Simple Summary
Interventional oncology provides minimally invasive alternatives to many traditional medical and surgical treatments, offering a potential cure, control, or palliative care for many types of cancer patients. The aim of this article is to comprehensively review new indications for locoregional interventional oncology treatments and summarize the expert discussion and report from the “MIOLive Meets SIO” (Society of Interventional Oncology) session during the last Mediterranean Interventional Oncology Live congress held in Rome, Italy.
Abstract
Interventional oncology (IO) employs image-guided techniques to perform minimally invasive procedures, providing lower-risk alternatives to many traditional medical and surgical therapies for cancer patients. Since its advent, due to rapidly evolving research development, its role has expanded to encompass the diagnosis and treatment of diseases across multiple body systems. In detail, interventional oncology is expanding its role across a wide spectrum of disease sites, offering a potential cure, control, or palliative care for many types of cancer patients. Due to its widespread use, a comprehensive review of the new indications for locoregional procedures is mandatory. This article summarizes the expert discussion and report from the “MIOLive Meet SIO” (Society of Interventional Oncology) session during the last MIOLive 2022 (Mediterranean Interventional Oncology Live) congress held in Rome, Italy, integrating evidence-reported literature and experience-based perceptions. The aim of this paper is to provide an updated review of the new techniques and devices available for innovative indications not only to residents and fellows but also to colleagues approaching locoregional treatments.
1. Introduction
Interventional oncology (IO) employs image-guided techniques to perform minimally invasive procedures, providing lower-risk alternatives to many traditional medical and surgical therapies in cancer patients. Since its advent, due to rapidly evolving research development, its role has expanded to encompass the diagnosis and treatment of diseases across multiple body systems. In detail, IO is expanding its role across a wide spectrum of disease sites, offering a potential cure, control, or palliative care for many types of cancer patients. Due to its widespread use, a comprehensive review of the new indications for locoregional procedures is mandatory [1]. This article summarizes the expert discussion and report from the MIOLive meets SIO (Society of Interventional Oncology) session during the last MIOLive 2022 (Mediterranean Interventional Oncology Live) congress held in Rome, Italy, integrating evidence-reported literature and experience-based perceptions. The aim of our paper is to integrate evidence-reported literature and experience-based perceptions while attempting to make the information easy to access in order to assist not only residents and fellows who are training in interventional radiology but also practicing colleagues who are attempting to gain further expertise with this locoregional procedures and to also highlight recent data and strategies to treat disease states not yet routine in IO practice.
2. Spine, Skull, and Skull Base Tumors
IO is one of the fastest growing clinical specialties for the treatment of skull and skull base tumors. CT and MRI are the preferred techniques to guide percutaneous interventions in these locations [2]. Representing a complex location, ablative procedures cannot be considered a “definitive” therapy yet. It is important to focus on the clinical picture of every single patient to choose the best therapy line in a multidisciplinary way.
2.1. Spinal Tumors
Spinal tumors represent one of the main targets of ablative procedures, particularly osteoid osteoma, osteoblastoma, and chondroblastoma as well as spine metastases. Technical progress in interventional radiology made the treatment of previously untreatable spinal tumors possible, such as those located in the body of cervical vertebrae. Among interventional radiology treatments in this district, radiofrequency ablation can be used to obtain local tumor control and pain relief alone or in combination with vertebroplasty procedures with good tumor control and low complication rates [3].
Cryoablation represents another safe and effective therapeutic technique [4]. A cryo-probe is positioned in the lesion whereas a thermocouple is placed in the posterior wall of the vertebral soma. It is important to remember that the freezing process continues for about 1 min after the cryo-probe is switched off; therefore, this process must be taken into account when calculating ablation times.
Thirty-minute neurophysiological monitoring, performed by placing electrodes in various districts of the body, can be helpful to monitor motor and sensitive systems, safely perform percutaneous ablations, and promptly stop the procedure if something is wrong. General anesthesia should be obtained before percutaneous ablation of these districts. When needed, hydrodissection is performed soon before ablation.
2.2. Desmoid Tumors
Cryoablation of large symptomatic cervical desmoid tumors that do not respond to first- and second-line medical treatment can be performed with multiple cryo-probes [5]. About 65% of desmoid tumors treated with cryoablation obtain good results.
2.3. Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Tumors
ENT tumors can be represented by various histological entities (i.e., squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, muco-epidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and esthesioneuroblastoma). Cryoablation of these tumors is usually performed as a last-line treatment after surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy in patients with no other treatment options [6]. The advantage of cryoablation is represented by the possibility of good ablation margins for better local disease control. Complications of cryoablation in these tumors can be represented by inhalation pneumopathy and dysphonia (due to injury of the recurrent nerve) in the case of nearby neoplasms.
2.4. Intrasinusal Frontal Hemangioma
Hemangiomas located in the frontal sinus can be painful [7]. CT-guided cryoablation can be performed in these tumors when surgery is not feasible. However, a combined approach in association with a surgical team can be performed: Surgical endoscopic checks and guidance for correct positioning of the cryo-probes can be helpful. In the case of aggressive hemangiomas, it is mandatory to perform cryoablation to preserve skin tissues as well as the frontal cerebral lobe. Adjacent soft tissue edema can occur in the early postprocedural setting, which is usually self-limiting. MRI is the best technique in guiding cryoablation in the case of soft tissue tumors, as it can better show the lesion, probe as well as ice ball.
2.5. Palatine Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Cryoablation of deep nasopharyngeal tumors, such as posterior palatine ones, is challenging due to the difficult location of the lesion and complex cryo-probe(s) positioning. The lips and tongue must be immobilized, granting full access to the tumor. Cryoablation can be considered in the case of tumors that are not suitable for surgical resection.
2.6. Glioblastoma
Recurrent glioblastoma can be also treated with cryoablation [8]. The association of cryoablation and systemic therapies (chemotherapy or immunotherapy) or radiation therapy leads to better survival rates than those techniques alone. Cryoablation determines tumor necrosis while increasing the immune response, which can be useful for combined treatments. To reduce cerebral edema, necrotic postablative tumor tissue could be surgically removed.
3. Deep Spaces of the Neck
The literature on this topic is scarce with limited case series. Treatment planning is crucial, as the correct approach to tumors in this area is mandatory to achieve good and safe results. The main indication for ablation of neck lesions is a localized disease without any other local treatment options (e.g., unfeasible or exhausted surgery and/or radiotherapy) and only undergoing systemic therapy [9]. While ablation may have a limited impact on survival, it can have a positive impact on the quality of life through local tumor control, leading to pain relief, reduction of mass effect as well as delay in the usage of feeding tubes (i.e., percutaneous gastrostomy or jejunostomy) and/or tracheostomy due to tumor obstruction [10,11]. Of note, a complete ablation margin may not always be feasible due to the lesion’s dimension and location next to critical structures [12]. Approaches to lesions in deep spaces of the neck are retromaxillary, retromolar trigone, transglandular, and transmuscular flap. With those approaches, up to 95% of lesions can be reached and treated percutaneously (as opposed to transorally). Ablative treatments and cryoablation in particular can potentially fill a treatment gap in recurrent or nonsurgical head and neck tumors. It is technically feasible, but more data are required to clearly determine the case selection and outcome matrix.
