Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Treating EGFR-Mutant Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis and Intracranial Intervention Have No Impact on Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
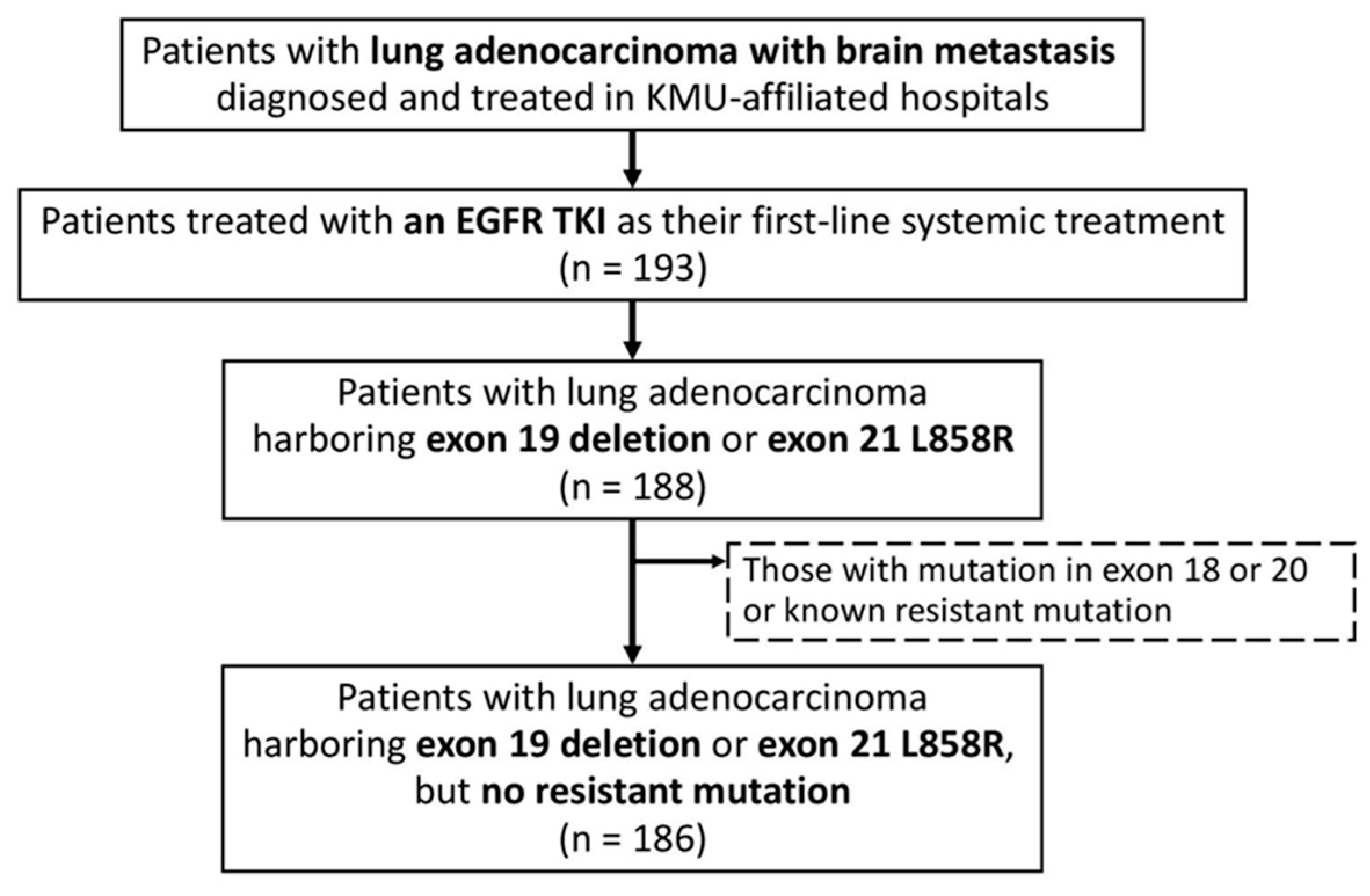
2.1. Patient Identification
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
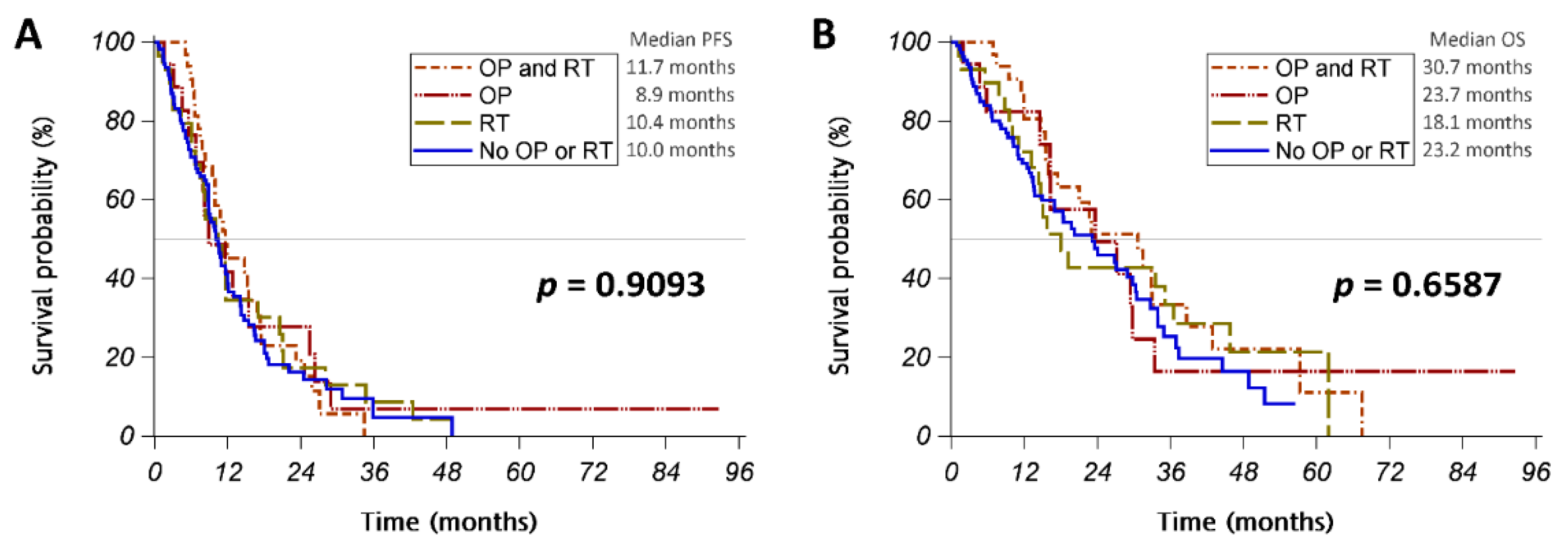
3.2. Intracranial Intervention
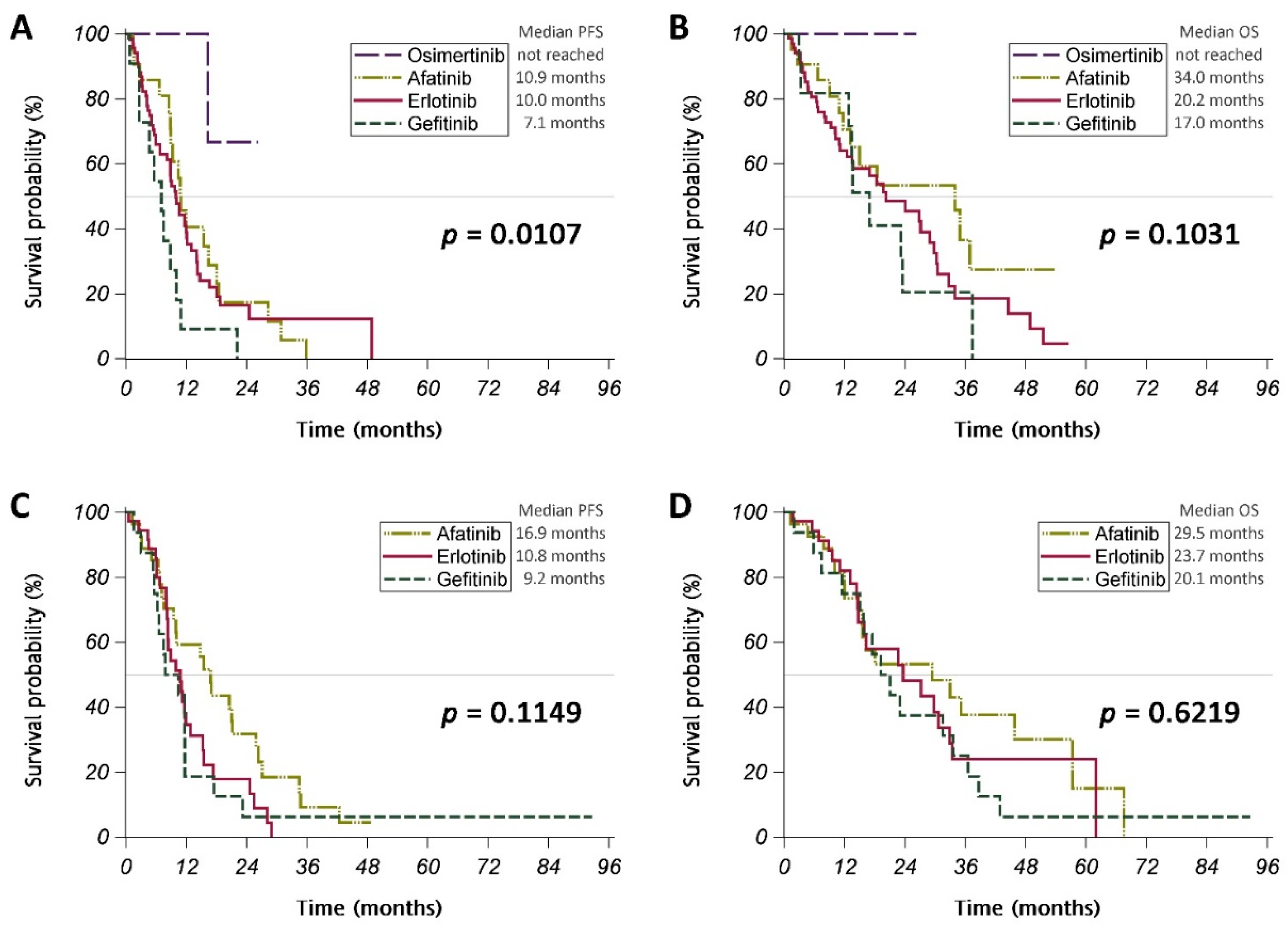
3.3. Different EGFR TKIs
3.4. Prognostic Factors for PFS and OS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Version | Factors | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| 2010 | KPS | ≤60 | 70–80 | 90–100 |
| Age | >60 | 50–60 | <50 | |
| Number of BM | ≥4 | 2–3 | 1 | |
| ECM | Present | Absent | ||
| 2017 | KPS | ≤70 | 80 | 90–100 |
| Age | ≥70 | <70 | ||
| Number of BM | ≥5 | 1–4 | ||
| ECM | Present | Absent | ||
| EGFR and ALK | Both negative or unknown | EGFR- or ALK-positive | ||
| 2022 | KPS | ≤70 | 80 | 90–100 |
| Age | ≥70 | <70 | ||
| Number of BM | ≥5 | 1–4 | ||
| ECM | Present | Absent | ||
| EGFR and ALK | Both negative or unknown | EGFR- or ALK-positive | ||
| PD–L1 | Negative or unknown | Positive | ||
| Variables | All Patients | No OP/RT | OP or RT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 186 | 107 | 79 | |
| Brain OP (operation for brain tumor) | 0 | 50 | ||
| Brain RT (radiotherapy for brain tumor) | 0 | 61 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 123 (66%) | 74 (69%) | 49 (62%) | 0.3096 |
| Male | 63 (34%) | 33 (31%) | 30 (38%) | |
| Age (year) | 65.5 ± 11.2 | 66.8 ± 11.0 | 63.8 ± 11.3 | 0.0688 |
| <65 | 92 (49%) | 49 (46%) | 43 (54%) | 0.2442 |
| ≥65 | 94 (51%) | 58 (54%) | 36 (46%) | |
| ECOG performance status | ||||
| 0–1 | 159 (85%) | 94 (88%) | 65 (82%) | 0.2863 |
| ≥2 | 27 (15%) | 13 (12%) | 14 (18%) | |
| Karnofsky performance status | ||||
| 100 | 12 (6%) | 8 (7%) | 4 (5%) | 0.2026 |
| 90 | 21 (11%) | 11 (10%) | 10 (13%) | |
| 80 | 125 (67%) | 77 (72%) | 48 (61%) | |
| 70 | 27 (15%) | 11 (10%) | 16 (20%) | |
| ≤60 | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | |
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Exon 19 deletion | 85 (46%) | 48 (45%) | 37 (47%) | 0.7892 |
| Exon 21 L858R | 102 (55%) | 60 (56%) | 42 (53%) | 0.6934 |
| PD-L1 † | ||||
| <1% | 29 (29%) | 17 (27%) | 12 (32%) | 0.5299 |
| ≥1% | 72 (71%) | 47 (73%) | 25 (68%) | |
| Number of brain metastases | ||||
| 1 | 63 (34%) | 29 (27%) | 34 (43%) | 0.0600 |
| 2–4 | 55 (30%) | 33 (31%) | 22 (28%) | |
| ≥5 | 68 (37%) | 45 (42%) | 23 (29%) | |
| Number of ECM sites | ||||
| 0 | 25 (13%) | 8 (7%) | 17 (22%) | 0.0174 |
| 1–2 | 91 (49%) | 54 (50%) | 37 (47%) | |
| ≥3 | 70 (38%) | 45 (42%) | 25 (32%) | |
| Site of ECM | ||||
| Lung metastasis | 99 (53%) | 65 (61%) | 34 (43%) | 0.0167 |
| Pleural metastasis/effusion | 81 (44%) | 53 (50%) | 28 (35%) | 0.0554 |
| Bone metastasis | 116 (62%) | 72 (67%) | 44 (56%) | 0.1067 |
| Liver metastasis | 26 (14%) | 20 (19%) | 6 (8%) | 0.0310 |
| Pericardial metastasis/effusion | 51 (27%) | 32 (30%) | 19 (24%) | 0.3762 |
| Adrenal metastasis | 23 (12%) | 13 (12%) | 10 (13%) | 0.9170 |
| Other metastasis | 12 (6%) | 8 (7%) | 4 (5%) | 0.5078 |
| GPA (version 2010) score | ||||
| ≥2.5 | 26 (14%) | 9 (8%) | 17 (22%) | 0.0021 |
| 1.5–2.0 | 66 (35%) | 33 (31%) | 33 (42%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 94 (51%) | 65 (61%) | 29 (37%) | |
| GPA (version 2017) score | ||||
| ≥2.5 | 36 (19%) | 12 (11%) | 24 (30%) | 0.0048 |
| 1.5–2.0 | 120 (65%) | 76 (71%) | 44 (56%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 30 (16%) | 19 (18%) | 11 (14%) | |
| GPA (version 2022) score | ||||
| ≥3.0 | 17 (9%) | 6 (6%) | 11 (14%) | 0.1327 |
