten randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 27–39. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, I.; López-Tarruella, S.; Picornell, A.; García-Saenz, J.Á.; Jerez, Y.; Hoadley, K.; Gómez, H.L.; Moreno, F.; Monte-Millan, M.D.; Márquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Pathological Response in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cohort Treated with Neoadjuvant Carboplatin and Docetaxel According to Lehmann’s Refined Classification. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C.; Mazouni, C.; Hess, K.R.; André, F.; Tordai, A.; Mejia, J.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, C.; Piao, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, F.; Xie, X. Prognostic function of Ki-67 for pathological complete response rate of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Tumori 2014, 100, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, D.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Tian, J.; Li, L.; Xu, F.; Zhou, E.; Yang, K. The predictive value of Ki-67 before neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, N.S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Jager, A.; Kok, M.; Debets, R.; van Deurzen, C.H.M. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Predictive Markers of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Qiu, J.; Wu, J.; Zeng, H.; Su, F.; Qiu, K.; Wu, J.; Yao, H. Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and the Expression of Topoisomerase IIα in the Prediction of the Clinical Outcome of Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer after Taxane-Anthracycline-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy 2017, 62, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Vicent, C.; Guerrero, A.; Gavilá, J.; Gozalbo, F.; Hernández, A.; Sandiego, S.; Algarra, M.A.; Calatrava, A.; Guillem-Porta, V.; Ruiz-Simón, A. Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.; Tian, T.; Rao, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Yang, W.; Shui, R. Predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treated triple-negative breast cancers. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.I.; Zhang, S. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte volume is a better predictor of neoadjuvant therapy response and overall survival in triple-negative invasive breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 80, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockstal, M.R.; Noel, F.; Guiot, Y.; Duhoux, F.P.; Mazzeo, F.; Van Marcke, C.; Fellah, L.; Ledoux, B.; Berlière, M.; Galant, C. Predictive markers for pathological complete response after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 49, 151634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, N.; Nakashima, C.; Nagamine, I.; Otagaki, S. The Effect of Intratumoral Interrelation among FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells on Treatment Response and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. KEYNOTE-522 Investigators. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall | Low sTILs (<20%) | High sTILs (≥20%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total patients | 408 | 265 | 143 | NA |
| Median age at diagnosis—years (range) | 51 (23–77) | 52 (24–77) | 49 (23–77) | 0.17 |
| BMI at diagnosis—n (%) | ||||
| Low (<25) | 111 (27) | 67 (25) | 44 (31) | 0.23 |
| High ≥25 | 297 (73) | 198 (75) | 99 (69) | |
| Tumor Stage—n (%) | ||||
| T1 | 66 (16) | 37 (14) | 29 (20) | |
| T2 | 273 (67) | 168 (63) | 105 (73) | <0.001 |
| T3 | 49 (12) | 42 (16) | 7 (5) | |
| T4 | 20 (5) | 18 (7) | 2 (1) | |
| Nodal Stage—n (%) | ||||
| N0 | 246 (60) | 165 (62) | 81 (57) | |
| N1 | 98 (24) | 56 (21) | 42 (29) | 0.01 |
| N2 | 10 (2) | 3 (2) | 7 (5) | |
| N3 | 54 (13) | 41 (15) | 13 (9) | |
| Clinical TNM Stage—n (%) | ||||
| I | 41 (10) | 28 (11) | 13 (9) | |
| II | 284 (70) | 177 (67) | 107 (75) | 0.22 |
| III | 83 (20) | 60 (22) | 23 (16) | |
| Histologic Grade—n (%) | ||||
| 1 | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 | |
| 2 | 51 (12) | 43 (16) | 8 (5) | 0.002 |
| 3 | 355 (87) | 220 (83) | 135 (95) | |
| Histologic Type—n (%) | ||||
| Invasive Ductal | 342 (84) | 213 (80) | 129 (90) | |
| Invasive Lobular | 3 (1) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | |
| Metaplastic | 44 (11) | 34 (13) | 10 (7) | 0.051 |
| Other * | 19 (4) | 16 (6) | 3 (2) | |
| Ki-67—n (%) | ||||
| Low (≤35%) | 72 (18) | 58 (22) | 14 (10) | |
| High (>35%) | 336 (82) | 207 (78) | 129 (90) | 0.003 |
| Androgen Receptor Expression—n (%) | ||||
| Low (<10%) | 309 (76) | 203 (77) | 106 (74) | 0.63 |
| High (≥10%) | 99 (24) | 62 (23) | 37 (26) | |
| PD-L1 Expression (CPS)—n (%) | ||||
| Negative (0) | 144 (35) | 132 (50) | 12 (8) | <0.001 |
| Positive (>0) | 264 (65) | 133 (50) | 131 (92) | |
| Pathologic Response—n (%) | ||||
| pCR/RCB-0 | 166 (41) | 81 (31) | 85 (59) | |
| RCB I | 61 (15) | 42 (16) | 19 (13) | <0.001 |
| RCB-II | 140 (34) | 112 (42) | 28 (20) | |
| RCB-III | 41 (10) | 30 (11) | 11 (8) |
| Computed Response Score | N | No. pCR | % pCR | 95% CI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 28 | 5 | 18 | 6–37 |
| 1 | 111 | 35 | 32 | 23–41 |
| 2 | 65 | 42 | 65 | 52–76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuhadra, N.; Sun, R.; Yam, C.; Rauch, G.M.; Ding, Q.; Lim, B.; Thompson, A.M.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Adrada, B.E.; Damodaran, S.; et al. Predictive Roles of Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Ki-67 in Pathologic Complete Response in an Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prospective Trial. Cancers 2023, 15, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133275
Abuhadra N, Sun R, Yam C, Rauch GM, Ding Q, Lim B, Thompson AM, Mittendorf EA, Adrada BE, Damodaran S, et al. Predictive Roles of Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Ki-67 in Pathologic Complete Response in an Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prospective Trial. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133275
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuhadra, Nour, Ryan Sun, Clinton Yam, Gaiane M. Rauch, Qingqing Ding, Bora Lim, Alastair M. Thompson, Elizabeth A. Mittendorf, Beatriz E. Adrada, Senthil Damodaran, and et al. 2023. "Predictive Roles of Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Ki-67 in Pathologic Complete Response in an Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prospective Trial" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133275
APA StyleAbuhadra, N., Sun, R., Yam, C., Rauch, G. M., Ding, Q., Lim, B., Thompson, A. M., Mittendorf, E. A., Adrada, B. E., Damodaran, S., Virani, K., White, J., Ravenberg, E., Sun, J., Choi, J., Candelaria, R., Arun, B., Ueno, N. T., Santiago, L., ... Huo, L. (2023). Predictive Roles of Baseline Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Ki-67 in Pathologic Complete Response in an Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prospective Trial. Cancers, 15(13), 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133275