- Retromaxillary: In the case of a retromaxillary approach, the maxilla is used as a landmark. This approach is mostly used for lesions located in the masticatory space and the pharyngeal and laryngeal mucosa (Figure 1).
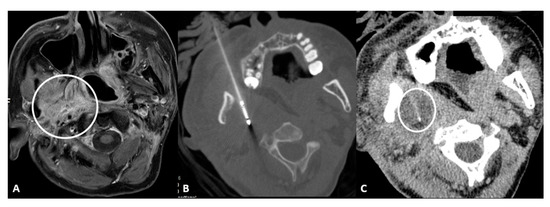
Figure 1.
56-year-old male with neuropathic pain due to right oropharyngeal squamocellular carcinoma recurrence after tracheostomy, neck lymph node dissection, mandibulotomy, right oropharyngeal resection with free anterolateral thigh flap. (A) T1-weighted postcontrast axial MRI scan showing malignant involvement of trigeminal nerve (circle). (B) Axial CT scan showing cryoablation needle placement. (C) Intraprocedural axial CT scan showing ice ball formation around the needle (circle).
- Retromolar trigone: This is the space between the last molar and the mandibular condyle. It is a space without many vessels/nerves or vital structures; therefore, it represents a safe approach to treating pharyngeal and laryngeal lesions. Tongue positioning is mandatory, as it can flop backward against the ablation site resulting in frost injury: Forceps and a laryngoscope should be used to displace the tongue with gauze away from the ablation site to avoid this occurrence. In the case of tumors near the carotid artery, the patient can manifest severe hypotension and bradycardia during ablation. The presence of coils or metallic devices in a previously embolized carotid artery leads both to a loss of the cold-sink effect as well as a stimulation of the vagus nerve with thermal conduction down the carotid body (leading to the diving reflex). Cessation of cryoablation usually leads to spontaneous resolution (Figure 2).
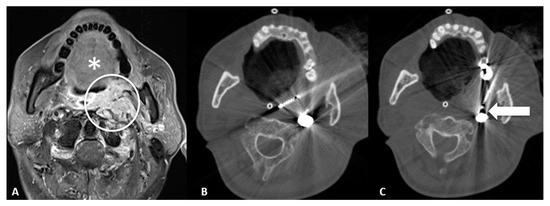
Figure 2.
65-year-old male with trismus, gagging, airway compromise, and bleeding episodes due to recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma of the left retropharyngeal/paravertebral space with circumferential carotid artery involvement, after previous radiation therapy and left neck dissection. (A) T1-weighted postcontrast axial MRI scan showing malignant involvement of the left retropharyngeal space (circle). Notice the tongue (*) which can flop backward during the general anesthesia and could contact the ablation site; care must be taken in blocking the tongue prior to ablation. (B) Axial CT scan showing cryoablation needle placement through the retromolar trigone. (C) Axial CT scan showing the cryoablation needle near the previously embolized left carotid artery (arrow), which can lead to diving reflex.
- Transglandular: This is a very useful approach in case of lesions in the pharyngeal space and prevertebral space, crossing the submandibular gland to reach these locations (Figure 3).
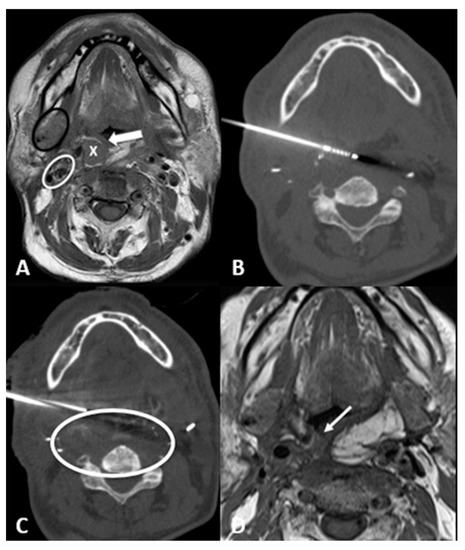
Figure 3.
63-year-old male with recurrence of supraglottic squamocellular carcinoma which underwent previous total pharyngolaryngectomy and bilateral neck dissection. (A) T1-weighted unenhanced axial MRI scan showing the tumor recurrence (X), the mucosa of the neopharynx (arrow), the right submandibular gland (black circle), and the right carotid space (white circle). (B) Axial CT scan showing the cryoprobe positioned in the lesion through a trans-submandibular gland approach. (C) Axial CT scan showing parallel needle placement for hydrodissection of peritumoral tissue. (D) One-month T1-weighted unenhanced axial MRI scan showing the postablation tumor shrinkage (arrow).
- Transflap: Useful in the case of early local tumor recurrence, in patients who underwent previous surgery, and myocutaneous flap reconstruction (Figure 4). The myocutaneous flap is usually devoid of significant vascularity and vital structures and presents a safe trajectory once it has been grafted [13].
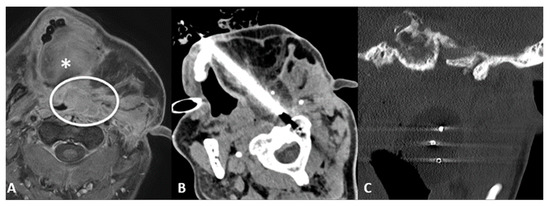
Figure 4.
70-year-old male with airway impairment and left postauricular discharge. Previous nasopharyngeal carcinoma and radiation-induced squamous cell carcinoma of maxilla which underwent maxillectomy, mandibulectomy, parotidectomy, and myocutaneous flap reconstruction. (A) T1-weighted postcontrast axial MRI scan showing extensive tumor recurrence (white circle), posterior to the tongue (*), threatening the airways and invading the left external auditory canal. (B) Axial CT scan showing cryoablation needle placement through the myocutaneous flap. (C) Coronal-oblique multiplanar reconstruction CT scan showing the ice ball formed by the three cryoprobes.
4. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer (BC) is a common malignancy with the second mortality rate in women worldwide; in China, the 5-year survival rate of patients affected by BC is about 83% while in occidental countries, it can be up to 90% [14,15].
Surgical techniques (mastectomy) are usually associated with psychological disorders in about 70% of patients [16,17]. In the 1990s, breast-conserving operations were recommended, but the recurrence rate was up to 21.6%.