| 1.5–2.5 | 149 (80%) | 88 (82%) | 61 (77%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 20 (11%) | 13 (12%) | 7 (9%) | |
| EGFR TKI | ||||
| Gefitinib | 27 (15%) | 11 (10%) | 16 (20%) | 0.0022 |
| Erlotinib | 104 (56%) | 68 (64%) | 36 (46%) | |
| Afatinib | 48 (26%) | 21 (20%) | 27 (34%) | |
| Osimertinib | 7 (4%) | 7 (7%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Anti-VEGF treatment | ||||
| No | 175 (94%) | 101 (94%) | 74 (94%) | 0.8366 |
| Yes | 11 (6%) | 6 (6%) | 5 (6%) |
| Variables | All Patients | No OP/RT | OP or RT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial treatment response | ||||
| Progressive disease (PD) | 18 (10%) | 11 (10%) | 7 (9%) | 0.9521 |
| Stable disease (SD) | 26 (14%) | 14 (13%) | 12 (15%) | |
| Partial response (PR) | 139 (75%) | 80 (75%) | 59 (75%) | |
| Complete response (CR) | 3 (2%) | 2 (2%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Disease control rate | 168 (90%) | 96 (90%) | 72 (91%) | 0.7462 |
| Response rate | 142 (76%) | 82 (77%) | 60 (76%) | 0.9133 |
| Initial intracranial treatment response † | ||||
| Intracranial progressive disease (iPD) | 9 (6%) | 3 (3%) | 6 (8%) | 0.1141 |
| Intracranial stable disease (iSD) | 28 (18%) | 11 (13%) | 17 (24%) | |
| Intracranial partial response (iPR) | 76 (48%) | 44 (51%) | 32 (44%) | |
| Intracranial complete response (iCR) | 46 (29%) | 29 (33%) | 17 (24%) | |
| Intracranial disease control rate | 150 (94%) | 84 (97%) | 66 (92%) | 0.1846 |
| Intracranial response rate | 122 (77%) | 73 (84%) | 49 (68%) | 0.0185 |
| Site of disease progression | ||||
| Intracranial progression | 48 (26%) | 25 (23%) | 23 (29%) | 0.3757 |
| Extracranial progression | 21 (11%) | 12 (11%) | 9 (11%) | 0.9698 |
| Lung | 5 (3%) | 4 (4%) | 1 (1%) | 0.3027 |
| Pleural nodule/effusion | 7 (4%) | 3 (3%) | 4 (5%) | 0.4235 |
| Bone | 9 (5%) | 5 (5%) | 4 (5%) | 0.9024 |
| Liver | 2 (1%) | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | 0.8286 |
| Adrenal gland | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | 0.2432 |
| Other | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 0.3889 |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariable Model 5 | Multivariable Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| OP (vs. no OP) | 0.97 [0.53–1.79] | ||
| RT (vs. no RT) | 0.76 [0.42–1.36] | ||
| OP or RT (vs. no OP or RT) | 1.05 [0.60–1.83] | 0.95 [0.51–1.77] | 1.02 [0.52–2.02] |
| EGFR TKI: (vs. gefitinib) | |||
| Erlotinib | 1.41 [0.54–3.70] | 1.36 [0.47–3.95] | 1.34 [0.44–4.11] |
| Afatinib | 1.59 [0.60–4.23] | 1.59 [0.57–4.45] | 1.58 [0.55–4.52] |
| Osimertinib | † | † | † |
| Anti-VEGF treatment (vs. no anti-VEGF) | 2.04 [0.63–6.65] | 1.81 [0.52–6.29] | 1.44 [0.39–5.39] |
| Male (vs. female) | 1.70 [0.94–3.07] | 1.51 [0.82–2.80] | 1.38 [0.74–2.58] |
| Age (≥65 vs. <65) | 0.71 [0.40–1.28] | 0.69 [0.37–1.29] | 0.65 [0.33–1.27] |
| ECOG PS (≥2 vs. ≤1) | 0.77 [0.31–1.96] | 0.94 [0.33–2.63] | 1.17 [0.40–3.41] |
| Exon 19 deletion vs. L858R | 0.76 [0.44–1.34] | 0.72 [0.39–1.32] | 0.73 [0.39–1.36] |
| PD-L1 ≥ 1% vs. PD-L1 < 1% or not tested | 1.43 [0.81–2.54] | 1.39 [0.75–2.56] | 1.50 [0.79–2.84] |
| Number of brain metastases (≥5 vs. <5) | 0.69 [0.38–1.27] | 0.66 [0.35–1.26] | 0.58 [0.29–1.14] |
| Extracranial metastasis (vs. no) | 1.12 [0.52–2.39] | 1.18 [0.53–2.63] | |
| Lung metastasis (vs. no) | 1.20 [0.69–2.09] | 1.37 [0.70–2.67] | |
| Pleural metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 0.87 [0.49–1.55] | 0.95 [0.47–1.95] | |
| Bone metastasis (vs. no) | 1.43 [0.79–2.60] | 1.32 [0.66–2.64] | |
| Liver metastasis (vs. no) | 1.16 [0.55–2.48] | 1.10 [0.46–2.63] | |
| Pericardial metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 0.86 [0.45–1.65] | 0.72 [0.32–1.60] | |