4.1. Locoregional Approaches
Common ablation techniques include cryoablation, laser, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and microwave ablation (MWA) [18]. Ablation techniques are minimally invasive and do not leave any scars; the ablated lesions gradually shrink, becoming impalpable [19]. Ablation procedures can be repeated for new lesions so that it is possible to protect breast tissue to the largest extent. Ablations have a very low complication rate. Compared to other ablation modalities, MWA has the highest technical efficacy rates (90–95%) [20]. When compared to breast-conserving surgery, MWA obtained better results in edema drainage, operation time, estimated blood loss, and, especially, cosmetic results [21].
Target lesions should be smaller than 2 cm in size and located apart from the nipple (Figure 5) [22,23,24]. Histological examination should be negative for sentinel lymph nodes with no pathological axillary lymph nodes at imaging.
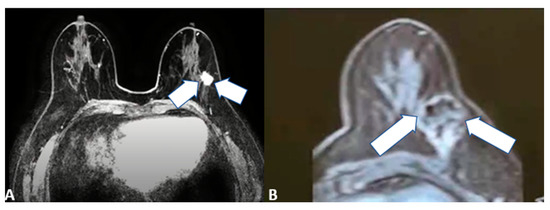
Figure 5.
64-year-old female patient with left invasive T1 breast cancer of 11 mm with a molecular subtype Luminal-A. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scan showing (A) baseline neoplastic lesion and (B) 5-month follow-up after microwave ablation with good ablation margins and central necrosis.
Ablative treatments can also represent a palliative ablation for larger lesions (Figure 6) as well as an alternative therapy for those patients who are not suitable for surgery or refuse resection and/or other treatment modalities (such as chemotherapy) for cosmetic reasons [25,26].
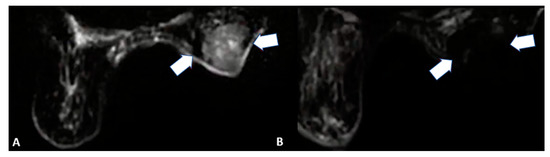
Figure 6.
85-year-old female patient with invasive right breast cancer with axillary metastases. Diffusion-weighted imaging MRI scan showing (A) baseline large neoplastic lesion infiltrating the skin and soft tissues (arrows) and (B) 4-month follow-up after microwave ablation with absent signal restriction (arrows).
Contraindications of ablative techniques are severe dysfunction of blood coagulation, pregnancy, or breastfeeding and severe cardiac or pulmonary impairment [27]. Before ablation, a detailed ultrasound (US) scan should be executed to measure lesion size and location, to study lesion margins, blood supply, and adjacency, and to schedule the ablation protocol: puncture route, ablation power and time, and anesthesia method. A US-guided 16 G needle biopsy needs to be executed prior to ablation to confirm the pathological diagnosis and perform immuno-histochemical examinations.
4.2. Key Points
If needed, hydrodissection can be performed by injecting saline solution between the tumor and the adjacent tissue using a 20/22 G needle to prevent thermal damage to nontarget structures (Figure 7) [24]. Different tumor histology needs different needle ablation power. For deeper tumors, 30–50 W of ablative power is recommended whereas for superficial ones, 20 W is the right ablation power due to the greater injury risk to the skin and soft tissues. Ablative approaches should be performed with a pullback technique to cover the tumor area [24].
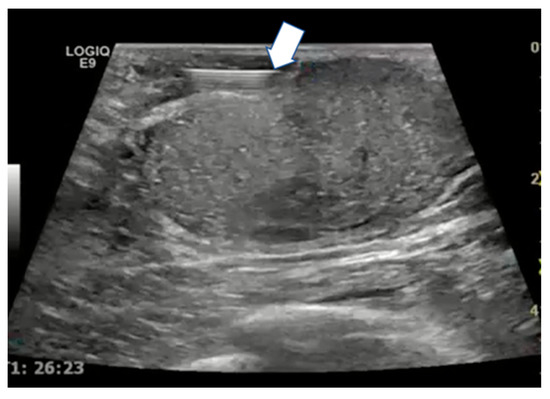
Figure 7.
Ultrasound scan with linear probe showing the tip of the needle used for hydrodissection (arrow) to inject saline between the tumor and the skin or ductal structures.
5. Intrahepatic Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Cholangiocellular carcinoma (CCA) is the second most common hepatic malignancy with an increasing incidence worldwide and poor prognosis: The overall survival is about 3 months, and the 5-year survival is less than 10% [28]. To date, the only curative treatment is surgical resection; however, less than 30% of patients are suitable for surgery [29]. Even with negative surgical margins, recurrence rates are very high (85% intrahepatic CCA—14% extrahepatic CCA) [30]. The median overall survival after resection is 18–33 months even with negative margins [31]. The CCA is very therapeutic resistant due to its marked genetic heterogeneity and complex tumor microenvironment [32].
5.1. Locoregional Approaches
The aim of locoregional therapies in intrahepatic CCA is to achieve oncological benefits, prevent tumor progression and its complication, improve overall survival, and represent a bridge to surgical resection or transplant [33]. Local ablative therapies are intended to eradicate all viable malignant cells within the designated target volume, sparing the normal surrounding tissues. These procedures can be repeatable and can also be done in an outpatient setting. Locoregional therapies also have an important role in the treatment of bleeding and pain management. At present, there are no formal guidelines for locoregional therapies in CCA management and unclear and limited literature evidence [34,35,36].
Standard indications for CCA ablation include ineligibility for surgery, small tumor size (up to 3 cm), and no extrahepatic spread. Lesion size is the most relevant factor to achieve complete ablation and reduced local recurrence rates or local tumor progression [33,37,38,39,40,41,42].
RFA is the most diffused locoregional treatment technique whereas MWA has some theoretical advantages (i.e., is less dependent on tissue’s electrical conductivity, is less influenced by the “heat-sink” effect, obtains higher intratumoral temperatures, reduced ablation time, and larger ablation zone) [43,44,45,46,47,48].
Many factors affect locoregional treatment outcomes: Intrahepatic CCA is a noncapsulated and tissue-infiltrating malignancy; therefore, a minimum of 10 mm of safety margin should be obtained to reduce the risk of local recurrence [49]. In addition, lymph node positivity and the superficial location of the tumor influence the results of the procedure. Due to the advanced stage of the diagnosis, most patients are not suitable for ablation; therefore, data on intrahepatic CCA ablation therapy are limited. In 2015, a review of seven observational studies on the ablation of primary and unresectable intrahepatic CCA was published: The overall survival ranged from 20 to 60 months, and treatment success depended on tumor size [41]. Three studies showed higher rates of residual neoplastic tissue when the tumor size was greater than 4.6 cm [50,51,52]. Another study showed a mean 5-year survival rate of 24% and a local tumor progression rate of 21% [53]. In conclusion, ablation prolongs survival rates in patients ineligible for surgery; furthermore, it is linked to lower complications, costs, and shorter hospital stays. A recent study comparing repeated resection versus thermal ablation in the treatment of tumor recurrence after the first resection showed that there were no differences in overall survival and disease-free survival rates [54]. Significant prognostic factors for overall survival included a solitary recurrent tumor and recurrent interval from the initial resection greater than 1 year. Major complications were more common in patients treated with repeated resections; therefore, it has been concluded that thermal ablation should be preferred over repeated resection in patients with intrahepatic recurrence smaller than 3 cm in size [54].
To date, transarterial therapies for intrahepatic CCA are indicated in cases of high tumor burden, in neoadjuvant settings, and when the position of the tumor is difficult/dangerous [55,56]. In a prospective trial with 115 patients who underwent conventional transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with different combinations of mitomycin, gemcitabine, and cisplatin, the median overall survival was 13 months from the initial TACE without any statistical differences between the regimens; in conclusion, TACE is a safe and palliative option in patients with the unresectable disease [57].
Child-Pugh B, hypovascular, and initially progressive disease are poor prognostic factors for patient survival [58,59,60]. Regarding TACE, a prospective trial with nine patients who underwent 30 TACE procedures combined with chemotherapy versus 11 patients treated with chemotherapy alone demonstrated that the overall survival was significantly better in the first group [61]. TACE plus chemotherapy appears to be safe and feasible with encouraging results.
Regarding transarterial radioembolization (TARE), a retrospective study of 19 chemorefractory patients who underwent TARE has shown that the median survival from diagnosis after the first TARE is about 11.5 months [62]. One more study considered 40 patients undergoing TACE versus TARE in order to understand which treatment to choose in patients with unresectable disease: 25 patients underwent TARE (39 treatments) and 15 underwent TACE (35 treatments) with similar demographics characteristics [63]. The results were similar in terms of overall response rate (TARE 4%, TACE 6%; p-value > 0.9), local control rate (TARE 48%, TACE 46%; p-value > 0.9), and adverse events (TARE 26%, TACE 20%; p-value > 0.9). Recently, a systematic review and meta-analysis were performed to compare TACE and TARE effects for intrahepatic CCA: The primary endpoint was overall survival, and the second endpoint was the clinical adverse effect and tumor overall response [64]. A total of 31 articles were included (1695 patients): 13 were on TACE and 18 were on TARE. Despite clinical and tumor characteristics heterogeneity, the results showed similar median survival and radiological objective response even though TARE showed a better adverse event profile (43% versus 58.5%). The decision on which modality to choose should be based on the experience of the operator and patient-specific factors, such as the liver functionality and lesion dimension (Figure 8) [65].
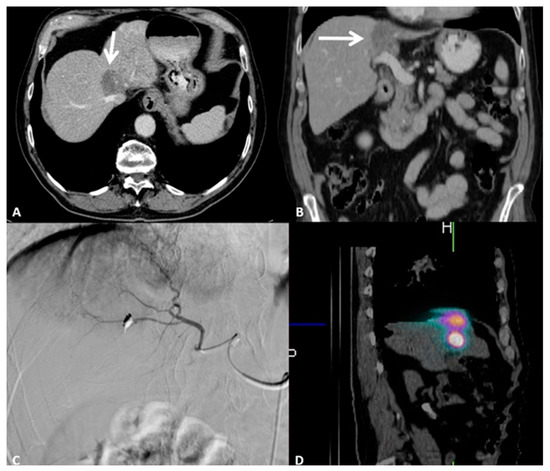
Figure 8.
79-year-old male patient presenting with pain in the right upper abdominal quadrant due to intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma. Performance Status One, no surgical indication; the patient underwent eight cycles of chemotherapy. (A) Contrast-enhanced axial CT scan showing a 3.5 cm lesion of the I-IV segment adjacent to the inferior vena cava and to the right hepatic vein. (B) Contrast-enhanced coronal CT scan showing how the lesion is adjacent to the portal vein. (C) Digital subtraction angiography runs showing super selective catheterization of the target vessel with intra-arterial administration of marked albumin macroaggregates, which serve as the diagnostic phase of radioembolization. (D) Single-photon emission computed tomography oblique reconstruction scan showing focal and selective uptake of marked albumin macroaggregates by the target lesion, confirming the catheter position for the therapeutic radioembolization.
Individualized dosimetry is mandatory for treatment planning and response prediction in CCA patients undergoing TARE. For a precise evaluation of the activity distribution and dose delivery, dose-response and toxicity investigations, and the therapeutic treatment of extrahepatic deposits, verification imaging studies after TARE are crucial. The majority of research on the use of SIRT in CCA makes use of treatment planning that delivers a mean absorbed dose of 120 Gy to the tumor and a threshold dose of no more than 50–70 Gy to the surrounding healthy liver parenchyma [66]. Various studies have shown sizable disparities between dosimetry verification studies performed after yttrium-90 TARE and the pretreatment predictive planning marked albumin macroaggregates: These differences may result from variations in the flow dynamics, catheter position, and particle size, weight, and density [67,68,69].
5.2. Key Points
Locoregional therapies are safe and effective in the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic CCA; these procedures offer a valid alternative for those patients who are ineligible for surgery and provide local tumor control in patients with recurrence after resection. Locoregional therapies obtain better results in the case of single and small (<3 cm) lesions. To date, there is no significant difference between RFA, MWA, TACE, and TARE in therapeutic efficacy; however, data are still limited, and further research is needed.
6. Lymphatics and Lymph Node Metastases
The major function of the lymphatic system is to allow the return of plasma proteins from extracellular space into the lumen of capillaries through the wall of endothelial cells [70]. Unfortunately, this pathway represents an easy way for tumors to spread into the organism [71].
The most important component of the lymph node is the stroma, formed by the cortex and the medulla. The cortex can be divided into the outer cortex (containing B-cells) and the paracortex (containing T-cells). The medulla consists of B-cells and macrophages. The lymph node produces new B- and T- cells [72,73].
Locoregional Approaches
The standard imaging method for the lymphatic system was represented by pedal lymphangiography; however, this procedure is technically challenging and requires the infusion of oily contrast medium over a period of hours [74]. In 1967, Hall and Krementz proposed intranodal lymphangiography (INL), but this procedure was not generalized until 2011 when Nadolski and Itkin demonstrated the feasibility of US-guided INL [75,76].
The main role of INL is the detection of lymphatic leaks (75% of lymphangiographies with a median fluoroscopy time of 60 min); however, it was soon clear that this technique could be often therapeutic, especially for the treatment of chylous effusions, due to the viscosity of Lipiodol [77,78]. A low effusion volume (<200 mL/day) predicts 97% success, and <500 mL/day predicts 70% success; generally, <1000 mL/day of volume effusion is a good predictor of clinical success. In the last five years, the importance of this procedure in relation to complications after pelvic or retroperitoneal surgery, such as lymphoceles (Figure 9), has been growing [79,80].