| Adrenal metastasis (vs. no) | 1.59 [0.62–4.07] | 2.30 [0.79–6.70] | |
| Other metastasis (vs. no) | 0.56 [0.08–4.10] | 0.52 [0.06–4.47] |
References
- Shi, A.A.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Temel, J.S.; Halpern, E.F.; Kuester, L.B.; Aquino, S.L. Does initial staging or tumor histology better identify asymptomatic brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer? J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2006, 1, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, O.; Saavedra-Perez, D.; Kuri, R.; Aviles-Salas, A.; Martinez, L.; Mendoza-Posada, D.; Castillo, P.; Astorga, A.; Guzman, E.; De la Garza, J. Brain metastasis development and poor survival associated with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective analysis. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taimur, S.; Edelman, M.J. Treatment options for brain metastases in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2003, 5, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuña, A.R.; Vega, M.A.; Sanchez, C.R.; Fernandez, V.M. Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Prognostic Factors in Patients with Surgical Resection. J. Neurol. Surg. A. Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2018, 79, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscetti, L.; Nelli, F.; Felici, A.; Rinaldi, M.; De Santis, S.; D’Auria, G.; Mansueto, G.; Tonini, G.; Sperduti, I.; Pollera, F.C. Up-front chemotherapy and radiation treatment in newly diagnosed nonsmall cell lung cancer with brain metastases: Survey by Outcome Research Network for Evaluation of Treatment Results in Oncology. Cancer 2007, 109, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearz, A.; Garassino, I.; Tiseo, M.; Caffo, O.; Soto-Parra, H.; Boccalon, M.; Talamini, R.; Santoro, A.; Bartolotti, M.; Murgia, V.; et al. Activity of Pemetrexed on brain metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 68, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Gervais, R.; Lena, H.; Hureaux, J.; Berard, H.; Paillotin, D.; Bota, S.; Monnet, I.; Chajara, A.; Robinet, G. Pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with asymptomatic inoperable brain metastases: A multicenter phase II trial (GFPC 07-01). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Girard, N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. Oncol. 2011, 12, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet. Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet. Oncol. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, G.Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Yan, H.H.; Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Erlotinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases: A phase II study (CTONG-0803). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, S.W.; Suh, C.; Lee, J.S. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metro, G.; Chiari, R.; Ricciuti, B.; Rebonato, A.; Lupattelli, M.; Gori, S.; Bennati, C.; Castrioto, C.; Floridi, P.; Minotti, V.; et al. Pharmacotherapeutic options for treating brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.J.; Shah, N.J.; Subramaniam, D.S. Management of Brain Metastases in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, V.; Welch, M.; Ravera, E.; Zampolin, R.L.; Sequist, L.V.; Halmos, B. Marked Differences in CNS Activity among EGFR Inhibitors: Case Report and Mini-Review. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, e135–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, Y.; Masago, K.; Masuda, S.; Mizuno, T.; Fukudo, M.; Ikemi, Y.; Sakamori, Y.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Katsura, T.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiya, A.; Tamiya, M.; Nishihara, T.; Shiroyama, T.; Nakao, K.; Tsuji, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Isa, S.I.; Omachi, N.; Okamoto, N.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration Rate and Efficacy of Afatinib in Patients with EGFR Mutation-positive Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, B.C.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, T.M.; Goldman, J.W.; Natale, R.B.; et al. Osimertinib in Patients With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Leptomeningeal Metastases: The BLOOM Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J. Clinical factors associated with treatment outcomes in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A case-control observational study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.R. Prospective memory impairment following whole brain radiotherapy in patients with metastatic brain cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5315–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Tsai, M.J.; Yang, C.J.; Hung, J.Y.; Chong, I.W. The Factors Predicting Concordant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation Detected in Liquid/Tissue Biopsy and the Related Clinical Outcomes in Patients of Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, M.J.; Lee, M.H.; Kuo, C.Y.; Shen, M.C.; Tsai, Y.M.; Chen, H.C.; Hung, J.Y.; Huang, M.S.; Chong, I.W.; et al. Lower starting dose of afatinib for the treatment of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma harboring exon 21 and exon 19 mutations. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Hung, J.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Wu, K.L.; Liu, T.C.; Chou, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Hsu, J.S.; Huang, M.S.; Chong, I.W. The salvage therapy in lung adenocarcinoma initially harbored susceptible EGFR mutation and acquired resistance occurred to the first-line gefitinib and second-line cytotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Pharm. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Tsai, M.J.; Hung, J.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Tsai, Y.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Hsu, J.F.; Liu, T.C.; Huang, M.S.; Chong, I.W. The clinical efficacy of Afatinib 30 mg daily as starting dose may not be inferior to Afatinib 40 mg daily in patients with stage IV lung Adenocarcinoma harboring exon 19 or exon 21 mutations. BMC Pharm. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Chao, S.T.; Sneed, P.K.; Luo, X.; Suh, J.; Roberge, D.; Bhatt, A.; Jensen, A.W.; Brown, P.D.; Shih, H.; et al. Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: A multi-institutional analysis of 4259 patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Estimating Survival in Patients With Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases: An Update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Lung Cancer Using Molecular Markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; De, B.; Li, J.; Carpenter, D.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Milligan, M.; Shih, H.A.; Kutuk, T.; Kotecha, R.; Higaki, H.; et al. Graded Prognostic Assessment (GPA) for Patients With Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases: Initial Report of the Small Cell Lung Cancer GPA and Update of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer GPA Including the Effect of Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Other Prognostic Factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getman, V.; Devyatko, E.; Dunkler, D.; Eckersberger, F.; End, A.; Klepetko, W.; Marta, G.; Mueller, M.R. Prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer with isolated brain metastases undergoing combined surgical treatment. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2004, 25, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.T.; Wu, W.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Chang, W.C.; Yang, S.H.; Shen, S.Y.; Su, J.; Chen, H.Y. Surgical resection of brain metastases prolongs overall survival in non-small-cell lung cancer. Am. J. Cancer. Res. 2021, 11, 6160–6172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Hao, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; He, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. First-line epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor alone or with whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases in patients with EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergonzini, C.; Kroese, K.; Zweemer, A.J.M.; Danen, E.H.J. Targeting Integrins for Cancer Therapy—Disappointments and Opportunities. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 863850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, S.S.; Abdel-Mawgood, A.L.; Ibrahim, S.A. EGFR-Dependent Extracellular Matrix Protein Interactions Might Light a Candle in Cell Behavior of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 766659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, R.J.; Macdonald, S.J.F.; Roper, J.A.; Jenkins, R.G.; Hatley, R.J.D. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for integrin inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Wei, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, T.; Yu, G. Construction of a prognostic risk assessment model for lung adenocarcinoma based on Integrin β family-related genes. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.C.; Ma, V.P.; Blanchard, A.; Urner, T.M.; Grandhi, S.; Salaita, K.; Mattheyses, A.L. EGFR activation attenuates the mechanical threshold for integrin tension and focal adhesion formation. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs238840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Perez-Soler, R. Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. Oncol. 2018, 19, e43–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Feng, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Xian, H.; Zhang, S. The concentration of erlotinib in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients With Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 33, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Chien, C.R.; Liao, W.C.; Chen, C.H.; Hsia, T.C.; Tu, C.Y.; Chen, H.J. The optimal therapy strategy for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A real-world study from Taiwan. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | All Patients | Gefitinib | Erlotinib | Afatinib | Osimertinib | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 186 | 27 | 104 | 48 | 7 | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 123 (66%) | 16 (59%) | 71 (68%) | 30 (63%) | 6 (86%) | 0.5197 |
| Male | 63 (34%) | 11 (41%) | 33 (32%) | 18 (38%) | 1 (14%) | |
| Age (years) | 65.5 ± 11.2 | 64.9 ± 13.2 | 66.5 ± 10.7 | 63.3 ± 10.6 | 68.9 ± 13.6 | 0.3470 |
| <65 | 92 (49%) | 16 (59%) | 47 (45%) | 26 (54%) | 3 (43%) | 0.5044 |
| ≥65 | 94 (51%) | 11 (41%) | 57 (55%) | 22 (46%) | 4 (57%) | |
| ECOG performance status | ||||||
| 0–1 | 159 (85%) | 23 (85%) | 90 (87%) | 42 (88%) | 4 (57%) | 0.1884 |
| ≥2 | 27 (15%) | 4 (15%) | 14 (13%) | 6 (13%) | 3 (43%) | |
| Karnofsky performance status | ||||||
| 100 | 12 (6%) | 3 (11%) | 7 (7%) | 1 (2%) | 1 (14%) | 0.2980 |
| 90 | 21 (11%) | 4 (15%) | 9 (9%) | 8 (17%) | 0 (0%) | |
| 80 | 125 (67%) | 16 (59%) | 74 (71%) | 32 (67%) | 3 (43%) | |
| 70 | 27 (15%) | 4 (15%) | 14 (13%) | 6 (13%) | 3 (43%) | |
| ≤60 | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| EGFR mutation | ||||||