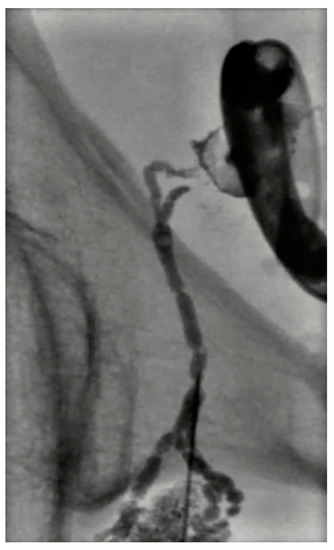
Figure 9.
Digital subtraction lymphangiography of a 54-year-old male with lymphocele after prostatectomy. A percutaneous drainage catheter was placed in the lymphocele; then a right obturatory lymphangiography and lymphatic embolization with cyanoacrylate were performed. The percutaneous drainage catheter was removed 2 days later.
Lymph node metastases are very important factors associated with cancer mortality; more specifically, the involvement of lymph nodes represents a predictor of poor prognosis. Current healing strategies for lymph node metastases are represented by chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and lymphadenectomy, but they are burdened by invasiveness, lack of selectivity, and, in the case of chemotherapy, limited access to lymph nodes. For these reasons, there is increased interest in intranodal therapies. The percutaneous administration of immunotherapy or chemotherapy in tumor-draining lymph nodes (regional lymph nodes are typically accessible under US guidance) has shown to be a promising technique [81,82,83,84].
On the other hand, in addition to the abovementioned therapeutic strategies, in recent years, some centers have begun to perform different ablative techniques targeting lymph node metastases. Ding et al. performed a metanalysis to assess the effectiveness and feasibility of thermal ablation, including RFA, MWA, and laser ablation (LA), for lymph node metastases from papillary thyroid carcinoma with interesting results: The total complication rate was 5% with 0% major complications. LA showed a lower complete disappearance rate than RFA whereas there were no significant differences between RFA and MWA in subgroup analysis [85]. Tao Pan et al. evaluated 6-month and 1-year overall survival rates in patients who underwent percutaneous CT-guided RFA of lymph node metastases from HCC, obtaining a 6-month and 1-year overall survival of 87.0% and 62.4%, respectively. Short-term stomach discomfort and a self-limited local hematoma were the only RFA side effects that occurred in a few patients [86]. These studies encourage the use of percutaneous ablation techniques on lymph node metastases, but the relative lack of data does not allow these methods to be introduced into routine clinical practice.
7. Bone Metastases
Ablation of bone metastases is indicated for pain palliation, local disease control, and fracture prevention. In case of palliation, it is recommended to consolidate osteolytic metastases with cement or through the use of screws. In the last few years, different studies have registered a growing use of ablation for oligometastatic diseases to the bone, in particular, for radiation-resistant lesions [87,88,89].
7.1. Locoregional Approaches
There are three principal indications to treat bone metastasis: moderate-severe pain (>4/10 on the VAS scale) focally localized, easily achievable lesion location, and prevention of complications (i.e., fractures). Up to 3–5 lesions can be treated in a single ablation session [90]. It is not possible to treat spine lesions associated with acute cord compression, widespread metastases, and lesions with active infection [91]. Lesions close to vital structures (arteries and nervous plexuses) should be treated carefully.
Bone metastases are often large lesions situated in weight-bearing locations (spine and pelvic bones). Moreover, bone metastases are frequently localized in areas that had previously undergone radiotherapy, so the bone structure is very unstable and at risk of fractures [92,93].
Cryoablation is the preferred ablative technique in the case of lesions involving the anterior part of the vertebral body whereas RFA is mostly performed in case of posteriorly located metastases [94,95].
Cementoplasty is often performed along the ablation to augment the effects and prevent fractures (Figure 10). It is important to keep in mind the risks of cementoplasty, such as the embolization of cementing material, perineural leak, or intra-articular extension. Consolidation with cement is not always required, as in non-weight-bearing lesions and sclerotic ones [96].
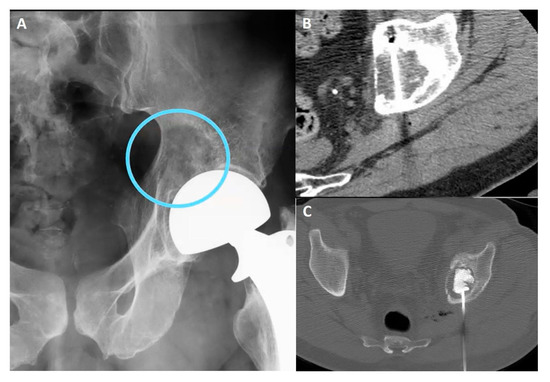
Figure 10.
(A) Pelvic X-ray showing osteolytic lesion of left periacetabular region (circle). (B) Axial CT scan showing cryoablation needle inserted in the osteolytic lesion. (C) Axial CT scan showing postcryoablation cementoplasty performed to augment the ablative results and to prevent bone fractures.
Spine lesions are often burdened by vertebral body collapse; therefore, to decide when cementoplasty is required or not, it is useful to consider the spine instability neoplastic score (SINS), which is based on various characteristics of vertebral metastases (e.g., location, pain, type of bone lesion (lytic, blastic, both)): a score higher than 7 points warrants surgical consultation to assess for instability prior to proceed with any ablative treatment [97].
In addition to cementoplasty, in locations where it is difficult to inject the cementing material, very good consolidation has been obtained using screws [98].
7.2. Key Points
The most important result of bone metastases treatment is pain reduction. Several studies have shown pain relief in 75–100% of patients with a pain score relief of approximately 5 points. The rate of complication was reasonably low [99,100]. The most common reported complication is postprocedural pain, typically for the initial 24-h in 70% of RFA, and it is generally managed with therapeutic lines, including nonopioids, opioid drugs, and steroids [101]. Another important treatment result is local tumor control: This is achieved in 85–95% of patients after the procedure both in the case of cryoablation and RFA [102,103]. Different studies have demonstrated the increasingly important role of local bone ablation, especially in the case of oligometastatic disease from renal cell carcinoma [104].
8. Conclusions
Interventional oncology is playing a pivotal emerging role in the management of many types of cancer patients. Treatments need to be both effective and safe with a mandatory aim to reduce the risk of complications, offering new potential treatment options with curative or palliative aims. Factors that contribute to this aim include an adequate multidisciplinary approach, correct indication, accurate treatment planning, and comprehensive knowledge of recent technological developments as well as clinical factors affecting treatment efficacy [105].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.I., A.G. (Afshin Gangi) and D.C.M.; methodology, R.I.; resources and data curation, R.I., A.G. (Afshin Gangi), U.P., P.L., E.S., A.N.K., D.F., S.N.G., M.M., A.K. and D.C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T., L.T. and D.D.L.; writing—review and editing, R.I., A.P., U.P., P.L., E.S., A.N.K., D.F., S.N.G., M.M., A.K. and D.C.M.; supervision, F.G., V.V., A.G., R.M. and C.C.; project administration, R.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Helmberger, T. The evolution of interventional oncology in the 21st century. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilseck, Z.M.; Lin, L.; Gemmete, J.J.; Pandey, A.S.; Srinivasan, A.; Chaudhary, N. Skull Base Neurointerventional Techniques. Neuroimaging Clin. 2021, 31, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagoo, N.S.; Haider, A.S.; Chen, A.L.; Vannabouathong, C.; Larsen, K.; Sharma, R.; Palmisciano, P.; Alamer, O.B.; Igbinigie, M.; Wells, D.B.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for spinal osteoid osteoma: A systematic review of safety and treatment outcomes. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 41, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Cazzato, R.L.; Gilkison, A.; Caudrelier, J.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous Treatments of Benign Bone Tumors. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 35, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auloge, P.; Garnon, J.; Robinson, J.M.; Thenint, M.A.; Koch, G.; Caudrelier, J.; Weiss, J.; Cazzato, R.L.; Kurtz, J.E.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous cryoablation for advanced and refractory extra-abdominal desmoid tumors. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, D.; Genden, E.; Posner, M.; Hashibe, M.; Boffetta, P. Head and neck cancer prevention: From primary prevention to impact of clinicians on reducing burden. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harar, R.P.; Wolfe, K.Q.; Kumar, S.; Gatland, D.J. Haemangioma of the frontal sinus. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2002, 116, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, A.; Cebula, H.; Cazzato, R.L.; Ramamurthy, N.; Garnon, J.; Debry, C.; Proust, F. “Keeping a Cool Head”: Percutaneous Imaging-Guided Cryo-ablation as Salvage Therapy for Recurrent Glioblastoma and Head and Neck Tumours. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, A.L.; Gold, M.M.; Miller, T.S.; Gold, T.; Owen, R.P.; Sanchez, L.S.; Farinhas, J.M.; Shifteh, K.; Bello, J.A. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation in the palliative treatment of recurrent advanced head and neck malignancies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokkappan, K.; Lim, M.Y.; Loke, S.C.; Karandikar, A.; Pua, U. Salvage Cryoablation of Recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinoma for Impending Airway Obstruction with Abscopal Effect. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1939–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenette, J.P.; Tuncali, K.; Himes, N.; Shyn, P.B.; Lee, T.C. Percutaneous Image-Guided Cryoablation of Head and Neck Tumors for Local Control, Preservation of Functional Status, and Pain Relief. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.B.; Kim, T.Y.; Shong, Y.K.; Hong, S.J. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation for treating locoregional recurrence from papillary thyroid cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, L.H.H.; Lim, M.Y.; Cheo, T.; Teo, H.L.; Pua, U. Percutaneous Management of Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer: Current Role and Evolving Principles in the Multidisciplinary Setting. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, J.; Wei, W. Global patterns of breast cancer incidence and mortality: A population-based cancer registry data analysis from 2000 to 2020. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelace, D.L.; McDaniel, L.R.; Golden, D. Long-Term Effects of Breast Cancer Surgery, Treatment, and Survivor Care. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2019, 64, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.K.; Kon, P.S.; Oberg, K.C.; Miles, D.A. Aesthetic outcomes in patients undergoing breast conservation therapy for the treatment of localized breast cancer. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Liang, P. Review of clinical tumor ablation advance in Asia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, B.H.; He, G.Z.; Wu, X.P.; Wang, L.X.; Wu, H.; Dou, J.P.; Han, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for 755 benign breast lesions: A prospective multicenter study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. A comparison of microwave ablation and bipolar radiofrequency ablation both with an internally cooled probe: Results in ex vivo and in vivo porcine livers. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Han, Z.Y.; Li, T.; Feng, W.Z.; Yu, X.L.; Luo, Y.C.; Wu, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.D.; Liang, P. Microwave Ablation Versus Nipple Sparing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer ≤ 5 cm: A Pilot Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 546883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Dou, J.; Yu, J.; Liang, P. Volume reduction for ≥ 2 cm benign breast lesions after ultrasound-guided microwave ablation with a minimum 12-month follow-up. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, B.H.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.Y.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Mu, M.J.; Liang, P. Ultrasound guided percutaneous microwave ablation of benign breast lesions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 79376–79386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wu, H.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Dou, J.; An, C.; Qi, E.; Yu, J.; Liang, P. Microwave ablation of benign breast tumors: A prospective study with minimum 12 months follow-up. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamija, E.; Singh, R.; Mishra, S.; Hari, S. Image-Guided Breast Interventions: Biopsy and Beyond. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2021, 31, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leylek, A.M.; Whitman, G.J.; Vilar, V.S.; Kisilevzky, N.; Faintuch, S. Radiofrequency ablation for breast cancer. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 16, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Zha, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Chen, L.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. US-guided percutaneous microwave coagulation of small breast cancers: A clinical study. Radiology 2012, 263, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavros, M.N.; Economopoulos, K.P.; Alexiou, V.G.; Pawlik, T.M. Treatment and Prognosis for Patients With Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolverato, G.; Kim, Y.; Alexandrescu, S.; Marques, H.P.; Lamelas, J.; Aldrighetti, L.; Clark Gamblin, T.; Maithel, S.K.; Pulitano, C.; Bauer, T.W.; et al. Management and Outcomes of Patients with Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Following Previous Curative-Intent Surgical Resection. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Paredes, A.Z.; Mehta, R.; Hyer, J.M.; Merath, K.; Sahara, K.; Bagante, F.; Beal, E.W.; Shen, F.; et al. Trends in the Incidence, Treatment and Outcomes of Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in the USA: Facility Type is Associated with Margin Status, Use of Lymphadenectomy and Overall Survival. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, J.L.; Braunlin, M.; Laversanne, M.; Valery, P.C.; Bray, F.; McGlynn, K.A. International trends in liver cancer incidence, overall and by histologic subtype, 1978-2007. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, J.; Galle, P.R.; Khan, S.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Park, J.W.; Patel, T.; Pawlik, T.M.; Gores, G.J. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, C.; Calandri, M.; Javle, M.; Odisio, B.C. Interventional radiology approaches for intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, R.; Acquafredda, F.; Ferraro, V.; Laera, L.; Surico, G.; Surgo, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Marini, S.; de’Angelis, N.; Memeo, R.; et al. Non-surgical treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Argirò, R.; Crocetti, L.; Rocco, B.; Bozzi, E.; Gasparrini, F.; Tanzilli, A.; Catalano, C.; Iezzi, R. Percutaneous Thermal Segmentectomy: Proof of Concept. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, A.; Kim, J.U.; Eliahoo, J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Khan, S.A. Ablative Therapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 9, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindoh, J. Ablative therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2017, 6, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.B.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Abbott, D.E.; Anaya, D.A.; Anders, R.; Are, C.; Bachini, M.; Borad, M.; Brown, D.; Burgoyne, A.; et al. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Ko, H.K.; Kim, K.W.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, P.N. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butros, S.R.; Shenoy-Bhangle, A.; Mueller, P.R.; Arellano, R.S. Radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Feasability, local tumor control, and long-term outcome. Clin. Imaging 2014, 38, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, H.; Dodd, G.D., 3rd; Chintapalli, K.N.; Wood, B.J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Hvizda, J.L.; Sewell, P.E.; Goldberg, S.N. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: Lessons learned from complications. Radiographics 2004, 24, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, S.; Gervais, D.A. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 30, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Goldberg, S.N. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 2011, 258, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slakey, D.P. Radiofrequency ablation of recurrent cholangiocarcinoma. Am. Surg. 2002, 68, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.A.; Liang, P.; Yu, X.L.; Cheng, Z.G.; Han, Z.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Yu, J. Sonography-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of intrahepatic primary cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.S.; Sampson, L.A.; Warner, T.F.; Mahvi, D.M.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 2005, 236, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.A.; Kinsman, K.A.; Schmit, G.D.; Atwell, T.D.; Schmitz, J.J.; Welch, B.T.; Callstrom, M.R.; Geske, J.R.; Kurup, A.N. Thermal ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Safety, efficacy, and factors affecting local tumor progression. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 3487–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, P.N. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, W205–W209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrafiello, G.; Laganà, D.; Cotta, E.; Mangini, M.; Fontana, F.; Bandiera, F.; Fugazzola, C. Radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Preliminary experience. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, Y.Y.; Hwang, J.I.; Chou, Y.H.; Wang, H.K.; Chiang, J.H.; Chang, C.Y. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2005, 21, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolani, G.; Vetrone, G.; Grazi, G.L.; Aramaki, O.; Cescon, M.; Ravaioli, M.; Serra, C.; Brandi, G.; Pinna, A.D. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Primary liver resection and aggressive multimodal treatment of recurrence significantly prolong survival. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.J.; Hu, P.; Wang, N.; Shen, Q.; Sun, A.X.; Kuang, M.; Qian, G.J. Thermal ablation versus repeated hepatic resection for recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Friedman, T.; Madoff, D.C. Update on Embolization Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koay, E.J.; Odisio, B.C.; Javle, M.; Vauthey, J.N.; Crane, C.H. Management of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: How do we decide among the various liver-directed treatments? Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2017, 6, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Naguib, N.N.; Nour-Eldin, N.E.; Bechstein, W.O.; Zeuzem, S.; Trojan, J.; Gruber-Rouh, T. Transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: Results and prognostic factors governing treatment success. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.I.; Madoff, D.C. Balloon-Assisted Transarterial Chemoembolization Segmentectomy: An Alternative Strategy in the Treatment of Hypovascular Oligometastatic Liver Metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyves, J.W.; Ziessman, H.A.; Ensminger, W.D.; Thrall, J.H.; Niederhuber, J.E.; Keyes, J.W., Jr.; Walker, S. Definition of hepatic tumor microcirculation by single photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT). J. Nucl. Med. 1984, 25, 972–977. [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, H.R.; Kelly, K.H.; Dod, K.S.; Byron, R.L., Jr. Studies on the blood supply of tumors in man. I. Fluorescence of cutaneous lesions. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1951, 11, 877–889. [Google Scholar]
- Poggi, G.; Amatu, A.; Montagna, B.; Quaretti, P.; Minoia, C.; Sottani, C.; Villani, L.; Tagliaferri, B.; Sottotetti, F.; Rossi, O.; et al. OEM-TACE: A new therapeutic approach in unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 32, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafi, S.; Piduru, S.M.; El-Rayes, B.; Kauh, J.S.; Kooby, D.A.; Sarmiento, J.M.; Kim, H.S. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable standard-chemorefractory intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Survival, efficacy, and safety study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinwande, O.; Shah, V.; Mills, A.; Noda, C.; Weiner, E.; Foltz, G.; Saad, N. Chemoembolization versus radioembolization for the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a single institution image-based efficacy and comparative toxicity. Hepat. Oncol. 2017, 4, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, C.; Solaini, L.; Vara, G.; Brandi, N.; Cappelli, A.; Modestino, F.; Cucchetti, A.; Golfieri, R. Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radioembolization for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-a Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Paz-Fumagalli, R.; Frey, G.; Sella, D.M.; McKinney, J.M.; Wang, W. Resin-based Yttrium-90 microspheres for unresectable and failed first-line chemotherapy intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Preliminary results. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levillain, H.; Bagni, O.; Deroose, C.M.; Dieudonné, A.; Gnesin, S.; Grosser, O.S.; Kappadath, S.C.; Kennedy, A.; Kokabi, N.; Liu, D.M.; et al. International recommendations for personalised selective internal radiation therapy of primary and metastatic liver diseases with yttrium-90 resin microspheres. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1570–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondergem, M.; Smits, M.L.; Elschot, M.; de Jong, H.W.; Verkooijen, H.M.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Nijsen, J.F.; Lam, M.G. 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin poorly predicts the intrahepatic distribution of 90Y resin microspheres in hepatic radioembolization. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willowson, K.P.; Eslick, E.M.; Bailey, D.L. Individualised dosimetry and safety of SIRT for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. EJNMMI Phys. 2021, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Shabanan, S.; Nezami, N.; Abdelsalam, M.E.; Sheth, R.A.; Odisio, B.C.; Mahvash, A.; Habibollahi, P. Selective Internal Radiation Therapy with Yttrium-90 for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review on Post-Treatment Dosimetry and Concomitant Chemotherapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3825–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, G.; Bocci, G.; Ribatti, D. Scholars and scientists in the history of the lymphatic system. J. Anat. 2017, 231, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayan, R.; Achen, M.G.; Stacker, S.A. Lymphatic vessels in cancer metastasis: Bridging the gaps. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard-Mack, C.L. Normal structure, function, and histology of lymph nodes. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; von der Weid, P.Y. Lymphatic system: An active pathway for immune protection. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 38, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guermazi, A.; Brice, P.; Hennequin, C.; Sarfati, E. Lymphography: An old technique retains its usefulness. Radiographics 2003, 23, 1541–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.C.; Krementz, E.T. Lymphangiography by lymph-node injection. JAMA 1967, 202, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolski, G.J.; Itkin, M. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intranodal lymphangiogram for thoracic duct embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Rouh, T.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Lehnert, T.; Harth, M.; Thalhammer, A.; Beeres, M.; Tsaur, I.; Hammersting, R.; Wichmann, J.L.; Vogl, T.J.; et al. Direct lymphangiography as treatment option of lymphatic leakage: Indications, outcomes and role in patient’s management. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannes, M.; Shin, D.; McCluskey, K.; Varma, R.; Santos, E. Comparative Analysis of Intranodal Lymphangiography with Percutaneous Intervention for Postsurgical Chylous Effusions. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandre-Lafont, E.; Krompiec, C.; Rau, W.S.; Krombach, G.A. Effectiveness of therapeutic lymphography on lymphatic leakage. Acta Radiol. 2011, 52, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamarthi, V.; Stecker, M.S.; Schenker, M.P.; Baum, R.A.; Killoran, T.P.; Suzuki Han, A.; O’Horo, S.K.; Rabkin, D.J.; Fan, C.M. Thoracic duct embolization and disruption for treatment of chylous effusions: Experience with 105 patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Takeda, K.; Sukhbaatar, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Mori, S.; Shiga, K.; Kodama, T. Intranodal pressure of a metastatic lymph node reflects the response to lymphatic drug delivery system. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4232–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, V.; Minehart, J.; Sterman, D.H. Local Immunotherapy of Cancer: Innovative Approaches to Harnessing Tumor-Specific Immune Responses. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, A.; Kumari, S.; Walczak, M.; Madsbu, U.; Hagtvedt, T.; Bogsrud, T.V.; Kvalheim, G.; Holte, H.; Aurlien, E.; Delabie, J.; et al. Sequential intranodal immunotherapy induces antitumor immunity and correlated regression of disseminated follicular lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Matsuki, D.; Tada, A.; Takeda, K.; Mori, S. New concept for the prevention and treatment of metastatic lymph nodes using chemotherapy administered via the lymphatic network. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, P.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Sang, L. Efficacy and Safety of Thermal Ablation for Treating Lymph Node Metastasis From Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Xie, Q.K.; Lv, N.; Li, X.S.; Mu, L.W.; Wu, P.H.; Zhao, M. Percutaneous CT-guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Lymph Node Oligometastases from Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score-matching Analysis. Radiology 2017, 282, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexis, N.; Parmeggiani, A.; Peta, G.; Spinnato, P.; Miceli, M.; Facchini, G. Minimally Invasive Interventional Procedures for Metastatic Bone Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4155–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana-Bawan, S.; David, E.; Sahgal, A.; Chow, E. Palliation of bone metastases-exploring options beyond radiotherapy. Ann Palliat Med 2019, 8, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoretti, N.; Gallo, G.; Bertrand, A.S.; Bard, R.L.; Kelekis, A. Percutaneous Facet Screw Fixation in the Treatment of Symptomatic Recurrent Lumbar Facet Joint Cyst: A New Technique. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, A.; Tsoumakidou, G.; Buy, X.; Quoix, E. Quality improvement guidelines for bone tumour management. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Yamakado, K.; Takaki, H.; Uraki, J.; Makita, M.; Oshima, F.; Takeda, K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful spinal tumors adjacent to the spinal cord with real-time monitoring of spinal canal temperature: A prospective study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 32, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, F.; Ladeira, K.; Pinho, F.; Saraiva, N.; Bonito, N.; Pinto, L.; Goncalves, F. Bone Metastases: An Overview. Oncol. Rev. 2017, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubiana-Hulin, M. Incidence, prevalence and distribution of bone metastases. Bone 1991, 12, S9–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auloge, P.; Cazzato, R.L.; Rousseau, C.; Caudrelier, J.; Koch, G.; Rao, P.; Chiang, J.B.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Complications of Percutaneous Bone Tumor Cryoablation: A 10-year Experience. Radiology 2019, 291, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, F.; de Baere, T.; Hakime, A.; Pearson, E.; Farouil, G.; Teriitehau, C.; Tselikas, L. Percutaneous osteosynthesis in the pelvis in cancer patients. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.Y.; Latich, I.; Toombs, C.; Mungur, A.; Conway, D.; Alder, K.; Ibe, I.; Lindskog, D.; Friedlaender, G. Minimally Invasive Image-Guided Ablation, Osteoplasty, Reinforcement, and Internal Fixation (AORIF) for Osteolytic Lesions in the Pelvis and Periarticular Regions of Weight-Bearing Bones. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.G.; DiPaola, C.P.; Ryken, T.C.; Bilsky, M.H.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Berven, S.H.; Harrop, J.S.; Fehlings, M.G.; Boriani, S.; Chou, D.; et al. A novel classification system for spinal instability in neoplastic disease: An evidence-based approach and expert consensus from the Spine Oncology Study Group. Spine 2010, 35, E1221–E1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, C.; Fancellu, A.; Ballicu, N.; Fele, R.M.; Sotgia, B.; Melis, L. CT-guided percutaneous screw fixation plus cementoplasty in the treatment of painful bone metastases with fractures or a high risk of pathological fracture. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.; Ahrar, K. Palliative interventions for pain in cancer patients. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 24, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marini, P.; Cazzato, R.L.; Auloge, P.; Koch, G.; Dalili, D.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous image-guided thermal ablation of bone metastases: A retrospective propensity study comparing the safety profile of radio-frequency ablation and cryo-ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; Palussière, J.; Auloge, P.; Rousseau, C.; Koch, G.; Dalili, D.; Buy, X.; Garnon, J.; De Marini, P.; Gangi, A. Complications Following Percutaneous Image-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Bone Tumors: A 10-year Dual-Center Experience. Radiology 2020, 296, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzato, R.L.; De Marini, P.; Leonard-Lorant, I.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Autrusseau, P.A.; Mayer, T.; Weiss, J.; Auloge, P.; Garnon, J.; et al. Percutaneous thermal ablation of sacral metastases: Assessment of pain relief and local tumor control. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2021, 102, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; Auloge, P.; De Marini, P.; Rousseau, C.; Chiang, J.B.; Koch, G.; Caudrelier, J.; Rao, P.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous image-guided ablation of bone metastases: Local tumor control in oligometastatic patients. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, C.S.; Ensor, J.E.; Ahrar, K.; Huang, S.Y.; Sabir, S.H.; Tannir, N.M.; Lewis, V.O.; Tam, A.L. Cryoablation of Bone Metastases from Renal Cell Carcinoma for Local Tumor Control. J. Bone Joint. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, A.; Arrigoni, F.; Bruno, F.; Palumbo, P.; Floridi, C.; Cazzato, R.L.; Reginelli, A.; Zappia, M.; Brunese, L.; Zugaro, L.; et al. Present role and future perspectives of interventional radiology in the treatment of painful bone lesions. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).