| Exon 19 deletion | 85 (46%) | 10 (37%) | 46 (44%) | 25 (52%) | 4 (57%) | 0.5591 |
| Exon 21 L858R | 102 (55%) | 17 (63%) | 59 (57%) | 23 (48%) | 3 (43%) | 0.5311 |
| PD-L1 † | ||||||
| <1% | 29 (29%) | 1 (33%) | 16 (24%) | 12 (43%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1701 |
| ≥1% | 72 (71%) | 2 (67%) | 50 (76%) | 16 (57%) | 4 (100%) | |
| Number of brain metastases | ||||||
| 1 | 63 (34%) | 15 (56%) | 31 (30%) | 15 (31%) | 2 (29%) | 0.0378 |
| 2–4 | 55 (30%) | 10 (37%) | 30 (29%) | 14 (29%) | 1 (14%) | |
| ≥5 | 68 (37%) | 2 (7%) | 43 (41%) | 19 (40%) | 4 (57%) | |
| Number of ECM sites | ||||||
| 0 | 25 (13%) | 4 (15%) | 15 (14%) | 6 (13%) | 0 (0%) | 0.6122 |
| 1–2 | 91 (49%) | 14 (52%) | 45 (43%) | 28 (58%) | 4 (57%) | |
| ≥3 | 70 (38%) | 9 (33%) | 44 (42%) | 14 (29%) | 3 (43%) | |
| Site of ECMs | ||||||
| Lung metastasis | 99 (53%) | 12 (44%) | 58 (56%) | 25 (52%) | 4 (57%) | 0.7590 |
| Pleural metastasis/effusion | 81 (44%) | 12 (44%) | 49 (47%) | 17 (35%) | 3 (43%) | 0.6064 |
| Bone metastasis | 116 (62%) | 18 (67%) | 63 (61%) | 30 (63%) | 5 (71%) | 0.8965 |
| Liver metastasis | 26 (14%) | 1 (4%) | 16 (15%) | 7 (15%) | 2 (29%) | 0.2844 |
| Pericardial metastasis/effusion | 51 (27%) | 6 (22%) | 31 (30%) | 11 (23%) | 3 (43%) | 0.5741 |
| Adrenal metastasis | 23 (12%) | 2 (7%) | 15 (14%) | 5 (10%) | 1 (14%) | 0.7504 |
| Other metastasis | 12 (6%) | 4 (15%) | 6 (6%) | 1 (2%) | 1 (14%) | 0.1424 |
| GPA (version 2010) score | ||||||
| ≥2.5 | 26 (14%) | 7 (26%) | 11 (11%) | 8 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 0.2945 |
| 1.5–2.0 | 66 (35%) | 11 (41%) | 37 (36%) | 15 (31%) | 3 (43%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 94 (51%) | 9 (33%) | 56 (54%) | 25 (52%) | 4 (57%) | |
| GPA (version 2017) score | ||||||
| ≥2.5 | 36 (19%) | 8 (30%) | 18 (17%) | 10 (21%) | 0 (0%) | 0.0552 |
| 1.5–2.0 | 120 (65%) | 19 (70%) | 65 (63%) | 32 (67%) | 4 (57%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 30 (16%) | 0 (0%) | 21 (20%) | 6 (13%) | 3 (43%) | |
| GPA (version 2022) score | ||||||
| ≥3.0 | 17 (9%) | 3 (11%) | 10 (10%) | 4 (8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1905 |
| 1.5–2.5 | 149 (80%) | 24 (89%) | 79 (76%) | 41 (85%) | 5 (71%) | |
| ≤1.0 | 20 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (14%) | 3 (6%) | 2 (29%) | |
| Anti-VEGF treatment | ||||||
| No | 175 (94%) | 27 (100%) | 95 (91%) | 47 (98%) | 6 (86%) | 0.1545 |
| Yes | 11 (6%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (9%) | 1 (2%) | 1 (14%) | |
| Brain OP (operation for brain tumor) | ||||||
| No | 136 (73%) | 16 (59%) | 80 (77%) | 33 (69%) | 7 (100%) | 0.0919 |
| Yes | 50 (27%) | 11 (41%) | 24 (23%) | 15 (31%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Brain RT (radiotherapy for brain tumor) | ||||||
| No | 125 (67%) | 14 (52%) | 80 (77%) | 24 (50%) | 7 (100%) | 0.0006 |
| Yes | 61 (33%) | 13 (48%) | 24 (23%) | 24 (50%) | 0 (0%) |
| Variables | All Patients | Gefitinib | Erlotinib | Afatinib | Osimertinib | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial treatment response | ||||||
| Progressive disease (PD) | 18 (10%) | 4 (15%) | 9 (9%) | 5 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 0.6378 |
| Stable disease (SD) | 26 (14%) | 6 (22%) | 16 (15%) | 4 (8%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Partial response (PR) | 139 (75%) | 17 (63%) | 77 (74%) | 38 (79%) | 7 (100%) | |
| Complete response (CR) | 3 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (2%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Disease control rate | 168 (90%) | 23 (85%) | 95 (91%) | 43 (90%) | 7 (100%) | 0.6325 |
| Response rate | 142 (76%) | 17 (63%) | 79 (76%) | 39 (81%) | 7 (100%) | 0.1390 |
| Initial intracranial treatment response † | ||||||
| Intracranial progressive disease (iPD) | 9 (6%) | 1 (5%) | 3 (3%) | 5 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 0.6033 |
| Intracranial stable disease (iSD) | 28 (18%) | 4 (20%) | 19 (22%) | 4 (9%) | 1 (14%) | |
| Intracranial partial response (iPR) | 76 (48%) | 9 (45%) | 43 (49%) | 20 (45%) | 4 (57%) | |
| Intracranial complete response (iCR) | 46 (29%) | 6 (30%) | 23 (26%) | 15 (34%) | 2 (29%) | |
| Intracranial disease control rate | 150 (94%) | 19 (95%) | 85 (97%) | 39 (89%) | 7 (100%) | 0.2667 |
| Intracranial response rate | 122 (77%) | 15 (75%) | 66 (75%) | 35 (80%) | 6 (86%) | 0.8749 |
| Site of disease progression | ||||||
| Intracranial progression | 48 (26%) | 5 (19%) | 24 (23%) | 19 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 0.0394 |
| Extracranial progression | 21 (11%) | 5 (19%) | 10 (10%) | 6 (13%) | 0 (0%) | 0.4469 |
| Lung | 5 (3%) | 1 (4%) | 3 (3%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.9439 |
| Pleural nodule/effusion | 7 (4%) | 3 (11%) | 2 (2%) | 2 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1516 |
| Bone | 9 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (6%) | 3 (6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.5455 |
| Liver | 2 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.8397 |
| Adrenal gland | 1 (1%) | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1155 |
| Other | 1 (1%) | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1155 |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariable Model 1 | Multivariable Model 1R | Multivariable Model 2 | Multivariable Model 2R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP (vs. no OP) | 0.90 [0.63–1.28] | ||||
| RT (vs. no RT) | 0.93 [0.66–1.30] | ||||
| OP or RT (vs. no OP or RT) | 0.89 [0.65–1.23] | 0.81 [0.56–1.15] | 0.79 [0.55–1.16] | ||
| EGFR TKI: (vs. gefitinib) | |||||
| Erlotinib | 0.75 [0.48–1.16] | 0.75 [0.44–1.27] | 0.79 [0.50–1.23] | 0.73 [0.42–1.27] | 0.76 [0.49–1.19] |
| Afatinib | 0.54 [0.33–0.88] * | 0.52 [0.31–0.89] * | 0.53 [0.32–0.87] * | 0.51 [0.30–0.88] * | 0.51 [0.31–0.84] ** |
| Osimertinib | 0.10 [0.01–0.75] * | 0.11 [0.01–0.83] * | 0.11 [0.01–0.81] * | 0.10 [0.01–0.77] * | 0.11 [0.02–0.83] * |
| Anti-VEGF treatment (vs. no anti-VEGF) | 0.81 [0.36–1.83] | 0.86 [0.37–2.00] | 0.94 [0.40–2.22] | ||
| Male (vs. female) | 1.54 [1.09–2.17] * | 1.52 [1.07–2.17] * | 1.50 [1.06–2.11] * | 1.64 [1.13–2.39] ** | 1.57 [1.11–2.23] * |
| Age (≥65 vs. <65) | 0.83 [0.60–1.15] | 0.82 [0.57–1.18] | 0.87 [0.60–1.27] | ||
| ECOG PS (≥2 vs. ≤1) | 0.74 [0.46–1.20] | 0.81 [0.48–1.35] | 0.86 [0.51–1.45] | ||
| Exon 19 deletion vs. L858R | 0.99 [0.72–1.36] | 0.87 [0.61–1.23] | 0.94 [0.67–1.34] | ||
| PD–L1 ≥ 1% vs. PD-L1 < 1% or not tested | 1.00 [0.72–1.40] | 1.04 [0.71–1.51] | 1.14 [0.77–1.68] | ||
| Number of brain metastases (≥5 vs. <5) | 0.87 [0.62–1.22] | 1.00 [0.70–1.43] | 1.02 [0.70–1.48] | ||
| Extracranial metastasis (vs. no) | 1.26 [0.80–1.99] | 1.47 [0.91–2.38] | 1.40 [0.89–2.22] | ||
| Lung metastasis (vs. no) | 1.12 [0.81–1.54] | 0.97 [0.67–1.39] | |||
| Pleural metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 1.29 [0.93–1.79] | 1.48 [0.98–2.23] | 1.38 [0.99–1.92] | ||
| Bone metastasis (vs. no) | 1.57 [1.12–2.21] ** | 1.66 [1.14–2.42] ** | 1.59 [1.13–2.23] ** | ||
| Liver metastasis (vs. no) | 0.99 [0.61–1.61] | 0.94 [0.55–1.60] | |||
| Pericardial metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 1.16 [0.80–1.67] | 0.93 [0.58–1.49] | |||
| Adrenal metastasis (vs. no) | 0.99 [0.59–1.64] | 0.87 [0.49–1.55] | |||
| Other site metastasis (vs. no) | 0.97 [0.48–1.99] | 1.35 [0.61–2.98] |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariable Model 3 | Multivariable Model 3R | Multivariable Model 4 | Multivariable Model 4R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP (vs. no OP) | 0.80 [0.53–1.21] | ||||
| RT (vs. no RT) | 0.81 [0.55–1.19] | ||||
| OP or RT (vs. no OP or RT) | 0.80 [0.55–1.17] | 0.89 [0.60–1.33] | 0.87 [0.57–1.33] | ||
| EGFR TKI: (vs. gefitinib) | |||||
| Erlotinib | 0.91 [0.56–1.46] | 0.83 [0.48–1.43] | 0.88 [0.54–1.42] | 0.87 [0.48–1.56] | 0.85 [0.52–1.39] |
| Afatinib | 0.63 [0.37–1.08] | 0.61 [0.34–1.10] | 0.63 [0.37–1.08] | 0.65 [0.36–1.19] | 0.63 [0.37–1.08] |
| Osimertinib | † | † | † | † | † |
| Anti-VEGF treatment (vs. no anti-VEGF) | 0.28 [0.04–1.99] | 0.35 [0.05–2.53] | 0.30 [0.04–2.24] | ||
| Male (vs. female) | 1.52 [1.03–2.26] * | 1.57 [1.04–2.36] * | 1.63 [1.09–2.44] * | 1.53 [1.00–2.34] * | 1.54 [1.03–2.29] * |
| Age (≥65 vs. <65) | 1.32 [0.91–1.91] | 1.43 [0.95–2.14] | 1.45 [0.99–2.12] | 1.48 [0.98–2.24] | 1.42 [0.97–2.08] |
| ECOG PS (≥2 vs. ≤1) | 0.72 [0.38–1.34] | 0.70 [0.36–1.37] | 0.65 [0.34–1.22] | 0.81 [0.41–1.59] | |
| Exon 19 deletion vs. L858R | 1.10 [0.76–1.59] | 1.10 [0.74–1.64] | 1.18 [0.79–1.77] | ||
| PD–L1 ≥ 1% vs. PD-L1 < 1% or not tested | 1.17 [0.79–1.72] | 1.20 [0.78–1.84] | 1.20 [0.77–1.88] | ||
| Number of brain metastases (≥5 vs. <5) | 0.88 [0.60–1.30] | 0.97 [0.63–1.47] | 0.91 [0.59–1.39] | ||
| Extracranial metastasis (vs. no) | 1.69 [0.97–2.93] | 1.92 [1.08–3.43] * | 1.99 [1.14–3.49] * | ||
| Lung metastasis (vs. no) | 1.36 [0.94–1.98] | 1.23 [0.81–1.88] | |||
| Pleural metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 1.13 [0.78–1.64] | 1.23 [0.77–1.97] | |||
| Bone metastasis (vs. no) | 1.38 [0.94–2.03] | 1.52 [0.98–2.37] | 1.43 [0.97–2.11] | ||
| Liver metastasis (vs. no) | 0.82 [0.45–1.49] | 0.66 [0.35–1.28] | |||
| Pericardial metastasis/effusion (vs. no) | 0.86 [0.56–1.32] | 0.64 [0.37–1.10] | |||
| Adrenal metastasis (vs. no) | 1.24 [0.70–2.17] | 1.19 [0.61–2.31] | |||
| Other site metastasis (vs. no) | 1.24 [0.57–2.67] | 1.07 [0.43–2.66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; Hung, J.-Y.; Wu, K.-L.; Tsai, Y.-M.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chuang, C.-H.; Lee, T.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Yang, C.-J.; et al. Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Treating EGFR-Mutant Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis and Intracranial Intervention Have No Impact on Clinical Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010187
Kuo C-Y, Tsai M-J, Hung J-Y, Wu K-L, Tsai Y-M, Tsai Y-C, Chuang C-H, Lee T-H, Chen H-C, Yang C-J, et al. Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Treating EGFR-Mutant Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis and Intracranial Intervention Have No Impact on Clinical Outcomes. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010187
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Chia-Yu, Ming-Ju Tsai, Jen-Yu Hung, Kuan-Li Wu, Ying-Ming Tsai, Yu-Chen Tsai, Cheng-Hao Chuang, Tai-Huang Lee, Huang-Chi Chen, Chih-Jen Yang, and et al. 2023. "Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Treating EGFR-Mutant Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis and Intracranial Intervention Have No Impact on Clinical Outcomes" Cancers 15, no. 1: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010187
APA StyleKuo, C.-Y., Tsai, M.-J., Hung, J.-Y., Wu, K.-L., Tsai, Y.-M., Tsai, Y.-C., Chuang, C.-H., Lee, T.-H., Chen, H.-C., Yang, C.-J., & Chong, I.-W. (2023). Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Treating EGFR-Mutant Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis and Intracranial Intervention Have No Impact on Clinical Outcomes. Cancers, 15(1), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010187






